Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 210-217.doi: 10.24920/003968
Special Issue: 人工智能与精准肿瘤学
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
External and Internal Validation of a Computer Assisted Diagnostic Model for Detecting Multi-Organ Mass Lesions in CT images
Lianyan Xu1, Ke Yan2, Le Lu2, Weihong Zhang1, Xu Chen3, Xiaofei Huo3, Jingjing Lu3( )
)
- 1Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2PAII Inc., Bethesda, MD 20817, USA
3Department of Radiology, Beijing United Family Hospital, Beijing 100015, China
-
Received:2021-07-10Accepted:2021-08-30Published:2021-09-30Online:2021-09-23
| A universal lesion detector (ULDor) using deep learning was evaluated for its ability to generalize in clinical setting via both external and internal validation. The performance was organ dependant and need further optimisation and iterative upgrades. |
Cite this article
Lianyan Xu, Ke Yan, Le Lu, Weihong Zhang, Xu Chen, Xiaofei Huo, Jingjing Lu. External and Internal Validation of a Computer Assisted Diagnostic Model for Detecting Multi-Organ Mass Lesions in CT images[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 210-217.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
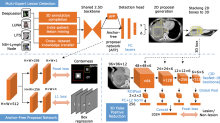
Figure 1.
Framework of the proposed algorithm model The anchor-free proposal (AFP) network and the 3D false positive reduction (FPR) network. AFP works as the backbone to generate initial proposals. FPR further classifies the 3D lesion proposals of the detector. The detector jointly learns from multiple datasets."
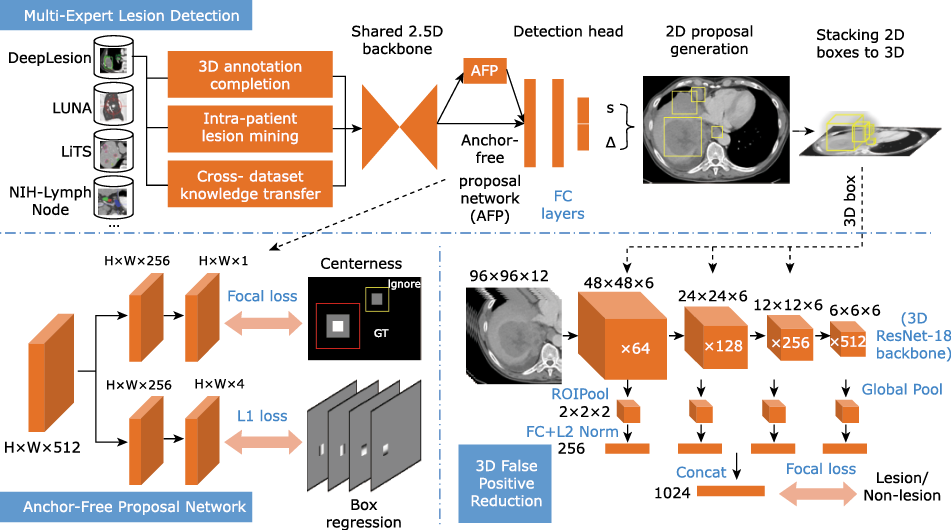
Table 1
Performance of the ULDor model in detection of multi-organ mass lesions in external validation"
| Organ | Model detected (n) | Radiologists detected (n) | TP (n) | FP (n) | FN (n) | PPV (%) | Sensitivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 128 | 109 | 101 | 27 | 8 | 78.9 | 92.7 |
| LN thorax | 131 | 109 | 60 | 71 | 49 | 45.8 | 55.1 |
| Kidneys | 10 | 12 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 70.0 | 58.3 |
| Thyroid | 14 | 12 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 42.9 | 50.0 |
| Thoracic spine | 7 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 85.7 | 100.0 |
| Adrenal | 7 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 12 | 85.7 | 33.3 |
| Spleen | 20 | 5 | 4 | 16 | 1 | 20.0 | 80.0 |
| Pancreas | 6 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 50.0 | 50.0 |
| Esophagus | 16 | 3 | 3 | 13 | 0 | 18.8 | 100.0 |
| Body wall | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Breasts | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 | NaN | 0 |
| Gallbladder | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | NaN | 0 |
| In total | 340 | 294 | 197 | 143 | 97 | 57.9 | 67.0 |
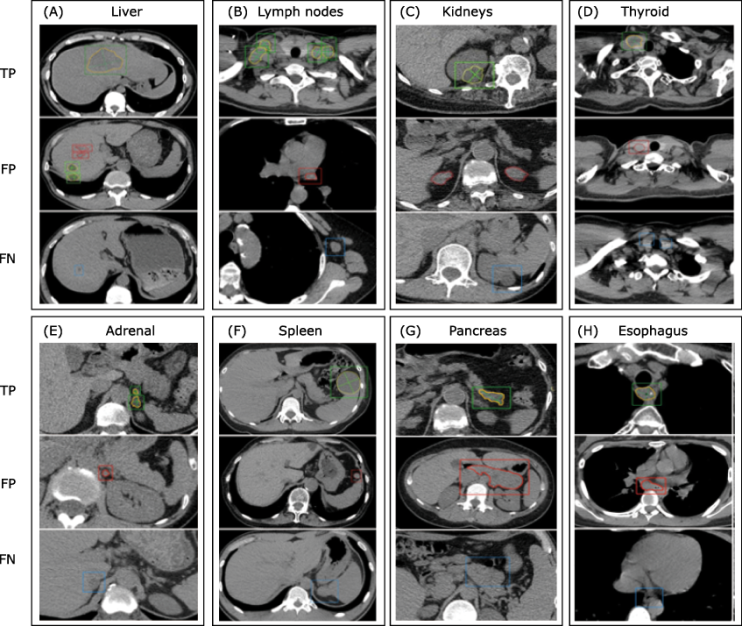
Figure 2.
