Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 107-113.doi: 10.24920/11806
红参水提液对大鼠体内阿司匹林代谢物的药代动力学影响
- 北京中医药大学 中药学院中药制药系,北京 100029 中国
-
收稿日期:2017-07-23出版日期:2018-06-30发布日期:2018-03-23 -
通讯作者:陆洋 E-mail:landocean28@163.com
Effect of Red Ginseng Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Aspirin Metabolite in Sprague Dawley Rats
Xue Yutao,Tan Ning,Yu Gangyan,Tan Li,Lu Yang( )
)
- Pharmaceutical Department, School of Chinese Materia Medica, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2017-07-23Published:2018-06-30Online:2018-03-23 -
Contact:Lu Yang E-mail:landocean28@163.com
摘要:
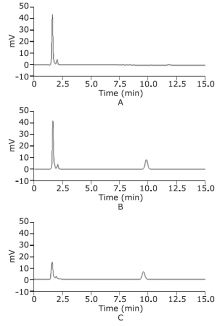
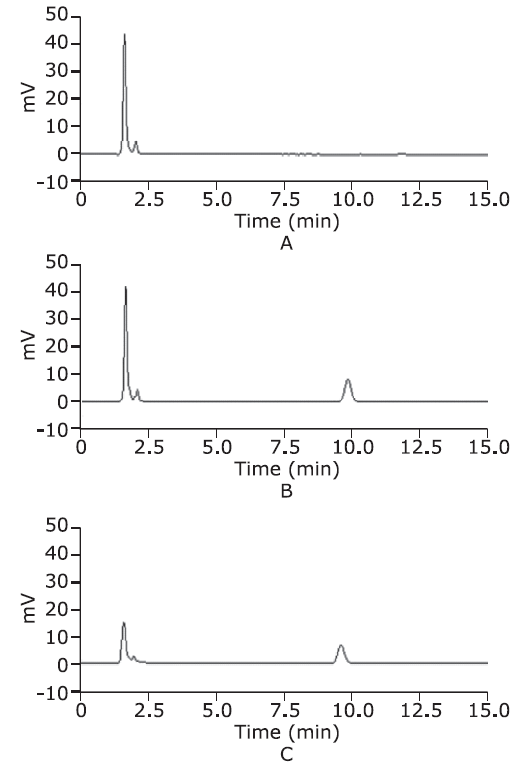
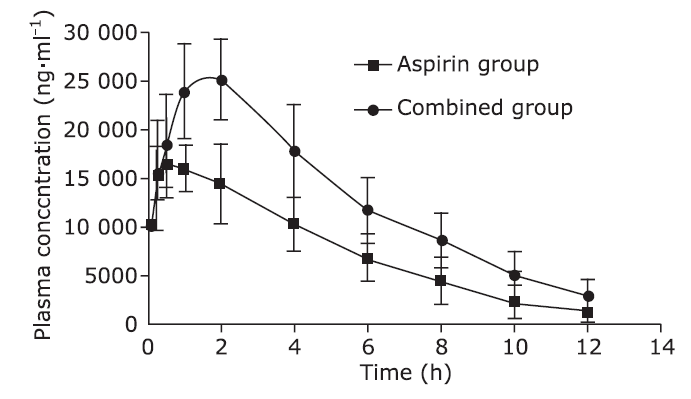
目的 探讨红参与阿司匹林联用对大鼠体内阿司匹林代谢物的药代动力学影响。方法 12只雄性SD大鼠随机均分为阿司匹林单用组(阿司匹林10.42 mg/kg)和红参、阿司匹林联用组(红参提取物0.5 mg/g + 阿司匹林10.42 mg/kg)。经灌胃给药。分别于灌胃前及灌胃后0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10及12 h经眼眶取血0.5 ml, 采用HPLC-UV分析大鼠血浆中阿司匹林代谢物——水杨酸的血药浓度,采用DAS3.0软件的非房室模型计算水杨酸的药代动力学参数,并对两组的参数进行比较。结果 与阿司匹林单用组相比,联用组的水杨酸最大血药浓度和药时曲线下面积显著增加(P<0.01),清除率显著降低(P<0.05)。结论 红参可能具有促进阿司匹林在大鼠体内吸收,延缓其代谢产物——水杨酸代谢的作用。
引用本文
Xue Yutao, Tan Ning, Yu Gangyan, Tan Li, Lu Yang. Effect of Red Ginseng Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Aspirin Metabolite in Sprague Dawley Rats[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 107-113.
