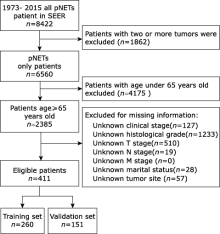
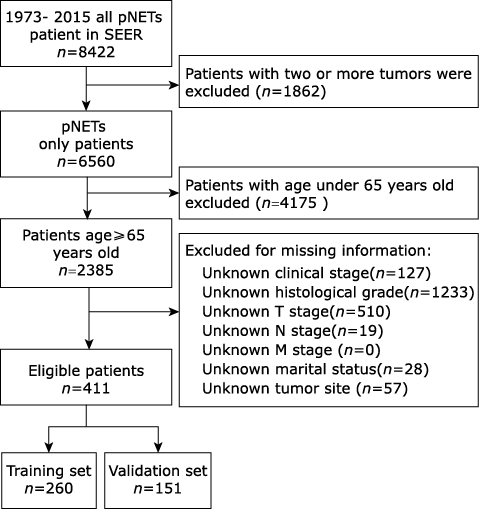
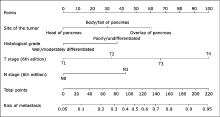
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 218-224.doi: 10.24920/003722
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Using a Nomogram to Preoperatively Predict Distant Metastasis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor in Elderly Patients
Gang Li, Yuntao Bing, Maolin Tian, Chunhui Yuan( ), Dianrong Xiu(
), Dianrong Xiu( )
)
- Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2020-02-20Accepted:2020-05-10Published:2021-09-30Online:2021-08-30 -
Contact:Chunhui Yuan,Dianrong Xiu E-mail:ychdoctor@163.com;xiudianrong1964@163.com
Cite this article
Gang Li, Yuntao Bing, Maolin Tian, Chunhui Yuan, Dianrong Xiu. Using a Nomogram to Preoperatively Predict Distant Metastasis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor in Elderly Patients[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 218-224.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Demographic, clinical and staging characteristics of training cohort and validation cohort [n(%)]"
| Characteristics | Training cohort (n=260) | Validation cohort (n=151) |
|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis of pNETs (yrs) | ||
| 65-74 | 162 (62.3) | 108 (71.5) |
| ≥75 | 98 (37.7) | 43 (28.5) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 147 (56.5) | 84 (55.6) |
| Female | 113 (43.5) | 67 (44.4) |
| Race | ||
| White | 211 (81.2) | 130 (86.1) |
| African American | 17 (6.5) | 16 (10.6) |
| Others* | 32 (12.3) | 5 (3.3) |
| Year of diagnosis | ||
| 2004-2009 | 90 (34.6) | 24 (15.9) |
| 2010-2014 | 170 (65.4) | 127 (84.1) |
| Tumor site | ||
| Head of pancreas | 98 (37.7) | 65 (43.0) |
| Body or tail of pancreas | 141 (54.2) | 75 (49.7) |
| Overlap# | 21 (8.1) | 11 (7.3) |
| Histological grade | ||
| Well/moderate differentiated | 201 (77.3) | 117 (77.5) |
| Poor/undifferentiated | 59 (22.7) | 34 (22.5) |
| T stage (6th edition) | ||
| T1 | 46 (17.7) | 33 (21.9) |
| T2 | 100 (38.5) | 61 (40.4) |
| T3 | 99 (38.1) | 43 (28.5) |
| T4 | 15 (5.8) | 14 (9.3) |
| N stage (6th edition) | ||
| N0 | 174 (66.9) | 101 (66.9) |
| N1 | 86 (33.1) | 50 (33.1) |
| M stage | ||
| M0 | 158 (60.8) | 91 (60.3) |
| M1 | 102 (39.2) | 60 (39.7) |
| Marital status | ||
| Unmarried‡ | 93 (35.8) | 44 (29.1) |
| Married | 167 (64.2) | 107 (70.9) |
Table 2
Logistic analyses on metastasis of elderly pNETs patients with the training cohort"
| Variables* | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | P | OR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Age at diagnosis (y/d) | |||||
| 65-74 | Reference | ||||
| ≥75 | 1.112 (0.666-1.857) | 0.684 | |||
