Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 242-249.doi: 10.24920/004219
血压变异性可能是缺血性脑卒中发生及预后的新预测因子
- 重庆医科大学附属第一医院 神经内科,重庆 400000,中国
-
收稿日期:2023-02-27接受日期:2023-05-16出版日期:2023-09-30发布日期:2023-06-09 -
通讯作者:* 吴绮思,E-mail:68713721@qq.com ;杨军,E-mail:yangweixiao222@sina.com 。
Blood Pressure Variability May Be a New Predictor for the Occurrence and Prognosis of Ischemic Stroke
Ke-Qiong Yan,Qi-Si Wu*( ),Jun Yang*(
),Jun Yang*( )
)
- Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400000, China
-
Received:2023-02-27Accepted:2023-05-16Published:2023-09-30Online:2023-06-09 -
Contact:* Qi-Si Wu, E-mail:68713721@qq.com ; Jun Yang, E-mail:yangweixiao222@sina.com .
摘要:
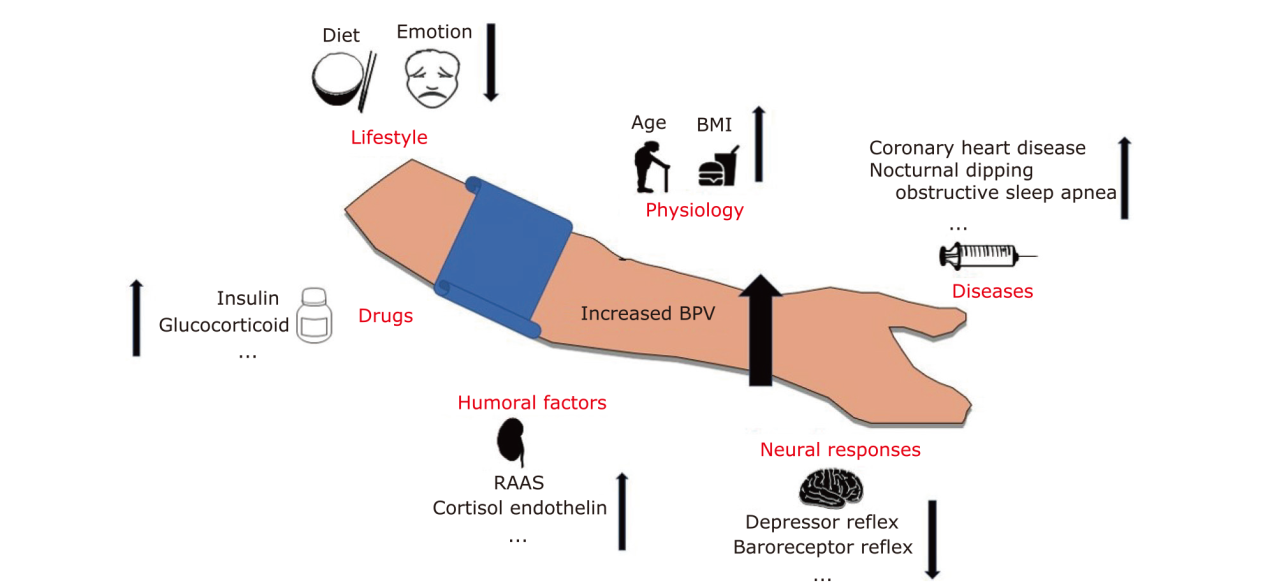
尽管近年来发病率和死亡率有所下降,但缺血性脑卒中(ischemic stroke, IS)仍然是脑血管疾病致死、致残的主要原因之一。干预可控性危险因素是临床管理IS的基础。高血压是IS最常见的可治疗危险因素之一,并与不良结局有关。动态血压监测结果显示高血压患者的血压变异性(blood pressure variability, BPV)高于非高血压患者。同时,BPV升高已被证明是IS的危险因素。BPV越高,IS发生的风险越高,卒中后的预后越差,无论是在急性期还是亚急性期。BPV受多因素影响,其变化反映了个体的生理病理改变。本文综述了目前BPV与IS关系的研究进展,旨在提高临床医生和IS患者对BPV的认识,探讨BPV升高是IS的可控危险因素。对于高血压患者,不仅需要控制血压平均水平,同时需要关注血压变异性,以更好地开展个性化血压管理。
引用本文
Ke-Qiong Yan, Qi-Si Wu, Jun Yang. Blood Pressure Variability May Be a New Predictor for the Occurrence and Prognosis of Ischemic Stroke[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(3): 242-249.
