Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 218-227.doi: 10.24920/004214
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of Medication Rules of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Malaria Treatment Based on Data Mining
Wen-Long Guo1, *( ), Hui-Juan Jiang1, Yan-Rong Li2, Jin-Long Yang1
), Hui-Juan Jiang1, Yan-Rong Li2, Jin-Long Yang1
- 1Science Teaching Department, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Dingxi 743000, Gansu Province, China
2Medical Teaching Department, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Dingxi 743000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-13Accepted:2023-06-06Published:2023-09-30Online:2023-06-28 -
Contact:* E-mail:dxszgwl@163.com .
| Malaria remains a global public health problem and continues to spread worldwide. This paper analyzes the prescription for malaria by drug statistics, constructs complex networks and cluster analysis to get the core drugs for malaria, and applies the Apriori algorithm to analyze the association rules to get the core drug pairs and drug combinations for malaria. |
Cite this article
Wen-Long Guo, Hui-Juan Jiang, Yan-Rong Li, Jin-Long Yang. Analysis of Medication Rules of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Malaria Treatment Based on Data Mining[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(3): 218-227.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1.
Statistical results of the frequency of herbal use (top 40)"
| Medicine name | Chinese name | Frequency/times |
|---|---|---|
| Radix Glycyrrhizae | Gan cao (甘草) | 200 |
| Rhizoma Pinelliae | Ban xia (半夏) | 100 |
| Radix Bupleuri | Chai hu (柴胡) | 99 |
| Radix Dichroae | Chang shan (常山) | 99 |
| Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae | Chen pi (陈皮) | 94 |
| Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis | Hou po (厚朴) | 77 |
| Poria | Fu ling (茯苓) | 69 |
| Ginseng | Ren shen (人参) | 67 |
| Fructus Tsaoko | Cao guo (草果) | 64 |
| Radix Scutellariae | Huang qin (黄芩) | 63 |
| Rhizoma Atractylodis | Cang zhu (苍术) | 57 |
| Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae | Bai zhu (白术) | 57 |
| Cinnabaris | Zhu sha (朱砂) | 56 |
| Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride | Qing pi (青皮) | 55 |
| Semen Arecae | Bing lang (槟榔) | 55 |
| Cortex Cinnamomi | Rou gui (肉桂) | 51 |
| Rhizoma Anemarrhenae | Zhi mu (知母) | 48 |
| Radix Angelicae Sinensis | Dang gui (当归) | 47 |
| Fructus Mume | Wu mei (乌梅) | 46 |
| Realgar | Xiong huang (雄黄) | 41 |
| Rhizoma Chuanxiong | Chuan xiong (川芎) | 41 |
| Carapax Trionycis | Bie jia (鳖甲) | 37 |
| Cablin Potchouli | Huo xiang (藿香) | 36 |
| Radix Aucklandiae | Mu xiang (木香) | 36 |
| Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei | Da huang (大黄) | 30 |
| Radix Paeoniae Alba | Bai shao (白芍) | 30 |
| Moschus | She xiang (麝香) | 29 |
| Rhizoma Cimicifugae | Sheng ma (升麻) | 29 |
| Dried ginger | Gan jiang (干姜) | 28 |
| Folium Perillae | Zi su ye (紫苏叶) | 26 |
| Radix Aconiti Lateralis Praeparata | Fu zi (附子) | 26 |
| Rhizoma Zingiberis Recens | Sheng jiang (生姜) | 26 |
| Fructus Aurantii | Zhi ke (枳壳) | 25 |
| Rhizoma Et Radix Notopterygii | Qiang huo (羌活) | 25 |
| Arsenic | Pi shuang (砒霜) | 24 |
| Chinese date | Da zao (大枣) | 24 |
| Arsenlite | Pi shi (砒石) | 23 |
| Fructus Crotonis | Ba dou (巴豆) | 23 |
| Semen Persicae | Tao ren (桃仁) | 22 |
| Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae | Bei mu (贝母) | 20 |
Table 2.