| Sex | |||||
| Male | Reference | ||||
| Female | 0.916 (0.554-1.515) | 0.733 | |||
| Race | |||||
| White | Reference | ||||
| The African American | 1.701 (0.631-4.584) | 0.294 | |||
| Others | 0.592 (0.261-1.341) | 0.209 | |||
| Marital status | |||||
| Unmarried | Reference | ||||
| Married | 0.899 (0.536-1.510) | 0.688 | |||
| Year of diagnosis | |||||
| 2004-2009 | Reference | ||||
| 2010-2014 | 0.826 (0.491-1.391) | 0.472 | |||
| Site of the tumor | |||||
| Head of pancreas | Reference | Reference | |||
| Body / tail of pancreas | 1.084 (0.635-1.852) | 0.768 | 2.282 (1.174-4.436) | 0.015 | |
| Overlap | 3.600 (1.328-9.756) | 0.012 | 4.659 (1.471-14.760) | 0.009 | |
| Histological grade | |||||
| Well / moderate differentiated | Reference | Reference | |||
| Poor / undifferentiated | 3.202 (1.756-5.836) | 0.000 | 2.600 (1.266-5.339) | 0.009 | |
| T stage | |||||
| T1 | Reference | Reference | |||
| T2 | 11.85 (2.709-51.80) | 0.001 | 8.913 (1.985-40.010) | 0.004 | |
| T3 | 24.34 (5.591-106.0) | 0.000 | 11.830 (2.530-55.350) | 0.002 | |
| T4 | 143.0 (18.310-1117) | 0.000 | 68.650 (8.020-587.600) | 0.000 | |
| N stage | |||||
| N0 | Reference | Reference | |||
| N1 | 5.194 (2.976-9.065) | 0.000 | 3.480 (1.807-6.703) | 0.000 | |
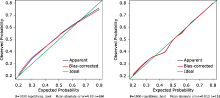
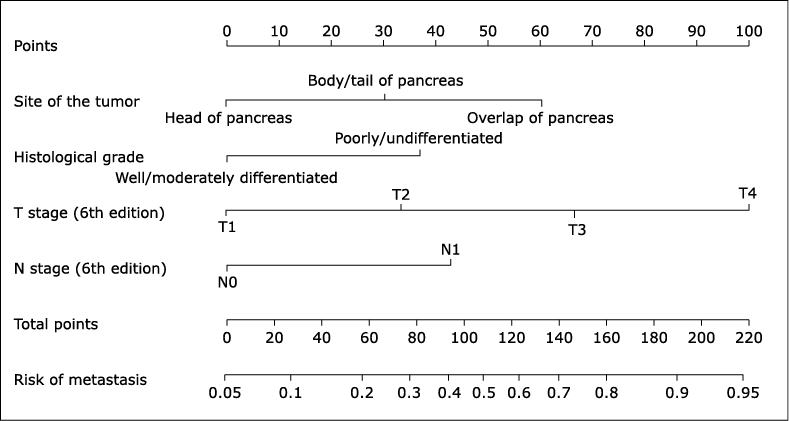
Figure 3.
The calibration curves for predicting distant metastasis in elderly pNETs patients by the established nomogram (A) Of the training cohort (internal calibration). (B) Of the validation cohort (external calibration). The “Apparent” and “Bias-corrected” lines represent perfect agreement between the predicted probabilities (x-axis) and the actual probabilities (y-axis). A perfectly accurate nomogram prediction model would result in a plot where the actual and predicted probabilities fall along the 45° line."

| 1. |
Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D, et al. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the united states. JAMA Oncol 2017; 3(10):1335-42. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0589.
doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0589 |
| 2. |
Hallet J, Law CH, Cukier M, et al. Exploring the rising incidence of neuroendocrine tumors: a population-based analysis of epidemiology, metastatic presentation, and outcomes. Cancer 2015; 121(4):589-97. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29099.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.29099 pmid: 25312765 |
| 3. |
Zhang J, Peng CS, Tian YH. Primary site surgery for elderly patients with distant metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: to do or not to do? Clin Interv Aging 2019; 14:1419-32. doi: 10.2147/cia.S209428.