"
| Author citation | Size (n) | BPV measures | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minhas et al. [ | 11,093 | CV | SBPV was significantly associated with poor outcomes in IS patients. |
| Kang et al. [ | 4,415 | SD | For patients with IS, BPV but not mean BP increased the 1-year risk of major vascular events. |
| Chung et al. [ | 1,161 | SD, CV | BPV was significantly associated with worse neurologic outcomes after IS. |
| Dai et al. [ | 2,325 | CV | IS recurrence was associated with both SBPV and DBPV. |
| Naito et al. [ | 626 | SD, CV | The SD of SBP and DBP, CV of DBP, and morning BP surge were associated with poor outcomes for IS. |
| Zhang et al. [ | 592 | SD, CV | SBPV was a critical predictor for short-term outcomes among patients with IS. |
| Martins et al. [ | 674 | SD | SBPV showed an association with 3-month clinical outcome for IS. |
| Geng et al. [ | 704 | SD, CV | SBPV was the strongest independent predictor of functional outcomes in IS patients. |
| de Havenon et al. [ | 1,891 | SD, CV | Increased SBPV was associated with worse neurologic outcome after IS. |
| Kamieniarz-Medrygal et al. [ | 174 | SD | In the acute phase of IS, the SD of BPV was robustly associated with 30-day outcomes. |
| Yong et al. [ | 615 | Successive variation in the BP profile | DBPV was an independent predictor of outcomes in IS patients. |
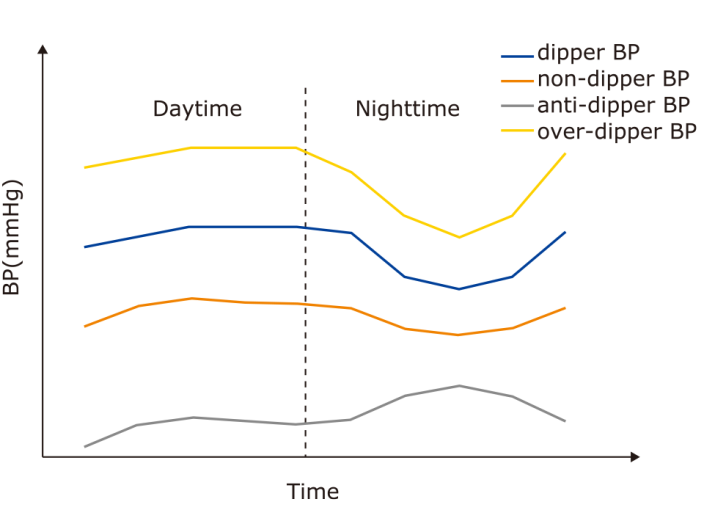
| Yamamoto et al. [ | 105 | [(mean daytime BP?mean nighttime BP)/average BP for 24 hours]×100% | Non-dipper BP had an adverse effect on the risk of recurrent IS and poor outcomes. |
| Dai et al. [ | 52,387 | CV | Visit-to-visit BPV was associated with the mortality rate of cerebrovascular disease. |
| Fukuda et al. [ | 2,566 | SD | Day-by-day BPV was associated with the 3-month functional outcome after acute IS. |
| Yang et al. [ | 367 | SD, CV | Increased day-by-day SBPV or DBPV in the IS was associated with a higher risk for unfavorable outcome at 3 months, independent of mean BP levels. |
| 1 | Johnson CO, Nguyen M, Roth GA, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Neurology 2019; 18(5): 439-58. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30034-1. |
| 2 | Feigin VL, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. The Lancet Neurology 2017; 16(11): 877-97. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30299-5. |
| 3 |
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019; 5 (1): 70. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8.
