Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 193-197.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.026
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
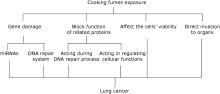
Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Caused By Cooking Fumes Exposure: A Minor Review△
Wang Chun-yan1, Liu Li-fang2, Liu Xiao-li1, Chen Wen-jun1, He Guo-ping1, *( )
)
- 1 Xiangya Nursing School, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China
2 Organ Transplant Department, Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China
-
Received:2016-08-30Published:2017-09-27Online:2017-09-27 -
Contact:He Guo-ping E-mail:Heguopping@csu.edu.cn
Cite this article
Wang Chun-yan, Liu Li-fang, Liu Xiao-li, Chen Wen-jun, He Guo-ping. Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Caused By Cooking Fumes Exposure: A Minor Review△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 193-197.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| 1. | Yu KP, Yang KR, Chen YC, Gong JY, Chen YP, Shih HC, et al.Indoor air pollution from gas cooking in five Taiwanese families. Build Environ 2015; 93(Part 2):258-66. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.06.024. |
| 2. | Park SS, Kang MS, Hwang J.Oil mist collection and oil mist-to-gas conversion via dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Sep Purif Technol 2015; 151(4): 324-31. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.07.059. |
| 3. | Kim C, Gao YT, Xiang YB, Barone-Adesi F, Zhang YW, Hosgood HD, et al.Home kitchen ventilation, cooking fuels, and lung cancer risk in a prospective cohort of never smoking women in Shanghai, China. Int J Cancer 2015; 136(3):632-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29020. |
| 4. | Liao L, Liu HT, Zhang BL.Biodegradability of pollutants from cooking fumes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2009; 82(4):428-34. doi: 10.1007/s00128-008-9595-2. |
| 5. | Kabir E, Kim KH.An investigation on hazardous and odorous pollutant emission during cooking activities. J Hazard Mater 2011; 188(1-3):443-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat. 2011.01.113. |
| 6. | Yao ZL, Li J, Wu BB, Hao XW, Yin Y, Jiang X.Characteristics of PAHs from deep-frying and frying cooking fumes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2015; 22(20):16110-20. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4837-4. |
| 7. | Wu CC, Bao LJ, Guo Y, Li SM, Zeng EY.Barbecue fumes: an overlooked source of health hazards in outdoor settings? Environ Sci Technol 2015; 49(17):10607-15. |
| 8. | Liu Y, Chen YY, Cao JY, Tao FB, Zhu XX, Yao CJ, et al.Oxidative stress, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest are induced in primary fetal alveolar type Ⅱ epithelial cells exposed to fine particulate matter from cooking oil fumes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2015; 22(13):9728-41. doi: 10.1007/ s11356-015-4140-4. |
| 9. | Yin ZH, Cui ZG, Guan P, Li XL, Wu W, Ren YW, et al.Interaction between polymorphisms in pre-miRNA genes and cooking oil fume exposure on the risk of lung cancer in Chinese non-smoking female population. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0128572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128572. |
| 10. | Ren YW, Yin ZH, Li K, Wan Y, Li XL, Wu W, et al.TGFbeta-1 and TGFBR2 polymorphisms, cooking oil fume exposure and risk of lung adenocarcinoma in Chinese nonsmoking females: a case control study. BMC Med Genet 2015; 16:22. doi: 10.1186/s12881-015-0170-5. |
| 11. | Phukan RK, Saikia BJ, Borah PK, Zomawia E, Sekhon GS, Mahanta J.Role of household exposure, dietary habits and glutathione S-transferases M1, T1 polymorphisms in susceptibility to lung cancer among women in Mizoram India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15(7):3253-60. doi: 10.7314/ apjcp.2014.15.7.3253. |
| 12. | Wang XR, Chiu YL, Qiu H, Au JSK, Yu ITS.The roles of smoking and cooking emissions in lung cancer risk among Chinese women in Hong Kong. Ann Oncol 2009; 20(4): 746-51. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn699. |
| 13. | Li MC, Yin ZH, Guan P, Li XL, Cui ZS, Zhang J, et al.XRCC1 polymorphisms, cooking oil fume and lung cancer in Chinese women nonsmokers. Lung Cancer 2008; 62(2):145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.03.002. |
