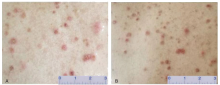
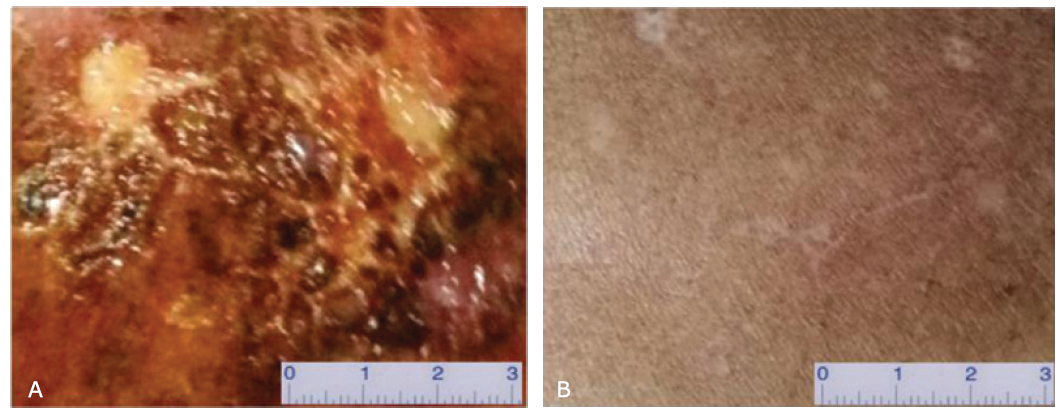
| 1. |
Pardoll DM . The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12(4):252-64. doi: 10.1038/nrc3239.
doi: 10.1038/nrc3239
|
| 2. |
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P , et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2015; 373(2):123-35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504627.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504627
|
| 3. |
Belum VR, Benhuri B, Postow MA , et al. Characterisation and management of dermatologic adverse events to agents targeting the PD-1 receptor. Eur J Cancer 2016; 60:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.02.010
|
| 4. |
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L , et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2015; 373(17):1627-39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507643.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
|
| 5. |
Rizvi NA, Mazières J, Planchard D , et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16(3):257-65. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70054-9.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70054-9
|
| 6. |
Gettinger S, Rizvi NA, Chow LQ , et al. Nivolumab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2016; 34(25):2980-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.9929.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.9929
pmid: 27354485
|
| 7. |
Haanen JBAG, Carbonnel F, Robert C, et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2017; 28(suppl_4):iv119-iv42. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx225.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx225
|
| 8. |
Spain L, Diem S, Larkin J . Management of toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev 2016; 44:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.02.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.02.001
pmid: 26874776
|
| 9. |
Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C , et al. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer 2005; 104(6):1129-37. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21324.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.21324
|
| 10. |
Barnett GC, West CM, Dunning AM , et al. Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9(2):134-42. doi: 10.1038/nrc2587.
doi: 10.1038/nrc2587
pmid: 2670578
|
| 11. |
McQuestion M . Evidence-based skin care management in radiation therapy: clinical update. Semin Oncol Nurs 2011; 27(2):e1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2011.02.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2011.02.009
pmid: 21514477
|
| 12. |
Ryan JL . Ionizing radiation: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J Invest Dermatol 2012; 132(3 Pt 2):985-93. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.411.
doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.411
|
| 13. |
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR , et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 2012; 366(26):2443-54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
|
| 14. |
Hodi FS , O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(8):711-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
|
| 15. |
Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I , et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 2011; 364(26):2517-26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104621.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104621
|
| 16. |
Weber JS, Yang JC, Atkins MB , et al. Toxicities of immunotherapy for the practitioner. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33(18):2092-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0379.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0379
|
| 17. |
Hasan Ali O, Diem S, Markert E , et al. Characterization of nivolumab-associated skin reactions in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology 2016; 5(11):e1231292. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1231292.
doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1231292
|
| 18. |
Hinrichs CS, Restifo NP . Reassessing target antigens for adoptive T-cell therapy. Nat Biotechnol 2013; 31(11):999-1008. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2725.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2725
pmid: 24142051
|
| 19. |
Singh M, Alavi A, Wong R , et al. Radiodermatitis: a review of our current understanding. Am J Clin Dermatol 2016; 17(3):277-92. doi: 10.1007/s40257-016-0186-4.
doi: 10.1007/s40257-016-0186-4
pmid: 27021652
|
| 20. |
Kim JH, Kolozsvary AJ, Jenrow KA , et al. Mechanisms of radiation-induced skin injury and implications for future clinical trials. Int J Radiat Biol 2013; 89(5):311-8. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.765055.
doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.765055
pmid: 23305180
|
| 21. |
Amber KT, MI Shiman, EV Badiavas . The use of antioxidants in radiotherapy-induced skin toxicity. Integr Cancer Ther 2014; 13(1):38-45. doi: 10.1177/1534735413490235.
doi: 10.1177/1534735413490235
pmid: 23729466
|
| 22. |
Holler V, Buard V, Gaugler MH , et al. Pravastatin limits radiation-induced vascular dysfunction in the skin. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129(5):1280-91. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.360.
doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.360
pmid: 19212344
|
| 23. |
Xie G, Gu D, Zhang L , et al. A rapid and systemic complete response to stereotactic body radiation therapy and pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2017; 18(8):547-51. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345389.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345389
|
| 24. |
Yuan Z, Fromm A, Ahmed KA , et al. Radiotherapy rescue of a nivolumab-refractory immune response in a patient with PD-L1-negative metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol 2017; 12(9):e135-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.029.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.029
|
| 25. |
Lu CS, Liu JH . Pneumonitis in cancer patients receiving anti-PD-1 and radiotherapies: three case reports. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017; 96(1):e5747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005747.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005747
|
| 26. |
Youinou P, Pers JO . The late news on baff in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9(12):804-6. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.06.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.06.011
pmid: 20656068
|
| 27. |
Sutherland AP, Ng LG, Fletcher CA , et al. BAFF augments certain Th1-associated inflammatory responses. J Immunol 2005; 174(9):5537-44.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5537
|
| 28. |
Zen M, Canova M, Campana C , et al. The kaleidoscope of glucorticoid effects on immune system. Autoimmun Rev 2011; 10(6):305-10. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.11.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.11.009
pmid: 21224015
|
| 29. |
Cain DW, Cidlowski JA . Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat Rev Immunol 2017; 17(4):233-47. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.1.
doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.1
|
| 30. |
de Golian E, Kwong BY, Swetter SM . Cutaneous complications of targeted melanoma therapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2016; 17:57. doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0434-0.
doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0434-0
pmid: 27645330
|
| 31. |
Nayar N, Briscoe K, Fernandez PP . Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like reaction with severe satellite cell necrosis associated with nivolumab in a patient with ipilimumab refractory metastatic melanoma. J Immunother 2016; 39(3):149-52. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000112.
doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000112
|
 )
)
 )
)