Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 20-30.doi: 10.24920/003680
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lrrc34 Is Highly Expressed in SSCs and Is Necessary for SSC Expansion In Vitro
Ou Jinhuan, Li Yiran, Wang Zhipeng, Jin Cheng, Li Kai, Lu Yan, Zou Dingfeng, Li Pengyu, Li Mengzhen, Miao Shiying, Wang Linfang, Song Wei( )
)
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, State Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & School of Basic Medicine Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100005, China
-
Received:2019-11-07Published:2020-03-31Online:2020-01-20 -
Contact:Song Wei E-mail:songwei@ibms.pumc.edu.cn
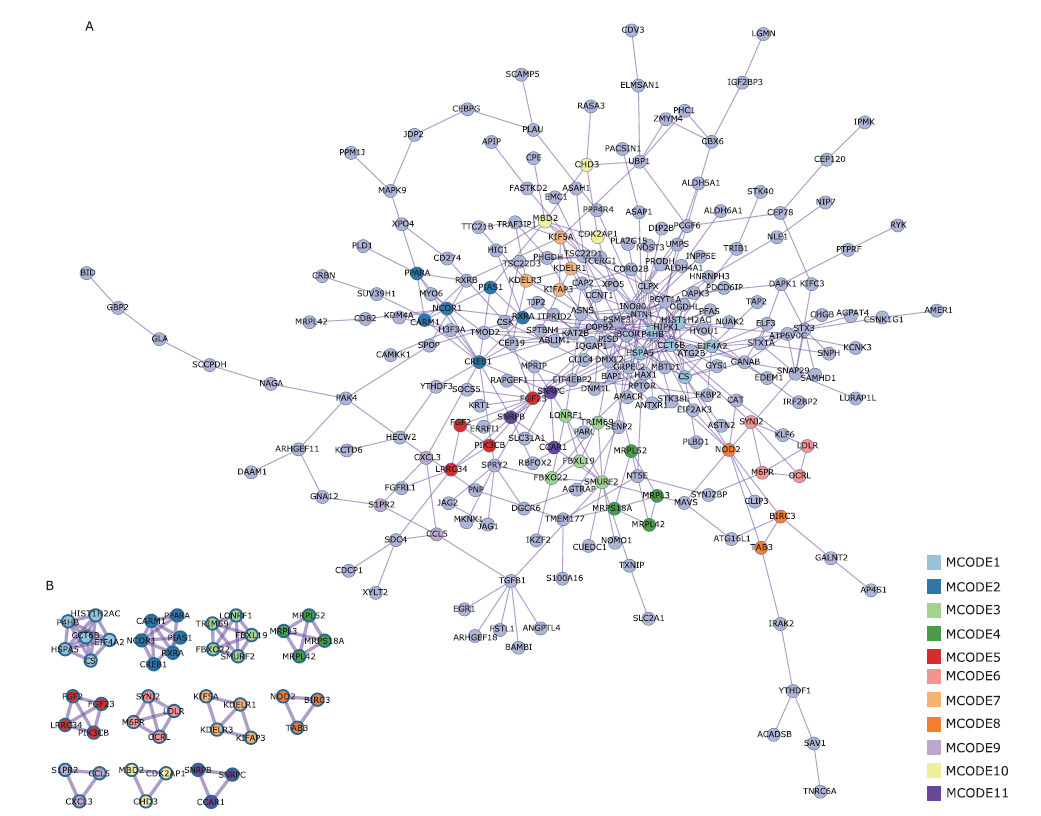
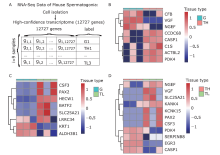
| Spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), a subpopulation of undifferentiated spermatogonia, are the sole stem cell pool in the germline that maintains male fertility by ensuring a balance between self-renewal and differentiation via the continuous production of sperm capable of fertilization. In this article, the authors identified Lrrc34 as a candidate gene that shows differential expression among ID4-EGFP+ spermatogonia subsets by using bioinformatic analysis. Based on the important role of fibroblast growth factor 2 in SSC self-renewal and the expression of Lrrc34 in pluripotent stem cells, they speculated that Lrrc34 might act as a regulator of SSC expansion or maintenance. Verification experiments confirmed that Lrrc34 is particularly highly expressed in SSCs and is required for SSC expansion. |
Cite this article
Ou Jinhuan, Li Yiran, Wang Zhipeng, Jin Cheng, Li Kai, Lu Yan, Zou Dingfeng, Li Pengyu, Li Mengzhen, Miao Shiying, Wang Linfang, Song Wei. Lrrc34 Is Highly Expressed in SSCs and Is Necessary for SSC Expansion In Vitro[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 20-30.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
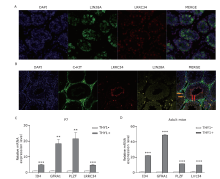
Figure 3.
