Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 142-150.doi: 10.24920/003991
硒蛋白脱碘酶的生物学功能及其在骨性关节炎患者中的表达
任晓梅1,张立2,辛宝1,刘启玲3,钱文文1,张荣强3,*( )
)
- 1陕西中医药大学公共卫生学院营养与食品卫生学教研室,陕西咸阳 712046
2青岛大学医学院附属烟台毓璜顶医院临床营养科,山东烟台 264000
3陕西中医药大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学教研室,陕西咸阳 712046
-
收稿日期:2021-09-06接受日期:2022-04-08出版日期:2022-06-30发布日期:2022-05-30 -
通讯作者:张荣强 E-mail:zhangrqxianyang@163.com
Biological Functions of Selenoprotein Iodothyronine Deiodinase and its Expression in Osteoarthritis
Xiaomei Ren1,Li Zhang2,Bao Xin1,Qiling Liu3,Wenwen Qian1,Rongqiang Zhang3,*( )
)
- 1Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
2Department of Clinical Nutrition, The Affiliated Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital of Qingdao University Medical College, Yantai, Shandong 264000, China
3Department of Epidemiology and Medical Statistics, School of Public Health, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
-
Received:2021-09-06Accepted:2022-04-08Published:2022-06-30Online:2022-05-30 -
Contact:Rongqiang Zhang E-mail:zhangrqxianyang@163.com
摘要:
目的 骨关节炎(osteoarthritis,OA)是一种常见的关节疾病,老年人尤其高发。碘甲状腺原氨酸脱碘酶(iodothyronine deiodinases,DIOs)作为一种重要的硒蛋白,在骨和关节疾病中发挥着关键作用。本研究旨在利用生物信息学方法探讨DIOs在OA发病机制中的作用。
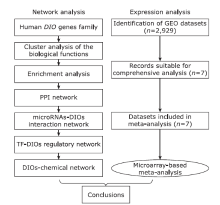
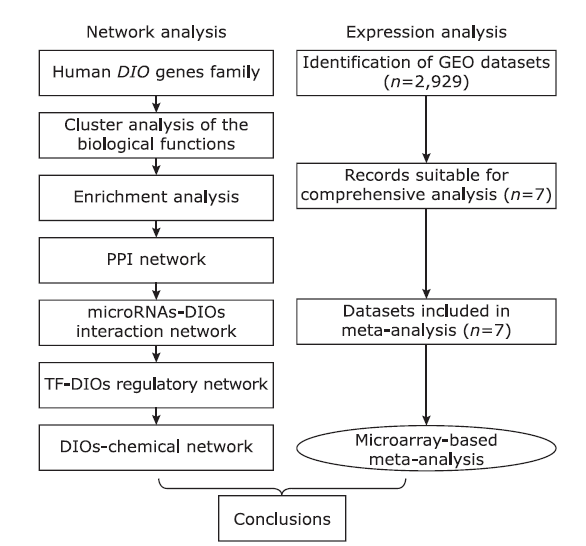
方法 通过对NCBI的GEO数据库中与OA相关的芯片数据进行数据挖掘,利用GenCLip 3.0,DAVID,STRING,Cytoscape和Network Analyst等工具分析DIOs的生物学功能,并用Review Manager5.3对数据进行Meta分析,研究DIOs在正常人和骨性关节炎患者中的表达。
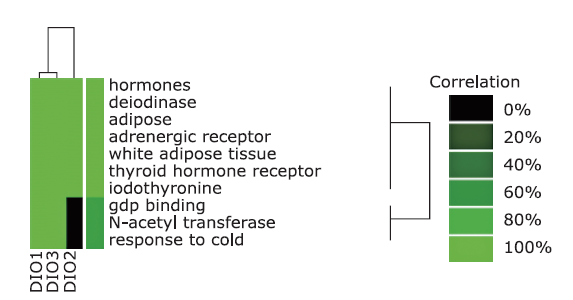
