
Latest Issue
Volume 40 , Issue 2 , 2025
-
Chinese Expert Consensus on the Definitions of Palliative Care and Hospice Care (2025) Enhanced Publication AI Introduction
“In the field of modern palliative care, Chinese experts have established consensus definitions for "palliative care" and "hospice care", highlighting the holistic nature of care and laying a foundation for discipline development, clinical practice, and public communication.”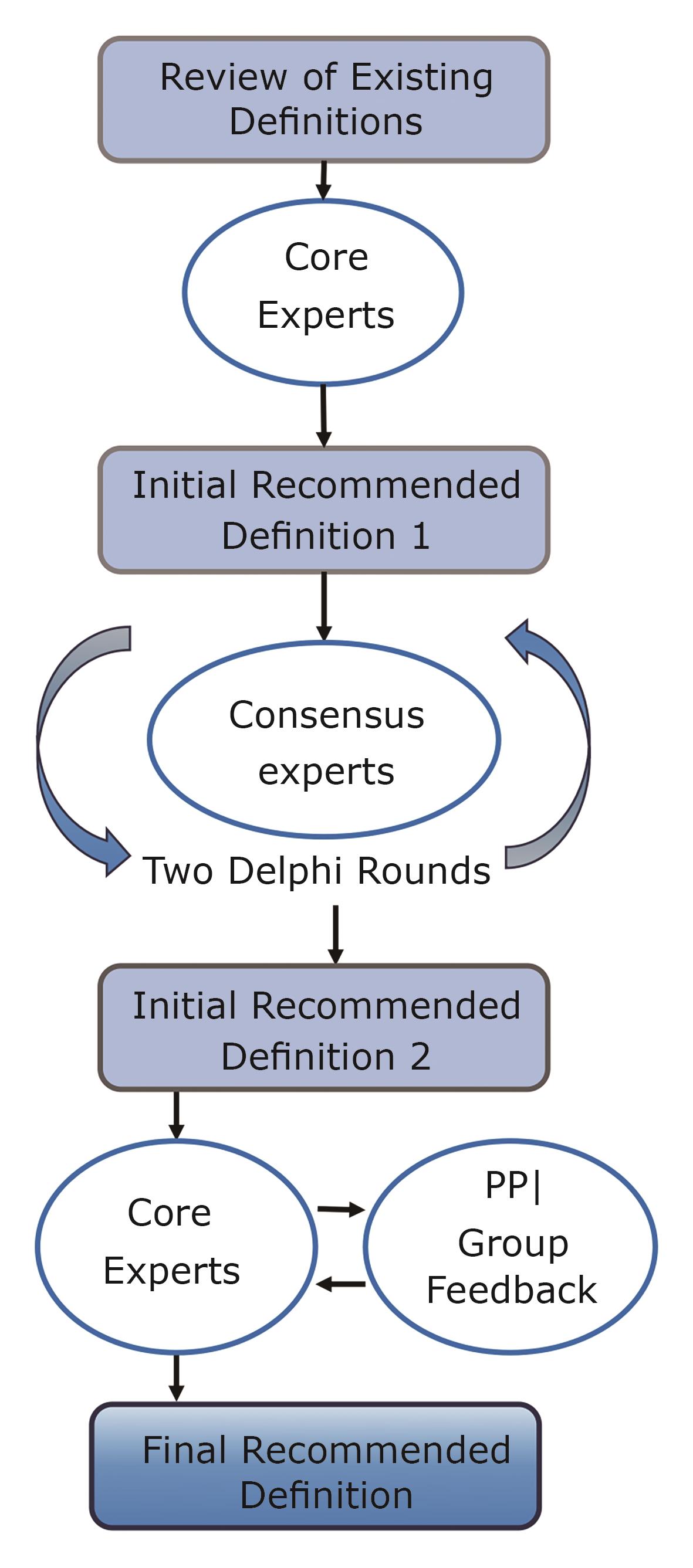 Abstract:Background and ObjectiveThe development of modern palliative care in China began in the 1980s and is currently in an accelerating phase. However, inconsistencies in terminology and concepts have hindered policy-making, clinical practice, and academic research. The Terminology of Clinical Medicine (2023 edition) has determined huan-he-yi-liao (缓和医疗) and an-ning-liao-hu (安宁疗护) as the formal terms of "palliative care" and "hospice care", respectively. To align with these terms, this study aims to establish expert consensus definitions tailored to the Chinese context. MethodsWe systematically retrieved and collected domestic and international literature and policy documents related to the definition of palliative care, then deconstructed and analyzed the relevant conceptual elements of these definitions. Core expert panel built the initial recommended definition upon the conceptual elements and consensus definition of palliative care by the International Association for Hospice and Palliative Care (IAHPC) through two rounds of online discussions. After nomination and selection, 61 professionals in the field of palliative care in China were invited to participate in the consensus expert group. Two rounds of Delphi consultation were conducted among the consensus experts, who were asked to score their agreement using Likert scale to the items in the initial recommended definition and the definition statements of palliative care and hospice care. Agreement rate of over 80% was considered as reaching consensus for each items. The core expert panel revised the items and the statements of recommended definitions based on the results from Delphi surveys. The final recommended definitions were formulated after feedback from patient and public involvement (PPI) group members.ResultsThe response rates for the first and second round of Delphi surveys were 83.6% and 100.0%, respectively. The agreement rates of the items and statements of the recommended definitions exceeded 90%. Accordingly, the definitions based on Chinese expert consensus are recommended. Palliative care is an active holistic approach aimed at patients of all ages suffering from life-threatening illness and their families and caregivers. It seeks to improve their quality of life by preventing, assessing, and relieving physical, psychological, social, and spiritual suffering. Hospice care is an integral part of palliative care, focusing on holistic care for patients at the end of life and their families and caregivers. Its goal is to help patients to maintain dignity and achieve a good death by alleviating physical, psychological, social, and spiritual distress without intentionally hastening or postponing death, meanwhile improve the quality of life for families and caregivers.ConclusionsThis study has established the Chinese expert consensus definitions of palliative care and hospice care in China, as well as the relationship between the two. The definitions highlight the holistic nature of palliative care, providing a foundation for discipline development, clinical practice, and public communication.Keywords:palliative care;hospice care;China;Delphi;definition2124|587|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:Background and ObjectiveThe development of modern palliative care in China began in the 1980s and is currently in an accelerating phase. However, inconsistencies in terminology and concepts have hindered policy-making, clinical practice, and academic research. The Terminology of Clinical Medicine (2023 edition) has determined huan-he-yi-liao (缓和医疗) and an-ning-liao-hu (安宁疗护) as the formal terms of "palliative care" and "hospice care", respectively. To align with these terms, this study aims to establish expert consensus definitions tailored to the Chinese context. MethodsWe systematically retrieved and collected domestic and international literature and policy documents related to the definition of palliative care, then deconstructed and analyzed the relevant conceptual elements of these definitions. Core expert panel built the initial recommended definition upon the conceptual elements and consensus definition of palliative care by the International Association for Hospice and Palliative Care (IAHPC) through two rounds of online discussions. After nomination and selection, 61 professionals in the field of palliative care in China were invited to participate in the consensus expert group. Two rounds of Delphi consultation were conducted among the consensus experts, who were asked to score their agreement using Likert scale to the items in the initial recommended definition and the definition statements of palliative care and hospice care. Agreement rate of over 80% was considered as reaching consensus for each items. The core expert panel revised the items and the statements of recommended definitions based on the results