Expression pattern of LRRC34 in SSCs. A and B. Protein localization of LRRC34 in the P7 (A) and adult (B) mouse testes. The red arrows indicate cells coexpressing LIN28A and LRRC34, whereas the yellow arrows indicate cells expressing LIN28A only. C and D. Relative mRNA expression levels in THY1-isolated spermatogonia from P7 (ID4: 1.005±0.0692 vs. 4.912±0.3223, P=0.0003, t=11.85; GFRA1: 1.005±0.0727 vs. 18.42±2.712, P=0.0030, t=6.419; PLZF: 1.006±0.0788 vs. 21.54±4.002, P=0.0068, t=5.129; LRRC34: 1.004±0.0662 vs. 4.740±0.2806, P=0.0002, t=12.96) and adult (ID4: 1.003±0.0566 vs. 22.11±0.2694, P=0.0000, t=76.67; GFRA1: 1.000±0.0402 vs. 48.89 ±0.9009, P=0.0000, t=53.10; PLZF: 1.002±0.0400 vs. 11.53±0.1405, P=0.0000, t=72.07; LRRC34: 1.033±0.1746 vs. 9.970±0.7089, P=0.0003, t=12.24) mouse testes. The means ± SEMs are shown in the stacked bar graphs. The significance of the differences in gene expression levels between the TYH1- and THY+ subpopulations were determined by t-test (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001;n=3 biological replicates)."
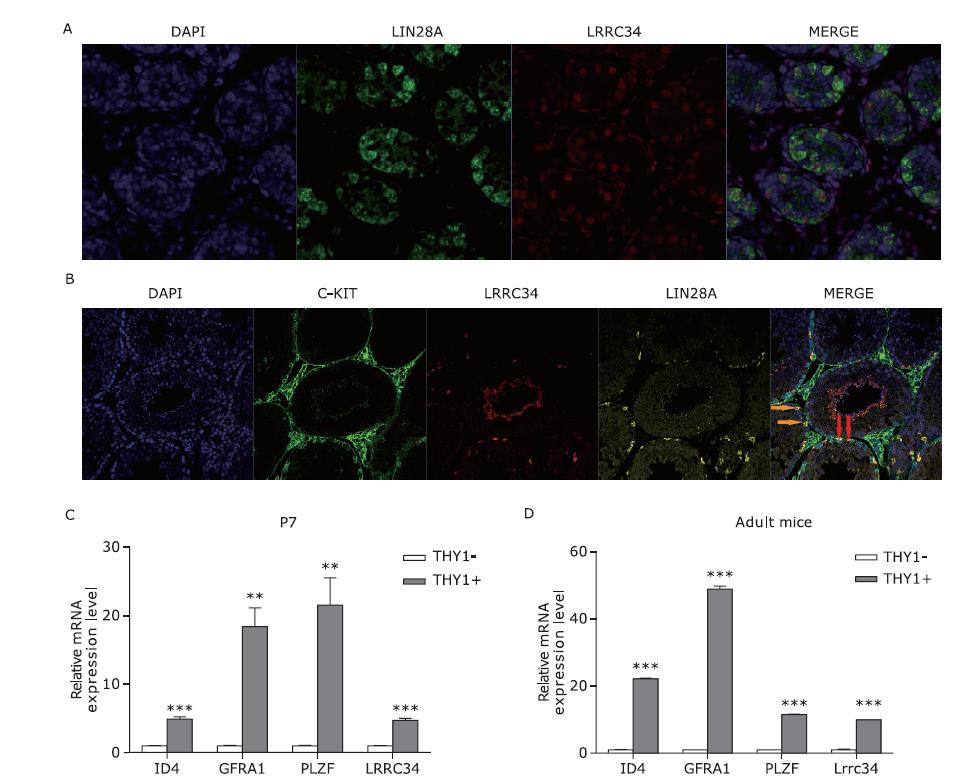
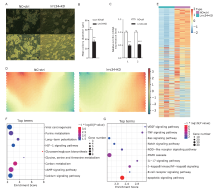
Figure 4.
