Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 20-28.doi: 10.24920/004148
基于GEO数据库食管癌关键基因和信号通路分析
宋安忆1,2,*( ),木兰1,代小勇1,王丽君1,黄来强1,*(
),木兰1,代小勇1,王丽君1,黄来强1,*( )
)
- 1深圳市基因与抗体治疗重点实验室,清华大学深圳国际研究生院,深圳518055,广东,中国
2清华大学化学系,北京100084,中国
Analysis of Significant Genes and Pathways in Esophageal Cancer Based on Gene Expression Omnibus Database
An-Yi Song1,2,*( ),Lan Mu1,Xiao-Yong Dai1,Li-Jun Wang1,Lai-Qiang Huang1,*(
),Lan Mu1,Xiao-Yong Dai1,Li-Jun Wang1,Lai-Qiang Huang1,*( )
)
- 1The Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Gene and Antibody Therapy, State Key Laboratory of Chemical Oncogenomics, Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute (TBSI), Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, Guangdong Province, China
2Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
摘要:
目的 基于GEO数据库,通过分析癌症组织的高表达基因,筛选用于免疫治疗的抗原靶点,并通过富集分析、PPI网络和生存分析等方法,探讨癌症相关的关键通路和分子机制。
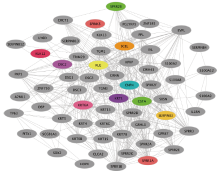
方法 通过筛选高表达基因,借助于TMHMM和IEDB平台,分析蛋白质的跨膜域和抗原表位。基于富集分析、PPI网络和生存分析的方法,对癌症发展相关的基因和信号通路进行分析。分析和绘图涉及的软件和平台包括Prism 8、R语言、Cytoscape、DAVID、STRING和GEPIA网站等。
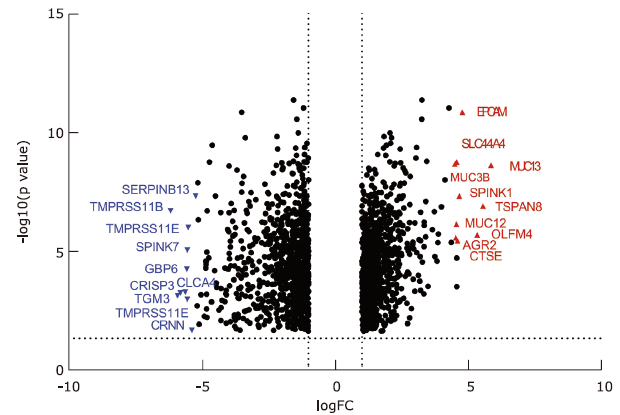
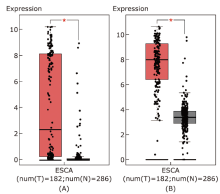
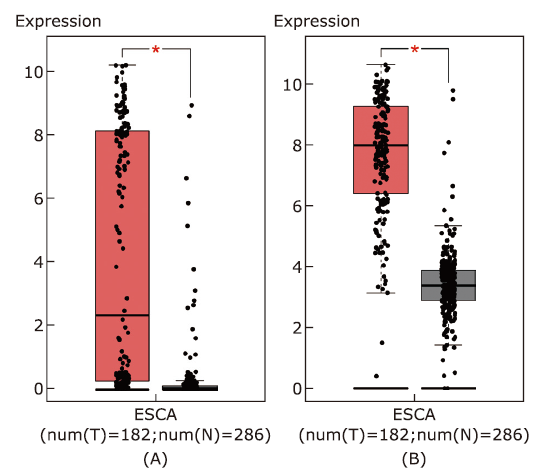
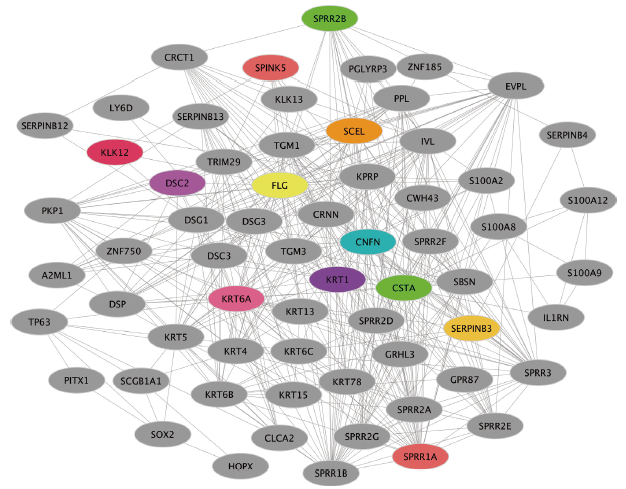
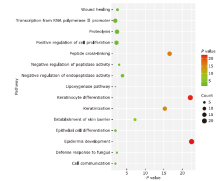
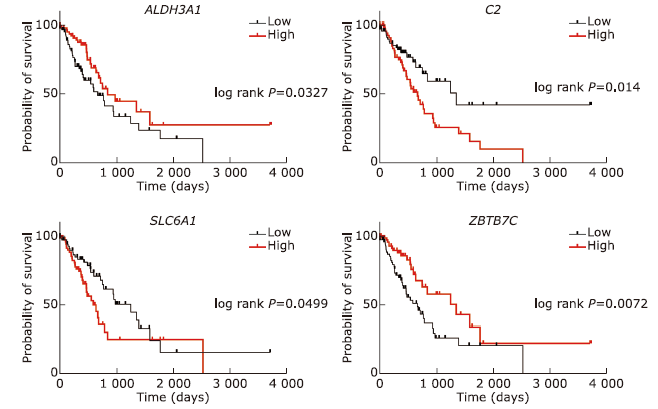
结果 MUC13和EPCAM基因在食管癌组织中高表达,并具有多个抗原识别位点。根据富集分析的结果,一系列基因与角质化过程相关。生存分析结果表明,基因ALDH3A1、C2、SLC6A1和ZBTB7C的生存曲线具有显著差异性。
结论 MUC13和EPCAM可能作为食管癌免疫治疗的抗原靶点和生物标志物。角质化过程可能在食管癌的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用。基因ALDH3A1, C2, SLC6A1和ZBTB7C可能与食管癌患者生存周期密切相关。