from Delphi surveys. The final recommended definitions were formulated after feedback from patient and public involvement (PPI) group members.ResultsThe response rates for the first and second round of Delphi surveys were 83.6% and 100.0%, respectively. The agreement rates of the items and statements of the recommended definitions exceeded 90%. Accordingly, the definitions based on Chinese expert consensus are recommended. Palliative care is an active holistic approach aimed at patients of all ages suffering from life-threatening illness and their families and caregivers. It seeks to improve their quality of life by preventing, assessing, and relieving physical, psychological, social, and spiritual suffering. Hospice care is an integral part of palliative care, focusing on holistic care for patients at the end of life and their families and caregivers. Its goal is to help patients to maintain dignity and achieve a good death by alleviating physical, psychological, social, and spiritual distress without intentionally hastening or postponing death, meanwhile improve the quality of life for families and caregivers.ConclusionsThis study has established the Chinese expert consensus definitions of palliative care and hospice care in China, as well as the relationship between the two. The definitions highlight the holistic nature of palliative care, providing a foundation for discipline development, clinical practice, and public communication.Keywords:palliative care;hospice care;China;Delphi;definition2124|587|0Updated:2025-06-30
Guideline & Consensus
-
Development and Initial Validation of the Multi-Dimensional Attention Rating Scale in Highly Educated Adults AI Introduction
“In the field of attention assessment, researchers have developed the Multi-dimensional Attention Rating Scale (MARS), a self-report tool that evaluates six-dimension attention levels. The MARS, based on Classical Test Theory, demonstrated high reliability and validity, offering a new tool for assessing multi-dimensional attention impairments in various mental disorders.” Abstract:ObjectiveTo report the development, validation, and findings of the Multi-dimensional Attention Rating Scale (MARS), a self-report tool crafted to evaluate six-dimension attention levels.MethodsThe MARS was developed based on Classical Test Theory (CTT). Totally 202 highly educated healthy adult participants were recruited for reliability and validity tests. Reliability was measured using Cronbach's alpha and test-retest reliability. Structural validity was explored using principal component analysis. Criterion validity was analyzed by correlating MARS scores with the Toronto Hospital Alertness Test (THAT), the Attentional Control Scale (ACS), and the Attention Network Test (ANT).ResultsThe MARS comprises 12 items spanning six distinct dimensions of attention: focused attention, sustained attention, shifting attention, selective attention, divided attention, and response inhibition.As assessed by six experts, the content validation index (CVI) was 0.95, the Cronbach's alpha for the MARS was 0.78, and the test-retest reliability was 0.81. Four factors were identified (cumulative variance contribution rate 68.79%). The total score of MARS was correlated positively with THAT (r = 0.60, P < 0.01) and ACS (r = 0.78, P < 0.01) and negatively with ANT's reaction time for alerting (r = -0.31, P = 0.049).ConclusionThe MARS can reliably and validly assess six-dimension attention levels in real-world settings and is expected to be a new tool for assessing multi-dimensional attention impairments in different mental disorders.Keywords:attention;Attentional Control Scale;Toronto Hospital Alertness Test;Attention Network Test516|256|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:ObjectiveTo report the development, validation, and findings of the Multi-dimensional Attention Rating Scale (MARS), a self-report tool crafted to evaluate six-dimension attention levels.MethodsThe MARS was developed based on Classical Test Theory (CTT). Totally 202 highly educated healthy adult participants were recruited for reliability and validity tests. Reliability was measured using Cronbach's alpha and test-retest reliability. Structural validity was explored using principal component analysis. Criterion validity was analyzed by correlating MARS scores with the Toronto Hospital Alertness Test (THAT), the Attentional Control Scale (ACS), and the Attention Network Test (ANT).ResultsThe MARS comprises 12 items spanning six distinct dimensions of attention: focused attention, sustained attention, shifting attention, selective attention, divided attention, and response inhibition.As assessed by six experts, the content validation index (CVI) was 0.95, the Cronbach's alpha for the MARS was 0.78, and the test-retest reliability was 0.81. Four factors were identified (cumulative variance contribution rate 68.79%). The total score of MARS was correlated positively with THAT (r = 0.60, P < 0.01) and ACS (r = 0.78, P < 0.01) and negatively with ANT's reaction time for alerting (r = -0.31, P = 0.049).ConclusionThe MARS can reliably and validly assess six-dimension attention levels in real-world settings and is expected to be a new tool for assessing multi-dimensional attention impairments in different mental disorders.Keywords:attention;Attentional Control Scale;Toronto Hospital Alertness Test;Attention Network Test516|256|0Updated:2025-06-30 -
