Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 173-186.doi: 10.24920/003984
Special Issue: 人工智能与精准肿瘤学
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-Omics and Its Clinical Application in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Progress and Future Opportunities
Wanshui Yang1, Hanyu Jiang2, Chao Liu3, 4, Jingwei Wei5, 6, 7, Yu Zhou5, 6, 7, 8, Pengyun Gong3, 4, Bin Song2, *( ), Jie Tian3, 4, 5, 6, 9, *(
), Jie Tian3, 4, 5, 6, 9, *( )
)
- 1Department of Nutrition, School of Public Health, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China
2Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
3Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Big Data-Based Precision Medicine, School of Medicine and Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
4Key Laboratory of Big Data-Based Precision Medicine (Beihang University), Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Beijing 100191, China
5Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
6Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing 100190, China
7University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
8School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi’an 710126, China
9Engineering Research Center of Molecular and Neuro Imaging of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi’an 710126, China
-
Received:2021-08-16Accepted:2021-09-14Published:2021-09-30Online:2021-09-17 -
Contact:Bin Song,Jie Tian E-mail:anicesong@vip.sina.com;jie.tian@ia.ac.cn
| This review is structured in five parts including multi-omics in the clinical workflow of HCC, design and implementation of clinical cohort for HCC omics Study, methodology of radiomics, genomics and proteomics in HCC, and final summary of current limitation and future opportunities of multi-omics in HCC studies. |
Cite this article
Wanshui Yang, Hanyu Jiang, Chao Liu, Jingwei Wei, Yu Zhou, Pengyun Gong, Bin Song, Jie Tian. Multi-Omics and Its Clinical Application in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Progress and Future Opportunities[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 173-186.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| 1. |
Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016; 2:16018. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.18.
doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.18 |
| 2. |
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL, London WT. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: an emphasis on demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis 2015; 19(2):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.01.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.01.001 |
| 3. | International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN 2018. Estimated age-standardized incidence rates (World) in 2020, liver, both sexes, all ages. Available from https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-map?v=2020&mode=population&mode_population=continents&population=900&populations=900&key=asr&sex=0&cancer=11&type=0&statistic=5&prevalence=0&population_groupearth&color_palette=default&map_scale=quantile&map_nb_colors=5&continent=0&rotate=%255B10%252C0%255D (2020). Accessed August 16, 2021. |
| 4. |
Tabrizian P, Jibara G, Shrager B, et al. Recurrence of hepatocellular cancer after resection: patterns, treatments, and prognosis. Ann Surg 2015; 261(5):947-55. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000710.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000710 |
| 5. |
Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018; 68(2):723-50. doi: 10.1002/hep.29913.
doi: 10.1002/hep.29913 |
| 6. |
Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017; 14(12):749-62. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141.
doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141 |
| 7. |
Wei J, Jiang H, Gu D, et al. Radiomics in liver diseases: Current progress and future opportunities. Liver Int 2020; 40(9):2050-63. doi: 10.1111/liv.14555.
