Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 1-8.doi: 10.24920/004319
Antiviral Effect of Extracellular Matrix Protein ABI3BP on Vesicular Stomatitis Virus and Its Mechanism: A Preliminary Study In Vitro
Xiang-Bo Meng1, 2, Mei-Hua Chen3, Nuo Xu1, 2, Tian-Qi Li1, 2, Shuai-Chen Li1, 2, Sun-Xin Zhou1, 2, Huan Chen4, *( ), Tong Zhang1, *(
), Tong Zhang1, *( )
)
- 1Department of Stomatology, the First Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
2Chinese PLA Medical School, Beijing 100853, China
3State Key Laboratory of Toxicology and Medical Countermeasures, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing 100850, China
4Baodi Clinical College, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 301800, China
-
Received:2023-10-20Accepted:2023-12-27Published:2024-03-31Online:2024-02-22 -
Contact:* Tong Zhang, E-mail:kqzhengji301@163.com ;Huan Chen, E-mail:1773524536@qq.com .
Cite this article
Xiang-Bo Meng, Mei-Hua Chen, Nuo Xu, Tian-Qi Li, Shuai-Chen Li, Sun-Xin Zhou, Huan Chen, Tong Zhang. Antiviral Effect of Extracellular Matrix Protein ABI3BP on Vesicular Stomatitis Virus and Its Mechanism: A Preliminary Study In Vitro[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2024, 39(1): 1-8.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
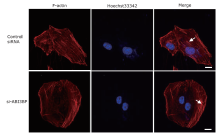
Figure 2.
Immunofluorescence images of F-actin in BJ-5ta cells before and after ABI3BP knockdown. BJ-5ta cells were transfected with siRNA of ABI3BP for 48 h and then stained with TRITC-Phalloidin. Red for F-actin and blue for Hoechst 33342. Scale bar: 5 μm. White arrows show the distribution of stress fiber structure."
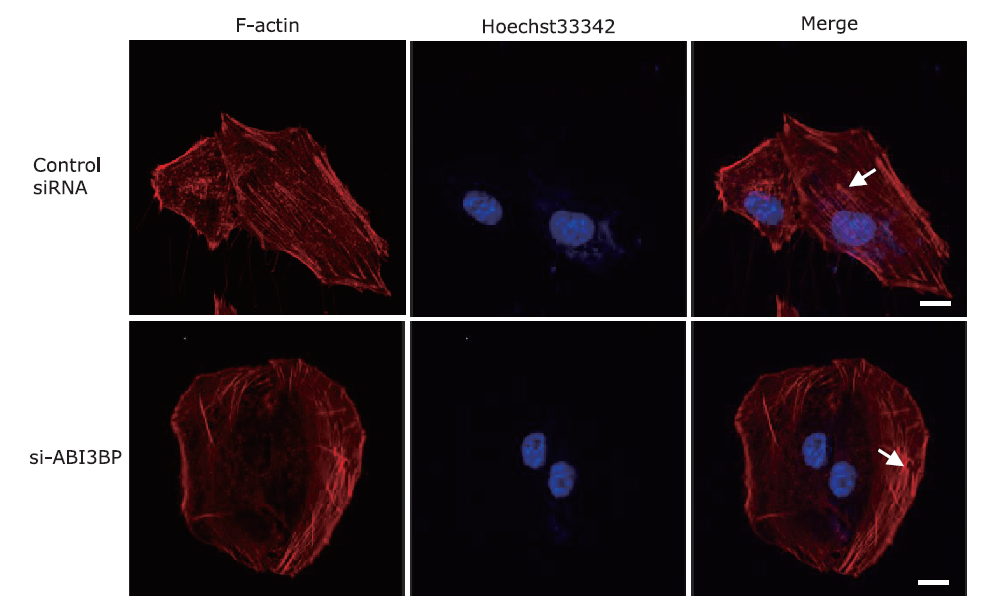
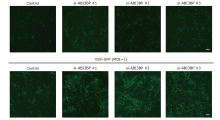
Figure 3.