Commonly used therapeutic Methods of 357 herbs"
| Therapeutic methods | Chinese term | Number of herbs | Therapeutic methods, n(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplementing | Bu xu (补虚) | 43 | 572(17.91) |
| Exterior-releasing | Jie biao (解表) | 26 | 373(11.68) |
| Heat-clearing | Qing re (清热) | 44 | 296(9.27) |
| Qi-rectifying | Li qi (理气) | 15 | 271(8.48) |
| Dampness-resolving | Hua shi (化湿) | 9 | 258(8.08) |
| Blood-invigorating and stasis-dissolving | Huo xue hua yu (活血化瘀) | 29 | 176(5.51) |
| Phlegm-dissolving and cough-panting-relieving | Hua tan zhi ke (化痰止咳) | 13 | 171(5.35) |
| Interior-warming | Wen li (温里) | 12 | 147(4.60) |
| Urination-promoting and dampness-percolating | Li shui qu shi (利水祛湿) | 20 | 125(3.91) |
| Emetic | Yong tu (涌吐) | 3 | 114(3.57) |
| Poison-attacking, insect-killing, and antipruritic | Gong du sha chong zhi yang (攻毒杀虫止痒) | 17 | 106(3.32) |
| Mind-calming | An shen (安神) | 15 | 86(2.69) |
| Purgative | Xie xia (泻下) | 13 | 83(2.60) |
| Detoxifying and muscle-activating | Ba du sheng ji (拔毒生肌) | 14 | 69(2.16) |
| Digestant | Xiao shi (消食) | 10 | 61(1.91) |
| Worm-expelling | Qu chong (驱虫) | 3 | 58(1.82) |
| Astringent | Shou se (收涩) | 5 | 57(1.78) |
| Wind-dampness- expelling | Qu feng shi (祛风湿) | 18 | 48(1.50) |
| Resuscitative | Kai qiao (开窍) | 5 | 45(1.41) |
| Liver-calming and wind-extinguishing | Ping gan xi feng (平肝息风) | 13 | 33(1.03) |
| Bleeding-stanching | Zhi xue (止血) | 9 | 14(0.44) |
| Others | 21 | 31(0.97) | |
| Total | 357 | 3194(100) |
Table 3.
Statistics of the properties, flavors, and meridian tropisms of 357 herbs in prescriptions for malaria, n (%)"
| Property | Number of herbs | Flavor | Number of herbs | Meridian tropism | Number of herbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warm | 100 (34) | Pungent | 135 (30) | Liver | 116 (21) |
