Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 157-167.doi: 10.24920/003504
• 论著 • 下一篇
中国不同地区健康人尿液蛋白质组的地域差异
吴建强1,2,秦伟伟3,潘利4,王小蓉2,张彪4,单广良4,*( ),高友鹤3,*(
),高友鹤3,*( )
)
- 1 中国医学科学院北京协和医院医学科学研究中心,中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院,北京 100730
2 中国医学科学院基础医学研究所病理生理学系,中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院,北京 100005
3 北京师范大学生命科学学院生物化学与分子生物学系,基因工程药物与生物技术北京重点实验室,北京 100875
4 流行病与卫生统计学系,中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院,北京 100005
-
收稿日期:2019-04-22出版日期:2019-09-30发布日期:2019-04-22 -
通讯作者:单广良,高友鹤 E-mail:guangliang_shan@163.com;gaoyouhe@bnu.edu.cn
Regional Differences of the Urinary Proteomes in Healthy Chinese Individuals
Wu Jianqiang1,2,Qin Weiwei3,Pan Li4,Wang Xiaorong2,Zhang Biao4,Shan Guangliang4,*( ),Gao Youhe3,*(
),Gao Youhe3,*( )
)
- 1 Medical Research Center, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China;2 Department of Pathophysiology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & School of Basic Medicine, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100005, China; 3 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Gene Engineering Drug and Biotechnology Beijing Key Laboratory, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China; 4 Department of Epidemiology and Statistics, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & School of Basic Medicine, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100005, China;
-
Received:2019-04-22Published:2019-09-30Online:2019-04-22 -
Contact:Shan Guangliang,Gao Youhe E-mail:guangliang_shan@163.com;gaoyouhe@bnu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 尿液是临床蛋白质组学研究的理想生物标志物来源。在多中心的临床研究中,研究对象存在地域性的生理差异很常见,本研究的目的是分析不同地区健康个体的尿液蛋白质组是否存在差异。
方法 本研究收集了中国海口、西安和西宁三个城市健康城市居民的尿液样本,并采用基于尿膜(Urimem)的方法保存尿液蛋白。使用液相色谱串联高分辨质谱分析比较了其中27名健康成人尿液样品的蛋白质组。
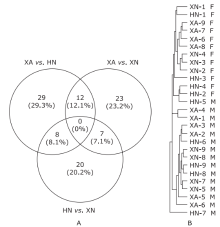
结果 基于label-free蛋白质组定量,我们从Urimem样品中共鉴定出1898种尿液蛋白,其中56个尿液蛋白在不同地区健康个体中差异表达。分层聚类分析显示:尿液蛋白质组的地域差异小于性别差异。对性别进行分层后,在男性样品中鉴定到17个差异蛋白,在女性样品中鉴定到93个差异蛋白。其中有些差异蛋白在既往临床研究中曾被作为疾病生物标志物。
结论 Urimem可以用于大规模尿液样品的蛋白保存,从而加速生物样本库的发展及尿液蛋白组疾病生物标志物的研究。地域差异是影响正常尿液蛋白质组的混杂因素,在未来基于人群的多中心的疾病标志物研究中应予以考虑。
引用本文
Wu Jianqiang, Qin Weiwei, Pan Li, Wang Xiaorong, Zhang Biao, Shan Guangliang, Gao Youhe. Regional Differences of the Urinary Proteomes in Healthy Chinese Individuals[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 157-167.
"
| Characteristics | Haikou | Xi’an | Xining | ANOVA P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 32.78±1.20 | 31.89±1.05 | 32.78±1.72 | 0.293 |
| Sex (n, male/female) | 5/4 | 5/4 | 5/4 | 1.000 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 115.00±12.61 | 110.56±13.13 | 109.11±10.61 | 0.572 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 72.44±7.07 | 68.78±9.65 | 68.89±7.13 | 0.554 |
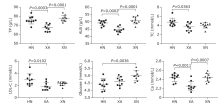
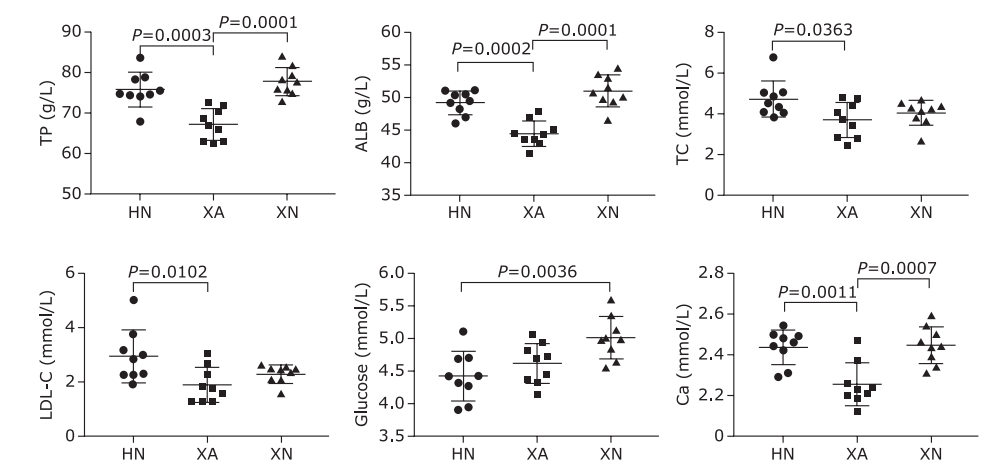
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.73±0.89 | 3.71±0.88 | 4.05±0.62 | 0.036 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.16±0.39 | 1.82±2.50 | 1.36±0.58 | 0.119 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.41±0.34 | 1.14±0.37 | 1.37±0.38 | 0.248 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.94±0.97 | 1.87±0.64 | 2.28±0.34 | 0.012 |
| TP (g/L) | 75.87±4.26 | 67.21±3.89 | 77.87±3.49 | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 49.24±1.82 | 44.97±1.94 | 51.04±2.47 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 19.79±15.31 | 17.78±10.95 | 19.96±11.13 | 0.894 |
| GGT (U/L) | 20.46±13.86 | 17.92±14.95 | 20.35±12.66 | 0.875 |
| ALP (U/L) | 71.87±20.07 | 64.28±14.68 | 74.59±17.22 | 0.443 |
| AST (U/L) | 23.77±14.84 | 17.08±4.13 | 23.19±7.91 | 0.308 |
| IgG (g/L) | 13.25±2.17 | 10.96±1.81 | 12.81±2.02 | 0.054 |
| IgA (g/L) | 2.26±0.83 | 1.91±0.54 | 2.27±0.71 | 0.467 |
| IgM (g/L) | 1.53±0.58 | 0.93±0.57 | 1.13±0.60 | 0.103 |
| Glu (mmol/L) | 4.42±0.38 | 4.61±0.31 | 5.01±0.33 | 0.004 |
| CrE (μmol/L) | 78.93±18.00 | 67.02±13.97 | 73.40±8.63 | 0.220 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 4.27±0.77 | 4.18±1.35 | 5.02±0.86 | 0.184 |
| UA (μmol/L) | 319.89±100.59 | 292.52±72.04 | 336.67±71.90 | 0.529 |
| Ca (mmol/L) | 2.44±0.09 | 2.25±0.11 | 2.45±0.09 | <0.001 |
| P (mmol/L) | 1.18±0.10 | 1.04±0.11 | 1.08±0.21 | 0.166 |
"
| UniProt ID | Protein name | Molecular weight (kDa) | Ratio | P value | Region | Biomarker use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P00915 | Carbonic anhydrase 1 | 29 | 2.33 | 0.016 | XA/XN | Dent disease, bladder cancer |
| P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain | 139 | 3.27 0.48 | 0.032 0.032 | HN/XA XA/XN | Acute pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, juvenile arthritis, diabetic nephropathy, colon cancer |
| P00749 | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator | 49 | 2.42 | 0.029 | XN/HN | Dent disease, bladder cancer |
| Q16270 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 | 29 | 2.16 | 0.027 | XN/HN | Heart failure, dent disease, acute kidney failure |
| Q6EMK4 | Vasorin | 72 | 2.14 | 0.006 | XN/HN | IgA glomerulonephritis |
| O00560 | Syntenin-1 | 32 | 0.37 0.50 | 0.007 0.025 | XA/XN HN/XN | Renal cell carcinoma |
| P03950 | Angiogenin | 17 | 2.32 | 0.032 | XN/HN | Dent disease, bladder cancer |
| P05164 | Myeloperoxidase | 84 | 0.09 6.23 | 0.011 0.018 | HN/XA XA/XN | Ureteropelvic junction obstruction |
| P04040 | Catalase | 60 | 7.61 | 0.029 | XA/XN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| P02743 | Serum amyloid P-component | 25 | 0.18 | 0.029 | HN/XA | Acute intestinal obstruction |
| Q9H6S3 | Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8-like protein 2 | 81 | 2.66 | 0.001 | XA/XN | Bladder cancer |
| P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein | 53 | 2.17 2.08 | 0.027 0.033 | HN/XN XA/HN | Diabetic nephropathy, Dent disease, bladder cancer, endometriosis, nephrotic syndrome, renal fibrosis |
| P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | 48 | 2.88 | 0.035 | HN/XA | Acute appendicitis, diabetic nephropathy, kidney transplant rejection, lung cancer |
| P15309 | Prostatic acid phosphatase | 45 | 2.94 2.90 | 0.029 0.029 | HN/XN XA/XN | Dent disease |
| P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | 23 | 2.83 | 0.007 | HN/XN | Acute kidney failure, ureteral obstruction |
| Q14126 | Desmoglein-2 | 122 | 2.15 | 0.027 | HN/XN | Heart failure, mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome |
"
| Xi’an | Haikou | Xining | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Peptide count | Peptides used for quantitation | Confidence score | Anova (p) | Max fold change | Highest mean condition | Lowest mean condition | Description | XA1 | XA2 | XA3 | XA4 | XA5 | XA6 | XA7 | XA8 | XA9 | HN1 | HN2 | HN3 | HN4 | HN5 | HN6 | HN7 | HN8 | HN9 | XN1 | XN2 | XN3 | XN4 | XN5 | XN6 | XN7 | XN8 | XN9 | ||
| P98164 | 127 | 97 | 9162 | 0.281883075 | 1.22302261 | HN | XN | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 2.58E+08 | 1.24E+08 | 1.52E+08 | 1.79E+08 | 95699630.22 | 156677803.7 | 126147158.2 | 141420865.3 | 103734119 | 254651747 | 202212703.6 | 130947323.2 | 171700487.8 | 281071611.1 | 145307719.8 | 134867253.1 | 145229896.7 | 128000010 | 169477537.2 | 134594070.8 | 143843736.5 | 103776692.8 | 130797146.3 | 171145958.6 | 171403394 | 123865828.8 | 154414755.4 | ||
| P98160 | 95 | 75 | 8280.32 | 0.664292461 | 1.336432921 | HN | XN | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPG2 PE=1 SV=4 | 7.99E+08 | 9.13E+08 | 1.86E+09 | 1.24E+09 | 1512869445 | 839540476.6 | 595382916.9 | 691621136.6 | 509880274.6 | 588583219.5 | 1129408520 | 541503972 | 1000164135 | 1349072452 | 1651709233 | 3305298998 | 795985658.6 | 673306984.8 | 467199813.4 | 1062339047 | 475283652.4 | 625423107 | 1135429619 | 1731348787 | 1017714914 | 850084658.9 | 892256123.9 | ||
| O60494 | 93 | 72 | 8223.86 | 0.113310067 | 1.242601828 | XA | XN | Cubilin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CUBN PE=1 SV=5 | 4.21E+08 | 3.34E+08 | 4.43E+08 | 3.39E+08 | 338333256.7 | 372940651.5 | 360868770.9 | 296764641.8 | 216144458.4 | 291152597.8 | 333019690.7 | 250776475.3 | 432151892.9 | 505698715 | 301866045.8 | 278175495.2 | 313650473.7 | 228210865.8 | 297312887.9 | 224987048.4 | 338615059.7 | 244694182.3 | 301569890.6 | 249897022.1 | 277491665.5 | 299884682.1 | 277800883.3 | ||
| P02768 | 66 | 57 | 7273.44 | 0.363098855 | 1.414226651 | XA | XN | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 3.34E+09 | 8.31E+09 | 9.19E+09 | 4.89E+09 | 3793818422 | 6774514255 | 7778611770 | 4993143994 | 11369803656 | 2356564062 | 5284686572 | 17479175436 | 4012854137 | 4001327095 | 4535623543 | 1193365301 | 5348116438 | 8321765797 | 4519469312 | 6345647732 | 4693717522 | 2441409305 | 6090703240 | 6105991013 | 4170903387 | 4333066448 | 4038916660 | ||
| Q9Y6R7 | 64 | 55 | 4455.58 | 0.24214925 | 2.384825146 | XN | XA | IgGFc-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCGBP PE=1 SV=3 | 19979139 | 14168945 | 22799120 | 10473253 | 28807865.17 | 10400673.66 | 24103960.02 | 9817702.814 | 18528519.82 | 52413282.58 | 16073152.96 | 24044859.11 | 6534266.555 | 30959195.93 | 15153507.94 | 11738627.67 | 37646513.62 | 14521918.96 | 70878051.27 | 16689800.85 | 10625589.03 | 11485580.8 | 15326173.09 | 16926323.74 | 45043316.32 | 140520350.4 | 51880837.68 | ||
| P01133 | 45 | 37 | 4322.48 | 0.065344884 | 1.515648311 | XA | HN | Pro-epidermal growth factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=EGF PE=1 SV=2 | 1.38E+09 | 8.29E+08 | 6.91E+08 | 5.32E+08 | 458151748.4 | 779139480.6 | 708274319.6 | 952329412.8 | 615965476 | 579266706.2 | 558936056.8 | 350936937.5 | 847551734.4 | 611785952.6 | 433660421.4 | 238527733.7 | 501706615.9 | 458410712.4 | 589155094.2 | 871207315.4 | 820418966 | 335160976.1 | 535364885.8 | 282492989.1 | 821134407.5 | 621489391.8 | 679346247.7 | ||
| P02787 | 46 | 39 | 4096.89 | 0.405071763 | 1.537201059 | HN | XN | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 75736855 | 2.67E+08 | 2.57E+08 | 99117531 | 169383528 | 114218732 | 172716977.5 | 135809898.2 | 290443416.1 | 104619553.6 | 214309792.2 | 471387167 | 161045627.1 | 175537519.7 | 313140290.9 | 42395475.24 | 276704757.9 | 196124334.2 | 188426320.4 | 129250633.9 | 113823975.7 | 84222604.66 | 247999805.5 | 248860190.7 | 112849431.8 | 75977160.73 | 70553948.2 | ||
| P02751 | 55 | 49 | 4049.67 | 0.796799455 | 1.034440071 | XA | HN | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 1.08E+08 | 1.2E+08 | 1.1E+08 | 1.11E+08 | 106652321.2 | 95279734.77 | 101112341.4 | 114476995.7 | 105908190.2 | 108525843.3 | 132503844 | 44013143.27 | 149421829.8 | 77634313.03 | 100921002.4 | 106076206.6 | 108797561.8 | 112880640.1 | 75902742.18 | 91823659.24 | 85553373.58 | 81942669.5 | 100738401.4 | 177612163.4 | 122594836.3 | 115146461.8 | 97717585.5 | ||
| Q09666 | 104 | 80 | 3813.96 | 0.763278368 | 1.337464278 | XA | XN | Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHNAK PE=1 SV=2 | 7430908 | 10782877 | 10348914 | 17422849 | 29180998.59 | 18158697.23 | 51880131.63 | 75177472.34 | 25317583.55 | 15480482.94 | 21628482.63 | 54761328.89 | 32603461.85 | 9443216.186 | 14186053.9 | 23913280.91 | 14890720.78 | 8711235.682 | 17239309.41 | 47305497.03 | 20580378.78 | 42453252.15 | 9843191.274 | 20527589.79 | 7632218.953 | 9985812.139 | 8138913.89 | ||
| P04745 | 27 | 4 | 3791.81 | 0.758040531 | 1.173625026 | XN | XA | Alpha-amylase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY1A PE=1 SV=2 | 48157460 | 21858379 | 19840587 | 19032572 | 27473750.21 | 39966981.1 | 25125939.76 | 11108655.01 | 34450848.87 | 13400641.91 | 18211955.95 | 12897209.57 | 24849429.79 | 64878164.49 | 32706434.68 | 42650449.53 | 32606729.46 | 31565984.25 | 45338027.48 | 25608450.95 | 17215512.06 | 63062034.43 | 22693814.37 | 41002930.23 | 27374599.68 | 22324101.96 | 25283717.21 | ||
| P01042 | 37 | 33 | 3785.1 | 0.120289357 | 1.266156373 | XN | XA | Kininogen-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KNG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 8.26E+09 | 5.74E+09 | 4.04E+09 | 5.99E+09 | 3898507131 | 4069784782 | 4105979987 | 6512608979 | 3372480670 | 5495632280 | 5626789376 | 3603164142 | 7051249708 | 7063918648 | 3003489667 | 4743884712 | 6497301863 | 5046146292 | 6106270825 | 5688429165 | 6611491312 | 5253428381 | 7500302302 | 5152042844 | 8995296878 | 5091327310 | 7830048161 | ||
| P02788 | 48 | 43 | 3760.54 | 0.972021882 | 1.593109547 | HN | XA | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 1.14E+08 | 2.15E+08 | 48420822 | 88407333 | 71220119.47 | 48758732.5 | 71168796.87 | 99305614.82 | 146814863.7 | 101794326.2 | 21363922.94 | 47980669.21 | 27032370.27 | 53149860.59 | 721160802.1 | 259828856.9 | 135671776.4 | 70498700.57 | 352862541.8 | 46425888.8 | 48270759.46 | 81120163.53 | 94396893.36 | 36822571.94 | 579322365.7 | 80079003.41 | 63194668.35 | ||
| P19961 | 27 | 3 | 3725.68 | 0.540446716 | 1.116019516 | XN | HN | Alpha-amylase 2B OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY2B PE=1 SV=1 | 25232678 | 38721711 | 21325761 | 21066004 | 21051507.86 | 31861269.96 | 22414111.37 | 17023355.78 | 22275286.49 | 14123327.18 | 22526348.24 | 12405060.74 | 41779637.69 | 33475355.85 | 27830022.54 | 7793461.745 | 23357351.45 | 25325612.22 | 28151033.44 | 29382176.86 | 27884014.22 | 35603656.54 | 27354833.92 | 30171023.83 | 18901428.23 | 20312165.48 | 15059393.02 | ||
| P04746 | 26 | 4 | 3704.45 | 0.543427443 | 1.241558876 | XN | HN | Pancreatic alpha-amylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY2A PE=1 SV=2 | 65834979 | 76019630 | 60297953 | 26012801 | 30645524.69 | 146982076.4 | 76584447.59 | 28385702.21 | 59620615.23 | 39500981.08 | 91687642.52 | 37948448.9 | 97225603 | 67088828 | 36154231.4 | 20452960.14 | 36667523.93 | 43486728.89 | 92047295.86 | 83413326.62 | 68724325.63 | 106997278.9 | 68064480.1 | 44842097.78 | 43379252.87 | 42365554.26 | 33963447.11 | ||
| P01024 | 68 | 45 | 3652.32 | 0.059772507 | 1.509859258 | XA | HN | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 49319045 | 21835224 | 28813387 | 39167509 | 36022203.31 | 30360547.5 | 38806581.15 | 34230945.59 | 38401878.12 | 21612551.78 | 12009986.94 | 60859985.6 | 22283589.18 | 7119660.131 | 27868107.33 | 15874560.56 | 27340765.58 | 14955869.4 | 61938195.24 | 23218201.27 | 18520728.35 | 12798000.32 | 26657215.47 | 8283128.017 | 33969937.87 | 22576414.24 | 20319679.71 | ||
| P35555 | 54 | 43 | 3585.25 | 0.756246343 | 1.154674157 | HN | XA | Fibrillin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 84189037 | 73975325 | 85746446 | 1.23E+08 | 80233104.94 | 86072228.53 | 72778227.92 | 72021089.94 | 73085420.77 | 79718929.71 | 152842416.2 | 45937070.5 | 119760644.2 | 98165208.69 | 73300312.55 | 140158715.1 | 54257478.12 | 103360610.8 | 69843933.29 | 110522704.1 | 89953862.09 | 78044050.14 | 72795343.62 | 145676563.2 | 96054468.84 | 80644676.47 | 88226419.74 | ||
| P12109 | 37 | 26 | 3553.58 | 0.627647562 | 1.129709334 | XA | HN | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 6.1E+08 | 2.69E+08 | 2.54E+08 | 5E+08 | 300293027.3 | 357998642 | 338005945.3 | 308603568.3 | 265604821.9 | 424245429.3 | 218438508.1 | 227367084.7 | 404593741.4 | 244145417.7 | 252116378 | 423493509.4 | 293846180.4 | 347492382.5 | 285964410.5 | 219120616.5 | 351621242.9 | 255980412.8 | 397858940.3 | 159302410.1 | 540176098.1 | 272685516.1 | 355046860.2 | ||
| P10253 | 37 | 31 | 3389.13 | 0.604609492 | 1.231408122 | XA | XN | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAA PE=1 SV=4 | 1.41E+08 | 4.47E+08 | 4.2E+08 | 1.57E+08 | 72621019.14 | 293037624.5 | 339303462.6 | 174979748.3 | 238155439.6 | 92547789.81 | 296815419.6 | 225757638.3 | 598269152.6 | 303122038.8 | 77533361.65 | 53752027.69 | 129016010.1 | 154142577.2 | 189821196.2 | 204227221.9 | 402108991.1 | 158795023.9 | 147155287.4 | 120261439.6 | 132659271.1 | 305254789.9 | 192957349.8 | ||
| P54802 | 24 | 20 | 3173.43 | 0.022721513 | 1.850476202 | HN | XN | Alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAGLU PE=1 SV=2 | 70430262 | 85259581 | 1.55E+08 | 37495642 | 88295846.86 | 59283960.66 | 60553452.81 | 77042562.37 | 46826801.82 | 74325942.65 | 67446388.14 | 60909155.49 | 138887115.4 | 139192187.6 | 58467428.06 | 50388850.28 | 128314498.3 | 31905840.18 | 58151542.79 | 52457543.46 | 51653849.38 | 44702947.05 | 55357817.98 | 18263096.87 | 46375917.19 | 44919531.09 | 33330966.51 | ||
| P02760 | 28 | 26 | 3099 | 0.392104264 | 1.808944366 | XA | XN | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 2.9E+09 | 1.52E+10 | 1.59E+10 | 5.87E+09 | 23723376774 | 5084891001 | 2461553359 | 4567677322 | 3925150848 | 2473074393 | 3960996978 | 2385339142 | 3296539506 | 4116895168 | 7842797374 | 11472715311 | 6960477529 | 7582430398 | 2093208279 | 2977156156 | 2202151811 | 4225540810 | 6098173794 | 10244194436 | 4862255944 | 6321539051 | 4976600492 | ||
| P00734 | 26 | 22 | 3069.76 | 0.66775085 | 1.087172011 | XN | XA | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 4.17E+08 | 4.65E+08 | 4.18E+08 | 8.36E+08 | 504209963.8 | 736787514.9 | 520955645.4 | 457515879.5 | 523181701.4 | 317322752.8 | 1027712079 | 270502017.6 | 816346903.2 | 545992536.1 | 386805962.1 | 239380729.7 | 402773606.7 | 912738936.1 | 579148873.3 | 793922556.2 | 823444946.4 | 418042715.4 | 448404773.3 | 772278850.8 | 371960514 | 655171151.6 | 440440905.5 | ||
