Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 309-319.doi: 10.24920/004060
急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者的梗死范围、心脏磁共振特征跟踪应变分析的区域心肌功能与梗死位置的关系
- 中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心放射科,北京 100853
-
收稿日期:2022-01-14接受日期:2022-04-19出版日期:2022-12-31发布日期:2022-05-30 -
通讯作者:李涛 E-mail:litaofeivip@163.com
Associations of Infarct Size and Regional Myocardial Function Examined by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Strain Analysis with the Infarct Location in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Jianing Cui,Yanan Zhao,Wei Wang,Tao Li*( )
)
- Department of Radiology, The First Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2022-01-14Accepted:2022-04-19Published:2022-12-31Online:2022-05-30 -
Contact:Tao Li E-mail:litaofeivip@163.com
摘要:
目的 定量评估初次接受经皮冠状动脉介入治疗的ST段抬高型心肌梗死(ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction,STEMI)患者的梗死范围、心脏磁共振特征跟踪(cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking,CMR-FT)应变分析的区域心肌功能与梗死位置的关系。
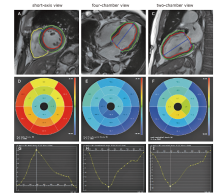
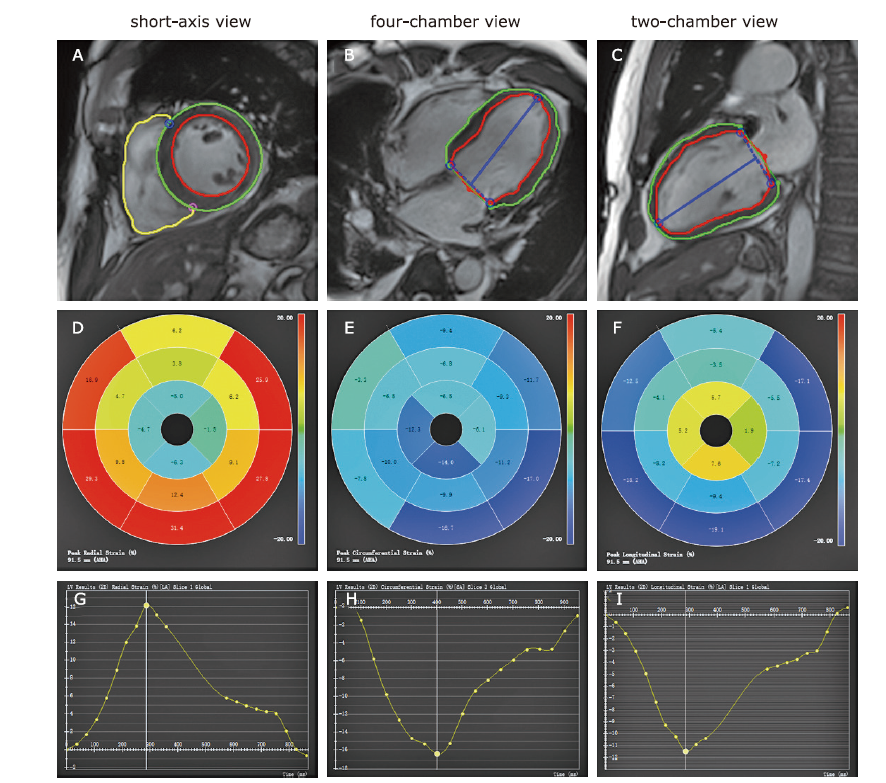
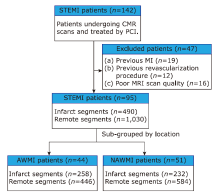
方法 本研究选取在我院进行再灌注治疗的STEMI患者,共纳入95例连续治疗成功的患者。我们对患者的心脏磁共振图像进行回顾性分析,并将患者分为前壁心肌梗死(anterior wall myocardial infarction,AWMI)和非前壁心肌梗死(nonanterior wall myocardial infarction,NAWMI)两组。我们采用晚期钆增强图像评估梗死特征;采用基于标准cine图像的CMR-FT技术评估整体和区域径向、周向和纵向应变及应变率。用Spearman或Pearson方法评估STEMI患者的梗死范围大小、CMR-FT应变分析的区域心肌功能与梗死位置的关系。
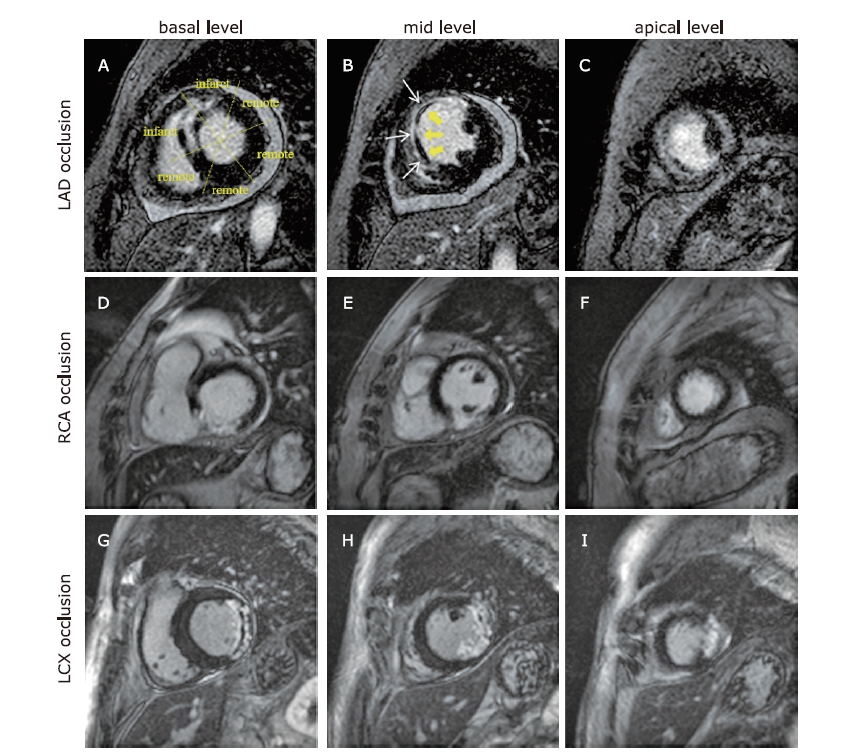
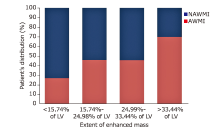
结果 纳入AWMI患者44例,NAWMI患者51例。与NAWMI组相比,AWMI组患者的左心室强化程度明显更高(27.47±11.89比21.06±12.08 %LV;t = 3.928,P = 0.008)。对梗死区的分析显示:与NAWMI组相比,AWMI组的径向、周向和纵向应变明显下降(Z =-20.873,-20.918,-10.357,P均 < 0.001)。在AWMI组中,左心室的容积(收缩末期容积指数)、总强化质量和强化质量的范围与梗死区应变的相关性最好(P均 < 0.001)。
结论 在经皮冠状动脉介入治疗的STEMI患者中,与NAWMI患者相比,AWMI患者的心肌损伤范围更广泛,梗死区的心肌功能更低。
引用本文
Jianing Cui, Yanan Zhao, Wei Wang, Tao Li. Associations of Infarct Size and Regional Myocardial Function Examined by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Strain Analysis with the Infarct Location in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(4): 309-319.