| Natural | 62 (21) | Sweet | 114 (25) | Lung | 93 (17) |
| Cold | 54 (19) | Bitter | 109 (24) | Heart | 75 (13) |
| Slightly cold | 25 (9) | Salty | 36 (8) | Kidney | 67 (12) |
| Cool | 21 (7) | Sour | 25 (5) | Stomach | 67 (12) |
| Slightly warm | 14 (5) | Light | 12 (3) | Spleen | 63 (11) |
| Hot | 9 (3) | Slightly bitter | 11 (2) | Large intestine | 41 (7) |
| Extremely hot | 3 (1) | Astringent | 8 (2) | Bladder | 24 (4) |
| Extremely cold | 2 (1) | Slightly sweet | 5 (1) | Small intestine | 8 (1) |
| Extremely warm | 1 (0) | Sanjiao | 3 (1) | ||
| Total | 277 | 455 (100) | 557 (100) |
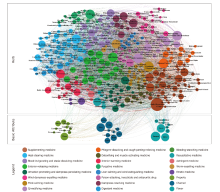
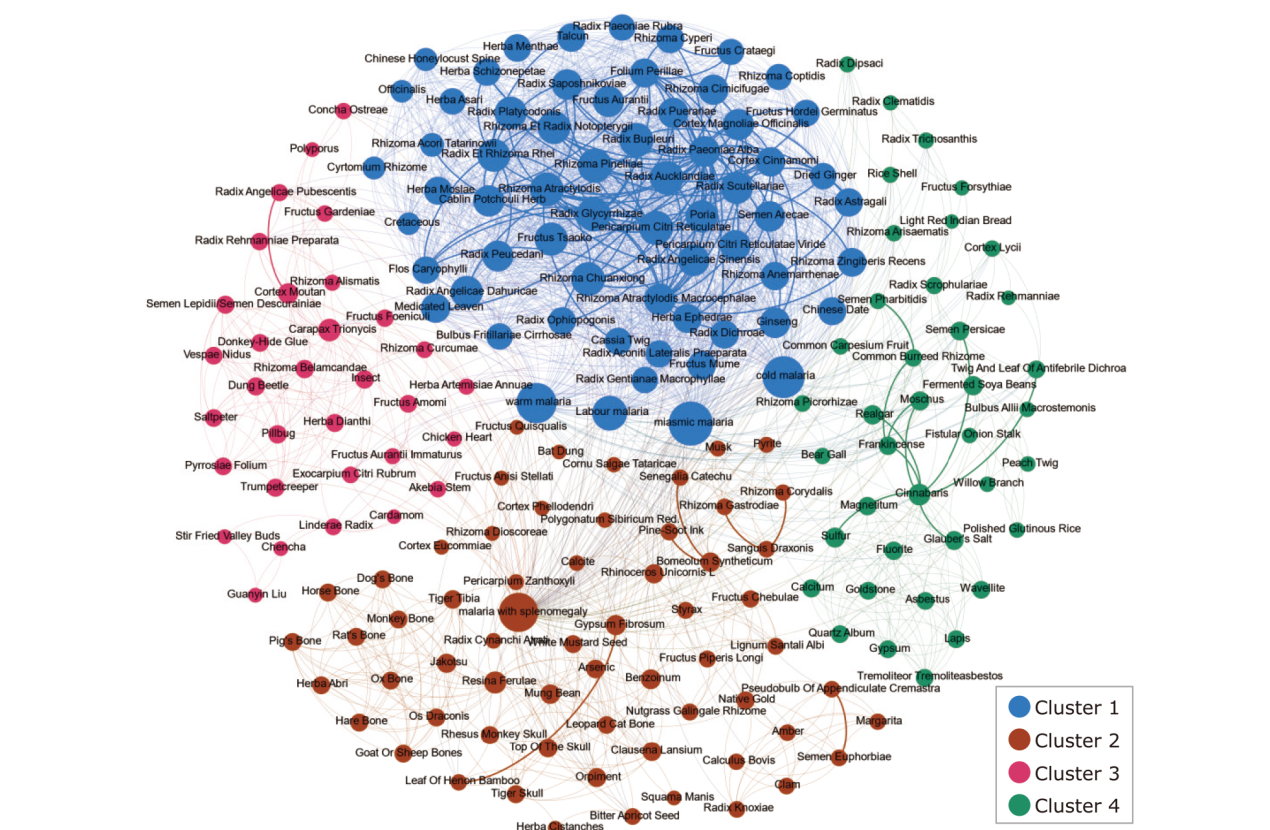
Figure 1
Complex network of herbs of the prescriptions for malaria in TCM. Each node in the herb area represents a herb, and the node size represents the number of drug citations. A larger node indicates more citations. The edge represents the formula’s typical citation relationship between the two drugs. A darker color of the side represents more citations, and different colors represent different drug classes. The basic attribute area represents the three essential attributes of herbs: property, flavor, and meridian tropism. The node size represents the number of drugs related to this attribute. A larger node represents more drugs belonging to this attribute. The legend area describes the classes and essential attributes of the herbs."

Table 4.
Information of cluster analysis for the complex network of herbs of the prescriptions for malaria in TCM"
| Cluster | Score (Density*#Nodes) | Nodes | Edges | Seed node |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.000 | 59 | 1417 | Ginseng (人参) |
| 2 | 9.033 | 61 | 277 | Resina Ferulae(阿魏) |
| 3 | 8.581 | 32 | 134 | Carapax Trionycis(鳖甲) |
| 4 | 8.579 | 39 | 173 | Radix Clematidis(威灵仙) |
Table 5.
