Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 184-193.doi: 10.24920/003558
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Downregulation of iASPP Expression Suppresses Proliferation, Invasion and Increases Chemosensitivity to Paclitaxel of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro
Liu Zhengzheng1, *( ), Kuang Weilu1, Zeng Wenjing3, Xiao Jianyun2, Tian Yongquan2, *(
), Kuang Weilu1, Zeng Wenjing3, Xiao Jianyun2, Tian Yongquan2, *( )
)
- 1 Department of Oncology, , Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, , Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
3 Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
-
Received:2019-07-02Published:2019-09-30Online:2019-07-02 -
Contact:Liu Zhengzheng,Tian Yongquan E-mail:lzzsmile@aliyun.com;tianyongquan@aliyun.com
Cite this article
Liu Zhengzheng, Kuang Weilu, Zeng Wenjing, Xiao Jianyun, Tian Yongquan. Downregulation of iASPP Expression Suppresses Proliferation, Invasion and Increases Chemosensitivity to Paclitaxel of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 184-193.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
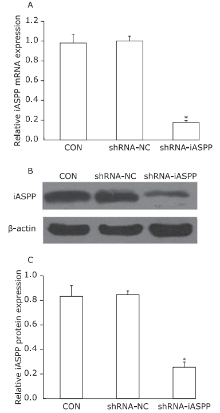
Figure 1.
Knockdown of iASPP expression by lentiviral vector-mediated shRNA interference in Tu686 cell lines. CON: non-infected cells; shRNA-NC: cells transfected with control shRNA lentiviral vector; shRNA-iASPP: cells transfected with iASPP lentiviral vector. A. Relative iASPP mRNA expression was detected by qPCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control (*P = 0.000, compared with the shRNA-NC group, Student’s t-test, n=3). B. Decreased protein expression of iASPP determined by Western blotting. C. Relative expression levels of iASPP protein (*P = 0.000, compared with the shRNA-NC group, Student’s t-test, n=3)."
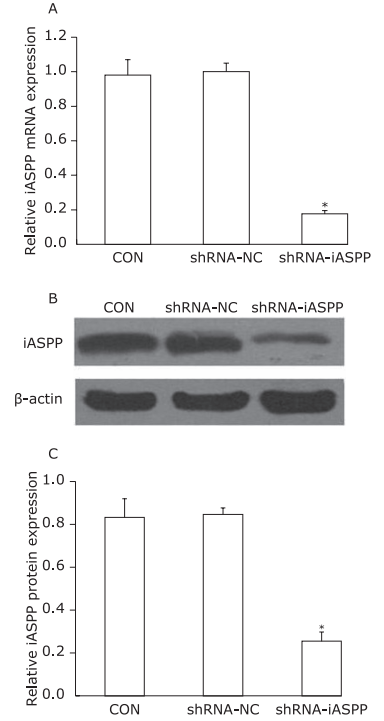

Figure 3.
The effect of knockdown of iASPP on cell apoptosis of Tu686 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative histograms showing apoptosis of CON (A), shRNA-NC (B) and shRNA-iASPP cells (C). The apoptosis ratio of shRNA-iASPP cell line was significantly higher than that of CON cell line and shRNA-NC cell line (D, *P = 0.000). Results of quantitative analysis represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments."