doi: 10.2147/CIA.S209428 pmid: 31496669 |
| 4. |
Bertani E, Fazio N, Botteri E, et al. Resection of the primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor in patients with unresectable liver metastases: possible indications for a multimodal approach. Surgery 2014; 155(4):607-14. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.12.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.12.024 |
| 5. |
Bilimoria KY, Talamonti MS, Tomlinson JS, et al. Prognostic score predicting survival after resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: analysis of 3851 patients. Ann Surg 2008; 247(3):490-500. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815b9cae.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815b9cae pmid: 18376195 |
| 6. |
Frilling A, Clift AK. Therapeutic strategies for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Cancer 2015; 121(8):1172-86. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28760.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.28760 pmid: 25274401 |
| 7. |
Cheng KK, Lim EY, Kanesvaran R. Quality of life of elderly patients with solid tumours undergoing adjuvant cancer therapy: a systematic review. BMJ open 2018; 8(1):e018101. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018101.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018101 |
| 8. |
Soto-Perez-de-Celis E, Cordoba R, Girones R, et al. Cancer and aging in Ibero-America. Clin Transl Oncol 2018; 20(9):1117-26. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1844-1.
doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1844-1 pmid: 29435944 |
| 9. |
Shamali A, De’Ath HD, Jaber B, et al. Elderly patients have similar short term outcomes and five-year survival compared to younger patients after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Int J Surg 2017; 45:138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.07.106.
doi: S1743-9191(17)30664-7 pmid: 28782662 |
| 10. | Surveillance, Epidemiology, End Results(SEER) Program. SEER*Stat Database: Incidence - SEER Research Data, 9 Registries, Nov 2020 Sub (1973-2015). |
| 11. | Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute SEER*Stat software, version <8.3.9.2>. Available from https://seer.cancer.gov/seerstat/. |
| 12. | R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available from https://www.R-project.org/. |
| 13. |
Li G, Tian ML, Bing YT, et al. Impact of a prior nonpancreatic malignancy on survival outcomes of patients with stage IV pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A population-based and propensity score matching study. Pancreas 2020; 49(8):1090-8. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001630.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001630 |
| 14. |
Salarbaks AM, Lindeboom R, Nijmeijer W. Pneumonia in hospitalized elderly hip fracture patients: the effects on length of hospital-stay, in-hospital and thirty-day mortality and a search for potential predictors. Injury 2020; 51(8):1846-50. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2020.05.017.
doi: S0020-1383(20)30424-1 pmid: 32482422 |
| 15. |
Guo R, Wang B, Wang Y, et al. Epidemiological analysis and the nomogram for possible risk factors for severe microtia. J Craniofac Surg 2021; 32(2):e184-e189. doi: 10.1097/scs.0000000000007068.
doi: 10.1097/scs.0000000000007068 |
| 16. |
D’Arrigo G, Gori M, Pitino A, et al. Statistical methods to assess the prognostic value of risk prediction rules in clinical research. Aging Clin Exp Res 2021; 33(2):279-83. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01542-y.
doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01542-y |
| 17. |
Li G, Tian ML, Bing YT, et al. Clinicopathological features and prognosis factors for survival in elderly patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine 2019; 98(11):e14576. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000014576.
doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000014576 |
| 18. |
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, et al. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16(4):e173-80. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71116-7.
doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71116-7 |
| 19. |
Liang W, Zhang L, Jiang G, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33(8):861-9. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.56.6661.
doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.56.6661 |
| 20. |
Pierorazio PM, Patel HD, Johnson MH, et al. Distinguishing malignant and benign renal masses with composite models and nomograms: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinically localized renal masses suspicious for malignancy. Cancer 2016; 122(21):3267-76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30268.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.30268 pmid: 27508947 |
| [1] | Liang Wang, Gang Li, Yun-tao Bing, Mao-lin Tian, Hangyan Wang, Chunhui Yuan, Dianrong Xiu. Does Prior Cancer Have an Influence on the Survival Outcomes of Patients with Localized Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors? [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 284-294. |
| [2] | Hong-min Zhang, Da-wei Liu, Xiao-ting Wang, Yun Long, Quan-hui Yang. Respiratory and Cardiac Characteristics of ICU Patients Aged 90 Years and Older: A Report of 12 Cases [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(1): 37-42. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|