Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 35-42.doi: 10.24920/003753
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
VEGF-C/VEGFR-3/iNOS Signaling in Osteosarcoma MG63 Cells Mediates Stimulatory Effects on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Proliferation
Jie Lv, Jie Yuan, Chaojian Xu, Jiaqi Hao, Yichuan Qin, Xiaoqiang Wang, Yongfeng Wang( )
)
- Department of Orthopaedics, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, China
-
Received:2020-04-11Accepted:2020-05-14Published:2021-02-07Online:2021-02-07 -
Contact:Yongfeng Wang E-mail:wyfwf8@163.com
Cite this article
Jie Lv,Jie Yuan,Chaojian Xu,Jiaqi Hao,Yichuan Qin,Xiaoqiang Wang,Yongfeng Wang. VEGF-C/VEGFR-3/iNOS Signaling in Osteosarcoma MG63 Cells Mediates Stimulatory Effects on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Proliferation[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 35-42.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
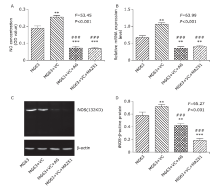
Figure 1.
Nitric oxide (NO) production and iNOS expression(mRNA and protein levels)in MG63 cells with different treatments. (A) NO levels in MG63 cell culture medium were assessed by a colorimetric method. (B) iNOS expression assessed by qRT-PCR. (C, D) iNOS expression levels determined by Western blot. VC (VEGF-C) binding with VEGFR-3 promoted NO release by up-regulating iNOS. n = 3 for each group. ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 compared to the MG63 group; ### P<0.001 compared to the MG63+VC group."

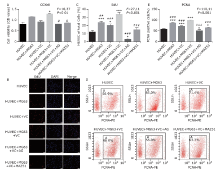
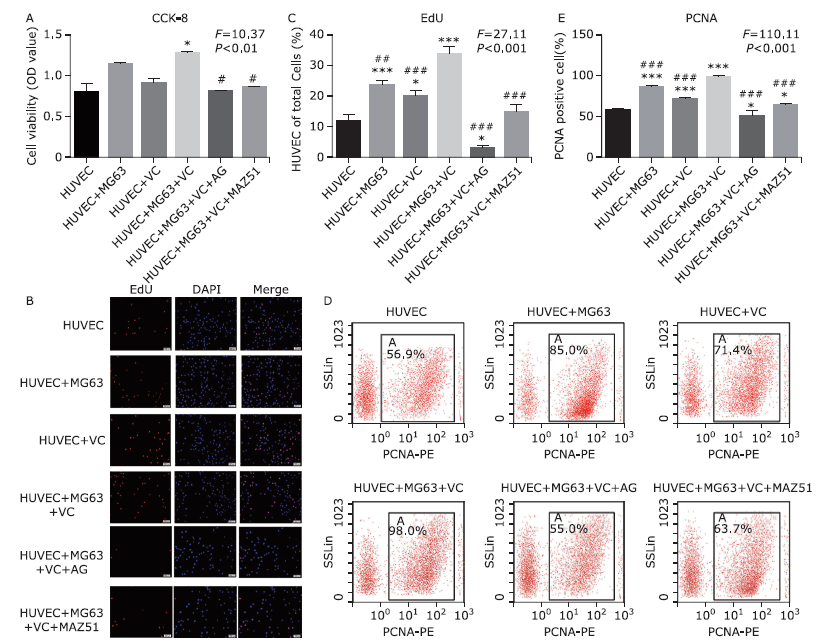
Figure 2.
The effects of MG63 cells with treatment of VEGF-C on HUVEC proliferation. Proliferation of HUVECs was assessed by CCK-8 (A), EdU (B and C) and PCNA expression (D and E) assays in co-incubation with MG63 cells and/or VC (VEGF-C), with MG63+VC+AG, and MG63+VC+MAZ51. n = 3 for each group. Bars in (B): 200 μm.* P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 compared with the HUVEC group; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 compared with the HUVEC+MG63+VC group."
