Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 110-119.doi: 10.24920/003794
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help
Jia Xu1, Xuan Wang1, *( ), Zhengyu Jin1, *(
), Zhengyu Jin1, *( ), Qin Wang1, Yan You2, Shitian Wang1, Tianyi Qian3, Huadan Xue1
), Qin Wang1, Yan You2, Shitian Wang1, Tianyi Qian3, Huadan Xue1
- 1Department of Radiology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Department of Pathology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Beijing 100102, China
-
Received:2020-09-15Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:Xuan Wang,Zhengyu Jin E-mail:dr_wangxuan@163.com;jinzy@pumch.cn
| The authors used longer time period of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-enhanced MRI to investigate liver function of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury rat models. The results indicated a longer time period of T1 mapping scanning had the potential to provide information about liver function of rats with liver fibrosis. |
Cite this article
Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
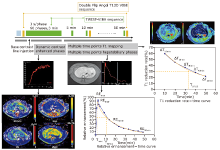
Figure 1.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocol and image analysis. The MRI protocol included dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) sequence, multiple hepatobiliary phase acquisitions, and T1 mapping series. The regions of interest were drawn and the MRI parameters were measured and calculated from different datasets include: 1) T1 relaxation time, T1 reduction rate (ΔT1) at different time points, and the elimination half-life of ΔT1 (TΔT1 1/2); 2) Relative enhancement (RE) at 3, 20, and 50 min, TRE1/2, Tmax, and REmax; 3) extravascular volume transfer (Ktrans), extravascular fluid volume (Ve), extravascular to plasma volume transfer (Kep), and initial area under the enhancement curve (iAUC). "
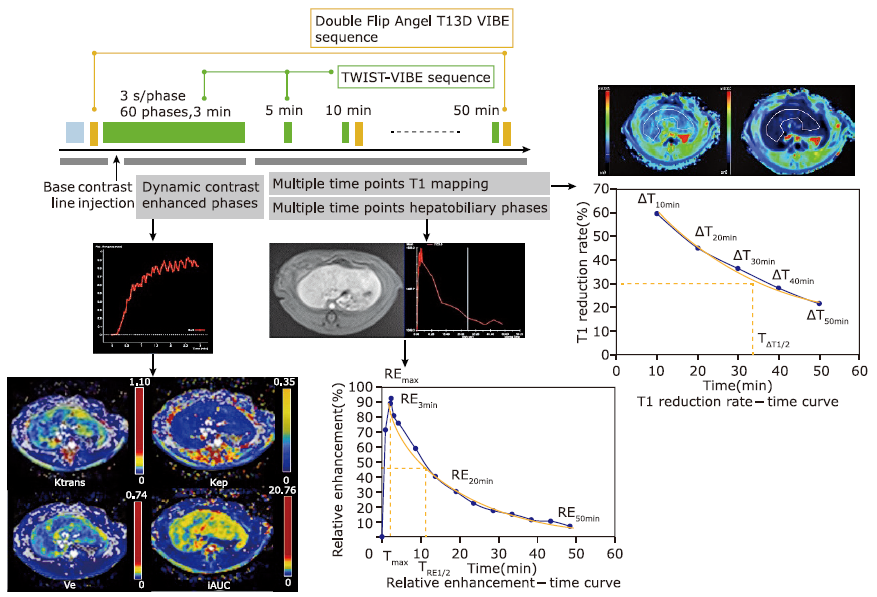
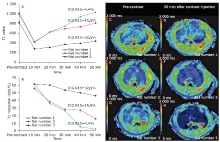
Figure 3.
The T1 value-time curve (A), T1 reduction rate-time curve (B), and T1 maps obtained before (C, E, G) and 50 min after Gd-EOB-DPTA administration (D, F, H) of three rat models with varying liver function. The indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min (ICG R15) values of rat number 1, rat number 2, and rat number 3 was 4.4%, 15.5%, and 32.5%, respectively. The worse the liver function was, the smaller T1 value and larger T1 reduction rate were found in the late hepatobiliary phase."