| P01833 | 35 | 25 | 3021.66 | 0.769197022 | 1.210160881 | HN | XA | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=PIGR PE=1 SV=4 | 6.33E+08 | 4.48E+08 | 4.69E+08 | 3.53E+08 | 247296331.1 | 436389892.1 | 492728347.9 | 443151104 | 524735592.2 | 355044401.9 | 777044610 | 563530732.6 | 877752748.3 | 980450729.1 | 327192541.8 | 273449493.3 | 396303211.8 | 346641387 | 460330496.5 | 479827343.6 | 366983195.5 | 326681518 | 424969776.2 | 670153941.2 | 554411969.1 | 573604223.2 | 323177530.4 | ||
| P00747;Q02325;Q15195 | 41 | 32 | 2994.68 | 0.382734391 | 1.856459005 | HN | XN | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 65242676 | 1.01E+08 | 1.16E+08 | 73050382 | 129122907.1 | 25784172.3 | 28436180.65 | 64647114.13 | 33611838.9 | 39070111.66 | 41436868.29 | 70128469.9 | 32655243.3 | 23836686.46 | 139114570.9 | 340718700.8 | 109457955.6 | 48118414.92 | 23965061.43 | 32325662.63 | 26197900.19 | 25187355.44 | 137764191.1 | 37688880.89 | 69360338.65 | 56289007.95 | 46139819.48 | ||
| P01009 | 33 | 23 | 2936.21 | 0.126568661 | 1.697882027 | HN | XA | Alpha-1-antitrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1.55E+08 | 1.99E+08 | 1.61E+08 | 79374719 | 152331498.3 | 199066222.4 | 231824191.3 | 115786772.9 | 169668536.5 | 437533465.3 | 277682099.6 | 403200876.5 | 211808402.4 | 326269664.9 | 142099141.7 | 49144699.1 | 368735199.4 | 266338601.1 | 332376620.4 | 174118178 | 195182705 | 140148554.5 | 100886270.1 | 82441368.52 | 119476206.4 | 132218361.8 | 201379528.7 | ||
| O00468 | 54 | 37 | 2884.26 | 0.18981114 | 1.325480673 | XA | HN | Agrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGRN PE=1 SV=4 | 28391911 | 39646743 | 37580302 | 21077666 | 29557072.6 | 15900297.08 | 15399444.37 | 23231271.61 | 20125785.64 | 11766704.66 | 12130298.32 | 10057068.71 | 14009427.07 | 9519748.578 | 33288958.41 | 27550250.98 | 26261732.71 | 29624683.06 | 12481410.25 | 19630311.12 | 15812025.89 | 13427744.7 | 24797684.66 | 24040451.56 | 22152815.46 | 26678027.91 | 23904002.14 | ||
| Q9UBG3 | 19 | 17 | 2833.08 | 0.947898611 | 2.055462713 | XA | HN | Cornulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRNN PE=1 SV=1 | 5326365 | 6417852 | 5816530 | 3113366 | 3877854.968 | 61634390.24 | 283816918.9 | 248436749.8 | 123866101.3 | 85905058.96 | 74050385.77 | 110211771.9 | 66039835.5 | 4282440.094 | 6801430.283 | 5187513.613 | 4030860.127 | 4628915.338 | 263263110.6 | 107549043.3 | 48039783.49 | 56633534.52 | 4581097.978 | 6007117.778 | 5496567.676 | 8576128.589 | 4952718.6 | ||
| Q9HC84 | 46 | 34 | 2814.6 | 0.080814843 | 1.887681829 | HN | XA | Mucin-5B OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC5B PE=1 SV=3 | 22334006 | 25522345 | 45621288 | 44635346 | 39892393.91 | 9077146.011 | 47606793.91 | 25370276.32 | 14758242.95 | 113600030.4 | 84289416.47 | 31343820.44 | 53792653.93 | 108131165.7 | 16150794.71 | 27083007.69 | 47352865.53 | 37024882.42 | 31691325.34 | 30728282.39 | 25600946.94 | 19127150.77 | 18932190.47 | 37985520.89 | 16214355.84 | 50086769.26 | 53488706.17 | ||
| P15144 | 37 | 24 | 2793.54 | 0.561357357 | 1.488840052 | HN | XN | Aminopeptidase N OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANPEP PE=1 SV=4 | 38526582 | 43417605 | 40122495 | 28727823 | 34401600.2 | 38547229.94 | 49446435.17 | 37867714.22 | 40269246.2 | 66127533.06 | 63867359.18 | 81442316.14 | 27485653.53 | 137823588.7 | 26222714.04 | 14766206.76 | 41065637.57 | 32024373.42 | 35451273.61 | 29884812.51 | 50667571.25 | 37279036.59 | 27516396.58 | 30033860.29 | 26815175.77 | 48562768.39 | 43458757.37 | ||
| Q7Z7M0 | 36 | 30 | 2713.99 | 0.343765344 | 1.309345014 | XA | XN | Multiple epidermal growth factor-like domains protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MEGF8 PE=1 SV=2 | 29221800 | 12532894 | 12961663 | 18727351 | 13117173.71 | 14074436.87 | 13356049.95 | 16862772.5 | 7806430.095 | 24406310.88 | 7041655.362 | 9832969.08 | 7408641.57 | 10563573.23 | 9474337.504 | 13149442.97 | 15835398.57 | 14138971.85 | 13953240.79 | 12064605.29 | 15481385.92 | 8509092.106 | 10671266.76 | 1660464.005 | 14122034.94 | 12533205.08 | 16905418.44 | ||
| P00450 | 29 | 24 | 2657.07 | 0.979179793 | 1.140754389 | HN | XN | Ceruloplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CP PE=1 SV=1 | 35423163 | 1.69E+08 | 56928546 | 32584196 | 45942589.18 | 30354237.18 | 20015431.02 | 25591973.45 | 34850635.43 | 42525767.21 | 22791240 | 77327512.68 | 26854771.69 | 13973075.3 | 87933945.93 | 14038586.04 | 92070918.81 | 90453294.54 | 56678331.14 | 22815650.53 | 40759129.3 | 55113629.48 | 88917967.49 | 40945781.6 | 35083076.94 | 36884889.47 | 33029299.37 | ||
| P06396 | 26 | 20 | 2632.12 | 0.493341319 | 2.133786294 | XA | XN | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 1.35E+08 | 2.82E+08 | 3.4E+08 | 3.9E+08 | 890870590.6 | 73362937.07 | 35564697.69 | 115871184.5 | 48247973.6 | 146201435.8 | 41177144.64 | 143378263.8 | 71412829.66 | 116496682.2 | 435559649.9 | 917724866.3 | 228479003.4 | 153573581.9 | 61337268.35 | 64899980.47 | 56996230.96 | 100723807.3 | 207263431 | 228945900.7 | 156269952.6 | 92003328.23 | 114028652.7 | ||
| P0C0L5;P0C0L4 | 43 | 33 | 2628.64 | 0.531353945 | 1.255857639 | HN | XN | Complement C4-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4B PE=1 SV=1 | 38580429 | 34125913 | 56277025 | 65951082 | 95082379.68 | 26058591.44 | 33794219.54 | 47510489.22 | 24075703.68 | 39842586.23 | 27063554.26 | 67084187.24 | 35630680.52 | 30369223.26 | 73678805.84 | 70718939.59 | 42445480.81 | 45119995.81 | 26749619.06 | 33891610.57 | 38975635.25 | 35169301.17 | 40207659.87 | 30510283.9 | 52730605.52 | 48465384.3 | 37250870.78 | ||
| Q12805 | 21 | 19 | 2571.33 | 0.676493993 | 1.640847019 | HN | XN | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFEMP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4.66E+08 | 2.8E+08 | 2.67E+08 | 5.54E+08 | 568544623.1 | 192359937.1 | 136056048.7 | 196892430.1 | 116958845.4 | 333939767.3 | 170674563.2 | 243871323.2 | 199332431 | 200859314.3 | 326584529.5 | 1697858786 | 283842500.2 | 329279459.2 | 276549508.1 | 255404377.3 | 204357511.7 | 192166683.8 | 282038609.2 | 266903159.4 | 312872393.6 | 226236895.9 | 290963656 | ||
| P04083 | 26 | 20 | 2538.78 | 0.913361265 | 2.573244798 | XN | HN | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 42396713 | 16911596 | 24709171 | 13224040 | 14155231.18 | 97748665.11 | 218277828.8 | 429501200 | 206534902.8 | 107094095.1 | 98354208.48 | 114325764.9 | 89662669.26 | 32745165.63 | 22992424.4 | 19259623.9 | 18468099.27 | 42229108.83 | 921520833.1 | 138536980.8 | 98309145.34 | 110245254 | 28197668.68 | 8645132.07 | 17091616.74 | 40143406.79 | 40065883.69 | ||
| Q14624 | 30 | 24 | 2515.78 | 0.545574825 | 1.137667417 | XN | HN | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 8.23E+08 | 1.34E+09 | 1.61E+09 | 1.25E+09 | 2389762096 | 1036735427 | 1248420274 | 758020692 | 757478339.6 | 958341592.2 | 455111933.1 | 1063166763 | 2077942555 | 390175593.4 | 1512868919 | 1986595362 | 864971308.5 | 1264390100 | 1383467546 | 1026500160 | 1077146348 | 1347014887 | 887890644.6 | 2387934939 | 1467411304 | 1260495860 | 1191337694 | ||
| P08582 | 31 | 26 | 2499.83 | 0.105644855 | 1.378998173 | XA | XN | Melanotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFI2 PE=1 SV=2 | 26704191 | 22274835 | 36070097 | 29342971 | 27346730.23 | 44018036.6 | 37298287.43 | 45465026.47 | 42131111.98 | 18369681.79 | 35869559 | 22101630.47 | 59667584.54 | 29638850.57 | 13415056.45 | 17883526.6 | 30570728.37 | 22991615.49 | 32685126.24 | 36051286.19 | 27697061.39 | 17797630.34 | 26944417.27 | 14107074.64 | 24205239.32 | 22916947.73 | 22868384.19 | ||
| P10451 | 15 | 14 | 2459.77 | 0.148838059 | 1.802224513 | HN | XA | Osteopontin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.24E+09 | 9.31E+08 | 1.2E+09 | 9.59E+08 | 1287147395 | 353707736.6 | 318649416.4 | 796944809.4 | 585530924.5 | 1723043200 | 2528638679 | 769735358.5 | 2470165281 | 1577595862 | 278729096 | 1206210598 | 2055194614 | 1234921206 | 566791114.7 | 2258077904 | 1042951395 | 1353390370 | 607384663.9 | 1634979762 | 696285335.9 | 2132298366 | 1503138816 | ||
| P22105;Q16473 | 46 | 35 | 2443.93 | 0.066147881 | 1.335899479 | XA | HN | Tenascin-X OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNXB PE=1 SV=3 | 69886562 | 53440176 | 57284534 | 52221599 | 35502597.91 | 63369561.42 | 69591445.8 | 70967500.4 | 59409661.86 | 31823734.23 | 47004229.7 | 24096028.46 | 83047064.64 | 40129215.96 | 49673849.59 | 53402460.98 | 31221691.01 | 37590979.98 | 38333159.97 | 54060273.22 | 50722486.51 | 25121021.35 | 39197012.17 | 44280666.53 | 71993736.98 | 48915291.22 | 49910870.59 | ||
| Q9UGT4 | 21 | 20 | 2425.37 | 0.573251797 | 1.221725934 | XA | XN | Sushi domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SUSD2 PE=1 SV=1 | 97803095 | 41451761 | 53111326 | 54545642 | 29991624.12 | 34630600.99 | 41739686.92 | 89374326.11 | 53077703.86 | 49132967.04 | 49620563.47 | 48760528.34 | 50694512.76 | 88273143.81 | 30142602.79 | 35481826.74 | 63373504.91 | 39887373.42 | 34304326.49 | 39044869.81 | 42174795.49 | 44379627.73 | 49274218.46 | 24596629.79 | 52947109.91 | 42845692.73 | 76191298.04 | ||
| Q9BXP8 | 37 | 33 | 2408.46 | 0.369874817 | 1.55529972 | HN | XN | Pappalysin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAPPA2 PE=1 SV=4 | 19295761 | 31909966 | 10969531 | 10194905 | 6935136.203 | 6724033.394 | 11782409.1 | 6028704.862 | 10358418.18 | 13119037.94 | 13136088.76 | 51001657.61 | 14336618.37 | 19223649.76 | 8228662.925 | 6360007.42 | 10560586.78 | 5942623.772 | 18869347.83 | 2527707.033 | 5560725.502 | 6324824.684 | 18755517.94 | 5379606.782 | 18179792.64 | 6499832.741 | 9144822.518 | ||
| Q08380 | 23 | 17 | 2405.22 | 0.080678923 | 1.296004398 | XA | HN | Galectin-3-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS3BP PE=1 SV=1 | 3.81E+08 | 3.25E+08 | 3.12E+08 | 2.19E+08 | 218874206.1 | 273649507.6 | 314298166.4 | 267701034 | 278214902.4 | 115964635.7 | 221667066.6 | 225947140.5 | 284032864.4 | 154790247.9 | 229862755.6 | 210003463.4 | 289225146.8 | 267344957.8 | 291223912.2 | 370926125.3 | 291422665.6 | 235509127.4 | 148138731.8 | 284961715.5 | 316303404.6 | 282376575 | 195060538.6 | ||
| P08571 | 19 | 16 | 2372.2 | 0.513040055 | 1.573873767 | XA | XN | Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD14 PE=1 SV=2 | 3.04E+08 | 8.78E+08 | 7.5E+08 | 4.84E+08 | 993343503.3 | 308274069.6 | 135568058.3 | 511518857.9 | 202299001.5 | 384705911.7 | 154025074.5 | 385721754.3 | 134598581.7 | 282660024.3 | 791090155.3 | 780202892.6 | 430383850 | 382132925.5 | 223403714.5 | 227475715.9 | 205538557.5 | 408547197.6 | 441681786.2 | 254775363.9 | 374905502.5 | 389677133.6 | 375748925.9 | ||
| P02774 | 28 | 23 | 2359.9 | 0.40283001 | 1.535421777 | HN | XN | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 69070559 | 51875142 | 40416449 | 49070215 | 46663420.13 | 70828521.34 | 70915247.55 | 34453735.58 | 61685505.26 | 161439424.6 | 114000901.4 | 130593358.6 | 79553642.99 | 69817184.9 | 45636309.43 | 18145634.67 | 37928179.62 | 59659641.55 | 73579062.21 | 62293713.59 | 60524231.22 | 49418235.11 | 30177630.09 | 52141066.86 | 45797048.58 | 45104230.48 | 47790437.49 | ||
| O00391 | 27 | 21 | 2358.24 | 0.021615212 | 1.531625672 | XA | HN | Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=QSOX1 PE=1 SV=3 | 35617656 | 15051366 | 20421761 | 27378170 | 15160801.79 | 23014672.85 | 28162638.74 | 22068100.3 | 22796485.15 | 5752739.93 | 17771077.74 | 12190110.83 | 30399964.48 | 6125994.892 | 13740783.5 | 19613018.23 | 12507775.99 | 18793375.21 | 24719343.82 | 28822621.83 | 17504596.6 | 13364004.14 | 18548900.28 | 17109783.2 | 27021457.57 | 18238894.58 | 20594675.74 | ||
| P07911 | 25 | 20 | 2342.91 | 0.811893701 | 1.512279356 | XN | XA | Uromodulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=UMOD PE=1 SV=1 | 1.17E+09 | 1.61E+09 | 2.34E+09 | 8.58E+08 | 568225100 | 1881787795 | 1910616281 | 1105389383 | 1621733527 | 1098545457 | 2830964793 | 4759620647 | 1454417170 | 2106633734 | 542061523.1 | 386152822.9 | 4377041654 | 1251422600 | 1035151638 | 1821028517 | 1321727117 | 1231010003 | 1182479664 | 7399052900 | 3910070521 | 991378596.1 | 864900559.6 | ||
| A8K2U0 | 37 | 24 | 2236.38 | 0.729573896 | 2.964357133 | XA | HN | Alpha-2-macroglobulin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2ML1 PE=1 SV=3 | 4198410 | 3105566 | 3133319 | 3556536 | 3365600.501 | 54896502.94 | 118857916 | 64536007.38 | 63611639.68 | 20209589.27 | 19126578.01 | 26355865.58 | 23571129.04 | 4082643.625 | 1946060.127 | 6515050.692 | 2876083.634 | 3017078.787 | 188141495.5 | 59699291.32 | 11976739.73 | 35082310.08 | 4111453.244 | 2749323.811 | 3409873.744 | 3314470.503 | 3441588.713 | ||
| P29508 | 28 | 12 | 2219.51 | 0.915618398 | 1.88630956 | XA | HN | Serpin B3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 4189307 | 3257082 | 3429980 | 3684479 | 5736199.161 | 61491224.93 | 123816838.5 | 54124685.08 | 56149667.8 | 22206400.46 | 55485060.17 | 35187019.21 | 32587402.6 | 4785616.669 | 4784204.653 | 3513540.287 | 4237420.129 | 4672310.123 | 51133979.27 | 43501057.11 | 17335550.49 | 81469112.61 | 3020985.237 | 7018358.769 | 4261032.09 | 3646388.821 | 4803712.495 | ||
| O75882 | 32 | 23 | 2209.06 | 0.944634771 | 1.091187907 | XA | XN | Attractin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATRN PE=1 SV=2 | 23001911 | 60113183 | 38790828 | 14971861 | 14653606.86 | 39322983.42 | 59599766.06 | 26389514.84 | 55244022.36 | 15172999.13 | 72703200.14 | 38000723.38 | 56809588.15 | 40618854.05 | 28003126.15 | 7137270.88 | 23922913.54 | 40069621.58 | 20840720.97 | 37126749.51 | 27959823.97 | 24083085.27 | 27377111.87 | 70107177.74 | 31770222.97 | 38119588.83 | 26951440.23 | ||
| Q8WZ75 | 15 | 12 | 2185.75 | 0.861757272 | 1.199351663 | XA | XN | Roundabout homolog 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ROBO4 PE=1 SV=1 | 6.73E+08 | 2E+08 | 2.9E+08 | 6.03E+08 | 147189793.9 | 234392655.1 | 249363028 | 257327944.6 | 320248451.2 | 394849822.5 | 374090920.5 | 319206518.2 | 554115335.4 | 162552155.6 | 136185008.9 | 230834982.1 | 265055206.9 | 336131704.2 | 147671460.2 | 262181505.7 | 357036405.5 | 180822163.8 | 410398167.2 | 291647360.3 | 281058464.9 | 266496761.6 | 283134523.9 | ||
| P20930 | 38 | 25 | 2158.99 | 0.934909743 | 1.178031452 | XN | HN | Filaggrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG PE=1 SV=3 | 4034697 | 2511898 | 2931499 | 5739889 | 3669882.19 | 2026034.517 | 4197596.11 | 21859111.52 | 3056846.691 | 3750411.253 | 4653291.161 | 3836168.511 | 4426523.145 | 2644546.571 | 6041059.392 | 9869660.35 | 3560652.842 | 3967533.981 | 1279176.745 | 6575718.458 | 3827307.198 | 8049282.866 | 2166514.784 | 11787375.56 | 2931432.341 | 7249601.111 | 6494255.502 | ||
| P02765 | 16 | 14 | 2101.96 | 0.267138957 | 3.389342745 | HN | XN | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 3.13E+08 | 4.4E+08 | 7.27E+08 | 6.02E+08 | 1663304581 | 170208753 | 307641189.2 | 400953477.8 | 138432351 | 531662250.9 | 199654870.9 | 329645059.1 | 101738441.6 | 309057285.5 | 967374382.1 | 5760448774 | 980832797.1 | 303220733.2 | 195877305.9 | 200132001 | 156411188.3 | 268760431.1 | 1029099874 | 131523193.7 | 245773686.9 | 249037221.2 | 321459918.9 | ||
| P01008 | 27 | 22 | 2101.39 | 0.072592911 | 1.688159761 | XA | XN | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 72524143 | 45582000 | 50760702 | 74175446 | 174517186.3 | 41890525.86 | 40438617.47 | 52657663.36 | 44982536.05 | 57887154.19 | 36677091.96 | 70184333.05 | 38811703.75 | 19531678.82 | 48572696.06 | 53367070.23 | 52798168.19 | 51477300.63 | 38859865.15 | 38578184.51 | 35531258.32 | 36491941.97 | 35328980.35 | 15448826.4 | 62002335.99 | 45674011.52 | 46037363.81 | ||
| Q93088 | 20 | 14 | 2096.93 | 0.282482351 | 1.831312252 | XA | HN | Betaine--homocysteine S-methyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BHMT PE=1 SV=2 | 1E+08 | 28982424 | 57323410 | 2.81E+08 | 17948152.79 | 106375311.3 | 120497654.7 | 124964314.4 | 72101289.63 | 117162370.9 | 40564327.56 | 91571658 | 53963441.79 | 20537096.06 | 39513656.02 | 27636075.14 | 54005852.74 | 51523626.5 | 134189842.1 | 68120708.2 | 177094039.7 | 107683578.8 | 87257068.5 | 44508158.79 | 37831360.9 | 46377625.28 | 44290561.81 | ||
| P04217 | 18 | 12 | 2095.32 | 0.47265209 | 1.909286922 | HN | XN | Alpha-1B-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=A1BG PE=1 SV=4 | 1.21E+08 | 2.95E+08 | 2E+08 | 1.71E+08 | 586434785.4 | 77474963.17 | 48443652.97 | 141732725.4 | 92632921.51 | 261182363.3 | 44910352.41 | 275782305.2 | 43624762.92 | 96346558.93 | 231911553.1 | 144571582.3 | 634437283.4 | 428174243.7 | 116466418.4 | 72990524.64 | 118840099.9 | 173013426.2 | 274208646.3 | 33920130.44 | 100206807.6 | 106290983.9 | 135868234.9 | ||
