Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 260-266.doi: 10.24920/003470
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Combined Effects of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Depression on Spatial Memory in Old Rats
Cai Cui1, *( ), Xu Changqing2, Jin Hualiang3, Li Bei4
), Xu Changqing2, Jin Hualiang3, Li Bei4
- 1 Department of Geriatrics, Hangzhou Red Cross Hospital, Hangzhou 310003, China
2 Department of Respiratory, the Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University,Hangzhou 330015, China
3 Department of Respiratory, Hangzhou 310006, China
4 Department of Geriatrics,Hangzhou First People’s Hospital, Hangzhou 310006, China;
-
Received:2018-03-09Accepted:2018-08-27Published:2018-12-30Online:2019-01-10 -
Contact:Cai Cui E-mail:caicui2003@aliyun.com
Cite this article
Cai Cui,Xu Changqing,Jin Hualiang,Li Bei. Combined Effects of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Depression on Spatial Memory in Old Rats[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(4): 260-266.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
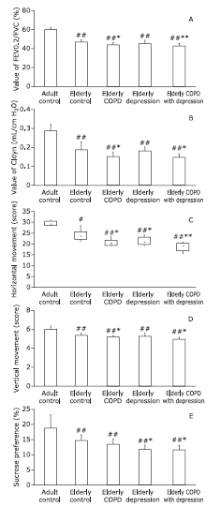
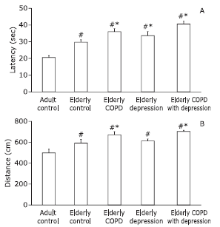
Figure 2.
Results of pulmonary function test, open-field test and sucrose preference test in controls and testing groups. A. FEV0.2/FVC; B. Cldyn; C. horizontal movement, expressed as median and quantile; D. vertical movement; E. sucrose preference index. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 compared to the adult control group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to the elderly control group. FEV0.2/FVC: ratio of forced expiratory volume at 0.2 s to the forced vital capacity; Cldyn, dynamic lung compliance; COPD, chronic obstruction pulmonary disease."

"
| Group | Serum | Hippocampus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD (U/mL) | MDA(nmol/mL) | SOD (U/mg prot) | MDA (nmol/mg prot) | ||
| Adult control | 9.50±0.48 | 1.24±0.36 | 8.16±0.47 | 1.17±0.20 | |
| Elderly control | 7.00±0.44## | 2.41±0.35# | 5.20±0.45## | 2.61±0.28# | |
| Elderly COPD | 5.86±0.49## | 2.85±0.33## | 4.97±0.33## | 2.82±0.44# | |
| Elderly depression | 6.11±0.55## | 2.70±0.18## | 5.14±0.66## | 2.94±0.49## | |
| Elderly COPD with depression | 5.15±0.52##* | 2.94±0.49##* | 3.68±0.57##* | 3.85±0.60##* | |
| [1] |
Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ , et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 Report. GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017; 195(5):557-82. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP |
| [2] |
Hanania NA, Sharma G, Sharafkhaneh A . COPD in the elderly patient. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 31(5):596-606. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1265900.
doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1265900 pmid: 20941660 |
| [3] |
Blanchette CM, Berry SR, Lane SJ . Advances in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among older adults. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2011; 17(2):84-9. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e32834316ff.
doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e32834316ff pmid: 21178625 |
| [4] |
Yuan YM. Aging and COPD. Chin J Clinician 2013; 7(2): 478-80. Chinese. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2013.02.008.
doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2013.02.008 |
| [5] |
Lou P, Zhu Y, Chen P . Prevalence and correlations with depression, anxiety and other features in outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China: a cross-sectional case control study. BMC Pulm Med 2012; 12:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-12-53.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-12-53 pmid: 22958576 |
| [6] |
Cui GM, Zhu ZM , Xue YC. Related factors of the influence of depressive disorder on senior patients with COPD. Chin J practical Mervous Dis 2013; 16(20):33-5. Chinese. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2013.20.018.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2013.20.018 |
| [7] |
Russo E, Citraro R, Davoli A , et al. Ameliorating effects of aripiprazole on cognitive functions and depressive-like behavior in a genetic rat model of absence epilepsy and mild-depression comorbidity. Neuropharmacology 2013; 64:371-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.039.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.039 |
| [8] |
Fernandez JW, Grizzell JA, Philpot RM , et al. Postpartum depression in rats: differences in swim test immobility, sucrose preference and nurturing behaviors. Behav Brain Res 2014; 272(4):75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.06.041.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.06.041 pmid: 24983658 |
| [9] |
Lee B, Sur B, Cho SG , et al. Effect of Beta-Asarone on Impairment of Spatial Working Memory and Apoptosis in the Hippocampus of Rats Exposed to Chronic Corticosterone Administration. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2015; 23(6):571-81. doi: 4062/biomolther.2015.027.
doi: 4062/biomolther.2015.027 pmid: 4624074 |
| [10] |
Ellison D, White D, Farrar FC . Aging population. Nurs Clin North Am 2015; 50(1):185-213. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2014.10.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2014.10.014 |
| [11] |
de Voogd JN, Wempe JB, Koeter GH , et al. Depressive symptoms as predictors of mortality in patients with COPD. Chest 2009; 135(3):619-25. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0078.
doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0078 pmid: 19029432 |
| [12] |
Chetta A, Foresi A, Marangio E , et al. Psychological implications of respiratory health and disease. Respiration 2005; 72(2):210-5. doi: 10.1159/000084056.
doi: 10.1159/000084056 pmid: 15824535 |
| [13] |
Moisieieva NV, Burya LV, Kapustianskaya AA , et al. Comprehensive patterns of comorbidity: COPD and depression. Aspects of treatment. Wiad Lek 2018; 7(3 pt 1):588-91.
pmid: 29783230 |
| [14] |
Bock K, Bendstrup E, Hilberg O , et al. Screening tools for evaluation of depression in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). A systematic review. Eur Clin Respir 2017; 4(1):1332931. doi: 10.1080/20018525.2017.1332931.
doi: 10.1080/20018525.2017.1332931 pmid: 28649311 |
| [15] |
Corlateanu A, Covantev S, Mathioudakis AG , et al. Prevalence and burden of comorbidities in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir Investig 2016; 54(6):387-96. doi: 10.1016 /j. resinv.2016.07.001.
doi: 10.1016 /j. resinv.2016.07.001 pmid: 27886849 |
| [16] |
Lavrencic LM, Richardson C, Harrison SL , et al. Is there a link between cognitive reserve and cognitive function in the oldest-old? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med 2018; 73(4):499-505. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx140.
doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx140 pmid: 28977420 |
| [17] |
van Beers M, Janssen DJA, Gosker HR , et al. Cognitive impairment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: disease burden, determinants and possible future interventions. Expert Rev Respir Med 2018; 12(12):1061-74. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2018.1533405.
doi: 10.1080/17476348.2018.1533405 |
| [18] |
Aras YG, Tunc A, Güngen BD , et al. The effects of depression, anxiety and sleep disturbances on cognitive impairment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cogn Neurodyn 2017; 11(6):565-71. doi: 10.1007/s11571-017-9449-x.
doi: 10.1007/s11571-017-9449-x pmid: 29147148 |
| [19] |
Burger C . Region-specific genetic alternations in the aging hippocampus: implications for cognitive aging. Front Aging Neurosci 2010; 2:140. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00140.
doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00140 |
| [20] |
Stockmeier CA, Mahajan GJ, Konick LC , et al. Cellular changes in the postmortem hippocampus in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56(9):640-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.08.022.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.08.022 |
| [21] |
Zhu J, Mu X, Zeng J , et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents cognitive impairment and hipppcamps senescence in a rat model of D-Galactose-induced Aging. PLoS One 2014; 9(6):e101291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101291.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101291 pmid: 24979747 |
| [22] |
Martínez-Aguilar, NE,Vargas-Cama?o ME,Hernández-Pliego RR,et al. Immunopathology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Rev Alerg Mex 2017; 64(3):327-46. doi: 10.29262/ram.v64i3.263.
doi: 10.29262/ram.v64i3.263 pmid: 29046030 |
| [23] |
Diniz BS, Mendes-Silva AP, Silva LB , et al. Oxidative stress markers imbalance in late-life depression. J Psychiatr Res 2018; 102:29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.02.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.02.023 pmid: 29574402 |
| [1] | Jianbo Xiu, Lanlan Li, Qi Xu. Minocycline Activates the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract-Associated Network to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 1-14. |
| [2] | Atefeh Beigi-khoozani, Amirmohammad Merajikhah, Mahdieh Soleimani. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Olfactory Bulb in Anosmic Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [3] | Xue Zhang, Yan Xu, Lijian Pei. Review of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder with Pain-Depression Comorbidity [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 316-322. |
| [4] | Chen Xu, Huo Xiaofei, Wu Zhe, Lu Jingjing. Advances of Artificial Intelligence Application in Medical Imaging of Ovarian Cancers [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 196-203. |
| [5] | Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [6] | Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [7] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [8] | Lv Shuangjie, Ding Yangnan, Pei Xiaoya, Zhao Xiang, Hao Delong, Zhang Zhuqin, Chen Houzao, Liu Depei. Vascular Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Aging-Related Genes in Angiotensin Ⅱ-Induced Hypertensive Mouse Aortas [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 43-53. |
| [9] | Ping Fen, Cao Qin, Lin Hua, Han Shuzhi. Antagonistic Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway Activation, Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Rats with PM2.5 Induced Lung Injuries [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 270-276. |
| [10] | Shi Ying-huan,Wang Qian. The Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Medical Imaging: Today and Its Future [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 71-75. |
| [11] | Xiao Yi,Liu Shiyuan. Collaborations of Industry, Academia, Research and Application Improve the Healthy Development of Medical Imaging Artificial Intelligence Industry in China [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 84-88. |
| [12] | Chinese Innovative Alliance of Industry, Education, Research and Application of Artificial Intelligence for Medical . Releasing of The White Paper on Medical Imaging Artificial Intelligence in China [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 89-89. |
| [13] | Wang Botao, Liu Mingxia, Chen Zhiye. Differential Diagnostic Value of Texture Feature Analysis of Magnetic Resonance T2 Weighted Imaging between Glioblastoma and Primary Central Neural System Lymphoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [14] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [15] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|