"
| Characteristic | Results |
|---|---|
| Age (yrs, mean ± SD) | 54.73 ± 10.74 |
| Sex [male, n (%)] | 83 (87.4) |
| Height [cm, median (IQR)] | 170 (168, 175) |
| Weight [kg, median (IQR)] | 76 (70, 85) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 1.91 ± 0.18 |
| Risk factors [n (%)] | |
| Smoking | 70 (73.7) |
| Family history of CAD | 9 (9.5) |
| Hypertension | 54 (56.8) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 17 (17.9) |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 28 (29.5) |
| Time interval CMR after PCI [d, mean ± SD] | 5.90 ± 2.75 |
| No. of vessels diseased [n (%)] | |
| 1 | 28 (29.5) |
| 2 | 38 (40.0) |
| 3 | 29 (30.5) |
| Infarct related artery [n (%)] | |
| LAD | 44 (46.3) |
| LCX | 9 (9.5) |
| RCA | 42 (44.2) |
"
| Items | AWMI (n = 44) | NAWMI (n = 51) | t/Z | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDVI [ml/m2, median (IQR)] | 69.13 (62.25, 86.76) | 74.96 (61.61, 87.96) | -0.735 | 0.462 |
| ESVI [ml/m2, median (IQR)] | 37.44 (31.41, 50.64) | 35.28 (29.38, 46.64) | -0.623 | 0.533 |
| SVI [ml/m2, median (IQR)] | 35.86 (27.16, 43.12) | 41.33 (31.47, 46.60) | -1.638 | 0.101 |
| EF [%, median (IQR)] | 47.31 (41.17, 52.44) | 51.99 (37.48, 55.57) | -1.317 | 0.188 |
| CO [L/min, median (IQR)] | 5.02 (4.44, 5.90) | 5.29 (4.73, 6.37) | -1.482 | 0.138 |
| CI [L/min·m2, median (IQR)] | 2.72 (2.37, 3.30) | 2.77 (2.52, 3.40) | -1.015 | 0.310 |
| HR [beat/min, median (IQR)] | 71.10 (62.45, 80.95) | 65.50 (58.00, 75.40) | -1.549 | 0.121 |
| Myocardial volume [ml, median (IQR)] | 94.10 (15.50, 123.60) | 92.98 (75.27, 121.40) | -0.037 | 0.970 |
| Myocardial mass [g, median (IQR)] | 113.82 (26.88, 134.76) | 96.22 (19.12, 127.90) | -0.761 | 0.446 |
| Extent of enhanced mass (%LV, mean ± SD) | 27.47 ± 11.89 | 21.06 ± 12.08 | 3.928 | 0.008 |
| Total enhanced volume [ml, median (IQR)] | 25.37 (12.98, 38.33) | 15.25 (8.27, 27.92) | -1.918 | 0.055 |
| Total enhanced mass (g, mean ± SD) | 30.46 ± 18.11 | 24.07 ± 16.58 | 3.784 | 0.056 |
| MVO volume [ml, median (IQR)] | 2.48 (1.55, 5.35) | 1.72 (0.92, 3.98) | -1.614 | 0.106 |
| MVO mass [g, median (IQR)] | 2.80 (1.62, 5.38) | 1.81 (0.96, 4.18) | -1.560 | 0.119 |
"
| Groups | No. of segments | Peak strain [median (IQR)] | Peak systolic strain rate [median (IQR)] | Peak diastolic strain rate [median (IQR)] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial (%) | Circumferential (%) | Longitudinal (%) | Radial (%/s) | Circumferential(%/s) | Longitudinal (%/s) | Radial (%/s) | Circumferential (%/s) | Longitudinal (%/s) | ||||
| Infarct segment | 490 | 12.96 (8.30, 18.95) | -9.97 (-13.26, -6.36) | -9.04 (-14.71, -4.01) | 0.83 (0.47, 1.27) | -0.69 (-0.96, -0.37) | -0.79 (-1.29, 0.62) | -0.88 (-1.33, 0.29) | 0.64 (-0.26, 0.93) | 0.78 (-0.33, 1.16) | ||
| Remote segment | 1,030 | 28.45 (19.57, 38.09) | -17.48 (-21.01, -13.54) | -13.99 (-18.55, -8.95) | 1.72 (1.22, 2.29) | -1.08 (-1.32, -0.85) | -1.13 (-1.54, -0.73) | -1.68 (-2.52, -1.09) | 1.00 (0.75, 1.29) | 0.96 (0.61, 1.36) | ||
| t/Z value | -20.873 | -20.918 | -10.357 | -19.067 | -16.586 | -7.825 | -16.731 | -15.100 | -5.454 | |||
