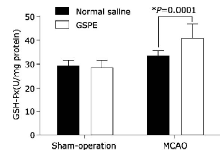
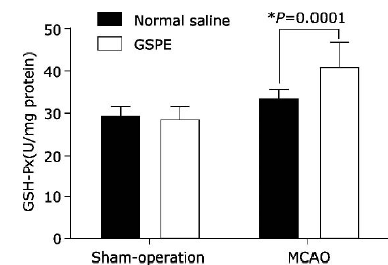
| 1. |
Feigin VL.Stroke epidemiology in the developing world. Lancet 2005; 365: 2160-1. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736 (05)66755-4.
|
| 2. |
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U.Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2009; 4: 461-70. doi:10.1111/j.1747-4949.2009.00387.x.
|
| 3. |
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C.The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010; 67: 181-98. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.002.
|
| 4. |
Chen T, Liu W, Chao X, et al.Neuroprotective effect of osthole against oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat cortical neurons: involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Neuroscience 2011; 183:203-11. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.038.
|
| 5. |
Mehlomakulu NN, Prior KJ, Setati ME, et al.Candida pyralidae killer toxin disrupts the cell wall of Brettanomyces bruxellensis in red grape juice. J Appl Microbiol 2017; 122:747-58. doi:10.1111/jam.13383.
|
| 6. |
Chen Q, Zhang R, Li WM, et al.The protective effect of grape seed procyanidin extract against cadmium-induced renal oxidative damage in mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2013; 36: 759-68. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.07. 006.
|
| 7. |
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al.Therapeutic Benefit of Intravenous Administration of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells After Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Stroke 2001; 32: 1005-11. doi:10.1161/01.STR.32.4.1005.
|
| 8. |
Gauvrit JY, Leclerc X, Pernodet M, et al.Value of MRI in the etiologic diagnosis of cerebral infarction. J Radiol 2005; 86:1080-9.
|
| 9. |
Pillai DR, Dittmar MS, Baldaranov D, et al.Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats-a 3 T MRI study on biphasic blood-brain barrier opening and the dynamics of edema formation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2009; 29:1846-55. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.106.
|
| 10. |
Liu F, Schafer DP, Mccullough LD.TTC, fluoro-Jade B and NeuN staining confirm evolving phases of infarction induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurosci Methods 2009; 179:1-8. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008. 12.028.
|
| 11. |
Kong X, Guan J, Ma W, et al.CD34 Over-expression is associated with Gliomas' higher WHO grade. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95:e2830. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000 000002830.
|
| 12. |
Bizzi I, Ghezzi P, Paudyal P.Health information quality of websites on periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 2017; 44:308-14. doi:10.1111/jcpe.12668.
|
| 13. |
Hattori K, Lee H, Hurn PD, et al.Cognitive deficits after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 2000; 31:1939-44.
|
| 14. |
Zanolin ME, Girardi P, Degan P, et al.Measurement of a urinary marker (8-hydroxydeoxy-guanosine, 8-OHdG) of DNA oxidative stress in epidemiological surveys: a pilot study. Int J Biol Markers 2015; 30: e341-5. doi:10.5301/ jbm.5000129.
|
| 15. |
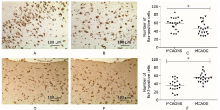
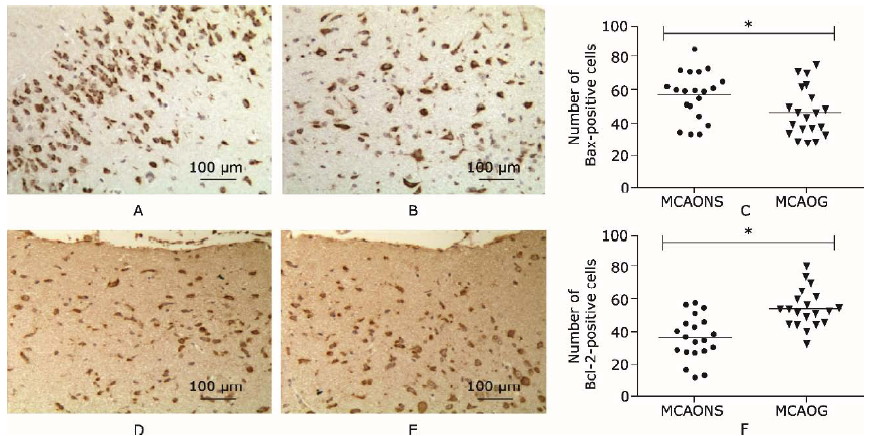
Liu G, Wang T, Wang T, et al.Effects of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral ischemia rats. Biomed Rep 2013; 1:861-7. doi:10.3892/br.2013. 153.
|
| 16. |
Zhang JQ, Gao BW, Wang J, et al.Critical role of FoxO1 in granulosa cell apoptosis caused by oxidative stress and protective effects of grape seed procyanidin B2. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016; 2016:6147345. doi:10.1155/2016/ 6147345.
|
| 17. |
Terra X, Montagut G, Bustos M, et al.Grape-seed procyanidins prevent low-grade inflammation by modulating cytokine expression in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem 2009; 20:210-8. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.02. 005.
|
| 18. |
Jin H, Liu M, Zhang X, et al.Grape seed procyanidin extract attenuates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting oxidative stress and pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells proliferation. J Nutr Biochem 2016; 36:81-8. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.07.006.
|
| 19. |
Yamakoshi J, Saito M, Kataoka S, et al.Safety evaluation of proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds. Food Chem Toxicol 2002; 40:599-607.
|
| 20. |
Shahjouei S, Cai PY, Ansari S, et al.Middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rodents: A step-by-step approach. J Vasc Interv Neurol 2016; 8:1-8.
|
| 21. |
Aleu A, Mellado P, Lichy C, et al.Hemorrhagic complications after off-label thrombolysis for ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007; 38:417-22. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000254 504.71955.05.
|
| 22. |
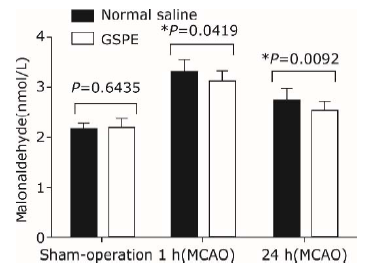
Kowalczuk K, Stryjecka-Zimmer M.The influence of oxidative stress on the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) in different areas of the rabbit brain. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 2002; 57:160-4.
|
| 23. |
Olsvik PA, Kristensen T, Waagbo R, et al.mRNA expression of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT and GSH-Px) and lipid peroxidative stress in liver of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) exposed to hyperoxic water during smoltification. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2005; 141:314-23. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2005.07.009.
|
| 24. |
Pallares V, Fernandez-Iglesias A, Cedo L, et al.Grape seed procyanidin extract reduces the endotoxic effects induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Free Radic Biol Med 2013; 60:107-14. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.02.007.
|
 )
)