| Q96PD5 | 16 | 14 | 2082.34 | 0.393527211 | 2.301811251 | XA | XN | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGLYRP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 87267159 | 2.83E+08 | 1.22E+08 | 97367264 | 329912148.1 | 45136739.75 | 17034217.29 | 34645304.99 | 28711118.57 | 69728222.27 | 31823441.82 | 17419385.19 | 47030899.5 | 31095028.32 | 138537975 | 165287050.2 | 75091947.58 | 93726970.11 | 50200847.98 | 22915380.8 | 40673008.45 | 67729781.93 | 60931334.62 | 10763283.65 | 57548285.17 | 63841330.15 | 79198113.05 | ||
| P05062 | 19 | 17 | 1979.99 | 0.164203244 | 1.857092003 | XA | HN | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOB PE=1 SV=2 | 1.11E+08 | 38436939 | 76497430 | 1.31E+08 | 11492717.6 | 147945319.1 | 129025529.6 | 141286995.5 | 81025342.04 | 132390965 | 42642419.14 | 73055857.68 | 44811915.06 | 63301269.85 | 21209073.98 | 19508856.32 | 33492540.95 | 37060205.66 | 55473881.24 | 44517788.96 | 87028469.48 | 101877316.2 | 65355322.77 | 18248325.63 | 37710975.28 | 39590737.19 | 34504156.05 | ||
| P05164 | 29 | 19 | 1960.22 | 0.100078836 | 4.964137947 | XA | HN | Myeloperoxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MPO PE=1 SV=1 | 6042310 | 5482063 | 4502593 | 8816486 | 6022407.665 | 124943757.4 | 125126094.4 | 20427491.18 | 72451521.38 | 14273089.45 | 3865858.288 | 7456239.981 | 4993372.374 | 7529257.423 | 22971898.9 | 4671037.374 | 3165071.643 | 6377223.798 | 13937251.67 | 9506831.663 | 8387911.836 | 19069400.49 | 3874843.814 | 2743878.696 | 11814729.3 | 9818315.54 | 6906513.039 | ||
| P07355;A6NMY6 | 28 | 19 | 1951.32 | 0.887672738 | 1.817179137 | XN | HN | Annexin A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 5773205 | 6270428 | 4735017 | 5730988 | 6427541.89 | 38660728.98 | 98014038.61 | 55074193 | 45734608.66 | 23016160.08 | 29545654.61 | 34861928.41 | 33295044.51 | 6801269.771 | 5744900.025 | 5569869.426 | 5803992.474 | 7621911.567 | 129668638.2 | 25071311.53 | 22455701.44 | 66148091.24 | 3686686.272 | 5684860.248 | 6170726.211 | 8845123.217 | 8953885.228 | ||
| P02671 | 28 | 20 | 1941.05 | 0.35269911 | 1.184515492 | HN | XN | Fibrinogen alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGA PE=1 SV=2 | 83956509 | 1.18E+08 | 1.12E+08 | 1.56E+08 | 105518748 | 97706509.16 | 75764508.49 | 81238105.18 | 66185939.25 | 151809842.5 | 84024583.67 | 68603596.21 | 95997632.29 | 102791548.8 | 87424903.74 | 120502931.3 | 109435452.3 | 148447263.6 | 56710825.82 | 79423544.84 | 52620600.58 | 78933971.58 | 69123070.63 | 153725297.2 | 168918950.6 | 86326149.28 | 72305458.26 | ||
| P02749 | 17 | 14 | 1939.28 | 0.592066765 | 1.271565602 | XA | XN | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 5.4E+08 | 5.41E+08 | 5.03E+08 | 3.7E+08 | 403545966.4 | 137380911.3 | 191428631.4 | 259902574.3 | 175188261.7 | 246660179.6 | 488405556.3 | 200732430.8 | 193162226.2 | 376183668.2 | 280758064.3 | 255608552.3 | 197276079.2 | 272020385.2 | 162956907.9 | 155565275.7 | 409846804.3 | 199734082.8 | 278096738.4 | 447673585.5 | 204878281.9 | 258274855.4 | 337598838.4 | ||
| P55287 | 24 | 15 | 1913.44 | 0.892504114 | 1.331835873 | XA | XN | Cadherin-11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH11 PE=1 SV=2 | 51408560 | 65529347 | 59725768 | 82115263 | 106895832.1 | 21683268.1 | 9494773.538 | 45107535.84 | 14544619.89 | 75529102.3 | 12682744.64 | 44520027.83 | 14065928.22 | 30094638.7 | 28577057.45 | 82084300.95 | 62912999.32 | 25071039.97 | 20236132.6 | 23206276.96 | 25647391.85 | 32908735.98 | 67168217.13 | 50718893.54 | 33107443.14 | 37726384.43 | 52044205.26 | ||
| P01857 | 16 | 6 | 1908.33 | 0.552779472 | 1.225289793 | XA | HN | Ig gamma-1 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.6E+09 | 1.56E+09 | 5.86E+08 | 4.73E+08 | 671492901.9 | 1027628898 | 1046221987 | 760732101.8 | 1036805841 | 722841463.3 | 914546626.6 | 1332792799 | 852825246.5 | 931670362.2 | 952731077.1 | 329456322.4 | 476658791.3 | 635095210.3 | 672327192.1 | 1128603852 | 588163098.9 | 324226771.8 | 800697435.1 | 758570399.1 | 1203628571 | 1034786725 | 774135827 | ||
| Q8NBJ4 | 23 | 19 | 1906.52 | 0.007998613 | 1.474365294 | HN | XA | Golgi membrane protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GOLM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 87327561 | 65280860 | 40446815 | 54257630 | 44102149.34 | 40539134.91 | 47467243.48 | 63534222.03 | 47280397.34 | 113665391.2 | 93540464.42 | 71449720.7 | 99406046.1 | 62301517.57 | 76607077.76 | 81020060.4 | 54166975.76 | 70629710.68 | 46222127.88 | 55446019.36 | 70439475.9 | 49176045.55 | 92729102.89 | 79601629.23 | 62441312.66 | 52736976.82 | 75680255.25 | ||
| Q12907 | 21 | 18 | 1888.68 | 0.889396579 | 1.074455631 | XA | HN | Vesicular integral-membrane protein VIP36 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LMAN2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.88E+08 | 5.11E+08 | 4.52E+08 | 3.31E+08 | 510295559.6 | 255562500.3 | 168687854.2 | 229034144.2 | 222885347.1 | 387451625.6 | 252212531 | 181109327.4 | 162600399 | 238357358.5 | 308923574.2 | 130138868.7 | 517832706.9 | 492060505.6 | 242396985 | 246039322.2 | 205472107.5 | 410928979.7 | 257980092.2 | 430066358.1 | 215362177.6 | 235508706.6 | 448260292.7 | ||
| P02538 | 34 | 2 | 1885.64 | 0.479792173 | 6.58421644 | XA | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 28590.46 | 20467.83 | 9752.882 | 148095 | 258617.5139 | 19309850.64 | 3032225.067 | 490892.6422 | 11452531.3 | 457342.8363 | 122211.5967 | 2807272.307 | 1780323.231 | 4429.075682 | 16790.84619 | 35252.43967 | 9299.648176 | 45006.48136 | 2278430.286 | 540365.7305 | 212713.1141 | 7176238.05 | 28497.41834 | 69525.27238 | 38634.48631 | 40874.37109 | 44144.92063 | ||
| P10909 | 24 | 17 | 1884 | 0.857123616 | 1.159426067 | XN | HN | Clusterin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLU PE=1 SV=1 | 5.3E+08 | 1.95E+08 | 1.65E+08 | 2.97E+08 | 193881114.5 | 224426197.4 | 182316070.7 | 237283407.9 | 201070957.3 | 273861050.5 | 179286858.7 | 148850694.4 | 237591583.7 | 130709844.5 | 194344630 | 380663574 | 283998286.6 | 262522742.6 | 337209854.1 | 203853035.7 | 272603969.8 | 251460742.5 | 356361955.3 | 68118331.99 | 370481825.1 | 243349061.5 | 321882602.7 | ||
| P06733 | 28 | 14 | 1868.74 | 0.004391106 | 1.759758894 | XA | XN | Alpha-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 45566074 | 20167887 | 28667156 | 54243712 | 29657591.75 | 31643488.09 | 32557082.96 | 50384502.26 | 24701827.56 | 35295372.82 | 18838705.27 | 38980542.25 | 19424765.31 | 12192665.32 | 19136941.43 | 15474166.9 | 16934665.13 | 18743013.14 | 15405843.59 | 17138355.07 | 29245428.25 | 23392265.24 | 35147990.24 | 10242448.12 | 18313698.78 | 16905967.89 | 14681204.37 | ||
| P14543 | 25 | 21 | 1866.99 | 0.772904752 | 1.090093236 | XA | HN | Nidogen-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NID1 PE=1 SV=3 | 44577000 | 86779050 | 88946316 | 66050508 | 89975665.4 | 65488068.76 | 44879907.11 | 45909907.35 | 70520016.41 | 63440214.05 | 42867804.78 | 35396504.55 | 71055152.07 | 65958860.02 | 85196626.75 | 49371651.13 | 73552982.14 | 66439886.18 | 54218958.87 | 51426683.59 | 53915557.03 | 67019032.01 | 67013067.46 | 105428163.6 | 84030182.1 | 49540832.13 | 64653172.19 | ||
| P13646;Q2M2I5 | 31 | 9 | 1857.42 | 0.531910181 | 3.179273887 | XA | HN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 1957361 | 2271798 | 2199953 | 1428073 | 3807746.746 | 123764119 | 34121110.89 | 19627250.66 | 90924812.34 | 4200502.471 | 3457635.198 | 45832773.52 | 24344550.59 | 1195382.809 | 3515759.304 | 1950736.268 | 1502177.545 | 2103059.949 | 23984000.01 | 16620857.22 | 3896850.958 | 59173326.58 | 1544775.691 | 1919563.608 | 1560617.73 | 2073341.762 | 2688802.777 | ||
| P68871;P02100 | 15 | 7 | 1854.97 | 0.173232369 | 9.355313161 | HN | XN | Hemoglobin subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBB PE=1 SV=2 | 22734706 | 17702269 | 11719372 | 11793765 | 124665350.4 | 45965911.5 | 18282690.62 | 169239966.3 | 466926466.1 | 23693516.75 | 41133654.75 | 2093377888 | 30667657.96 | 26658935.01 | 44419412.04 | 42869118.05 | 460288859.5 | 145491538.7 | 81902897.88 | 11560663.47 | 13980874.94 | 11897043.52 | 26519873.72 | 32062892.69 | 18159818.43 | 62693902.01 | 52125637.64 | ||
| P01834 | 9 | 9 | 1835.36 | 0.867430411 | 1.135925879 | HN | XN | Ig kappa chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGKC PE=1 SV=1 | 8.62E+09 | 1.11E+10 | 7.02E+09 | 7.96E+09 | 15741286532 | 3906808933 | 4157126231 | 6252306624 | 3001144575 | 8816241139 | 3391179167 | 8773337160 | 3805467345 | 6214225225 | 13744899766 | 12907902575 | 7325076842 | 6073365672 | 6553074306 | 4582495496 | 3889445273 | 5380650371 | 9792780878 | 15492392813 | 5698965694 | 4708805988 | 6450976446 | ||
| P25311 | 22 | 14 | 1830.12 | 0.912144416 | 1.836348201 | XA | XN | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AZGP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 25018283 | 6.44E+08 | 2.78E+08 | 40418216 | 577916843 | 90370581.33 | 55536487.69 | 62527257.92 | 90657683.67 | 51418371.64 | 31789883.23 | 94750927.05 | 36890132.89 | 118043876.7 | 452488373.4 | 169325461.6 | 189369069.9 | 198741404.3 | 33796333.92 | 43290435.69 | 44691369.8 | 94356085.65 | 189901306.8 | 202604756.9 | 136321557.9 | 151540855.8 | 118869174.8 | ||
| Q16270 | 17 | 13 | 1790.76 | 0.362717403 | 1.402633949 | XN | HN | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP7 PE=1 SV=1 | 5.87E+08 | 3E+08 | 1.72E+08 | 2.83E+08 | 210138073.6 | 278513383 | 160122008.5 | 239269682.1 | 267549659 | 169339940.9 | 137046383.7 | 150532935.7 | 384384115.8 | 68198218.96 | 206536272 | 243840158.6 | 413516688.7 | 569290898.9 | 386601402.8 | 544413801.9 | 459040891.1 | 247187146.6 | 356182661.3 | 65207565.3 | 450975233.4 | 333093877.9 | 443227792.3 | ||
| Q92896 | 31 | 25 | 1738.96 | 0.118193091 | 1.619765909 | XA | HN | Golgi apparatus protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 20936615 | 7508326 | 5881046 | 13452162 | 9659283.202 | 9782767.304 | 9097284.025 | 13098047.36 | 7808610.375 | 2471545.035 | 3295625.125 | 5380917.679 | 7655533.536 | 2343471.506 | 8088581.654 | 9557257.757 | 8762735.578 | 12467907.47 | 10007647.72 | 8492975.762 | 8415565.274 | 8617577.048 | 10491661.26 | 1461832.552 | 10659172.02 | 10774442.9 | 10154093.66 | ||
| Q14515 | 21 | 21 | 1731.57 | 0.402203792 | 1.704516819 | XA | HN | SPARC-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPARCL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.15E+08 | 11087368 | 24622737 | 45017197 | 15743855.69 | 30859158.44 | 36568048.38 | 19746838.21 | 15107104.95 | 18082500.61 | 18429645.59 | 27735527.83 | 21714534.24 | 4861726.227 | 33418887.35 | 20288126.89 | 12966099.24 | 26287147.98 | 13202045.69 | 16210677.24 | 19624243.76 | 10547436.13 | 53899959.46 | 8753181.734 | 30985544.72 | 21509582.48 | 36868838.84 | ||
| P04264 | 25 | 16 | 1714.8 | 0.482098648 | 3.964225471 | XA | XN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 3575770 | 4325977 | 5761341 | 2458050 | 3748985.659 | 190239591.4 | 53396334.57 | 14154090.23 | 97895947.91 | 4707189.504 | 15896596.2 | 55441200.07 | 26173166.11 | 2782917.23 | 1956849.387 | 4200981.793 | 4199304.494 | 3495572.953 | 17015449.33 | 29106253.92 | 3211019.061 | 24037282.41 | 3353694.198 | 7309224.301 | 4421810.326 | 2836630.654 | 3444944.081 | ||
| Q5SZK8 | 35 | 24 | 1712.61 | 0.209209533 | 1.300509785 | XA | XN | FRAS1-related extracellular matrix protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FREM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 11254125 | 4636016 | 6391516 | 9579464 | 7273909.576 | 6847879.383 | 6988224.861 | 8051710.115 | 6158761.21 | 6919919.01 | 7601298.411 | 5086618.119 | 8340530.42 | 13870893.74 | 6284526.624 | 3516114.735 | 6521133.879 | 4895865.766 | 4463439.565 | 7794613.957 | 5464689.421 | 3477472.675 | 6008630.318 | 3582919.741 | 6852948.022 | 5834957.295 | 8178229.585 | ||
| P02647 | 27 | 23 | 1699.9 | 0.470769335 | 1.657334787 | HN | XN | Apolipoprotein A-I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 41061223 | 18283554 | 33369755 | 86122750 | 40034345.05 | 28038533.07 | 33418776.09 | 26667570.47 | 45482523.32 | 42994015.74 | 25120843.1 | 193850110.7 | 23084405.72 | 20146455.03 | 31838453.3 | 26123183.75 | 30005203.17 | 31071972.47 | 17435108.09 | 32033891.38 | 29074378.3 | 25073290.05 | 42644853.29 | 20729203.16 | 26936927.04 | 30963177.52 | 31083188.22 | ||
| Q16769 | 14 | 13 | 1687.48 | 0.51455614 | 1.41912894 | HN | XN | Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=QPCT PE=1 SV=1 | 2.73E+08 | 2.3E+08 | 2.06E+08 | 4.24E+08 | 408450028.5 | 373516577.4 | 198385599.1 | 559665786.8 | 232395458.1 | 943980652.5 | 92985281.23 | 333921427.3 | 391435104 | 267509905.7 | 288924185.3 | 751429204 | 469164164.8 | 572293236.9 | 428876252.3 | 131095074 | 352754343.2 | 257657128.3 | 153238416.4 | 386330918.2 | 278063820.1 | 380451989.4 | 528832681.7 | ||
| P05155 | 18 | 12 | 1679.23 | 0.856846846 | 1.148952797 | HN | XA | Plasma protease C1 inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPING1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.71E+08 | 1.46E+08 | 95426577 | 71536825 | 123670458.5 | 146161581.4 | 216618720.4 | 95246399.37 | 196241663 | 185140790.5 | 231129217.5 | 159424777.8 | 146471697.6 | 262542862.7 | 100734620.1 | 48828184.97 | 140555084.9 | 174440781.6 | 227520161.8 | 144019777.7 | 190953623.9 | 128697598.8 | 56814515.73 | 99176243 | 107002838.6 | 173482582.4 | 164729576 | ||
| Q03154 | 21 | 18 | 1678.64 | 0.34818041 | 1.426189412 | XA | HN | Aminoacylase-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACY1 PE=1 SV=1 | 48432052 | 16290841 | 40606443 | 48454988 | 11529619.3 | 62699282.75 | 59388988.41 | 58656436.86 | 48073922.82 | 39550807.24 | 26403479.65 | 67509809.43 | 42704495.77 | 29456853.8 | 21247059.32 | 13215755.46 | 16866044.24 | 19399292.63 | 29439394.62 | 21323803.38 | 55281496.1 | 52311682.06 | 38872632.41 | 24619542.31 | 27643176.41 | 26399431.99 | 25593959.99 | ||
| P60709;P63261 | 19 | 4 | 1673.97 | 0.021352902 | 2.288582676 | XA | XN | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 1.08E+08 | 26671995 | 38269534 | 1.12E+08 | 23789580.84 | 57245129.22 | 62781048.49 | 129535352.8 | 62590410.88 | 76494806.33 | 35888231.49 | 82061322.74 | 46191281.45 | 43592499.82 | 42586841.36 | 18842880.74 | 22451345.2 | 24712472.25 | 22449946.17 | 29822570.39 | 49189819.94 | 37489970.27 | 46190304.86 | 11094443.12 | 23555881.64 | 28309974.46 | 23038829.01 | ||
| P22891 | 18 | 14 | 1653.81 | 0.011828533 | 1.823360842 | XA | HN | Vitamin K-dependent protein Z OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROZ PE=1 SV=2 | 1.84E+08 | 83264063 | 76201295 | 95481954 | 85004664.57 | 70202309.2 | 116803893.7 | 120094671.6 | 75045074.93 | 79238614.77 | 53286717.94 | 45620918.34 | 70366138 | 55086502.83 | 53995161.87 | 12638074.68 | 48742612.29 | 78034231.25 | 86940218.25 | 55838295.89 | 46539291.29 | 83916914.91 | 45923944.41 | 115162762.2 | 95926615.95 | 54923126.94 | 120247475.3 | ||
| P01859 | 17 | 7 | 1635.89 | 0.747734936 | 1.125893483 | XN | HN | Ig gamma-2 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHG2 PE=1 SV=2 | 3.82E+08 | 1.5E+09 | 1.05E+09 | 9.89E+08 | 1224241437 | 764910516.9 | 395828882.6 | 1177099006 | 936895145.7 | 913585117.3 | 706473844.5 | 1365562481 | 837343547.8 | 472478446.3 | 645631937.2 | 233347520.6 | 1441453725 | 1673699963 | 1527144519 | 802104692.5 | 1127010324 | 901082083.6 | 1937525378 | 1074309278 | 473674339.7 | 842671689.6 | 647657945.8 | ||
| Q02818 | 20 | 14 | 1628.93 | 0.785121363 | 1.177308384 | XN | HN | Nucleobindin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUCB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 22421618 | 9454192 | 7525143 | 13943388 | 9095947.135 | 10070272.19 | 9858612.837 | 11111808.47 | 11849516.4 | 6695881.836 | 6917776.691 | 8967600.269 | 13469981.83 | 5986163.883 | 9509303.769 | 18776233.28 | 10261348.33 | 14223660.56 | 4932607.413 | 12581530.37 | 11357838.63 | 7664500.933 | 20898840.69 | 5511065.38 | 15460605.56 | 12172202 | 21039003.93 | ||
| P15309 | 18 | 13 | 1626.94 | 0.289494824 | 1.611899531 | HN | XN | Prostatic acid phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACPP PE=1 SV=3 | 66220488 | 1.61E+08 | 96901043 | 89826114 | 366219582 | 60799538.6 | 86672626.85 | 88365673.65 | 74949588.08 | 40869773.45 | 110147594.5 | 58715020.64 | 113038820.4 | 447219119.5 | 228347000.3 | 69671957.05 | 107694742.1 | 282084096 | 30658098.48 | 35729982.4 | 38747544.98 | 24774424.08 | 77981182.8 | 56757643 | 224517078.6 | 275226401 | 139999075.7 | ||
| P02790 | 26 | 19 | 1619.7 | 0.229307963 | 1.324520813 | XA | HN | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 1.09E+08 | 2.42E+08 | 1.59E+08 | 1.4E+08 | 197910098 | 108920569.3 | 185260504 | 63613410.38 | 122504573.6 | 102396309.7 | 108154134.8 | 144963451.7 | 181411707 | 45977027.32 | 159981740.9 | 86547139.25 | 70690773.02 | 102142204.2 | 118634035.4 | 143563308.6 | 142408367.3 | 124754122.3 | 88552751.9 | 107251011.9 | 110799600.8 | 119174195 | 119992281.2 | ||
| P04259 | 32 | 2 | 1619.33 | 0.217607234 | 1.980125325 | XA | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 239442.2 | 311336.3 | 283532.1 | 296778.9 | 273291.306 | 1638525.73 | 502708.353 | 257067.5206 | 1137220.747 | 273299.6105 | 309775.3443 | 571733.8936 | 240651.8563 | 220102.9254 | 256775.6041 | 284883.1178 | 173878.5327 | 163641.7942 | 563316.8013 | 251412.4213 | 253466.9193 | 1198017.684 | 241461.3264 | 247997.9797 | 201698.0214 | 383314.0474 | 220575.1008 | ||
