Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 100-106.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.013
彩色多普勒超声对婴幼儿血管瘤治疗方式选择的临床评价
- 1 南京医科大学附属儿童医院皮肤科,南京,210008,中国
2 南京医科大学第一附属医院皮肤科, 南京, 210029,中国
Clinical Evaluation of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Selecting the Optimal Treatment Modality for Infantile Hemangioma△
Li Min1, Liu Juan2, Maya Valeska2, Luo Dan2,*( ), Zhou Bingrong2,*(
), Zhou Bingrong2,*( )
)
- 1 Department of Dermatology, Children's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210008, China
2 Department of Dermatology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210029, China
摘要:
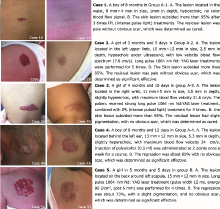
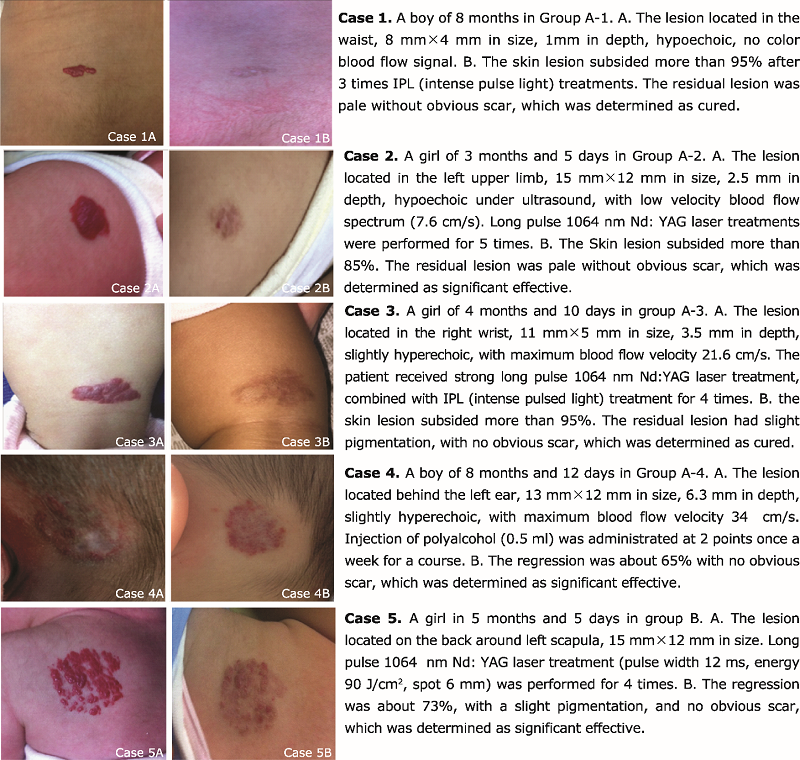
目的 比较彩色多普勒超声引导下选择1064nmNd:YAG激光、强脉冲光(intense pulsed light, IPL)和聚桂醇注射的不同治疗方法与单纯采用激光治疗婴儿血管瘤的疗效与安全性。方法 将临床确诊为婴儿血管瘤的患者随机分为A组(治疗前进行彩色多普勒超声检查)和B组(无超声检查的经验性治疗)。A组根据超声显示的病变深度分为4个亚组:A-1组:强脉冲光治疗(深度<1.2 mm);A-2组:长脉宽1064 nmNd:YAG激光治疗(1.2mm≤深度< 3.0 mm);A-3组:长脉宽1064 nmNd:YAG激光和强脉冲光联合治疗(3.0mm≤深度< 5.0 mm);A-4组:聚桂醇注射治疗(深度≥ 5.0 mm)。B组全部采用长脉宽1064 nmNd:YAG激光治疗。随访三月,根据病变治疗前后的变化评估治疗的疗效,并记录两组病患所发生的不良反应,对两组治愈率、有效率及不良反应率进行统计学比较。结果 共收集113例患儿,128处皮损。A组85例患儿的平均年龄(6.8±7.9)月,B组28例患者的平均年龄(6.9±9.9)月。A组血管瘤的深度范围0.5~7.8 mm,平均3.27±1.07 mm,A-1、A-2、A-3和A-4各亚组的平均深度分别为0.8±0.37 mm、2.2±0.44 mm、4.2±0.64 mm和6.2±0.73 mm。A组治愈率(64.5% vs 56.3%, U=3.378, P=0.045)和有效率(89.5% vs 78.1%, U=4.163, P=0.041)显著高于B组。A组不良反应发生率(水疱20.0%,色素沉着46.9%, 瘢痕形成17.7%)低于B组(水疱21.9%,色素沉着60.4%,瘢痕形成25.0%),其中色素沉着和瘢痕发生率两组差异有统计学意义(U=3.884, P=0.034; U=4.016, P=0.032)。结论 彩色多普勒超声引导下选择长脉宽1064 nmNd:YAG激光、强脉冲光、或聚桂醇注射等治疗方法,对婴儿血管瘤的治疗效果和安全性优于未经超声检查单纯采用激光治疗,提示彩色多普勒超声有助于婴儿血管瘤治疗方式的优选。