Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 239-247.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.048
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental Study on the Protection of Agrimony Extracts from Different Extracting Methods against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury△
Zhu Huiyuan1, 3, Bie Yulong1, Wang Jiang1, Gao Jing2, Yang Bingyue2, Wan Haitong3, *( )
)
- 1Department of Basic Medicine, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
2Department of Pharmacy, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
3Institute of Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, China
-
Received:2017-03-16Published:2017-12-30Online:2017-12-30 -
Contact:Wan Haitong E-mail:wanhaitong@zcmu.edu.cn
Cite this article
Zhu Huiyuan, Bie Yulong, Wang Jiang, Gao Jing, Yang Bingyue, Wan Haitong. Experimental Study on the Protection of Agrimony Extracts from Different Extracting Methods against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 239-247.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Primer sequences of rat's genes: P53, Hsp70 and GAPDH"
| Primer | Exon/cDNA | Fragment size (bp) | Sequence (5’- 3’) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P53 | P53 | 158 | Forward | GGCTCCGACTATACCACTATCCACT |
| Reverse | GGACAGGCACAAACACGAACCTCA | |||
| Hsp70 | Hsp70 | 74 | Forward | GCAGTGACCTTTCCTGTCCATTC |
| Reverse | GTGCTGCTGTTGACACTGTTGCTAT | |||
| GAPDH | GAPDH | 105 | Forward | GAATTCCCAGTAAGTGCGGGTCATA |
| Reverse | CGAGGGCCTCACTAAACCATC |
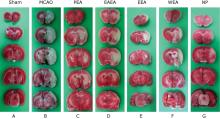
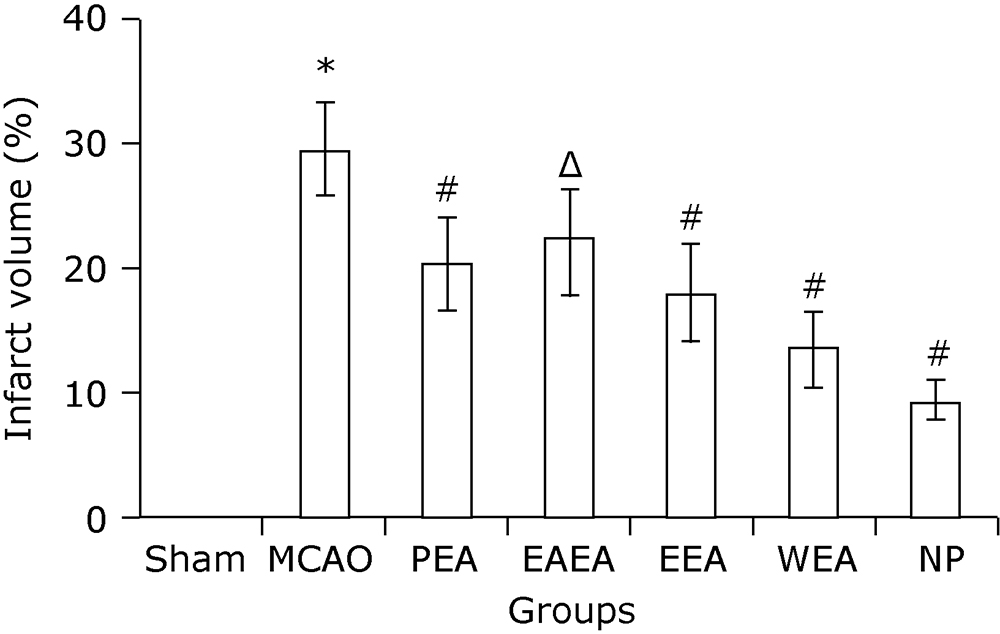
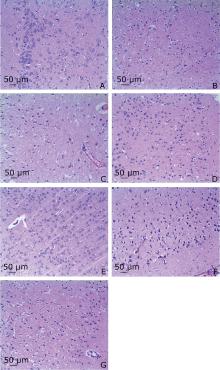
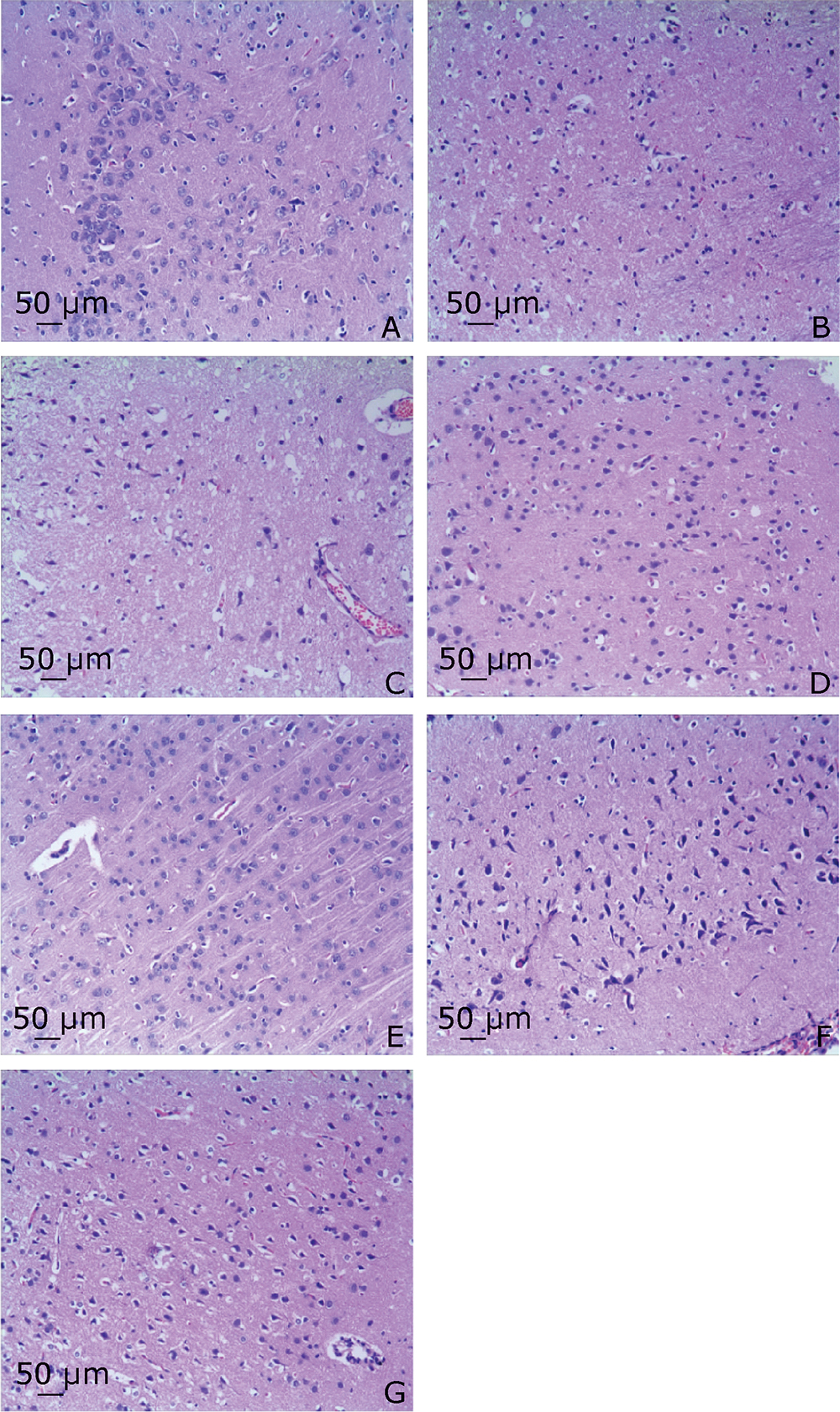
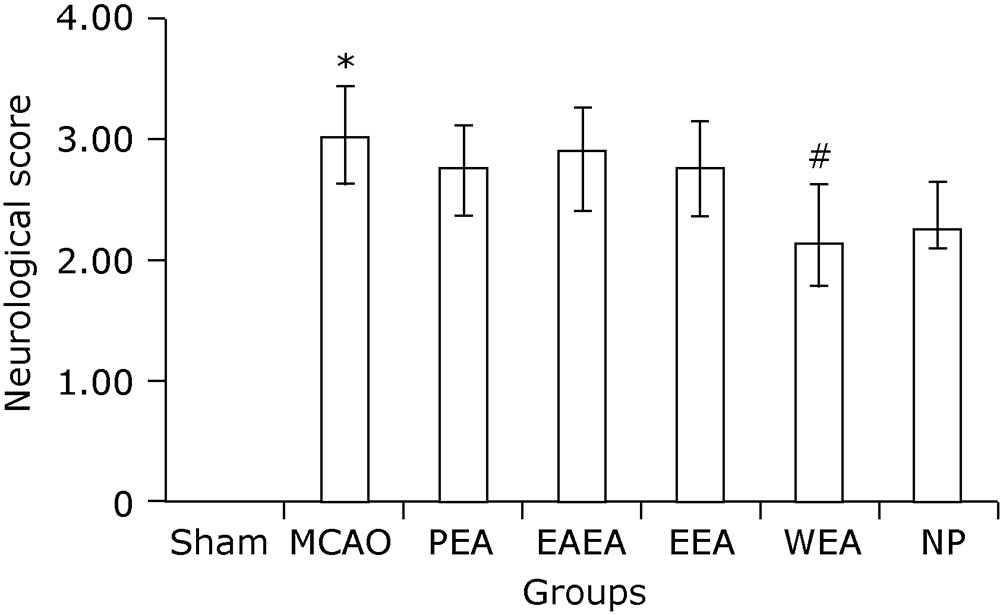
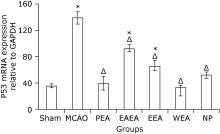
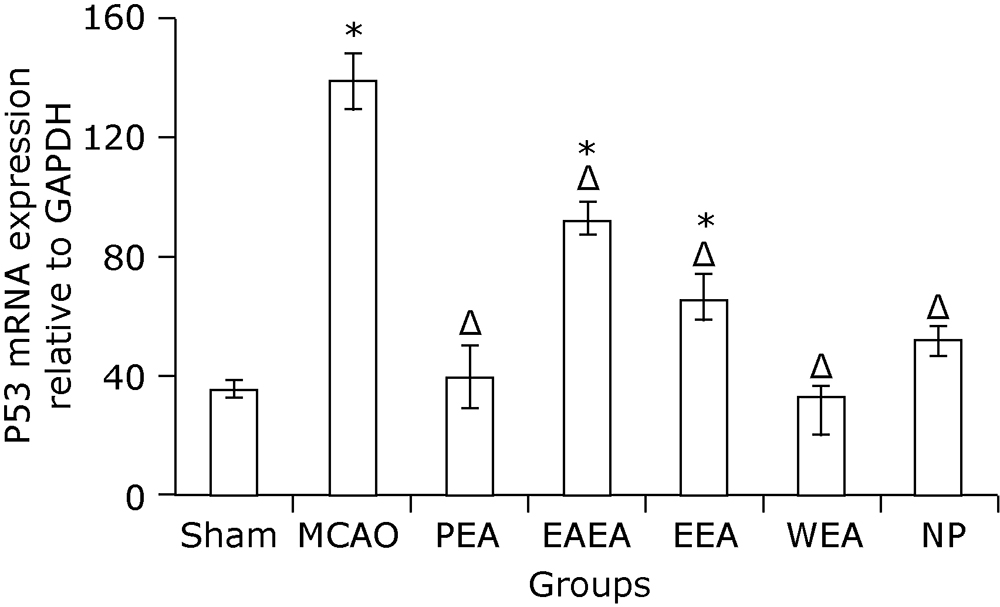
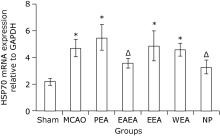
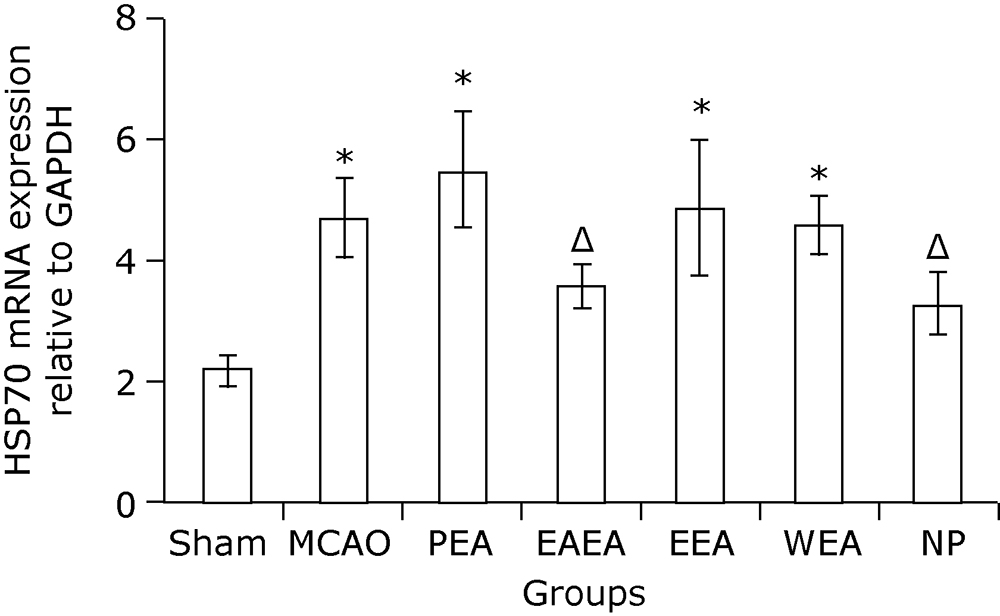
Figure 1.