| P05154 | 21 | 14 | 1587.71 | 0.018053236 | 1.775432449 | XN | HN | Plasma serine protease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 2.31E+08 | 2.5E+08 | 2.19E+08 | 1.46E+08 | 169191441.7 | 346507588.6 | 174243235.8 | 203504994.4 | 228902247.4 | 69420586.25 | 80751561.42 | 83863766.43 | 153026426.9 | 61643432.7 | 180480865.6 | 121340220.2 | 165517499.3 | 215553773.1 | 373624341.2 | 255072433.9 | 222351090.5 | 181463505.9 | 200621314.4 | 43573913.01 | 251023310.6 | 202125182 | 279220950.7 | ||
| P07288 | 14 | 11 | 1581.62 | 0.88675175 | 2.289410036 | XA | XN | Prostate-specific antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.8E+08 | 1.34E+08 | 90163193 | 5.19E+08 | 2415890625 | 14424923.36 | 15200688.02 | 67284506.79 | 12594482.99 | 181387534.8 | 11243151.54 | 16766540.1 | 15228452.73 | 281580404.5 | 363761047.9 | 218120241.1 | 239170154.5 | 785472253.5 | 16570991.61 | 12954545.22 | 18352369.22 | 13287581.01 | 155439151.9 | 233748777.4 | 234508122.1 | 485605541 | 335724267.7 | ||
| P33908 | 22 | 12 | 1579.62 | 0.20009849 | 1.612785975 | XA | HN | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase IA OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN1A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 84006640 | 24965377 | 35365979 | 48793985 | 23561268.26 | 16377399.93 | 22866626.92 | 50210891.53 | 24818578.23 | 14725565.93 | 15887854.96 | 21287310.66 | 24005295.46 | 15628887.42 | 24550713.7 | 47196403.07 | 24446579.02 | 17485689.97 | 16923322.63 | 21571040.82 | 20551179.03 | 9668921.331 | 44341186.36 | 11937110.07 | 49779944.6 | 31042244.17 | 41609401.88 | ||
| P05156 | 23 | 17 | 1576.45 | 0.382785478 | 1.184181821 | XA | HN | Complement factor I OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFI PE=1 SV=2 | 62742063 | 43069858 | 39065408 | 35271761 | 28737619.42 | 44611867.1 | 31865304.42 | 48723361.77 | 40845914.6 | 13445673.3 | 36230412.78 | 41911430.92 | 56635827.93 | 6499698.215 | 36522564.05 | 31105775.81 | 41264708.55 | 53001804.97 | 46468342.72 | 39969806.06 | 37756922.27 | 26527429.63 | 36677255.64 | 18761705.12 | 41351050.15 | 29520596.15 | 48952402.96 | ||
| P04406 | 18 | 13 | 1576.03 | 0.254126591 | 1.759822638 | XA | HN | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 70501934 | 17365352 | 34780479 | 1.43E+08 | 20488079.33 | 51086433.85 | 47053571.45 | 115044585.6 | 50077002.43 | 63543632.45 | 25607567.44 | 58636764.21 | 30976834.53 | 16294936.25 | 22301759.74 | 34579373.51 | 33074713.78 | 27115787.41 | 48215578.65 | 29586006.43 | 67328296.33 | 52282631.59 | 49626193.07 | 11477111.21 | 35437099.45 | 39556937.35 | 20904537.62 | ||
| Q96RW7 | 26 | 14 | 1572.35 | 0.840633226 | 1.103697479 | HN | XN | Hemicentin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HMCN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 60919985 | 69269887 | 67719858 | 66288555 | 40752321.81 | 61581301.97 | 56175456.26 | 58372846.47 | 37335386.99 | 37280896.05 | 131910143.2 | 22172171.01 | 67771556.94 | 68871816.35 | 64647053.24 | 26963098.18 | 59445519.79 | 52908174.71 | 53694455.45 | 61525378.64 | 47983863.73 | 44745884.38 | 40719383.85 | 103258755.1 | 47221402.39 | 35934883.42 | 46905341.93 | ||
| P06727 | 25 | 14 | 1565.35 | 0.358947999 | 1.831230448 | XA | XN | Apolipoprotein A-IV OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA4 PE=1 SV=3 | 10675586 | 6048775 | 16960273 | 24066932 | 33278882.61 | 4013734.554 | 9921145.336 | 8317604.18 | 7245484.626 | 8377615.844 | 4009304.819 | 39448495.78 | 2544591.621 | 3074563.53 | 14840743.34 | 20362477.78 | 12783646.02 | 5826777.897 | 3182840.806 | 7125536.812 | 6956940.895 | 3794478.764 | 10551033.07 | 3624963.849 | 9285816.072 | 10359673.44 | 10936984.85 | ||
| O14773 | 13 | 11 | 1555.02 | 0.460112047 | 1.40726733 | XA | XN | Tripeptidyl-peptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.08E+08 | 77154093 | 1.7E+08 | 2.16E+08 | 130558843.1 | 70028702.82 | 62835721.62 | 101083546.4 | 38309466.22 | 83831626.25 | 26388684.79 | 54212269.11 | 44809873.63 | 54910998.19 | 65864240.22 | 220659681.4 | 162440247.9 | 110282366.3 | 62481019.04 | 42073298.67 | 96269914.91 | 60542470.45 | 152365582.6 | 23578463.73 | 89975385.2 | 74548534.35 | 90377550.7 | ||
| Q9BRK3 | 18 | 13 | 1553.58 | 0.008956303 | 1.63649572 | XA | HN | Matrix-remodeling-associated protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MXRA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.1E+08 | 50218489 | 88641739 | 50128554 | 59335661.01 | 51806165.16 | 63998145.98 | 86714237.37 | 66315741.39 | 39511694.29 | 31498879.35 | 26335401.29 | 40384349.83 | 21380021.78 | 54053560.59 | 50232170.85 | 65786135.2 | 53969177.61 | 39718177.18 | 57925788.46 | 65365893.04 | 33961453.23 | 83812580.63 | 45949145.12 | 66173566.19 | 75014116.83 | 93865036.96 | ||
| P07602 | 24 | 20 | 1549.32 | 0.445947989 | 1.235774608 | XA | XN | Proactivator polypeptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSAP PE=1 SV=2 | 6.61E+09 | 2.34E+09 | 3.89E+09 | 5.24E+09 | 3827111678 | 4451502065 | 4565866910 | 5787282160 | 3422777546 | 6612923877 | 1454024363 | 707729997.8 | 1600318993 | 6426722455 | 2444675845 | 1673800499 | 6445668892 | 9081095664 | 3831156865 | 2730581103 | 4344733243 | 5448724432 | 5107902150 | 814383007.2 | 1892547902 | 3637689481 | 4670023375 | ||
| P00749 | 18 | 13 | 1538.76 | 0.18789252 | 1.405240115 | XN | HN | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLAU PE=1 SV=2 | 1.3E+08 | 87262664 | 67712753 | 63313012 | 46239527.53 | 62487475.16 | 66744054.56 | 70570692.95 | 59978076 | 26009511.23 | 20476186.4 | 34421979.12 | 50381941.5 | 19738604.56 | 64382624.74 | 102705454.3 | 104056353.9 | 59409335.18 | 102313801.7 | 65798725.19 | 94993869.88 | 58070136.66 | 82323843.47 | 14423766 | 105732460.8 | 97775668.64 | 55306059.98 | ||
| P19835 | 20 | 16 | 1516.19 | 0.297776114 | 1.412973917 | XN | XA | Bile salt-activated lipase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEL PE=1 SV=3 | 51061812 | 53669883 | 19342613 | 49998066 | 35471195.05 | 109271480.3 | 37281891.36 | 40323584.53 | 42043116.67 | 98305118.2 | 82937800.43 | 36894519.01 | 134757565.5 | 54293016.25 | 83630454.54 | 37587302.19 | 48905112.74 | 39135465.88 | 135176781.3 | 69340491.41 | 80140408.93 | 39439170.6 | 49046630.77 | 20238432.2 | 61598755.95 | 56043532.31 | 108513486.2 | ||
| P16870 | 19 | 14 | 1515.52 | 0.952441152 | 1.069193449 | HN | XN | Carboxypeptidase E OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPE PE=1 SV=1 | 44776241 | 23692079 | 28334925 | 36835775 | 49532254.17 | 31689726.13 | 30291175.39 | 34043751.89 | 21180471.3 | 28605831.12 | 20172715.37 | 21383620.55 | 47003506.66 | 41709530.57 | 38311966.87 | 45634168.51 | 20211438.79 | 39789529.07 | 33860193.22 | 24460599.56 | 25084542.32 | 30520796.98 | 25888329.31 | 30289504.25 | 41756674.73 | 34112142.46 | 37252210.47 | ||
| Q14767 | 29 | 25 | 1492.44 | 0.084047785 | 1.300316553 | XN | HN | Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTBP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 20804228 | 18760852 | 18959633 | 25362554 | 14368881.87 | 12380879.51 | 15958147.97 | 11244515.48 | 19226875.05 | 10236037.67 | 15872886.52 | 8003118.608 | 14411211.08 | 10047740.18 | 18817800.85 | 15283175.97 | 15958381.95 | 21686353.18 | 14944042.41 | 18891185.51 | 18633443.51 | 12192629.95 | 19638910.33 | 23807680.88 | 18393300.82 | 23315764.48 | 19636012.12 | ||
| Q12860 | 28 | 19 | 1490.7 | 0.42363753 | 1.133317957 | XA | XN | Contactin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNTN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 35357568 | 27060909 | 22513594 | 23254766 | 23097128.97 | 16861941.44 | 25035645.6 | 26390689.76 | 23492966.27 | 15255491.17 | 24301717.89 | 20242442.31 | 35139611.54 | 19767903.39 | 25120619.33 | 24728338.24 | 26393829.14 | 27927890.28 | 18511386.48 | 20311081.08 | 18321100.82 | 18998966.81 | 26882631.11 | 20578836.41 | 22418370.92 | 23146059.96 | 27656480.03 | ||
| P55291 | 22 | 17 | 1490.51 | 0.75908993 | 2.156034966 | HN | XN | Cadherin-15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH15 PE=1 SV=1 | 7381361 | 46358829 | 8644252 | 18111604 | 9239373.723 | 2924143.256 | 2858903.163 | 5652113.883 | 2642393.033 | 20161807.26 | 1854564.163 | 3197998.65 | 1224086.262 | 6182604.659 | 5700636.436 | 54173054.6 | 12502250.04 | 6676169.175 | 4363032.589 | 3538798.626 | 3609364.354 | 3932913.011 | 7012538.215 | 9636682.433 | 5709839.528 | 4807164.234 | 9185288.605 | ||
| Q3LXA3 | 21 | 17 | 1485.08 | 0.252835246 | 2.072302269 | XA | HN | Bifunctional ATP-dependent dihydroxyacetone kinase/FAD-AMP lyase (cyclizing) OS=Homo sapiens GN=DAK PE=1 SV=2 | 13291578 | 1816155 | 11238969 | 30110624 | 3623341.916 | 10663456.41 | 6419174.56 | 27327965.9 | 12811139.28 | 7869455.95 | 3637353.669 | 14973049.04 | 6607379.29 | 3886481.856 | 4154343.56 | 7152524.216 | 4155235.176 | 4169049.095 | 6549973.342 | 6841012.745 | 17172526.86 | 13868181.98 | 14030412.82 | 2477206.583 | 7387670.574 | 8089771.89 | 5937099.285 | ||
| P07339 | 18 | 13 | 1480.36 | 0.084836321 | 1.369518007 | XA | XN | Cathepsin D OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSD PE=1 SV=1 | 1.27E+08 | 1.28E+08 | 1.25E+08 | 1.98E+08 | 183088494.7 | 189291161.3 | 143711328.7 | 111443693 | 120847569.4 | 87704504.52 | 123508189.3 | 152456276.5 | 150668531.5 | 291259244.9 | 104665801.5 | 116089946.7 | 133769330.4 | 112267704.2 | 146836073.2 | 96325757.1 | 101906582.4 | 93866788.27 | 108153085.8 | 34956280.81 | 144450238.3 | 133919693 | 107817700.9 | ||
| P02042 | 15 | 8 | 1476.9 | 0.195807442 | 9.122484795 | HN | XN | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 403423.5 | 635262.9 | 861873.6 | 625224.7 | 3162288.279 | 1971144.486 | 1365250.425 | 4768472.831 | 11550467.93 | 1385149.154 | 776321.1805 | 64356422.72 | 501470.5349 | 827155.0971 | 1208081.732 | 1436099.649 | 11992438.81 | 2462101.175 | 2810164.88 | 916193.3328 | 229245.0981 | 1393925.986 | 633238.4976 | 793713.8705 | 265062.9977 | 1266661.341 | 1003428.048 | ||
| P02649 | 22 | 15 | 1466.31 | 0.497600539 | 1.211192502 | XA | HN | Apolipoprotein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOE PE=1 SV=1 | 48116921 | 22924157 | 26359744 | 45737302 | 20643791.75 | 23750298.89 | 24308135.81 | 28594459.15 | 47767610.89 | 43255298.04 | 14402881.38 | 13769874.77 | 17947985.86 | 13548810.34 | 30981021.38 | 42792427.43 | 29484958.29 | 31766052.18 | 17984175.55 | 18787032.19 | 32492543.04 | 18922151.66 | 52160664.55 | 11781294.25 | 38360301.49 | 27675853.02 | 33079990.97 | ||
| P12830 | 20 | 15 | 1443.13 | 0.348629633 | 1.552227047 | XA | HN | Cadherin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 18586495 | 2.3E+08 | 1.45E+08 | 84318155 | 71886608.57 | 50831068.33 | 55337303.33 | 32943636.34 | 74465861.31 | 38044234.25 | 17487559.17 | 32829046.89 | 33368684.25 | 31506707.1 | 156948383.7 | 31500877.3 | 78665835.94 | 71811314.57 | 59275754.62 | 56248827.14 | 40031262.4 | 145011436.9 | 85337675.89 | 157532490.1 | 36654355.79 | 42556618.36 | 48030581.35 | ||
| P01011 | 22 | 14 | 1440.88 | 0.278216937 | 1.649385727 | HN | XN | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA3 PE=1 SV=2 | 18428867 | 1.54E+08 | 88244540 | 21698752 | 38634486.02 | 14827883.32 | 21164050.07 | 32475740.29 | 24296949.87 | 89085215.26 | 47395385.42 | 98422410.84 | 28000615.69 | 44556309.41 | 54073948.73 | 17839771.08 | 60978479.94 | 35244050.48 | 37170502.68 | 23764530.57 | 20054372.45 | 32169854.5 | 24929075.18 | 52652349.99 | 33029856.28 | 35449490.67 | 29127428.83 | ||
| Q02383 | 19 | 16 | 1434.99 | 0.293736085 | 9.080553847 | XA | XN | Semenogelin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 502959.3 | 573325.5 | 940704 | 710168.4 | 662958.1883 | 1105471.61 | 656797.6236 | 54584521.51 | 952395.2847 | 3025727.098 | 655507.6118 | 985972.8983 | 13751114.34 | 457728.6027 | 966885.7893 | 624525.9775 | 1182614.403 | 5827091.642 | 692707.5113 | 892745.5169 | 406121.3024 | 524869.0988 | 481036.2346 | 751900.7576 | 552567.378 | 1539819.014 | 841669.2836 | ||
| P01876 | 16 | 5 | 1424.22 | 0.275267255 | 1.311348545 | XN | HN | Ig alpha-1 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5.13E+08 | 2.57E+08 | 1.75E+08 | 1.79E+08 | 217011961.2 | 255868612.4 | 364226846.7 | 351727737.6 | 226242447.2 | 219092271.4 | 355396259.7 | 433227825.3 | 244242163 | 113774995.8 | 188693836.6 | 142417631.1 | 129538953.9 | 236985586.3 | 241665382.1 | 383655179.3 | 315294255 | 182108872.7 | 244341735.5 | 256074424.5 | 454495308.8 | 477433601.7 | 150727861.6 | ||
| P19013 | 27 | 11 | 1421.55 | 0.644611206 | 2.111044001 | XA | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 5982899 | 4800535 | 5538922 | 4907313 | 7849023.789 | 89088134.42 | 13065092.6 | 14457348.97 | 18811661.65 | 5516418.299 | 3520465.082 | 20449582.99 | 9803615.768 | 4497834.081 | 8253919.764 | 14120780.16 | 5267861.879 | 6493492.217 | 29232093.66 | 13871372.78 | 4789539.52 | 53797880.5 | 6201547.932 | 5933355.23 | 4941693.144 | 3313420.26 | 6892770.419 | ||
| P60174 | 16 | 12 | 1417.95 | 0.933642438 | 1.063869903 | HN | XN | Triosephosphate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPI1 PE=1 SV=3 | 43086010 | 12952556 | 11130143 | 16044017 | 19703858.06 | 25797219.4 | 25641654.15 | 25778476.95 | 15909973.84 | 36230875.23 | 19554768.24 | 43544833.27 | 10219173.15 | 20567451.14 | 14961862.94 | 11264634.89 | 18727773.75 | 23061854.04 | 20309679.44 | 19908289.56 | 41962006.01 | 31292041.98 | 18921889.92 | 7986401.842 | 11438632.34 | 15216579.75 | 19202689.32 | ||
| Q02487 | 13 | 10 | 1415.03 | 0.464290022 | 1.334226865 | XA | XN | Desmocollin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSC2 PE=1 SV=1 | 32004728 | 71305725 | 49224657 | 98961767 | 61838511.7 | 28435386.94 | 28325789.34 | 40769859.34 | 29351756.8 | 69158005.28 | 24357079.86 | 39758879.2 | 24556208.39 | 26750740.13 | 33746096.31 | 86225473.68 | 44944359.21 | 45708549.68 | 29804316.28 | 34100746.7 | 30503034.07 | 35427053.58 | 56409562.89 | 65569030.38 | 26116340.32 | 25378216.91 | 26634224.06 | ||
| P01860 | 16 | 4 | 1403.28 | 0.72814435 | 1.952404055 | XA | HN | Ig gamma-3 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHG3 PE=1 SV=2 | 36080457 | 15565757 | 4410141 | 3487680 | 5286277.186 | 50772048.42 | 3591991.897 | 50825989.12 | 49370879.22 | 18011081.23 | 17759405.12 | 24887608.48 | 5961493.487 | 2392200.511 | 8830628.924 | 17452943.52 | 5444934.537 | 11629487.76 | 8348470.395 | 13009335.35 | 5011680.863 | 20072108.68 | 12944737.96 | 11028587.1 | 28888265.8 | 6581101.037 | 9276734.193 | ||
| P23142 | 18 | 15 | 1397.81 | 0.720441016 | 1.365883402 | HN | XN | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 49673328 | 38069686 | 39231023 | 58055998 | 59845401.01 | 21121230.64 | 20752749.02 | 25830136.07 | 12629062.33 | 80496363.73 | 20072429.03 | 41683666.66 | 18313123.15 | 20446310.52 | 33633898.86 | 113794589.7 | 43092752.32 | 40823394.25 | 19692077.51 | 44043820.54 | 28701983.65 | 28053911.9 | 46222576.56 | 27356471.38 | 31067916.61 | 29133058.86 | 47625495.42 | ||
| Q96KP4 | 26 | 18 | 1393.2 | 0.081309084 | 1.751314931 | XA | HN | Cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNDP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 55165796 | 11180484 | 32812079 | 76469874 | 23328945.89 | 27119607.7 | 24460318.93 | 58087794.43 | 26688861.98 | 21572819.42 | 13065312.67 | 28537231.57 | 14800585.64 | 10304050.11 | 20070048.7 | 48177143.76 | 17142490.13 | 17794317.28 | 14480667.96 | 14899666.83 | 24345487.05 | 20390568.03 | 54606751.09 | 6705605.79 | 29819947.14 | 17450066.6 | 15408069.99 | ||
| P08697 | 16 | 13 | 1377.36 | 0.108253473 | 1.324744397 | HN | XN | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 46779683 | 24030909 | 31804298 | 55360761 | 48604584.45 | 25516622.14 | 34528990.22 | 32115057.11 | 29110281.18 | 37101985.1 | 31901563.44 | 37125952.83 | 38245339.69 | 25858016.72 | 38310407.72 | 66825662.3 | 33397722.88 | 39112643.37 | 19779095.02 | 24046206.3 | 23549358.14 | 11964319.56 | 46064929.61 | 18623672.56 | 51742549.51 | 39812503.86 | 27018433.83 | ||
| P01877 | 13 | 2 | 1368.9 | 0.813575759 | 1.403061011 | XN | XA | Ig alpha-2 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHA2 PE=1 SV=3 | 43889405 | 38961217 | 10902864 | 3236099 | 39953596.14 | 31987216.27 | 70306719.31 | 22755782.31 | 15708447.27 | 6461631.675 | 57909093.65 | 68498656.37 | 39801999.79 | 28163385.05 | 29095110.74 | 11742353.98 | 6291593.244 | 47344904.13 | 9234001.624 | 53554877.44 | 26675118.97 | 23478054.87 | 82701262.2 | 101512143.1 | 5476017.901 | 62743519.72 | 24256935.3 | ||
| P01019 | 13 | 12 | 1368.14 | 0.09765961 | 2.022274956 | HN | XN | Angiotensinogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGT PE=1 SV=1 | 19306702 | 49524959 | 56572928 | 29666918 | 127297395.4 | 24193197.87 | 19964080.77 | 26346617.46 | 18230156.09 | 58526391.3 | 20260660.86 | 41823907.49 | 16956296.89 | 75926330.97 | 80983562.31 | 67247781.37 | 38329449.91 | 14456389.86 | 19969756.2 | 14782283.84 | 16746071.55 | 21335334.55 | 29386367.11 | 11265800.22 | 42568212.89 | 26997412.54 | 21921269.73 | ||
