Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 265-272.doi: 10.24920/004282
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Differentiation Between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Mimics Using Quantitative Analysis of Fasciculation with Muscle Ultrasound
Jing Fan1, Yi Li2, Jing-Wen Niu1, Nan Hu1, Yu-Zhou Guan1, Li-Ying Cui1, Ming-Sheng Liu1, *( )
)
- 1Department of Neurology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730
2Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310000
-
Received:2023-07-10Accepted:2023-09-08Published:2023-12-30Online:2023-10-09 -
Contact:Ming-Sheng Liu E-mail:liumingsheng_pumch@163.com
Cite this article
Jing Fan, Yi Li, Jing-Wen Niu, Nan Hu, Yu-Zhou Guan, Li-Ying Cui, Ming-Sheng Liu. Differentiation Between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Mimics Using Quantitative Analysis of Fasciculation with Muscle Ultrasound[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(4): 265-272.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the three groups"
| Variables | ALS (n = 139) | NR (n = 61) | HC (n = 22) | t/χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs, mean ± SD) | 53.1 ± 12.5 | 48.7 ± 17.7 | 53.6 ± 11.7 | 31.5 | < 0.001 |
| Sex, female [n (%)] | 64 (46) | 17 (27.9) | 10 (45.5) | 5.99 | 0.05 |
| Height (cm, mean ± SD) | 166.1 ± 0.7 | 167.7 ± 0.7 | 169.0 ± 1.3 | 5.22 | 0.073 |
| Weight (kg, mean ± SD) | 65.3 ± 1.2 | 73.4 ± 2.5 | 63.8 ± 2.7 | 13.7 | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 23.6 ± 0.4 | 28.6 ± 3.6 | 22.3 ± 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.003 |
| Disease duration (months, mean ± SD) | 15.1 ± 1.1 | 34.9 ± 5.9 | 19.1 ± 7.9 | 1.7 | 0.41 |
| ALSFRSR (score, mean ± SD) | 41.1 ± 5.1 | - | - | ||
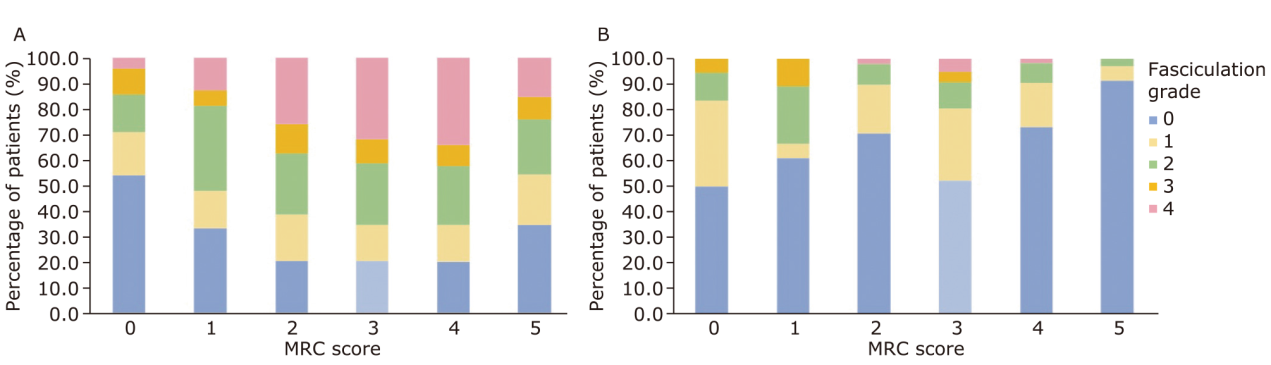
| MRC score (% of patients) | |||||
| 0 | 2.15 | 1.85 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 2.15 | 1.85 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 9.50 | 4.90 | 0 | ||
| 3 | 14.60 | 16.90 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 24.70 | 24.50 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 46.90 | 50.50 | 100 |
| 1. |
Misawa S, Noto Y, Shibuya K, et al. Ultrasonographic detection of fasciculations markedly increases diagnostic sensitivity of ALS. Neurology 2011; 77(16):1532-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318233b36a.
pmid: 21940619 |
| 2. |
Walker FO, Donofrio PD, Harpold GJ, et al. Sonographic imaging of muscle contraction and fasciculations: a correlation with electromyography. Muscle Nerve 1990; 13(1):33-9. doi: 10.1002/mus.880130108.
pmid: 2183044 |
| 3. |
Reimers CD, Ziemann U, Scheel A, et al. Fasciculations: clinical, electromyographic and ultrasonographic assessment. J Neurol 1996; 243(8):579-84. doi: 10.1007/BF00900945.
pmid: 8865024 |
| 4. |
Scheel AK, Toepfer M, Kunkel M, et al. Ultrasonographic assessment of the prevalence of fasciculations in lesions of the peripheral nervous system. J Neuroimaging 1997; 7(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/jon19977123.