Gross specimen observation on cerebral infarction of MCAO mice with and without treatment (TTC staining). A. Sham-operated group; B. MCAO mice without treatment; C. PEA, MCAO mice treated with petroleum ether extract of Agrimonia pilosa; D. EAEA, MCAO mice treated with ethyl acetate extract of Agrimonia pilosa; E. EEA, MCAO mice treated with ethanol extract of Agrimonia pilosa; F. WEA, MCAO mice treated with water extract of Agrimonia pilosa; G. NP, MCAO mice treated with nimodipine."

Table 2
Na+/K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activity of the experimental groups (n=8)"
| Group | Na+/K+-ATPase (U/mg prot/hour) | Ca2+-ATPase (U/mg prot/hour) |
|---|---|---|
| Sham | 10.25±1.28 | 4.45±0.39 |
| MCAO | 3.67±0.48* | 1.28±0.26* |
| PEA | 4.42±1.25 | 2.64±0.44 |
| EAEA | 6.20±1.09 | 3.86±1.06△ |
| EEA | 5.48±0.93 | 1.21±0.53 |
| WEA | 7.56±0.85△ | 3.59±0.22# |
| NP | 7.59±1.02△ | 3.23±1.03# |
| 1. | Gao HJ, Liu PF, Li PW, Huang ZY, Yu FB, Lei T, et al. Ligustrazine monomer against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res 2015; 10: 832-40. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.156991. |
| 2. | Fisher M.New approaches to neuroprotective drug development. Stroke 2011; 42: S24-27. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA. 110.592394. |
| 3. | Langhorne P, Bernhardt J, Kwakkel G.Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 2011;377: 1693-702. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60325-5. |
| 4. | Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA.Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003; 4:399-415. doi: 10.1038/nrn1106. |
| 5. | Ivanova D, Vankova D, Nashar M.Agrimonia eupatoria tea consumption in relation to markers of inflammation, oxidative status and lipid metabolism in healthy subjects. Arch Physiol Biochem 2013; 119: 32-7. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2012.729844. |
| 6. | Nho KJ, Chun JM, Kim HK.Agrimonia pilosa ethanol extract induces apoptotic cell death in HepG2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2011; 138: 358-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.008. |
| 7. | Pan Y, Liu HX, Zhuang YL, Ding L, Chen LX. Qiu F. Studies on isolation and identification of flavonoids in herbs of Agrimonia pilosa. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008; 33: 2925-8. Chinese. |