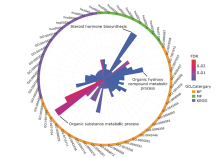
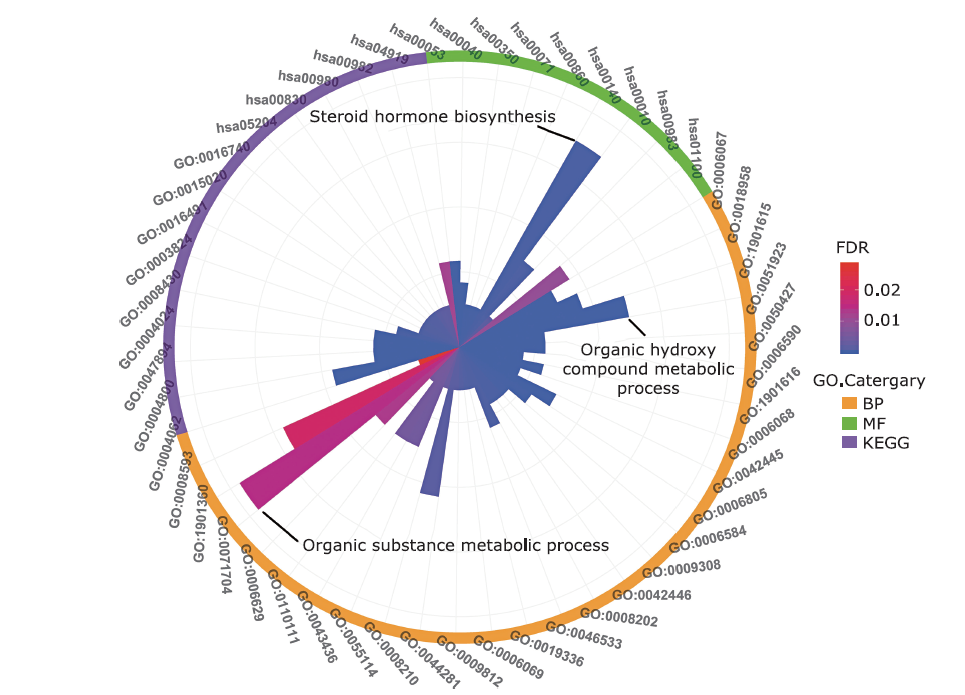
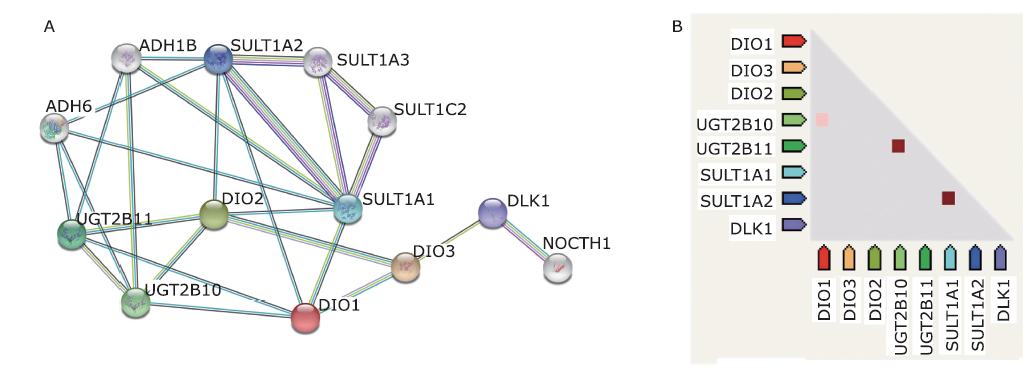
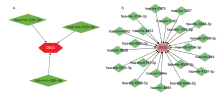
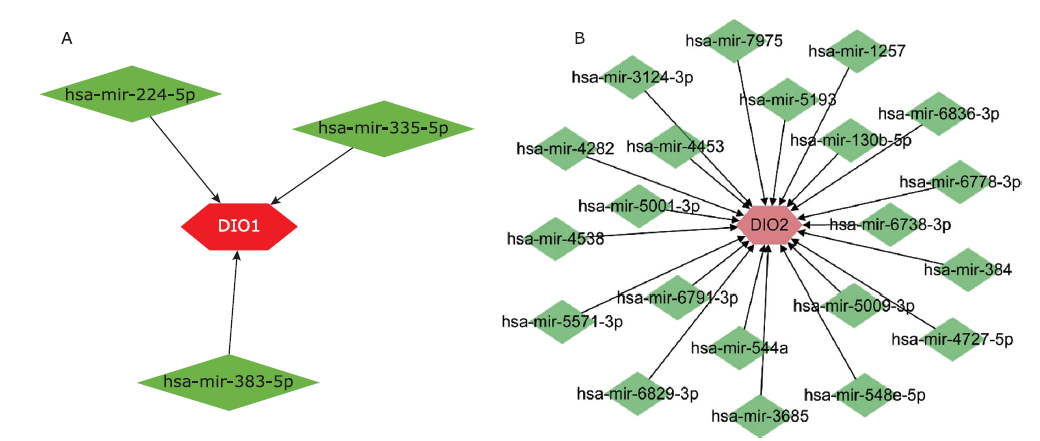
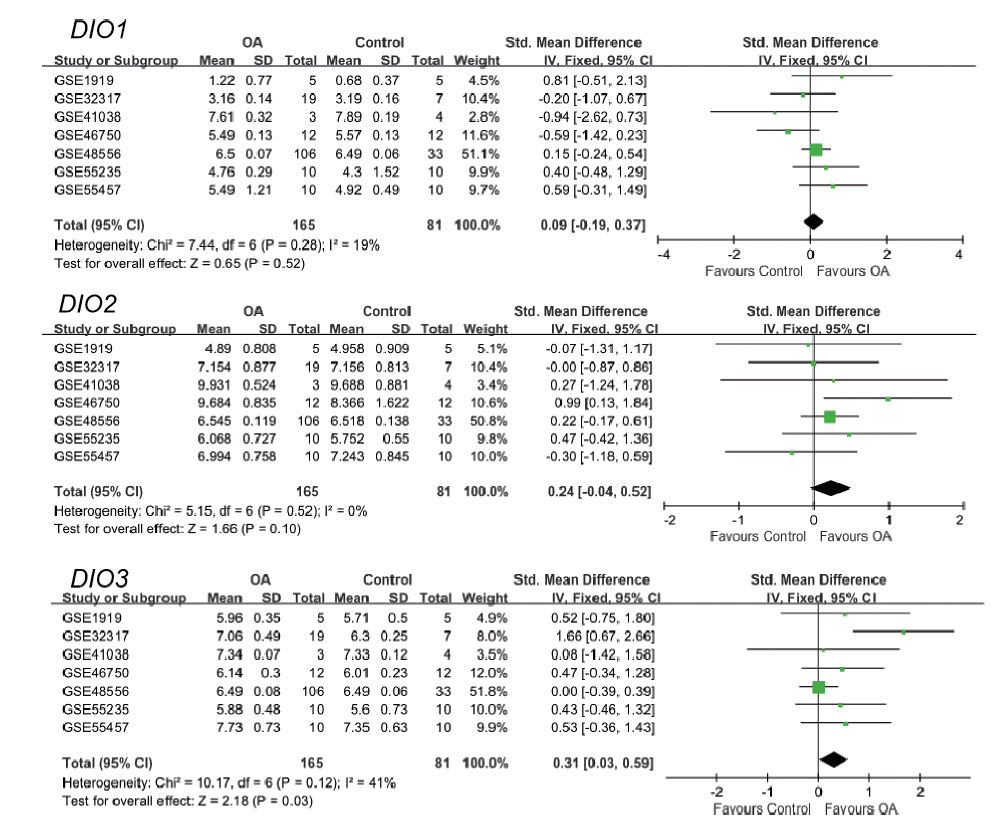
结果 聚类分析显示:DIOs的功能与甲状腺激素受体和碘甲状腺原氨酸有关。GO分析显示:DIOs主要参与乙醇代谢和含酚化合物代谢等生物过程,还与外源生物的细胞色素P450代谢和甲状腺激素信号传导有关。SULT1A1是PPI网络的核心节点。miRNAs和甲状腺激素与DIO1和DIO2存在交互作用。Meta分析显示:DIO3的表达在OA患者中显著上调(P <0.05)。
结论 DIOs的主要生物学功能与甲状腺激素的调节密切相关,而DIO3的上调表达可能在OA的发生中发挥关键作用。
引用本文
Xiaomei Ren, Li Zhang, Bao Xin, Qiling Liu, Wenwen Qian, Rongqiang Zhang. Biological Functions of Selenoprotein Iodothyronine Deiodinase and its Expression in Osteoarthritis[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(2): 142-150.
