Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 54-64.doi: 10.24920/003598
慢性缺氧改变外周血转录组模式
- 1中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院,国家心血管病中心 阜外心血管病医院, 心血管疾病国家重点实验室 北京 100037
2海交通大学医学院附属上海儿童医学中心 上海市小儿先天性心脏病研究所,上海 200127
3温州医科大学附属第二医院育英儿童医院儿童心脏中心 温州医科大学心脏发育与转化医学研究所,浙江,温州 325027
-
收稿日期:2019-05-20出版日期:2020-03-31发布日期:2020-01-20 -
通讯作者:张浩 E-mail:drzhanghao@yahoo.com
Transcriptional Profile Alteration of Peripheral Blood in Chronic Hypoxia
Wang Tingting1,Xing Junyue1,Zhang Lijing3,Zhang Hao1,2,*( )
)
- 1State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Diseases, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100037, China
2Heart Center and Shanghai Institution of Pediatric Congenital Heart Diseases, Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, National Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China
3Children's Heart Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital, Institute of Cardiovascular Development and Translational Medicine, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325027, China
-
Received:2019-05-20Published:2020-03-31Online:2020-01-20 -
Contact:Zhang Hao E-mail:drzhanghao@yahoo.com
摘要:
目的 多种生理和病理状态都会伴随着慢性缺氧,例如紫绀型先天性心脏病(CCHD)。这种慢性缺氧可能会干扰基因的转录过程。然而,在缺氧条件下外周血转录组模式的改变尚无报道。故本工作旨在探讨慢性缺氧条件下,外周血转录组模式的变化。
方法 本研究使用慢性缺氧大鼠模型模拟CCHD患者的低氧状态。两组Sprague-Dawley大鼠(每组n=6)分别暴露于低氧(10%O2)或常氧(21%O2)条件下饲养3周。每周测量大鼠体重。缺氧处理结束后,采集两组大鼠外周血并提取总RNA进行RNA-Seq。经过质量评估后,通过Illumina Hiseq平台对文库进行测序。筛选差异表达基因(DEG),筛选条件为FDR(false discovery rate)<0.05且FC(fold change)>2。进行DEG的功能注释和聚类分析,并选取出padj(adjusted P-value)<0.05的条目。
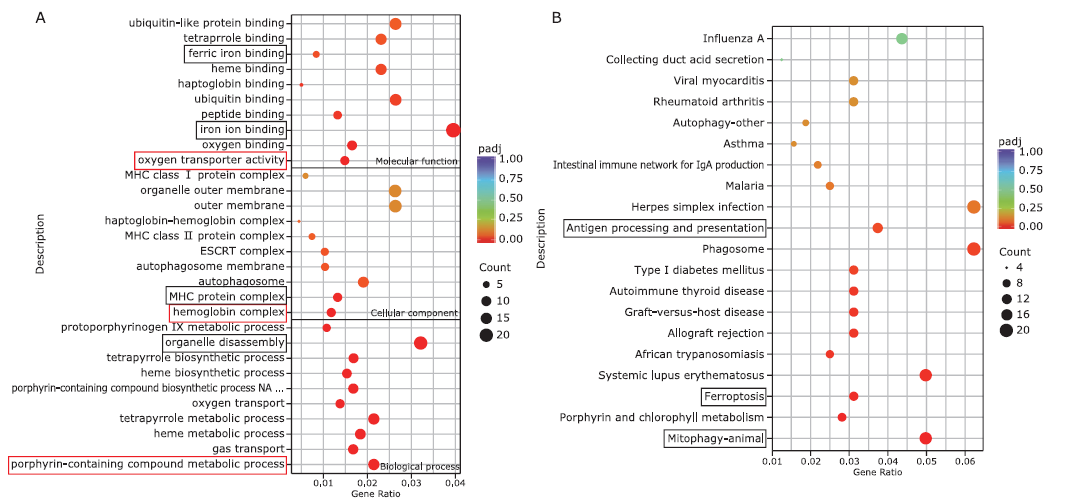
结果 低氧组大鼠体重较对照组明显降低(P<0.01)。RNA-Seq结果表明:两组的转录组模式有显著差异。共鉴定出了872个差异表达的基因。在缺氧组中,共有803个基因下调,只有69个基因上调。对872个基因的功能富集分析表明:它们涉及了多个生物学过程,例如含卟啉的化合物代谢过程,血红蛋白复合物和氧转运蛋白活性等。
结论 我们的研究表明慢性缺氧大鼠模型外周血的转录组模式发生了显著改变。为进一步了解CCHD患者的生理和病理变化提供了理论基础和研究方向。
引用本文
Wang Tingting, Xing Junyue, Zhang Lijing, Zhang Hao. Transcriptional Profile Alteration of Peripheral Blood in Chronic Hypoxia[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 54-64.