| Q6EMK4 | 15 | 10 | 1364.71 | 0.052413959 | 1.497446962 | XN | HN | Vasorin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VASN PE=1 SV=1 | 4.57E+08 | 3.92E+08 | 3.89E+08 | 4.56E+08 | 343447190.6 | 549714288.6 | 426856278.2 | 452139095.4 | 451477169.9 | 427794098.2 | 206956308.3 | 187730100.3 | 220020697.4 | 467879713.4 | 335463323.7 | 279722135 | 488677812.8 | 566733808.7 | 595663340.9 | 578330991.3 | 706785866.8 | 429496679.4 | 513133123 | 179740519.1 | 579054304.5 | 703543415.1 | 477597599.5 | ||
| P22792 | 17 | 12 | 1359.16 | 0.662790351 | 1.199082817 | XA | XN | Carboxypeptidase N subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 1.23E+08 | 26238267 | 37604699 | 44263298 | 39033629.88 | 43700494.01 | 40447006.5 | 46853413.03 | 30792813.17 | 48309540.68 | 44297908.31 | 24361655.02 | 64825532.63 | 39661919.97 | 35316072.95 | 48234234.6 | 41667044.89 | 26805903.25 | 34058779.13 | 22007828.5 | 32862517.41 | 32276326.56 | 47454335.04 | 24105020.44 | 91245251.85 | 33041010.22 | 42972409.49 | ||
| P02753 | 14 | 10 | 1342.43 | 0.651455092 | 2.123727055 | HN | XN | Retinol-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBP4 PE=1 SV=3 | 68321146 | 1.17E+08 | 1.68E+08 | 1.08E+08 | 334049517.3 | 90283326.95 | 38058729.02 | 71260900.52 | 74943354.67 | 42059375.06 | 106780947.3 | 43066837.51 | 169776879.3 | 124598683.9 | 183974797.1 | 923591606.7 | 53778396.98 | 78510032.66 | 38763629.7 | 51878894.54 | 49013669.22 | 118751234.1 | 73714843.43 | 133915038.1 | 132149194 | 98565873.11 | 116034536.4 | ||
| Q8IUL8 | 23 | 16 | 1330.32 | 0.858965723 | 1.020395713 | XN | HN | Cartilage intermediate layer protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CILP2 PE=2 SV=2 | 23683207 | 19614063 | 17623723 | 19618440 | 15697625.47 | 21268568.5 | 18144698.18 | 31559705.09 | 22579257.26 | 18161747.89 | 27409373.41 | 13154534.85 | 24235345.38 | 16233877.24 | 10218505.06 | 37213026.75 | 17546909.73 | 23333988.05 | 20876462.53 | 27559813.67 | 27105553.11 | 20271581.18 | 19723812.36 | 14188194.2 | 23987425.61 | 21466888.27 | 16151922.76 | ||
| P16278 | 19 | 12 | 1329.1 | 0.126810194 | 1.515641954 | XA | XN | Beta-galactosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 27929666 | 32391054 | 81943939 | 29317376 | 22470558.78 | 31615604.5 | 64824554.36 | 51648399.36 | 39788716.65 | 23344590.59 | 44641604.28 | 45709529.57 | 56876588.53 | 51689429.08 | 32781515.3 | 26156209.55 | 31466589.69 | 16437833.31 | 21845687.28 | 18906391.51 | 33375328.59 | 11926990.06 | 44067277.19 | 20210525.28 | 31107051.36 | 51732991.69 | 18819902.51 | ||
| P69905 | 10 | 9 | 1314.38 | 0.208990783 | 25.25552074 | HN | XN | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 19892864 | 9192808 | 11428935 | 20350556 | 119878458.4 | 36920844.11 | 12950965.64 | 177796894 | 305188529.9 | 11907650.44 | 28488835.19 | 4962885456 | 15424181.81 | 15992796.25 | 27968210.42 | 19759491.71 | 613517599.1 | 132480757.2 | 70179131.96 | 8461802.67 | 7853890.016 | 4977948.744 | 15512664.44 | 16930305.98 | 12512767.06 | 53937330.82 | 40412412.15 | ||
| P01871 | 15 | 3 | 1306.45 | 0.396813061 | 1.326195604 | HN | XA | Ig mu chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHM PE=1 SV=3 | 50604282 | 1.42E+08 | 59838635 | 1.15E+08 | 92883460.3 | 84311447.02 | 32537815.57 | 16324278.13 | 40890855.08 | 135580495.8 | 60593249.83 | 156827833.4 | 121908162.6 | 60675892.44 | 134139162.9 | 73486808.53 | 31066607.74 | 66684130.05 | 61870440.28 | 92608257.87 | 83161125.93 | 42256318.19 | 55559107.22 | 114894459 | 83424576.28 | 64544594.16 | 38027634.4 | ||
| P01861 | 13 | 4 | 1303.67 | 0.812061321 | 1.20544338 | XA | XN | Ig gamma-4 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHG4 PE=1 SV=1 | 61616583 | 84274392 | 41242335 | 29862005 | 324255851.1 | 35605191.01 | 15633513.26 | 33350930.34 | 30388254.47 | 69512881.31 | 31322642.02 | 87541086.57 | 24397318.59 | 25880175.33 | 165206155.6 | 48131849.56 | 34293220.79 | 96411433.32 | 11057981.43 | 16354693.53 | 30632703.13 | 37899559.77 | 125650764.9 | 189143086.3 | 68918503.49 | 22660496.2 | 42070330.98 | ||
| P00558 | 20 | 12 | 1295.24 | 0.294660147 | 1.359388455 | XA | XN | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 18679371 | 7378358 | 11848771 | 10608115 | 8849012.475 | 17634473.06 | 24890282.97 | 17742996.43 | 20393409.14 | 25717048.49 | 12530000.38 | 25472143.75 | 11720418.38 | 13596508.79 | 6158045.039 | 9729211.925 | 9591338.802 | 12964690.06 | 13517413.24 | 10378936.52 | 22208781.45 | 15416805.8 | 6773579.878 | 3985161.524 | 7988743.49 | 10401664.28 | 10863385.88 | ||
| P13647 | 30 | 10 | 1294.87 | 0.425161419 | 2.961587906 | XA | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 924765.2 | 878668.2 | 502125.9 | 215400.9 | 504786.3823 | 15542856.49 | 5388187.222 | 5180219.35 | 11602275.57 | 359473.622 | 1119326.905 | 5063281.376 | 4414807.369 | 1045335.93 | 443694.5074 | 558645.7076 | 381234.7904 | 370092.3905 | 2299593.224 | 4450879.574 | 1313758.089 | 10931360.56 | 1431813.033 | 630955.2986 | 806611.7689 | 765688.8473 | 662663.4551 | ||
| Q7Z5L0 | 7 | 5 | 1294.61 | 0.632827478 | 1.193140116 | XN | XA | Vitelline membrane outer layer protein 1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VMO1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2.72E+08 | 1.86E+08 | 1.16E+08 | 1.25E+08 | 191443607 | 142663845.6 | 140238474 | 176185308.1 | 192526708.7 | 187353674.2 | 368486932.5 | 104671783.7 | 367883839.7 | 107268625.9 | 117592066.5 | 73652106.36 | 148525599.4 | 133727678.7 | 142635406.7 | 86272433.29 | 165675709.9 | 138731861.1 | 287014199.7 | 283259097.9 | 178990925.3 | 193740330.9 | 364208221 | ||
| P07476 | 21 | 19 | 1281.71 | 0.820644576 | 1.069594314 | XA | HN | Involucrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=IVL PE=1 SV=2 | 2201221 | 1851860 | 1525343 | 3232737 | 1800617.547 | 11439523.5 | 39537552.25 | 31834089.78 | 7171525.766 | 4940697.452 | 26757855.3 | 21014933.17 | 32060788.77 | 1590696.386 | 1686039.583 | 3131711.376 | 1852252.629 | 1014207.989 | 4094174.439 | 74978961.66 | 4995342.382 | 6297325.235 | 1719958.083 | 1687869.838 | 2141910.192 | 1378314.126 | 1567156.299 | ||
| P06702 | 13 | 11 | 1274.41 | 0.969087965 | 3.135737463 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 14066405 | 10298293 | 8909613 | 12711352 | 7122078.957 | 260944005 | 722054089.9 | 361581101.1 | 747946975.2 | 79985214.45 | 135485156.1 | 410073395.7 | 270682450.5 | 17822016.74 | 62625882.01 | 6827920.926 | 12512143.67 | 9027568.108 | 2539949168 | 230563772 | 108855369.7 | 190454921.4 | 7615656.766 | 11175472.99 | 39454729.82 | 13791379.74 | 9686590.527 | ||
| Q9UKU9 | 19 | 13 | 1267.27 | 0.118459605 | 1.524056485 | XA | XN | Angiopoietin-related protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANGPTL2 PE=2 SV=1 | 43436644 | 33957093 | 51327954 | 56188997 | 57927245.51 | 42117667.55 | 39277920.85 | 38211515.27 | 23041364.15 | 16822512.03 | 11888285.91 | 27137514.3 | 32157756.16 | 6873611.748 | 41738691.33 | 92872263.28 | 38248150.99 | 29007667.45 | 14417949.69 | 30772997.19 | 17753831.18 | 19211500.83 | 41463872.74 | 14766942.28 | 45586322.1 | 34080668.01 | 34880374.63 | ||
| O43451 | 26 | 18 | 1264.7 | 0.958308387 | 1.094775628 | HN | XA | Maltase-glucoamylase, intestinal OS=Homo sapiens GN=MGAM PE=1 SV=5 | 7860638 | 15744024 | 11291020 | 8532881 | 5491171.25 | 9343764.602 | 16421415.33 | 10283418.43 | 15906894.9 | 9029544.172 | 16376601.55 | 19888318.37 | 12454273.92 | 21734606.23 | 5974162.28 | 7129120.51 | 9490318.328 | 8358794.967 | 14132337.31 | 7974076.778 | 11189250.98 | 10808233.16 | 10834487.26 | 7358861.732 | 6225063.968 | 24778594.56 | 11127619.5 | ||
| Q9ULI3 | 16 | 11 | 1260.66 | 0.07679537 | 1.579205402 | HN | XA | Protein HEG homolog 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEG1 PE=1 SV=3 | 48567115 | 37745775 | 42440035 | 1.15E+08 | 51242919.42 | 43178044.53 | 42234319.33 | 33500480.58 | 37843380.65 | 122420425.6 | 68261314.61 | 21849431.04 | 83809231.82 | 85883017.52 | 46495946.61 | 147296171.2 | 76202152.21 | 61446982.67 | 53207574.31 | 59045066.83 | 65948315.39 | 58230898.36 | 82028680.03 | 77742726.17 | 72264902.9 | 57632963.29 | 86150099.34 | ||
| P13645 | 21 | 12 | 1254.16 | 0.183843811 | 6.207408057 | XA | XN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 1292649 | 442574.3 | 1543960 | 847831.6 | 485905.0888 | 31332269.69 | 11543679.97 | 3137185.703 | 17260649.52 | 944350.3142 | 7129718.628 | 3141049.24 | 5026956.787 | 634612.1462 | 688753.757 | 498013.3967 | 452836.9643 | 417843.5339 | 2601123.353 | 2480372.313 | 711166.9958 | 1767090.79 | 616144.8382 | 567403.6604 | 516428.0461 | 811747.2987 | 864923.7975 | ||
| O94919 | 14 | 13 | 1249.74 | 0.161623273 | 2.265705514 | XA | HN | Endonuclease domain-containing 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENDOD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4015038 | 46712631 | 35745145 | 7656928 | 19186409.39 | 5385266.302 | 5388717.948 | 7798758.522 | 9181478.692 | 3224225.675 | 3675593.288 | 6224101.778 | 2411544.537 | 7349970.69 | 15498019.71 | 7241831.897 | 11164823.81 | 5473220.174 | 7035482.754 | 5936965.572 | 5935768.011 | 16314095.39 | 10464578.31 | 30930746.34 | 10558144.2 | 8343792.775 | 6549744.008 | ||
| O75594 | 7 | 5 | 1246.85 | 0.957953458 | 1.127445235 | HN | XN | Peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGLYRP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3.36E+08 | 2.53E+08 | 2.62E+08 | 4.1E+08 | 501096746.5 | 265005789.7 | 158781648.3 | 368473439 | 151749595.8 | 827863143.5 | 297513826.3 | 193389562.2 | 208424979.5 | 200182733.9 | 201692641 | 419021720.5 | 177889891.6 | 290935478.7 | 194616917.4 | 377999353.6 | 255920605.1 | 267331109.6 | 169556132.7 | 469997141.5 | 289387058 | 212444471.4 | 261240165.7 | ||
| P05090 | 15 | 13 | 1243.2 | 0.859071167 | 1.059251748 | XN | HN | Apolipoprotein D OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOD PE=1 SV=1 | 3.76E+09 | 3.94E+09 | 2.13E+09 | 2.86E+09 | 2580695486 | 1355022147 | 717570637.7 | 1282857954 | 1569167684 | 2900584371 | 629955713.6 | 1648054969 | 509992992.2 | 1687089035 | 2357156650 | 4254212844 | 3082707546 | 2703895789 | 1973740485 | 1816158145 | 2218506533 | 2064221719 | 5826847844 | 1291269649 | 2280798087 | 1608442532 | 1865288246 | ||
| P48594 | 20 | 6 | 1239.1 | 0.745306742 | 3.010700637 | XA | HN | Serpin B4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB4 PE=1 SV=2 | 232100.8 | 50894.17 | 237949.7 | 352998.8 | 173655.9482 | 1519297.906 | 3439496.884 | 5103803.914 | 7170420.307 | 2628876.568 | 609676.0143 | 1185540.289 | 503587.8269 | 112264.4527 | 172049.6074 | 454153.4323 | 207591.7314 | 198141.8895 | 8448477.416 | 674250.6187 | 835198.824 | 1585067.3 | 342773.0102 | 172270.0577 | 158451.9187 | 295503.1707 | 63483.25562 | ||
| P02750 | 15 | 10 | 1233.05 | 0.196001723 | 2.34809149 | HN | XN | Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 7386706 | 1.24E+08 | 98888049 | 14196406 | 104722912.8 | 11262534.5 | 9997924.381 | 26307066.93 | 20579224.06 | 44652519.65 | 18428831.58 | 188783328.6 | 13822877.75 | 71348660.44 | 71613252.14 | 49162493.56 | 39111657.83 | 36881698.74 | 15045984.53 | 13770012.83 | 10559388.2 | 52993530.11 | 32615702.5 | 41170270.21 | 12531511.35 | 24646892.68 | 24002534.34 | ||
| O95336 | 12 | 10 | 1232.66 | 0.062938041 | 2.03611829 | HN | XN | 6-phosphogluconolactonase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGLS PE=1 SV=2 | 31733404 | 34410746 | 45393433 | 39003137 | 37296726.68 | 24625421.74 | 23973369.16 | 27957024.09 | 18464332.07 | 128977609.3 | 18347150.31 | 31163054.72 | 12602745.84 | 62480910.4 | 29575671.42 | 55108981.86 | 32014788.37 | 35625625.52 | 16922224.59 | 21674585.01 | 25323863.88 | 11550369.05 | 26216548.37 | 11212315.47 | 32552314.95 | 20947477.99 | 32948511.36 | ||
| P08107;P48741 | 21 | 7 | 1230.83 | 0.476605866 | 1.666554198 | XA | XN | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A/1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1A PE=1 SV=5 | 800792.7 | 359009.9 | 677349.4 | 826355.6 | 420779.5741 | 1227054.709 | 2076243.505 | 2752369.864 | 2847563.365 | 1490555.092 | 1259421.109 | 1580154.974 | 1959501.67 | 700051.2092 | 825754.6989 | 2276488.658 | 241097.2363 | 294271.2538 | 1238739.281 | 1063169.065 | 952783.3325 | 1585501.78 | 725962.8389 | 247074.8387 | 461869.2233 | 530678.7341 | 387217.4637 | ||
| P09467 | 18 | 13 | 1228.74 | 0.541384795 | 1.577760762 | XA | HN | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBP1 PE=1 SV=5 | 10311582 | 10786337 | 16356263 | 12937978 | 4229904.015 | 35416439.63 | 66881808.3 | 21194568.15 | 43453204.87 | 11083593.85 | 16431096.84 | 26975578.51 | 35946835.6 | 20771160.13 | 6228250.446 | 6792378.277 | 6006039.814 | 10197057.74 | 13735967.75 | 15733643.65 | 25409050.03 | 25622648.73 | 13792764.61 | 18010399.51 | 7619087.17 | 12715359.77 | 8222010.086 | ||
| P19022 | 14 | 9 | 1223.66 | 0.330141878 | 1.377151185 | XN | XA | Cadherin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH2 PE=1 SV=4 | 24876841 | 69131190 | 44397049 | 42112610 | 17436751.01 | 51241846.16 | 58455872.5 | 27744167.43 | 75935879.39 | 34075517.34 | 94878372.91 | 23888392.3 | 63249428.65 | 43869779.55 | 44128640.08 | 7536176.374 | 54980868.87 | 53493309.32 | 55829464.77 | 53969912.56 | 80550751.94 | 56605788.87 | 37479461.1 | 151007252.8 | 37542329.67 | 51342524.16 | 42139150.37 | ||
| Q92820 | 16 | 13 | 1223.15 | 0.122997994 | 1.546268815 | XA | HN | Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GGH PE=1 SV=2 | 31886920 | 38829257 | 1.16E+08 | 35399240 | 26858751.72 | 54942201.42 | 60019177.78 | 34792911.1 | 67138105.07 | 14176003.89 | 27505951.92 | 28491488.55 | 90808981.56 | 24855861.01 | 27656913.08 | 14371454.09 | 50200496.73 | 23469953.39 | 31131895.01 | 24910632.84 | 77118204.31 | 22294375.8 | 56569842.45 | 26295528.18 | 37894632.29 | 61294102.39 | 32846158.77 | ||
| P11597 | 17 | 13 | 1222.33 | 0.376804732 | 1.887379317 | HN | XA | Cholesteryl ester transfer protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CETP PE=1 SV=2 | 9425569 | 9628447 | 9582110 | 13660342 | 40946263.23 | 5206028.847 | 3312609.288 | 9988633.91 | 3911028.182 | 31343365.91 | 2471526.476 | 14899397.6 | 4106964.486 | 7076836.483 | 28636126.24 | 38479491.14 | 42604744.47 | 29803991.01 | 8267520.749 | 5573462.49 | 7025781.32 | 16291917.77 | 41875276.15 | 3126344.959 | 11855996.39 | 10525146.21 | 12565372.65 | ||
| P35858 | 15 | 12 | 1222.32 | 0.036076341 | 1.973324091 | XA | HN | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex acid labile subunit OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFALS PE=1 SV=1 | 11635908 | 5880031 | 8332129 | 6564278 | 3223194.96 | 3586863.32 | 4065592.831 | 14122384.92 | 10159025.9 | 2492967.73 | 3925681.238 | 1398948.195 | 3440613.535 | 1385534.967 | 7352998.639 | 4438531.233 | 7901079.943 | 1905059.1 | 2751293.282 | 2973465.278 | 3582761.467 | 1173348.025 | 6246440.326 | 787534.8556 | 7077724.901 | 5443721.316 | 5159147.468 | ||
| P05543 | 18 | 13 | 1222.15 | 0.222716757 | 1.994999546 | HN | XN | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 13766558 | 91545840 | 37993625 | 13454387 | 15652488.28 | 11508678.94 | 8593988.449 | 21468943.33 | 17823361.87 | 54948633.2 | 18025462.57 | 87889128.22 | 17760855.95 | 46438204.73 | 30261858.33 | 5495630.747 | 79770528.22 | 38564956.86 | 34626970.23 | 10220916.06 | 20475582.75 | 39130899.73 | 12827225.38 | 30171901.75 | 8208480.09 | 17987008.16 | 16403820.47 | ||
| P18065 | 18 | 11 | 1219.9 | 0.312749762 | 1.351574817 | XN | HN | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.21E+08 | 55257165 | 49260017 | 50064284 | 61646643.21 | 59958845.15 | 51888779.42 | 61620927.23 | 49620376.64 | 41697007.6 | 21596963.3 | 60012137.6 | 38687360.49 | 22235591.59 | 54032543.64 | 72222311.93 | 90817060.39 | 109444965.5 | 94720816.8 | 80521134.76 | 74215710.9 | 39396481.24 | 89973605.37 | 27409276.39 | 73811594.82 | 66130476.68 | 144132256 | ||
| P12111 | 29 | 20 | 1214.65 | 0.055736977 | 1.531192297 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 7427316 | 5001483 | 7054739 | 5438086 | 9064136.079 | 8533329.232 | 8277425.466 | 6415129.969 | 6502192.422 | 8920458.683 | 10219946.18 | 4203476.885 | 8514508.461 | 11018603.22 | 7635912.378 | 16821657.28 | 5317332.135 | 4851173.424 | 5716456.419 | 6761131.042 | 5253876.112 | 6784963.517 | 4673686.734 | 6274134.473 | 5536285.904 | 4597738.981 | 5017883.12 | ||
| P07195 | 18 | 10 | 1212.4 | 0.159977351 | 1.711594957 | XA | XN | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHB PE=1 SV=2 | 12423267 | 8322780 | 12900691 | 24952223 | 5440681.936 | 16396898.57 | 20725414.04 | 15587396.09 | 14249453.43 | 18494313.81 | 11705865 | 23049505.23 | 12427440.68 | 25489208.27 | 4593125.333 | 2908471.753 | 9374205.537 | 5781356.067 | 9771676.197 | 6051920.35 | 11208586.87 | 14753673.03 | 10406082.06 | 4928615.116 | 7818369.602 | 5717302.349 | 5879876.467 | ||