| 1. | Messerschmitt PJ, Garcia RM, Abdul-Karim FW, et al.Osteosarcoma. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2009; 17(8): 515-27. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e31818d5fcb. |
| 2. | Dai Z, Tang H, Pan Y, et al.Gene expression profiles and pathway enrichment analysis of human osteosarcoma cells exposed to sorafenib. FEBS Open Bio 2018; 8(5):860-7. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12428. |
| 3. | Hameed M, Mandelker D. Tumor syndromes predisposing to osteosarcoma. Adv Anat Pathol 2018; 25(4):217-22. doi:10.1097/PAP.0000000000000190. |
| 4. | Wang J, Cao L, Wu J, et al.Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 regulates NOB1 expression by sponging miR-326 and promotes tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol 2018; 52(1):77-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4187. |
| 5. |
Nieto-Coronel MT, López-Vásquez AD, Marroquín-Flores D, et al.Central nervous system metastasis from osteosarcoma: Case report and literature review. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 2018; 23(4):266-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2018.06.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2018.06.003 pmid: 30090025 |
| 6. | Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, et al. Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2018; 18(1):39-50. doi:10.1080/14737140.2018.1413939. |
| 7. | Briccoli A, Rocca M, Salone M, et al.Resection of recurrent pulmonary metastases in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer 2005; 104(8):1721-25. doi:10.1002/cncr.21369. |
| 8. | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA.Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144(5):646-74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. |
| 9. | Segaliny AI, Mohamadi A, Dizier B, et al.Interleukin-34 promotes tumor progression and metastatic process in osteosarcoma through induction of angiogenesis and macrophage recruitment. Int J Cancer 2015; 137(1): 73-85. doi:10.1002/ijc.29376. |
| 10. | Yang X, Zhou W, Liu S.SPAG9 controls the cell motility, invasion and angiogenesis of human osteosarcoma cells. Exp Ther Med 2016; 11(2): 637-44. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2932. |
| 11. | Qu W, Wang Y, Wu Q, et al.Emodin inhibits HMGB1induced tumor angiogenesis in human osteosarcoma by regulating SIRT1. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8(9): 15054-64. |
| 12. | Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M.Anti-tumor and anti-metastatic actions of wogonin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis roots through anti-lymphangiogenesis. Phytomedicine 2013; 20(3-4): 328-36. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.10.016. |
| 13. | Folkman J.What is the role of endothelial cells in angiogenesis? Lab Invest 1984; 51(6): 601-4. |
| 14. |
Dong Z, Nor JE.Transcriptional targeting of tumor endothelial cells for gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2009; 61(7-8): 542-53. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.02.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.02.006 pmid: 19393703 |
| 15. |
Kang JX, Liu A.The role of the tissue omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in regulating tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2013; 32(1-2): 201-10. doi:10.1007/s10555-012-9401-9.
pmid: 23090260 |
| 16. |
Zhao J, Zhang ZR, Zhao N, et al.VEGF silencing inhibits human osteosarcoma angiogenesis and promotes cell apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8(8): 12411-7. doi:10.1007/s12013-015-0692-7.
pmid: 26550152 |
| 17. | Abdeen A, Chou AJ, Healey JH, et al.Correlation between clinical outcome and growth factor pathway expression in osteogenic sarcoma. Cancer 2009; 115(22): 5243-50. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24562. |
| 18. | Park HR, Min K, Kim HS, et al.Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and its receptor in osteosarcomas. Pathol Res Pract 2008; 204(8): 575-82. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2008.01.015. |
| 19. | Chien MH, Ku CC, Johansson G, et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) promotes angiogenesis by induction of COX-2 in leukemic cells via the VEGF-R3/JNK/AP-1 pathway. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30(12): 2005-13. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp244. |
| 20. | Curiel TJ, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al.Dendritic cell subsets differentially regulate angiogenesis in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2004; 64(16): 5535-8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1272. |
| 21. |
Lahdenranta J, Hagendoorn J, Padera TP, et al.Endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Res 2009; 69(7): 2801-8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4051.
pmid: 19318557 |
| 22. | Fukumura D, Kashiwagi S, Jain RK.The role of nitric oxide in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6(7): 521-34. doi:10.1038/nrc1910. |
| 23. | Chen WL, Feng HJ, Li JS, et al.Expression and pathological relevance of inducible nitric oxide synthase in osteosarcoma of the jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007; 36(6):541-4. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2007.02.012. |
| 24. |
Cullis ER, Kalber TL, Ashton SE, et al.Tumour overexpression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) increases angiogenesis and may modulate the antitumour effects of the vascular disrupting agent ZD6126. Microvasc Res 2006; 71(2):76-84. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2006.01.004.
pmid: 16530791 |
| 25. |
Ellie E, Loiseau H, Lafond F, et al.Differential expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in humanbrain tumours. Neuroreport 1995; 7(1): 294-6. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199512290-00070.
pmid: 8742473 |
| 26. |
Loibl S, Buck A, Strank C, et al.The role of early expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 2005; 41(2):265-71. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2004.07.010.
pmid: 15661552 |
| 27. |
Ekmekcioglu S, Ellerhorst JA, Prieto VG, et al.Tumor iNOS predicts poor survival for stage III melanoma patients. Int J Cancer 2006; 119(4):861-6. doi:10.1002/ijc.21767.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.21767 pmid: 16557582 |
| 28. |
Dias S, Choy M, Alitalo K, et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C signaling through FLT-4 (VEGFR-3) mediates leukemic cell proliferation, survival, and resistance to chemotherapy. Blood 2002; 99(6): 2179-84. doi:10.1182/blood.V99.6.2179.
doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.6.2179 pmid: 11877295 |
| 29. | Watanabe T, Sugaya M, Atkins AM, et al.Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen prolongs the life span of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Virol 2003; 77(11): 6188-96. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.11.6188-6196.2003. |
| [1] | Ye-qi Sun, Peng Chen, Qiang Zhao. Pulmonary Carcinosarcoma with Intracardiac Extension: a Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(3): 193-195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

