Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 257-264.doi: 10.24920/003874
• Original Articles • Next Articles
Effect of Focused Cardiac Ultrasound in Combination with Lung Ultrasound on Critically Ill Patients: A Multicenter Observational Study in China
Hongmin Zhang1, Lina Zhang2, Lixia Liu3, Ying Zhu4, Wanhong Yin5, Wei He6, Xiuling Shang7, Yangong Chao8, Liwen Lv9, Xiaoting Wang1, *, Dawei Liu1, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group
- 1Department of Critical Care Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Department of Critical Care Medicine, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China
3Department of Critical Care Medicine, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
4Department of Critical Care Medicine, Affiliated Hangzhou First People’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310006, China
5Department of Critical Care Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
6Department of Critical Care Medicine, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100730, China
7Department of Critical Care Medicine, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China
8Department of Critical Care Medicine, The First Hospital of Tsinghua University, Beijing 100016, China
9Department of Emergency Medicine, The People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, China
-
Received:2021-01-08Published:2021-12-31Online:2021-10-09 -
Contact:Xiaoting Wang
Cite this article
Hongmin Zhang, Lina Zhang, Lixia Liu, Ying Zhu, Wanhong Yin, Wei He, Xiuling Shang, Yangong Chao, Liwen Lv, Xiaoting Wang, Dawei Liu, Chinese Critical Ultrasound Study Group . Effect of Focused Cardiac Ultrasound in Combination with Lung Ultrasound on Critically Ill Patients: A Multicenter Observational Study in China[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 257-264.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Comparisons of features of the two groups of patients"
| Items | Early phase (n=502) | Later phase (n=490) | t or Z or χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male [n (%)] | 287 (57.2) | 301 (61.4) | 1.862 | 0.172 |
| Age (yr, mean±SD) | 61±18 | 59±17 | 1.849 | 0.064 |
| APACHEⅡ | 15 (11, 21) | 17 (11, 23) | -0.924 | 0.270 |
| SOFA [score, median (interquartile range)] | 6 (4, 8) | 6 (4, 8) | -0.662 | 0.508 |
| Diagnosis [n (%)] | ||||
| High risk surgery | 183 (36.5) | 187 (37.8) | 0.310 | 0.578 |
| Respiratory failure | 130 (25.9) | 152 (31.0) | 3.200 | 0.074 |
| Shock | 84 (16.7) | 66 (13.5) | 2.058 | 0.151 |
| Shock+Respiratory failure | 39 (7.8) | 29 (5.9) | 1.330 | 0.249 |
| Others* | 118 (23.5) | 114 (23.3) | 0.008 | 0.929 |
| HR [bpm, median (interquartile range)] | 92 (77, 114) | 98 (79, 110) | -0.012 | 0.991 |
| MAP [mmHg, median (interquartile range)] | 88 (77, 102) | 88 (80, 98) | -0.273 | 0.785 |
| NE infusion [n, (%)] | 103 (20.5) | 115 (23.5) | 0.725 | 0.124 |