Representative immunofluorescence images of BJ-5ta cells treated with vesicular stomatitis virus-green fluorescent protein (VSV-GFP) at varying virus loads. BJ-5ta cells were transfected with siRNA of ABI3BP for 48 h and then stimulated with VSV-GFP for 12 h (MOI 0.1, MOI 1). Scale bar: 100 μm."
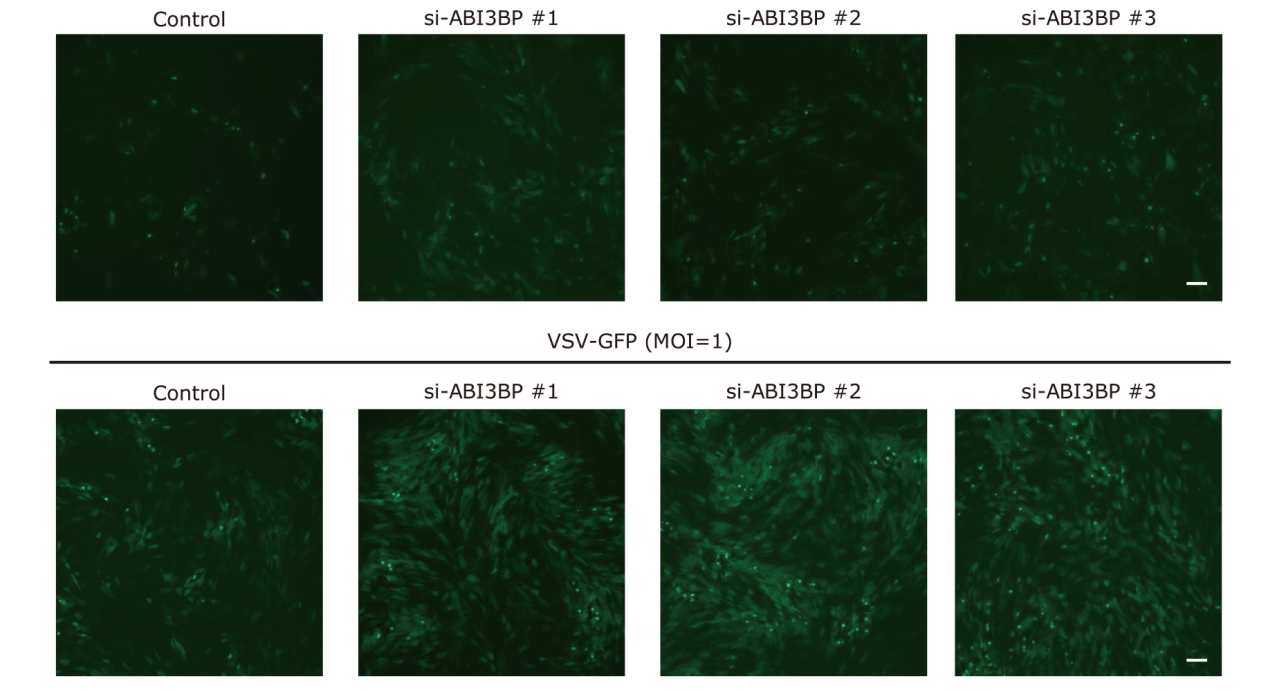
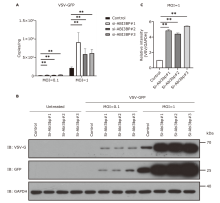
Figure 4.
The expression of VSV-G in BJ-5ta cells after ABI3BP knockdown. BJ-5ta cells were knocked down with siRNA for 48 h and then stimulated with VSV-GFP for 12 h. (A) The genome copy number of VSV-GFP detected by RT-qPCR; (B) the expression of VSV-G detected by Western blot. (C) Densitometric analysis based on three independent experiments to quantify ratio of VSV-GFP (MOI: 1) to GAPDH. Each experiment was repeated three times. **P<0.01."