pmid: 31601801 |
| 4 | Kuriakose D, Xiao Z. Pathophysiology and treatment of stroke: present status and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21 (20): doi: 10.3390/ijms21207609. |
| 5 |
Putaala J. Ischemic Stroke in Young Adults. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2020; 26 (2): 386-414. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000833.
pmid: 32224758 |
| 6 |
Liu L, Chen W, Zhou H, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of ischaemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2020; 5 (2): 159-76. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000378.
pmid: 32561535 |
| 7 |
Xu T, Zhang Y, Bu X, et al. Blood pressure reduction in acute ischemic stroke according to time to treatment: a subgroup analysis of the China Antihypertensive Trial in Acute Ischemic Stroke trial. J Hypertens 2017; 35 (6): 1244-51. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001288.
pmid: 28169880 |
| 8 |
Turin TC, Okamura T, Afzal AR, et al. Hypertension and lifetime risk of stroke. J Hypertens 2016; 34 (1): 116-22. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000753.
pmid: 26556566 |
| 9 |
Lattanzi S, Brigo F, Silvestrini M. Blood pressure variability and stroke: A risk marker of outcome and target for intervention. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2021; 23 (1): 103-5. doi: 10.1111/jch.14092.
pmid: 33125836 |
| 10 |
Xu J, Liu Y, Wang A, et al. Blood pressure fluctuation pattern and stroke outcomes in acute ischemic stroke. Hypertens Res 2019; 42 (11): 1776-82. doi: 10.1038/s41440-019-0292-9.
pmid: 31451721 |
| 11 |
Toyoda K, Yamagami H, Kitagawa K, et al. Blood pressure level and variability during long-term prasugrel or clopidogrel medication after stroke: PRASTRO-I. Stroke 2021; 52 (4): 1234-43. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032824.
pmid: 33563017 |
| 12 | Webb AJS, Mazzucco S, Li L, et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure variability on beat-to-beat monitoring after transient ischemic atack and stroke. Stroke 2018; 49 (1): 62-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019107. |
| 13 |
Parati G, Ochoa JE, Lombardi C, et al. Blood pressure variability: assessment, predictive value, and potential as a therapeutic target. Curr Hypertens Rep 2015; 17 (4): 537. doi: 10.1007/s11906-015-0537-1.
pmid: 25790801 |
| 14 | Wang R, Liu Y, Yang P, et al. Blood pressure fluctuation during hospitalization and clinical outcomes within 3 months after ischemic stroke. Hypertension 2022; 79 (10): 2336-45. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19629. |
| 15 | Appiah KO, Nath M, Manning L, et al. Increasing blood pressure variability predicts poor functional outcome following acute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021; 30 (1): 105466. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105466. |
| 16 |
Sugiura T, Takase H, Machii M, et al. Blood pressure variability and the development of hypertensive organ damage in the general population. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2022; 24 (11): 1405-14. doi: 10.1111/jch.14526.
pmid: 35708714 |
| 17 | Bencivenga L, De Souto Barreto P, Rolland Y, et al. Blood pressure variability: a potential marker of aging. Ageing Res Rev 2022; 80 101677. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101677. |
| 18 |
Parati G, Stergiou GS, Dolan E, et al. Blood pressure variability: clinical relevance and application. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2018; 20 (7): 1133-7. doi: 10.1111/jch.13304.
pmid: 30003704 |
| 19 |
Hernandez MF, Chang TI. The need to reduce variability in the study of blood pressure variability. Am J Kidney Dis 2023; 81 (4): 379-81. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.10.008.