"
| Category | GO term ID | Biological function | Gene number | FDR value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0006067 | Ethanol metabolism process | 5 | 3.30×10-9 |
| GO:0018958 | Phenol-containing compound metabolic process | 6 | 4.10×10-9 | |
| GO:1901615 | Organic hydroxy compound metabolic process | 8 | 1.79×10-8 | |
| GO:0051923 | Sulfation | 4 | 1.32×10-7 | |
| GO:0050427 | 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphosulfate metabolic process | 4 | 3.72×10-7 | |
| GO:0006590 | Thyroid hormone generation | 3 | 8.60×10-6 | |
| MF | GO:0004062 | Aryl sulfotransferase activity | 4 | 1.27×10-8 |
| GO:0004800 | Thyroxine 5’-deiodinase activity | 3 | 1.37×10-7 | |
| GO:0047894 | Flavonol 3-sulfotransferase activity | 2 | 4.88×10-5 | |
| GO:0004024 | Alcohol dehydrogenase activity, zinc-dependent | 2 | 1.10×10-4 | |
| GO:0008430 | Selenium binding | 2 | 1.30×10-4 | |
| GO:0003824 | Catalytic activity | 11 | 3.00×10-4 | |
| KEGG pathway | hsa05204 | Chemical carcinogenesis | 6 | 1.65×10-10 |
| hsa00830 | Retinol metabolism | 4 | 9.05×10-7 | |
| hsa00980 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | 4 | 9.05×10-7 | |
| hsa00982 | Drug metabolism by cytochrome P450 | 4 | 9.05×10-7 | |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 3 | 2.60×10-4 | |
| hsa00053 | Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 2 | 6.00×10-4 |
| 1. |
Ogden C, Carroll M, Lawman H, et al. Trends in obesity prevalence among children and adolescents in the United States, 1988-1994 through 2013-2014. JAMA 2016; 315(21):2292-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.6361.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.6361 |
| 2. |
Mac J, Kan H, Chiu K, et al. Antiobesity medication use among overweight and obese adults in the United States: 2015-2018. Endocr Pract 2021; 27(11):1139-48. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.07.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.07.004 |
| 3. |
Berenbaum F, Walker C. Osteoarthritis and inflammation: a serious disease with overlapping phenotypic patterns. Postgrad Med 2020; 132(4):377-84. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1730669.
doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1730669 pmid: 32100608 |
| 4. |
Safiri S, Kolahi A, Smith E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79(6):819-28. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216515.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216515 |
| 5. |
Xiao S, Chen L. The emerging landscape of nanotheranostic-based diagnosis and therapy for osteoarthritis. J Control Release 2020; 328:817-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.11.007.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.11.007 |
| 6. |
Geyer M, Schönfeld C. Novel insights into the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2018; 14(2):98-107. doi: 10.2174/1573397113666170807122312.