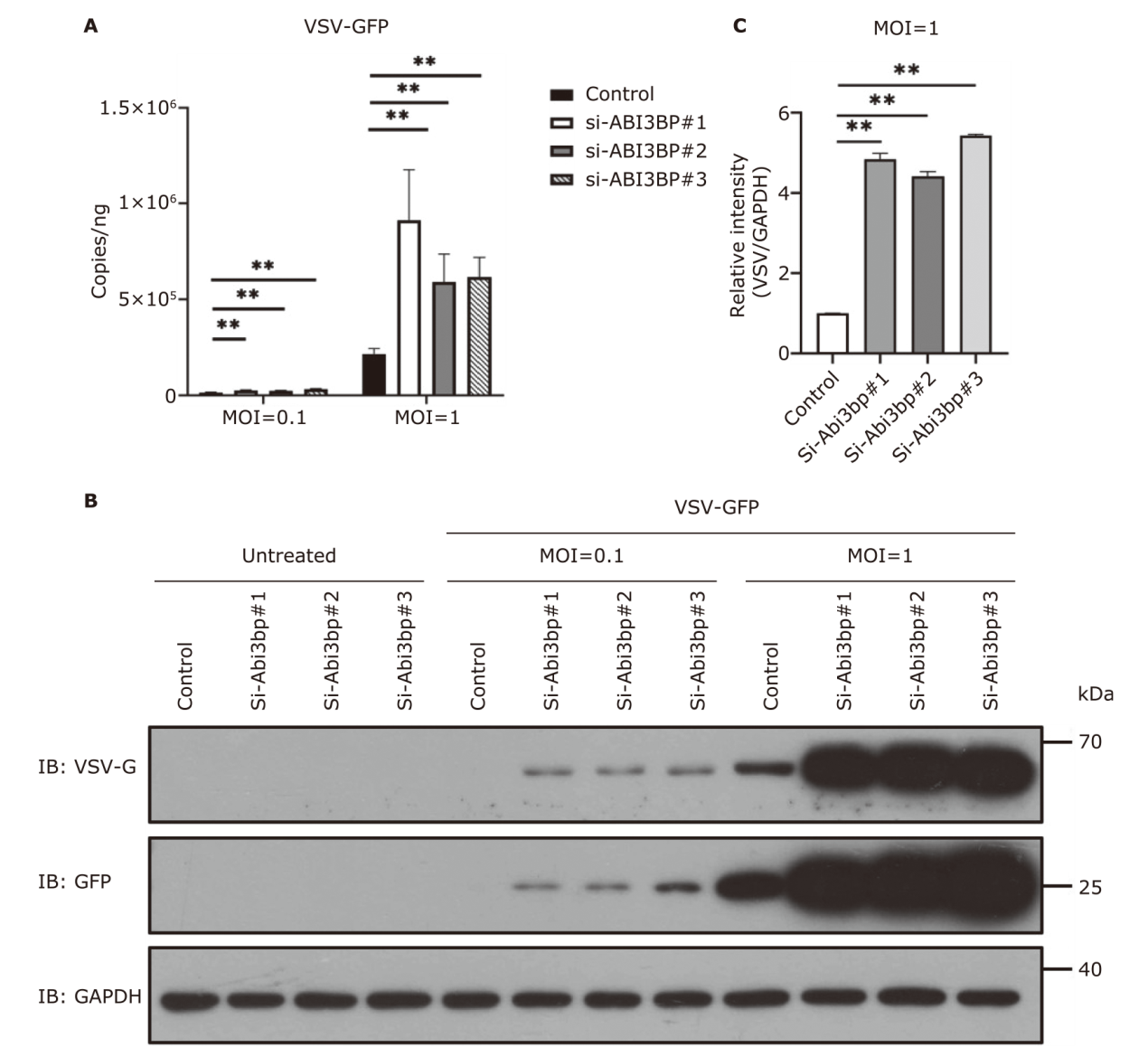

Figure 5.
