Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 171-180.doi: 10.24920/004135
• Scientific Data Sharing and Reuse:Original Article • Next Articles
Semi-supervised Long-tail Endoscopic Image Classification
Runnan Cao1, 2, Mengjie Fang1, 2, Hailing Li3, Jie Tian2, 3, 4, Di Dong1, 2, *( )
)
- 1School of Artificial Intelligence, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
2CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, the State Key Laboratory of Management and Control for Complex Systems, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Big Data-Based Precision Medicine, School of Engineering Medicine, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4Engineering Research Center of Molecular and Neuro Imaging of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi’an 710126, China
-
Received:2022-06-30Accepted:2022-09-09Published:2022-09-30Online:2022-09-27 -
Contact:Di Dong E-mail:di.dong@ia.ac.cn
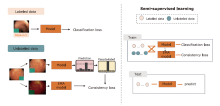
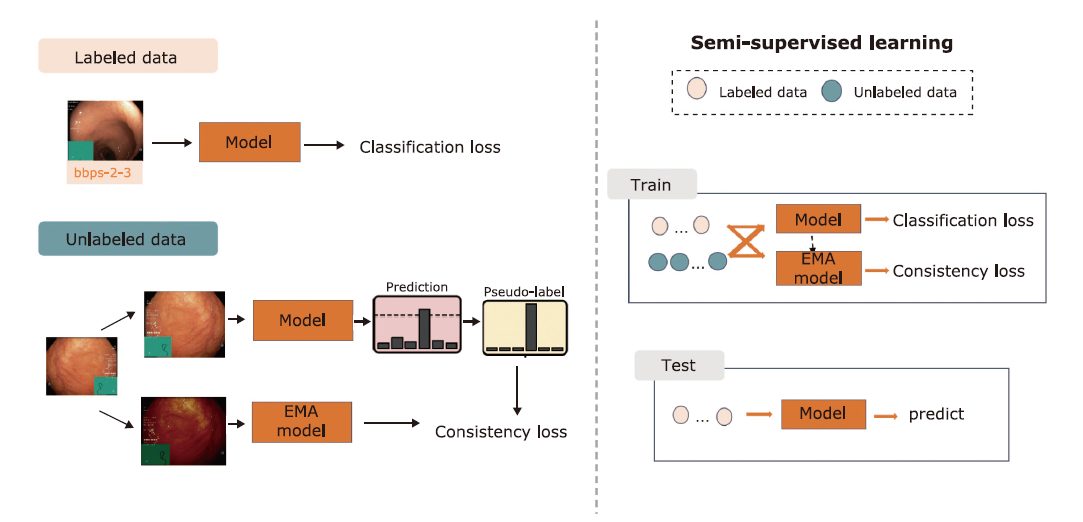
| Semi-supervised learning is more suitable for real-world applications and has become a hot new direction in the field of deep learning in recent years. The authors explored semi-supervised long-tail endoscopic image classification in HyperKvasir and found that semi-supervised learning algorithms can improve the classification performance for semi-supervised long-tail endoscopic image classification, especially when the labeled data is extremely limited, which may benefit the building of assisted diagnosis systems for low-volume hospitals. |
Cite this article
Runnan Cao, Mengjie Fang, Hailing Li, Jie Tian, Di Dong. Semi-supervised Long-tail Endoscopic Image Classification[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(3): 171-180.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1.
The classification performance of fully-supervised and semi-supervised classification under different ratio of labeled training data"
| Ratio | Algorithm | Macro average | Micro average | MCC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | ||||
| 20% | Fully-supervised | 0.5709 | 0.5684 | 0.5649 | 0.8856 | 0.8856 | 0.8856 | 0.8761 | |
| Semi-supervised | 0.5766 | 0.5759 | 0.5698 | 0.8935 | 0.8935 | 0.8935 | 0.8850 | ||
| 50% | Fully-supervised | 0.6011 | 0.6012 | 0.5965 | 0.9062 | 0.9062 | 0.9062 | 0.8983 | |
| Semi-supervised | 0.5918 | 0.5980 | 0.5912 | 0.9071 | 0.9071 | 0.9071 | 0.8994 | ||
| 100% | Fully-supervised | 0.6466 | 0.6297 | 0.6330 | 0.9146 | 0.9146 | 0.9146 | 0.9075 | |
| Semi-supervised | 0.6329 | 0.6247 | 0.6233 | 0.9165 | 0.9165 | 0.9165 | 0.9095 | ||
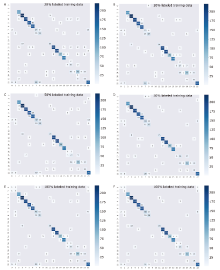
Figure 3.
