Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 69-76.doi: 10.24920/11811
• 论著 • 下一篇
6 4层多排CT对冠状动脉旁路移植术后的中期随访:影响桥血管通畅性的危险因素研究
- 解放军总医院 放射科,北京 100853,中国
Midterm Follow-up of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting with 64-Slice Multi-detector Computed Tomography: Identification of Risk Factors Affecting Graft Patency
Li Tao,Yang Li( ),Zhang Weiguo,Luo Chuncai,Huang Zili,Li Jinfeng,Li Xin
),Zhang Weiguo,Luo Chuncai,Huang Zili,Li Jinfeng,Li Xin
- Radiology Department, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
摘要:
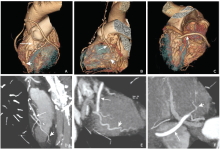
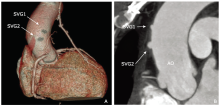
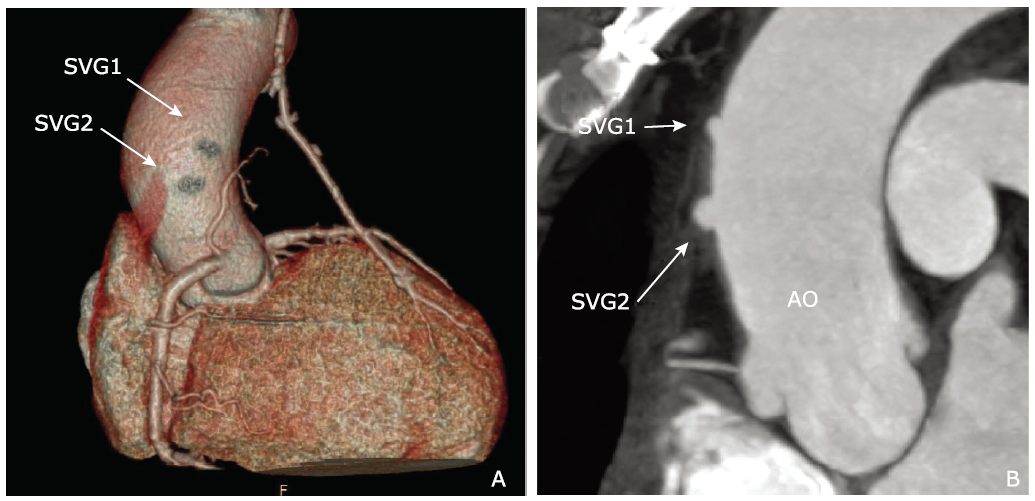
目的 使用64层多排螺旋CT评价冠状动脉旁路移植术后左内乳动脉桥(LIMA)和大隐静脉桥(SVG)血管的通畅性,并探讨影响冠脉旁路移植术后中期桥血管通畅性的危险因素。方法 收集2012年8月至2015年12月接受冠脉旁路移植手术及并术后采用64层多排螺旋CT(MDCT)随访的病例。根据CT表现将桥血管的通畅状态分为通畅及不通畅两大类。搜集患者的临床资料及影像资料并比较通畅组和不通畅组间的差异。采用单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析影响桥血管通畅性的危险因素。结果 341个患者中有330支LIMA桥血管(326支吻合到前降支LAD,4支吻合到右冠状动脉RCA)和564支SVG桥血管(100支吻合到对角支D,220支吻合到钝缘支OM,238支吻合到右冠脉血流灌注区)。吻合到OM和右冠脉血流灌注区的SVG桥血管的通畅率明显高于吻合到D的通畅率(χ 2=15.471, P=0.004)。吻合口近端靶血管狭窄程度小于90%是LIMA桥血管闭塞的独立危险因素(OR =0.015, 95% CI=0.01-0.14, P=0.000),而高脂血症(OR =1.52, 95% CI=1.0-2.5, P=0.048)、糖尿病(OR =1.28, 95% CI=0.90-2.26, P=0.045)及出现胸痛或呼吸困难等冠心病症状(OR=1.81,95% CI=1.33-4.15,P=0.003) 是SVG桥血管闭塞的独立危险因素.结论 当冠状动脉旁路移植术吻合口近端前降支的狭窄率小于90%时,LIMA桥血管中期闭塞的危险性升高。高脂血症、糖尿病史及典型的冠心病的症状是SVG桥血管中期闭塞的危险因素。吻合口远端靶血管的选择也是影响SVG术后通畅性的重要因素。