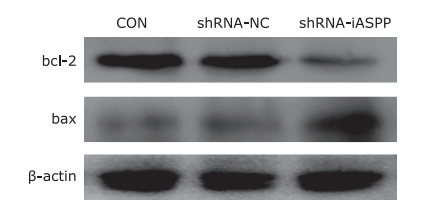
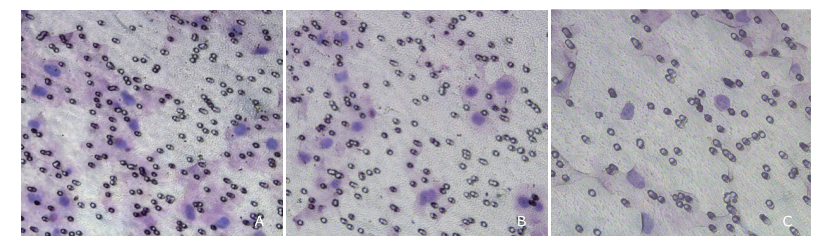
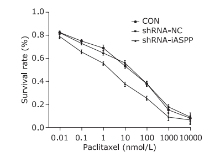
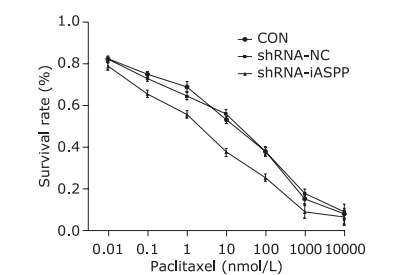
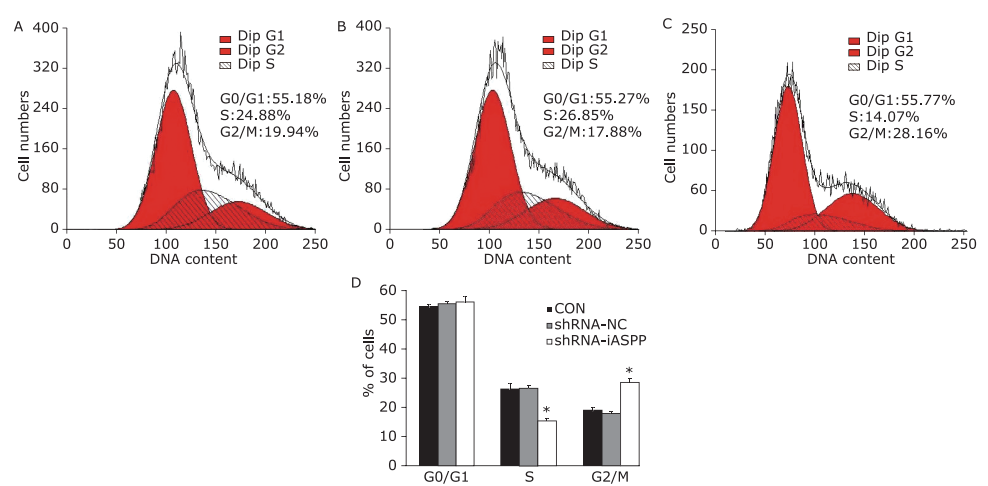
| 1. |
J-Fatokun F, Jayaratne R, Morawska L , et al. Corona ions from overhead transmission voltage powerlines: effect on direct current electric field and ambient particle concentration levels. Environ Sci Technol 2010; 44(1):526-31. doi: 10.1021/es9024063.
|
| 2. |
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63(1):11-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21166.
|
| 3. |
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J , et al. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60(5):277-300. doi: 10.3322/caac.20073.
|
| 4. |
Hardisson D . Molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2003; 260(9):502-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-003-0581-3.
|
| 5. |
Chin D, Boyle GM, Theile DR , et al. Molecular introduction to head and neck cancer (HNSCC) carcinogenesis. Br J Plast Surg 2004; 57(7):595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.06.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.06.010
|
| 6 |
Trigiante G, Lu X . ASPP [corrected] and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6(3):217-26. doi: 10.1038/nrc1818.
|
| 7. |
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ , et al. iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet 2003; 33(2):162-7. doi: 10.1038/ng1070.
|
| 8. |
Zhang X, Wang M, Zhou C , et al. The expression of iASPP in acute leukemias. Leuk Res 2005; 29(2):179-83. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2004.07.001.
|
| 9. |
Lu B, Guo H, Zhao J , et al. Increased expression of iASPP, regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated NF-kappaB activation, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010; 139(6):2183-94. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.049.
|
| 10. |
Jiang L, Siu MK, Wong OG , et al. iASPP and chemoresistance in ovarian cancers: effects on paclitaxel-mediated mitotic catastrophe. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17(21):6924-33. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0588.
|
| 11. |
Wang L, Li Y, Li L , et al. Role of Kruppel-like factor 4 in regulating inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 in the progression of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 2018; 15(5):6865-72. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8203.
|
| 12. |
Yin L, Lin Y, Wang X , et al. The family of apoptosis-stimulating proteins of p53 is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients. Oncol Lett 2018; 15(5):6409-17. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8151.
|
| 13. |
Chen J, Xie F, Zhang L , et al. iASPP is over-expressed in human non-small cell lung cancer and regulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells through a p53 associated pathway. BMC Cancer 2010; 10:694. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-694.
|
| 14. |
Zhang B, Xiao HJ, Chen J , et al. Inhibitory member of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP) family promotes growth and tumorigenesis in human p53-deficient prostate cancer cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2011; 14(3):219-24. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2011.25.