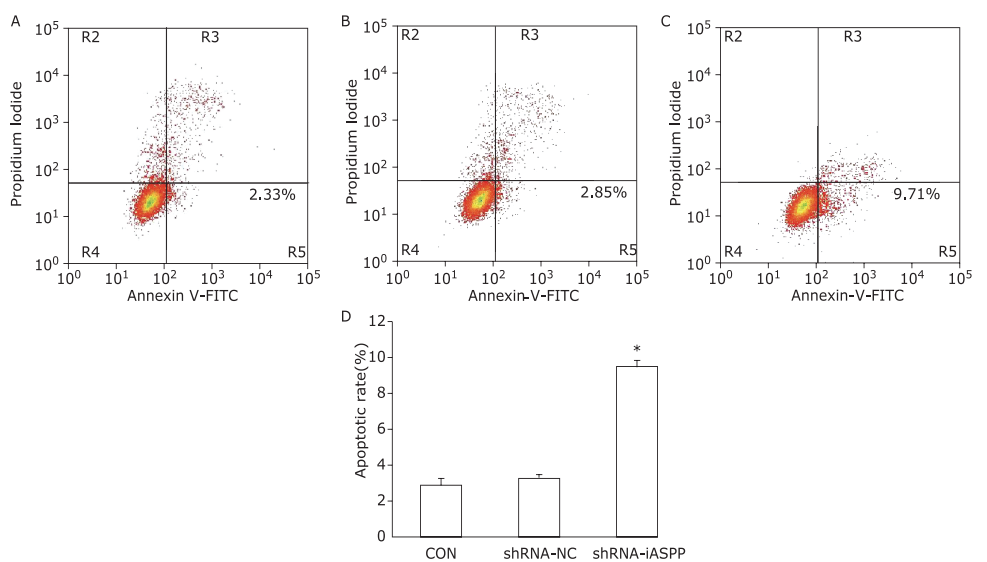
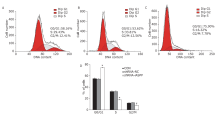
Figure 4.
The effect of knockdown of iASPP on cell cycle distribution of Tu686 cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative histograms showing cell cycle distribution of CON (A), shRNA-NC (B) and shRNA-iASPP cells (C). The percentage of shRNA-iASPP cells in G0/G1 phase was strikingly increased (*P=0.000), whereas the percentage of cells in S phase and G2/M phase decreased significantly (D) (both *P=0.000). Results of quantitative analysis represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments."
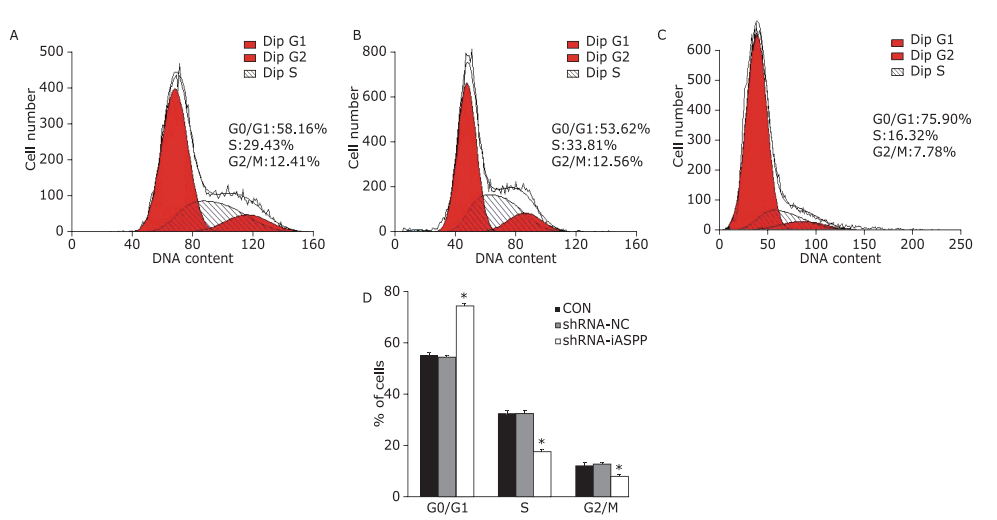
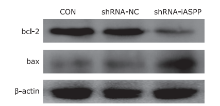
Figure 5.
The effect of knockdown of iASPP expression on the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in Tu686 cells was analyzed by western blotting. As shown above, downregulation of iASPP expression obviously inhibited the expression of anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2, but significantly increased pro-apoptotic protein bax expression."