RNA-seq data analyses of the transcriptome characteristics after Lrrc34 knockdown. A. The colony size of lrrc34-KD SSCs cultured in vitro was decreased compared with that of the negative control NC-ctrl SSCs. (bar = 14.9 μm) B. The average diameter was quantified using ImageJ (61.09±4.242 vs. 34.70±3.624 μm, P=0.0015, t=4.731, n = 5 biological replicates). The data are presented as the means ± SEMs. C. Lrrc34 was knocked down according to the relative mRNA level (1.002±0.0402 vs. 0.4768±0.0512, P=0.0013, t=8.064; 1.003±0.0505 vs. 0.5206±0.0166, P=0.0008, t=9.067, n = 3 biological replicates). D. The overall transcriptome divergency between the lrrc34-KD and NC-ctrl SSCs was profiled by an SOM. E. The DEGs between lrrc34-KD and NC-ctrl SSCs are presented in a heat map [P<0.05, logFC > 1 or < -1]. F and G. The signaling pathways enriched with upregulated (E) or downregulated (F) DEGs between lrrc34-KD and NC-ctrl SSCs are presented using a Bubble diagram."

| 1. | Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Shinohara T . Spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal and development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2013; 29:163-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122353. |
| 2. | Kubota H, Brinster RL . Spermatogonial stem cells. Biol Reprod 2018; 99(1):52-74. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy077. |
| 3. | Ibtisham F, Wu J, Xiao M , et al. Progress and future prospect of in vitro spermatogenesis. Oncotarget 2017; 8(39):66709-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19640. |
| 4. | Mei XX, Wang J, Wu J . Extrinsic and intrinsic factors controlling spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Asian J Androl 2015; 17(3):347-54. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.148080. |
| 5. | Lührig S, Siamishi I, Tesmer-Wolf M , et al. Lrrc34, a novel nucleolar protein, interacts with npm1 and ncl and has an impact on pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 2014; 23(23):2862-74. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0470. |
| 6. | Kobe B, Kajava AV . The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2001; 11(6):725-32. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(01)00266-4. |
| 7. | Dickson KA, Haigis MC, Raines RT . Ribonuclease inhibitor: structure and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 2005; 80:349-74. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(05)80009-1. |
| 8. | Corbett AH, Koepp DM, Schlenstedt G , et al. Rna1p, a Ran/TC4 GTPase activating protein, is required for nuclear import. J Cell Biol 1995; 130(5):1017-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1017. |
| 9. | Paik JK, Kang R, Cho Y , et al. Association between genetic variations affecting mean telomere length and the prevalence of hypertension and coronary heart disease in Koreans. Clin Nutr Res 2016; 5(4):249-60. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2016.5.4.249. |
| 10. | Wu M, Assassi S, Salazar GA , et al. Genetic susceptibility loci of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia do not represent risk for systemic sclerosis: a case control study in Caucasian patients. Arthritis Res Ther 2016; 18:20. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0923-3. |
| 11. | Love MI, Huber W, Anders S . Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014; 15(12):550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. |
| 12. | Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L , et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012; 7(3):562-78. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016. |
| 13. | Gene Ontology Consortium . Gene Ontology Consortium: going forward. Nucleic Acids Res 2015; 43(Database issue):D1049-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1179. |
| 14. | Kanehisa M, Goto S . KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28(1):27-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27. |
| 15. | Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y , et al. ClusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012; 16(5):284-7. doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118. |
| 16. | von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D , et al. STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31(1):258-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg034. |
