Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 194-198.doi: 10.24920/003482
CT血管成像对严重咯血急诊处理的应用价值
- 1 北京第六医院放射科,北京 100007
2 中国医学科学院北京协和医院放射科,北京 100730
Value of CT-Angiography in the Emergency Management of Severe Hemoptysis
Chen Ying1,Wang Kefei2,Wang Zhiwei2,*( ),Liu Changzhu1,Jin Zhengyu2
),Liu Changzhu1,Jin Zhengyu2
- 1 Department of Radiology, Peking the 6th Hospital, Beijing 100007, China
2 Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
摘要:
目的 探讨急诊咯血患者支气管动脉的多排CT血管成像的影像解剖特点,并评估其对急诊咯血患者处理的应用价值。
方法 回顾性分析2013年1月1日至2015年12月31日急诊就诊的严重咯血患者(24小史咯血量≥100 ml)的临床与影像数据。讨论这些患者的多排CT血管成像图像特点、治疗方法和结局。
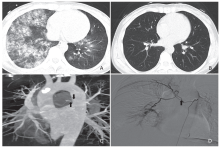
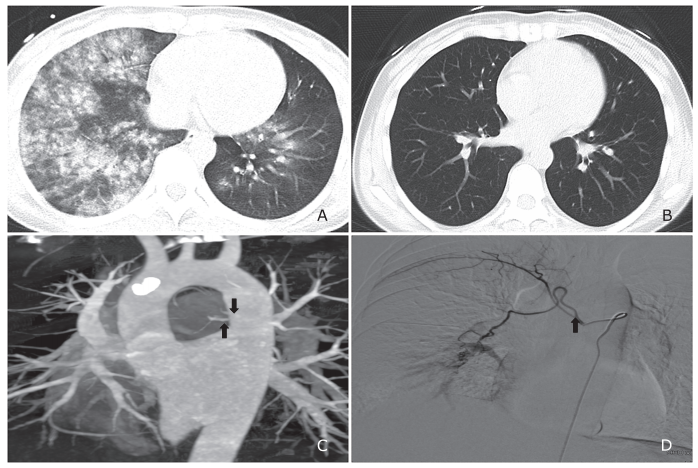
结果 共108例患者进行了多排CT血管成像检查。引起咯血病因主要为支气管扩张(44%)、结核(26%)和肿瘤(18%)。多排CT血管成像能显示197条支气管动脉和相关的35条非支气管体部动脉。位于纵膈气管分叉水平的支气管动脉的平均直径为2.8±1.2 mm。接受保守治疗的52例患者的支气管动脉的平均直径为2.9±1.1 mm,与56例接受栓塞治疗患者的支气管动脉平均直径无显著性差异(2.7±1.1 mm,P=0.94)。栓塞治疗的技术成功率为95%(53/56)。随访患者的临床治愈率为94%(50/53)。
结论 对于严重咯血患者,多排CT血管成像能显示出血相关支气管动脉和非支气管体部动脉的解剖特点。然而,通过多排CT血管成像测量的支气管动脉直径不能作为患者是否需要支气管动脉栓塞治疗的指征。