| 8. | Correia HS, Batista MT, Dinis TC.The activity of an extract and fraction of Agrimonia eupatoria L. against reactive species. Biofactors 2007; 29:91-104. doi: 10.1002/biof.552029209. |
| 9. | Seo UM, Nguyen DH, Zhao BT, Min BS, Woo MH.Flavanonol glucosides from the aerial parts of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb and their acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects. Carbohydr Res 2017; 445:75-9. doi: 10.1016/j.carres. 2017.04.014. |
| 10. | Zhu L, Chen J, Tan J, Liu X, Wang B.Flavonoids from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb: Free Radical Scavenging and DNA Oxidative Damage Protection Activities and Analysis of Bioactivity-Structure Relationship Based on Molecular and Electronic Structures. Molecules 2017; 22: 195. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030195. |
| 11. | Kim SB, Hwang SH, Suh HW, Lim SS.Phytochemical Analysis of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb, Its Antioxidant Activity and AldoseReductase Inhibitory Potential. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 379. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020379. |
| 12. | Liu X, Zhu L, Tan J, Zhou X, Xiao L, Yang X, et al.Glucosidase inhibitory activity and antioxidant activity of flavonoid compound and triterpenoid compound from Agrimonia Pilosa Ledeb. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14:12. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-12. |
| 13. | Wang J, Chao F, Han F, Zhang G, Xi Q, Li J, et al.PET demonstrates functional recovery after transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cells in a rat model of cerebral ischemic injury. J Nucl Med 2013; 54: 785-92. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.111112. |
| 14. | Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R.Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989; 20: 84-91. doi: 10.1161/01.str. 20.1.84. |