| 17. | Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O , et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 2003; 13(11):2498-504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303. |
| 18. | Baazm M, Abolhassani F, Abbasi M , et al. An improved protocol for isolation and culturing of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Cell Reprogram 2013; 15(4):329-36. doi: 10.1089/cell.2013.0008. |
| 19. | Li L, Wang M, Wang M , et al. A long non-coding RNA interacts with Gfra1 and maintains survival of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Cell Death Dis 2016; 7:e2140. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.24. |
| 20. | Mutoji K, Singh A, Nguyen T , et al. TSPAN8 expression distinguishes spermatogonial stem cells in the prepubertal mouse testis. Biol Reprod 2016; 95(6):117. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.144220. |
| 21. | Fu J, Gaetani S, Oveisi F , et al. Oleylethanolamide regulates feeding and body weight through activation of the nuclear receptor PPAR-alpha. Nature 2003; 425(6953):90-3. doi: 10.1038/nature01921. |
| 22. | Chakravarthy MV, Lodhi IJ, Yin L , et al. Identification of a physiologically relevant endogenous ligand for PPARalpha in liver. Cell 2009; 138(3):476-88. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.036. |
| 23. | Schmutz I, Ripperger JA, Baeriswyl-Aebischer S , et al. The mammalian clock component PERIOD2 coordinates circadian output by interaction with nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 2010; 24(4):345-57. doi: 10.1101/gad.564110. |
| 24. | Alenghat T, Meyers K, Mullican SE , et al. Nuclear receptor corepressor and histone deacetylase 3 govern circadian metabolic physiology. Nature 2008; 456(7224):997-1000. doi: 10.1038/nature07541. |
| 25. | Aninye IO, Matsumoto S, Sidhaye AR , et al. Circadian regulation of Tshb gene expression by Rev-Erbalpha (NR1D1) and nuclear corepressor 1 (NCOR1). J Biol Chem 2014; 289(24):17070-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569723. |
| 26. | Gau D, Lemberger T, von Gall C , et al. Phosphorylation of CREB Ser142 regulates light-induced phase shifts of the circadian clock. Neuron 2002; 34(2):245-53. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00656-6. |
| 27. | Ma X, Zhang H, Yuan L , et al. CREBL2, interacting with CREB, induces adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem J 2011; 439(1):27-38. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101475. |
| 28. | Shyu HW, Hsu SH, Hsieh-Li HM , et al. Forced expression of RNF36 induces cell apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 2003; 287(2):301-13. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00110-1. |
| 29. | Spaich S, Will RD, Just S , et al. F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 22 is a cardiac-enriched F-box protein that regulates sarcomeric protein turnover and is essential for maintenance of contractile function in vivo. Circ Res 2012; 111(12):1504-16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.271007. |
| 30. | Chandhoke AS, Karve K, Dadakhujaev S , et al. The ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 suppresses TGFbeta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a sumoylation-regulated manner. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23(5):876-88. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.152. |
| 31. | Cai Y, Huang G, Ma L , et al. Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, interacts with PDE4B and attenuates liver fibrosis through miR-132 mediated CTGF inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2018; 1865(2):297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.10.011. |
| 32. | Lee J, Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Inoue K , et al. Akt mediates self-renewal division of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Development 2007; 134(10):1853-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.003004. |
| 33. | Feng LX, Ravindranath N, Dym M . Stem cell factor/c-kit up-regulates cyclin D3 and promotes cell cycle progression via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/p70 S6 kinase pathway in spermatogonia. J Biol Chem 2000; 275(33):25572-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002218200. |