 Abstract:ObjectiveTo identify risk factors contributing to prolonged postoperative length of stay (LOS) in very elderly patients following hip fracture surgery, with a focus on postoperative complications and the impact of different anesthesia approaches.MethodsThis retrospective single-center cohort study enrolled patients aged 90 years or older who underwent hip fracture surgery at Peking Union Medical College Hospital between January 31, 2013 and December 31, 2023. Relevant perioperative data were collected. The primary outcome was postoperative LOS, and the study cohort was divided into two groups: postoperative LOS ≤ 7 days and LOS > 7 days. Logistic regression was performed to identify factors related to prolonged postoperative LOS.ResultsA total of 155 patients were included. The average age was 92.7 ± 2.6 years. There were 73 (47%) patients with postoperative LOS > 7 days. Postoperative pneumonia was the only factor associated with a prolonged postoperative LOS (OR = 2.12, 95% CI [1.09, 4.16], P = 0.028). Neither the type of anesthesia (regional vs. general anesthesia, OR = 1.00, 95% CI [0.53, 1.90], P = 0.993) nor the method of airway management (laryngeal mask ventilation vs. spontaneous breathing, OR = 1.46, 95% CI [0.58, 3.76], P = 0.424; endotracheal intubation vs. spontaneous breathing, OR = 0.82, 95% CI [0.39, 1.69], P = 0.592) showed a significant association with a prolonged postoperative LOS. Preoperative chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (OR = 2.78, 95% CI [1.05, 7.65], P = 0.040) and preoperative neutrophil count (OR = 1.13, 95% CI [1.01, 1.26], P = 0.029) were both significantly associated with the occurrence of postoperative pneumonia, while anesthesia type and airway management method were not.ConclusionsPostoperative pneumonia was associated with prolonged postoperative LOS in very elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery, whereas anesthesia types and airway management methods show no association with prolonged postoperative LOS or postoperative pneumonia. Preoperative comorbidities, especially respiratory conditions and systemic inflammation, potentially play a substantial role in postoperative recovery.Keywords:very elderly;hip fracture;anesthesia type;length of hospital stay;postoperative pneumonia80|95|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:ObjectiveTo identify risk factors contributing to prolonged postoperative length of stay (LOS) in very elderly patients following hip fracture surgery, with a focus on postoperative complications and the impact of different anesthesia approaches.MethodsThis retrospective single-center cohort study enrolled patients aged 90 years or older who underwent hip fracture surgery at Peking Union Medical College Hospital between January 31, 2013 and December 31, 2023. Relevant perioperative data were collected. The primary outcome was postoperative LOS, and the study cohort was divided into two groups: postoperative LOS ≤ 7 days and LOS > 7 days. Logistic regression was performed to identify factors related to prolonged postoperative LOS.ResultsA total of 155 patients were included. The average age was 92.7 ± 2.6 years. There were 73 (47%) patients with postoperative LOS > 7 days. Postoperative pneumonia was the only factor associated with a prolonged postoperative LOS (OR = 2.12, 95% CI [1.09, 4.16], P = 0.028). Neither the type of anesthesia (regional vs. general anesthesia, OR = 1.00, 95% CI [0.53, 1.90], P = 0.993) nor the method of airway management (laryngeal mask ventilation vs. spontaneous breathing, OR = 1.46, 95% CI [0.58, 3.76], P = 0.424; endotracheal intubation vs. spontaneous breathing, OR = 0.82, 95% CI [0.39, 1.69], P = 0.592) showed a significant association with a prolonged postoperative LOS. Preoperative chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (OR = 2.78, 95% CI [1.05, 7.65], P = 0.040) and preoperative neutrophil count (OR = 1.13, 95% CI [1.01, 1.26], P = 0.029) were both significantly associated with the occurrence of postoperative pneumonia, while anesthesia type and airway management method were not.ConclusionsPostoperative pneumonia was associated with prolonged postoperative LOS in very elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery, whereas anesthesia types and airway management methods show no association with prolonged postoperative LOS or postoperative pneumonia. Preoperative comorbidities, especially respiratory conditions and systemic inflammation, potentially play a substantial role in postoperative recovery.Keywords:very elderly;hip fracture;anesthesia type;length of hospital stay;postoperative pneumonia80|95|0Updated:2025-06-30 - “In the field of medical technology management, a bibliometric analysis reveals a steady increase in research output and a shift in focus from basic medical needs to emergency response and medical information security. The United States, Italy, and the United Kingdom are the main contributors, with the United States leading in both publication volume and academic impact. Cross-border cooperation is led by authors from the United Kingdom and the United States, and the top five institutions are primarily located in Canada and Spain. Future research should emphasize interdisciplinary and international collaboration.”
 Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore potential keywords, research clusters, collaborative pattern, and research trends in the field of medical technology management (MTM) through bibliometric analysis, providing insights for researchers, policy makers, and hospital administrators.MethodsA retrieval formula was applied to the title, abstract, and keywords in the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, along with system-recommended terms, to identify articles on MTM. A total of 181 articles published between 1974 and 2022 were retained for quantitative analysis. The global trend of research output; total citations, average citations, and H-index; and bibliographic coupling, co-authorship, and keyword co-occurrence were analyzed using VOSviewer.ResultsThe number of articles on MTM has been steadily increasing year by year. The focus of research has shifted from addressing basic medical needs to prioritizing emergency response and medical information security. The United States, Italy, and the United Kingdom emerged as the main contributors, with the United States leading in both volume of publications (60 articles) and academic impact (H-index = 21). Authors from the United Kingdom and the United States led the way in cross-border cooperation. The top five institutions, ranked by total link strength among cross-institutional authors, were primarily located in Canada and Spain.ConclusionsThe field of MTM has experienced stable growth over the past three decades (1993–2022). The shift of research focus has prompted a heightened emphasis on protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of medical data. Future research should emphasize interdisciplinary and professional collaboration, as well as international cooperation and open sharing of knowledge.Keywords:medical technology management;global research;research trend;bibliometric analysis164|123|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore potential keywords, research clusters, collaborative pattern, and research trends in the field of medical technology management (MTM) through bibliometric analysis, providing insights for researchers, policy makers, and hospital administrators.MethodsA retrieval formula was applied to the title, abstract, and keywords in the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, along with system-recommended terms, to identify articles on MTM. A total of 181 articles published between 1974 and 2022 were retained for quantitative analysis. The global trend of research output; total citations, average citations, and H-index; and bibliographic coupling, co-authorship, and keyword co-occurrence were analyzed using VOSviewer.ResultsThe number of articles on MTM has been steadily increasing year by year. The focus of research has shifted from addressing basic medical needs to prioritizing emergency response and medical information security. The United States, Italy, and the United Kingdom emerged as the main contributors, with the United States leading in both volume of publications (60 articles) and academic impact (H-index = 21). Authors from the United Kingdom and the United States led the way in cross-border cooperation. The top five institutions, ranked by total link strength among cross-institutional authors, were primarily located in Canada and Spain.ConclusionsThe field of MTM has experienced stable growth over the past three decades (1993–2022). The shift of research focus has prompted a heightened emphasis on protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of medical data. Future research should emphasize interdisciplinary and professional collaboration, as well as international cooperation and open sharing of knowledge.Keywords:medical technology management;global research;research trend;bibliometric analysis164|123|0Updated:2025-06-30 -
Causal Relationships Between Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activation and Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Lipid Metabolism Dysregulation: A Mendelian Randomization Study Enhanced Publication AI Introduction