| P21695 | 19 | 13 | 1207.75 | 0.204131637 | 2.479320064 | XA | HN | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD(+)], cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPD1 PE=1 SV=4 | 14251556 | 1629324 | 3750560 | 23526659 | 1167411.426 | 9980245.882 | 7915564.52 | 15590720.61 | 4963637.687 | 6946697.982 | 1797256.065 | 7948450.101 | 2255748.445 | 2576476.647 | 2024854.747 | 3527302.442 | 2627055.641 | 3682601.622 | 5113568.446 | 3118681.325 | 8965406.464 | 7287091.345 | 12137698.88 | 2077694.167 | 3793473.051 | 2840066.16 | 2570373.453 | ||
| P53634 | 15 | 13 | 1206.4 | 0.326683439 | 1.399173368 | XA | XN | Dipeptidyl peptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSC PE=1 SV=2 | 9957435 | 16401834 | 38771143 | 10931096 | 15912570.59 | 11964897.2 | 15188871.49 | 11679963.14 | 17255708.97 | 6871107.971 | 13537775.41 | 17343258.13 | 29348277.84 | 23757287.01 | 14155958.87 | 16369336.04 | 10819600.41 | 6636348.985 | 8655749.28 | 7921503.114 | 10114406.12 | 8762426.187 | 12517763.38 | 16725629.06 | 17789625.52 | 13211973.37 | 10123063.83 | ||
| P04004 | 15 | 12 | 1200.52 | 0.260789977 | 1.290128008 | XA | HN | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 1.81E+08 | 1.53E+08 | 1.2E+08 | 1.07E+08 | 104691701.5 | 43915750.02 | 65334149.79 | 95644295.59 | 82271041.16 | 47980778.09 | 45338519.45 | 32295129.58 | 86812619.1 | 32513629.23 | 82720432.15 | 132575242.9 | 121592768.8 | 157115038.5 | 85064947.64 | 96480960.64 | 105611741 | 75353593.47 | 103730492.8 | 49776486.99 | 113366890.8 | 107708866.1 | 164281205.5 | ||
| Q86T13 | 10 | 8 | 1197.46 | 0.711842368 | 1.153173102 | XN | XA | C-type lectin domain family 14 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC14A PE=1 SV=1 | 53357713 | 52936282 | 66353230 | 64489273 | 55962264.12 | 37174455.74 | 42921095.69 | 40433244.46 | 39838255.99 | 48442882.24 | 30648122.09 | 50796305.58 | 52993942.03 | 52747518.53 | 51276537.5 | 82941536.67 | 49625482.9 | 45269515.14 | 43502116.55 | 39241060.42 | 43148859.39 | 54873980.51 | 62469165.12 | 122429480.4 | 62612777.2 | 50527891.76 | 44119248.36 | ||
| P02766 | 10 | 9 | 1187.53 | 0.250253096 | 1.95492667 | HN | XN | Transthyretin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTR PE=1 SV=1 | 17754992 | 31045648 | 21108903 | 31390457 | 36842274.56 | 19888686.14 | 23293191.33 | 17907888.47 | 32121900.12 | 19618194.39 | 25273729.14 | 108647018.9 | 23479180.64 | 96774193.66 | 18885162.15 | 79344887.41 | 15001546.4 | 17931279.72 | 19586327.31 | 22758498.81 | 21961535.62 | 24365576.27 | 18260837.38 | 38855415.58 | 16715917.69 | 26157086.14 | 18484780.9 | ||
| Q9HAT2 | 16 | 14 | 1181.48 | 0.466657956 | 1.195783591 | XA | XN | Sialate O-acetylesterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIAE PE=1 SV=1 | 16883557 | 19275908 | 22277067 | 11640261 | 15530987.63 | 25906097.27 | 23610747.2 | 16875027.22 | 23300797.95 | 10108781.91 | 20240063.94 | 12463878.28 | 37630915.37 | 21027302.53 | 15493639.18 | 9049554.516 | 15426991.64 | 19346450.32 | 16319191.51 | 14409804.37 | 16432633.56 | 13874205.86 | 19794405.76 | 18636456.21 | 15068406.66 | 16625436.1 | 15438269.07 | ||
| P27487 | 29 | 21 | 1179.18 | 0.152467776 | 1.571768667 | HN | XN | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 21709096 | 14625688 | 15175091 | 12957421 | 15256046.25 | 11318976.32 | 18954526.03 | 17079921.9 | 10685378.47 | 19513466.71 | 34007970.16 | 29174530.51 | 12556364.17 | 36146764.43 | 11662506.21 | 9168618.134 | 11691766.42 | 10829488.66 | 12114327.48 | 13187090.24 | 15417286.92 | 12838444.71 | 10276873 | 13463456.49 | 9419241.135 | 11081417.11 | 13383284.85 | ||
| P00751 | 18 | 15 | 1176.51 | 0.214154953 | 2.815028639 | HN | XN | Complement factor B OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFB PE=1 SV=2 | 12171547 | 10813066 | 11671119 | 15708710 | 42089034.95 | 6360796.088 | 5378373.832 | 7209857.369 | 5948728.583 | 11361244.23 | 4462860.397 | 39984607.43 | 5557589.165 | 4673261.836 | 32944154.32 | 87442034.72 | 15607690.84 | 11161981.84 | 6018012.914 | 8731434.023 | 4200740.018 | 4814783.33 | 7701490.02 | 5219648.235 | 19637942.17 | 10771088.19 | 8639587.856 | ||
| P00738 | 18 | 5 | 1174.05 | 0.449055763 | 2.843396367 | XN | XA | Haptoglobin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HP PE=1 SV=1 | 1630605 | 508917.2 | 338798.5 | 1845320 | 1778668.625 | 1197687.811 | 1494479.886 | 2932172.036 | 1841855.645 | 3200474.579 | 2950619.72 | 8919923.402 | 439942.3455 | 389346.8395 | 9569406.924 | 2700709.548 | 5176214.571 | 1274845.563 | 759024.8308 | 947159.9448 | 981022.7087 | 1534171.991 | 650318.8279 | 9514068.334 | 721522.9718 | 14092253.47 | 9381091.071 | ||
| Q9HCU0 | 16 | 10 | 1167.7 | 0.35939896 | 1.245396578 | HN | XN | Endosialin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD248 PE=1 SV=1 | 2.24E+08 | 1.04E+08 | 1.37E+08 | 2.23E+08 | 108861689.7 | 122402953.1 | 85009072.05 | 158064562.1 | 83835191.22 | 229181847.9 | 208560747.7 | 76721020.82 | 164387506.9 | 155415618.8 | 110509540.7 | 193034700.9 | 146163515.7 | 191165356.3 | 111393686.1 | 114017063.2 | 115067284.3 | 96911505.36 | 141498229.8 | 153830642.4 | 119602820.3 | 115220249.9 | 216932510.4 | ||
| Q13510 | 16 | 15 | 1166.57 | 0.231463917 | 1.450614107 | XA | XN | Acid ceramidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASAH1 PE=1 SV=5 | 49248508 | 54668190 | 1.42E+08 | 1.46E+08 | 53020517.15 | 63470322.37 | 50980904.92 | 52660725.75 | 54010484.84 | 48091358.95 | 38714735.84 | 49147333 | 47693866.4 | 117221809.7 | 44677732.75 | 96868402.07 | 81616836.91 | 51853459.42 | 48736760.86 | 31078901.69 | 70084440.24 | 33930038.45 | 62321820.75 | 30733466.29 | 54458297.9 | 71264084.24 | 56196795.5 | ||
| Q9UN70 | 21 | 15 | 1164.82 | 0.44240945 | 1.173605501 | XN | XA | Protocadherin gamma-C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHGC3 PE=1 SV=1 | 12455126 | 6028537 | 5693494 | 7930616 | 6006448.884 | 7232070.592 | 4581715.239 | 7758118.371 | 7499621.885 | 7738395.885 | 11567606.6 | 6165325.608 | 9600003.35 | 9945590.508 | 4877999.981 | 3927665.114 | 11982094.92 | 9329297.258 | 7472447.028 | 7544056.916 | 11084578.63 | 6493478.017 | 9745635.494 | 7963226.437 | 6611973.318 | 9536474.532 | 10050483.36 | ||
| P21810 | 12 | 9 | 1156.35 | 0.491807248 | 1.363798713 | XA | HN | Biglycan OS=Homo sapiens GN=BGN PE=1 SV=2 | 34026080 | 11987271 | 18538544 | 24006736 | 13649499.69 | 4910299.488 | 7027446.399 | 25371696.36 | 7639091.5 | 2976480.554 | 12825079.55 | 4746748.919 | 6980897.883 | 9727461.318 | 13095548.58 | 21316721.24 | 11269655.92 | 24963446.38 | 4600444.871 | 10059387.13 | 5663824.711 | 2636002.897 | 19088849.79 | 4963941.933 | 14663508.33 | 22243523.43 | 24715956.79 | ||
| P09603 | 10 | 8 | 1152.76 | 0.366066743 | 1.133861608 | XN | XA | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSF1 PE=1 SV=2 | 56768063 | 45968006 | 45365237 | 59612191 | 58357613.78 | 43367105.61 | 27752544.85 | 46391279.02 | 31207383.17 | 45326425.46 | 48387103.43 | 39289424.51 | 49570218.23 | 50884864.2 | 37686858.04 | 41094537.09 | 48519696.81 | 60483009.23 | 49794214.9 | 51184315.31 | 46209143.94 | 39471149.22 | 46078086.51 | 79782004.53 | 57788874.28 | 50466546.93 | 49539465.8 | ||
| Q01469;A8MUU1 | 12 | 12 | 1147.47 | 0.938210391 | 1.964369085 | XA | XN | Fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=FABP5 PE=1 SV=3 | 12389195 | 4031133 | 2838949 | 6503818 | 2181357.201 | 29381400.02 | 110644724.2 | 30876805.27 | 69196173.51 | 11122145.15 | 69647016.35 | 44659098.56 | 37876632.81 | 9223698.93 | 4291812.264 | 7051096.151 | 5716542.517 | 8760068.211 | 10229560.05 | 31572435.9 | 15858055.26 | 41194195.13 | 6728744.852 | 4007160.246 | 7464158.321 | 8065491.427 | 11332944.97 | ||
| Q96NY8 | 14 | 12 | 1142.44 | 0.351120872 | 1.216123644 | HN | XA | Poliovirus receptor-related protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVRL4 PE=1 SV=1 | 25118231 | 29769853 | 28986951 | 17994539 | 23074061.29 | 29586430.61 | 24459401.05 | 23168003.43 | 26578064.53 | 30993765.01 | 46335465.45 | 14454977.64 | 37730817.34 | 30899769.7 | 24704024.61 | 24241200.5 | 30954396.4 | 37856276.29 | 29240965.96 | 24360075.14 | 33293098.57 | 24999349.88 | 24867858 | 35453185.01 | 21561131.49 | 30232855.26 | 33787960.21 | ||
| P16444 | 15 | 14 | 1140.77 | 0.400321363 | 1.276346843 | HN | XN | Dipeptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPEP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 16402031 | 11240719 | 14861567 | 16944234 | 13429464.06 | 14605166.27 | 14168972.65 | 15727493.53 | 8762590.762 | 18586172.98 | 22726070.54 | 15826711.91 | 9281152.942 | 29537617.01 | 8768854.477 | 6713022.554 | 18971214.22 | 7587539.795 | 10673818.9 | 9327622.753 | 6219130.498 | 9499888.169 | 12635338.3 | 5479893.05 | 8368127.346 | 21589617.76 | 24326356.16 | ||
| P39060 | 17 | 10 | 1140.51 | 0.49643669 | 1.124765649 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-1(XVIII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL18A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 1E+08 | 55696508 | 53223696 | 1.03E+08 | 54979092.65 | 77719421.91 | 72915320.82 | 78655508.75 | 66187731.26 | 76018694.95 | 88093702.7 | 49225826.85 | 80703560.78 | 101225187.4 | 51973594.08 | 60785303.14 | 67798694.46 | 87036169.87 | 68540391.94 | 57428186.46 | 100084773 | 46665574.26 | 35630858.14 | 83106458.21 | 81098170.57 | 62487937.48 | 54289956.6 | ||
| P15289 | 12 | 9 | 1134.49 | 0.831211867 | 1.12628505 | XA | HN | Arylsulfatase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARSA PE=1 SV=3 | 33955071 | 71479269 | 1.21E+08 | 70100106 | 31393349.98 | 74138877.34 | 26069278.18 | 52716477.86 | 63141510.57 | 36902560.09 | 64651661.03 | 41847036.89 | 74313458.49 | 90663217.96 | 32230123.19 | 18770512.06 | 57299471.84 | 66326684.93 | 38232622.28 | 27840897.7 | 58126602.84 | 92834622.31 | 54731856.3 | 76108033.94 | 37772641.14 | 77507976.07 | 65489900.36 | ||
| P06870 | 10 | 9 | 1132.57 | 0.877256652 | 1.526465292 | HN | XN | Kallikrein-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK1 PE=1 SV=2 | 47955744 | 3.14E+08 | 1.35E+08 | 50689387 | 53481159.07 | 323310524.6 | 173105950.3 | 68427733.03 | 278221405.6 | 66517850.35 | 602576523.9 | 29828094.25 | 473038864 | 128748121.5 | 159612153.5 | 21048189.45 | 51804577.34 | 98719359.05 | 67860569.91 | 104771199.3 | 102336342.8 | 52817398.04 | 106541673.9 | 234993562.8 | 274417818 | 70052294.76 | 55276182.26 | ||
| Q6UXB8 | 10 | 8 | 1122.2 | 0.798228265 | 2.466450428 | XA | XN | Peptidase inhibitor 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PI16 PE=1 SV=1 | 7333776 | 42571847 | 40818018 | 10490696 | 183980675.3 | 7564145.658 | 4598792.703 | 13474031.56 | 9956023.748 | 11932307.74 | 5842753.153 | 14129535.28 | 6553615.237 | 8058816.789 | 49702234.77 | 14162684.95 | 35044261.15 | 26884696.66 | 8889128.039 | 7363846.87 | 6169018.182 | 14292193.06 | 21112250.06 | 27346899.55 | 9842583.22 | 19474421.12 | 15570252.98 | ||
| O43707 | 28 | 12 | 1119.36 | 0.304281705 | 1.93459427 | XA | HN | Alpha-actinin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTN4 PE=1 SV=2 | 3360156 | 524472.3 | 1526956 | 4825612 | 1817457.93 | 3960610.683 | 4875620.867 | 13010163.24 | 6502992.3 | 2319862.408 | 1543462.417 | 7559402.19 | 4414587.367 | 748342.9099 | 1736577.097 | 1238470.498 | 670960.1042 | 653356.0113 | 15306944.94 | 1561899.391 | 3413694.453 | 2745315.948 | 3052878.882 | 369006.4817 | 1768405.029 | 1085116.055 | 897479.923 | ||
| P14618 | 19 | 15 | 1113.53 | 0.288227531 | 1.5452499 | XA | XN | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKM PE=1 SV=4 | 6390355 | 5488659 | 7245153 | 13986091 | 7330574.009 | 9737303.978 | 13473206.59 | 17234187.6 | 14859093.47 | 40865573.76 | 6980491.625 | 12580986.34 | 4347862.706 | 5255486.908 | 9457524.477 | 7982895.682 | 3401135.227 | 3814808.789 | 7247194.652 | 5469842.554 | 10592465.25 | 8940778.157 | 7447517.421 | 4318540.191 | 8317245.545 | 5525914.301 | 4101110.164 | ||
| P05452 | 13 | 10 | 1102.21 | 0.016240709 | 1.653234405 | HN | XN | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 64626918 | 24238870 | 21687282 | 45676641 | 20511744.36 | 28449474.87 | 23829020.89 | 24571847.07 | 35847166.54 | 75315495.05 | 37552883.8 | 50063285.93 | 57445216.88 | 52325824.73 | 33348365.21 | 22195459.53 | 44691041.38 | 37481334.91 | 29484384.89 | 19538179.71 | 32094330.94 | 36326008.65 | 36599988.82 | 16213922.93 | 24771533.87 | 25731180.02 | 27492566.89 | ||
| P25325 | 12 | 9 | 1095.77 | 0.91997889 | 1.400164645 | HN | XN | 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MPST PE=1 SV=3 | 15840869 | 9167160 | 19158954 | 27163076 | 9507549.307 | 5873190.719 | 8703700.77 | 9548751.827 | 2797215.478 | 7070165.313 | 2968892.004 | 6231480.749 | 3238348.842 | 4684475.081 | 28810367.11 | 44488876.23 | 14477119.72 | 13865855.22 | 6914598.375 | 5415123.88 | 10648597.76 | 8549290.194 | 13687702.44 | 2182056.066 | 14372750.74 | 9610974.664 | 18490893.97 | ||
| P28799 | 16 | 14 | 1095.08 | 0.223986338 | 1.35743879 | XN | XA | Granulins OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRN PE=1 SV=2 | 3.85E+08 | 3.99E+08 | 3.1E+08 | 3.41E+08 | 202253994.4 | 386554033.9 | 478908486.5 | 316375225.9 | 682182257.9 | 654863930.6 | 567697580.7 | 259229675.4 | 611531291.2 | 544610496.6 | 158769339.5 | 159512102.2 | 679452111.3 | 560126821.6 | 461943477.3 | 472415843.1 | 676830993.6 | 709301968.1 | 471986023.9 | 569638189.8 | 405008982.7 | 549111874.3 | 435663141.2 | ||
| O94910 | 17 | 14 | 1095.02 | 0.168118768 | 1.25321703 | XN | HN | Latrophilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LPHN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 12373797 | 8816256 | 8216407 | 10373973 | 7371044.862 | 11125577.3 | 8849809.232 | 9710380.133 | 12208661.85 | 9640884.633 | 13246801.15 | 4453321.236 | 15619828.59 | 8087543.298 | 4478061.071 | 5900388.851 | 8113538.377 | 11693752.34 | 11062994.37 | 13421803.51 | 13826579.07 | 9346001.965 | 8417853.009 | 15818755.69 | 7680010.662 | 11680637.9 | 10549345.89 | ||
| P08294 | 11 | 8 | 1091.18 | 0.20921285 | 1.364502643 | XA | HN | Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOD3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.13E+08 | 56607724 | 54485861 | 40001580 | 25250860.93 | 23582682.05 | 39890516.23 | 47012411.3 | 68963770.93 | 9070196.926 | 58152150.72 | 23726895.43 | 76514799.69 | 15033031.95 | 59639440.77 | 17371818.55 | 37477515.26 | 46578349.49 | 57174310.42 | 37216249.73 | 35537282.36 | 37670223 | 31775092.42 | 45956906.97 | 71873846.21 | 52759602.9 | 47622294.86 | ||
| P11142 | 22 | 11 | 1084.18 | 0.319851353 | 1.679128831 | XA | XN | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 5363817 | 1738099 | 3362638 | 6724783 | 2123814.106 | 6851698.784 | 8607937.328 | 11624084.93 | 9298773.439 | 7625437.575 | 7991176.907 | 9638167.496 | 6994128.454 | 4374267.304 | 3042569.655 | 1851618.482 | 1803463.069 | 2210824.316 | 6929632.046 | 3440388.297 | 5593901.424 | 4831116.884 | 3531470.589 | 1707745.85 | 2197864.768 | 2386784.164 | 2550466.391 | ||
| P21399 | 19 | 12 | 1082.1 | 0.088553145 | 2.081232004 | XA | HN | Cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACO1 PE=1 SV=3 | 7750724 | 1315973 | 3736996 | 5369907 | 1134045.536 | 5450616.021 | 8758065.021 | 6781201.662 | 3507277.491 | 2681178.189 | 1434055.866 | 5111282.45 | 2693970.762 | 2254807.871 | 1677177.063 | 1672110.424 | 1925253.944 | 1597699.819 | 2791478.358 | 2133393.508 | 5846493.619 | 3921544.579 | 4415213.593 | 1181319.768 | 4025031.336 | 1922647.43 | 1930581.942 | ||
| P08572 | 19 | 13 | 1080.28 | 0.471931596 | 1.290626155 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-2(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 80724537 | 85428865 | 50979651 | 70066630 | 101659304.4 | 30578826.73 | 26322520.84 | 51986626.07 | 27780775.86 | 102683429.4 | 30918374.45 | 119929136.9 | 41898051.01 | 63137591.23 | 106437515.6 | 105832333 | 56097975.64 | 43782783.39 | 68276387.62 | 37850265.9 | 39189819.62 | 49929219.59 | 70400971.58 | 88359727 | 46503295.48 | 53584491.2 | 65589378.89 | ||
| Q14393 | 24 | 19 | 1079.69 | 0.02731236 | 1.35699994 | XA | XN | Growth arrest-specific protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAS6 PE=1 SV=2 | 7616142 | 6631835 | 8317925 | 5867998 | 6187245.646 | 5388138.518 | 7201673.885 | 6996730.614 | 5503700.485 | 7791942.259 | 3973801.545 | 5838210.156 | 5083146.19 | 6130385.163 | 3922160.411 | 5676665.003 | 5845755.52 | 3821695.503 | 4243412.883 | 5766068.268 | 5880043.387 | 5415655.836 | 4443383.168 | 2087014.094 | 4786071.034 | 6237850.231 | 5143000.588 | ||
| Q14118 | 14 | 11 | 1072.88 | 0.991658459 | 1.048153476 | XA | XN | Dystroglycan OS=Homo sapiens GN=DAG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 61544544 | 22506851 | 23063825 | 47401734 | 24340077.81 | 16665910.89 | 22483377.95 | 35102818.79 | 22696378.38 | 29309203.32 | 15137354.22 | 21865374.85 | 27153572.66 | 45534626.2 | 24904621.18 | 55965044.09 | 27746411.79 | 19433199.01 | 23310090.94 | 23040861.63 | 33693568.39 | 16069928.41 | 37809952.58 | 16661521 | 40708829.14 | 28443937.17 | 43395980.16 | ||
