Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 123-128.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.016
• Case Report • Previous Articles Next Articles
Trigeminal Ganglioneuroma in the Middle-posterior Cranial Fossa: a Case Report△
Wang Ting1, Ma Lin1, Lou Xin1, Bu Bo2, *( )
)
- 1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
2Department of neurosurgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2016-06-06Published:2017-06-30Online:2017-06-10 -
Contact:Bu Bo E-mail:surgeon301@126.com
Cite this article
Wang Ting, Ma Lin, Lou Xin, Bu Bo. Trigeminal Ganglioneuroma in the Middle-posterior Cranial Fossa: a Case Report△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 123-128.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
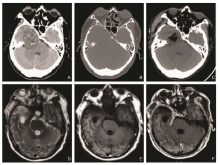
Figure 1.
Images of cranial CT scan and postoperative MRI.A. A heterogeneous low-density mass in size of 4.2cm×5.2cm in the right middle-posterior cranial fossa with dotty calcification inside. B. Bone window image showed absorption and thinning of the sphenoid and ethmoid bone. C. Postoperative CT image demonstrated complete resection of the tumor. D-F. Postoperative MRI images (T2WI,T1WI, and enhanced T1WI) five months after the operation showed the tumor was resected completely with no residue and recurrence."
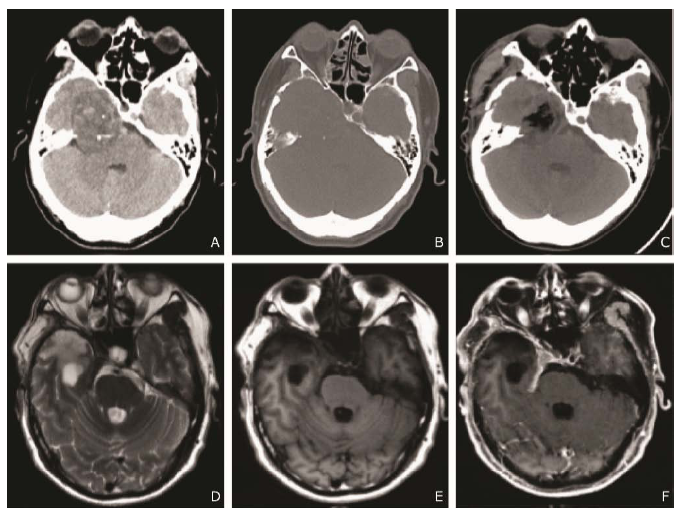
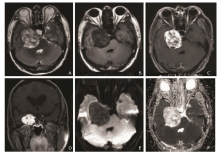
Figure 2.
MRI findings on pre- and post-contrast MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging before operation. A. Axial T2WI image and B. Axial T1WI image showed a well-defined mass with heterogeneous signal intensity in the right middle-posterior cranial fossa. C. Remarkable heterogeneous enhancement on contrast enhanced axial T1WI. D. Coronal contrast enhanced T1WI image showed the lesion surround the right internal jugular vein. E. Diffusion-weighed imaging (b=1000 s/mm2) revealed a hypointensity tumor. F. Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping showed relatively hyperintensity of the tumor."
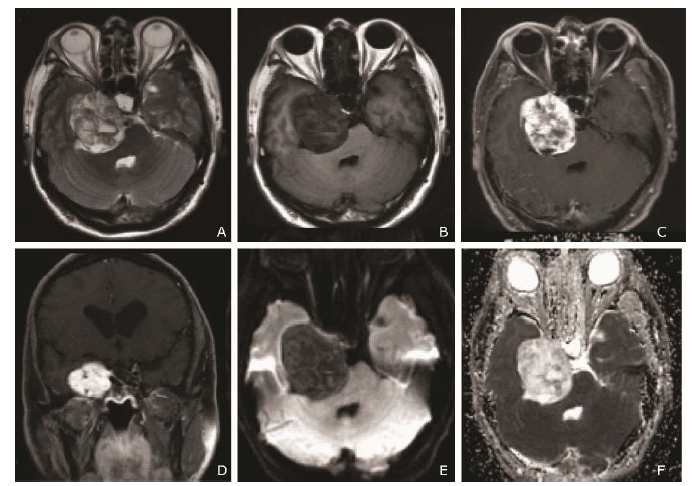
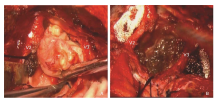
Figure 3.
