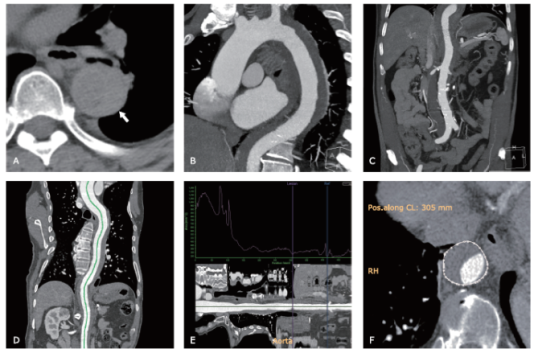
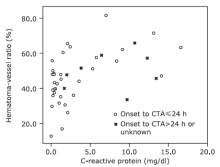
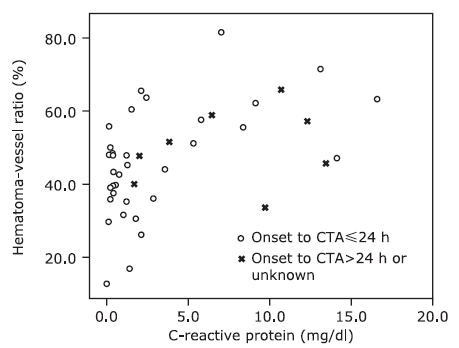
| 1. |
Kuehl H, Eggebrecht H, Boes T , et al. Detection of inflammation in patients with acute aortic syndrome: comparison of FDG-PET/CT imaging and serological markers of inflammation. Heart 2008; 94(11):1472-7. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2007.127282.
|
| 2. |
Gorla R, Erbel R, Kuehl H , et al. Prognostic value of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT imaging in acute aortic syndromes: comparison with serological biomarkers of inflammation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2015; 31(8):1677-85. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0725-8.
|
| 3. |
Kitai T, Kaji S, Kim K , et al. Prognostic value of sustained elevated C-reactive protein levels in patients with acute aortic intramural hematoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014; 147(1):326-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.11.030.
|
| 4. |
Mussa FF, Horton JD, Moridzadeh R , et al. Acute aortic dissection and intramural hematoma: a systematic review. JAMA 2016; 316(7):754-63. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.10026.
|
| 5. |
Yoshida S, Akiba H, Tamakawa M , et al. Thoracic involvement of type A aortic dissection and intramural hematoma: diagnostic accuracy——comparison of emergency helical CT and surgical findings. Radiology 2003; 228(2):430-5. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2282012162.
|
| 6. |
Sueyoshi E, Matsuoka Y, Imada T , et al. New development of an ulcerlike projection in aortic intramural hematoma: CT evaluation. Radiology 2002; 224(2):536-41. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2242011009.
|
| 7. |
Kitai T, Kaji S, Yamamuro A , et al. Detection of intimal defect by 64-row multidetector computed tomography in patients with acute aortic intramural hematoma. Circulation 2011; 124(11 Suppl):S174-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.037416.
|
| 8. |
Moral S, Cuellar H, Avegliano G , et al. Clinical implications of focal intimal disruption in patients with type B intramural hematoma. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017; 69(1):28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.045.
|
| 9. |
Jiang D, Kuang F, Lai Y , et al. Certain aortic geometries and hemodynamics are associated with FID development and impact the evolution of uncomplicated type B intramural hematoma during the acute phase. J Card Surg 2019; 34(5):337-47. doi: 10.1111/jocs.14040.
|
| 10. |
Wu MT, Wang YC, Huang YL , et al. Intramural blood pools accompanying aortic intramural hematoma: CT appearance and natural course. Radiology 2011; 258(3):705-13. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10101270.
|
| 11. |
Taguchi E, Nishigami K, Miyamoto S , et al. Impact of shear stress and atherosclerosis on entrance-tear formation in patients with acute aortic syndromes. Heart Vessels 2014; 29(1):78-82. doi: 10.1007/s00380-013-0328-z.
|
| 12. |
Craiem D, El Batti S, Casciaro ME , et al. Age-related changes of thoracic aorta geometry used to predict the risk for acute type B dissection. Int J Cardiol 2017; 228:654-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.125.
|
| 13. |
Watanabe S, Hanyu M, Arai Y , et al. Initial medical treatment for acute type A intramural hematoma and aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg 2013; 96(6):2142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.06.060.
|
| 14. |
Song JK, Yim JH, Ahn JM , et al. Outcomes of patients with acute type a aortic intramural hematoma. Circulation 2009; 120(21):2046-52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.879783.
|
| 15. |
Lee YK, Seo JB, Jang YM , et al. Acute and chronic complications of aortic intramural hematoma on follow-up computed tomography: incidence and predictor analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2007; 31(3):435-40. doi: 10.1097/01.rct.0000250112.87585.8e.
|
| 16. |
Liu YJ, Zhang QY, Du ZK , et al. Long-term follow-up and clinical implications in Chinese patients with aortic intramural hematomas. Int J Cardiol 2018; 270:268-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.06.077.
|
| 17. |
Clyne B, Olshaker JS . The C-reactive protein. J Emerg Med 1999; 17(6):1019-25. doi: 10.1016/s0736-4679(99)00135-3.
|
| 18. |
Wen D, Du X, Dong JZ , et al. Value of D-dimer and C reactive protein in predicting inhospital death in acute aortic dissection. Heart 2013; 99(16):1192-7. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304158.
|
| 19. |
Schillinger M, Domanovits H, Bayegan K , et al. C-reactive protein and mortality in patients with acute aortic disease. Intensive Care Med 2002; 28(6):740-5. doi: 10.1007/s00134-002-1299-1.
|
| 20. |
Makita S, Ohira A, Tachieda R , et al. Behavior of C-reactive protein levels in medically treated aortic dissection and intramural hematoma. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86(2):242-4. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(00)00869-9.
|
| 21. |
Uchida K, Imoto K, Karube N , et al. Intramural haematoma should be referred to as thrombosed-type aortic dissection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2013; 44(2):366-9. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt040.
|
| 22. |
Ferrera C, Vilacosta I, Gomez-Polo JC , et al. Evolution and prognosis of intramural aortic hematoma. Insights from a midterm cohort study. Int J Cardiol 2017; 249:410-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.09.170.
|
| 23. |
Vardhanabhuti V, Nicol E, Morgan-Hughes G , et al. Recommendations for accurate CT diagnosis of suspected acute aortic syndrome (AAS)―on behalf of the British Society of Cardiovascular Imaging (BSCI)/British Society of Cardiovascular CT (BSCCT). Br J Radiol 2016; 89(1061):20150705. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150705.
|
| 24. |
Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA , et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55(14):e27-e129. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.015.
|
 ),Jin Xin,Wu Jian,Chang Ruiping,Zhang Jing
),Jin Xin,Wu Jian,Chang Ruiping,Zhang Jing