doi: 10.1111/liv.14555 |
| 8. |
Zhou Y, He L, Huang Y, et al. CT-based radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for preoperative prediction of early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017; 42(6):1695-704. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1072-0.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1072-0 |
| 9. |
Cozzi L, Dinapoli N, Fogliata A, et al. Radiomics based analysis to predict local control and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy. BMC Cancer 2017; 17(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3847-7.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3847-7 |
| 10. |
Naganawa S, Enooku K, Tateishi R, et al. Imaging prediction of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using computed tomography texture analysis. Eur Radiol 2018; 28(7):3050-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5270-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5270-5 |
| 11. |
Kew MC. Synergistic interaction between aflatoxin B1 and hepatitis B virus in hepatocarcinogenesis. Liver Int 2003; 23(6):405-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2003.00869.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2003.00869.x |
| 12. |
Seehawer M, Heinzmann F, D’Artista L, et al. Necroptosis microenvironment directs lineage commitment in liver cancer. Nature 2018; 562(7725):69-75. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0519-y. Erratum in Nature 2018; 564(7735):E9. doi 10.1038/s41586-018-0723-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0723-9 |
| 13. |
Yuan D, Huang S, Berger E, et al. Kupffer cell-derived Tnf triggers cholangiocellular tumorigenesis through JNK due to chronic mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS. Cancer Cell 2017; 31(6):771- 89. e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.05.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.05.006 |
| 14. |
Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, et al. Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis. Gastroenterology 2017; 152(4):745-61. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.048.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.048 |
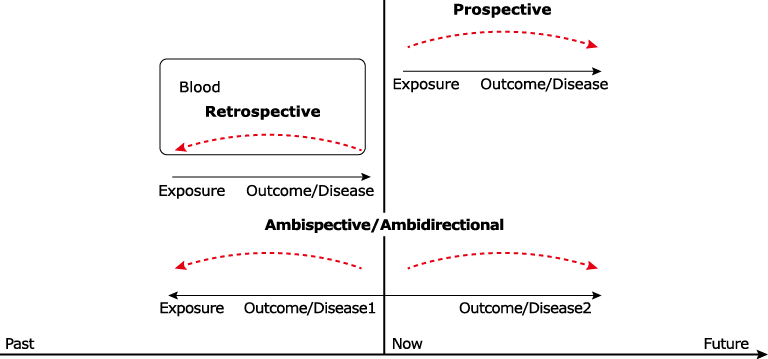
| 15. |
Li Z, Mao Y, Huang W, et al. Texture-based classification of different single liver lesion based on SPAIR T2W MRI images. BMC Med Imaging 2017; 17(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0212-x.
doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0212-x |
| 16. |
Trivizakis E, Manikis GC, Nikiforaki K, et al. Extending 2-D convolutional neural networks to 3-D for advancing deep learning cancer classification with application to MRI liver uumor differentiation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 2019; 23(3):923-30. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2886276.
doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2886276 |
| 17. |
Jiang H, Liu X, Chen J, et al. Man or machine? Prospective comparison of the version 2018 EASL, LI-RADS criteria and a radiomics model to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2019; 19(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0266-9.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0266-9 |
| 18. |
Yao Z, Dong Y, Wu G, et al. Preoperative diagnosis and prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma: radiomics analysis based on multi-modal ultrasound images. BMC Cancer 2018; 18(1):1089. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5003-4.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5003-4 |
| 19. |
Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Grigioni AD, et al. Preoperative prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma tumour grade and micro-vascular invasion by means of artificial neural network: a pilot study. J Hepatol 2010; 52(6):880-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.12.037.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.12.037 |
| 20. |
Zhou W, Zhang L, Wang K, et al. Malignancy characterization of hepatocellular carcinomas based on texture analysis of contrast-enhanced MR images. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 45(5):1476-84. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25454.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25454 |
| 21. |
Wu M, Tan H, Gao F, et al. Predicting the grade of hepatocellular carcinoma based on non-contrast-enhanced MRI radiomics signature. Eur Radiol 2019; 29(6):2802-11. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5787-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5787-2 |
| 22. |
Ye Z, Jiang H, Chen J, et al. Texture analysis on
doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.05.10 |
|
gadoxetic acid enhanced-MRI for predicting Ki-67 status in hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. Chin J Cancer Res 2019; 31(5):806-17. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.05.10.
doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.05.10 |
|
| 23. |
Wei J, Jiang H, Zeng M, et al. Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma via deep learning: a multi-center and prospective validation study. Cancers (Basel) 2021; 13(10):2368. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102368.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13102368 |
| 24. |
Xu X, Zhang HL, Liu QP, et al. Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2019; 70(6):1133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.023 |
| 25. |
Banerjee S, Wang DS, Kim HJ, et al. A computed tomography radiogenomic biomarker predicts microvascular invasion and clinical outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015; 62(3):792-800. doi: 10.1002/hep.27877.