"
| Genes | Degree | Log2FC | Genes | Degree | Log2FC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubb | 56 | 1.54 | Kctd7 | 22 | 1.74 | |
| Cdc20 | 37 | 1.84 | Asb1 | 22 | 1.51 | |
| Anapc2 | 31 | 1.25 | Trim21 | 22 | 1.44 | |
| Fzr1 | 30 | 1.36 | Rnf25 | 22 | 1.15 | |
| Dctn2 | 26 | 1.37 | Asb6 | 22 | 1.18 | |
| Dctn3 | 25 | 1.11 | Ccnf | 22 | 1.61 | |
| Ube2l6 | 25 | 1.94 | Ube2e2 | 22 | 1.12 | |
| Aurka | 23 | 1.48 | Lmo7 | 22 | 1.07 | |
| Ube2o | 23 | 1.20 | Herc6 | 22 | 1.64 | |
| Nedd4l | 23 | 1.17 | Rnf123 | 22 | 1.17 | |
| Asb11 | 22 | 1.66 | Traip | 22 | 2.11 | |
| Fbxo7 | 22 | 1.75 | Uba52 | 22 | 1.05 | |
| Rnf114 | 22 | 2.17 | Pigz | 20 | 2.35 | |
| Klhl25 | 22 | 1.88 | Polr2e | 19 | 1.85 | |
| Klhl42 | 22 | 1.21 | Tubb4b | 19 | 1.47 |
| 1. | Lopez-Barneo J, Pardal R, Ortega-Sáenz P . Cellular mechanism of oxygen sensing. Annu Rev Physiol 2001; 63:259-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.259. |
| 2. | Palmer BF, Clegg DJ . Oxygen sensing and metabolic homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2014; 397(1-2):51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.08.001. |
| 3. | Bayer C, Shi K, Astner ST , et al. Acute versus chronic hypoxia: why a simplified classification is simply not enough. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011; 80(4):965-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.049. |
| 4. | Zayour D, Azar ST, Azar N , et al. Endocrine changes in a rat model of chronic hypoxia mimicking cyanotic heart disease. Endocr Res 2003; 29(2):191-200. doi: 10.1081/erc-120022301. |
| 5. | Zabala LM, Guzzetta NA . Cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD): focus on hypoxemia, secondary erythrocytosis, and coagulation alterations. Paediatr Anaesth 2015; 25(10):981-9. doi: 10.1111/pan.12705. |
| 6. | Burke AP, Virmani R . Pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction. Med Clin North Am 2007; 91(4):553-72; ix. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2007.03.005. |
| 7. | Nathaniel TI, Williams-Hernandez A, Hunter AL , et al. Tissue hypoxia during ischemic stroke: adaptive clues from hypoxia-tolerant animal models. Brain Res Bull 2015; 114:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.02.006. |
| 8. | Marchiq I, Pouyssegur J . Hypoxia, cancer metabolism and the therapeutic benefit of targeting lactate/H + symporters . J Mol Med (Berl) 2016; 94(2):155-71. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1307-x. |
| 9. | Jobe AH, Bancalari E . Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163(7):1723-9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.7.2011060. |
| 10. | Barjaktarevic I, Cooper CB . Supplemental oxygen therapy for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 36(4):552-66. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1556058. |
| 11. | Waldman JD, Wernly JA . Cyanotic congenital heart disease with decreased pulmonary blood flow in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 1999; 46(2):385-404. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70125-5. |
| 12. | Chelly J, Concordet JP, Kaplan JC , et al. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1989; 86(8):2617-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. |
| 13. | Ning W, Chu TJ, Li CJ , et al. Genome-wide analysis of the endothelial transcriptome under short-term chronic hypoxia. Physiol Genomics 2004; 18(1):70-8. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00221.2003. |
| 14. | Ord JJ, Streeter EH, Roberts IS , et al. Comparison of hypoxia transcriptome in vitro with in vivo gene expression in human bladder cancer. Br J Cancer 2005; 93(3):346-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602666. |
| 15. | Liew CC, Ma J, Tang HC , et al. The peripheral blood transcriptome dynamically reflects system wide biology: a potential diagnostic tool. J Lab Clin Med 2006; 147(3):126-32. doi: 10.1016/j.lab.2005.10.005. |
| 16. | Tawk B, Schwager C, Deffaa O , et al. Comparative analysis of transcriptomics based hypoxia signatures in head- and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 2016; 118(2):350-8. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.11.027. |
| 17. | Yuhong L, Tana W, Zhengzhong B , et al. Transcriptomic profiling reveals gene expression kinetics in patients with hypoxia and high altitude pulmonary edema. Gene 2018; 651:200-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.052. |
| 18. | Satoh K, Kagaya Y, Nakano M , et al. Important role of endogenous erythropoietin system in recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Circulation 2006; 113(11):1442-50. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.105.583732. |
| 19. | Jung F, Weiland U, Johns RA , et al. Chronic hypoxia induces apoptosis in cardiac myocytes: a possible role for Bcl-2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 286(2):419-25. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5406. |
| 20. | Corno AF, Milano G, Samaja M , et al. Chronic hypoxia: a model for cyanotic congenital heart defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002; 124(1):105-12. doi: 10.1067/mtc.2002.121302. |