pmid: 36646618 |
| 20 | Chi XL, Wang XY, Guo ZR, et al. Relationships between blood pressure variability and silent cerebral infarction in patients with primary hypertension. Artery Res 2018; 24 40-6. doi: 10.1016/j.artres.2018.11.001. |
| 21 | Haverkamp RA, Melis RJF, Claassen J, et al. Day-to-day home blood pressure variability and all-cause mortality in a memory clinic population. J Alzheimers Dis 2022; 85 (3): 1219-31. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215002. |
| 22 | Hisamatsu T, Ohkubo T. Home blood pressure variability and target organ damage. Hypertens Res 2022; 45 (3): 543-5. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00844-6. |
| 23 |
Chen Y, Xiong H, Wu D, et al. Relationship of short-term blood pressure variability with carotid intima-media thickness in hypertensive patients. Biomed Eng Online 2015; 14: 71. doi: 10.1186/s12938-015-0059-8.
pmid: 26204889 |
| 24 | Tatasciore A, Di Nicola M, Tommasi R, et al. From short-term blood pressure variability to atherosclerosis: relative roles of vascular stiffness and endothelial dysfunction. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2020; 22 (7): 1218-27. doi: 10.1111/jch.13871. |
| 25 |
Hisamatsu T, Miura K, Ohkubo T, et al. Home blood pressure variability and subclinical atherosclerosis in multiple vascular beds: a population-based study. J Hypertens 2018; 36 (11): 2193-203. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001810.
pmid: 29939942 |
| 26 |
Gironacci MM, Cerniello FM, Longo Carbajosa NA, et al. Protective axis of the renin-angiotensin system in the brain. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014; 127 (5): 295-306. doi: 10.1042/CS20130450.
pmid: 24827941 |
| 27 | Miao CY, Su DF. The importance of blood pressure variability in rat aortic and left ventricular hypertrophy produced by sinoaortic denervation. J Hypertens 2002; 20 (9): 1865-72. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200209000-00033. |
| 28 | Miao CY, Zhang LM, Yuan WJ, et al. Angiotensin Ⅱ and AT1 receptor in hypertrophied ventricles and aortas of sinoaortic-denervated rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2003; 24(8): 812-8. |
| 29 |
Wu L, Iwai M, Nakagami H, et al. Roles of angiotensin Ⅱ type 2 receptor stimulation associated with selective angiotensin Ⅱ type 1 receptor blockade with valsartan in the improvement of inflammation-induced vascular injury. Circulation 2001; 104(22): 2716-21. doi: 10.1161/hc4601.099404.
pmid: 11723025 |
| 30 | Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM. From bedside to bench to bedside: role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in remodeling of resistance arteries in hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004; 287 (2): H435-46. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00262.2004. |
| 31 |
Inaba S, Iwai M, Tomono Y, et al. Exaggeration of focal cerebral ischemia in transgenic mice carrying human Renin and human angiotensinogen genes. Stroke 2009; 40 (2): 597-603. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.519801.
pmid: 19023100 |
| 32 |
Zhang C, Chen H, Xie HH, et al. Inflammation is involved in the organ damage induced by sinoaortic denervation in rats. J Hypertens 2003; 21 (11): 2141-8. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200311000-00024.
pmid: 14597858 |
| 33 |
Hickey JV, Salmeron ET, Lai JM. Twenty-four-hour blood pressure variability after acute ischemic stroke. Crit Care Nurs Q 2002; 25 (2): 1-12; quiz 74-15. doi: 10.1097/00002727-200208000-00002.
pmid: 12211332 |
| 34 |
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E, et al. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010; 375 (9718): 895-905. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60308-X.
pmid: 20226988 |
| 35 |
Gosmanova EO, Mikkelsen MK, Molnar MZ, et al. Association of systolic blood pressure variability with mortality, coronary heart disease, stroke, and renal disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016; 68 (13): 1375-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.06.054.
pmid: 27659458 |
| 36 |
Wang H, Li M, Xie SH, et al. Visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure variability and stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Med Sci 2019; 39 (5): 741-7. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2100-9.
pmid: 31612391 |
| 37 | Chen YK, Ni ZX, Li W, et al. Diurnal blood pressure and heart rate variability in hypertensive patients with cerebral small vessel disease: a case-control study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021; 30 (5): 105673. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105673. |
| 38 |
Kario K, Shimada K. Risers and extreme-dippers of nocturnal blood pressure in hypertension: antihypertensive strategy for nocturnal blood pressure. Clin Exp Hypertens 2004; 26 (2): 177-89. doi: 10.1081/ceh-120028556.