Effect of ABI3BP knockdown on the expression levels of p-IRF3 and p-TBK1 in VSV-GFP-stimulated BJ-5ta cells. (A) BJ-5ta cells transfected with siRNA for 48 h and stimulated with VSV-GFP (MOI 1) for 12 h and then detected by Western blotting. Densitometric analysis based on three independent experiments to quantify the ratios of p-IRF3 to IRF3 (B) and p-TBK1 to TBK1 (C), respectively. Each experiment was repeated three times. **P<0.01."

| 1. | Walton TE, Webb PA, Kramer WL, et al. Epizootic vesicular stomatitis in Colorado, 1982: epidemiologic and entomologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1987; 36(1): 166-76. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.166. |
| 2. | Walker PJ, Firth C, Widen SG, et al. Evolution of genome size and complexity in the rhabdoviridae. PLoS Pathog 2015; 11(2): e1004664. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004664. |
| 3. | Liu G, Cao W, Salawudeen A, et al. Vesicular stomatitis virus: from agricultural pathogen to vaccine vector. Pathogens 2021; 10(9): 1902. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091092. |
| 4. |
Clarke DK, Nasar F, Lee M, et al. Synergistic attenuation of vesicular stomatitis virus by combination of specific G gene truncations and N gene translocations. J Virol 2007; 81(4): 2056-64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01911-06.
pmid: 17151112 |
| 5. |
Novella IS. Contributions of vesicular stomatitis virus to the understanding of RNA virus evolution. Curr Opin Microbiol 2003; 6(4): 399-405. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(03)00084-5.
pmid: 12941412 |
| 6. |
Hastie E, Cataldi M, Marriott I, et al. Understanding and altering cell tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virus Res 2013; 176(1-2): 16-32. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.06.003.
pmid: 23796410 |
| 7. | Fletcher P, O’Donnell KL, Doratt BM, et al. Single-dose VSV-based vaccine protects cynomolgus macaques from disease after Taï Forest virus infection. Emerg Microbes Infect 2023; 12(2): 2239950. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2239950. |
| 8. | Marek J, Hanesch L, Krabbe T, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy with chimeric VSV-NDV synergistically supports RIG-I-dependent checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2023; 30: 117-31. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.08.001. |
| 9. |
Matsuda S, Iriyama C, Yokozaki S, et al. Cloning and sequencing of a novel human gene that encodes a putative target protein of Nesh-SH3. J Hum Genet 2001; 46(8): 483-6. doi: 10.1007/s100380170049.
pmid: 11501947 |
| 10. | Delfín DA, DeAguero JL, McKown EN. The extracellular matrix protein ABI3BP in cardiovascular health and disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 2019; 6: 23. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00023. |
| 11. | Feng Y, Han X, Zhang Z, et al. ABI3BP is a prognosis biomarker related with clinicopathological features and immunity infiltration of lung tumor. Front Genet 2022; 13: 1085785. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1085785. |
| 12. | Latini FR, Hemerly JP, Oler G, et al. Re-expression of ABI3-binding protein suppresses thyroid tumor growth by promoting senescence and inhibiting invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer 2008; 15(3): 787-99. doi: 10.1677/erc-08-0079. |
| 13. | Li P, Yuan H, Kuang X, et al. Network module function enrichment analysis of lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2022; 101(47): e31798. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000031798. |
| 14. | Cai H, Li Y, Qin D, et al. The depletion of ABI3BP by microRNA-183 promotes the development of esophageal carcinoma. Mediat Inflamm 2020; 2020: 3420946. doi: 10.1155/2020/3420946. |
| 15. | Feng Y, Tao F, Qiao H, et al. A pan-cancer analysis of ABI3BP: a potential biomarker for prognosis and immunoinfiltration. Front Oncol 2023; 13: 1159725. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1159725. |
| 16. |
Hodgkinson CP, Naidoo V, Patti KG, et al. ABI3BP is a multifunctional autocrine/paracrine factor that regulates mesenchymal stem cell biology. Stem Cells 2013; 31(8): 1669-82. doi: 10.1002/stem.1416.