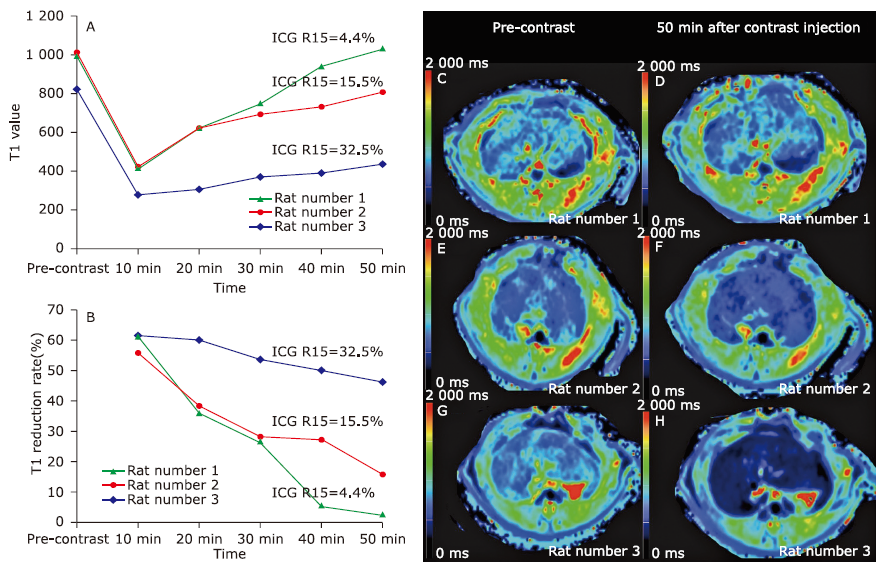
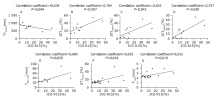
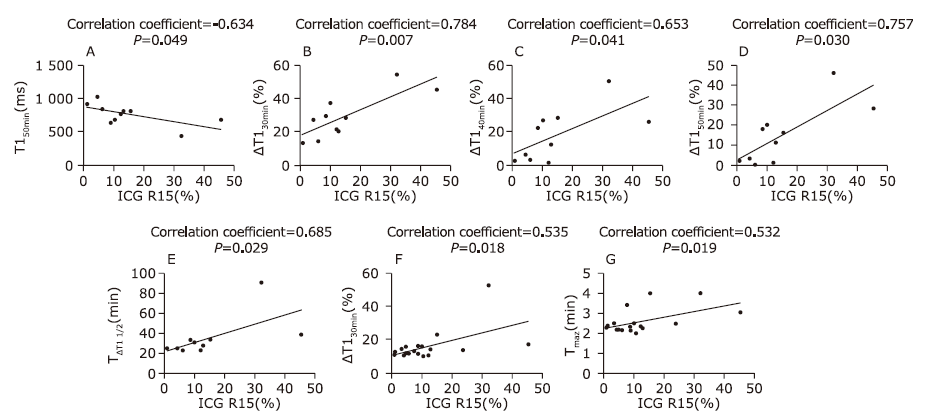
Figure 4.
Scattergrams showing the relationships between the T1 mapping parameters, relative enhancement parameters, and indocyanine green retention rate at 15 minutes (ICG R15). T1 relaxation time at 50 min showed a significant negative correlation with ICG R15 (A, r=-0.634, P=0.049). ΔT1 30min, ΔT1 40min, ΔT1 50min showed significant positive correlations with ICG R15 (B, r=0.784, P=0.007; C, r=0.653, P=0.041; and D, r=0.757, P=0.030, respectively). TΔT1 1/2 showed a significant positive correlation with ICG R15 (E, r=0.685, P=0.029). TRE1/2 and Tmax showed significant positive correlation with ICG R15 (F, r=0.535, P=0.018; G, r=0.532, P=0.019). "
| [1.] |
Hammond JS, Guha IN, Beckingham IJ, et al. Prediction, prevention and management of postresection liver failure. Br J Surg 2011; 98(9):1188-200. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7630.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.7630 pmid: 21725970 |
| [2.] |
Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N, et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: Consensus-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig Dis 2011; 29(3):339-64. doi: 10.1159/000327577.
doi: 10.1159/000327577 |
| [3.] |
Geisel D, Ludemann L, Hamm B, et al. Imaging-based liver function tests—past, present and future. Rofo 2015; 187(10):863-71. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1553306.
doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1553306 pmid: 26230140 |
| [4.] |
Van Beers BE, Pastor CM, Hussain HK. Primovist, eovist: what to expect? J Hepatol 2012; 57(2):421-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.031.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.031 |
| [5.] |
Ba-Ssalamah A, Bastati N, Wibmer A, et al. Hepatic gadoxetic acid uptake as a measure of diffuse liver disease: where are we? J Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 45(3):646-59. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25518.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25518 pmid: 27862590 |
| [6.] |
Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Liver parenchymal enhancement of hepatocyte-phase images in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging: which biological markers of the liver function affect the enhancement? J Magn Reson Imaging 2009; 30(5):1042-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21956.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.21956 pmid: 19856436 |
| [7.] |
Verloh N, Haimerl M, Zeman F, et al. Assessing liver function by liver enhancement during the hepatobiliary phase with Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI at 3 Tesla. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(5):1013-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3108-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3108-y pmid: 24531844 |
| [8.] |
Sato Y, Matsushima S, Inaba Y, et al. Preoperative estimation of future remnant liver function following portal vein embolization using relative enhancement on gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Korean J Radiol 2015; 16(3):523-30. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.523.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.523 |
| [9.] |
Ippolito D, Pecorelli A, Famularo S, et al. Assessing liver function: diagnostic efficacy of parenchymal enhancement and liver volume ratio of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI study during interstitial and hepatobiliary phase. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2019; 44(4):1340-9. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1812-9.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1812-9 pmid: 30411177 |
| [10.] |
Ryeom HK, Kim SH, Kim JY, et al. Quantitative evaluation of liver function with MRI using Gd-EOB-DTPA. Korean J Radiol 2004; 5(4):231-9. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.4.231.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.4.231 |
| [11.] |
Saito K, Ledsam J, Sourbron S, et al. Measuring hepatic functional reserve using low temporal resolution Gd-EOB-DTPA dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a preliminary study comparing galactosyl human serum albumin scintigraphy with indocyanine green retention. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(1):112-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2983-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2983-y |
| [12.] |
Ning J, Yang Z, Xie S, et al. Hepatic function imaging using dynamic Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI and pharmacokinetic modeling. Magn Reson Med 2017; 78(4):1488-95. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26520.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26520 pmid: 27785826 |
| [13.] |
Sourbron S, Sommer WH, Reiser MF, et al. Combined quantification of liver perfusion and function with dynamic gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2012; 263(3):874-83. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110337.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110337 pmid: 22623698 |
| [14.] |
Katsube T, Okada M, Kumano S, et al. Estimation of liver function using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2011; 46(4):277-83. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318200f67d.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318200f67d |
| [15.] |
Haimerl M, Verloh N, Zeman F, et al. Assessment of clinical signs of liver cirrhosis using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced 3T MRI. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e85658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085658.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085658 |
| [16.] |
Haimerl M, Verloh N, Fellner C, et al. MRI-based estimation of liver function: Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced T1 relaxometry of 3T vs. the MELD score . Sci Rep 2014; 4:5621. doi: 10.1038/srep05621.
doi: 10.1038/srep05621 |
| [17.] |
Kamimura K, Fukukura Y, Yoneyama T, et al. Quantitative evaluation of liver function with T1 relaxation time index on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI: comparison with signal intensity-based indices. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 40(4):884-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24443.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.24443 |
| [18.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Qiu WJ, et al. Comparison of 10- and 20-min hepatobiliary phase images on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for liver function assessment in clinic. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017; 42(9):2272-8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2 |
| [19.] |
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Kim E, et al. Quantitative liver function analysis: volumetric T1 mapping with fast multisection B1 inhomogeneity correction in hepatocyte-specific contrast-enhanced liver MR imaging. Radiology 2017; 282(2):408-17. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152800.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152800 |
| [20.] |
Nakagawa M, Namimoto T, Shimizu K, et al. Measuring hepatic functional reserve using T1 mapping of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced 3T MR imaging: a preliminary study comparing with 99mTc GSA scintigraphy and signal intensity based parameters. Eur J Radiol 2017; 92:116-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.011 |
| [21.] |
Ding Y, Rao SX, Chen C, et al. Assessing liver function in patients with HBV-related HCC: a comparison of T(1) mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging with DWI. Eur Radiol 2015; 25(5):1392-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3542-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3542-x |
| [22.] |
Yuan J, Chow SK, Yeung DK, et al. Quantitative evaluation of dual-flip-angle T1 mapping on DCE-MRI kinetic parameter estimation in head and neck. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2012; 2(4):245-53. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.11.04.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.11.04 |
| [23.] |
Kim KA, Herigault G, Kim MJ, et al. Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced hepatic MR imaging: comparison between a centric technique and a linear approach with partial Fourier along both slice and phase directions. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 33(1):160-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22436.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22436 |
| [24.] |
Sheng RF, Wang HQ, Yang L, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance. Dig Liver Dis 2017; 49(7):789-95. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.02.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.02.006 |
| [25.] |
Kundel HL, Polansky M. Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 2003; 228(2):303-8. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2282011860.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2282011860 |
| [26.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Huang LJ, et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for assessment of liver function in rabbit fibrosis model: comparison of hepatobiliary phase images obtained at 10 and 20 min. Radiol Med 2017; 122(4):239-47. doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1 |
| [27.] |
Haimerl M, Schlabeck M, Verloh N, et al. Volume-assisted estimation of liver function based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR relaxometry. Eur Radiol 2016; 26(4):1125-33. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3919-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3919-5 |
| [28.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Qiu WJ, et al. Evaluating segmental liver function using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI with a 3.0 Tesla. BMC Med Imaging 2017; 17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0192-x.
doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0192-x |
| [29.] |
Unal E, Idilman IS, Karcaaltincaba M. Multiparametric or practical quantitative liver MRI: towards millisecond, fat fraction, kilopascal and function era. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 11(2):167-82. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1271710.
doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1271710 |
| [30.] |
Yoneyama T, Fukukura Y, Kamimura K, et al. Efficacy of liver parenchymal enhancement and liver volume to standard liver volume ratio on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for estimation of liver function. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(4):857-65. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3086-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3086-5 |
| [31.] |
Tsuda N, Matsui O. Signal profile on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver cirrhosis induced in rats: correlation with transporter expression. Eur Radiol 2011; 21(12):2542-50. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2228-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2228-x |
| [32.] |
Saito S, Obata A, Kashiwagi Y, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver in Mrp2-deficient rats using the hepatobiliary contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA. Invest Radiol 2013; 48(7):548-53. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182856a06.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182856a06 |
| [33.] |
Hinrichs H, Hinrichs JB, Gutberlet M, et al. Functional gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). Eur Radiol 2016; 26(4):1116-24. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3913-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3913-y pmid: 26205638 |
| [34.] |
Yamada T, Kashiwagi Y, Rokugawa T, et al. Evaluation of hepatic function using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in melanocortin 4 receptor-deficient mice as a model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Magn Reson Imaging 2019; 57:210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.11.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.11.013 |
| [35.] |
Zhang W, Kong X, Wang ZJ, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA for the evaluation of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0129621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129621.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129621 |
| [36.] |
Yang JF, Zhao ZH, Zhang Y, et al. Dual-input two-compartment pharmacokinetic model of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(13):3652-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3652.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3652 |
| [1] | Atefeh Beigi-khoozani, Amirmohammad Merajikhah, Mahdieh Soleimani. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Olfactory Bulb in Anosmic Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [3] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [4] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [5] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [6] | Li Ping, Zhu Liang, Wang Xuan, Xue Huadan, Wu Xin, Jin Zhengyu. Imaging Diagnosis of Type Ⅲ Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [7] | Chen Zhiye, Liu Mengqi, Ma Lin. Cortical Thinning Pattern of Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Surface-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [8] | Li Lihui, Huang Houbin, Chen Zhiye. Early Diagnosis of Recurrent Optic Neuritis Using Contrast-Enhanced T2 Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging: a Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [9] | Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [10] | Liu Mengqi, Chen Zhiye, Ma Lin. Reliability of Three Dimentional Pseudo-continuous Arterial Spin Labeling: A Volumetric Cerebral Perfusion Imaging with Different Post-labeling Time and Functional State in Health Adults [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [11] | Pan Haipeng, Lao Qun, Fei Zhenghua, Yang Li, Zhou Haichun, Lai Can. MR Lymphangiography for Focal Disruption of the Thoracic Duct in Chylothorax of an Infant: a Case Report and Literature Review△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 265-268. |
| [12] | Chen Zhiye, Zang Xiujuan, Liu Mengqi, Liu Mengyu, Li Jinfeng, Gu Zhaoyan, Ma Lin. Abnormal Alterations of Cortical Thickness in 16 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot MRI Study△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82. |
| [13] | Wang Ting, Ma Lin, Lou Xin, Bu Bo. Trigeminal Ganglioneuroma in the Middle-posterior Cranial Fossa: a Case Report△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 123-128. |
| [14] | Yu Wang, Zi-yuan Liu, Wan-chen Dou, Wen-bin Ma, Ren-zhi Wang, Yi Guo. Application of Preoperative CT/MRI Image Fusion in Target Positioning for Deep Brain Stimulation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(3): 161-167. |
| [15] | Xiang Quan, Tie-hu Ye, Si-fang Lin, Liang Zou, Shou-yuan Tian. Propofol Affects Different Human Brain Regions Depending on Depth of Sedation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(3): 135-142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|