pmid: 15038628 |
| 39 |
Gasecki D, Kwarciany M, Kowalczyk K, et al. Blood pressure management in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Hypertens Rep 2020; 23 (1): 3. doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-01120-7.
pmid: 33305339 |
| 40 | Akhtar N, Al-Jerdi S, Kamran S, et al. Night-time non-dipping blood pressure and heart rate: an association with the risk of silent small vessel disease in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol 2021; 12 719311. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.719311. |
| 41 |
Yan B, Peng L, Dong Q, et al. Reverse-dipper pattern of blood pressure may predict lacunar infarction in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Neurol 2015; 22 (6): 1022-5. doi: 10.1111/ene.12659.
pmid: 25614275 |
| 42 |
Zhang Q, Zhou B, Ma Y, et al. Blood pressure visit-to-visit variability and outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail 2021; 8 (5): 3984-96. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13542.
pmid: 34405581 |
| 43 |
Rothwell PM. Limitations of the usual blood-pressure hypothesis and importance of variability, instability, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010; 375 (9718): 938-48. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60309-1.
pmid: 20226991 |
| 44 |
Hata Y, Kimura Y, Muratani H, et al. Office blood pressure variability as a predictor of brain infarction in elderly hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 2000; 23 (6): 553-60. doi: 10.1291/hypres.23.553.
pmid: 11131265 |
| 45 |
Kikuya M, Ohkubo T, Metoki H, et al. Day-by-day variability of blood pressure and heart rate at home as a novel predictor of prognosis: the Ohasama study. Hypertension 2008; 52 (6): 1045-50. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.104620.
pmid: 18981332 |
| 46 |
Johansson JK, Niiranen TJ, Puukka PJ, et al. Prognostic value of the variability in home-measured blood pressure and heart rate: the Finn-Home Study. Hypertension 2012; 59 (2): 212-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.178657.
pmid: 22215704 |
| 47 | Dicker D, Maya I, Vasilevsky V, et al. Blood pressure variability in acute ischemic stroke depends on hemispheric stroke location. Blood Press 2006; 15 (3): 151-6. doi: 10.1080/08037050600772755. |
| 48 |
Lundholm MD, Rooney M, Maas MB, et al. Wake-up stroke is associated with greater nocturnal mean arterial pressure variability. Stroke 2017; 48 (6): 1668-70. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.016202.
pmid: 28455315 |
| 49 |
Kitamura J, Ueno H, Nagai M, et al. Blood pressure variability in acute ischemic stroke: influence of infarct location in the insular cortex. Eur Neurol 2018; 79 (1-2): 90-9. doi: 10.1159/000486306.
pmid: 29334680 |
| 50 |
Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yonemura K, et al. Hypertension and neurovascular compression of the left lateral medulla oblongata in ischemic stroke. Eur Neurol 2001; 46 (2): 70-4. doi: 10.1159/000050766.
pmid: 11528154 |
| 51 |
Ciriello J, Caverson MM, Polosa C. Function of the ventrolateral medulla in the control of the circulation. Brain Res 1986; 396 (4): 359-91. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(86)90005-6.
pmid: 3542115 |
| 52 |
Han SW, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. A new subtype classification of ischemic stroke based on treatment and etiologic mechanism. Eur Neurol 2007; 57 (2): 96-102. doi: 10.1159/000098059.
pmid: 17179712 |
| 53 |
Gao S, Wang YJ, Xu AD, et al. Chinese ischemic stroke subclassification. Front Neurol 2011; 2: 6. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2011.00006.
pmid: 21427797 |
| 54 |
Muntner P, Whittle J, Lynch AI, et al. Visit-to-visit variability of blood pressure and coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and mortality: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163 (5): 329-38. doi: 10.7326/M14-2803.
pmid: 26215765 |
| 55 |
Diaz KM, Veerabhadrappa P, Kashem MA, et al. Relationship of visit-to-visit and ambulatory blood pressure variability to vascular function in African Americans. Hypertens Res 2012; 35 (1): 55-61. doi: 10.1038/hr.2011.135.