doi: 10.2174/1573397113666170807122312 pmid: 28782470 |
| 7. |
Labunskyy V, Hatfield D, Gladyshev V. Selenoproteins: molecular pathways and physiological roles. Physiol Rev 2014; 94(3):739-77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00039.2013.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00039.2013 |
| 8. |
Bianco A, Kim B. Deiodinases: implications of the local control of thyroid hormone action. J Clin Invest 2006; 116(10):2571-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI29812.
doi: 10.1172/JCI29812 |
| 9. |
Bomer N, Hollander W, Ramos Y, et al. Underlying molecular mechanisms of DIO 2 susceptibility in symptomatic osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74(8):1571-9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204739.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204739 pmid: 24695009 |
| 10. |
Bianco A, Kim B. Pathophysiological relevance of deiodinase polymorphism. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2018; 25(5):341-6. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000428.
doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000428 |
| 11. |
Hernandez A, Stohn J. The type 3 deiodinase: epigenetic control of brain thyroid hormone action and neurological function. Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19(6):1804. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061804.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19061804 |
| 12. |
Morimura T, Tsunekawa K, Kasahara T, et al. Expression of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in human osteoblast is stimulated by thyrotropin. Endocrinology 2005; 146(4):2077-84. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1432.
doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1432 pmid: 15650076 |
| 13. |
Sakane Y, Kanamoto N, Yamauchi I, et al. Regulation of type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase by LXRα. PLoS One 2017;12(6): e0179213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179213.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179213 |
| 14. |
Jiao X, Sherman BT, Huang da W, et al. DAVID-WS: a stateful web service to facilitate gene/protein list analysis. Bioinformatics 2012; 28(13):1805-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts251.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts251 |
| 15. |
Szklarczyk D, Gable A, Lyon D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 2019; 47(D1):D607-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1131.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1131 |
| 16. |
Holmås S, Puig RR, Acencio ML, et al. The Cytoscape BioGateway App: explorative network building from the BioGateway triple store. Bioinformatics 2019; 36(6):1966-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz835.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz835 |
| 17. |
Sondag G, Haqqi T. The role of microRNAs and their targets in osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2016; 18(8):56. doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0604-x.
doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0604-x |
| 18. |
Zhou G, Soufan O, Ewald J, et al. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2019; 47(W1):W234-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz240.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz240 |
| 19. |
Chaudhuri K, Chatterjee R. MicroRNA detection and target prediction: integration of computational and experimental approaches. DNA Cell Biol 2007; 26(5):321-37. doi: 10.1089/dna.2006.0549.
doi: 10.1089/dna.2006.0549 pmid: 17504028 |
| 20. |
Sobhan M, Mehdinejad M, Jamaladini M, et al. Association between aspartic acid repeat polymorphism of the asporin gene and risk of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2017; 51(5):409-15. doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2017.08.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2017.08.001 |
| 21. |
Ungethuem U, Haeupl T, Witt H, et al. Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics 2010; 42A(4):267-82. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2010.
doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2010 pmid: 20858714 |
| 22. |
Wang Q, Rozelle AL, Lepus CM, et al. Identification of a central role for complement in osteoarthritis. Nat Med 2011; 17(12):1674-9. doi: 10.1038/nm.2543.
doi: 10.1038/nm.2543 |
| 23. |
Thomas G, Duan R, Pettit A, et al. Expression profiling in spondyloarthropathy synovial biopsies highlights changes in expression of inflammatory genes in conjunction with tissue remodelling genes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2013; 14:354. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-354.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-354 |
| 24. |
Lambert C, Dubuc J, Montell E, et al. Gene expression pattern of cells from inflamed and normal areas of osteoarthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014; 66(4):960-8. doi: 10.1002/art.38315.