“In a groundbreaking study, researchers have uncovered the causal link between cytoplasmic unactivated mineralocorticoid receptor levels and the risk of tubulointerstitial nephritis, as well as its impact on lipid metabolism in diabetic kidney disease patients. This discovery could pave the way for new therapeutic strategies using MR-antagonists to mitigate renal damage and associated complications.”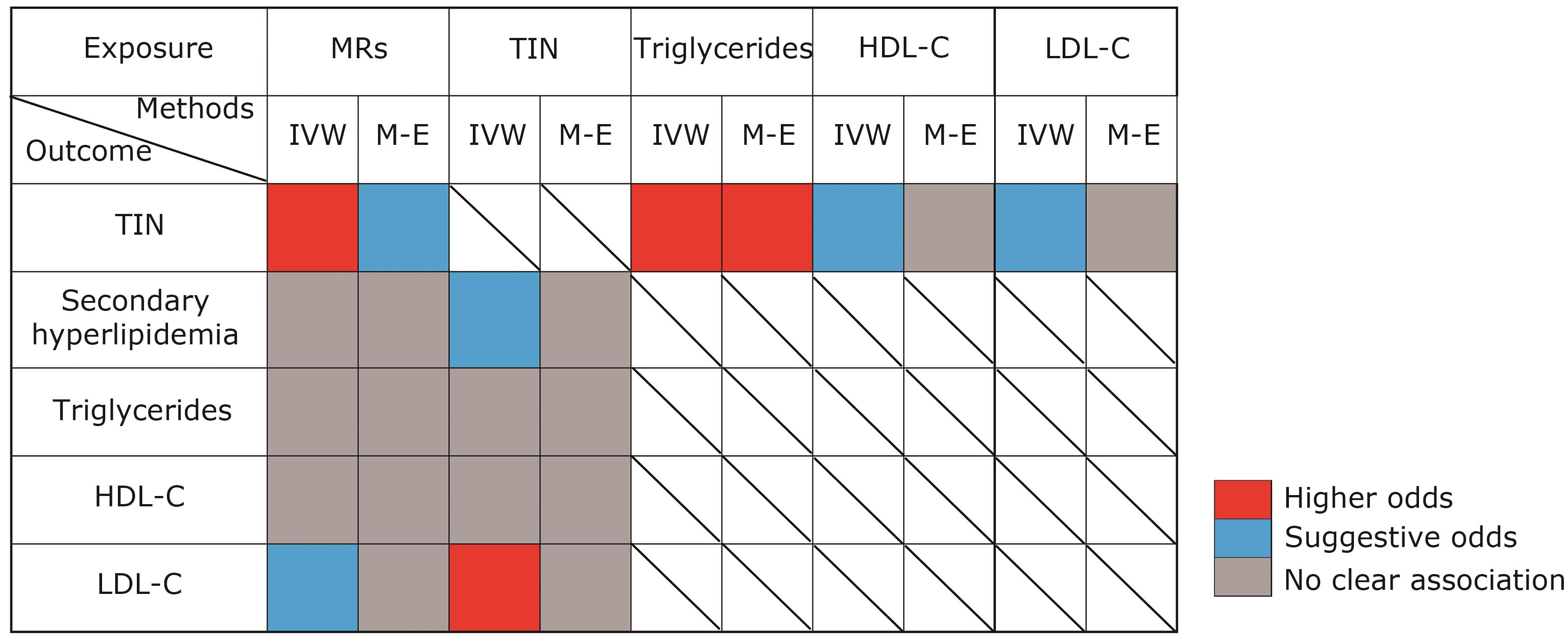 Abstract:ObjectiveTo clarify the causal relationship between the level of cytoplasmic unactivated mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) and the development of tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), and to evaluate the impact of MR on dyslipidemia, particularly secondary hyperlipemia, in patients with diabetic kidney disease.MethodsWe conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization study using genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data. Genetic variants associated with MR levels were selected as exposures, with TIN and lipid profiles [including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol] as outcomes. A two-step Mendelian randomization approach was used to assess TIN as a mediator, employing inverse variance weighted regression as the primary analysis, supplemented by Mendelian randomization-Egger, weighted median, and sensitivity analyses.ResultsCytoplasmic unactivated MR level exhibited a significant causal association with a decreased risk of TIN (OR = 0.8598, 95% CI [0.7775–0.9508], P < 0.001). Although no significant causal relationship was identified between MR level and secondary hyperlipemia, a potential association of cytoplasmic unactivated MR level with lower LDL-C levels was observed (OR = 0.9901, 95% CI [0.9821–0.9983], P = 0.018). Additionally, TIN exhibited causal links with secondary hyperlipemia (OR = 1.0016, 95% CI [1.0002–1.0029], P = 0.020) and elevated LDL-C (OR = 1.0111, 95% CI [1.0024–1.0199], P = 0.012), particularly LDL-C in European males (OR = 1.0230, 95% CI [1.0103–1.0358], P < 0.001). Inverse Mendelian randomization analysis revealed causal relationships between TIN and genetically predicted triglyceride (OR = 0.7027, 95% CI [0.6189–0.7978], P < 0.001), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (OR = 1.1247, 95% CI [1.0019–1.2626], P = 0.046), and LDL-C (OR = 0.8423, 95% CI [0.7220–0.9827], P = 0.029). Notably, TIN mediated 16.7% of the causal association between MR and LDL-C levels.ConclusionsMR plays a critical role in the development of TIN and lipid metabolism, highlighting the potential of MR-antagonists in reducing renal damage and lipid metabolism-associated complications.Keywords:mineralocorticoid receptor;tubulointerstitial nephritis;lipid metabolism;Mendelian randomization91|57|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:ObjectiveTo clarify the causal relationship between the level of cytoplasmic unactivated mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) and the development of tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), and to evaluate the impact of MR on dyslipidemia, particularly secondary hyperlipemia, in patients with diabetic kidney disease.MethodsWe conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization study using genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data. Genetic variants associated with MR levels were selected as exposures, with TIN and lipid profiles [including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol] as outcomes. A two-step Mendelian randomization approach was used to assess TIN as a mediator, employing inverse variance weighted regression as the primary analysis, supplemented by Mendelian randomization-Egger, weighted median, and sensitivity analyses.ResultsCytoplasmic unactivated MR level exhibited a significant causal association with a decreased risk of TIN (OR = 0.8598, 95% CI [0.7775–0.9508], P < 0.001). Although no significant causal relationship was identified between MR level and secondary hyperlipemia, a potential association of cytoplasmic unactivated MR level with lower LDL-C levels was observed (OR = 0.9901, 95% CI [0.9821–0.9983], P = 0.018). Additionally, TIN exhibited causal links with secondary hyperlipemia (OR = 1.0016, 95% CI [1.0002–1.0029], P = 0.020) and elevated LDL-C (OR = 1.0111, 95% CI [1.0024–1.0199], P = 0.012), particularly LDL-C in European males (OR = 1.0230, 95% CI [1.0103–1.0358], P < 0.001). Inverse Mendelian randomization analysis revealed causal relationships between TIN and genetically predicted triglyceride (OR = 0.7027, 95% CI [0.6189–0.7978], P < 0.001), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (OR = 1.1247, 95% CI [1.0019–1.2626], P = 0.046), and LDL-C (OR = 0.8423, 95% CI [0.7220–0.9827], P = 0.029). Notably, TIN mediated 16.7% of the causal association between MR and LDL-C levels.ConclusionsMR plays a critical role in the development of TIN and lipid metabolism, highlighting the potential of MR-antagonists in reducing renal damage and lipid metabolism-associated complications.Keywords:mineralocorticoid receptor;tubulointerstitial nephritis;lipid metabolism;Mendelian randomization91|57|0Updated:2025-06-30