pmid: 9038428 |
| 5. |
Wenzel S, Herrendorf G, Scheel A, et al. Surface EMG and myosonography in the detection of fasciculations: a comparative study. J Neuroimaging 1998; 8(3):148-54. doi: 10.1111/jon199883148.
pmid: 9664850 |
| 6. | Grimm A, Prell T, Décard BF, et al. Muscle ultrasonography as an additional diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clinl Neurophysiol 2015; 126(4):820-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.06.052. |
| 7. |
Johansson MT, Ellegaard HR, Tankisi H, et al. Fasciculations in nerve and muscle disorders-a prospective study of muscle ultrasound compared to electromyography. Clin Neurophysiol 2017; 128(11):2250-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.08.031.
pmid: 29028499 |
| 8. |
Tsuji Y, Noto Y, Kitaoji T, et al. Difference in distribution of fasciculations between multifocal motor neuropathy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 2020; 131(12):2804-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2020.08.021.
pmid: 33137570 |
| 9. | Tsuji Y, Noto Y, Shiga K, et al. A muscle ultrasound score in the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clinical Neurophysiol 2017; 128(6):1069-74. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.02.015. |
| 10. | Takamatsu N, Nodera H, Mori A, et al. Which muscle shows fasciculations by ultrasound in patients with ALS? J Med Investigation 2016; 63(1-2):49-53. doi: 10.2152/jmi.63.49. |
| 11. |
Hobson-Webb LD, Simmons Z. Ultrasound in the diagnosis and monitoring of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a review. Muscle Nerve 2019; 60(2):114-23. doi: 10.1002/mus.26487.
pmid: 30989697 |
| 12. |
O’gorman CM, Weikamp JG, Baria M, et al. Detecting fasciculations in cranial nerve innervated muscles with ultrasound in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2017; 56(6):1072-6. doi: 10.1002/mus.25676.
pmid: 28457000 |
| 13. |
Rajabkhah S, Moradi K, Okhovat AA, et al. Application of muscle ultrasound for the evaluation of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an observational cross-sectional study. Muscle Nerve 2020; 62(4):516-21. doi: 10.1002/mus.27036.
pmid: 32710682 |
| 14. |
Avidan R, Fainmesser Y, Drory VE, et al. Fasciculation frequency at the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease burden and activity. Muscle Nerve 2021; 63(2):204-8. doi: 10.1002/mus.27125.
pmid: 33216387 |
| 15. |
Tsugawa J, Dharmadasa T, Ma Y, et al. Fasciculation intensity and disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 2018; 129(10):2149-54. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.07.015.
pmid: 30114663 |
| 16. |
Wannop K, Bashford J, Wickham A, et al. Fasciculation analysis reveals a novel parameter that correlates with predicted survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 2021; 63(3):392-6. doi: 10.1002/mus.27139.
pmid: 33290574 |
| 17. |
de Carvalho M, Dengler R, Eisen A, et al. Electrodiagnostic criteria for diagnosis of ALS. Clin Neurophysiol 2008; 119(3):497-503. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2007.09.143.
pmid: 18164242 |
| 18. |
Latov N. Diagnosis of CIDP. Neurology 2002; 59(12 Suppl 6):S2-6. doi: 10.1212/wnl.59.12_suppl_6.s2.
pmid: 12499464 |
| 19. |
Van den Bergh PY, Hadden RD, Bouche P, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—first revision. Eur J Neurol 2010; 17(3):356-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02930.x.
pmid: 20456730 |
| 20. |
Pareyson D, Marchesi C. Diagnosis, natural history, and management of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8(7):654-67. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70110-3
pmid: 19539237 |
| 21. | Muhle C, Metzner J, Weinert D, et al. Classification system based on kinematic MR imaging in cervical spondylitic myelopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1998; 19(9):1763-71. |
| 22. |
Paternostro-Sluga T, Grim-Stieger M, Posch M, et al. Reliability and validity of the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale and a modified scale for testing muscle strength in patients with radial palsy. J Rehabil Med 2008; 40(8):665-71. doi: 10.2340/16501977-0235.
pmid: 19020701 |
| 23. | Duarte ML, Iared W, Oliveira ASB, et al. Ultrasound versus electromyography for the detection of fasciculation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiol Bras 2020; 53(2):116-21. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2019.0055. |
| [1] | Yong Liu, Si-Yuan Yao, Xi Zhou, Shu-Zhong Liu, Yan-Yan Bian. Association Between Constipation and a Reduction in Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Preoperative Patients with Thoracic Spinal Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(2): 109-116. |
| [2] | Chen Zhiye, Liu Mengqi, Ma Lin. Cortical Thinning Pattern of Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Surface-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [3] | Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|