| MV [n, (%)] | 264 (52.6) | 279 (56.9) | 1.893 | 0.169 |
Table 2
Comparisons of results of ultrasound examination [n (%)]"
| Items | Early phase (n=502) | Later phase (n=490) | Z or χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of examination [min, median (interquartile range)] | 15 (11, 30) | 15 (12, 30) | -1.495 | 0.135 |
| FCU | ||||
| Structure abnormality* | 92 (18.3) | 94 (19.2) | 0.120 | 0.730 |
| Left ventricular systolic function | ||||
| Normal | 364 (72.5) | 343 (70.0) | 0.763 | 0.382 |
| Moderately abnormal | 120 (23.9) | 132 (26.9) | 1.205 | 0.272 |
| Severely abnormal | 18 (3.6) | 15 (3.1) | 0.212 | 0.645 |
| IVC | ||||
| Dilated and fixed | 173 (34.5) | 129 (26.3) | 7.751 | 0.005 |
| Moderate | 240 (47.8) | 276 (56.3) | 7.208 | 0.007 |
| Small and collapsed | 89 (17.7) | 85 (17.3) | 0.025 | 0.874 |
| RV dysfunction | 7 (1.4) | 9 (1.8) | 0.306 | 0.580 |
| LU | ||||
| A profile | 212 (42.2) | 181(36.9) | 2.903 | 0.088 |
| A’ or B’+lung point | 8 (1.6) | 11(2.2) | 0.560 | 0.454 |
| B profile | 35 (7.0) | 29 (5.9) | 0.456 | 0.499 |
| Other profiles* | 247 (49.2) | 269 (54.9) | 3.222 | 0.073 |
Table 3
Comparison of treatment change between the two groups [n (%)]"
| Items | Early phase (n=502) | Later phase (n=490) | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
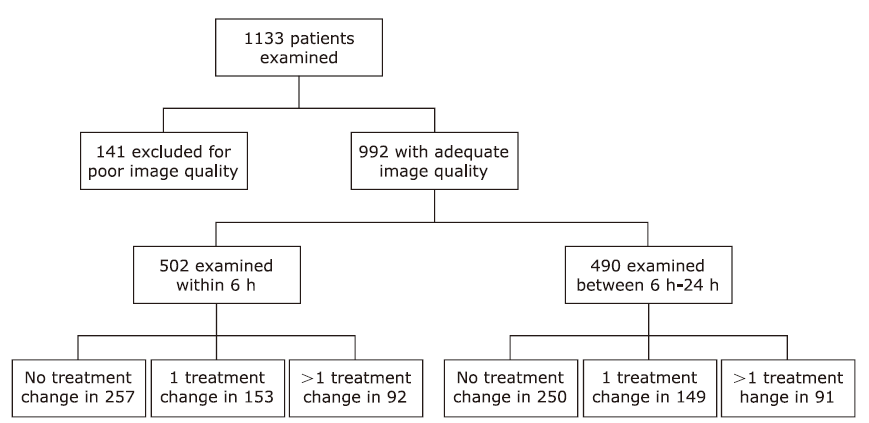
| Patients with treatment change | 245 (48.8) | 240 (49.0) | 0.003 | 0.956 |
| One treatment change | 153 (30.5) | 149 (30.4) | 0.001 | 0.991 |
| More than one treatment change | 92 (18.3) | 91 (18.6) | 0.010 | 0.921 |
| Volume expansion | 47 (9.4) | 44 (9.0) | 0.044 | 0.835 |
| Negative fluid balance | 166 (33.1) | 139 (28.4) | 2.573 | 0.109 |
| Inotrope | 28 (5.6) | 39 (8.0) | 2.233 | 0.135 |
| Norepinephrine adjustment | 37 (7.4) | 22 (4.5) | 3.679 | 0.055 |
| Drainage of pericardial effusion | 3 (0.6) | 0 | 2.937 | 0.087 |
| Ventilator adjustment | 93 (18.5) | 104 (21.2) | 1.135 | 0.287 |
| Drainage of pleural cavity | 23 (4.6) | 24 (4.9) | 0.055 | 0.815 |
| In need of other type of ultrasound examination | 91 (18.1) | 97 (19.8) | 0.449 | 0.503 |
| In need of CT | 88 (17.5) | 98 (20.0) | 0.993 | 0.319 |
| In need of CCO monitoring | 39 (7.8) | 26 (5.3) | 2.456 | 0.117 |
Table 4
Results of logistic regression analysis for factors associated with treatment change"
| Risk factors | OR | 95%CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.987 | 0.969-1.005 | 0.157 |
| APAHCEⅡ | 0.997 | 0.991-1.003 | 0.379 |
| SOFA | 1.034 | 0.946-1.130 | 0.465 |
| Respiratory failure | 2.357 | 1.284-4.326 | 0.006 |
| Shock | 1.733 | 0.896-3.353 | 0.103 |
| Timing of examination | 0.725 | 0.407-1.291 | 0.275 |
| 1. |
Greenstein YY, Littauer R, Narasimhan M, et al. Effectiveness of a critical care ultrasonography course. Chest 2017; 151(1):34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.08.1465.