Research Article
-
Risk Identification and Regulation for China's Anti-Commercial Bribery in Medical Device Procurement and Sales Industry AI Introduction
“Reporting on the latest research in the medical device procurement and sales sector, the article introduces its research progress in the field of anti-commercial bribery. Expert xx established the preventive regulatory framework, which provides solutions to effectively reduce commercial bribery risks and prevent illegal and non-compliant conduct.” Abstract:In China, the regulatory framework for medical device procurement and sales, particularly concerning anti-commercial bribery, relies heavily on punitive mechanisms applied after violations occur. Consequently, there is an urgent need to establish a scientific risk regulation framework as a complementary approach. Effective risk-oriented regulatory models require precise identification of risk areas in commercial bribery. Focusing on several major procurement scenarios such as centralized bulk-buying, tendering and bidding processes, in-hospital procurement, and online purchasing, this article analyzes the structural factors contributing to these risks, represented by the absence of certification mechanisms, lack of transparency in information disclosure, and inadequate checks and balances. Based on official risk assessment results, this study applies the theory of power and responsibility to propose a preventive regulatory framework that combines industry self-discipline and administrative oversight. By combining these approaches, the framework aims to develop regulatory measures that can effectively reduce commercial bribery risks and prevent illegal and non-compliant conduct.Keywords:anti-corruption;medical devices;anti-commercial bribery;risk regulation125|122|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:In China, the regulatory framework for medical device procurement and sales, particularly concerning anti-commercial bribery, relies heavily on punitive mechanisms applied after violations occur. Consequently, there is an urgent need to establish a scientific risk regulation framework as a complementary approach. Effective risk-oriented regulatory models require precise identification of risk areas in commercial bribery. Focusing on several major procurement scenarios such as centralized bulk-buying, tendering and bidding processes, in-hospital procurement, and online purchasing, this article analyzes the structural factors contributing to these risks, represented by the absence of certification mechanisms, lack of transparency in information disclosure, and inadequate checks and balances. Based on official risk assessment results, this study applies the theory of power and responsibility to propose a preventive regulatory framework that combines industry self-discipline and administrative oversight. By combining these approaches, the framework aims to develop regulatory measures that can effectively reduce commercial bribery risks and prevent illegal and non-compliant conduct.Keywords:anti-corruption;medical devices;anti-commercial bribery;risk regulation125|122|0Updated:2025-06-30
Think Tank Forum
-
Construction of a Research Public Platform Based on Hierarchical Management and Precise Services: Experience of West China Hospital AI Introduction