Core herbs (n=61) for the prescriptions for malaria in TCM"
| ID | Herb name | ID | Herb name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 32 | Radix Angelicae Dahuricae (白芷) |
| 2 | Cinnabaris (朱砂) | 33 | Fructus Mume (乌梅) |
| 3 | Rhinoceros Unicornis L (犀角) | 34 | Cablin Potchouli (藿香) |
| 4 | Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (陈皮) | 35 | Radix Aconiti Lateralis Praeparata (附子) |
| 5 | Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏) | 36 | Flos Caryophylli (丁香) |
| 6 | Radix Aucklandiae (木香) | 37 | Rhizoma Cyperi (香附) |
| 7 | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡) | 38 | Radix Puerariae (葛根) |
| 8 | Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei (大黄) | 39 | Talcun |
| 9 | Cortex Cinnamomi (肉桂) | 40 | Rhizoma Zingiberis Recens (生姜) |
| 10 | Radix Scutellariae (黄芩) | 41 | Semen Persicae (桃仁) |
| 11 | Radix Dichroae (常山) | 42 | Radix Ophiopogonis (麦冬) |
| 12 | Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis (厚朴) | 43 | Radix Astragali (黄芪) |
| 13 | Radix Angelicae Sinensis (当归) | 44 | Folium Perillae (紫苏叶) |
| 14 | Ginseng (人参) | 45 | Radix Saposhnikoviae (防风) |
| 15 | Rhizoma Atractylodis (苍术) | 46 | Medicated Leaven (神曲) |
| 16 | Poria (茯苓) | 47 | Rhizoma Coptidis (黄连) |
| 17 | Moschus (麝香) | 48 | Herba Ephedrae (麻黄) |
| 18 | Carapax Trionycis (鳖甲) | 49 | Rhizoma Curcumae (莪术) |
| 19 | Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride (青皮) | 50 | Chinese date (大枣) |
| 20 | Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae (白术) | 51 | Cortex Moutan (丹皮) |
| 21 | Rhizoma Et Radix Notopterygii (羌活) | 52 | Bitter Apricot seed (杏仁) |
| 22 | Rhizoma Chuanxiong (川芎) | 53 | Fermented soya beans (豉) |
| 23 | Realgar (雄黄) | 54 | Cassia Twig (桂枝) |
| 24 | Semen Arecae (槟榔) | 55 | Gypsum Fibrosum (石膏) |
| 25 | Rhizoma Cimicifugae (升麻) | 56 | Akebia Stem (木桶) |
| 26 | Frankincense (乳香) | 57 | Common Burreed Rhizome (三棱) |
| 27 | Rhizoma Anemarrhenae (知母) | 58 | Herba Artemisiae Annuae (青蒿) |
| 28 | Radix Paeoniae Alba (白芍) | 59 | Linderae Radix (乌药) |
| 29 | Dried ginger (干姜) | 60 | Maire Sophora (黑豆) |
| 30 | Fructus Aurantii (枳壳) | 61 | Bomeolum Syntheticum (冰片) |
| 31 | Fructus Tsaoko (草果) |
Table 6.
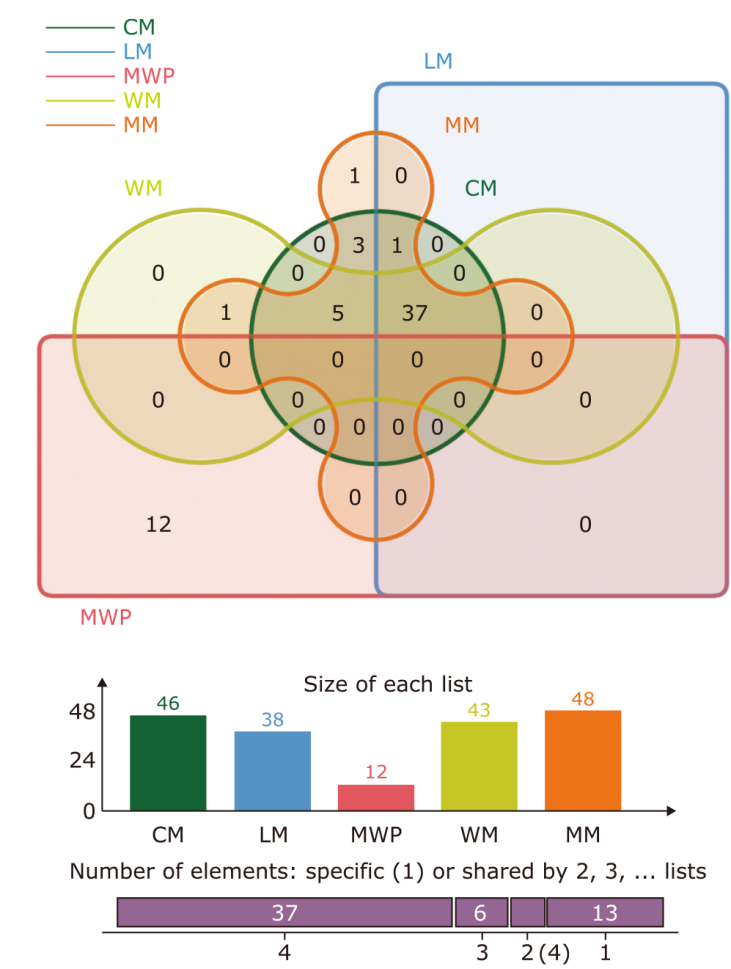
Core herbs used for treating different malaria syndromes"
| Intersection | Count | Items |
|---|---|---|
| Labour malaria, cold malaria, miasmic malaria, and warm malaria | 37 | Fructus Mume (乌梅), Rhizoma Chuanxiong (川芎), Rhizoma Atractylodis (苍术), Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis (厚朴), Fructus Tsaoko (草果), Radix Dichroae (常山), Radix Bupleuri (柴胡), Rhizoma et Radix Notopterygii (羌活), Rhizoma Zingiberis Recens (生姜), Herba Ephedrae (麻黄), Rhizoma Cimicifugae (升麻), Cassia Twig (桂枝), Radix Scutellariae (黄芩), Herba Artemisiae Annuae (青蒿), Cortex Cinnamomi (肉桂), dried ginger (干姜), Radix Aconiti Lateralis Praeparata (附子), Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏), Radix Platycodonis (桔梗), Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae (贝母), Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei (大黄), Radix Aucklandiae (木香), Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride (青皮), Radix Angelicae Sinensis (当归), ginseng (人参), Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草), Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae (白术), Radix Paeoniae Alba (白芍), Chinese date (大枣), Radix Astragali (黄芪), Radix Ophiopogonis (麦冬), Radix Rehmanniae Preparata (熟地黄), poria (茯苓), Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae (秦艽), and Semen Arecae (槟榔) |
| Cold malaria and miasmic malaria | 3 | Cablin Potchouli (藿香), Fructus Amomi (砂仁), and Rhizoma Cyperi (香附) |
| Cold malaria, miasmic malaria, and warm malaria | 5 | Radix Puerariae (葛根), Radix Angelicae Dahuricae (白芷), Folium Perillae (紫苏叶), Radix Saposhnikoviae (防风), and Rhizoma Coptidis (黄连) |
| Labour malaria, cold malaria, and miasmic malaria | 1 | Radix Peucedani (前胡) |
| Miasmic malaria and warm malaria | 1 | Herba Asari (细辛) |
| Miasmic malaria | 1 | Herba Menthae (薄荷) |
| Malaria with splenomegaly | 12 | Flos Caryophylli (丁香), Rhizoma Curcumae (莪术), Fructus Foeniculi (小茴香), Medicated Leaven (神曲), Exocarpium Citri Rubrum (橘红), Radix Angelicae Pubescentis (独活), Fructus Aurantii Immaturus (枳实), Cinnabaris (朱砂), Carapax Trionycis (鳖甲), Cortex Moutan (丹皮), Fructus Crataegi (山楂), and Concha Ostreae (牡蛎) |
Table 7.
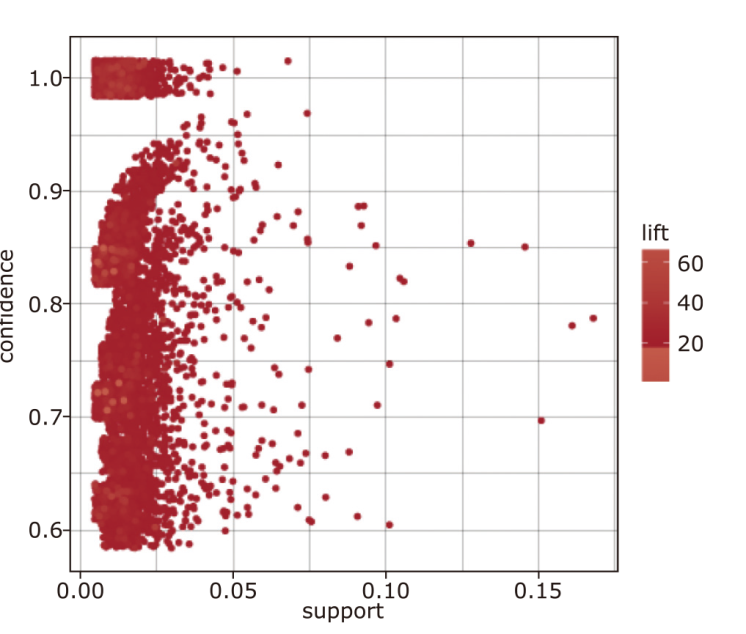
Binomial rules in association rules of core herbs for treating malaria"
| ID | From | To | Support | Confidence | Lift | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Radix Scutellariae (黄芩) | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡) | 0.11 | 0.81 | 3.77 | 51 |
| 2 | Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis (厚朴) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.15 | 0.86 | 1.98 | 67 |
| 3 | Poria | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.13 | 0.86 | 1.97 | 59 |
| 4 | Rhizoma Chuanxiong (川芎) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.08 | 0.85 | 1.97 | 35 |
| 5 | Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae (白术) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.1 | 0.81 | 1.86 | 46 |
| 6 | Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (陈皮) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.16 | 0.8 | 1.84 | 75 |
| 7 | Radix Scutellariae (黄芩) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.11 | 0.79 | 1.83 | 50 |
| 8 | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.17 | 0.78 | 1.79 | 77 |
| 9 | Rhizoma Atractylodis (苍术) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.1 | 0.77 | 1.78 | 44 |
| 10 | Ginseng (人参) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.11 | 0.73 | 1.69 | 49 |
| 11 | Fructus Tsaoko (草果) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.1 | 0.72 | 1.66 | 46 |
| 12 | Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.15 | 0.71 | 1.64 | 71 |
Table 8.
Tripartite rules in association rules of core herbs for treating malaria"
| ID | From | To | Support | Confidence | Lift | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草), Radix Scutellariae (黄芩) | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡) | 0.09 | 0.84 | 3.91 | 42 |