pmid: 21814215 |
| 56 |
Malik EZ, Abdulhadi B, Mezue KN, et al. Clinical hypertension: blood pressure variability. Dis Mon 2018; 64 (1): 5-13. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2017.08.003.
pmid: 28939280 |
| 57 |
Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, et al. Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 2007; 115 (4): 459-67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.628875.
pmid: 17242284 |
| 58 | Heshmatollah A, Ma Y, Fani L, et al. Visit-to-visit blood pressure variability and the risk of stroke in the Netherlands: a population-based cohort study. PLoS Med 2022; 19 (3): e1003942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003942. |
| 59 | Lee SR, Choi YJ, Choi EK, et al. Blood pressure variability and incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation: a nationwide population-based study. Hypertension 2020; 75 (2): 309-15. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13708. |
| 60 | Olbers J, Gille A, Ljungman P, et al. High beat-to-beat blood pressure variability in atrial fibrillation compared to sinus rhythm. Blood Press 2018; 27 (5): 249-55. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2018.1436400. |
| 61 |
Minhas JS, Wang X, Lavados PM, et al. Blood pressure variability and outcome in acute ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: a post hoc analysis of the HeadPoST study. J Hum Hypertens 2019; 33 (5): 411-8. doi: 10.1038/s41371-019-0193-z.
pmid: 30894658 |
| 62 |
Kang J, Kim BJ, Yang MH, et al. Blood pressure variability in subacute stage and risk of major vascular events in ischemic stroke survivors. J Hypertens 2019; 37 (10): 2000-6. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002126.
pmid: 31157740 |
| 63 |
Appiah KOB, Patel M, Panerai RB, et al. Increased blood pressure variability following acute stroke is associated with poor long-term outcomes: a systematic review. Blood Press Monit 2019; 24 (2): 67-73. doi: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000366.
pmid: 30762597 |
| 64 | Chung JW, Kim N, Kang J, et al. Blood pressure variability and the development of early neurological deterioration following acute ischemic stroke. J Hypertens 2015; 33 (10): 2099-106. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000675. |
| 65 |
Dai L, Cheng A, Hao X, et al. Different contribution of SBP and DBP variability to vascular events in patients with stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2020; 5 (2): 110-5. doi: 10.1136/svn-2019-000278.
pmid: 32606082 |
| 66 | Naito H, Hosomi N, Kuzume D, et al. Increased blood pressure variability during the subacute phase of ischemic stroke is associated with poor functional outcomes at 3 months. Sci Rep 2020; 10 (1): 811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57661-z. |
| 67 |
Zhang Y, Wang H, Xu K, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure variability within the first 24 hours after admission and outcomes of acute ischemic stroke. J Am Soc Hypertens 2018; 12 (3): 195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2017.12.012.
pmid: 29396105 |
| 68 |
Martins AI, Sargento-Freitas J, Jesus-Ribeiro J, et al. Blood pressure variability in acute ischemic stroke: the role of early recanalization. Eur Neurol 2018; 80 (1-2): 63-7. doi: 10.1159/000492627.
pmid: 30227441 |
| 69 |
Geng X, Liu X, Li F, et al. Blood pressure variability at different time periods within first 24 hours after admission and outcomes of acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2020; 22 (2): 194-204. doi: 10.1111/jch.13785.
pmid: 32049416 |
| 70 | de Havenon A, Stoddard G, Saini M, et al. Increased blood pressure variability after acute ischemic stroke increases the risk of death: a secondary analysis of the Virtual International Stroke Trial Archive. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis 2019; 8: 2048004019856496. doi: 10.1177/2048004019856496. |
| 71 |
Manning LS, Rothwell PM, Potter JF, et al. Prognostic significance of short-term blood pressure variability in acute stroke: systematic review. Stroke 2015; 46 (9): 2482-90. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010075.
pmid: 26243226 |
| 72 |
Tang S, Xiong L, Fan Y, et al. Stroke outcome prediction by blood pressure variability, heart rate variability, and baroreflex sensitivity. Stroke 2020; 51 (4): 1317-20. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027981.