|
| 15. |
Liu Z, Zhang X, Huang D , et al. Elevated expression of iASPP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Med Oncol 2012; 29(5):3381-8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0306-9.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0306-9
|
| 16. |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25(4):402-8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
|
| 17. |
Liu Y, Zhang X, Qiu Y , et al. Clinical significance of EphA2 expression in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2011; 137(5):761-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0936-2.
|
| 18. |
Liu Z, Kuang W, Zhou Q , et al. TGF-beta1 secreted by M2 phenotype macrophages enhances the stemness and migration of glioma cells via the SMAD2/3 signalling pathway. Int J Mol Med 2018; 42(6):3395-403. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3923.
|
| 19. |
Gan W, Zhao H, Li T , et al. CDK1 interacts with iASPP to regulate colorectal cancer cell proliferation through p53 pathway. Oncotarget 2017; 8(42):71618-29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17794.
|
| 20. |
Ma Y, Zhu B, Liu X , et al. iASPP overexpression is associated with clinical outcome in spinal chordoma and influences cellular proliferation, invasion, and sensitivity to cisplatin in vitro. Oncotarget 2017; 8(40):68365-80. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20190.
|
| 21. |
Lu W, Yu T, Liu S , et al. FHL2 interacts with iASPP and impacts the biological functions of leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2017; 8(25):40885-95. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16617.
|
| 22. |
Dong P, Xiong Y, Watari H , et al. Suppression of iASPP-dependent aggressiveness in cervical cancer through reversal of methylation silencing of microRNA-124. Sci Rep 2016; 6:35480. doi: 10.1038/srep35480.
|
| 23. |
Li G, Wang R, Gao J , et al. RNA interference-mediated silencing of iASPP induces cell proliferation inhibition and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in U251 human glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 350(1-2):193-200. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0698-9.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0698-9
|
| 24. |
Liu T, Li L, Yang W , et al. iASPP is important for bladder cancer cell proliferation. Oncol Res 2011; 19(3-4):125-30.
|
| 25. |
Morris EV, Cerundolo L, Lu M , et al. Nuclear iASPP may facilitate prostate cancer progression. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5:e1492. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.442.
|
| 26. |
Liang S, Gong X, Zhang G , et al. MicroRNA-140 regulates cell growth and invasion in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma by targeting iASPP. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2016; 48(2):174-81. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv127.
|
| 27. |
Liang XG, Meng WT, Hu LJ , et al. MicroRNA-184 modulates human central nervous system lymphoma cells growth and invasion by targeting iASPP. J Cell Biochem 2017; 118(9):2645-53. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25856.
|
| 28. |
Chen J, Xiao H, Huang Z , et al. MicroRNA124 regulate cell growth of prostate cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014; 7(5):2283-90.
|
| 29. |
Liu K, Zhao H, Yao H , et al. MicroRNA-124 regulates the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Biomed Res Int 2013; 2013:867537. doi: 10.1155/2013/867537.
|
| 30. |
Zhao WH, Wu SQ, Zhang YD . Downregulation of miR-124 promotes the growth and invasiveness of glioblastoma cells involving upregulation of PPP1R13L. Int J Mol Med 2013; 32(1):101-7. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1365.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1365
|
| 31. |
Zhao H, Peng R, Liu Q , et al. The lncRNA H19 interacts with miR-140 to modulate glioma growth by targeting iASPP. Arch Biochem Biophys 2016; 610:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.09.014.
|
| 32. |
Xiong Y, Sun F, Dong P , et al. iASPP induces EMT and cisplatin resistance in human cervical cancer through miR-20a-FBXL5/BTG3 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2017; 36(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0520-6.
|
| 33. |
Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR , et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(17):1705-15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa070956.
|
| 34. |
Rapidis AD, Trichas M, Stavrinidis E , et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: final results from a phase II study with docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with a four-year follow-up. Oral Oncol 2006; 42(7):675-84. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.12.006.
|
| 35. |
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C , et al. Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(17):1695-704. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa071028.
|
| 36. |
Yu J, Li L, Huang C . Downregulation of inhibition of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (iASPP) suppresses cisplatin-resistant gastric carcinoma in vitro. Med Sci Monit 2017; 23:5542-49.
|
| 37. |
Jia Y, Peng L, Rao Q , et al. Oncogene iASPP enhances self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells and facilitates their resistance to chemotherapy and irradiation. FASEB J 2014; 28(7):2816-27. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-244632.
doi: 10.1096/fj.13-244632
|
| 38. |
Cao L, Huang Q, He J , et al. Elevated expression of iASPP correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance/radioresistance in FIGO Ib1-IIa squamous cell cervical cancer. Cell Tissue Res 2013; 352(2):361-9. doi: 10.1007/s00441-013-1569-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-013-1569-y
|
| 39. |
Liu H, Wang M, Diao S , et al. siRNA-mediated down-regulation of iASPP promotes apoptosis induced by etoposide and daunorubicin in leukemia cells expressing wild-type p53. Leuk Res 2009; 33(9):1243-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.02.016.
|
 ),匡韦陆1,曾文静3,肖健云2,田勇泉2,*(
),匡韦陆1,曾文静3,肖健云2,田勇泉2,*( )
)
 ),Kuang Weilu1,Zeng Wenjing3,Xiao Jianyun2,Tian Yongquan2,*(
),Kuang Weilu1,Zeng Wenjing3,Xiao Jianyun2,Tian Yongquan2,*( )
)