Photographs of intra-operative findings. A. After the focal skull removed, the dura was exposed and extradural tumor was identifiable. B. Cystic component of the intratumoral cavity (asterisk). Maxillary and mandibular nerve were well reserved while the tumor was resected completely. V2, maxillary nerve; V3, mandibular nerve; T, tumor."
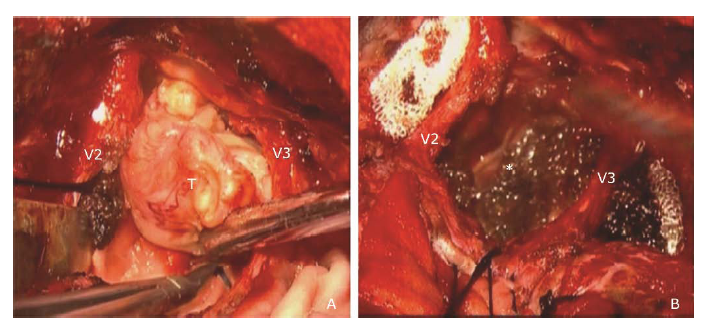
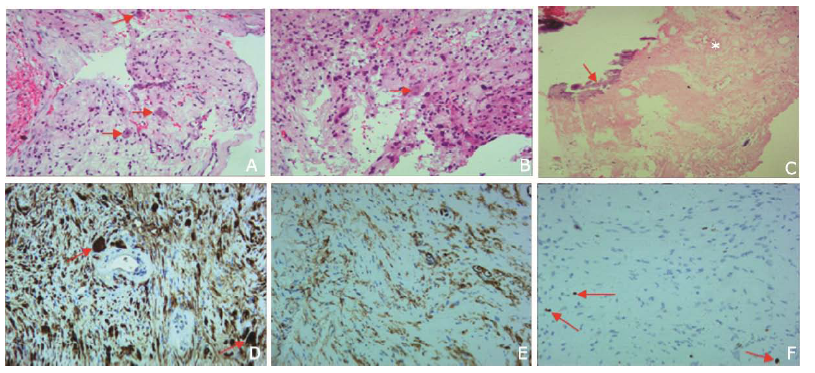
Figure 4.
Histological findings of ganglioneuroma. A. Mixture of large ganglion cells (arrows) and spindle-shaped Schwann-like cells (H&E staining, 400×). B. Dysplastic ganglion cell with binucleated cell (arrow) (H&E staining, 400×). C. Calcification (arrow) and hyaline degeneration (asterisk) in tumor (H&E staining, 100×). D. S-100 positive cells accompanied with giant ganglion cells (arrows) supporting the neurogenic nature of the tumor (S-100 protein immunohistochemical staining, 400×). E. CD34 positive cells presented in blood vessels, indicating angiogenesis of the tumor (CD34 immunohistochemical staining, 400×). F. 3% Ki-67 positive cells confirmed the benign neoplasm (arrows) (Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining, 400×)."
