Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 201-209.doi: 10.24920/004102
基于机器学习的脓毒症死亡率预测模型对比研究
- 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院医学信息研究所/图书馆,北京 100020,中国
-
收稿日期:2022-04-21接受日期:2022-08-10出版日期:2022-09-30发布日期:2022-09-20 -
通讯作者:李姣 E-mail:li.jiao@imicams.ac.cn
Comparison of Mortality Predictive Models of Sepsis Patients Based on Machine Learning
Ziyang Wang,Yushan Lan,Zidu Xu,Yaowen Gu,Jiao Li*( )
)
- Institute of Medical Information/Medical Library, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2022-04-21Accepted:2022-08-10Published:2022-09-30Online:2022-09-20 -
Contact:Jiao Li E-mail:li.jiao@imicams.ac.cn
摘要:
目的 比较五个机器学习模型和SAPS II评分在预测脓毒症患者30天内死亡率方面的表现。
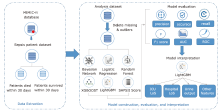
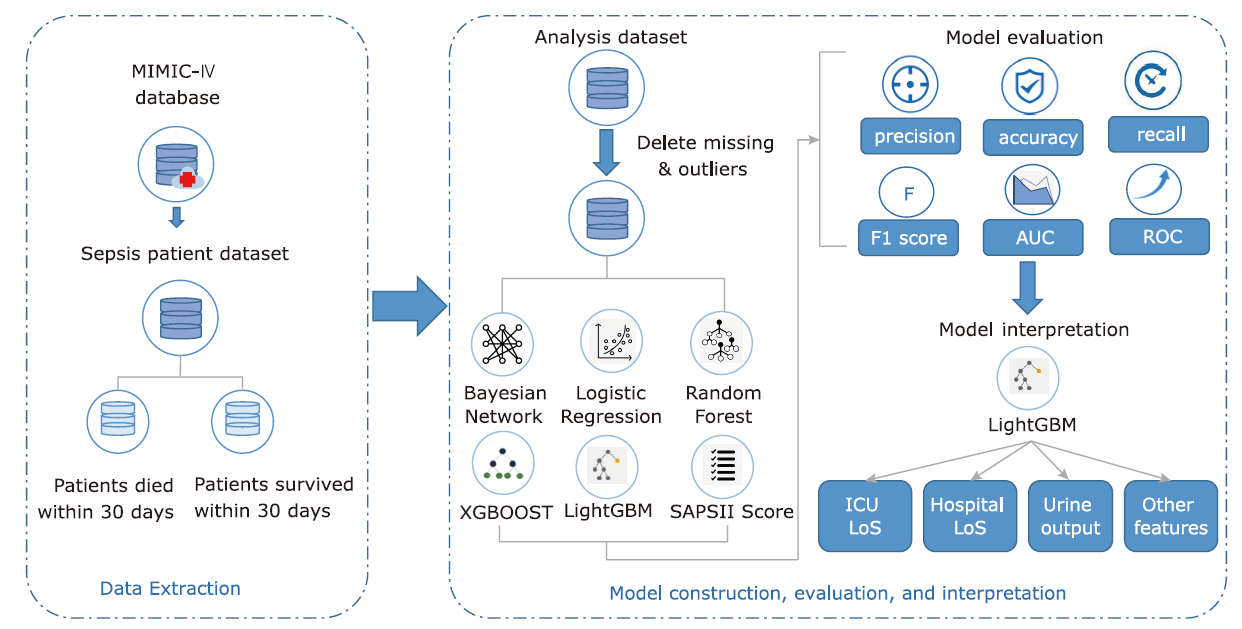
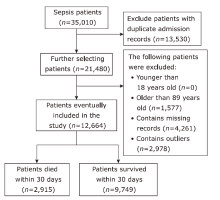
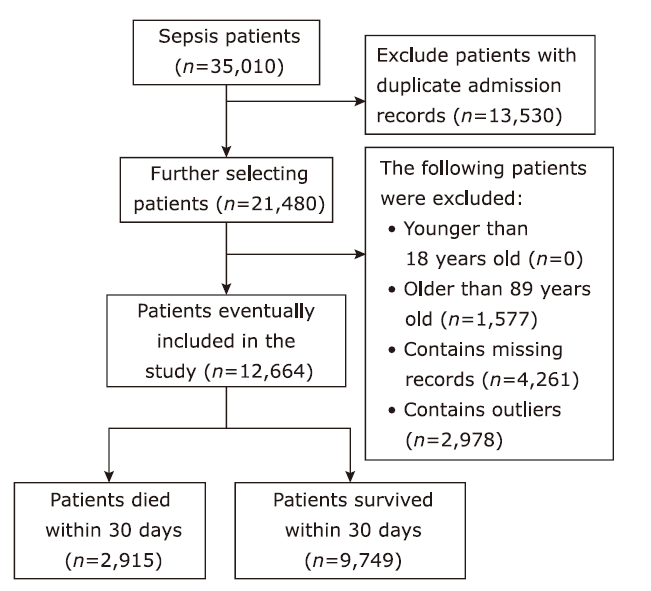
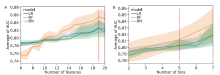
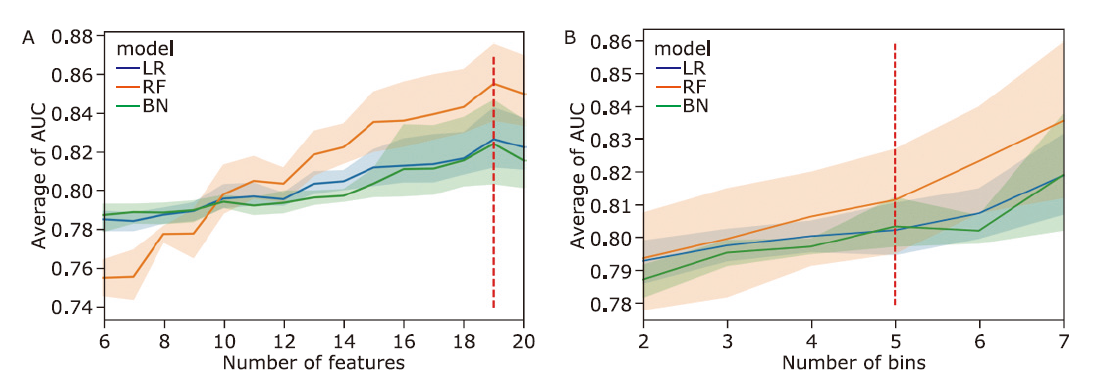
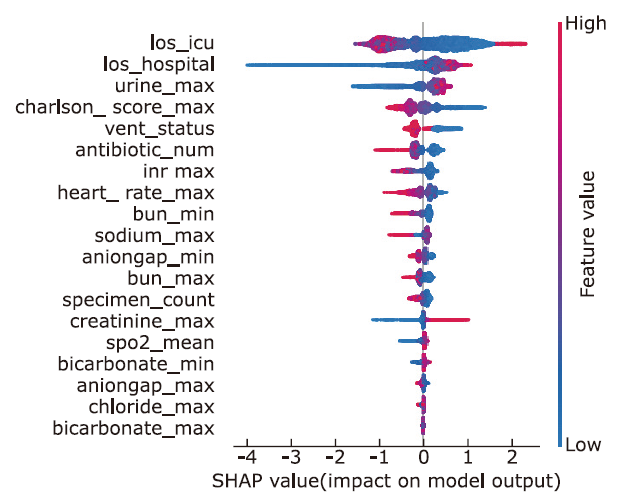
方法 从MIMIC-IV数据库中提取败血症患者相关数据,生成临床特征,并通过互信息法和网格搜索进行特征筛选。构建逻辑回归、随机森林、LightGBM、XGBoost等机器学习模型,预测脓毒症患者30天内死亡率。此外,还获得了包括准确率、精确度、召回率、F1得分和受试者工作特性曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)在内的五个模型评估指标。最后,在外部数据集中验证了模型的效果。
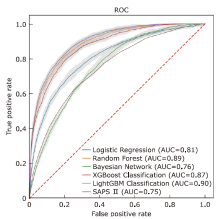
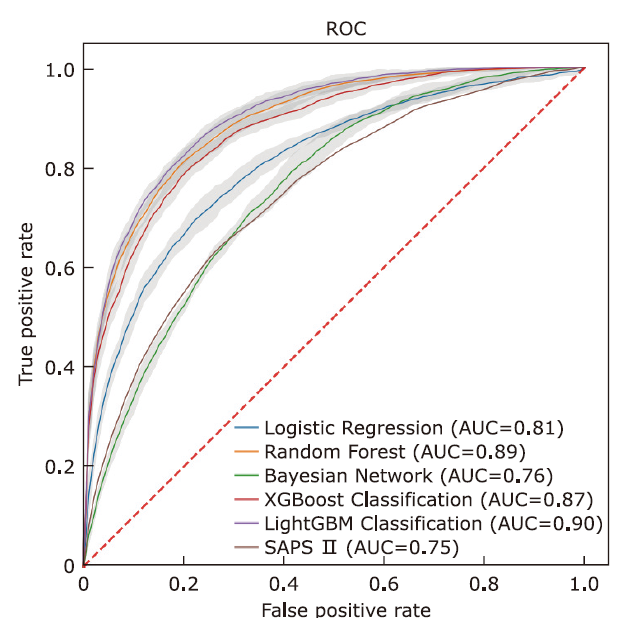
结果 LightGBM的表现优于其他方法,取得了最高的AUC(0.900)、准确率(0.808)和精确度(0.559)。所有机器学习模型的表现都优于SAPS II评分(AUC=0.748)。在外部数据集的验证中LightGBM的AUC达到0.883。
结论 机器学习模型在预测败血症患者的死亡率方面被认为是比传统的SAPS II评分更有效的方法。
引用本文
Ziyang Wang, Yushan Lan, Zidu Xu, Yaowen Gu, Jiao Li. Comparison of Mortality Predictive Models of Sepsis Patients Based on Machine Learning[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(3): 201-209.
"
| NO | Feature | MIC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | urine_max | 0.0441 |
| 2 | los_hospital | 0.0418 |
| 3 | aniongap_max | 0.0370 |
| 4 | specimen_count | 0.0347 |
| 5 | antibiotic_num | 0.0346 |
| 6 | bun_max | 0.0325 |
| 7 | bun_min | 0.0303 |
| 8 | aniongap_min | 0.0295 |
| 9 | bicarbonate_min | 0.0273 |
| 10 | inr_max | 0.0271 |
| 11 | creatinine_max | 0.0270 |
| 12 | vent_status | 0.0224 |
| 13 | los_ICU | 0.0223 |
