Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 252-259.doi: 10.24920/003477
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Longitudinal Measurement of Hemodynamic Changes within the Posterior Optic Nerve Head in Rodent Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Ma Jin1, Chen Ting1, 2, Wang Yiwei1, Zhao Chan1, Li Donghui1, Wang Meng1, Gan Linyang1, Zhong Yong1, *
- 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China;
2 Department of Ophthalmology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430060 China
-
Received:2018-05-07Accepted:2018-09-03Published:2018-12-30Online:2018-12-10 -
Contact:Zhong Yong
Cite this article
Ma Jin, Chen Ting, Wang Yiwei, Zhao Chan, Li Donghui, Wang Meng, Gan Linyang, Zhong Yong. Longitudinal Measurement of Hemodynamic Changes within the Posterior Optic Nerve Head in Rodent Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(4): 252-259.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
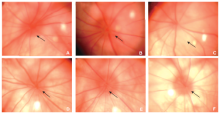
Figure 1.
Fundus photographs of optic nerve head (ONH) in naive rats and rNAION rats. A. The border of the ONH in a naive rat eye was distinct (arrow); B. in rNAION rats, blurring of the ONH border (arrow) observed 3 hours after disease induction, indicating edema; C. diameter of the ONH enlarged and reached the maximum (arrow) 1 day after disease induction; D. five days after induction, edema of the ONH resolved almost completely; E. the appearance of the ONH returned to normal on day 14; F. the ONH was apparently pale with reduction in size on day 90. rNAION: rat model of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy; ONH: optic nerve head."
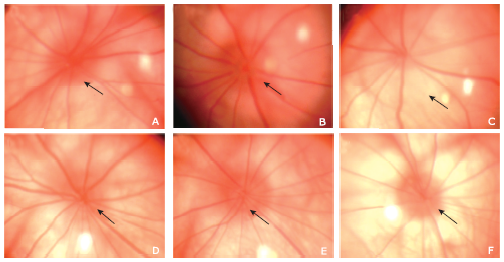
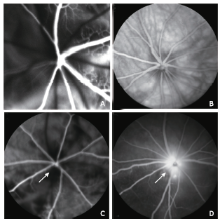
Figure 2.
Representative FFA images of a naive eye and an rNAION eye 3 hours after disease induction. A. normal fluorescein perfusion of the choroidal and retinal vasculature in the early phase of FFA in a naive eye. B. normal fluorescein distribution in the fundus in the late phase of FFA in a naive eye; C. FFA imaging 3 seconds after injection (early phase) of an rNAION eye showed filling defects in the choroid and the ONH (arrow); D. late phase imaging of the same eye showed marked dye leakage (arrow) from the ONH. FFA: fundus fluorescein angiography."
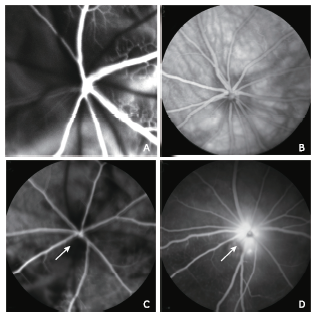
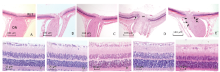
Figure 3.
Representative histologic sections of ONH and retina in naive and rNAION eyes (H&E stain). A. longitudinal sections of the ONH in naive eyes, B. in the laser-only eyes and C. in the RB-only eyes showed normal histology and anatomy of the optic nerve and peripapillary retina. D. On day 1 after rNAION induction, the ONH was edematous with thickened nerve fiber bundles (double asterisks) and peripapillary retinal detachment (arrow). E. On day 90 after induction, there was a reduced number of RGC axons (long arrow) accompanied by gliosis and cellular infiltration (short arrow). F. naive eyes, G. laser-only eyes, H. RB-only eyes, and I. eyes 1 day after rNAION induction. The RGCs in peripapillary retina were closely packed in a single layer with normal density. J. On day 90 after rNAION induction, there was an obvious reduction in density of the RGCs in retina, while the cell densities in the INL and ONL remained mainly unchanged. (magnifying power: A-E, 50×; F-J, 200×). RB: rose bengal; RGC: retinal ganglion cell; INL: inner nuclear layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer."
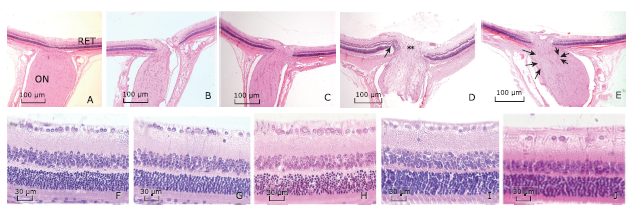
Figure 4.
