Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 159-162.doi: 10.24920/004208
• Case Report • Previous Articles
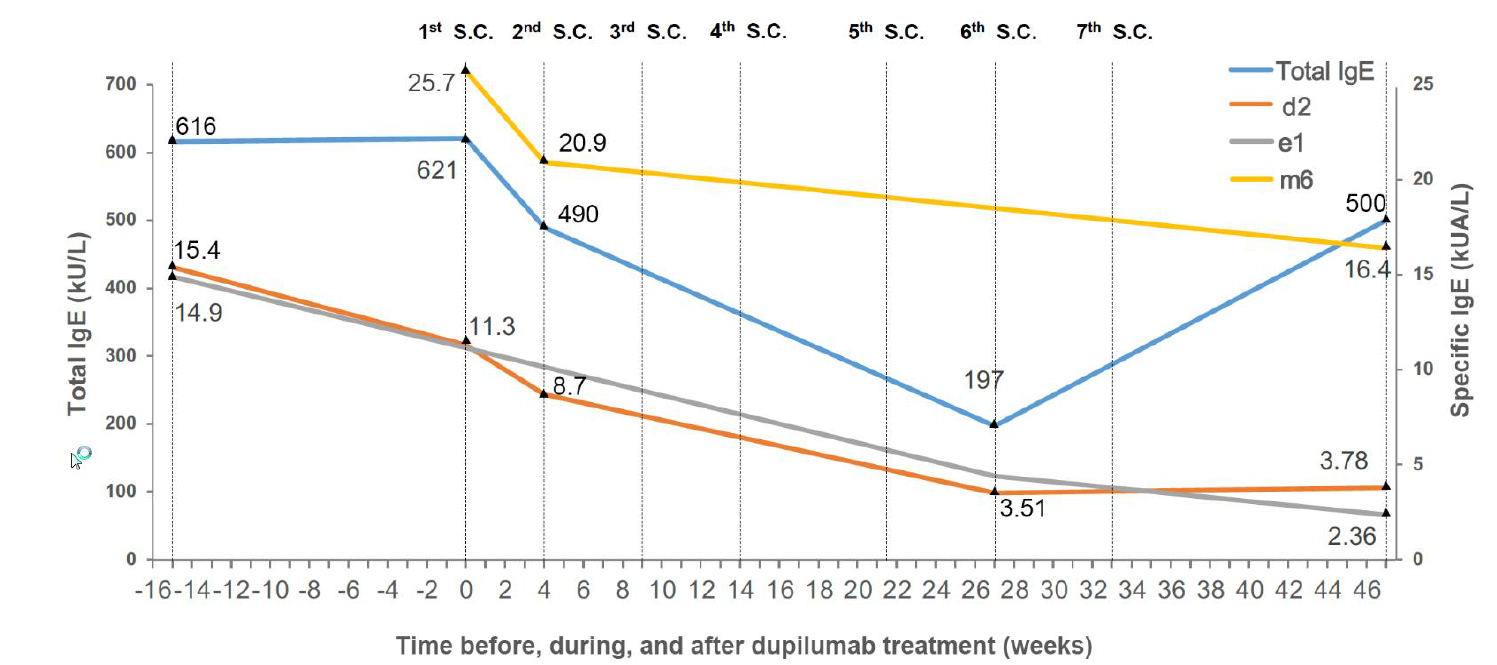
Dupilumab for Treatment of Food-Dependent, Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: Report of One Case
Li-Ping Zhu, Rui Tang, Qing Wang, Hong Li*( )
)
- Allergy Department, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2023-01-28Accepted:2023-04-24Published:2023-06-30Online:2023-05-18 -
Contact:*Hong Li, E-mail:lihong@pumch.cn
Cite this article
Li-Ping Zhu, Rui Tang, Qing Wang, Hong Li. Dupilumab for Treatment of Food-Dependent, Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: Report of One Case[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(2): 159-162.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
Schwartz LB, Delgado L, Craig T, et al. Exercise-induced hypersensitivity syndromes in recreational and competitive athletes: a PRACTALL consensus report (what the general practitioner should know about sports and allergy). Allergy 2008 ; 63(8): 953-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01802.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01802.x |
| [2] |
Manabe T, Oku N, Aihara Y. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis among junior high school students: a 14-year epidemiological comparison. Allergol Int 2015 ; 64(3): 285-6. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.01.007.
doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.01.007 |
| [3] |
Muñoz-Bellido FJ, Moreno E, Dávila I. Dupilumab: A review of present indications and off-label uses. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2022; 32(2): 97-115. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0682.
doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0682 |
| [4] |
Otani T, Iwamoto H, Horimasu Y, et al. Effect of dupilumab in a patient with severe asthma complicated with recurrent anaphylaxis: a case report. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2023 ; 33(3). doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0840.
doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0840 |
| [5] |
Cardona V, Ansotegui IJ, Ebisawa M, et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ J 2020 ; 13(10): 100472. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100472.
doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100472 |
| [6] |
Brockow K, Kneissl D, Valentini L, et al. Using a gluten oral food challenge protocol to improve diagnosis of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015 ; 135(4): 977-84.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.024 |
| [7] |
Hanakawa Y, Tohyama M, Shirakata Y, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: a case related to the amount of food allergen ingested. Br J Dermatol 1998 ; 138(5): 898-900. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.02254.x.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.02254.x |
| [8] |
Jiang NN, Wen LP, Li H, et al. A New Diagnostic Criteria of Wheat-Dependent, Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 2018 ; 131(17): 2049-54. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.239304.
doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.239304 |
| [9] |
Jiang N, Yin J, Wen L, et al. Characteristics of anaphylaxis in 907 chinese patients referred to a tertiary allergy center: a retrospective study of 1,952 episodes. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2016; 8(4): 353-61. doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.4.353.
doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.4.353 |
| [10] |
Bian S, Zhang P, Li L, et al. Anaphylaxis associated with allergen specific immunotherapy, omalizumab, and dupilumab: a real world study based on the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 767999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.767999.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.767999 |
| [11] |
Li L, Wang Z, Cui L, et al. Anaphylactic risk related to omalizumab, benralizumab, reslizumab, mepolizumab, and dupilumab. Clin Transl Allergy 2021 ; 11(4): e12038. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12038.
doi: 10.1002/clt2.12038 |
| [12] |
Niggemann B, Beyer K. Factors augmenting allergic reactions. Allergy 2014 ; 69(12): 1582-7. doi: 10.1111/all.12532.
doi: 10.1111/all.12532 |
| [13] |
Yamauchi T, Sasaki S, Lee ES, et al. Dupilumab treatment ameliorates clinical and hematological symptoms, including blood eosinophilia, in patients with atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol 2021 ; 60(2): 190-5. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15183.
doi: 10.1111/ijd.15183 |
| [14] |
Burton OT, Darling AR, Zhou JS, et al. Direct effects of IL-4 on mast cells drive their intestinal expansion and increase susceptibility to anaphylaxis in a murine model of food allergy. Mucosal Immunol 2013 ; 6(4): 740-50. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.112.
doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.112 |
| [15] |
Dispenza MC, Krier-Burris RA, Chhiba KD, et al. Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibition effectively protects against human IgE-mediated anaphylaxis. J Clin Invest 2020 ; 130(9): 4759-70. doi: 10.1172/JCI138448.
doi: 10.1172/JCI138448 |
| [16] |
Tanno LK, Simons FER, Sanchez-Borges M, et al. Applying prevention concepts to anaphylaxis: A call for worldwide availability of adrenaline auto-injectors. Clin Exp Allergy 2017 ; 47(9): 1108-14. doi: 10.1111/cea.12973.
doi: 10.1111/cea.12973 |
| [1] | Xiang-yi Kong, Yi Yang*, Jian Guan, Ren-zhi Wang. Probiotics’ Preventive Effect on Pediatric Food Allergy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(3): 144-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|