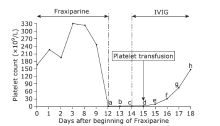
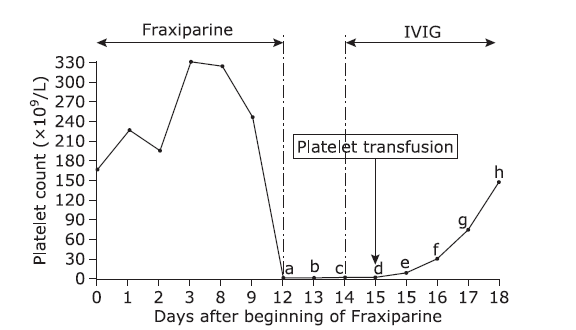
| 1. |
Visentin GP, Ford SE, Scott JP , et al. Antibodies from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis are specific for platelet factor 4 complexed with heparin or bound to endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1994; 93(1):81-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI116987.
doi: 10.1172/JCI116987
pmid: 8282825
|
| 2. |
Warkentin TE. Clinical presentation of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Semin Hematol 1998; 35(4 Suppl 5):9-16; discussion 35-6.
doi: 10.1016/S0145-2126(98)00095-2
pmid: 9855179
|
| 3. |
Greinacher A, Selleng S . How I evaluate and treat thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit patient. Blood 2016; 128(26):3032-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-693655.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-693655
pmid: 28034871
|
| 4. |
Cuker A, Gimotty PA, Crowther MA , et al. Predictive value of the 4Ts scoring system for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood 2012; 120(20):4160-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-443051.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-443051
pmid: 22990018
|
| 5. |
Khandelwal S, Arepally GM . Immune pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost 2016; 116(5):792-8. doi: 10.1160/TH16-01-0074.
doi: 10.1160/TH16-01-0074
|
| 6. |
Greinacher A, Farner B, Kroll H , et al. Clinical features of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia including risk factors for thrombosis. A retrospective analysis of 408 patients. Thromb Haemost 2005; 94(1):132-5. doi: 10.1160/TH04-12-0825.
doi: 10.1160/TH04-12-0825
|
| 7. |
Warkentin TE, Makris M, Jay RM , et al. A spontaneous prothrombotic disorder resembling heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Med 2008; 121(7):632-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.012.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.012
|
| 8. |
Jay RM, Warkentin TE . Fatal heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) during warfarin thromboprophylaxis following orthopedic surgery: another example of ‘spontaneous’ HIT? J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6(9):1598-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03040.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03040.x
pmid: 18513213
|
| 9. |
Warkentin TE, Basciano PA, Knopman J , et al. Spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome: 2 new cases and a proposal for defining this disorder. Blood 2014; 123(23):3651-4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-549741.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-549741
pmid: 24677540
|
| 10. |
Pruthi RK, Daniels PR, Nambudiri GS , et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) during postoperative warfarin thromboprophylaxis: a second example of postorthopedic surgery ‘spontaneous’ HIT. J Thromb Haemost 2009; 7(3):499-501. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03263.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03263.x
pmid: 19087219
|
| 11. |
Ketha S, Smithedajkul P, Vella A , et al. Adrenal haemorrhage due to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost 2013; 109(4):669-75. doi: 10.1160/TH12-11-0865.
doi: 10.1160/TH12-11-0865
pmid: 23389301
|
| 12. |
Okata T, Miyata S, Miyashita F , et al. Spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome without any proximate heparin exposure, infection, or inflammatory condition: atypical clinical features with heparin-dependent platelet activating antibodies. Platelets 2015; 26(6):602-7. doi: 10.3109/09537 104.2014.979338.
doi: 10.3109/09537104.2014.979338
pmid: 25383922
|
| 13. |
Bito S, Miyata S, Migita K , et al. Mechanical prophylaxis is a heparin-independent risk for anti-platelet factor 4/heparin antibody formation after orthopedic surgery. Blood 2016; 127(8):1036-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-06-651620.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-06-651620
pmid: 26659923
|
| 14. |
Warkentin TE . Knee replacement and HIT without heparin. Blood 2016; 127(8):961-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-12-687665.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-12-687665
pmid: 26917737
|
| 15. |
Wester JP, Haas FJ, Biesma DH , et al. Thrombosis and hemorrhage in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in seriously ill patients. Intensive Care Med 2004; 30(10):1927-34. doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2334-1.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2334-1
pmid: 15156309
|
| 16. |
Arnold DM , NaziI, WarkentinTE, et al. Approach to the diagnosis and management of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. Transfus Med Rev 2013; 27(3):137-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2013.05.005.
doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2013.05.005
pmid: 23845922
|
| 17. |
Tvito A, Bakchoul T, Rowe JM , et al. Severe and persistent heparin-induced thrombocytopenia despite fondaparinux treatment. Am J Hematol 2015; 90(7):675-8. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23971.
doi: 10.1002/ajh.23971
pmid: 25683147
|
| 18. |
Betrosian AP, Theodossiades G, Balla M , et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: correction of severe bleeding complication with intravenous immune globulin. Intensive Care Med 2004; 30(11):2136; author reply 2137. doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2437-8.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-004-2437-8
pmid: 15365610
|
| 19. |
British Committee for Standards in Haematology, Blood Transfusion Task Force . Guidelines for the use of platelet transfusions. Br J Haematol 2003; 122(1):10-23.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04468.x
|
| 20. |
Goel R, Ness PM, Takemoto CM , et al. Platelet transfusions in platelet consumptive disorders are associated with arterial thrombosis and in-hospital mortality. Blood 2015; 125(9):1470-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-605493.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-605493
pmid: 25588677
|
| 21. |
Cuker A . Management of the multiple phases of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost 2016; 116(5):835-42. doi: 10.1160/TH16-02-0084.
doi: 10.1160/TH16-02-0084
pmid: 27075525
|
| 22. |
Liang SX, Pinkevych M, Khachigian LM , et al. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia: development of a novel NOD/SCID mouse model to evaluate clearance of circulating platelets by drug-dependent antibodies and the efficacy of IVIG. Blood 2010; 116(11):1958-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-268326.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-268326
pmid: 20566900
|
| 23. |
Greinacher A . Clinical practice. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 2015; 373(3):252-61. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1411910.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1411910
|
| 24. |
Linkins LA, Dans AL, Moores LK , et al. Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012; 141(2 Suppl):e495S-e530S. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2303.
doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2303
|
| 25. |
Linkins LA, Warkentin TE, Pai M , et al. Design of the rivaroxaban for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2014; 38(4):485-92. doi: 10.1007/s11239-014-1064-7.
doi: 10.1007/s11239-014-1064-7
pmid: 24549975
|
| 26. |
Sachais BS, Rux AH, Cines DB , et al. Rational design and characterization of platelet factor 4 antagonists for the study of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2012; 119(25):5955-62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-406801.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-406801
pmid: 22452981
|
 )
)