| 14 | charlson_score_max | 0.0185 |
| 15 | bicarbonate_max | 0.0181 |
| 16 | chloride_max | 0.0180 |
| 17 | heart_rate_max | 0.0173 |
| 18 | sodium_max | 0.0160 |
| 19 | spo2_mean | 0.0158 |
"
| Features | All (n=12,664) | Survival (n=9,749) | Death (n=2,915) | t/χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aniongap_max (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 16.99 ± 5.37 | 19.43 ± 6.36 | 16.26 ± 4.81 | 24.85 | <0.001 |
| aniongap_min (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 13.12 ± 3.70 | 14.72 ± 4.47 | 12.64 ± 3.29 | 23.32 | <0.001 |
| antibiotic_num (mean±SD) | 6.31 ± 5.72 | 8.38 ± 6.00 | 5.69 ± 5.48 | 21.67 | <0.001 |
| bicarbonate_max (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 24.34 ± 4.71 | 23.39 ± 5.44 | 24.62 ± 4.43 | -11.14 | <0.001 |
| bicarbonate_min (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 21.15 ± 5.21 | 19.46 ± 6.04 | 21.65 ± 4.82 | -17.93 | <0.001 |
| bun_max (mg/L, mean±SD) | 32.40 ± 25.09 | 42.77 ± 29.93 | 29.30 ± 22.54 | 22.46 | <0.001 |
| bun_min (mg/L, mean±SD) | 26.98 ± 21.93 | 35.84 ± 26.48 | 24.33 ± 19.61 | 21.75 | <0.001 |
| charlson_score_max (mean±SD) | 6.59 ± 3.03 | 7.63 ± 2.94 | 6.28 ± 2.98 | 21.79 | <0.001 |
| creatinine_max (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 1.64 ± 1.49 | 2.03 ± 1.56 | 1.53 ± 1.45 | 15.45 | <0.001 |
| chloride_max (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 106.21 ± 6.73 | 106.4 ± 6.29 | 105.58 ± 7.98 | 14.26 | <0.001 |
| inr_max (mean±SD) | 1.73 ± 1.27 | 2.11 ± 1.62 | 1.61 ± 1.11 | 15.47 | <0.001 |
| los_hospital (days, mean±SD) | 13.03 ± 13.76 | 11.73 ± 15.19 | 13.42 ± 13.28 | -5.42 | <0.001 |
| los_ICU (days, mean±SD) | 6.16 ± 6.80 | 7.14 ± 5.79 | 5.87 ± 7.05 | 9.85 | <0.001 |
| heart_rate_max (bpm, mean±SD) | 107.82 ± 21.48 | 106.05 ± 20.48 | 113.73 ± 23.60 | -14.54 | <0.001 |
| spo2_mean (%, mean±SD) | 96.94 ± 2.25 | 97.09 ± 1.95 | 96.44 ± 2.99 | 14.49 | <0.001 |
| sodium_max (mmol/L, mean±SD) | 140.14 ± 5.36 | 140.32 ± 6.65 | 140.08 ± 4.91 | 1.81 | 0.0696 |
| specimen_count (mean±SD) | 6.11 ± 5.51 | 8.14 ± 5.81 | 5.51 ± 5.26 | 21.91 | <0.001 |