| 1. | Oderda M, Cattaneo E, Soria F, et al.Adrenal ganglioneuroma with multifocal retroperitoneal extension: A challenging diagnosis. Scientific World J 2011; 11: 1548-53. doi:10.1100/tsw.2011.144. |
| 2. | Kim SK, Jeong MY, Kang HK, et al.Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging findings in a patient with trigeminal ganglioneuroma. Korean J Radiol 2013; 14: 118-21. doi:10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.118. |
| 3. | Abe T, Asano T, Manabe T, et al.Trigeminal ganglioneuroma. Brain Tumor Pathol 1999; 16: 49-53. |
| 4. | Nakaguchi H, Murakami M, Matsuno A, et al.Ganglioneuroma originating from the trigeminal nerve in the middle cranial fossa. Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2012; 52: 95-8. doi:10.2176/nmc.52.95. |
| 5. | Bekelis K, Meiklejohn DA, Missios S, et al.Ganglioneuroma of the internal auditory canal presenting as a vestibular schwannoma. Skull Base Reports 2011; 1: 89-94. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1276722. |
| 6. | Ozluoglu LN, Yilmaz I, Cagici CA, et al.Ganglioneuroma of the internal auditory canal: a case report. Audiol Neurootol 2007; 12: 160-4. doi:10.1159/000099018. |
| 7. | Arseni C, Horvath L, Carp N, et al.Intracranial ganglioneuromas in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1975; 32: 279-86. |
| 8. | Estefano J, Algaba J, Gorostiaga F, et al.Ganglioneuroma of the middle ear. Apropos of a case. An Otorrinolaringol Ibero Am 1992; 19: 5-12. |
| 9. | Lonergan GJ, Schwab CM, Suarez ES, et al.Neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2002; 22: 911-34. doi:10.1148/radiographics.22.4.g02jl15911. |
| 10. | Hayes FA, Green AA, Rao BN.Clinical manifestations of ganglioneuroma. Cancer 1989; 63: 1211-4. ? |
| 11. | Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, et al.The international neuroblastoma pathology classification (the Shimada system). Cancer 1999; 86: 364-72. |
| 12. | Kleihaus PCW, ed. WHO Classification of Tumors. In: Pathology and Genetics: Tumors of the Nervous system. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2000. P 96-8. |
| 13. | Ichikawa T, Ohtomo K, Araki T, et al.Ganglioneuroma: computed tomography and magnetic resonance features. Br J Radiol 1996; 69: 114-21. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-69- 818-114. |
| 14. | Zhang Y, Nishimura H, Kato S, et al.MRI of ganglioneuroma: histologic correlation study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2001; 25: 617-23. |
| 15. | Gahr N, Darge K, Hahn G, et al.Diffusion-weighted MRI for differentiation of neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma/ganglioneuroma. Eur J Radiol 2011; 79: 443-6. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.04.005. |
| [1] | Atefeh Beigi-khoozani, Amirmohammad Merajikhah, Mahdieh Soleimani. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Olfactory Bulb in Anosmic Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [3] | Dasheng Li,Dawei Wang,Nana Wang,Haiwang Xu,He Huang,Jianping Dong,Chen Xia. An Insight of the First Community Infected COVID-19 Patient in Beijing by Imported Case: Role of Deep Learning-Assisted CT Diagnosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 66-71. |
| [4] | Jian Cao, Guorong Wang, Zhiwei Wang, Zhengyu Jin. CT Texture Analysis: A Potential Biomarker for Evaluating KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [5] | Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [6] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [7] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [8] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [9] | Li Ping, Zhu Liang, Wang Xuan, Xue Huadan, Wu Xin, Jin Zhengyu. Imaging Diagnosis of Type Ⅲ Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [10] | Li Lihui, Huang Houbin, Chen Zhiye. Early Diagnosis of Recurrent Optic Neuritis Using Contrast-Enhanced T2 Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging: a Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [11] | Chen Zhiye, Liu Mengqi, Ma Lin. Cortical Thinning Pattern of Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Surface-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [12] | Li Tao, Yang Li, Zhang Weiguo, Luo Chuncai, Huang Zili, Li Jinfeng, Li Xin. Midterm Follow-up of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting with 64-Slice Multi-detector Computed Tomography: Identification of Risk Factors Affecting Graft Patency [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 69-76. |
| [13] | Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [14] | Liu Mengqi, Chen Zhiye, Ma Lin. Reliability of Three Dimentional Pseudo-continuous Arterial Spin Labeling: A Volumetric Cerebral Perfusion Imaging with Different Post-labeling Time and Functional State in Health Adults [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | Pan Haipeng, Lao Qun, Fei Zhenghua, Yang Li, Zhou Haichun, Lai Can. MR Lymphangiography for Focal Disruption of the Thoracic Duct in Chylothorax of an Infant: a Case Report and Literature Review△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 265-268. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