pmid: 31964286 |
| 73 | Kamieniarz-Medrygal M, Lukomski T, Kazmierski R. Short-term outcome after ischemic stroke and 24-h blood pressure variability: association and predictors. Hypertens Res 2021; 44 (2): 188-96. doi: 10.1038/s41440-020-00534-9. |
| 74 |
Yong M, Diener HC, Kaste M, et al. Characteristics of blood pressure profiles as predictors of long-term outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2005; 36 (12): 2619-25. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000189998.74892.24.
pmid: 16254220 |
| 75 |
Yamamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Oiwa K, et al. Adverse effect of nighttime blood pressure on the outcome of lacunar infarct patients. Stroke 1998; 29 (3): 570-6. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.3.570.
pmid: 9506594 |
| 76 |
Dai L, Song L, Li X, et al. Association of visit-to-visit blood pressure variability with the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in general population. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2018; 20 (2): 280-8. doi: 10.1111/jch.13192.
pmid: 29457332 |
| 77 |
Fukuda K, Kai H, Kamouchi M, et al. Day-by-day blood pressure variability and functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke: fukuoka stroke registry. Stroke 2015; 46 (7): 1832-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009076.
pmid: 26069262 |
| 78 | Yang C, Liu K, Song Y, et al. Day-by-day blood pressure variability is associated with neurological functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol 2020; 11 566825. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.566825. |
| 79 |
Ko Y, Park JH, Yang MH, et al. The significance of blood pressure variability for the development of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2010; 41 (11): 2512-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.595561.
pmid: 20947842 |
| 80 |
Kim TJ, Park HK, Kim JM, et al. Blood pressure variability and hemorrhagic transformation in patients with successful recanalization after endovascular recanalization therapy: a retrospective observational study. Ann Neurol 2019; 85 (4): 574-81. doi: 10.1002/ana.25434.
pmid: 30761582 |
| 81 |
Liu K, Yan S, Zhang S, et al. Systolic blood pressure variability is associated with severe hemorrhagic transformation in the early stage after thrombolysis. Transl Stroke Res 2016; 7 (3): 186-91. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0458-6.
pmid: 26892891 |
| 82 |
Delgado-Mederos R, Ribo M, Rovira A, et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure variability after thrombolysis in acute stroke. Neurology 2008; 71 (8): 552-8. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000318294.36223.69.
pmid: 18550860 |
| 83 | Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019; 50 (12): e344-e418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211. |
| 84 |
Rouch L, Cestac P, Sallerin B, et al. Visit-to-visit blood pressure variability is associated with cognitive decline and incident dementia: the S.AGES cohort. Hypertension 2020; 76 (4): 1280-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14553.
pmid: 32862710 |
| 85 |
Bohm M, Schumacher H, Leong D, et al. Systolic blood pressure variation and mean heart rate is associated with cognitive dysfunction in patients with high cardiovascular risk. Hypertension 2015; 65 (3): 651-61. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04568.
pmid: 25583157 |
| 86 |
Kim Y, Lim JS, Oh MS, et al. Blood pressure variability is related to faster cognitive decline in ischemic stroke patients: PICASSO subanalysis. Sci Rep 2021; 11 (1): 5049. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83945-z.
pmid: 33658545 |
| 87 |
Hilkens NA, Klijn CJM, Richard E. Blood pressure, blood pressure variability and the risk of poststroke dementia. J Hypertens 2021; 39 (9): 1859-64. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002841.
pmid: 33710171 |
| [1] | 吕双杰, 丁杨楠, 裴小雅, 赵翔, 郝德龙, 张祝琴, 陈厚早, 刘德培. 血管转录组测序发现血管紧张素2诱导的高血压小鼠动脉组织衰老相关基因改变[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 43-53. |
| [2] | 钟海兰, 徐崇利, 陈广胜, 陈秀梅. 杓型与非杓型高血压患者的血浆干细胞因子及其受体表达水平研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 232-238. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|