Confusion matrix of fully-supervised and semi-supervised classification. (A-B), (C-D), and (E-F) show the performance under 20%, 50%, and 100% labeled training data, respectively. (A), (C), and (E) are results of fully-supervised; (B), (D), and (F) are results of semi-supervised."

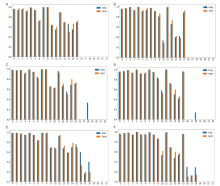
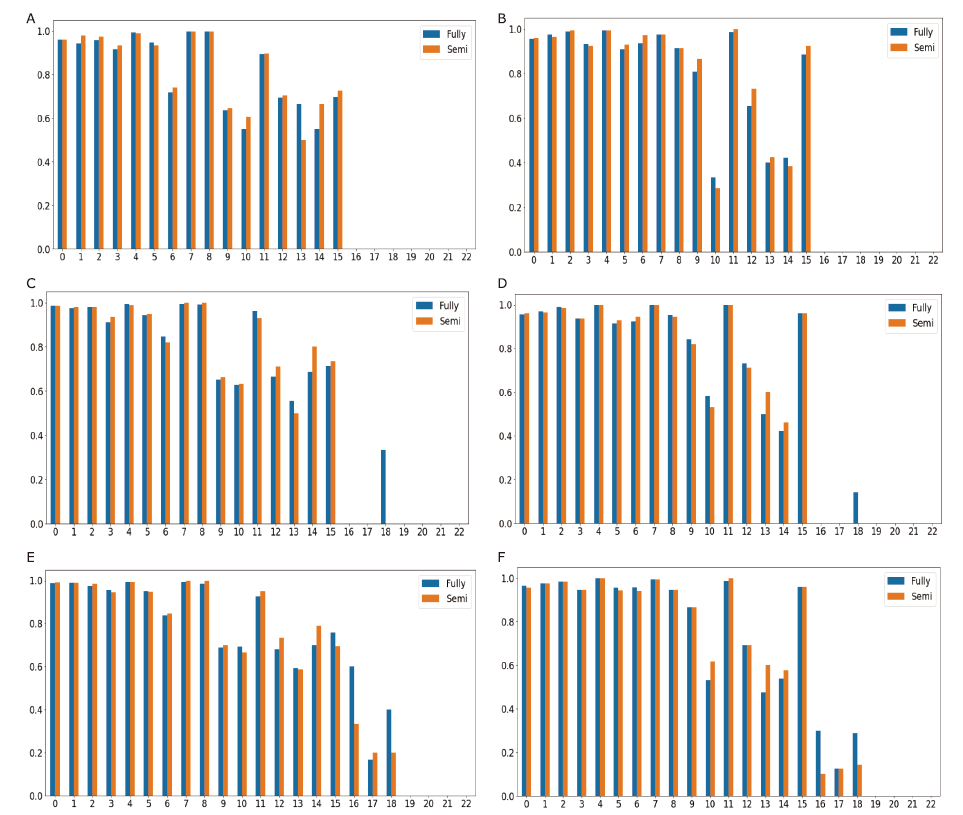
Figure 4.
Labeling bias comparison by pre-class precision and recall. (A-B), (C-D), and (E-F) show the performance under 20%, 50%, and 100% labeled training data, respectively. (A), (C), and (E) are the results of pre-class precision; (B), (D), and (F) are the results of pre-class recall."
| 1. |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71(3):209-49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 |
| 2. |
Asplund J, Kauppila JH, Mattsson F, et al. Survival trends in gastric adenocarcinoma: a population-based study in Sweden. Ann Surg Oncol 2018; 25(9):2693-702. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6627-y.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6627-y pmid: 29987609 |
| 3. |
Hosokawa O, Hattori M, Douden K, et al. Difference in accuracy between gastroscopy and colonoscopy for detection of cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2007; 54(74):442-4. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.115394.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.115394 |
| 4. |
Sivak M. Gastrointestinal endoscopy: past and future. Gut 2006; 55(8):1061-4. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.086371.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.086371 pmid: 16849338 |
| 5. |
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 2017; 42:60-88. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005.
doi: S1361-8415(17)30113-5 pmid: 28778026 |
| 6. |
Dong D, Tang Z, Wang S, et al. The role of imaging in the detection and management of covid-19: a review. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 2020; 14:16-29. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2020.2990959.
doi: 10.1109/RBME.2020.2990959 |
| 7. |
Liu Z, Wang S, Di Dong JW, et al. The applications of radiomics in precision diagnosis and treatment of oncology: opportunities and challenges. Theranostics 2019; 9(5): 1303. doi: 10.7150/thno.30309.