| 21. | Von Mering C, Jensen LJ, Snel B , et al. STRING: known and predicted protein-protein associations, integrated and transferred across organisms. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33(Database issue):D433-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki005. |
| 22. | Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E , et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc 2007; 2(10):2366-82. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.324. |
| 23. | Radom-Aizik S, Zaldivar FP, Nance DM , et al. Growth inhibition and compensation in response to neonatal hypoxia in rats. Pediatr Res 2013; 74(2):111-20. doi: 10.1038/pr.2013.80. |
| 24. | Clemente C, Barnes J, Shinebourne E , et al. Are infant behavioural feeding difficulties associated with congenital heart disease? Child Care Health Dev 2001; 27(1):47-59. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.2001.00199.x. |
| 25. | Costello CL, Gellatly M, Daniel J , et al. Growth restriction in infants and young children with congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 2015; 10(5):447-56. doi: 10.1111/chd.12231. |
| 26. | Varan B, Tokel K, Yilmaz G . Malnutrition and growth failure in cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease with and without pulmonary hypertension. Arch Dis Child 1999; 81(1):49-52. doi: 10.1136/adc.81.1.49. |
| 27. | Matos SM, Sarmento S, Moreira S , et al. Impact of fetal development on neurocognitive performance of adolescents with cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 2014; 9(5):373-81. doi: 10.1111/chd.12152. |
| 28. | McQuillen PS, Goff DA, Licht DJ . Effects of congenital heart disease on brain development. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 2010; 29(2):79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ppedcard.2010.06.011. |
| 29. | Johnson AB, Denko N, Barton MC . Hypoxia induces a novel signature of chromatin modifications and global repression of transcription. Mutat Res 2008; 640(1-2):174-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.01.001. |
| 30. | Masuo S, Terabayashi Y, Shimizu M , et al. Global gene expression analysis of Aspergillus nidulans reveals metabolic shift and transcription suppression under hypoxia. Mol Genet Genomics 2010; 284(6):415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0576-x. |
| 31. | Storz JF, Moriyama H . Mechanisms of hemoglobin adaptation to high altitude hypoxia. High Alt Med Biol 2008; 9(2):148-57. doi: 10.1089/ham.2007.1079. |
| 32. | Nikinmaa M . Haemoglobin function in vertebrates: evolutionary changes in cellular regulation in hypoxia. Respir Physiol 2001; 128(3):317-29. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5687(01)00309-7. |
| 33. | Storz JF . Hemoglobin-oxygen affinity in high-altitude vertebrates: is there evidence for an adaptive trend? J Exp Biol 2016; 219(Pt 20):3190-203. doi: 10.1242/jeb.127134. |
| 34. | Siebenmann C, Robach P, Lundby C . Regulation of blood volume in lowlanders exposed to high altitude. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2017; 123(4):957-66. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00118.2017. |
| 35. | Xia M, Chao Y, Jia J , et al. Changes of hemoglobin expression in response to hypoxia in a Tibetan schizothoracine fish, Schizopygopsis pylzovi. J Comp Physiol B 2016; 186(8):1033-43. doi: 10.1007/s00360-016-1013-1. |
| 36. | Simpson RJ , McKie AT. Iron and oxygen sensing: a tale of 2 interacting elements? Metallomics 2015; 7(2):223-31. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00225c. |
| 37. | Robach P, Cairo G, Gelfi C , et al. Strong iron demand during hypoxia-induced erythropoiesis is associated with down-regulation of iron-related proteins and myoglobin in human skeletal muscle. Blood 2007; 109(11):4724-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-040006. |
| 38. | Frise MC, Cheng HY, Nickol AH , et al. Clinical iron deficiency disturbs normal human responses to hypoxia. J Clin Invest 2016; 126(6):2139-50. doi: 10.1172/jci85715. |
| 39. | Dressel R, Walter L, Gunther E . Genomic and funtional aspects of the rat MHC, the RT1 complex. Immunol Rev 2001; 184:82-95. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1840108.x. |
| 40. | Sethumadhavan S, Silva M, Philbrook P , et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) downregulate antigen-presenting MHC class I molecules limiting tumor cell recognition by T cells. PLoS One 2017; 12(11):e0187314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187314. |
| 41. | Murthy A, Gerber SA, Koch CJ , et al. Intratumoral hypoxia reduces IFN-γ-mediated immunity and MHC Class I induction in a preclinical tumor model. Immunohorizons 2019; 3(4):149-60. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1900017. |
| 42. | Kajiwara T, Tanaka T, Kukita K , et al. Hypoxia augments MHC class I antigen presentation via facilitation of ERO1-alpha-mediated oxidative folding in murine tumor cells. Eur J Immunol 2016; 46(12):2842-51. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646525. |