Representative cross sections of ON in naive and rNAION eyes (Toluidine blue stain, 200×). A. cross section of ON in naive eye showed tightly packed axonal bundles by the pial septate (S); B. cross section of ON on day 90 after rNAION induction, an apparent reduction in central axonal bundle density with increased septal thickness was observed. AxB: axonal bundle. ON: optic nerve."
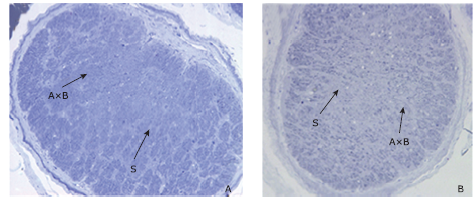
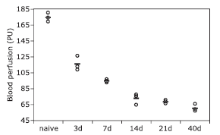
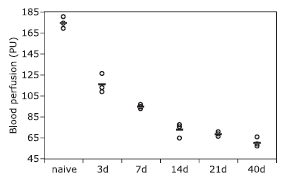
Figure 5.
The hemodynamic changes in blood flow kinetics of posterior ONH in naive rats and rNAION rats at different time points after disease induction. The posterior ONH blood perfusion measurements in rNAION rats were significantly lower than that in naive rats (all P<0.0001). Statistically significant reductions of optic nerve blood flow were detected between day 3 and day 7, day 7 and day 14 after disease induction (both P<0.01)."
| [1] |
Johnson LN, Arnold AC . Incidence of nonarteritic and arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Population-based study in the state of Missouri and Los Angeles County, California. J Neuroophthalmol 1994; 14(1):38-44. doi: 10.1097/00041327-199403000-00011.
doi: 10.1097/00041327-199403000-00011 pmid: 8032479 |
| [2] |
Hattenhauer MG, Leavitt JA, Hodge DO , et al. Incidence of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1997; 123(1):103-7. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70999-7.
doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70999-7 pmid: 9186104 |
| [3] |
Riva CE, Geiser M, Petrig BL . Ocular blood flow assessment using continuous laser Doppler flowmetry. Acta Ophthalmol 2010; 88(6):622-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2009.01621.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2009.01621.x pmid: 19860779 |
| [4] |
Feke GT . Retrobulbar haemodynamics in non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2006; 90(11):1334-5. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2006.0101329.
doi: 10.1136/bjo.2006.0101329 pmid: 1857495 |
| [5] |
Hayreh SS . Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res 2009; 28(1):34-62. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.11.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.11.002 |
| [6] |
Bernstein SL, Guo Y, Slater BJ , et al. Neuron stress and loss following rodent anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in double-reporter transgenic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48(5):2304-10. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0486.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0486 pmid: 17460295 |
| [7] |
Maekubo T, Chuman H, Kodama Y , et al. Evaluation of inner retinal thickness around the optic disc using optical coherence tomography of a rodent model of nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2012; 57(3):327-32. doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0195-7.
doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0195-7 |
| [8] |
Maekubo T, Chuman H, Nao-I N . Laser speckle flowgraphy for differentiating between nonarteritic ische-mic optic neuropathy and anterior optic neuritis. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2013; 57(4):385-90. doi: 10.1007/s10384-013-0246-8.
doi: 10.1007/s10384-013-0246-8 pmid: 23695410 |
| [9] |
Wei X, Balne PK, Meissner KE , et al. Assessment of flow dynamics in retinal and choroidal microcirculation. Surv Ophthalmol 2018; 63(5):646-64. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2018.03.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2018.03.003 |
| [10] |
Chen CT, Hsiu H, Fan JS , et al. Complexity analysis of beat-to-beat skin-surface laser-doppler flowmetry signals in stroke patients. Microcirculation 2015; 22(5):370-7. doi: 10.1111/micc.12206.
doi: 10.1111/micc.12206 pmid: 25904285 |
| [11] |
Goltsov A, Anisimova AV, Zakharkina M , et al. Bifurcation in blood oscillatory rhythms for patients with ischemic stroke: a small scale clinical trial using laser doppler flowmetry and computational modeling of vasomotion. Front Physiol 2017; 8:160. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00160.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00160 pmid: 5362641 |
| [12] |
Geiser MH, Truffer F, Evequoz H , et al. Schlieren laser Doppler flowmeter for the human optical nerve head with the flicker stimuli. J Biomed Opt 2013; 18(12):127001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.12.127001.
doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.12.127001 pmid: 24296999 |
| [13] |
Gallice M, Zhou T, Aptel F , et al. Hypoxic, hypercapnic, and hyperoxic responses of the optic nerve head and subfoveal choroid blood flow in healthy humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2017; 58(12):5460-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21855.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-21855 pmid: 29059313 |
| [14] |
Mentek M, Truffer F, Chiquet C , et al. Compact laser doppler flowmeter (LDF) fundus camera for the assessment of retinal blood perfusion in small animals. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0134378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134378.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134378 pmid: 4520556 |
| [15] |
Bernstein SL, Guo Y, Kelman SE , et al. Functional and cellular responses in a novel rodent model of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44:4153-62.
doi: 10.1007/s10439-009-9749-3 pmid: 14507856 |
| [16] |
Guo Y, Mehrabian Z, Bernstein SL . The rodent model of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (rNAION). J Vis Exp 2016; ( 117), e54504. doi: 10.3791/ 54504.
doi: 10.3791/ 54504 pmid: 27911358 |
| [17] |
Wang RS, Lv PL, Wang WJ , et al. Establishing an experimental model of photodynamically induced anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Vis Neurosci 2011; 28(2):155-62. doi: 10.1017/S0952523810000398.
doi: 10.1017/S0952523810000398 pmid: 21356144 |
| [18] |
Nicholson JD, Puche AC, Guo Y , et al. PGJ(2) provides prolonged CNS stroke protection by reducing white matter edema. PLoS One 2012; 7(12):e50021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050021.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050021 pmid: 23284631 |
| [19] |
Chuman H, Maekubo T, Osako T , et al. Rodent model of nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy and its electrophysiological evaluation. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2012; 56(5):518-27. doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0167-y.
doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0167-y pmid: 22864772 |
| [20] |
Ma J, Jiang L, Zhong Y , et al. Neuroprotective effect on retinal ganglion cells by transpupillary laser irradiation of the optic nerve head. Neurosci Lett 2010; 476(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.01.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.01.001 pmid: 20060436 |
| [21] |
Slater BJ, Vilson FL, Guo Y , et al. Optic nerve inflammation and demyelination in a rodent model of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54(13):7952-61. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12064.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12064 pmid: 3854773 |
| [22] |
Goldenberg-Cohen N, Guo Y, Margolis F , et al. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction after induction of experimental anterior optic nerve ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46(8):2716-25. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0547.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0547 pmid: 16043843 |
| [23] |
Chuman H, Maekubo T, Osako T , et al. Effects of L-arginine on anatomical and electrophysiological deterioration of the eye in a rodent model of nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2013; 57(4):402-9. doi: 10.1007/s10384-013-0250-z.
doi: 10.1007/s10384-013-0250-z pmid: 23712653 |
| [24] |
Osako T, Chuman H, Maekubo T , et al. Effects of steroid administration and transcorneal electrical stimulation on the anatomic and electrophysiologic deterioration of nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy in a rodent model. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2013; 57(4):410-5. doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0203-y.
doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0203-y pmid: 23657677 |
| [25] |
Hayreh SS . Blood flow in the optic nerve head and factors that may influence it. Prog Retin Eye Res 2001; 20(5):595-624. doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(01)00005-2.
doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(01)00005-2 pmid: 11470452 |
| [26] |
Arnold AC . Pathogenesis of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. J Neuroophthalmol 2003; 23(2):157-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2009.06.008 pmid: 20006051 |
| [27] |
Wang YW, Chen T, Ma J , et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of RGC death and axon degeneration in the rat model of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 2016; 52(12):918-23. Chinese. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2016.12.009.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2016.12.009 |
| [28] |
Piper C, Fortune B, Cull G , et al. Basal blood flow and autoregulation changes in the optic nerve of rhesus monkeys with idiopathic bilateral optic atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54(1):714-21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9773.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9773 pmid: 23287792 |
| [29] |
Chiba N, Omodaka K, Yokoyama Y , et al. Association between optic nerve blood flow and objective examinations in glaucoma patients with generalized enlargement disc type. Clin Ophthalmol 2011; 5:1549-56. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S22097.
doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S22097 pmid: 22125400 |
| [30] |
Hwang JC, Konduru R, Zhang X , et al. Relationship among visual field, blood flow, and neural structure measurements in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53(6):3020-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8552.
doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8552 pmid: 22447865 |
| [1] | Li Zifei, Liu Qingliang, Wang Xiaojun, Luan Jie. The Characteristics of Blood Supply and Tissue Hypoxia in Pathological Scars [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 113-118. |
| [2] | Yan-bing Xu, Nai-zhi Wang, Li-li Yang, Hua-dong Cui, Hong-xia Xue, Ning Zhang*. Expression of Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Nonreceptor Type 22 in the Synovium of Collagen-Induced Arthritis Rats [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(2): 85-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