“In the field of medical research platform construction, West China Hospital has made significant progress. The hospital has established a hierarchical management system and precise service model, which provides solutions to enhance resource efficiency and support major scientific research tasks.”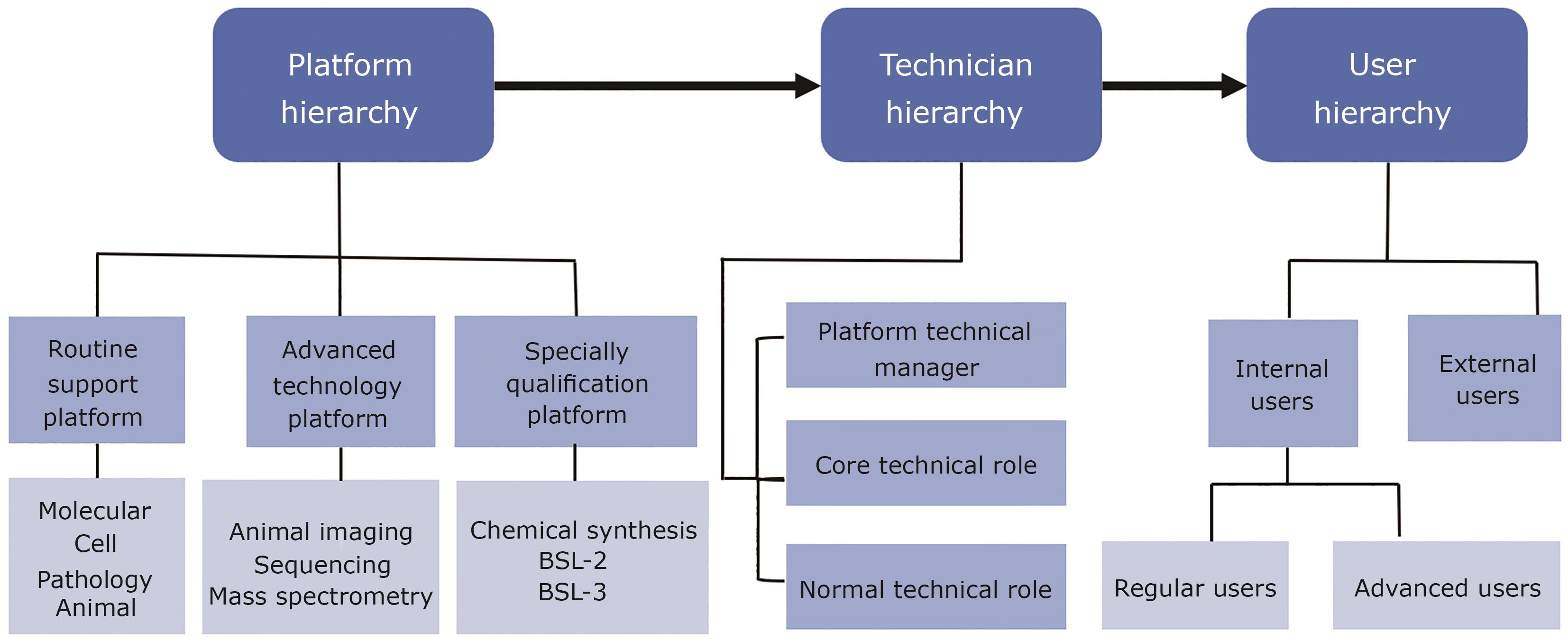 Abstract:With the development of education and technology, the construction of research public platforms has emerged as a critical initiative for many universities and top-tier public hospitals. The core and most fundamental function of a basic public platform is to aggregate large instruments and specific resources, providing open services for instrumental analysis and sample testing. Optimized management and high-quality, efficient services are essential for such platforms. This article elucidates the construction of a research public platform in West China Hospital, focusing on the adoption of hierarchical management and precise services. The core of the hierarchical management lies in building a multi-level service platform composed of routine support platforms, advanced technology platforms, and specially qualification platforms, while establishing a talent hierarchy that differentiates between core and routine positions. This structure is designed to accurately meet the diverse needs of users and enhance resource efficiency. By implementing user access control with differentiated permissions for internal and external users and a dynamic credit-based review system, the laboratory can ensure safe and efficient operations. The four service modes—instrument usage, in-lab experiments, sample testing, and collaborative projects—are precisely aligned with various research scenarios. Proactive engagement with grant-funded projects, customized services for research groups, and a multidimensional training system further strengthen the platform's support for major scientific research tasks. Through systematic management and service innovation, this model achieves efficient integration and sustainable development of platform resources, providing a valuable reference for the construction of public platforms in similar medical institutions.Keywords:research public platform;hierarchical management;precise services;biomedical experiment55|79|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:With the development of education and technology, the construction of research public platforms has emerged as a critical initiative for many universities and top-tier public hospitals. The core and most fundamental function of a basic public platform is to aggregate large instruments and specific resources, providing open services for instrumental analysis and sample testing. Optimized management and high-quality, efficient services are essential for such platforms. This article elucidates the construction of a research public platform in West China Hospital, focusing on the adoption of hierarchical management and precise services. The core of the hierarchical management lies in building a multi-level service platform composed of routine support platforms, advanced technology platforms, and specially qualification platforms, while establishing a talent hierarchy that differentiates between core and routine positions. This structure is designed to accurately meet the diverse needs of users and enhance resource efficiency. By implementing user access control with differentiated permissions for internal and external users and a dynamic credit-based review system, the laboratory can ensure safe and efficient operations. The four service modes—instrument usage, in-lab experiments, sample testing, and collaborative projects—are precisely aligned with various research scenarios. Proactive engagement with grant-funded projects, customized services for research groups, and a multidimensional training system further strengthen the platform's support for major scientific research tasks. Through systematic management and service innovation, this model achieves efficient integration and sustainable development of platform resources, providing a valuable reference for the construction of public platforms in similar medical institutions.Keywords:research public platform;hierarchical management;precise services;biomedical experiment55|79|0Updated:2025-06-30
Special Report
- “Reporting on a significant case in urological medicine, an 85-year-old man who underwent prostate cancer surgery in 2011 and used a penile clamp for severe stress incontinence developed a urethral diverticulum. The condition was treated with surgical excision and urethroplasty, but incontinence persisted. This case underscores the potential complications of using penile clamps as an alternative to artificial urinary sphincters, highlighting the need for caution and periodic removal to prevent serious urethral issues.”