| 43. | Wang Q, Liu C, Zhu F , et al. Reoxygenation of hypoxia-differentiated dentritic cells induces Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. Mol Immunol 2010; 47(4):922-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.09.038. |
| 44. | Ayala A, Ertel W, Chaudry IH . Trauma-induced suppression of antigen presentation and expression of major histocompatibility class II antigen complex in leukocytes. Shock 1996; 5(2):79-90. |
| 45. | Yang JB, Zhao ZB, Liu QZ , et al. FoxO1 is a regulator of MHC-II expression and anti-tumor effect of tumor-associated macrophages. Oncogene 2018; 37(9):1192-204. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0048-4. |
| 46. | Wu X, Kong X, Chen D , et al. SIRT1 links CIITA deacetylation to MHC II activation. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39(22):9549-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr651. |
| 47. | Schonenberger MJ, Kovacs WJ . Hypoxia signaling pathways: modulators of oxygen-related organelles. Front Cell Dev Biol 2015; 3:42. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00042. |
| 48. | Kubli DA, Gustafsson AB . Mitochondria and mitophagy: the yin and yang of cell death control. Circ Res 2012; 111(9):1208-21. doi: 10.1161/circresaha. 112.265819. |
| 49. | Fuhrmann DC, Wittig I, Heide H , et al. Chronic hypoxia alters mitochondrial composition in human macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013; 1834(12):2750-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.09.023. |
| 50. | Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA , et al. Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 2008; 283(16):10892-903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800102200. |
| 51. | Wu H, Chen Q . Hypoxia activation of mitophagy and its role in disease pathogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal 2015; 22(12):1032-46. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6204. |
| 52. | Band M, Joel A, Hernandez A , et al. Hypoxia-induced BNIP3 expression and mitophagy: in vivo comparison of the rat and the hypoxia-tolerant mole rat, Spalax ehrenbergi. FASEB J 2009; 23(7):2327-35. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-122978. |
| 53. | Chua B, Kao RL, Rannels DE , et al. Inhibition of protein degradation by anoxia and ischemia in perfused rat hearts. J Biol Chem 1979; 254(14):6617-23. |
| 54. | Chang JM, Hwang DY, Chen SC , et al. B7-1 expression regulates the hypoxia-driven cytoskeleton rearrangement in glomerular podocytes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2013; 304(1):F127-36. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00108.2012. |
| 55. | Bouvry D, Planès C, Malbert-Colas L , et al. Hypoxia-induced cytoskeleton disruption in alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006; 35(5):519-27. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0478OC. |
| 56. | VanWinkle WB, Snuggs M, Buja LM . Hypoxia-induced alterations in cytoskeleton coincide with collagenase expression in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1995; 27(12):2531-42. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1995.0040. |
| 57. | Coucha M, Abdelsaid M, Li W , et al. Nox4 contributes to the hypoxia-mediated regulation of actin cytoskeleton in cerebrovascular smooth muscle. Life Sci 2016; 163:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.08.018. |
| 58. | Huang D, Cao L, Xiao L , et al. Hypoxia induces actin cytoskeleton remodeling by regulating the binding of CAPZA1 to F-actin via PIP2 to drive EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2019; 448:117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.042. |
| 59. | Zieseniss A . Hypoxia and the modulation of the actin cytoskeleton—emerging interrelations. Hypoxia (Auckl) 2014; 2:11-21. doi: 10.2147/hp.s53575. |
| 60. | Guo H, Zheng H, Wu J , et al. The key role of microtubules in hypoxia preconditioning-induced nuclear translocation of HIF-1alpha in rat cardiomyocytes. PeerJ 2017; 5:e3662. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3662. |
| 61. | Fischer MG, Heeger S, Hacker U , et al. The mitotic arrest in response to hypoxia and of polar bodies during early embryogenesis requires Drosophila Mps1. Curr Biol 2004; 14(22):2019-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.008. |
| 62. | Kyle UG, Earthman CP, Pichard C , et al. Body composition during growth in children: limitations and perspectives of bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 2015; 69(12):1298-305. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2015.86. |
| 63. | Pelkonen O . Metabolism and pharmacokinetics in children and the elderly. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2007; 3(2):147-8. doi: 10.1517/17425255.3.2.147. |
| 64. | Pascual V, Medrano LM, López-Palacios N , et al. Different gene expression signatures in children and adults with celiac disease. PLoS One 2016; 11(2):e0146276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146276. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|