Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 120-126.doi: 10.24920/003856
垂体瘤切除术后突发感音神经性聋—病例系列报告及文献复习
- 1中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院耳鼻喉科 北京 100730
2中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院放射科 北京 100730
3中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院神经外科 北京 100730
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss after Pituitary Adenoma Resection—A Case Series with Literature Review
Yi Wang1,Zhuhua Zhang2,*( ),Wei Lian3,*(
),Wei Lian3,*( )
)
- 1Department of Otolaryngology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Department of Clinical Radiology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3Department of Neurosurgery, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
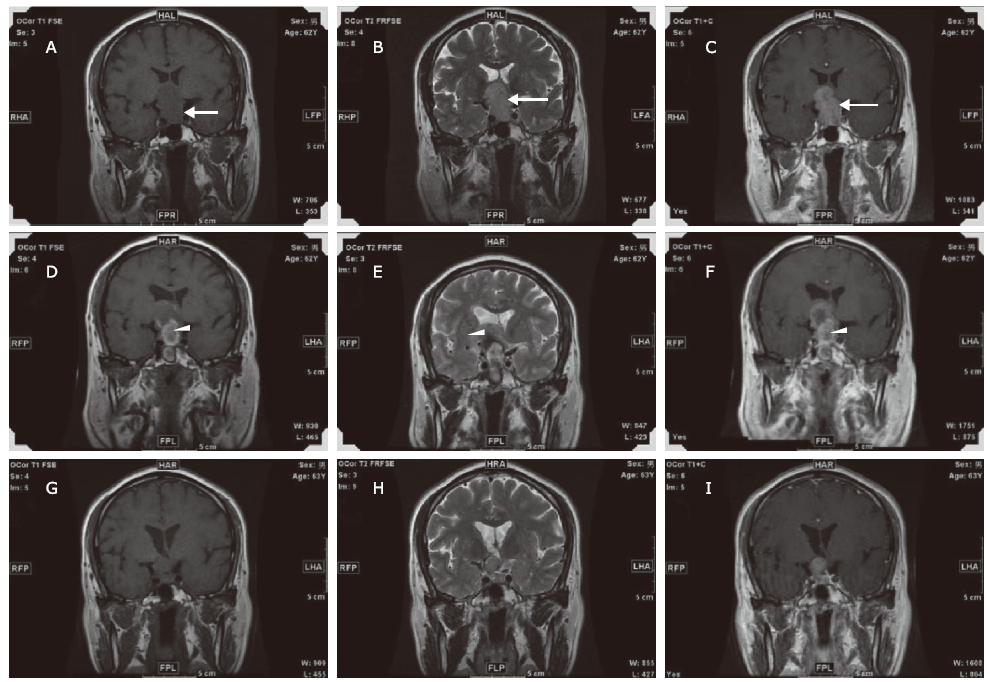
目的 经蝶垂体瘤术后术后患者较少出现延迟的突发性感音神经性聋。本研究报告了3例垂体瘤患者,术后无脑脊液漏或脑膜炎,但是在术后3至7日发生突发性感音神经性聋,并讨论了可能的致聋原因。
方法 对3例经蝶垂体瘤术后延迟出现突发性感音神经性聋病例,报告其病史、突发性聋的发生时间、伴随症状如头痛、耳鸣、眩晕、耳闷等,以及术后MRI表现、治疗、听力恢复等情况。
结果 术后3至7日突发极重度感音神经性聋的3例患者,听力下降前全都伴发头痛、耳鸣、眩晕。1例有间断反复发作的眩晕、耳闷、波动性听力下降,持续至术后1个月。2例有动脉硬化、冠心病史或脑梗史。3例患者中2例术后第1天MRI显示梗阻性脑积水。在口服泼尼松、鼓室注射低塞米松、服用神经营养药物和扩血管药物3至8个月之后,3例患者听力均有部分恢复。术后梗阻性脑积水和内听动脉缺血可能造成术后耳聋。
结论 经蝶垂体瘤术后梗阻性脑积水和迷路动脉缺血可能引起延迟出现的突发性感音神经性聋。