| 15. | Wang Z, Song F, Li J, Zhang Y, Ye Y, Yang J, et al.PET Demonstrates Functional Recovery after Treatment by Danhong Injection in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 430757. doi: 10.1155/2014/430757. |
| 16. | Sun L, Jin Y, Dong L, Sumi R, Jahan R, Li Z.The neuroprotective effects of Coccomyxa gloeobotrydiformis on the ischemic stroke in a rat model. Int J Biol Sci 2013; 9: 811-17. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6734. |
| 17. | Wan L, Cheng Y, Luo Z, Guo H, Zhao W, Gu Q, et al.Neuroprotection, learning and memory improvement of a standardized extract from Renshen Shouwu against neuronal injury and vascular dementia in rats with brain ischemia. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 165: 118-26. doi: 10.1016/ j.jep.2015.02.027. |
| 18. | Guo Z, Cao G, Yang H, Zhou H, Li L, Cao Z, et al.A combination of four active compounds alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in correlation with inhibition of autophagy and modulation of AMPK/mTOR and JNK pathways. J Neurosci Res 2014; 92: 1295-306. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23400. |
| 19. | Chen L, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Dang X, Xie R, Li Z, et al.Protective effect of Sheng-Nao-Kang decoction on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 151: 228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.015. |
| 20. | Liu Y, Ling Y, Hu W, Xie L, Yu L, Qian X, et al.The herb medicine formula "chong lou fu fang" increases the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents and down-regulates the expression of chemotherapeutic agent resistance-related genes in human gastric cancer cells in vitro. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; 2011: 834231. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep175. |
| 21. | Chaturvedi RK, Beal MF.Mitochondrial approaches for neuroprotection. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2008; 1147: 395-412. doi: 10.1196/annals.1427.027. |
| 22. | Ying W.NAD+ and NADH in brain functions, brain diseases and brain aging. Front Biosci 2007; 12: 1863-88. doi: 10.2741/2194. |