| O95967 | 12 | 11 | 1072.56 | 0.947782221 | 1.405432447 | HN | XN | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFEMP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 22542917 | 14439292 | 9957678 | 15121833 | 27698655.26 | 11115715.48 | 7264937.757 | 9925055.208 | 7568159.389 | 17332390.22 | 7426019.91 | 9204167.941 | 11018724.75 | 4071623.3 | 16756295.45 | 70469541.23 | 20587017.25 | 13566412.77 | 10602206.84 | 13799900.98 | 11373207.89 | 9170779.457 | 22250676.71 | 10180580.24 | 15806705.98 | 13121820.91 | 14960847.99 | ||
| Q92673 | 25 | 21 | 1071.64 | 0.233908932 | 1.338851169 | XA | XN | Sortilin-related receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SORL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6435445 | 2990576 | 3699168 | 3186247 | 2593812.65 | 3965877.223 | 3295610.672 | 3331964.734 | 3157075.018 | 4684817.014 | 5023240.584 | 2217002.568 | 4789513.413 | 5472491.017 | 2341981.664 | 1477213.991 | 2545174.879 | 2169818.914 | 3119972.25 | 2265305.334 | 2431088.331 | 1749554.093 | 2651596.965 | 2359163.9 | 3479464.649 | 2965900.055 | 3368848.657 | ||
| Q9NPG4 | 20 | 16 | 1070.36 | 0.473559339 | 1.3473334 | HN | XN | Protocadherin-12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDH12 PE=2 SV=1 | 15732527 | 10224536 | 11188658 | 18189579 | 16926691.33 | 8679891.357 | 3858344.456 | 11358656.67 | 6330187.851 | 22792289.1 | 7538576.052 | 8268875.021 | 6699059.935 | 13034914.97 | 9425445.778 | 17875480.56 | 25016711.88 | 17466654.3 | 8952478.126 | 9855543.539 | 11156465.66 | 8460200.007 | 19026014.67 | 7413401.017 | 7996663.704 | 11176915.83 | 11052372.83 | ||
| P07858 | 11 | 9 | 1065.32 | 0.780430217 | 1.919521446 | HN | XN | Cathepsin B OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSB PE=1 SV=3 | 18420186 | 11526356 | 35945803 | 46247605 | 14694773.94 | 11600944.55 | 11297620.41 | 17793830.98 | 25441096.85 | 11180270.37 | 5982593.832 | 15323316.67 | 16793374.41 | 10050777.56 | 30604605.93 | 185658403 | 10779778.47 | 11489741.27 | 8729281.344 | 7743342.245 | 8898542.524 | 13876710.99 | 34412306.34 | 9980313.888 | 26658465.95 | 29380440.65 | 15496180.14 | ||
| Q9UBC9 | 18 | 15 | 1064.85 | 0.956147174 | 1.11228498 | XN | XA | Small proline-rich protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR3 PE=1 SV=2 | 9752629 | 6669882 | 6531074 | 5089837 | 7782861.292 | 276621567.1 | 1028385502 | 1255966922 | 583957636 | 191650765 | 1224625813 | 1187571264 | 752186128.4 | 4724891.319 | 13286907.9 | 10077256.26 | 6436782.208 | 7305115.058 | 534148614.7 | 1179291464 | 500407630.8 | 1264524352 | 5906856.04 | 20253465.2 | 13388819.31 | 11506061 | 8481984.588 | ||
| P50895 | 14 | 13 | 1062.56 | 0.988406656 | 1.067231638 | HN | XN | Basal cell adhesion molecule OS=Homo sapiens GN=BCAM PE=1 SV=2 | 13100407 | 12347304 | 10387726 | 6233650 | 10133619.24 | 9802333.888 | 9976457.468 | 8482048.922 | 15143375.3 | 11406448.12 | 12348604.73 | 6590103.982 | 12901427.3 | 8618993.95 | 7699484.558 | 4260350.508 | 19202923.37 | 16716219.78 | 9040994.852 | 9209469.171 | 10162011.33 | 9690111.428 | 7530491.585 | 9795315.441 | 8511573.227 | 14832044.83 | 14689007.03 | ||
| Q13332 | 22 | 15 | 1056.01 | 0.092024739 | 1.283089026 | XA | HN | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase S OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRS PE=1 SV=3 | 11911776 | 13035710 | 10779980 | 13691103 | 15483595.76 | 9739701.681 | 13210775.83 | 12858838.01 | 11452839.93 | 5510389.296 | 8988850.612 | 9890305.468 | 13623254.34 | 7065294.894 | 11033188.26 | 15485257.7 | 8260306.144 | 7560563.95 | 7639877.747 | 10205079.07 | 8779642.242 | 7841107.024 | 11846136.3 | 17072501.49 | 16296294.26 | 13320667.08 | 9570219.872 | ||
| O75487 | 17 | 13 | 1051.74 | 0.676081554 | 1.296219754 | XN | HN | Glypican-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPC4 PE=1 SV=4 | 10199062 | 5120374 | 5222535 | 4918697 | 5434392.801 | 5158198.172 | 4046973.736 | 11393499.99 | 3541364.53 | 2324141.252 | 4163053.156 | 3912215.766 | 3675581.365 | 9330783.509 | 5738889.137 | 5825613.161 | 6127923.972 | 3899641.551 | 5942420.435 | 7697906.676 | 6962283.353 | 2166171.79 | 6359837.219 | 1462722.905 | 12134668.14 | 7300116.533 | 8300965.762 | ||
| O00187 | 10 | 8 | 1050.98 | 0.39604601 | 1.737662324 | XA | HN | Mannan-binding lectin serine protease 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MASP2 PE=1 SV=4 | 2.88E+08 | 2.4E+08 | 1.88E+08 | 2.34E+08 | 258384202.5 | 38139481.64 | 57380881.54 | 171346449.7 | 44786501.3 | 100228219.5 | 117051329.1 | 78643789.54 | 33746222.42 | 67063505.79 | 150763158.5 | 74778342.74 | 152276940.2 | 100398395.1 | 52779118.93 | 31728985.28 | 31079105.65 | 41114942.2 | 209197961.1 | 227079281.3 | 203303975 | 87434903.46 | 160394881.4 | ||
| O15197 | 14 | 12 | 1038.09 | 0.081337016 | 1.568009947 | XA | HN | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHB6 PE=1 SV=4 | 27567449 | 9902235 | 10270101 | 24920201 | 18164354.49 | 35221876.38 | 42539649.19 | 22965913.92 | 26618235.77 | 21223119.24 | 18453517.39 | 12956371.31 | 13144883.76 | 16533835.1 | 10530916.47 | 15713801.36 | 16120821.35 | 14460891.9 | 27262007.76 | 13278501.32 | 15275701.21 | 13525790.53 | 19178420.75 | 14672475.34 | 19358759.28 | 13156477.56 | 18286673.01 | ||
| P00966 | 18 | 15 | 1026.93 | 0.076819574 | 2.490153491 | XA | HN | Argininosuccinate synthase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 20875520 | 3396388 | 13391003 | 42389447 | 4065996.404 | 13162691.34 | 13566516.82 | 27302411.64 | 9622526.648 | 7265809.594 | 7340338.307 | 7727667.353 | 8837046.079 | 5766448.587 | 6068095.704 | 8746165.808 | 4172076.706 | 3419079.419 | 4818229.007 | 5545903.884 | 6967123.989 | 6067735.934 | 33656503.23 | 3333830.16 | 10199891.71 | 7960994.444 | 7441559.614 | ||
| P04792 | 15 | 12 | 1023.1 | 0.803094036 | 1.701909024 | XA | XN | Heat shock protein beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 24661997 | 7595601 | 10853687 | 54685316 | 8509778.166 | 56848090.6 | 96193779.28 | 234758002.4 | 95048369.32 | 53447135.81 | 35065916.44 | 108325723.9 | 120625471.8 | 10811826.28 | 8164346.045 | 21899250.73 | 13181876.06 | 11604913.57 | 83319924.61 | 50490227.34 | 57283572.92 | 77697246.46 | 21827779.74 | 7407106.944 | 17958131.67 | 16417879.97 | 13770934.97 | ||
| P04075 | 18 | 9 | 1021.25 | 0.653522359 | 1.065118389 | XN | HN | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOA PE=1 SV=2 | 3481574 | 2103855 | 2105703 | 4981014 | 2107937.246 | 6387515.933 | 11336145.02 | 16597373.56 | 10966411.17 | 29118121.68 | 5714215.651 | 7897418.608 | 3388115.053 | 2397644.522 | 4117391.166 | 1417953.592 | 1439181.235 | 1996842.035 | 37255383.93 | 6002392.146 | 4729890.794 | 4801718.339 | 1462054.497 | 817641.7679 | 2647793.969 | 1804360.973 | 1709100.395 | ||
| Q07075 | 25 | 16 | 1019.31 | 0.161815288 | 2.260616735 | HN | XN | Glutamyl aminopeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENPEP PE=1 SV=3 | 1506158 | 4884190 | 8772689 | 1264797 | 4922357.927 | 2010518.832 | 1882691.526 | 1897514.545 | 2915344.018 | 2842312 | 3489237.47 | 15042767.59 | 2826138.322 | 15822357.39 | 4049058.262 | 3747693.928 | 3897719.674 | 1205713.155 | 1487912.825 | 1200149.009 | 2130367.456 | 1661250.431 | 3920487.351 | 4670087.835 | 2411203.229 | 3149731.634 | 2779677.259 | ||
| P30740 | 14 | 10 | 1018.31 | 0.813838686 | 2.075832255 | XA | HN | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1139513 | 1267418 | 1004752 | 1460295 | 1089541.227 | 9410516.342 | 23999167.53 | 11671636.86 | 25040228.28 | 8947478.009 | 8277906.731 | 9076889.221 | 3853537.072 | 975466.1975 | 2553764.439 | 1318892.242 | 928645.2744 | 719259.3493 | 28577741.48 | 10327300.08 | 2634448.303 | 6759741.846 | 1274833.989 | 915388.8402 | 2256636.587 | 1332261.434 | 848520.1466 | ||
| Q9UHL4 | 15 | 10 | 1018.3 | 0.213092936 | 1.601131736 | XA | HN | Dipeptidyl peptidase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPP7 PE=1 SV=3 | 3059285 | 13366206 | 20368765 | 4482455 | 7001129.682 | 8826259.43 | 8027904.146 | 5215774.642 | 9979140.424 | 5021887.593 | 4406682.876 | 11000498.92 | 1973589.235 | 8737068.823 | 7549843.535 | 4246681.806 | 4386240 | 2846345.294 | 6032003.275 | 3003824.481 | 8803730.643 | 7215994.72 | 10599325.49 | 2929554.667 | 6419565.959 | 8718493.227 | 5206601.288 | ||
| P01034 | 9 | 8 | 1008.21 | 0.075615559 | 1.427563838 | HN | XN | Cystatin-C OS=Homo sapiens GN=CST3 PE=1 SV=1 | 3.18E+08 | 1.56E+08 | 82325661 | 1.75E+08 | 95923009.95 | 90671813.08 | 92173798.8 | 141505662 | 83154214 | 318733530.8 | 154889438.1 | 137361979.8 | 191102480.4 | 226253447.9 | 124309397.6 | 186150115.8 | 133526400.9 | 179013714.7 | 129385370.7 | 94187850.42 | 126565630.8 | 111702991.1 | 210726746.2 | 69617690.98 | 149407545.4 | 105106698.8 | 160053703.9 | ||
| P34896 | 15 | 10 | 1004.82 | 0.039122242 | 1.763462349 | XA | HN | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, cytosolic OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHMT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 7916454 | 3579471 | 6622017 | 9177960 | 3030436.228 | 11779312.81 | 10891290.93 | 13984262.25 | 8804959.054 | 8245444.287 | 5960957.467 | 8844735.076 | 4524144.237 | 3427138.378 | 3118823.997 | 3358874.314 | 3131632.774 | 2364025.786 | 4776864.825 | 4811966.399 | 8317290.122 | 8459023.161 | 6224268.735 | 6834410.434 | 4563292.103 | 4081195.623 | 3913714.056 | ||
| Q9Y2E5 | 19 | 14 | 998.85 | 0.877474647 | 1.078231227 | HN | XN | Epididymis-specific alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2B2 PE=1 SV=4 | 5745235 | 6338363 | 13445773 | 7129037 | 3910186.982 | 9939196.918 | 11829110.92 | 9711158.466 | 8808897.967 | 5885977.15 | 8921097.87 | 11782788.67 | 26651066.74 | 5946555.156 | 6663607.524 | 2930425.24 | 5682162.49 | 4689138.641 | 7014752.112 | 10455873.02 | 4063909.256 | 9394185.314 | 12577666.03 | 8509394.107 | 6784631.688 | 8916775.338 | 5692688.043 | ||
| Q9UIV8 | 16 | 12 | 996.37 | 0.866685422 | 1.812017121 | XA | HN | Serpin B13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB13 PE=2 SV=2 | 1227899 | 1432957 | 1050177 | 1186825 | 729066.847 | 4736422.68 | 13109370.26 | 14168344.4 | 9659715.415 | 4921770.436 | 5234182.74 | 6262184.463 | 3742249.127 | 1581540.662 | 998199.1934 | 1106456.779 | 1158837.13 | 1098514.929 | 26209355.56 | 4863227.987 | 2824883.835 | 5064309.432 | 857092.7229 | 2337755.379 | 877681.0358 | 1174972.407 | 1673740.964 | ||
| P78324 | 12 | 2 | 982.03 | 0.272061816 | 1.652894373 | XA | XN | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIRPA PE=1 SV=2 | 1077672 | 2927983 | 2960253 | 1432271 | 932297.5551 | 682486.7668 | 1502274.516 | 572799.0126 | 4077202.003 | 1819002.424 | 1646133.904 | 388801.1694 | 2467917.811 | 1288737.727 | 1421090.77 | 588647.3647 | 712510.5446 | 361815.5661 | 489045.433 | 438687.7844 | 2186615.421 | 2653316.627 | 542752.8061 | 521902.2851 | 1286297.955 | 776363.6326 | 884976.4824 | ||
| P51654 | 13 | 11 | 980 | 0.726402829 | 1.231064458 | XN | HN | Glypican-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPC3 PE=1 SV=1 | 23223219 | 16270591 | 14383028 | 17308804 | 15481860.09 | 9410885.422 | 8265263.814 | 27526943.66 | 12431335.84 | 8541356.479 | 12509141.62 | 8580714.022 | 11693902.22 | 29645024.49 | 15040650.17 | 18804767.15 | 14551311.48 | 15723573.9 | 17760106.33 | 14408607.81 | 20162133.3 | 8636306.281 | 23504597.05 | 5493368.588 | 27904650.62 | 22924475.24 | 25510795.9 | ||
| Q04756 | 14 | 11 | 975.74 | 0.324442317 | 1.255088577 | XN | XA | Hepatocyte growth factor activator OS=Homo sapiens GN=HGFAC PE=1 SV=1 | 4689431 | 6555546 | 4328042 | 4042116 | 4951469.327 | 2588806.944 | 3018503.468 | 3734679.269 | 3376386.259 | 2945268.472 | 4033853.21 | 3096167.579 | 2865730.663 | 2645401.646 | 6224478.897 | 4788274.324 | 5782124.734 | 6235555.268 | 4502120.609 | 4402308.055 | 9133351.277 | 4282126.187 | 8004204.432 | 4765228.977 | 4303562.105 | 4098180.33 | 3304869.716 | ||
| O75339 | 19 | 15 | 973.5 | 0.935096631 | 1.056938799 | XN | HN | Cartilage intermediate layer protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CILP PE=1 SV=4 | 21889336 | 14696476 | 13606367 | 22491546 | 18420863.61 | 13988834.29 | 7389496.049 | 11011050.85 | 10741893.01 | 13526260.07 | 10504887.77 | 18755742.55 | 13661292.52 | 10812127.12 | 9899465.085 | 21690779.45 | 14247087.69 | 15218583.35 | 13018911.34 | 15515511.39 | 11055302.99 | 8989552.447 | 19334964.21 | 22690641.17 | 15903221.42 | 13028974.41 | 16085317.99 | ||
| P14550 | 15 | 9 | 954.83 | 0.070251828 | 2.466908674 | XA | HN | Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP(+)] OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 12671708 | 2714675 | 9552838 | 27160884 | 2850260.078 | 7959048.925 | 10777969.35 | 20984939.18 | 12806565.08 | 6147370.596 | 4132580.543 | 7470624.19 | 7716442.101 | 3406835.315 | 3098824.625 | 4712436.837 | 3417708.417 | 3465424.88 | 5993850.233 | 4535165.496 | 9899032.031 | 6179778.043 | 17844145.37 | 1337364.757 | 6343634.934 | 6189084.357 | 6143077.97 | ||
| P43121 | 19 | 16 | 952.82 | 0.854703285 | 1.005195956 | HN | XA | Cell surface glycoprotein MUC18 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MCAM PE=1 SV=2 | 7047862 | 20686551 | 16186759 | 3618932 | 8449893.408 | 11336034.24 | 9739394.092 | 6162032.002 | 12450114.46 | 5785925.455 | 7777692.475 | 9736516.313 | 9409223.53 | 10167867.17 | 8860507.003 | 3291629.951 | 27407209.37 | 13738137.56 | 15292408.71 | 9128118.321 | 9030180.449 | 11439353 | 12044500.6 | 12605945.77 | 6069432.023 | 10264592.27 | 10067281.78 | ||
| P55290 | 11 | 10 | 945.06 | 0.59720319 | 1.172989686 | HN | XA | Cadherin-13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH13 PE=1 SV=1 | 97613303 | 1.77E+08 | 1.95E+08 | 1.59E+08 | 220952575.3 | 88715388.87 | 55598491.6 | 101745941.5 | 70804832.35 | 103462009.7 | 119563798.9 | 68111924.4 | 107558729.1 | 211264176.7 | 169635072.2 | 227838661.4 | 164356844.3 | 197219624.1 | 92596890.72 | 156593125.6 | 103691540.6 | 128592509.4 | 117898200.3 | 276718613.1 | 124626681.2 | 132137553.9 | 125962602 | ||
| P39059 | 9 | 8 | 940.57 | 0.000890765 | 1.687747755 | XA | XN | Collagen alpha-1(XV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL15A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 81277776 | 76178559 | 68282066 | 99144940 | 78338562.09 | 92605557.4 | 48823648.81 | 107394746.6 | 71314117.58 | 35432558.58 | 47609889.29 | 40881266.75 | 85015878.61 | 67123676.08 | 48704308.67 | 60483623.05 | 73000862.08 | 51925676.41 | 62335569.49 | 31710539.03 | 64030985.26 | 30681124.21 | 40315923.43 | 60336040.13 | 47910257.33 | 46720127.38 | 44554269.94 | ||
| P04279 | 14 | 9 | 939.88 | 0.53804805 | 4.790865093 | XA | XN | Semenogelin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2059404 | 2130190 | 1687600 | 1561043 | 1301064.892 | 1716545.795 | 1657866.125 | 87496673.73 | 1395552.958 | 4897506.116 | 3461878.085 | 3565334.6 | 15348469.17 | 2024260.522 | 1938563.319 | 1032327.763 | 3902363.252 | 5701748.142 | 2141393.099 | 1315178.655 | 2015059.575 | 1925271.424 | 2110675.211 | 2214870.782 | 1878391.368 | 5199068.637 | 2283118.601 | ||
| O43505 | 12 | 10 | 938.62 | 0.639858486 | 1.175507041 | XA | HN | N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=B3GNT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 25712781 | 11827837 | 9545549 | 16371686 | 12473169.83 | 14792678.12 | 10480720.82 | 14859732.17 | 11593388.04 | 15045014.92 | 10432568.15 | 5528538.29 | 14506895.85 | 11501111.28 | 11429264.62 | 17491936.83 | 11944795.67 | 10717728.63 | 15302197.66 | 13831220.88 | 12855859.93 | 13140530.83 | 13246841.07 | 1970329.486 | 18069499.09 | 11660461.56 | 14217102.42 | ||
| P08670;P07196 | 22 | 11 | 937.22 | 0.422912907 | 2.859969706 | XA | XN | Vimentin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VIM PE=1 SV=4 | 845598.2 | 513592.7 | 613540.4 | 1022342 | 957214.5008 | 5720485.085 | 5060904.322 | 2386395.31 | 15988200.97 | 2553735.773 | 796014.9034 | 5957115.857 | 894250.1961 | 925763.5563 | 3455425.86 | 3959894.058 | 1018333.598 | 742326.4133 | 2303770.59 | 1904839.653 | 499435.5224 | 2072227.685 | 523950.8413 | 1605108.885 | 1358017.984 | 634022.129 | 675068.6837 | ||
| P98095 | 10 | 9 | 933.14 | 0.900205765 | 1.436992242 | XA | XN | Fibulin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2.42E+08 | 91088709 | 1.54E+08 | 7.13E+08 | 302530887.3 | 115580582.6 | 81999436.89 | 124133594.3 | 83981221.43 | 322524403.3 | 103204220.8 | 57318271.52 | 98049800.93 | 136684644.7 | 131767636.4 | 370952433 | 232428861.5 | 213494690.1 | 107933991.8 | 156506005.3 | 120712836.2 | 103345200.7 | 176795218.6 | 155183881.6 | 139400318.2 | 146346767.5 | 222036255.9 | ||
| Q6UX06 | 16 | 14 | 932.18 | 0.386284271 | 1.708547755 | XA | XN | Olfactomedin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=OLFM4 PE=1 SV=1 | 36502160 | 4045706 | 7322260 | 5758176 | 3823904.66 | 3323394.211 | 5190600.034 | 3152721.543 | 7123392.88 | 10581055.82 | 3960700.864 | 8588957.444 | 3348555.992 | 19134336.29 | 5952485.104 | 12286615.89 | 8764969.994 | 1861086.81 | 6801710.348 | 3322733.508 | 4031224.834 | 1689287.405 | 1750819.159 | 4927065.562 | 7465120.384 | 9190928.74 | 5445157.22 | ||
