Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 204-209.doi: 10.24920/003962
所属专题: 人工智能与精准肿瘤学
基于深度学习算法的胃炎组织病理学诊断系统
巴伟1,王书浩2,刘灿城2,王跃峰2,石怀银1,宋志刚1,*( )
)
- 1中国人民解放军总医院医学院病理科,北京 100853,中国
2透彻影像人工智能实验室,北京 100853,中国
Histopathological Diagnosis System for Gastritis Using Deep Learning Algorithm
Wei Ba1,Shuhao Wang2,Cancheng Liu2,Yuefeng Wang2,Huaiyin Shi1,Zhigang Song1,*( )
)
- 1Department of Pathology, Chinese PLA General Hospital & Medical School, Beijing 100853, China
2Artificial Intelligence Lab, Thorough Images,Beijing 100853, China
摘要:
目的 开发一种用于慢性胃炎病理分类的深度学习算法,并使用全切片病理图像(whole slide images,WSI)评估其性能。
方法 回顾性收集解放军总医院胃活检标本1,250例(胃炎1,128例,正常胃黏膜122例)。分别使用1,008张和100张WSIs,基于DeepLab v3(ResNet-50)架构训练和验证深度学习算法,并在142张WSIs的独立测试集上测试该算法对不同胃炎亚型的诊断效能。
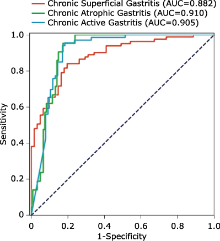
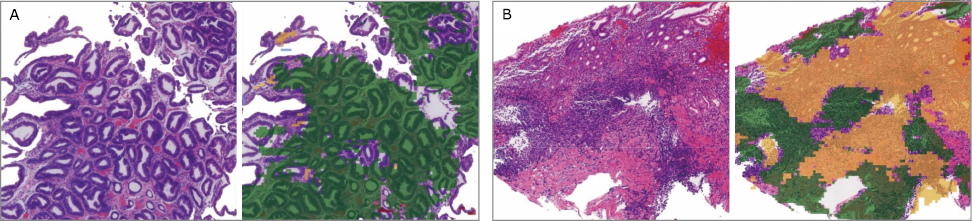
结果 模型为测试集中的慢性浅表性胃炎(chronic superficial gastritis,CSuG)、慢性活动性胃炎(chronic active gastritis,CAcG)和慢性萎缩性胃炎(chronic atrophic gastritis,CAtG)作出诊断所生成的受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线的曲线下面积分别为0.882、0.905和0.910。深度学习算法对CSuG、CAcG和CAtG分类的敏感性和特异性分别为0.790和1.000(准确度0.880)、0.985和0.829(准确度0.901)、0.952和0.992(准确度0.986)。对三种不同类型胃炎诊断的总体准确度为 0.867。通过在 WSI 中标记算法识别的可疑区域,可以生成更为透明和可解释的诊断结果。
结论 深度学习算法使用WSI对慢性胃炎进行病理学分型具有较高的准确性。通过预先标记出不同类型胃炎的区域,深度学习算法可以作为辅助诊断工具,提高病理医生的工作效率。