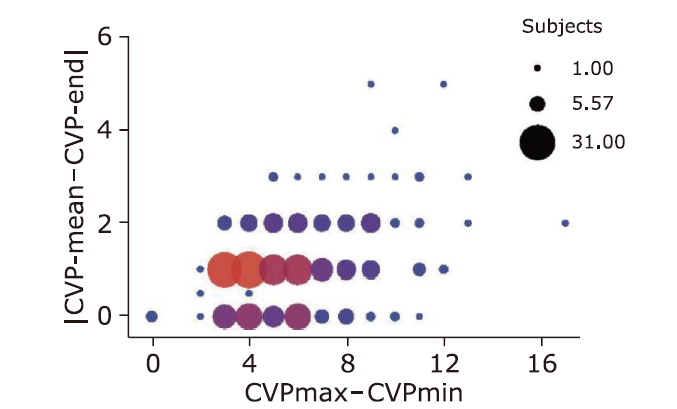
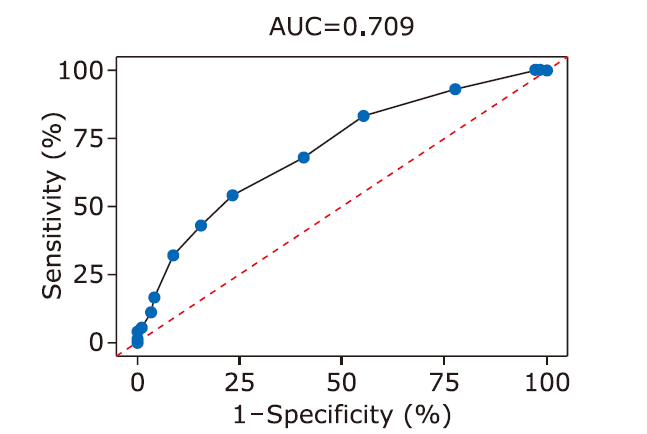
| 1 |
Berlin DA, Bakker J. Starling curves and central venous pressure. Crit Care 2015 ; 19(1): 55. doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0776-1.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0776-1
|
| 2 |
Long Y, Su LX, Zhang Q, et al. Elevated mean airway pressure and central venous pressure in the first day of mechanical ventilation indicated poor outcome. Crit Care Med 2017 ; 45(5): e485-92. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002290.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002290
|
| 3 |
Magder S. Right atrial pressure in the critically ill how to measure, what is the value, what are the limitations? Chest 2017 ; 151(4): 908-16. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.026.
doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.026
|
| 4 |
Chen H, Zhu Z, Zhao C, et al. Central venous pressure measurement is associated with improved outcomes in septic patients: an analysis of the MIMIC-III database. Crit Care (London, England) 2020 ; 24(1):433. doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03109-9.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03109-9
|
| 5 |
Wang XT, Yao B, Liu DW, et al. Central venous pressure dropped early is associated with organ function and prognosis in septic shock patients: a retrospective observational study. Shock 2015 ; 44(5):426-30. doi:10.1097/shk.0000000000000445.
doi: 10.1097/shk.0000000000000445
|
| 6 |
Li DK, Du W. Central venous pressure value can assist in adjusting norepinephrine dosage after the initial resuscitation of septic shock. Chin Med J (Engl) 2019 ; 132(10): 1159-65. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000000238.
doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000000238
|
| 7 |
Yang Q, Chen W, Wen Y, et al. Association between wait time of central venous pressure measurement and outcomes in critical patients with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study. Front Public Health 2022; 10: 893683. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.893683.
doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.893683
|
| 8 |
Tang R, Peng JN, Wang DX. Central venous pressure measurement is associated with improved outcomes in patients with or at risk for acute respiratory distress syndrome: an analysis of the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV Database. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022; 9: 858838. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.858838.
doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.858838
|
| 9 |
Hu B, Xiang H, Liang H, et al. Assessment effect of central venous pressure in fluid resuscitation in the patients with shock: a multi-center retrospective research. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013 ; 126(10): 1844-9.
|
| 10 |
Backer DD, Vincent JL. Should we measure the central venous pressure to guide fluid management? Ten answers to 10 questions. Crit Care 2018; 22. doi:10.1186/s13054-018-1959-3.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-1959-3
|
| 11 |
Backer DD, Cecconi M, Chew MS, et al. A plea for personalization of the hemodynamic management of septic shock. Crit Care 2022 ; 26(1):372. doi:10.1186/s13054-022-04255-y.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04255-y
|
| 12 |
Legrand M, Soussi S, Depret F. Cardiac output and CVP monitoring... to guide fluid removal. Crit Care 2018; 22. doi:10.1186/s13054-018-2016-y.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2016-y
|
| 13 |
Backer DD, Aissaoui N, Cecconi M, et al. How can assessing hemodynamics help to assess volume status? Intensive Care Med 2022 ; 48(10):1482-94. doi:10.1007/s00134-022-06808-9.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06808-9
|
| 14 |
Reems MM and M Aumann. Central venous pressure: principles, measurement, and interpretation. Compendium (Yardley, PA) 2012 ; 34(1): E1.
|
| 15 |
Pasion E, Good L, Tizon J, et al. Evaluation of the monitor cursor-line method for measuring pulmonary artery and central venous pressures. Am J Crit Care 2010 ; 19(6):511-21. doi:10.4037/ajcc2010502.
doi: 10.4037/ajcc2010502
|
| 16 |
Kleinman B, Powell S, Kumar P, et al. The fast flush test measures the dynamic response of the entire blood pressure monitoring system. Anesthesiology 1992 ; 77(6):1215-20. doi:10.1097/00000542-199212000-00024.
doi: 10.1097/00000542-199212000-00024
|
| 17 |
Watanabe H, Yagi SI, Namiki A. Recommendation of a clinical impulse response analysis for catheter calibration-dumping coefficient and natural frequency are incomplete parameters for clinical evaluation. J Clin Monit Comput 2006 ; 20(1): 37-42. doi:10.1007/S10877-005-9008.
doi: 10.1007/S10877-005-9008
|
| 18 |
Roger C, Muller L, Riou B, et al. Comparison of different techniques of central venous pressure measurement in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth 2017 ; 118(2):223-31. doi:10.1093/bja/aew386.
doi: 10.1093/bja/aew386
|
| 19 |
Hamzaoui O, Teboul JL. Central venous pressure (CVP). Intensive Care Med 2022 ; 48(10): 1498-500. doi:10.1007/s00134-022-06835-6.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06835-6
|
| 20 |
Lakhal K, Ehrmann S, Runge I, et al. Central venous pressure measurements improve the accuracy of leg raising-induced change in pulse pressure to predict fluid responsiveness. Intensive Care Medicine 2010 ; 36(6):940-8. doi:10.1007/s00134-010-1755-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1755-2
|
| 21 |
AACN practice alert: PA/CVP Monitoring in Adults. 2016; Available from: www.aacn.org/clinical-resources/practice-alerts/pulmonary-artery-pressure-measurement.
|
| 22 |
Jain RK, Antonio BL, Bowton DL, et al. Variability in central venous pressure measurements and the potential impact on fluid management. Shock 2010 ; 33(3): 253-7. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181b2bb22.
doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181b2bb22
|
 ),赖晓丽2,赵美玲3,刘大为1,隆云1
),赖晓丽2,赵美玲3,刘大为1,隆云1
 ),Xiao-Li Lai2,Mei-Ling Zhao3,Da-Wei Liu1,Yun Long1
),Xiao-Li Lai2,Mei-Ling Zhao3,Da-Wei Liu1,Yun Long1