doi: 10.7150/thno.30309 |
| 8. |
Poon CC, Jiang Y, Zhang R, et al. Ai-Doscopist: a real-time deep-learning-based algorithm for localising polyps in colonoscopy videos with edge computing devices. NPJ Digit Med 2020; 3(1):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-0281-z.
doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-0281-z |
| 9. |
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Johansen D, et al. A comprehensive study on colorectal polyp segmentation with resunet++, conditional random field and test-time augmentation. IEEE JBHI 2021; 25(6):2029-40. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3049304.
doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3049304 |
| 10. |
Hsu CC, Ma HT, Lee JY SSSNet: Small-scale-aware siamese network for gastric cancer detection. 2019 16th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS): IEEE, 2019, 1-5. doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2019.8909849.
doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2019.8909849 |
| 11. |
Hu H, Gong L, Dong D, et al. Identifying early gastric cancer under magnifying narrow-band images with deep learning: a multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 93(6):1333-1341. e3. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.11.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.11.014 pmid: 33248070 |
| 12. |
Dong D, Tang L, Li ZY, et al. Development and validation of an individualized nomogram to identify occult peritoneal metastasis in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2019; 30(3):431-8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz001.
doi: S0923-7534(19)31081-6 pmid: 30689702 |
| 13. |
Gong L, Wang M, Shu L, et al. Automatic captioning of early gastric cancer via magnification endoscopy with narrow band imaging. Gastrointest Endosc 2022. S0016-5107(22)01836-3. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.07.019.
doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.07.019 |
| 14. |
Hirasawa T, Aoyama K, Tanimoto T, et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images. Gastric Cancer 2018; 21(4):653-60. doi: 10.1007/s10120-018-0793-2.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-018-0793-2 pmid: 29335825 |
| 15. |
Luo H, Xu G, Li C, et al. Real-time artificial intelligence for detection of upper gastrointestinal cancer by endoscopy: a multicentre, case-control, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol 2019; 20(12):1645-54. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30637-0.
doi: S1470-2045(19)30637-0 pmid: 31591062 |
| 16. |
Yoon HJ, Kim S, Kim JH, et al. A lesion-based convolutional neural network improves endoscopic detection and depth prediction of early gastric cancer. J Clin Med 2019; 8(9): 1310. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091310.
doi: 10.3390/jcm8091310 |
| 17. |
Ikenoyama Y, Hirasawa T, Ishioka M, et al. Detecting Early Gastric Cancer: Comparison between the diagnostic ability of convolutional neural networks and endoscopists. Dig Endosc 2021; 33(1):141-50. doi: 10.1111/den.13688.
doi: 10.1111/den.13688 |
| 18. |
Bernal J, Tajkbaksh N, Sanchez FJ, et al. Comparative validation of polyp detection methods in video colonoscopy: results from the Miccai 2015 Endoscopic Vision Challenge. IEEE T Med Imaging 2017; 36(6):1231-49. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2664042.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2664042 pmid: 28182555 |
| 19. |
Angermann Q, Bernal J, Sánchez-Montes C, et al. Towards real-time polyp detection in colonoscopy videos: Adapting still frame-based methodologies for video sequences analysis. // Computer Assisted and Robotic Endoscopy and Clinical Image-Based Procedures 2017; 29-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67543-5_3.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67543-5_3 |
| 20. |
Pogorelov K, Randel KR, Griwodz C, et al. Kvasir: A multi-class image dataset for computer aided gastrointestinal disease detection. // Proceedings of the 8th ACM on Multimedia Systems Conference 2017;164-9. doi: 10.1145/3193289.
doi: 10.1145/3193289 |
| 21. |
Hicks SA, Thambawita V, Hammer HL, et al. Acm Multimedia Biomedia 2020 Grand Challenge overview. // Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia 2020;4655-8. doi: 10.1145/3394171.3416287.
doi: 10.1145/3394171.3416287 |
| 22. |
Zhu XJ. Semi-supervised learning literature survey. University of Wisconsin-Madison 2006. doi: 10.1.1.103.1693.
doi: 10.1.1.103.1693 |
| 23. |
Borgli H, Thambawita V, Smedsrud PH, et al. Hyperkvasir, a comprehensive multi-class image and video dataset for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Sci Data 2020; 7(1):1-14. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00622-y.