| urine_max (ml, mean±SD) | 1,751.39 ± 1,253.79 | 1,284.30 ± 1,234.80 | 1,891.05 ± 1,225.37 | -23.32 | <0.001 |
| vent_status [n(%)]* | 12,664 (100) | 9,749 (77) | 2,915 (23) | 503.11 | <0.001 |
"
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAPS Ⅱ Score | 0.725 | 0.430 | 0.604 | 0.502 | 0.748 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.751(0.02)# | 0.486(0.03)# | 0.719(0.06)# | 0.571(0.02)# | 0.807(0.01)# |
| Bayesian Network | 0.654(0.03)# | 0.378(0.02)# | 0.773(0.06)* | 0.507(0.01)# | 0.756(0.01)# |
| Random Forest | 0.806(0.02)# | 0.558(0.04) | 0.807(0.05) | 0.657(0.01) | 0.891(0.01)* |
| XGBoost | 0.795(0.02) | 0.541(0.04) | 0.804(0.05) | 0.645(0.02)* | 0.875(0.01)# |
| LightGBM | 0.808(0.02) | 0.559(0.04) | 0.834(0.04) | 0.668(0.02) | 0.900(0.01) |
| 1. |
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016; 315(8):801-10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 pmid: 26903338 |
| 2. |
Martin GS. Sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: changes in incidence, pathogens and outcomes. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2012; 10(6):701-6. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.50.
doi: 10.1586/eri.12.50 pmid: 22734959 |
| 3. |
Song J, Park DW, Moon S, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of interleukin-6, pentraxin 3, and procalcitonin levels among sepsis and septic shock patients: a prospective controlled study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions. BMC Infect Dis 2019; 19:68. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4618-7.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4618-7 |
| 4. |
Xie J, Wang H, Kang Y, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in Chinese ICUs: A national cross-sectional survey. Crit Care Med 2020; 48(3):e209-e218. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004155.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004155 |
| 5. |
Zhao L, Zhao L, Wang YY, et al. Platelets as a prognostic marker for sepsis: a cohort study from the MIMIC-III database. Medicine 2020; 99(45):e23151. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023151.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023151 |