doi: 10.1002/hep.27877 |
| 26. |
Sun R, Limkin EJ, Vakalopoulou M, et al. A radiomics approach to assess tumour-infiltrating CD8 cells and response to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: an imaging biomarker, retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol 2018; 19(9):1180-91. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30413-3.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30413-3 |
| 27. |
Chen S, Feng S, Wei J, et al. Pretreatment prediction of immunoscore in hepatocellular cancer: a radiomics-based clinical model based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI imaging. Eur Radiol 2019; 29(8):4177-87. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5986-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5986-x |
| 28. |
Hectors SJ, Lewis S, Besa C, et al. MRI radiomics features predict immuno-oncological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol 2020; 30(7):3759-69. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06675-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06675-2 |
| 29. |
Yuan C, Wang Z, Gu D, et al. Prediction early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for curative ablation using a radiomics nomogram. Cancer Imaging 2019; 19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0207-7.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0207-7 |
| 30. |
Ji GW, Zhu FP, Xu Q, et al. Radiomic features at contrast-enhanced CT predict recurrence in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-institutional study. Radiology 2020; 294(3):568-79. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020191470.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020191470 |
| 31. |
Hui TCH, Chuah TK, Low HM, et al. Predicting early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma with texture analysis of preoperative MRI: a radiomics study. Clin Radiol 2018; 73(12):1056. e11- 1056. e16. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2018.07.109.
doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2018.07.109 |
| 32. |
Park HJ, Kim JH, Choi SY, et al. Prediction of therapeutic response of hepatocellular carcinoma to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization based on pretherapeutic dynamic CT and textural findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017; 209(4):w211-w220. doi: 10.2214/AJR.16.17398.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.16.17398 |
| 33. |
Kim J, Choi SJ, Lee SH, et al. Predicting survival using pretreatment CT for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial chemoembolization: comparison of models using radiomics. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2018; 211(5):1026-34. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.19507.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.19507 |
| 34. |
Blanc-Durand P, van der Gucht A, Jreige M, et al. Signature of survival: a 18F-FDG PET based whole-liver radiomic analysis predicts survival after 90Y-TARE for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017; 9(4):4549-58. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23423.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23423 |
| 35. |
Mulé S, Thiefin G, Costentin C, et al. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: pretreatment contrast-enhanced CT texture parameters as predictive biomarkers of survival in patients treated with sorafenib. Radiology 2018; 288(2):445-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171320.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171320 |
| 36. |
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021; 7(1):6. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3.
doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3 |
| 37. |
Calderaro J, Ziol M, Paradis V, et al. Molecular and histological correlations in liver cancer. J Hepatol 2019; 71(3):616-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.001 |
| 38. |
Zucman-Rossi J, Villanueva A, Nault JC, et al. Genetic landscape and biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015; 149(5):1226- 39.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.05.061.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.05.061 |
| 39. |
Totoki Y, Tatsuno K, Covington KR, et al. Trans-ancestry mutational landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma genomes. Nat Genet 2014; 46(12):1267-73. doi: 10.1038/ng.3126.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3126 |
| 40. |
Ahn SM, Jang SJ, Shim JH, et al. Genomic portrait of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: implications of RB1 and FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology 2014; 60(6):1972-82. doi: 10.1002/hep.27198.
doi: 10.1002/hep.27198 |
| 41. |
Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouzé E, et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Genet 2015; 47(5):505-11. doi: 10.1038/ng.3252.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3252 |
| 42. |
Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, et al. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 2012; 44(6):694-8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2256.
doi: 10.1038/ng.2256 |
| 43. |
Nault JC, Mallet M, Pilati C, et al. High frequency of telomerase reverse-transcriptase promoter somatic mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma and preneoplastic lesions. Nat Commun 2013; 4:2218. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3218. Erratum in Nat Commun 2013; 4:2577. doi 10.1038/ncomms3577.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms3577 |
| 44. |
Paterlini-Bréchot P, Saigo K, Murakami Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene 2003; 22(25):3911-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206492.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206492 |
| 45. |
Bayard Q, Meunier L, Peneau C, et al. Cyclin A2/E1 activation defines a hepatocellular carcinoma subclass with a rearrangement signature of replication stress. Nat Commun 2018; 9(1):5235. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07552-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07552-9 |
| 46. |
Chiang DY, Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, et al. Focal gains of VEGFA and molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68(16):6779-88. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0742.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0742 |
| 47. |
Bressac B, Kew M, Wands J, et al. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature 1991; 350(6317):429-31. doi: 10.1038/350429a0.