| 34. | Blume-Jensen P, Jiang G, Hyman R , et al. Kit/stem cell factor receptor-induced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase is essential for male fertility. Nat Genet 2000; 24(2):157-62. doi: 10.1038/72814. |
| 35. | Chan F, Oatley MJ, Kaucher AV , et al. Functional and molecular features of the Id4+ germline stem cell population in mouse testes. Genes Dev 2014; 28(12):1351-62. doi: 10.1101/gad.240465.114. |
| 36. | Mäkelä JA, Koskenniemi JJ, Virtanen HE , et al. Testis development. Endocr Rev 2019; 40(4):857-905. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00140. |
| 37. | Zheng K, Wu X, Kaestner KH , et al. The pluripotency factor LIN28 marks undifferentiated spermatogonia in mouse. BMC Dev Biol 2009; 9:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-38. |
| 38. | Helsel AR, Yang QE, Oatley MJ , et al. ID4 levels dictate the stem cell state in mouse spermatogonia. Development 2017; 144(4):624-34. doi: 10.1242/dev.146928. |
| 39. | Buaas FW, Kirsh AL, Sharma M , et al. Plzf is required in adult male germ cells for stem cell self-renewal. Nat Genet 2004; 36(6):647-52. doi: 10.1038/ng1366. |
| 40. | He Z, Jiang J, Hofmann MC , et al. Gfra1 silencing in mouse spermatogonial stem cells results in their differentiation via the inactivation of RET tyrosine kinase. Biol Reprod 2007; 77(4):723-33. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.062513. |
| 41. | Chen SR, Liu YX . Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal and spermatocyte meiosis by Sertoli cell signaling. Reproduction 2015; 149(4):R159-67. doi: 10.1530/REP-14-048. |
| 42. | Karin M, Greten FR . NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5(10):749-59. doi: 10.1038/nri1703. |
| 43. | Karin M, Lawrence T, Nizet V . Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell 2006; 124(4):823-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.016. |
| 44. | Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T , et al. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 2001; 22(2):153-83. doi: 10.1210/edrv.22.2.0428. |
| 45. | Baud V, Karin M . Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 2001; 11(9):372-7. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02064-5. |
| 46. | Wu X, Oatley JM, Oatley MJ , et al. The POU domain transcription factor POU3F1 is an important intrinsic regulator of GDNF-induced survival and self-renewal of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Biol Reprod 2010; 82(6):1103-11. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.083097. |
| [1] | Zhu Yimin, Xu Fuying. Up-regulation of Let-7a Expression Induces Gastric Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(1): 44-47. |
| [2] | Yun-jie Chen, Hai-tao Jiang, Jing-yu Cao. Influence of Photodynamic Therapy on Apoptosis and Invasion of Human Cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 Cell Line [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(4): 252-259. |
| [3] | Jin-hui Shao, Gui-hua Feng. Inhibition Mechanism of Novel Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrazin-4(5H)-one Derivatives Against Proliferation of A549 and H322 Cancer Cells [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(4): 260-265. |
| [4] | Ling Li, Hong-jie Li, Jian-sheng zhi, Hong Chen, Wen-li Xie. ZM-66, a New Podophyllotoxin Derivative Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in K562/ADM Cells [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(3): 174-179. |
| [5] | Zong-ming Wan, Lu Liu, Jian-yu Li, Rui-xin Li, Yong Guo, Hao Li, Jian-ming Zhang, Xi-zheng Zhang. Mechanical Stimulus Inhibits the Growth of a Bone Tissue Model Cultured In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2013, 28(4): 218-224. |
| [6] | Hong-bo Yang, Wen-jie Zheng, Xuan Zhang, Fu-lin Tang. Induction of Endothelial Cell Apoptosis by Anti-alpha-enolase Antibody [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2011, 26(3): 152-157. |
| [7] | Jian-ling Tao, Xiong-zhong Ruan, Hang Li, Xue-mei Li and Xue-wang Li. Lipids-induced Apoptosis Is Aggravated by Acyl-coenzyme A: Cholesterol Acyltransferase Inhibitor [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(2): 76-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|