| 14. | Hung HS, Wu WJ, Cheng YW, Wu TC, Chang KL, Lee H.Association of cooking oil fumes exposure with lung cancer: involvement of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in cell survival and proliferation in vitro. Mutat Res 2007; 628(2):107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.12.005. |
| 15. | Yu ITS, Chiu YL, Au JSK, Wong TW, Tang JL.Dose-response relationship between cooking fumes exposures and lung cancer among Chinese nonsmoking women. Cancer Res 2006; 66(9):4961-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2932. |
| 16. | Metayer C, Wang ZY, Kleinerman RA, Wang LD, Brenner AV, Cui HX, et al.Cooking oil fumes and risk of lung cancer in women in rural Gansu, China. Lung Cancer 2002; 35(2): 112-7. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5002(01)00412-3. |
| 17. | Wu SC, Yen GC.Effects of cooking oil fumes on the genotoxicity and oxidative stress in human lung carcinoma (A-549) cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2004; 18(5):571-80. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2004.01.004. |
| 18. | Lee T, Gany F.Cooking oil fumes and lung cancer: a review of the literature in the context of the U.S. population. J Immigr Minor Health 2013; 15(3):646-52. doi: 10.1007/s10903-012-9651-1. |
| 19. | Mohammed MO, Song WW, Ma WL, Li WL, Khan AU, Ibrahim MA, et al. Potential toxicological and cardiopulmonary effects of PM 2.5 exposure and related mortality: findings of recent studies published during 2003-2013. Biomed Environ Sci 2016; 29(1):66-79. doi: 10.3967/bes2016.007. |
| 20. | Wu M, Che W, Zhang Z Enhanced sensitivity to DNA damage induced by cooking oil fumes in human OGG1 deficient cells Environ Mol Mutagen 2008; 49(4):265-75. doi: 10.1002/em.20381. |
| 21. | Mi HH Optical emission spectroscopy in cooking exhaust from a wet scrubber/atmospheric plasma reactor Aerosol Air Qual Res 2014; 10(6):1665-74. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2014.01.0002. |
| 22. | Xue X, Liao WT, Chang HC, Chen SJ, Lin CC, Hsieh LT The joint effect of hOGG1, APE1, and ADPRT polymorphisms and cooking oil fumes on the risk of lung adenocarcinoma in Chi-nese non-smoking females PLoS One 2013; 8(8):e71157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071157. |
| 23. | Yin ZH, Su M, Li XL, Li MC, Ma R, He QC, et al. ERCC2, ERCC1 polymorphisms and haplotypes, cooking oil fume and lung adenocarcinoma risk in Chinese non-smoking females J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2009; 28:153. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-153 . |
| 24. | Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dove R, Rozalski R, Gachowski D, Siomek A, et al. DNA repair is responsible for the presence of oxidatively damaged DNA lesions in urine Mutat Res 2005; 574(1):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.01.022. |
| 25. | Pan CH, Chan CC, Wu KY Effects on Chinese restaurant workers of exposure to cooking oil fumes: a cautionary note on urinary 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008; 17(12):3351-7. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0075.. |
| 26. | Lewis BP, Shih L, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets Cell 2003; 115(7):787-98. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)01018-3. |
| 27. | Petermann E, Keil C, Oei SL Roles of DNA ligase III and XRCC1 in regulating the switch between short patch and long patch BER DNA Repair (Amst) 2006; 5(5):544-55. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.12.008. |
| 28. | Josyula S, Lin J, Xue XN, Rothman N, Lan Q, Rohan TE, et al. Household air pollution and cancers other than lung: a me-ta-analysis Environ Health 2015; 14: 24. doi: 10.1186/s12940-015-0001-3. |
| 29. | Cao J, Ding R, Wang Y, Chen DJ, Guo DM, Liang CM, et al. Toxic effect of cooking oil fumes in primary fetal pulmonary type II-like epithelial cells Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2013; 36(2):320-31. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2013.04.011. |
| 30. | Che Z, Liu Y, Chen YY, Cao JY, Liang CM, Wang L, et al. The apoptotic pathways effect of fine particulate from cooking oil fumes in primary fetal alveolar type II epithelial cells Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 2014; 761:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.01.004. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|