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
"
| Groups | n | Peak strain [median (IQR)] | Peak systolic strain rate [median (IQR)] | Peak diastolic strain rate [median (IQR)] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial (%) | Circumferential (%) | Longitudinal (%) | Radial (%/s) | Circumferential(%/s) | Longitudinal (%/s) | Radial (%/s) | Circumferential (%/s) | Longitudinal (%/s) | |||||
| Global | AWMI | 44 patients | 18.78 (15.97, 22.32) | -12.80±3.47* | -9.87 (-12.02, -8.20) | 0.98 (0.89,1.30) | -0.72 (-0.83,-0.62) | -0.60 (-0.70, -0.49) | -0.94 (-1.18,-0.64) | 0.65 (0.50,0.75) | 0.53 (0.45, 0.67) | ||
| NAWMI | 51 patients | 22.84 (18.17,26.63) | -14.36±3.14* | -12.50 (-13.45, -10.56) | 1.16 (0.89,1.48) | -0.78 (-0.88,-0.62) | -0.72 (-0.82, -0.61) | -0.98 (-1.40,-0.77) | 0.64 (0.54,0.82) | 0.62 (0.52, 0.76) | |||
| t/Z value | -2.575 | 0.001 | -4.146 | -1.280 | -0.702 | -3.181 | -1.709 | -1.112 | -2.580 | ||||
| P value | 0.010 | 0.025 | <0.001 | 0.200 | 0.483 | 0.001 | 0.087 | 0.266 | 0.010 | ||||
| Infarct zone | AWMI | 258 segments | 12.49 (7.32,18.03) | -9.54 (-12.70,-5.72) | -6.95 (-12.10,3.22) | 0.81 (0.34,1.21) | -0.67 (-0.98,0.27) | -0.62 (-1.13,0.63) | -0.81 (-1.26,0.58) | 0.64 (-0.50,0.91) | 0.63 (-0.51,0.97) | ||
| NAWMI | 232 segments | 13.82 (8.77,20.63) | -10.24 (-14.00, -7.17) | -11.68 (-16.10, -6.54) | 0.89 (0.53,1.30) | -0.71 (-0.93,-0.43) | -0.98 (-1.44,0.53) | -0.93 (-1.47,-0.47) | 0.64 (0.38,0.97) | 0.95 (0.51,1.31) | |||
| t/Z value | -2.139 | -2.086 | -6.785 | -1.909 | -1.038 | -3.634 | -2.606 | -1.824 | -4.950 | ||||
| P value | 0.032 | 0.037 | <0.001 | 0.056 | 0.299 | <0.001 | 0.009 | 0.068 | <0.001 | ||||
| [1] |
Reisinger E, Fuerstenberg T, Malyar NM, et al. German nationwide data on current trends and management of acute myocardial infarction: discrepancies between trials and real-life. Eur Heart J 2014; 35(15):979-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu043.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu043 pmid: 24558113 |
| [2] |
Offi M, Patrono C, Collet JP, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2016; 37(3):267-15. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv320.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv320 pmid: 26320110 |
| [3] |
O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2013; 127(4):529-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.11.018.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.11.018 |
| [4] |
Stone PH, Raabe DS, Jaffe AS, et al. Prognostic significance of location and type of myocardial infarction: independent adverse outcome associated with anterior location. J Am Coll Cardiol 1988; 11(3):453-63. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)91517-3.
doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)91517-3 pmid: 3278032 |
| [5] |
De Luca G, Suryapranata H, van ‘t Hof AW, et al. Prognostic assessment of patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with primary angioplasty: implications for early discharge. Circulation 2004; 109(22):2737-43. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131765.73959.87.