| 23. | Liu D, Gharavi R, Pitta M, Gleichmann M, Mattson MP.Nicotinamide prevents NAD+ depletion and protects neurons against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia: NAD+ consumption by SIRT1 may endanger energetically compromised neurons. Neuromolecular Med 2009; 11: 28-42. doi: 10.1007/s12017-009-8058-1. |
| 24. | Chan PH.Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke. 1996; 27: 1124-29. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.27.6.1124. |
| 25. | Yamada J, Yoshimura S, Yamakawa H, Sawada M, Nakagawa M, Hara S, et al.Cell permeable ROS scavengers, Tiron and Tempol, rescue PC12 cell death caused by pyrogallol or hypoxia/reoxygenation. Neurosci Res 2003; 45:1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0168-0102(02)00196-7. |
| 26. | Song D, Xu J, Du T, Yan E, Hertz L,Walz W. Inhibition of brain swelling after ischemia-reperfusion by beta-adrenergic antagonists: correlation with increased K+ and decreased Ca2+ concentrations in extracellular fluid. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014: 873590. doi: 10.1155/2014/873590. |
| 27. | de Lores Arnaiz GR, Ordieres MG. Brain Na(+), K(+)-ATPase Activity In Aging and Disease. Int J Biomed Sci 2014; 10: 85-102. |
| 28. | Song T, Liu J, Tao X, Deng JG.Protection effect of atorvastatin in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats by blocking the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Genet Mol Res 2014; 13: 10632-42. doi: 10.4238/2014.December.18.5. |
| 29. | Christophe M, Nicolas S.Mitochondria: a target for neuroprotective interventions in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Curr Pharm Des 2006; 12: 739-57. doi: 10.2174/138161206775474242 . |
| 30. | Macmanus JP, Buchan AM, Hill IE, Rasquinha I, Preston E.Global-ischemia can cause DNA fragmentation indicative of apoptosis in rat brain. Neuroscience Letters 1993; 164: 89-92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90864-h. |
| 31. | Wang LY, Liu J, Li Y, Li B, Zhang YY, Jing ZW.Time-dependent variation of pathways and networks in a 24-hour window after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. BMC Syst Biol 2015; 9:11. doi: 10.1186/s12918-015-0152-4. |