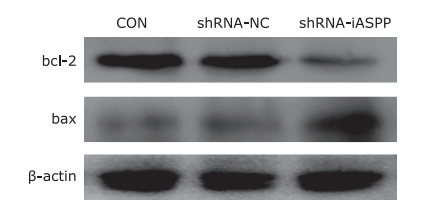
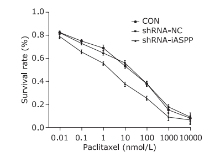
Figure 7.
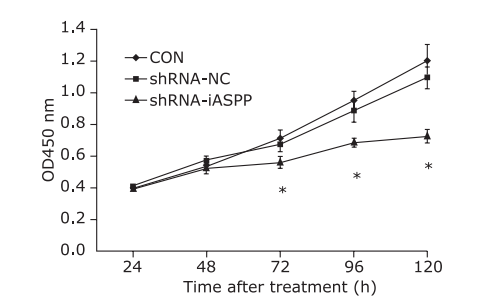
Knockdown of iASPP expression can strengthen chemosensitivity of HNSCC Tu686 cell line to paclitaxel. CON, shRNA-NC and shRNA-iASPP cells were treated with increasing concentrations of paclitaxel for 48 h, and the cell survival rate was assessed by CCK-8 assays. Results represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments."
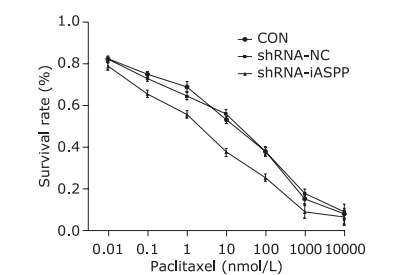

Figure 8.
The effect of knockdown of iASPP expression on cell apoptosis of Tu686 cells treated with paciltaxel for 24 hours was analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative histograms showing apoptosis of CON (A), shRNA-NC (B) and shRNA-iASPP cells (C). The apoptosis ratio of shRNA-iASPP cells was significantly higher than that of CON cells and shRNA-NC cells (D) (*P=0.000). Results of graphic D represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments."

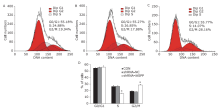
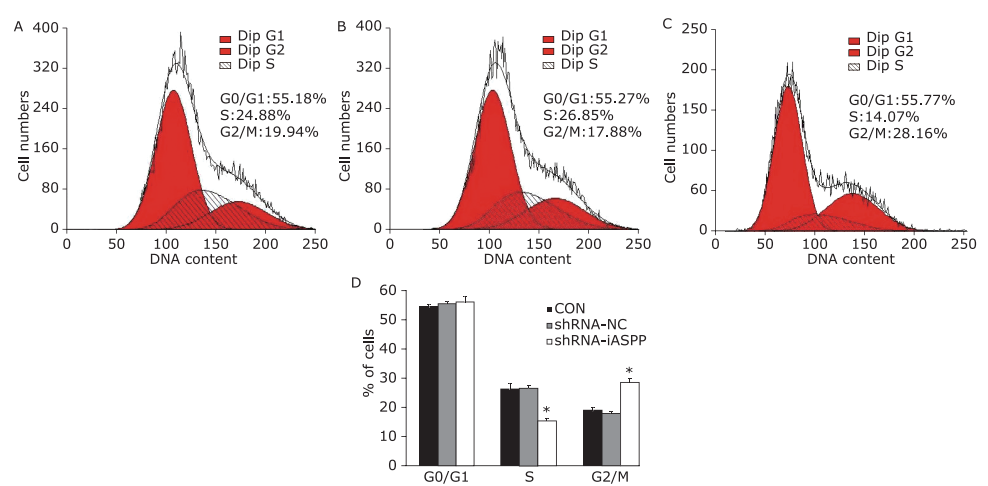
Figure 9.