Table 2
Extraction recovery and matrix effect evaluated with salicylic acid sample solution at the three concentration levels in rat plasma§ (%)"
| Actual concentration of salicylic acid (ng?ml-1) | Extraction recovery | Matrix effect |
|---|---|---|
| 501.5 | 80.96±7.57 | 82.83±9.49 |
| 3009 | 86.34±3.48 | 83.90±3.07 |
| 20 060 | 89.53±1.55 | 88.40±1.49 |
Table 4
Comparisons of pharmacokinetic parameters of salicylic acid in the plasma of the two-group rats§ (n=6)"
| Groups | AUC(0-t) (ng?ml-1?h-1) | Cmax (ng?ml-1) | MRT(0-t)(h) | Tmax (h) | t1/2z (h) | CLz/F (L?h-1?kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspirin group | 93 204.13±24 873.73 | 17 339.63±2 738.64 | 3.69±0.71 | 1.17±0.68 | 1.86±0.83 | 0.11±0.04 |
| Combined group | 156 191.26±41 214.72** | 25 999.77±3 679.22** | 4.14±0.32 | 1.50±0.54 | 2.79±1.38 | 0.06±0.02* |
| 1. |
Collaborators M C O D. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015; 385(9963):117-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 |
| 2. |
Baigent C, Kappelle LJ, Algra A , et al. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. BMJ 2002; 324(7329):71-86. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7329.71.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7329.71 |
| 3. |
Antithrombotic Trialists’ ( ATT) Collaboration. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomized trials. Lancet 2009; 373(9678):1849-60. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1 pmid: 19482214 |
| 4. |
Baigent C . For and against: aspirin for everyone older than 50? Against. BMJ 2005; 330(7505):1440-1. doi: 10.1136/bmj.330.7505.1442.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.330.7505.1442 pmid: 15961818 |
| 5. |
Bulugahapitiya U, Siyambalapitiya S, Sithole J , et al. Age threshold for vascular prophylaxis by aspirin in patients without diabetes. Heart 2008; 94(11):1429-32. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2008.150698.
doi: 10.1136/hrt.2008.150698 pmid: 18708419 |
| 6. |
Dehmer SP, Maciosek MV, Flottemesch TJ , et al. Aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: a decision analysis for the U.S. preventive services task force. Ann Intern Med 2016; 164(12):777-86. doi: 10.7326/M15-2129.
doi: 10.7326/M15-2129 |
| 7. |
Tian ZH, Pang HH, Du SY , et al. Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on the pharmacokinetics of aspirin in rats. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2017; 1040:136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.12.007.
doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.12.007 pmid: 27978468 |
| 8. |
Chen WK, Ju WZ , Tan HS. Effects of mailuoning injection in combination with aspirin on salicylic acid pharmacokinetics in rats. Pharm Clin Res 2009; 17(4):283-6. Chinese. doi: 10.13664/j.cnki.pcr.2009.04.013.
doi: 10.13664/j.cnki.pcr.2009.04.013 |
| 9. | Cheng ZM . The study on public recognition of processed ginseng’s health-care effects [dissertation]. Beijing: China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, 2012. |
| 10. |
Jin L, Cho JY, Kim WK . Anti-inflammation effect of exercise and Korean red ginseng in aging model rats with diet-induced atherosclerosis. Nutr Res Pract 2014; 8(3):284-91. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2014.8.3.284.
doi: 10.4162/nrp.2014.8.3.284 pmid: 24944773 |
| 11. |
Kwak YS, Kyung JS, Kim JS , et al. Anti-hyperlipidemic effects of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng. Biol Pharm Bull 2010; 33(3):468-72. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.468.
doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.468 pmid: 20190411 |
| 12. |
Jin YR, Yu JY, Lee JJ , et al. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activities of Korean red ginseng extract. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2007; 100(3):170-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00033.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.00033.x pmid: 17309520 |
| 13. |
Lee HS, Kim MR, Park Y , et al. Fermenting red ginseng enhances its safety and efficacy as a novel skin care anti-aging ingredient: in vitro and animal study. J Med Food 2012; 15(11):1015-23. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2187.
doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2187 pmid: 3491619 |
| 14. |
Hong CE, Lyu SY . Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of Korean red ginseng extract in human keratinocytes. Immune Netw 2011; 11(1):42-9. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.1.42.
doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.1.42 |
| 15. |
Jinya LU, Chen J , Cai H. Clinical efficacy of shexiang baoxin pill combined with aspirin in treating elder patients with coronary heart disease. Jiangsu Med J 2015; 41(1):44-7. Chinese. doi: 10.19460/j.cnki.0253-3685.2015.01.016.
doi: 10.19460/j.cnki.0253-3685.2015.01.016 |
| 16. |
Zhang T. The clinical effect of xuesaitong combined with aspirin in acute cerebral infarction. J Aerospace Med 2016; 27(4):428-9. Chinese. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2016.04.011.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2016.04.011 |
| 17. |
Tian L. Pharmacokinetics of aspirin after single and multiple doses in healthy subjects. Chin J New Drugs 2006; 15(16):1393-6. Chinese. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-3734.2006.16.022.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-3734.2006.16.022 |
| 18. |
Ijaz A, Bhatti HN, Rasheed S , et al. Pharmacokinetic study of aspirin in healthy female volunteers. Pak J Bio Sci 2003; 6(16):1404-7. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2003.1404.1407.
doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2003.1404.1407 |
| 19. |
Jacob MC, Favre M, Bensa JC . Membrane cell permeabilization with saponin and multiparametric analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry A 1991; 12(6):550-8. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120612.
doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120612 pmid: 1764979 |
| 20. |
Sim JS, Zhao HL, Li DW , et al. Effects of saponins from the root bark of aralia elata on the transport of chondroitin sulfate in caco-2 cell monolayers and rats. Biol Pharm Bull 2005; 28(6):1043-8. doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.1043.
doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.1043 pmid: 15930742 |
| 21. |
Wang B, Wang J, Huang SQ , et al. Genetic polymorphism of the human cytochrome p450 2c9 gene and its clinical significance. Curr Drug Metab 2009; 10(7):781-834. doi: 10.2174/138920009789895480.
doi: 10.2174/138920009789895480 pmid: 3222219925388 |
| 22. |
Agúndez JA, Garcíamartín E, Martínez C . Genetically based impairment in cyp2c8- and cyp2c9-dependent nsaid metabolism as a risk factor for gastrointestinal bleeding: is a combination of pharmacogenomics and metabolomics required to improve personalized medicine? Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2009; 5(6):607-20. doi: 10.1517/17425250902970998.
doi: 10.1517/17425250902970998 |
| 23. |
He N, Edeki T . The inhibitory effects of herbal components on cyp2c9 and cyp3a4 catalytic activities in human liver microsomes. Am J Ther 2004; 11(3):206-12. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200405000-00009.
doi: 10.1097/00045391-200405000-00009 pmid: 15133536 |
| 24. |
Derry S, Loke YK . Risk of gastrointestinal haemorrhage with long term use of aspirin: meta-analysis. BMJ 2000; 321(7270):1183-7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7270.1183.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7270.1183 pmid: 11073508 |
| 25. |
Sørensen HT, Mellemkjær L, Blot WJ , et al. Risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding associated with use of low-dose aspirin. Am J Gastroenterol 2000; 95(9):2218-24. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9270(00)0104-06.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-9270(00)0104-06 |
| 26. |
Huang ES, Strate LL, Ho WW , et al. Long-term use of aspirin and the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Med 2011; 124(5):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.12.022.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.12.022 pmid: 3086018 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|