| 2 | Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis (厚朴), Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (陈皮) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.09 | 0.89 | 2.05 | 40 |
| 3 | Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis (厚朴), Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.09 | 0.88 | 2.02 | 42 |
| 4 | Pericarpium Citri Reticulataee (陈皮), Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.09 | 0.87 | 2.00 | 40 |
| 5 | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡), Radix Scutellariae (黄芩) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.09 | 0.82 | 1.90 | 42 |
| 6 | Radix Bupleuri (柴胡), Rhizoma Pinelliae (半夏) | Radix Glycyrrhizae (甘草) | 0.08 | 0.76 | 1.75 | 38 |
| 1 | Malaria. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017; 3(1): 17051. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.51. |
| 2 | World Health Organization. World malaria report 2022. 2022. https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme. |
| 3 | Hussein MIH, Albashir AAD, Elawad OAMA, et al. Malaria and COVID-19: unmasking their ties. Malar J, 2020; 19(1): 457. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03541-w. |
| 4 |
Zupko RJ, Nguyen TD, Wesolowski A, et al. National-scale simulation of human movement in a spatially coupled individual-based model of malaria in Burkina Faso. Sci Rep, 2023; 13(1): 321. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26878-5.
pmid: 36609584 |
| 5 | Li LJ. Guidelines for malaria diagnosis and treatment. China Tropical Medicine 2022; 22(08)(04): 695-702. doi: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2022.08.01. |
| 6 | Talman A M, Clain J, Duval R, et al. Artemisinin Bioactivity and Resistance in Malaria Parasites. Trends in Parasitol, 2019; 35(12): 953-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.09.005. |
| 7 | Ward KE, Fidock DA, Bridgford JL. Plasmodium falciparum resistance to artemisinin-based combination therapies. Curr Opin Microbiol 2022; 69: 102193. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102193. |
| 8 | Arya A, Kojom FLP, Chaudhry S, et al. Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) and drug resistance molecular markers: A systematic review of clinical studies from two malaria endemic regions - India and sub-Saharan Africa. Int J Parasitol-Drug 2021; 15: 43-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2020.11.006. |
| 9 | Xiong A, Prakash P, Gao X, et al. K13-Mediated Reduced Susceptibility to Artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum Is Overlaid on a Trait of Enhanced DNA Damage Repair. Cell Rep 2020; 32(5): 107996. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107996. |
| 10 |
Erhunse N, Sahal D. Protecting future antimalarials from the trap of resistance: Lessons from artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) failures. J Pharm Anal 2021; 11(5): 541-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.07.005.