doi: 10.1038/350429a0 |
| 48. |
Wang B, Huang G, Wang D, et al. Null genotypes of GSTM1 and GSTT1 contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma risk: evidence from an updated meta-analysis. J Hepatol 2010; 53(3):508-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.03.026.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.03.026 |
| 49. |
Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet 2008; 40(12):1461-5. doi: 10.1038/ng.257.
doi: 10.1038/ng.257 |
| 50. |
Buch S, Stickel F, Trépo E, et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat Genet 2015; 47(12):1443-8. doi: 10.1038/ng.3417.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3417 |
| 51. |
Rebouissou S, Nault JC. Advances in molecular classification and precision oncology in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2020; 72(2):215-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.017 |
| 52. |
Hoshida Y, Nijman SM, Kobayashi M, et al. Integrative transcriptome analysis reveals common molecular subclasses of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2009; 69(18):7385-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1089.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1089 |
| 53. |
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and integrative genomic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 2017; 169(7):1327- 41. e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.046.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.046 |
| 54. |
Lee JS, Heo J, Libbrecht L, et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat Med 2006; 12(4):410-6. doi: 10.1038/nm1377.
doi: 10.1038/nm1377 |
| 55. |
Boyault S, Rickman DS, de Reyniès A, et al. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology 2007; 45(1):42-52. doi: 10.1002/hep.21467.
doi: 10.1002/hep.21467 |
| 56. |
Sia D, Jiao Y, Martinez-Quetglas I, et al. Identification of an immune-specific class of hepatocellular carcinoma, based on molecular features. Gastroenterology 2017; 153(3):812-26. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.007.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.007 |
| 57. |
Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D, et al. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018; 15(10):599-616. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4.
doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4 |
| 58. |
Erstad DJ, Fuchs BC, Tanabe KK. Molecular signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma: a step toward rationally designed cancer therapy. Cancer 2018; 124(15):3084-104. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31257.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.31257 |
| 59. |
Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, et al. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004; 40(3):667-76. doi: 10.1002/hep.20375.
doi: 10.1002/hep.20375 |
| 60. |
Calderaro J, Couchy G, Imbeaud S, et al. Histological subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma are related to gene mutations and molecular tumour classification. J Hepatol 2017; 67(4):727-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.014 |
| 61. |
Lachenmayer A, Alsinet C, Savic R, et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18(18):4997-5007. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2322.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2322 |
| 62. |
Ruiz de Galarreta M, Bresnahan E, Molina-Sánchez P, et al. β-Catenin activation promotes immune escape and resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Discov 2019; 9(8):1124-41. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0074.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0074 |
| 63. |
Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, et al. Prospective cohort study of transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in 8510 patients. Gastroenterology 2006; 131(2):461-9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.05.021.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.05.021 |
| 64. |
Lazcano G, Papuzinski C, Madrid E, et al. General concepts in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology: observational studies with cohort design. Medwave 2019; 19(11):e7748. Spanish and English. doi: 10.5867/medwave.2019.11.7748.
doi: 10.5867/medwave.2019.11.7748 |
| 65. |
Kim S, Shin J, Kim DY, et al. Radiomics on Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of postoperative early and late recurrence of single hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2019; 25(13):3847-55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2861.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2861 |
| 66. |
Grimes DA, Schulz KF. Cohort studies: marching towards outcomes. Lancet 2002; 359(9303):341-5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07500-1.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07500-1 |
| 67. |
Font C, Carmona-Bayonas A, Beato C, et al. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of cancer patients with suspected and unsuspected pulmonary embolism: the EPIPHANY study. Eur Respir J 2017; 49(1):1600282. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00282-2016.
doi: 10.1183/13993003.00282-2016 |
| 68. |
Liu L, Nevo D, Nishihara R, et al. Utility of inverse probability weighting in molecular pathological epidemiology. Eur J Epidemiol 2018; 33(4):381-92. doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0346-8.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0346-8 |
| 69. |
Dettori JR. Loss to follow-up. Evid Based Spine Care J 2011; 2(1):7-10. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1267080.
doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1267080 |
| 70. |
Ferreira JC, Patino CM. Loss to follow-up and missing data: important issues that can affect your study results. J Bras Pneumol 2019; 45(2):e20190091. doi: 10.1590/1806-3713/e20190091.