Examples of lesion detection and segmentation results of the ULDor model on the real-world CT image test sets. For detection, boxes in green, red, and blue are TPs, FPs and FNs, respectively. For segmentation, the green lines are ground-truth diameters, the yellow and red contours show lesions’ masks. TP, true positive; FP, false positive; FN, false negative."
| 1. |
Dreyer KJ, Geis JR. When machines think: radiology’s next frontier. Radiology 2017; 285(3):713-8. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017171183.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017171183 pmid: 29155639 |
| 2. |
Cheng CT, Wang YR, Chen HW, et al. A scalable physician-level deep learning algorithm detects universal trauma on pelvic radiographs. Nat Commun 2021; 12(1):1066. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21311-3.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21311-3 |
| 3. |
Korfiatis P, Kline TL, Lachance DH, et al. Residual deep convolutional neural network predicts MGMT methylation status. J Digit Imaging 2017; 30(5):622-8. doi: 10.1007/s10278-017-0009-z.
doi: 10.1007/s10278-017-0009-z |
| 4. |
Nam JG, Kim M, Park JC, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm detecting 10 common abnormalities on chest radiographs. Eur Respirat J 2021; 57(5):2003061. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03061-2020.
doi: 10.1183/13993003.03061-2020 |
| 5. |
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Ball RL, et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLOS Med 2018; 15(11):e1002686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002686.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002686 |
| 6. |
Monteiro M, Newcombe VFJ, Mathieu F, et al. Multiclass semantic segmentation and quantification of traumatic brain injury lesions on head CT using deep learning: an algorithm development and multicentre validation study. Lancet Digit Health 2020; 2(6):e314-e322. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30085-6.
doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30085-6 |
| 7. |
Benndorf M, Burnside ES, Herda C, et al. External validation of a publicly available computer assisted diagnostic tool for mammographic mass lesions with two high prevalence research datasets. Med Physic 2015; 42(8):4987-96. doi: 10.1118/1.4927260.
doi: 10.1118/1.4927260 |
| 8. |
Si K, Xue Y, Yu XZ, et al. Fully end-to-end deep-learning-based diagnosis of pancreatic tumors. Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1982-90. doi: 10.7150/thno.52508.
doi: 10.7150/thno.52508 |
| 9. |
Masood A, Sheng B, Li P, et al. Computer-assisted decision support system in pulmonary cancer detection and stage classification on CT images. J Biomed Inform 2018; 79:117-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.01.005.
doi: S1532-0464(18)30007-8 pmid: 29366586 |
| 10. |
Yan K, Wang X, Lu L, et al. DeepLesion: automated mining of large-scale lesion annotations and universal lesion detection with deep learning. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2018; 5(3):036501. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.5.3.036501.
doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.5.3.036501 |
| 11. |
Yan K, Cai JZ, Zheng YJ, et al. Learning from multiple datasets with heterogeneous and partial labels for universal lesion detection in CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2020; Dec 28, 2020; E-pub ahead of print. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3047598.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3047598 |
| 12. |
Cai JZ, Yan K, Cheng CT, et al. Deep volumetric universal lesion detection using light-weight pseudo 3D convolution and surface point regression. In: Martel A.L. et al. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2020. MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12264. p.3-13. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_1.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_1 |
| 13. |
Yan K, Tang YB, Peng YF, et al. Multitask universal lesion analysis network for joint lesion detection, tagging, and segmentation, In: Shen D. et al. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2019. MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11769. p. 194-202. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_22.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_22 |
| 14. |
Tang YB, Yan K, Tang YX, et al. ULDor: A universal lesion detector for CT scans with pseudo masks and hard negative example mining. 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), 2019. p. 833-6. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759478.
doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759478 |
| 15. |
Setio AA, Traverso A, de Bel T, et al. Validation, comparison, and combination of algorithms for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: the LUNA16 challenge. Med Image Anal 2017; 42:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.06.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.06.015 |
| 16 | 16. Bilic P, Christ FP, Vorontsov E, et al. The Liver Tumor Segmentation Benchmark (LiTS). arXiv:1901.04056vi [preprint], 2019. Available from. The Liver Tumor Segmentation Benchmark (LiTS). arXiv:1901.04056vi [preprint], 2019. Available from http://arxiv.org/abs/1901.04056. Accessed June 20, 2021. |
| 17 |
17. Roth H, Lu L, Seff A, et al. (2015). A new 2.5 D representation for lymph node detection in CT [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. doi: 10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.AQIIDCNM.
doi: 10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.AQIIDCNM |
| 18 | 18. Antonelli M, Reinke A, Bakas S, et al. The Medical Segmentation Decathlon. arXiv: 2106. 05735v1 [preprint], 2021. Available from https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05735. Accessed June 20, 2021. |
| 19. | National Cancer Institute. Cancer Data Access System. The National Lung Screening Trial (NLST). Available from https://cdas.cancer.gov/nlst/. Accessed June 20, 2021. |
| 20. |
Nin CS, de Souza VVS, Do Amaral RH, et al. Thoracic lymphadenopathy in benign diseases: a state of the art review. Respir Med 2016; 112:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.01.021.
doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.01.021 |
| 21. |
Wu ZJ, Wang ZJ, Zheng ZY, et al. Risk factors for lymph node metastasis and survival outcomes in colorectal neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Manag Res 2020; 12:7151-64. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S256723.
doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S256723 |
| 22. |
Li ZH, Zhang S, Zhang JG, et al. MVP-Net: multi-view FPN with position-aware attention for deep universal lesion detection. In: Shen D et al. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2019 MICCAI 2019. MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11769. p.13-21. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_2.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_2 |
| 23. |
Tao QY, Ge ZY, Cai JF, et al. Improving deep lesion detection using 3D contextual and spatial attention. In: Shen D et al. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2019. MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11769. p.185-93. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_21.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_21 |
| 24. |
Zhang S, Xu JC, Chen YC, et al. Revisiting 3D context modeling with supervised pre-training for universal lesion detection in CT slices, In: Martel AL et al. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - MICCAI 2020. MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12264. p.542-51. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_53.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59719-1_53 |
| [1] | Chun Wang, Qinxue Chang, Xiaomeng Wang, Keyun Wang, He Wang, Zhuang Cui, Changping Li. Prostate Cancer Risk Prediction and Online Calculation Based on Machine Learning Algorithm [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(3): 210-217. |
| [2] | Wei Ba, Shuhao Wang, Cancheng Liu, Yuefeng Wang, Huaiyin Shi, Zhigang Song. Histopathological Diagnosis System for Gastritis Using Deep Learning Algorithm [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 204-209. |
| [3] | Jiazheng Li, Lei Tang. Radiomics in Antineoplastic Agents Development: Application and Challenge in Response Evaluation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 187-195. |
| [4] | Dasheng Li,Dawei Wang,Nana Wang,Haiwang Xu,He Huang,Jianping Dong,Chen Xia. An Insight of the First Community Infected COVID-19 Patient in Beijing by Imported Case: Role of Deep Learning-Assisted CT Diagnosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 66-71. |
| [5] | Li Peilin, Yuan Zhenming, Tu Wenbo, Yu Kai, Lu Dongxin. Medical Knowledge Extraction and Analysis from Electronic Medical Records Using Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 133-139. |
| [6] | Shi Ying-huan,Wang Qian. The Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Medical Imaging: Today and Its Future [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 71-75. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