The effect of knockdown of iASPP expression on cell cycle distribution of Tu686 cells treated with paciltaxel for 24 hours was analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative histograms showing cell cycle distribution of CON (A), shRNA-NC (B) and shRNA-iASPP cells (C). The percentage of shRNA-iASPP cells in G2/M phase was strikingly increased (*P=0.000), and the percentage of cells in S phase decreased significantly (*P=0.000). Results of graphic D represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments."
| 1. | J-Fatokun F, Jayaratne R, Morawska L , et al. Corona ions from overhead transmission voltage powerlines: effect on direct current electric field and ambient particle concentration levels. Environ Sci Technol 2010; 44(1):526-31. doi: 10.1021/es9024063. |
| 2. | Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63(1):11-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21166. |
| 3. | Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J , et al. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60(5):277-300. doi: 10.3322/caac.20073. |
| 4. | Hardisson D . Molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2003; 260(9):502-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-003-0581-3. |
| 5. |
Chin D, Boyle GM, Theile DR , et al. Molecular introduction to head and neck cancer (HNSCC) carcinogenesis. Br J Plast Surg 2004; 57(7):595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.06.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.06.010 |
| 6 | Trigiante G, Lu X . ASPP [corrected] and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6(3):217-26. doi: 10.1038/nrc1818. |
| 7. | Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ , et al. iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet 2003; 33(2):162-7. doi: 10.1038/ng1070. |
| 8. | Zhang X, Wang M, Zhou C , et al. The expression of iASPP in acute leukemias. Leuk Res 2005; 29(2):179-83. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2004.07.001. |
| 9. | Lu B, Guo H, Zhao J , et al. Increased expression of iASPP, regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated NF-kappaB activation, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010; 139(6):2183-94. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.049. |
| 10. | Jiang L, Siu MK, Wong OG , et al. iASPP and chemoresistance in ovarian cancers: effects on paclitaxel-mediated mitotic catastrophe. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17(21):6924-33. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0588. |
| 11. | Wang L, Li Y, Li L , et al. Role of Kruppel-like factor 4 in regulating inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 in the progression of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 2018; 15(5):6865-72. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8203. |
| 12. | Yin L, Lin Y, Wang X , et al. The family of apoptosis-stimulating proteins of p53 is dysregulated in colorectal cancer patients. Oncol Lett 2018; 15(5):6409-17. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8151. |
| 13. | Chen J, Xie F, Zhang L , et al. iASPP is over-expressed in human non-small cell lung cancer and regulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells through a p53 associated pathway. BMC Cancer 2010; 10:694. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-694. |
| 14. | Zhang B, Xiao HJ, Chen J , et al. Inhibitory member of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP) family promotes growth and tumorigenesis in human p53-deficient prostate cancer cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2011; 14(3):219-24. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2011.25. |
| 15. |
Liu Z, Zhang X, Huang D , et al. Elevated expression of iASPP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Med Oncol 2012; 29(5):3381-8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0306-9.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0306-9 |
| 16. | Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25(4):402-8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. |
| 17. | Liu Y, Zhang X, Qiu Y , et al. Clinical significance of EphA2 expression in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2011; 137(5):761-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0936-2. |
| 18. | Liu Z, Kuang W, Zhou Q , et al. TGF-beta1 secreted by M2 phenotype macrophages enhances the stemness and migration of glioma cells via the SMAD2/3 signalling pathway. Int J Mol Med 2018; 42(6):3395-403. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3923. |
| 19. | Gan W, Zhao H, Li T , et al. CDK1 interacts with iASPP to regulate colorectal cancer cell proliferation through p53 pathway. Oncotarget 2017; 8(42):71618-29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17794. |