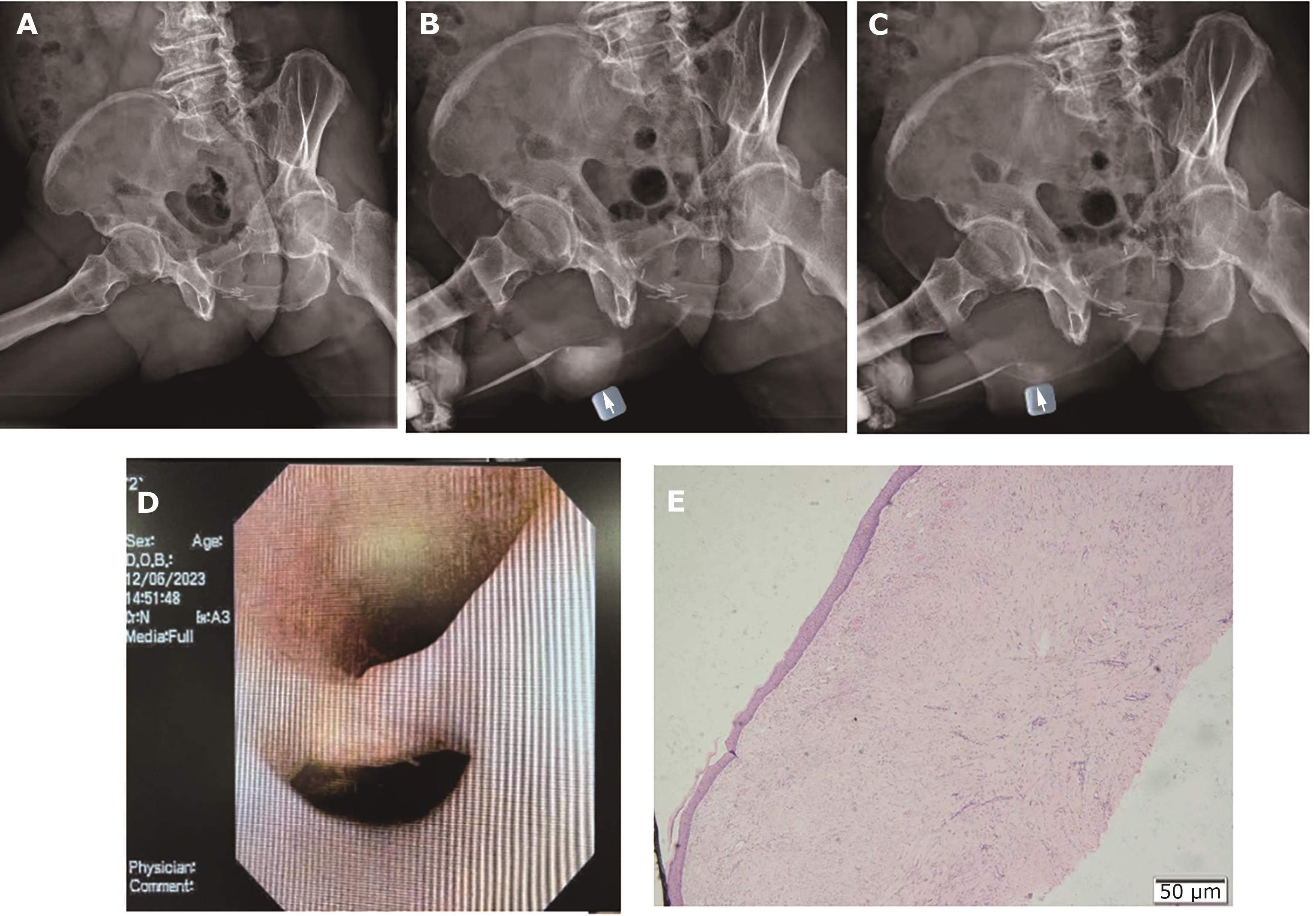 Abstract:We report a case involving an 85-year-old man who underwent laparoscopic radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer in 2011. During follow-up, he required long-term use of a penile clamp to manage urination due to permanent severe stress incontinence. In February 2023, he presented with a painless cystic mass in the scrotum. Upon pressing the mass with hand, fluid drained from the external urethral orifice, causing the mass to shrink in size, although it returned to its original size a few hours later. Urography and cystoscopy showed a globular urethral diverticulum located anteriorly. The patient underwent surgical excision of the diverticulum along with urethroplasty. Postoperatively, the urinary stress incontinence persisted, but he declined any further surgical intervention. An artificial urinary sphincter is currently the first-line treatment for male urinary incontinence. However, devices such as penile clamps can serve as an alternative when considering surgical suitability or cost. It is important to note that these devices can lead to serious complications such as urethral erosion, stricture, or diverticulum. Therefore, caution is advised when using such devices, and they should be removed periodically at short intervals.Keywords:prostate cancer;prostatectomy;artificial urinary sphincter;urethral diverticulum;stress incontinence174|249|0Updated:2025-06-30
Abstract:We report a case involving an 85-year-old man who underwent laparoscopic radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer in 2011. During follow-up, he required long-term use of a penile clamp to manage urination due to permanent severe stress incontinence. In February 2023, he presented with a painless cystic mass in the scrotum. Upon pressing the mass with hand, fluid drained from the external urethral orifice, causing the mass to shrink in size, although it returned to its original size a few hours later. Urography and cystoscopy showed a globular urethral diverticulum located anteriorly. The patient underwent surgical excision of the diverticulum along with urethroplasty. Postoperatively, the urinary stress incontinence persisted, but he declined any further surgical intervention. An artificial urinary sphincter is currently the first-line treatment for male urinary incontinence. However, devices such as penile clamps can serve as an alternative when considering surgical suitability or cost. It is important to note that these devices can lead to serious complications such as urethral erosion, stricture, or diverticulum. Therefore, caution is advised when using such devices, and they should be removed periodically at short intervals.Keywords:prostate cancer;prostatectomy;artificial urinary sphincter;urethral diverticulum;stress incontinence174|249|0Updated:2025-06-30
Case Report
0