| 6. |
Chen H, Zhu Z, Zhao C, et al. Central venous pressure measurement is associated with improved outcomes in septic patients: an analysis of the MIMIC-III database. Crit Care 2020; 24(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03109-9.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03109-9 |
| 7. |
Zhu C, Xu Z, Gu Y, et al. Prediction of post-stroke urinary tract infection risk in immobile patients using machine learning: an observational cohort study. J Hosp Infect 2022; 122:96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2022.01.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2022.01.002 pmid: 35045341 |
| 8. |
Wang Y, Sun F, Hong G, et al. Thyroid hormone levels as a predictor marker predict the prognosis of patients with sepsis. Am J Emerg Med 2021; 45:42-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.02.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.02.014 pmid: 33652253 |
| 9. |
Hou N, Li M, He L, et al. Predicting 30-days mortality for MIMIC-III patients with sepsis-3: a machine learning approach using XGboost. J Transl Med 2020; 18:462. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02620-5.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02620-5 pmid: 33287854 |
| 10. |
Feng M, McSparron JI, Kien DT, et al. Transthoracic echocardiography and mortality in sepsis: analysis of the MIMIC-III database. Intens Care Med 2018; 44(6): 884-92. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5208-7.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5208-7 |
| 11. |
Hou N, Li M, He L, et al. Predicting 30-days mortality for MIMIC-III patients with sepsis-3: a machine learning approach using XGboost. J Transl Med 2020; 18:462. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02620-5.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02620-5 pmid: 33287854 |
| 12. |
Wang D, Li J, Sun Y, et al. A machine learning model for accurate prediction of sepsis in ICU patients. Front Public Health 2021; 9: 754348. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.754348.
doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.754348 |
| 13. | Johnson A, Bulgarelli L, Pollard T, et al. MIMIC-IV (version 0.4). PhysioNet 2020. https://doi.org/10.13026/a3wn-hq05. |
| 14. |
Uusitalo L. Advantages and challenges of Bayesian networks in environmental modelling. Ecol Modell 2007; 203(3): 312-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.11.033.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.11.033 |
| 15. |
Mihaljević B, Bielza C, Larrañaga P. Bayesian networks for interpretable machine learning and optimization. Neurocomputing 2021; 456:648-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.138.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.138 |
| 16. |
Hanko M, Grendár M, Snopko P, et al. Random forest-based prediction of outcome and mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury undergoing primary decompressive craniectomy. World Neurosurg 2021; 148: e450-e458. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.01.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.01.002 pmid: 33444843 |
| 17. |
Davagdorj K, Pham VH, Theera-Umpon N, et al. XGBoost-based framework for smoking-induced noncommunicable disease prediction. Int J Environment Res Public Health 2020; 17(18): e6513. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186513.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186513 |
| 18. |
Zhang C, Lei X, Liu L. Predicting metabolite-disease associations based on lightgbm model. Front Genet 2021; 12: 660275. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.660275.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.660275 |
| 19. |
Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F. A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 1993; 270(24): 2957-63. doi: 10.1001/jama.270.24.2957.
doi: 10.1001/jama.270.24.2957 |
| 20. |
Moreno-Torres V, Royuela A, Múñez E, et al. Better prognostic ability of NEWS2, SOFA and SAPS-II in septic patients. Medicina Cinica 2021; 159(5):224-9. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2021.10.021.
doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2021.10.021 |
| 21. |
Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NKJ, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis 2015 ;15(5): 581-614. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)70112-X.
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)70112-X |
| 22. | Zhang ZQ. Effect of changes in urine volume on prognosis of patients with sepsis and acute kidney injury after continuous renal replacement therapy. Chin Med Pharm 2021; 11(12): 178-82. |
| 23. | Lundberg S, Lee SI. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions, carXiv: 1705.07874. Available from: http://doi.org/1048550/arXiv.1705.07874. |
| 24. |
Dugar S, Choudhary C, Duggal A. Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based management. Cleveland Clin J Med 2020; 87(1): 53-64. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.18143.
doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.18143 |
| 25. |
Vincent JL, Ferguson A, Pickkers P, et al. The clinical relevance of oliguria in the critically ill patient: analysis of a large observational database. Criti Care 2020; 24: 171. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02858-x.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02858-x |
| [1] | 陈旭, 霍晓菲, 吴哲, 陆菁菁. 人工智能在卵巢癌医学影像中的应用进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 196-203. |
| [2] | 李佳铮, 唐磊. 影像组学在抗肿瘤药物临床试验疗效评估中的应用和挑战[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 187-195. |
| [3] | 尹俊雄, 余诚, 魏丽霞, 余传勇, 刘红星, 杜明洋, 孙丰, 王崇骏, 王小姗. 基于机器学习的脑卒中高危人群无症状性颈动脉狭窄的检测研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 297-305. |
| [4] | 史颖欢,王乾. 人工智能赋能医学影像的现状与前景[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 71-75. |
| [5] | 关健. 健康和医学领域的人工智能:期许、伦理挑战和治理[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 76-83. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|