| 32 | 32.Guo C, Yin Y, Duan J, Zhu Y, Yan J,Wei G. Neuroprotective effect and underlying mechanism of sodium danshensu [3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid from Radix and Rhizoma Salviae miltiorrhizae = Danshen] against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Phytomedicine 2015; 22: 283-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.12.001. |
| 33. | Nho KJ, Chun JM, Kim HK.Agrimonia pilosa ethanol extract induces apoptotic cell death in HepG2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2011; 138: 358-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jep. 2011.09.008. |
| 34. | Yang X, Zhang L, Jiang SQ, Gong PL, Zeng FD.Effect of dauricine on apoptosis and expression of apoptogenic protein after transient focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2009; 34: 78-83. |
| 35. | Tounai H, Hayakawa N, Kato H, Araki T.Immunohistochemical study on distribution of NF-kappaB and p53 in gerbil hippocampus after transient cerebral ischemia: effect of pitavastatin. Metab Brain Dis 2007; 22: 89-104. doi: 10.1007/s11011-006-9040-3. |
| 36. | Gu ZT, Li L, Wu F, Zhao P, Yang H, Liu YS.Heat stress induced apoptosis is triggered by transcription-independent p53, Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and the subsequent Bax mitochondrial translocation. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 11497. doi: 10.1038/srep11497. |
| 37. | Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O, Chittenden T, Pancoska P. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Molecular Cell 2003; 11: 577-90. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00050-9. |
| 38. | Gong JL, Zhu BM, Murshid A, Adachi H, Song B, Lee A.T Cell Activation by Heat Shock Protein 70 Vaccine Requires TLR Signaling and Scavenger Receptor Expressed by Endothelial Cells-1. J Immunol 2009; 183: 3092-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901235. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|