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131765.73959.87 pmid: 15159293 |
| [6] |
Amin ST, Morrow DA, Braunwald E, et al. Dynamic TIMI risk score for STEMI. J Am Heart Assoc 2013; 2(1):e003269. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.003269.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.003269 |
| [7] |
Emrich T, Halfmann M, Schoepf UJ, et al. CMR for myocardial characterization in ischemic heart disease: state-of-the-art and future developments. Eur Radiol Exp 2021; 5(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s41747-021-00208-2.
doi: 10.1186/s41747-021-00208-2 pmid: 33763757 |
| [8] |
Backhaus SJ, Kowallick JT, Stiermaier T, et al. Culprit vessel-related myocardial mechanics and prognostic implications following acute myocardial infarction. Clin Res Cardiol 2020; 109(3):339-49. doi: 10.1007/s00392-019-01514-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00392-019-01514-x pmid: 31278521 |
| [9] |
Smiseth OA, T orp H, Opdahl A, et al. Myocardial strain imaging: how useful is it in clinical decision making? Eur Heart J 2016; 37(15):1196-207. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv529.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv529 pmid: 26508168 |
| [10] |
Schuster A, Hor KN, Kowallick JT, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance myocardial feature tracking: concepts and clinical applications. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2016; 9(4):e004077. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.004077.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.004077 |
| [11] |
Shetye A, Nazir SA, Squire IB, et al. Global myocardial strain assessment by different imaging modalities to predict outcomes after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a systematic review. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(12):948-60. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.948.
doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.948 pmid: 26730301 |
| [12] |
Kirkpatrick JN, Vannan MA, Narula J, et al. Echocardiography in heart failure: applications, utility, and new horizons. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007; 50(5):381-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.03.048.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.03.048 pmid: 17662389 |
| [13] |
Bodi V. Strain by feature tracking: a short summary of the journey of CMR in STEMI. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2019; 12(7 Pt 1):1199-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.08.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.08.009 |
| [14] |
Zghal FM, Boudiche S, Haboubi S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of strain imaging in predicting myocardial viability after an ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99(19): e19528. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019528.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019528 |
| [15] |
Eitel I, Stiermaier T, Lange T, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance myocardial feature tracking for optimized prediction of cardiovascular events following myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2018; 11(10):1433-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.11.034.
doi: S1936-878X(17)31176-2 pmid: 29454776 |
| [16] |
Valente F, Gutierrez L, Rodríguez-Eyras L, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance longitudinal strain analysis in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a comparison with speckle-tracking echocardiography. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc 2020; 29:100560. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2020.100560.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2020.100560 |
| [17] |
Nazir SA, Shetye AM, Khan JN, et al. Inter-study repeatability of circumferential strain and diastolic strain rate by CMR tagging, feature tracking and tissue tracking in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2020; 36(6):1133-46. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01806-8.
doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01806-8 pmid: 32152811 |
| [18] |
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2012; 33(20):2551-67. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs184.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs184 pmid: 22922414 |
| [19] |
Eite I, Desch S, Fuernau G, et al. Prognostic significance and determinants of myocardial salvage assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance in acute reperfused myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55(22):2470-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.01.049.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.01.049 pmid: 20510214 |
| [20] |
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2002; 105(4):539-42. doi: 10.1161/hc0402.102975.
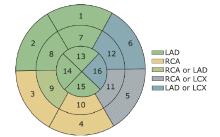
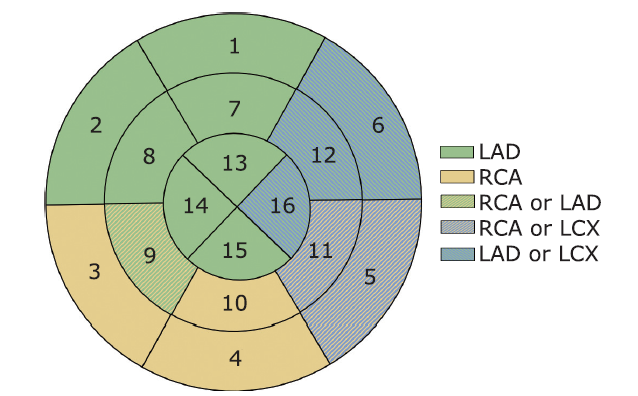
doi: 10.1161/hc0402.102975 pmid: 11815441 |
| [21] |
Mahmarian JJ, Pratt CM, Boyce TM, et al. The variable extent of jeopardized myocardium in patients with single vessel coronary artery disease: quantification by thallium 201 single photon emission computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991; 17(2):355-62. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80099-3.
doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80099-3 pmid: 1991891 |
| [22] |
Lee JT, Ideker RE, Reimer KA. Myocardial infarct size and location in relation to coronary vascular bed at risk in man. Circulation 1981; 64(3):526-34. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.3.526.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.3.526 pmid: 7261285 |
| [23] |
Elsman P, van ‘t Hof AW, de Boer MJ, et al. Impact of infarct location on left ventricular ejection fraction after correction for enzymatic infarct size in acute myocardial infarction treated with primary coronary intervention. Am Heart J 2006; 151(6): 1239.e9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2005.12.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2005.12.006 |
| [24] |
Reinstadler SJ, Thiele H, Eite I. Risk stratification by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging after ST -elevation myocardial infarction. Curr Opin Cardiol 2015; 30(6):681-9. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000227.
doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000227 pmid: 26398412 |
| [25] |
Eite I, de Waha S, Wöhrle J, et al. Comprehensive prognosis assessment by CMR imaging after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 64(12):1217-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.06.1194.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.06.1194 pmid: 25236513 |
| [26] |
Wu KC. CMR of microvascular obstruction and hemorrhage in myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2012; 14(1): 68. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-14-68.
doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-14-68 |
| [27] |
Reindl M, Holzknecht M, Tiller C, et al. Impact of infarct location and size on clinical outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Int J Cardiol 2020; 301:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.11.123.
doi: S0167-5273(19)33043-8 pmid: 31761400 |
| [28] |
Podlesnikar T, Pizarro G, Fernández-Jiménez R, et al. Left ventricular functional recovery of infarcted and remote myocardium after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (METOCARD-CNIC randomized clinical trial substudy). J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2020; 22 (1): 44. doi: 10.1186/s12968-020-00638-8.
doi: 10.1186/s12968-020-00638-8 |
| [29] |
Li S, Zhao L, Lu A, et al. Comparison of left ventricular global strain in anterior and non-anterior wall myocardial infarction with CMR tissue tracking. Front Physiol 2020; 11:530108. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.530108.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.530108 |
| [30] |
Bogaert J, Bosmans H, Maes A, et al. Remote myocardial dysfunction after acute anterior myocardial infarction: impact of left ventricular shape on regional function: a magnetic resonance myocardial tagging study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000; 35(6):1525-34. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00601-x.
doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00601-x pmid: 10807456 |
| [31] |
Claus P, Omar AMS, Pedrizzetti G, et al. Tissue tracking technology for assessing cardiac mechanics: principles, normal values, and clinical applications. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2015; 8(12):1444-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.11.001.
doi: S1936-878X(15)00845-1 pmid: 26699113 |
| [1] | 赵亚男, 崔佳宁, 张兴华, 李金锋, 陈仕敏, 岳修正, 李涛. ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者微血管阻塞与心脏磁共振测定的整体和局部心肌功能的关系[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(1): 11-19. |
| [2] | 黄学伟, 邓克穷, 秦娟娟, 雷昉, 张兴元, 汪文鑫, 林立金, 郑宇明, 幺冬爱, 卢惠明, 刘烽, 陈立东, 张桂兰, 刘跃平, 杨琼玉, 蔡菁菁, 折志刚, 李红良. 血脂与左心室肥厚的联系—1项来自于回顾性研究的新证据[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(2): 103-117. |
| [3] | 刘智坚, 胡高频, 费美莹, 殷召, 时全星, 孙飞. 短期大剂量阿托伐他汀对初发急性前壁心肌梗死患者左心室重构的影响[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 84-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|