pmid: 34765267 |
| 11 | Lin MX, Zhu JP, Zhang M. Discussion on the theoretical debate of treating malaria based on traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J Tradit Chin Medi Pharma (China) 2015; 30(11): 3821-3. doi: CNKI:SUN:BXYY.0.2015-11-005. |
| 12 | Tu Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat Med 2011; 17(10): 1217-20. doi: 10.1038/nm.2471. |
| 13 | TCMID (Traditional Chinese Medicines Integrated Database). http://www.megabionet.org/tcmid/. |
| 14 | Meng XY, Wang YL. Study on polysyllabic malarious names. Jilin J Chin Med (China) 2016; 36(07): 746-9+56. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.jlzyy.2016.07.028. |
| 15 | Zhang Z. Six meridians based on disease and syndrome differentiation. Proceedings of the 16th Zhongjing Academic Seminar of the Chinese Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China, 2008. |
| 16 | Yu X, Fu C. A review on the prevention and control of malaria in Yunnan during the period of the Republic of China. Guizhou Ethn Stud 2020; 41(12): 123-30. doi: 10.13965/j.cnki.gzmzyj10026959.2020.12.016. |
| 17 | Tang S, Zhou D, Pan Y. Summary of syndrome and treatment of lingnan malaria. J Basic Chin Med 2019; 25(12): 1650-2. doi: 10.19945/j.cnki.issn.1006-3250.2019.12.007. |
| 18 | Nian H. Study on the name of “Malaria” before Tang dynasty. Fujian Univ Tradit Chin Med (China) 2022. doi: 10.27021/d.cnki.gfjzc.2022.000310. |
| 19 | Jiang JM. Study on malaria prevention and treatment in Song dynasty; Northwest Normal University (China), 2022. doi: 10.27410/d.cnki.gxbfu.2022.000081. |
| 20 | Wang B, Meng FT, Zhang Y, et al. Comparative study of ZHANG Zhongjing and WU Jutong on treatment of malaria. Journal of Shandong Univ Tradit Chin Med (China) 2022; 46(03): 318-21. doi: 10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2022.03.008. |
| 21 | Liu SH, Li SS, Hou YJ, et al. Ancient and modern literature on clinical application of Biejia Jianwan in Medical Treasures of the Golden Chamber. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae (China), 2020; 26(06): 12-7. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20192321. |
| 22 | Feng YR, Yu ZF, Jiang DM, et al. On the application of Bupleurum Chinense in Zhang Xichun’s Medical Records of Reference to the West to stop malaria. Glob Tradit Chin Med (China) 2022; 15(11): 1903-6. |
| 23 | Qin HW, Wang YZ, Yang MQ, et al. Medicinal textual research of Tsaoko Fructus. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae (China) 2021; 27(06): 139-48. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20210216. |
| 24 | Sun Y, Zhao X, Xia XH, et al. Pharmacological effects and attenuating toxicity of Dichroae Radix and Febrifugine. Mod Chin Med (China): 1-9. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20220325004. |
| 25 | Zhou LP. Study on the patterns of compatibility and treatment features of prescriptions containing Bupleri Redix-Scutellariae Radix during past dynasties. Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019. |
| 26 | Chen YH. Analysis of Wang Mengying’s medical case of malaria treated by adding and subtracting Xiao Chai Hu Tang. J Tradit Chin Med 1959;(08): 43-4. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.1959.08.018. |
| 27 | Guo JZ, Wan F, Li X, et al. Effects of bupleurum saponin d on lipid peroxidation and trace elements of zinc and calcium in rats with hepatic fibrosis. Pharm Clin of Chin Materia Medica 2009; 25(03): 11-4. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZYYL.0.2009-03-009. |
| 28 |
Wilson J, Rockett K, Jallow M, et al. Analysis of IL10 haplotypic associations with severe malaria. Genes Immun 2005; 6(6): 462-6.
pmid: 15933743 |
| 29 |
Grau GE, Fajardo LF, Piguet PF, et al. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science 1987; 237(4819): 1210-2. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918.
pmid: 3306918 |
| 30 | Tovar AC, Ramírez-Montoya J, Velasco MC, et al. IL-4, IL-10, CCL2 and TGF-β as potential biomarkers for severity in Plasmodium vivax malaria. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2022; 16(9): e0010798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010798. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|