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00622-y |
| 24. |
Pogorelov K, Riegler M, Halvorsen P, et al. Medico Multimedia Task at Mediaeval 2018. // CEUR Workshop Proceedings: Technical University of Aachen 2018;1-4. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2012.15244.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2012.15244 |
| 25. |
Harzig P, Einfalt M, Lienhart R. Automatic disease detection and report generation for gastrointestinal tract examination // Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia 2019; 2573-7. doi: 10.1145/3343031.3356066.
doi: 10.1145/3343031.3356066 |
| 26. |
Weese J, Lorenz C. Four challenges in medical image analysis from an industrial perspective. Med Image Anal 2016; 44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.06.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.06.023 |
| 27. |
Chapelle O, Scholkopf B, Zien A. (Chapelle, O. Et Al., Eds.; 2006). IEEE Trans Neural Netwlearn Syst 2009; 20(3): 542. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2015974.
doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2015974 |
| 28. |
Madani A, Ong JR, Tibrewal A, et al. Deep echocardiography: data-efficient supervised and semi-supervised deep learning towards automated diagnosis of cardiac disease. NPJ Digit Med 2018; 1(1):1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41746-018-0065-x.
doi: 10.1038/s41746-018-0065-x |
| 29. |
Su H, Shi X, Cai J, et al. Local and global consistency regularized mean teacher for semi-supervised nuclei classification. IN: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention: Springer 2019; 559-67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_62.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32239-7_62 |
| 30. |
Lee D-H. Pseudo-Label:The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. IN: Workshop on challenges in representation learning, International Conference on Machine Learning 2013; 896. doi: 10.1.1.664.354.
doi: 10.1.1.664.354 |
| 31. |
Sajjadi M, Javanmardi M, Tasdizen T. Regularization with stochastic transformations and perturbations for deep semi-supervised learning. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2016; 29. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1606.04586.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1606.04586 |
| 32. |
Sohn K, Berthelot D, Carlini N, et al. Fixmatch: Simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2020; 33:596-608. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2001.07685.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2001.07685 |
| 33. |
Rahman MM, Davis DN. Addressing the class imbalance problem in medical datasets. Int Mach Learn 2013; 3(2): 224. doi: 10.7763/IJMLC.2013.V3.307.
doi: 10.7763/IJMLC.2013.V3.307 |
| 34. |
Zhou B, Cui Q, Wei X-S, et al. Bbn: Bilateral-branch network with cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2020; 9719-28. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00974.
doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00974 |
| 35. |
Cao KD, Wei C, Gaidon A, et al. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2019; 32. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1906.07413.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1906.07413 |
| 36. |
Kang B, Xie S, Rohrbach M, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition. arXiv preprint 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1910.09217.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1910.09217 |
| 37. |
Kim J, Hur Y, Park S, et al. Distribution aligning refinery of pseudo-label for imbalanced semi-supervised learning. Adv in Neural Inf Process Syst 2020; 33:14567-79. doi: 10.48550/arXiv:2007.08844.
doi: 10.48550/arXiv:2007 |
| 38. |
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, et al. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. // Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018; 4510-4520. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474.
doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474 |
| 39. |
Wang Y, Yao Q, Kwok JT, et al. Generalizing from a few examples: a survey on few-shot learning. ACM Comput Surv 2020 ;53(3):1-34. doi: 10.1145/3386252.
doi: 10.1145/3386252 |
| [1] | Wei Ba, Shuhao Wang, Cancheng Liu, Yuefeng Wang, Huaiyin Shi, Zhigang Song. Histopathological Diagnosis System for Gastritis Using Deep Learning Algorithm [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 204-209. |
| [2] | Chen Xu, Huo Xiaofei, Wu Zhe, Lu Jingjing. Advances of Artificial Intelligence Application in Medical Imaging of Ovarian Cancers [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 196-203. |
| [3] | Wang Zheng, Zhao Qinghua, Yang Jinglin, Zhou Feng. Enhancing Quality of Patients Care and Improving Patient Experience in China with Assistance of Artificial Intelligence [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 286-288. |
| [4] | Yang Xiaolin, Wang Zhe, Pan Hongjie, Zhu Yan. Ontology: Footstone for Strong Artificial Intelligence [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 277-280. |
| [5] | Shi Ying-huan,Wang Qian. The Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Medical Imaging: Today and Its Future [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 71-75. |
| [6] | Xiao Yi,Liu Shiyuan. Collaborations of Industry, Academia, Research and Application Improve the Healthy Development of Medical Imaging Artificial Intelligence Industry in China [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 84-88. |
| [7] | Guan Jian. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and Medicine: Promises, Ethical Challenges and Governance [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 76-83. |
| [8] | Chinese Innovative Alliance of Industry, Education, Research and Application of Artificial Intelligence for Medical . Releasing of The White Paper on Medical Imaging Artificial Intelligence in China [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 89-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|