doi: 10.1590/1806-3713/e20190091 |
| 71. |
Ogino S, Chan AT, Fuchs CS, et al. Molecular pathological epidemiology of colorectal neoplasia: an emerging transdisciplinary and interdisciplinary field. Gut 2011; 60(3):397-411. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.217182.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.217182 |
| 72. |
López de Maturana E, Alonso L, Alarcón P, et al. Challenges in the integration of omics and non-omics data. Genes (Basel) 2019; 10(3):238. doi: 10.3390/genes10030238.
doi: 10.3390/genes10030238 |
| 73. |
López de Maturana E, Pineda S, Brand A, et al. Toward the integration of Omics data in epidemiological studies: still a “long and winding road”. Genet Epidemiol 2016; 40(7):558-69. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21992.
doi: 10.1002/gepi.21992 |
| 74. |
Lehmann TM, Gönner C, Spitzer K. Survey: interpolation methods in medical image processing. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1999; 18(11):1049-75. doi: 10.1109/42.816070.
doi: 10.1109/42.816070 |
| 75. |
Lehmann T, Oberschelp W, Pelikan E, et al. Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin: Grundlagen, Modelle, Methoden, Anwendungen. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2013. German. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-60487-4.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-60487-4 |
| 76. |
Yang Q, Wei J, Hao X, et al. Improving B-mode ultrasound diagnostic performance for focal liver lesions using deep learning: a multicentre study. EBioMedicine 2020; 56:102777. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102777.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102777 |
| 77. |
Zhao M, Zhang Z, Chow TWS. Trace ratio criterion based generalized discriminative learning for semi-supervised dimensionality reduction. Pattern Recognit 2012; 45(4):1482-99. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.10.008.
doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.10.008 |
| 78. |
Zhao Z, Liu H. Spectral feature selection for supervised and unsupervised learning. ICML 2007: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on machine learning. June 20-24, 2007; Corvalis Oregon, USA. Vol. 227. p. 1151-1157. doi: 10.1145/1273496.1273641.
doi: 10.1145/1273496.1273641 |
| 79. | Nie F, Huang H, Cai X, et al. Efficient and robust feature selection via Joint _2, 1-Norms Minimization. In: NIPS 2010: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. December 6-11, 2010; Vancouver, Cananda. Vol 2.p. 1813-1821. |
| 80. |
Cai D, Zhang C, He X. Unsupervised Feature Selection for Multi-Cluster Data. Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. KDD 2010. July 25-28, 2010; Washington DC, USA. 2010. p. 333-342. doi: 10.1145/1835804.1835848.
doi: 10.1145/1835804.1835848 |
| 81. |
Zhang P, Feng J, Wu X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of candidate genes and pathways related to hepatocellular carcinoma in China: a study based on public databases. Pathol Oncol Res 2021; 27:588532. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.588532.
doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.588532 |
| 82. |
Zhou X, Shi M, Cao J, et al. S100 calcium binding protein A10, a novel oncogene, promotes the proliferation, invasion, and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Genet 2021; 12:695036. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.695036.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.695036 |
| 83. |
Chen DB, Xie XW, Zhao YJ, et al. RFX5 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through transcriptional activation of KDM4A. Sci Rep 2020; 10(1):14538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71403-1.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71403-1 |
| 84. |
Huo J, Wu L, Zang Y. Construction and validation of a reliable six-gene prognostic signature based on the TP53 alteration for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 2021; 11:618976. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.618976.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.618976 |
| 85. |
Sun Y, Wu L, Zhong Y, et al. Single-cell landscape of the ecosystem in early-relapse hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 2021; 184(2):404- 21. e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.041.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.041 |
| 86. |
Li N, Long Y, Fan X, et al. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2009; 28(1):122. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-122.
doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-122 |
| 87. |
Wei D, Zeng Y, Xing X, et al. Proteome differences between hepatitis B Virus genotype-B- and genotype-C-induced hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics. J Proteome Res 2016; 15(2):487-98. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00838.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00838 |
| 88. |
Du Z, Liu X, Wei X, et al. Quantitative proteomics identifies a plasma multi-protein model for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 2020; 10(1):15552. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72510-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72510-9 |
| 89. |
Gao Q, Zhu H, Dong L, et al. Integrated proteogenomic characterization of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 2019; 179(2): 561- 77. e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.052. Erratum in: Cell 2019; 179(5):1240. doi 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.038.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.038 |
| 90. |
Zhang F, Wang Y, Chen G, et al. Growing human hepatocellular tumors undergo a global metabolic reprogramming. Cancers (Basel) 2021; 13(8):1980. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081980.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13081980 |
| 91. |
Lu S, Cai S, Peng X, et al. Integrative transcriptomic, proteomic and functional analysis reveals ATP1B3 as a diagnostic and potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol 2021; 12:636614. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636614.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636614 |
| 92. |
Wang L, Zhang Z, Li Y, et al. Integrated bioinformatic analysis of RNA binding proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 2020; 13(2):2480-505. doi: 10.18632/aging.202281.
doi: 10.18632/aging.202281 |
| 93. |
Segal E, Sirlin CB, Ooi C, et al. Decoding global gene expression programs in liver cancer by noninvasive imaging. Nat Biotechnol 2007; 25(6):675-80. doi: 10.1038/nbt1306.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1306 |
| 94. |
McCague C, Beer L. Radioproteomics in patients with ovarian cancer. Br J Radiol 2021; 94(1125):20201331. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201331.
doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201331 |
| 95. |
Badic B, Tixier F, Cheze Le Rest C, et al. Radiogenomics in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021; 13(5):973. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050973.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13050973 |
| 96. |
Lo Gullo R, Daimiel I, Morris EA, et al. Combining molecular and imaging metrics in cancer: radiogenomics. Insights Imaging 2020; 11(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0795-6.
doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0795-6 |
| [1] | Jin Lu,Shaoguang An,Junjie Ma,Yue Yang,Lei Zhang,Peng Yu,Heng Tao,Yunfan Chen,Haoxuan Zhang. Topoisomerase Ⅱα Gene as a Marker for Prognostic Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bioinformatics Analysis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(4): 331-339. |
| [2] | Chen Xu, Huo Xiaofei, Wu Zhe, Lu Jingjing. Advances of Artificial Intelligence Application in Medical Imaging of Ovarian Cancers [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 196-203. |
| [3] | Jiazheng Li, Lei Tang. Radiomics in Antineoplastic Agents Development: Application and Challenge in Response Evaluation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 187-195. |
| [4] | Qiong Chen,Xuefeng Yang. Research Progress in Targeted Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 57-65. |
| [5] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [6] | Wu Jianqiang, Qin Weiwei, Pan Li, Wang Xiaorong, Zhang Biao, Shan Guangliang, Gao Youhe. Regional Differences of the Urinary Proteomes in Healthy Chinese Individuals [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 157-167. |
| [7] | Dong Dexin, Ji Zhigang, Li Hanzhong, Yan Weigang, Zhang Yushi. Preliminary Application of WCX Magnetic Bead-Based Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry in Analyzing the Urine of Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 248-252. |
| [8] | Zhang Xiufen, Yu Bo, Zhang Fuzheng, Guo Zijian, Li Lihua. microRNA-18a Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion Through Inhibiting Dicer l Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(1): 34-43. |
| [9] | Jian-bo Xu, Gang Xu, Guo-feng Chen, Dian-hua Gu, Jian-huai Zhang, Fu-zhen Qi*. Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Hypersplenic Thrombocytopenia and Situs Inversus Totalis: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(2): 134-136. |
| [10] | Ye Jin, Li Zhou, Ke-min Jin, and Bao-cai Xing. Expression of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-2 is Negatively Associated with Invasive Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2013, 28(1): 16-19. |
| [11] | Yao Zhang, Hua Zhang, Au Elizabeth, Xiao-qing Liu. Epidemiology of Hepatitis B and Associated Liver Diseases in China [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2012, 27(4): 243-248. |
| [12] | Ting-ting He, and Jia-he Tian*. Application of Positron Emission Tomography Molecular Probes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Biological Imaging [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2011, 26(2): 113-118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|