doi: 10.1002/art.38315 |
| 25. |
Ramos YF, Bos SD, Lakenberg N, et al. Genes expressed in blood link osteoarthritis with apoptotic pathways. Ann Rheum Dis 2014; 73(10):1844-53. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203405.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203405 |
| 26. |
Woetzel D, Huber R, Kupfer P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther 2014; 16(2):R84. doi: 10.1186/ar4526.
doi: 10.1186/ar4526 |
| 27. | Ma H, Wu W, Yang X, et al. Genetic effects of common polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha gene on osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8(8):13446-54. |
| 28. |
Köhrle J. Selenium and the thyroid. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2015; 22(5):392-401. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000190.
doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000190 pmid: 26313901 |
| 29. |
Bianco AC, da Conceição RR. The deiodinase trio and thyroid hormone signaling. Methods Mol Biol 2018; 1801:67-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7902-8_8.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7902-8_8 |
| 30. |
Dubin RL, Hall CM, Pileri CL, et al. Thermostable (SULT1A1) and thermolabile (SULT1A3) phenol sulfotransferases in human osteosarcoma and osteoblast cells. Bone 2001; 28(6):617-24. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00463-x.
doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00463-x |
| 31. |
Tong Z, Li H, Goljer I, et al. In vitro glucuronidation of thyroxine and triiodothyronine by liver microsomes and recombinant human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos 2007; 35(12):2203-10. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.016972.
doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.016972 |
| 32. |
Endisha H, Rockel J, Jurisica I, et al. The complex landscape of microRNAs in articular cartilage: biology, pathology, and therapeutic targets. JCI Insight 2018; 3(17):e121630. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121630.
doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121630 |
| 33. |
Zhang P, Gao G, Zhou Z, et al. microRNA-130b downregulation potentiates chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting SOX9. Braz J Med Biol Res 2021; 54(4): e10345. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010345.
doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010345 |
| 34. |
Zhang W, Cheng P, Hu W, et al. Correction: inhibition of microRNA-384-5p alleviates osteoarthritis through its effects on inhibiting apoptosis of cartilage cells via the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting SOX9. Cancer Gene Ther 2020; 27(10-11):836-7. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0202-y.
doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0202-y |
| 35. |
Zhang L, Sui C, Zhang Y, et al. Knockdown of hsa_circ_0134111 alleviates the symptom of osteoarthritis via sponging microRNA-224-5p. Cell Cycle 2021; 20(11):1052-66. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1919838.
doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1919838 |
| 36. |
Zhang RK, Li GW, Jiang D, et al. Transcription factors analysis of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis based on gene expression profiles. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2018; 31(2):165-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.02.014
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.02.014 |
| 37. |
Yi P, Xu X, Yao J, et al. Analysis of mRNA expression and DNA methylation datasets according to the genomic distribution of CpG sites in osteoarthritis. Front Genet 2021; 12:618803. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.618803.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.618803 |
| 38. |
Luobu Z, Wang L, Jiang D, et al. CircSCAPER contributes to IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis in vitro via miR-140-3p/EZH2 axis. Bone Joint Res 2022; 11(2):61-72. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.112.BJR-2020-0482.R2.
doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.112.BJR-2020-0482.R2 |
| 39. |
Wang Z, Ni S, Zhang H, et al. Silencing SGK1 alleviates osteoarthritis through epigenetic regulation of CREB1 and ABCA1 expression. Life Sci 2021; 268: 118733. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118733.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118733 |
| 40. |
Nagase H, Nagasawa Y, Tachida Y, et al. Deiodinase 2 upregulation demonstrated in osteoarthritis patients cartilage causes cartilage destruction in tissue-specific transgenic rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21(3):514-23. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.12.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.12.013 |
| 41. |
Meulenbelt I, Bos SD, Chapman K, et al. Meta-analyses of genes modulating intracellular T3 bio-availability reveal a possible role for the DIO3 gene in osteoarthritis susceptibility. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70(1):164-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.133660.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.133660 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|