pmid: 23666637 |
| 17. |
Song N, Qi Q, Cao R, et al. MAVS O-GlcNAcylation is essential for host antiviral immunity against lethal RNA viruses. Cell Rep 2019; 28(9): 2386-96. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.085.
pmid: 31461653 |
| 18. |
Latini FR, Hemerly JP, Freitas BC, et al. ABI3 ectopic expression reduces in vitro and in vivo cell growth properties while inducing senescence. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-11.
pmid: 21223585 |
| 19. | Dai Z, Pendergast AM. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity. Genes Dev 1995; 9(21): 2569-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2569. |
| 20. | Bae J, Sung BH, Cho IH, et al. NESH regulates dendritic spine morphology and synapse formation. PLOS ONE 2012; 7(4): e34677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034677. |
| 21. | Miyazaki K, Matsuda S, Ichigotani Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel human gene (NESH) which encodes a putative signaling molecule similar to e3B1 protein. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) 2000; 1493(1-2): 237-41. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(00)00158-5. |
| 22. |
Hodgkinson CP, Gomez JA, Payne AJ, et al. ABI3BP regulates cardiac progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Circ Res 2014; 115(12): 1007-16. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.115.304216.
pmid: 25296984 |
| 23. | Manabe R, Tsutsui K, Yamada T, et al. Transcriptome-based systematic identification of extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105(35): 12849-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803640105. |
| 24. |
Roberts KL, Baines JD. Actin in herpesvirus infection. Viruses 2011; 3 (4): 336-46. doi: 10.3390/v3040336.
pmid: 21994736 |
| 25. | Nelemans T, Kikkert M. Viral innate immune evasion and the pathogenesis of emerging RNA virus infections. Viruses 2019; 11(10): 961. doi: 10.3390/v11100961. |
| 26. |
Stefan KL, Kim MV, Iwasaki A, et al. Commensal microbiota modulation of natural resistance to virus infection. Cell 2020; 183(5): 1312-24. doi: 0.1016/j.cell.2020.10.047.
pmid: 33212011 |
| 27. |
Roers A, Hiller B, Hornung V. Recognition of endogenous nucleic acids by the innate immune system. Immunity 2016; 44(4): 739-54. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.002.
pmid: 27096317 |
| 28. |
Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, et al. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 2005; 122(5): 669-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.012.
pmid: 16125763 |
| 29. |
Binder M, Eberle F, Seitz S, et al. Molecular mechanism of signal perception and integration by the innate immune sensor retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I). J Biol Chem 2011; 286(31): 27278-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m111.256974.
pmid: 21659521 |
| 30. |
Ren Z, Ding T, Zuo Z, et al. Regulation of MAVS expression and signaling function in the antiviral innate immune response. Front Immunol 2020; 11: 1030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01030.
pmid: 32536927 |
| 31. | Zheng Z, Zhao M, Shan H, et al. Noncanonical autophagy is a new strategy to inhibit HSV-1 through STING1 activation. Autophagy 2023; 19(12): 3096-112. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2237794. |
| 32. | Chakravarty S, Subramanian G, Popli S, et al. Interferon-stimulated gene TDRD 7 interacts with AMPK and inhibits its activation to suppress viral replication and pathogenesis. mBio 2023; 14(5): e0061123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00611-23. |
| [1] | Rui Min, Mei Li, Jiang-feng Mao, Feng Gu, Hui-juan Zhu, Wen-hui Li, Yu-xiu Li*. Hypercalcemia Appeared in a Patient with Glucagonoma Treated with Octreotide Acetate Long-acting Release [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2012, 27(3): 182-184. |
| [2] | Bin Yin, Ke-han Li, Tai An, Tao Chen and Xiao-zhong Peng. Nectin-like Molecule 1 Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of U251 Glioma Cells by Regulating the Expression of An Extracellular Matrix Protein Osteopontin [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(2): 100-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|