doi: S0012-3692(16)59161-2 pmid: 27645689 |
| 2. |
Dinh VA, Giri PC, Rathinavel I, et al. Impact of a 2-day critical care ultrasound course during fellowship training: a pilot study. Crit Care Res Pract 2015; 2015:675041. doi: 10.1155/2015/675041.
doi: 10.1155/2015/675041 pmid: 26346694 |
| 3. |
Via G, Hussain A, Wells M, et al. International evidence-based recommendations for focused cardiac ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2014; 27(7):683.e1-683.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.05.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.05.001 |
| 4. |
Andruszkiewicz P, Sobczyk D, Gorkiewicz-Kot I, et al. Reliability of focused cardiac ultrasound by novice sonographer in preoperative anaesthetic assessment: an observational study. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2015; 13:45. doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0039-y.
doi: 10.1186/s12947-015-0039-y |
| 5. |
Kanji HD, McCallum J, Sirounis D, et al. Limited echocardiography-guided therapy in subacute shock is associated with change in management and improved outcomes. J Crit Care 2014; 29(5):700-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.04.008.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.04.008 |
| 6. |
Lichtenstein D. Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Curr Opin Crit Care 2014; 20(3):315-22. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000096.
doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000096 pmid: 24758984 |
| 7. |
Manno E, Navarra M, Faccio L, et al. Deep impact of ultrasound in the intensive care unit: the “ICU-sound” protocol. Anesthesiology 2012; 117(4):801-9. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318264c621.
doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318264c621 |
| 8. |
Sekiguchi H, Harada Y, Villarraga HR, et al. Focused cardiac ultrasound in the early resuscitation of severe sepsis and septic shock: a prospective pilot study. J Anesth 2017; 31(4):487-93. doi: 10.1007/s00540-017-2312-8.
doi: 10.1007/s00540-017-2312-8 pmid: 28144779 |
| 9. |
Vincent JL, De Backer D. Circulatory shock. N Engl J Med 2013; 369(18):1726-34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1208943.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1208943 |
| 10. |
Monastesse A, Girard F, Massicotte N, et al. Lung ultrasonography for the assessment of perioperative atelectasis: a pilot feasibility study. Anesth Analg 2017; 124(2):494-504. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001603.
doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001603 pmid: 27669555 |
| 11. |
Theerawit P, Sutherasan Y, Ball L, et al. Respiratory monitoring in adult intensive care unit. Expert Rev Respir Med 2017; 11(6):453-68. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2017.1325324.
doi: 10.1080/17476348.2017.1325324 |
| 12. |
Via G, Storti E, Gulati G, et al. Lung ultrasound in the ICU: from diagnostic instrument to respiratory monitoring tool. Minerva Anestesiol 2012; 78(11):1282-96.
pmid: 22858877 |
| 13. |
Volpicelli G, Caramello V, Cardinale L, et al. Bedside ultrasound of the lung for the monitoring of acute decompensated heart failure. Am J Emerg Med 2008; 26(5):585-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2007.09.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2007.09.014 pmid: 18534289 |
| 14. |
Martindale JL, Secko M, Kilpatrick JF, et al. Serial sonographic assessment of pulmonary edema in patients with hypertensive acute heart failure. J Ultrasound Med 2018; 37(2):337-45. doi: 10.1002/jum.14336.
doi: 10.1002/jum.14336 pmid: 28758715 |
| 15. |
Tsou PY, Kurbedin J, Chen YS, et al. Accuracy of point-of-care focused echocardiography in predicting outcome of resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Resuscitation 2017; 114:92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2017.02.021.
doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2017.02.021 |
| 16. |
Repessé X, Charron C, Vieillard-Baron A. Acute cor pulmonale in ARDS: rationale for protecting the right ventricle. Chest 2015; 147(1):259-65. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-0877.
doi: S0012-3692(15)30257-9 pmid: 25560864 |
| 17. |
Vignon P, Repessé X, Vieillard-Baron A, et al. Critical care ultrasonography in acute respiratory failure. Crit Care 2016; 20(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1400-8.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1400-8 |
| 18. |
Marcelino PA, Marum SM, Fernandes AP, et al. Routine transthoracic echocardiography in a general Intensive Care Unit: an 18 month survey in 704 patients. Eur J Intern Med 2009; 20(3):e37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2008.09.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2008.09.015 |
| 19. |
Randazzo MR, Snoey ER, Levitt MA, et al. Accuracy of emergency physician assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and central venous pressure using echocardiography. Acad Emerg Med 2003; 10(9):973-7.
pmid: 12957982 |
| 20. |
Vieillard-Baron A. Assessment of right ventricular function. Curr Opin Crit Care 2009; 15(3):254-60. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e32832b70c9.
doi: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e32832b70c9 pmid: 19451815 |
| 21. |
Zhang Z, Xu X, Ye S, et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of the respiratory variation in the inferior vena cava diameter is predictive of fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 2014; 40(5):845-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2013.12.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2013.12.010 |
| 22. |
Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2010; 23(7):685-713; quiz 786-8. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2010.05.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2010.05.010 |
| 23. |
Lichtenstein DA. Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Ann Intensive Care 2014; 4(1):1. doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-4-1.
doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-4-1 pmid: 24401163 |
| 24. |
Zieleskiewicz L, Muller L, Lakhal K, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound in intensive care units: assessment of 1073 procedures in a multicentric, prospective, observational study. Intensive Care Med 2015; 41(9):1638-47. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3952-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3952-5 pmid: 26160727 |
| 25. |
Miglioranza MH, Picano E, Badano LP, et al. Pulmonary congestion evaluated by lung ultrasound predicts decompensation in heart failure outpatients. Int J Cardiol 2017; 240:271-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.02.150.
doi: S0167-5273(16)33236-3 pmid: 28606680 |
| 26. |
Lee CW, Kory PD, Arntfield RT. Development of a fluid resuscitation protocol using inferior vena cava and lung ultrasound. J Crit Care 2016; 31(1):96-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.09.016.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.09.016 |
| 27. | Lichtenstein D. FALLS-protocol: lung ultrasound in hemodynamic assessment of shock. Heart Lung Vessel 2013; 5(3):142-7. |
| 28. |
Lewandowski K, Lewandowski M. Epidemiology of ARDS. Minerva Anestesiol 2006; 72(6):473-7.
pmid: 16682918 |
| 29. |
Krishnan S, Schmidt GA. Acute right ventricular dysfunction: real-time management with echocardiography. Chest 2015; 147(3):835-46. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1335.
doi: S0012-3692(15)39682-3 pmid: 25732449 |
| 30. |
Alsaddique A, Royse AG, Royse CF, et al. Repeated monitoring with transthoracic echocardiography and lung ultrasound after cardiac surgery: feasibility and impact on diagnosis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2016; 30(2):406-12. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.08.033.
doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.08.033 pmid: 26723882 |
| [1] | Cui Wang, Xiaodong Deng, Hongmin Zhang, Dawei Liu, Xiaoting Wang. Study on Image Acquisition of Transthoracic Echocardiography in Mechanically Ventilated ICU Patients [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 323-329. |
| [2] | Wei-yun Chen, Xue-rong Yu*, Jiao Zhang, Qing Yuan, Yu-guang Huang. Effect of Point-of-care Hemoglobin/Hematocrit Devices and Autologous Blood Salvage on Reduction of Perioperative Allogeneic Blood Transfusion [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(2): 83-88. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|