| 20. | Ma Y, Zhu B, Liu X , et al. iASPP overexpression is associated with clinical outcome in spinal chordoma and influences cellular proliferation, invasion, and sensitivity to cisplatin in vitro. Oncotarget 2017; 8(40):68365-80. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20190. |
| 21. | Lu W, Yu T, Liu S , et al. FHL2 interacts with iASPP and impacts the biological functions of leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2017; 8(25):40885-95. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16617. |
| 22. | Dong P, Xiong Y, Watari H , et al. Suppression of iASPP-dependent aggressiveness in cervical cancer through reversal of methylation silencing of microRNA-124. Sci Rep 2016; 6:35480. doi: 10.1038/srep35480. |
| 23. |
Li G, Wang R, Gao J , et al. RNA interference-mediated silencing of iASPP induces cell proliferation inhibition and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in U251 human glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 350(1-2):193-200. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0698-9.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0698-9 |
| 24. | Liu T, Li L, Yang W , et al. iASPP is important for bladder cancer cell proliferation. Oncol Res 2011; 19(3-4):125-30. |
| 25. | Morris EV, Cerundolo L, Lu M , et al. Nuclear iASPP may facilitate prostate cancer progression. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5:e1492. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.442. |
| 26. | Liang S, Gong X, Zhang G , et al. MicroRNA-140 regulates cell growth and invasion in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma by targeting iASPP. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2016; 48(2):174-81. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv127. |
| 27. | Liang XG, Meng WT, Hu LJ , et al. MicroRNA-184 modulates human central nervous system lymphoma cells growth and invasion by targeting iASPP. J Cell Biochem 2017; 118(9):2645-53. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25856. |
| 28. | Chen J, Xiao H, Huang Z , et al. MicroRNA124 regulate cell growth of prostate cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014; 7(5):2283-90. |
| 29. | Liu K, Zhao H, Yao H , et al. MicroRNA-124 regulates the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Biomed Res Int 2013; 2013:867537. doi: 10.1155/2013/867537. |
| 30. |
Zhao WH, Wu SQ, Zhang YD . Downregulation of miR-124 promotes the growth and invasiveness of glioblastoma cells involving upregulation of PPP1R13L. Int J Mol Med 2013; 32(1):101-7. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1365.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1365 |
| 31. | Zhao H, Peng R, Liu Q , et al. The lncRNA H19 interacts with miR-140 to modulate glioma growth by targeting iASPP. Arch Biochem Biophys 2016; 610:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.09.014. |
| 32. | Xiong Y, Sun F, Dong P , et al. iASPP induces EMT and cisplatin resistance in human cervical cancer through miR-20a-FBXL5/BTG3 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2017; 36(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0520-6. |
| 33. | Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR , et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(17):1705-15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa070956. |
| 34. | Rapidis AD, Trichas M, Stavrinidis E , et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: final results from a phase II study with docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with a four-year follow-up. Oral Oncol 2006; 42(7):675-84. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.12.006. |
| 35. | Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C , et al. Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(17):1695-704. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa071028. |
| 36. | Yu J, Li L, Huang C . Downregulation of inhibition of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (iASPP) suppresses cisplatin-resistant gastric carcinoma in vitro. Med Sci Monit 2017; 23:5542-49. |
| 37. |
Jia Y, Peng L, Rao Q , et al. Oncogene iASPP enhances self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells and facilitates their resistance to chemotherapy and irradiation. FASEB J 2014; 28(7):2816-27. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-244632.
doi: 10.1096/fj.13-244632 |
| 38. |
Cao L, Huang Q, He J , et al. Elevated expression of iASPP correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance/radioresistance in FIGO Ib1-IIa squamous cell cervical cancer. Cell Tissue Res 2013; 352(2):361-9. doi: 10.1007/s00441-013-1569-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00441-013-1569-y |
| 39. | Liu H, Wang M, Diao S , et al. siRNA-mediated down-regulation of iASPP promotes apoptosis induced by etoposide and daunorubicin in leukemia cells expressing wild-type p53. Leuk Res 2009; 33(9):1243-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.02.016. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|