| P16152 | 15 | 10 | 927.01 | 0.004150263 | 1.689522679 | XA | HN | Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CBR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 22048987 | 14184163 | 18442637 | 24936899 | 8595396.499 | 15310642.33 | 23187414.37 | 32051110.46 | 18042876.25 | 9480915.263 | 18402247.52 | 11558805.14 | 12165540.34 | 9276896.217 | 11775668.25 | 15045158.84 | 7606576.346 | 9333206.746 | 7903708.883 | 11584443.89 | 11361255.25 | 10623128.84 | 15020216.5 | 12307073.1 | 18900902.97 | 12418066.36 | 12745574.71 | ||
| Q6V0I7 | 32 | 19 | 925.29 | 0.186916048 | 1.409054156 | XA | HN | Protocadherin Fat 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAT4 PE=1 SV=2 | 11179213 | 5800030 | 5094961 | 12505298 | 7264876.294 | 7821089.899 | 5309835.276 | 6817187.405 | 4927669.356 | 5082109.291 | 3846318.134 | 2864406.945 | 5469044.442 | 5018437.461 | 5759291.093 | 6210430.657 | 6156567.294 | 6944421.158 | 8876363.016 | 4728445.295 | 4808654.925 | 7169873.632 | 8679991.996 | 2246211.719 | 5500087.498 | 7336849.759 | 8537562.012 | ||
| Q9BY67 | 13 | 7 | 923.12 | 0.631824563 | 1.159699739 | XN | HN | Cell adhesion molecule 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CADM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 39058252 | 71299527 | 36553426 | 15398781 | 32113525.07 | 78747538.01 | 71933824.67 | 40798746.13 | 91135158.62 | 69513298.89 | 42584801.67 | 49220405.15 | 43860970.17 | 53926087.08 | 31785552.78 | 13611980.94 | 90111900.76 | 74960752.36 | 108961032.6 | 62284869.21 | 69842931.26 | 58443447.63 | 32922317.47 | 56423147.1 | 33022933.43 | 69219215.21 | 53446980.77 | ||
| Q08174 | 20 | 13 | 921.39 | 0.795677805 | 1.120376731 | HN | XA | Protocadherin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 22500565 | 20641408 | 19772880 | 26106932 | 23000332.41 | 12242521.85 | 8033631.257 | 13188455.95 | 12620104.05 | 33245551.66 | 16409058.33 | 13093480.24 | 12387295.73 | 20163567.02 | 18183819.31 | 11596227.01 | 25719470.85 | 26340743.33 | 12302013.25 | 12084245.05 | 14439919.05 | 16125898.47 | 26142402.53 | 30338997.83 | 16495449.22 | 14987669.08 | 20385162.95 | ||
| P05451;P48304 | 10 | 8 | 921.34 | 0.842120693 | 1.519809156 | XA | XN | Lithostathine-1-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=REG1A PE=1 SV=3 | 3673249 | 77432600 | 40278936 | 16903259 | 21736757.17 | 8937679.125 | 19456473.63 | 6649603.17 | 63268515.1 | 8772294.554 | 12359044.01 | 19213151.17 | 12234074.89 | 10596640.69 | 51741956.38 | 40485684.6 | 9528362.436 | 8956919.987 | 9126989.584 | 15853879.16 | 5750703.559 | 25387344.2 | 17095490.6 | 47730972.94 | 11227390.97 | 19240434.3 | 18566736.65 | ||
| O60437 | 36 | 19 | 916.08 | 0.063890973 | 1.872911041 | XA | XN | Periplakin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPL PE=1 SV=4 | 3700904 | 9037120 | 9224896 | 6208567 | 21894551.25 | 5556618.353 | 7976953.26 | 17086086.78 | 12235794.3 | 9392219.316 | 4921709.482 | 9008964.33 | 10108009.49 | 3645688.69 | 16641381.02 | 18542851.07 | 6441779.863 | 5248592.237 | 5094108.384 | 6146665.505 | 2150907.153 | 5367758.107 | 7974798.614 | 8996232.674 | 4758977.159 | 3335520.897 | 5788434.952 | ||
| Q6UVK1 | 24 | 17 | 912.02 | 0.212231176 | 1.290872624 | XA | HN | Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSPG4 PE=1 SV=2 | 17838162 | 16258436 | 18018724 | 9702949 | 9821585.862 | 23500117.31 | 19306000.26 | 17324235.22 | 16993559.42 | 12804757.49 | 19613275.93 | 13126873.01 | 22212341.83 | 10628563.54 | 12249962.72 | 4022531.613 | 10512324.46 | 10072164.37 | 15634091.59 | 12767548.09 | 18257820.83 | 9245926.557 | 10634593.9 | 20042234.02 | 16046718.22 | 13501891.67 | 10623202.33 | ||
| P09668 | 12 | 8 | 904.8 | 0.440668285 | 1.196926088 | HN | XN | Pro-cathepsin H OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSH PE=1 SV=4 | 14454599 | 13657966 | 8310457 | 22732753 | 15818232.37 | 14343226.86 | 10644186.82 | 13388848.94 | 13477112.42 | 12082310.21 | 9892659.616 | 8821677.28 | 11632240.33 | 25831264.6 | 14615927.6 | 11994579.97 | 16346061.5 | 22174823.58 | 20303290.98 | 14589269.59 | 16736175.98 | 12871345.24 | 8667190.113 | 9753442.66 | 2530561.948 | 10740887.2 | 15252933.85 | ||
| P26992 | 11 | 9 | 904.6 | 0.712105887 | 1.204415079 | XN | XA | Ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNTFR PE=1 SV=2 | 18266430 | 24225937 | 16023364 | 22593007 | 14933256.5 | 20395367.48 | 7123081.781 | 18684249.93 | 18138682.23 | 23902991.67 | 18338710.94 | 13764897.33 | 30131593.86 | 19154761.76 | 15859472.67 | 10272156.48 | 18543861.49 | 19764441.9 | 20003102.11 | 16926306.74 | 15636162.08 | 28331287.56 | 16238510.35 | 50559558.92 | 15382251.05 | 16835145.66 | 13255833.65 | ||
| Q15828 | 9 | 8 | 903.32 | 0.578303747 | 2.525291753 | HN | XN | Cystatin-M OS=Homo sapiens GN=CST6 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.01E+08 | 1.38E+08 | 1.16E+08 | 1.99E+08 | 295783575.6 | 65114145.95 | 34751887.65 | 74543694.44 | 44939683.76 | 99365929.43 | 98155479.55 | 55600604.37 | 50591266.31 | 115374764.8 | 211554289 | 1443364687 | 139263100 | 73682614.6 | 56589353.52 | 116961892.3 | 39398963.79 | 57553407.99 | 199817891.9 | 139820465.7 | 103118412.9 | 85482669.65 | 106876157 | ||
| O76076 | 8 | 7 | 894.71 | 0.580330696 | 1.182134971 | HN | XA | WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WISP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 97729720 | 45145840 | 59416170 | 1.17E+08 | 68156828.96 | 52010021.6 | 29616122.33 | 40155716.46 | 38553806.91 | 80919947.23 | 100013084.9 | 28409342.12 | 64355407.93 | 58112513.92 | 45038305.83 | 144166720.1 | 42349325.07 | 83902952.54 | 63998435.84 | 64509375.84 | 70910916.3 | 33503223.82 | 56668950.95 | 97709456.99 | 80942621.4 | 73414107.24 | 96651839.12 | ||
| P00352 | 17 | 12 | 889.27 | 0.439247954 | 1.529026417 | HN | XN | Retinal dehydrogenase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH1A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 10392356 | 4933266 | 6547034 | 10745039 | 2910994.083 | 14637822.17 | 16517997.52 | 14220814.38 | 8512063.661 | 9779509.317 | 15358352.06 | 21325124.06 | 17105777.52 | 16798237.46 | 2565524.793 | 3155718.353 | 5860197.385 | 3210572.241 | 16663940.77 | 5489070.457 | 8003754.824 | 10452159.52 | 4465131.803 | 2010311.64 | 5989644.776 | 5195902.982 | 3965118.627 | ||
| P04180 | 12 | 8 | 886.88 | 0.250418073 | 1.197760776 | XA | XN | Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCAT PE=1 SV=1 | 17871279 | 17880023 | 11421114 | 15002314 | 12901386.95 | 18176200.61 | 13467936.29 | 18834379.05 | 12031622.68 | 12576342.85 | 14254564.77 | 16617370.66 | 11899919.28 | 17394295.86 | 12278831.33 | 8197182.699 | 19853841.68 | 12994122.21 | 16118507.71 | 15098315.7 | 14396913.3 | 17992281.88 | 9379949.709 | 9186524.889 | 10633429.24 | 12220951.27 | 9842688.766 | ||
| Q8NFZ8 | 12 | 9 | 886.35 | 0.729985462 | 1.275828433 | XA | HN | Cell adhesion molecule 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CADM4 PE=1 SV=1 | 8943977 | 21168177 | 14643208 | 5597919 | 4644137.898 | 19438084.16 | 28325432.63 | 11838477.64 | 34003938.19 | 5403030.162 | 23977417.73 | 12577724.72 | 20969907.39 | 16011746.1 | 10700252.27 | 6125533.956 | 9440444.785 | 11269910.73 | 21815689.38 | 16264121.77 | 14627743.07 | 13341333.39 | 8251905.436 | 19916045.66 | 12014020.62 | 16100633.98 | 9051546.56 | ||
| O00533 | 21 | 16 | 885.54 | 0.62719749 | 1.40946077 | XA | HN | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHL1 PE=1 SV=4 | 11212336 | 10054096 | 13731015 | 14648861 | 5102284.867 | 2483871.458 | 9997887.525 | 15546952.54 | 2053768.326 | 2286073.599 | 7221829.496 | 5090447.922 | 4580912.572 | 6945489.035 | 9277477.616 | 2392894.502 | 8145162.002 | 14246611.97 | 3278592.745 | 11239802.94 | 2427382.21 | 2041180.997 | 9059169.013 | 9825088.128 | 1924820.18 | 18819372.23 | 9535821.652 | ||
| Q9NZP8 | 13 | 9 | 883.71 | 0.885068146 | 1.115310102 | XA | XN | Complement C1r subcomponent-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1RL PE=1 SV=2 | 69864851 | 47640700 | 37919039 | 55794935 | 32860653.76 | 35582540.43 | 24278165.48 | 71174641.81 | 31445698.52 | 76789071.7 | 54184406.31 | 45897335.36 | 23086157.03 | 41392113.61 | 22815416.18 | 19620361.25 | 56974042.04 | 50103768.76 | 55083998.47 | 36201386.02 | 44560232.97 | 47725283.7 | 43630480.9 | 17892616.34 | 45411307.82 | 35330205.15 | 38692007.86 | ||
| P00491 | 12 | 7 | 876.51 | 0.159180319 | 1.721750221 | XA | HN | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PNP PE=1 SV=2 | 4188202 | 3052442 | 2894204 | 5155552 | 1882870.668 | 11490907.6 | 12415746.21 | 7241016.104 | 8261984.751 | 3865627.732 | 3092105.831 | 10357476.7 | 3817588.179 | 5903713.725 | 1942366.136 | 693453.473 | 1695329.405 | 1495946.764 | 5809691.389 | 4069698.469 | 5752066.912 | 10204783.11 | 2580971.384 | 1748903.381 | 2060099.401 | 2153105.727 | 1377455.821 | ||
| P30041 | 11 | 5 | 864.71 | 0.388433251 | 1.473990723 | XA | HN | Peroxiredoxin-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX6 PE=1 SV=3 | 14595997 | 3325313 | 5539517 | 20625867 | 3685100.253 | 9319995.32 | 8927721.949 | 16013657.35 | 7845370.589 | 12257991.42 | 5316037.761 | 11433706.07 | 4801351.419 | 7010566.429 | 3460521.334 | 8049352.382 | 3296040.932 | 5350758.989 | 8428403.271 | 3969132.243 | 11513953.25 | 10513501.43 | 10819339.95 | 1325492.14 | 6491067.577 | 4791341.268 | 4137131.606 | ||
| O00241 | 12 | 9 | 863.96 | 0.834770894 | 1.175272591 | XA | HN | Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIRPB1 PE=1 SV=5 | 2425241 | 15668778 | 5638863 | 3492765 | 2108912.054 | 5529098.968 | 5974263.881 | 3255805.777 | 7790591.989 | 4091325.353 | 9766421.541 | 2113921.064 | 3193275.134 | 6065032.903 | 5991727.168 | 1833427.052 | 4980983.63 | 6110512.635 | 3534152.449 | 4451255.52 | 3328772.2 | 6738875.369 | 3828827.228 | 9948185.346 | 4438927.303 | 7135821.576 | 4774897.833 | ||
| Q06830 | 14 | 10 | 863.92 | 0.966957383 | 1.123116287 | XA | XN | Peroxiredoxin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX1 PE=1 SV=1 | 41203391 | 10080361 | 13456998 | 47013624 | 10857295.56 | 41198999.24 | 33622383.81 | 51519717.17 | 27814555.04 | 67809897.15 | 29974297.47 | 42183489.79 | 27015137.49 | 14826738.84 | 22980207.49 | 15800319.93 | 13731788 | 25839285.95 | 45089661.83 | 20816978.36 | 49554788.19 | 34691609.96 | 31899642.77 | 9853343.836 | 17871033.56 | 18122320.99 | 18528641.47 | ||
| P14384 | 12 | 9 | 863.61 | 0.094397364 | 1.400922038 | XA | HN | Carboxypeptidase M OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPM PE=1 SV=2 | 9671251 | 14122836 | 9148271 | 8840949 | 7883098.504 | 14033871.56 | 18110056.69 | 9697713.831 | 20213564.66 | 4879299.503 | 12004503.24 | 4967870.98 | 12493980.29 | 14219367.32 | 8686329.108 | 3749645.694 | 7566001.058 | 11181631.89 | 6063804.218 | 13870871.53 | 8016729.845 | 7268544.052 | 12333389.57 | 8108714.093 | 8769312.478 | 7866338.787 | 8734079.233 | ||
| P30039 | 12 | 12 | 861.67 | 0.02662795 | 2.562046154 | XA | HN | Phenazine biosynthesis-like domain-containing protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PBLD PE=1 SV=2 | 6015111 | 6583559 | 6047653 | 11223560 | 2766846.514 | 20204173.18 | 16223029.39 | 16223449.5 | 7630370.893 | 8417452.543 | 2864836.081 | 5934047.799 | 3364634.579 | 4948391.626 | 2714213.009 | 1666140.246 | 3901227.258 | 2456066.878 | 7492068.343 | 5923429.397 | 12637019.46 | 22773300.88 | 6692501.065 | 1805295.037 | 3214549.952 | 6368721.12 | 2668850.563 | ||
| P07204 | 8 | 6 | 860.34 | 0.298478556 | 1.173014129 | XN | HN | Thrombomodulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBD PE=1 SV=2 | 32574326 | 17266241 | 18884670 | 27444685 | 22158062.76 | 18150820.73 | 17710911.35 | 21332320.19 | 21396631.12 | 13827173.29 | 33961094.41 | 9332896.539 | 26453829.23 | 22145167.74 | 13295428.38 | 3957140.06 | 22983223.87 | 33914003.89 | 22602987.25 | 24049644.58 | 28182765.28 | 16818001.9 | 18703056.25 | 34100475.22 | 20120032.38 | 23008048.15 | 23404990.38 | ||
| Q96JQ0 | 16 | 12 | 855.68 | 0.683620967 | 1.207162215 | HN | XA | Protocadherin-16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCHS1 PE=2 SV=1 | 15873351 | 7571252 | 7695550 | 11273947 | 6410576.865 | 8945742.405 | 17382850 | 12439815.62 | 9702515.118 | 26468010.21 | 17793904.89 | 7937117.412 | 14934595.9 | 16368225.49 | 6210791.35 | 4301302.786 | 11159975.01 | 12277649.02 | 11542620.7 | 10837161.95 | 13380481.06 | 10101043.64 | 13091516.16 | 14085024.46 | 9760004.002 | 11654315.68 | 14721726.27 | ||
| P54760 | 14 | 9 | 846.95 | 0.459712141 | 1.25271778 | XA | XN | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHB4 PE=1 SV=2 | 5713490 | 8032640 | 10979529 | 10281133 | 8923207.308 | 7606580.612 | 3554392.885 | 7774662.683 | 4628577.508 | 4825929.322 | 10719558.41 | 3393151.976 | 7393797.344 | 9059785.556 | 5936332.132 | 6174431.716 | 7598648.219 | 5163166.882 | 4650882.14 | 6096680.772 | 3496398.012 | 5461779.083 | 7765132.472 | 6855648.863 | 7513339.554 | 4763893.459 | 7274472.5 | ||
| P13796 | 19 | 12 | 846.78 | 0.518717396 | 2.205201344 | XA | XN | Plastin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCP1 PE=1 SV=6 | 1145075 | 661785.7 | 794821 | 1270765 | 584360.434 | 5758340.487 | 8164439.965 | 3018931.094 | 13567418.85 | 12830179.07 | 1665156.415 | 2631165.143 | 1132243.099 | 1734869.191 | 6686408.171 | 961971.3331 | 798408.189 | 652922.8101 | 6355604.22 | 544339.0333 | 545385.6974 | 1170348.166 | 1158482.048 | 957436.2665 | 2630204.776 | 746621.3512 | 1747698.613 | ||
| P08603;Q02985 | 23 | 17 | 845.59 | 0.302718702 | 1.29242108 | XA | HN | Complement factor H OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFH PE=1 SV=4 | 8621513 | 3711227 | 3233632 | 6314947 | 4566773.524 | 4160027.766 | 4500576.175 | 4854026.496 | 3689548.128 | 2996488.483 | 1857103.331 | 6862580.786 | 3218497.329 | 1698427.633 | 2920014.991 | 6478084.29 | 3811492.333 | 3932890.289 | 4818704.928 | 7856581.966 | 3954461.188 | 2743143.618 | 4494652.068 | 1256096.966 | 3824732.872 | 3663121.819 | 4068732.38 | ||
| P09211 | 8 | 7 | 839.57 | 0.184344162 | 1.618147052 | HN | XN | Glutathione S-transferase P OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 29658008 | 12782790 | 17485898 | 35763432 | 17427341.88 | 22180223.39 | 24795263.57 | 41154462.38 | 33044633.22 | 60181700.24 | 39434672.11 | 37401970.79 | 31737335.96 | 34120647.56 | 10744808.43 | 13860720.75 | 10768583.94 | 15063069.56 | 15475972.71 | 10109890.71 | 21861715.49 | 17352479.56 | 19747173.33 | 21279751.24 | 24767315.57 | 12441065.23 | 13510055.82 | ||
| P01023 | 19 | 14 | 834.19 | 0.635890728 | 1.48645133 | HN | XN | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 3781583 | 2540390 | 1814530 | 2170071 | 3670872.309 | 5129365.001 | 5335594.951 | 4777146.298 | 9671873.741 | 3829414.957 | 4006263.108 | 26866234.02 | 4371735.448 | 1818151.785 | 2094450.99 | 2237003.905 | 2467454.794 | 2300120.724 | 14062419.16 | 3806756.684 | 3612422.462 | 2005706.173 | 2603816.043 | 2475248.708 | 1688494.621 | 1516579.171 | 1859546.908 | ||
| Q86TH1 | 16 | 12 | 832.95 | 0.040267582 | 1.66122174 | XA | HN | ADAMTS-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTSL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 7786021 | 3132474 | 2946004 | 5763313 | 3112715.415 | 6901401.281 | 3873796.708 | 4392756.714 | 4588036.831 | 1731753.153 | 1162758.697 | 2472719.232 | 2144187.281 | 1248726.545 | 2247686.319 | 3276306.013 | 6931714.471 | 4365634.102 | 7688119.503 | 5518311.254 | 3361283.947 | 4325004.789 | 5567410.173 | 1107383.155 | 6307597.287 | 2903106.428 | 4692067.636 | ||
| P35558 | 20 | 14 | 831.21 | 0.1336348 | 2.856931439 | XA | XN | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic [GTP] OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 5944852 | 1201241 | 5142921 | 23470057 | 539931.2472 | 3425999.573 | 3504433.611 | 7373795.832 | 1458612.298 | 1373385.909 | 1527316.408 | 5491904.844 | 1933299.472 | 948106.644 | 1085620.778 | 4412878.14 | 1016826.216 | 748435.6289 | 1132895.326 | 1877165.956 | 1834714.411 | 1871823.159 | 3959202.209 | 1537837.796 | 3242557.993 | 1698994.109 | 1067802.604 | ||
| P51688 | 14 | 12 | 830.29 | 0.132473177 | 1.554932357 | XA | XN | N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SGSH PE=1 SV=1 | 4360796 | 8705054 | 27023247 | 14764768 | 8863359.192 | 10762446.62 | 13085258.48 | 13253122.45 | 11648471.47 | 13080446.45 | 4264867.713 | 7435527.234 | 17010580.52 | 9320584.399 | 5224316.432 | 3290519.755 | 10389945.2 | 5628782.184 | 4851975.478 | 3469161.387 | 6735387.556 | 9960083.249 | 11591422.78 | 7215482.55 | 8754389.199 | 11810153.64 | 7940829.407 | ||
| P29622 | 12 | 7 | 830.03 | 0.632230757 | 1.347603644 | XN | HN | Kallistatin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA4 PE=1 SV=3 | 11402828 | 2971890 | 2196774 | 6692099 | 9372700.769 | 4553994.981 | 5645919.801 | 7235178.622 | 3907719.563 | 4897181.649 | 3696145.872 | 6159290.867 | 5230001.418 | 3695381.623 | 4035934.669 | 3892530.565 | 6066266.455 | 3105936.352 | 8044299.478 | 5418773.974 | 4402015.877 | 6480267.972 | 10501058.52 | 1244477.134 | 4771288.594 | 7215264.195 | 6876037.825 | ||
| Q5TFQ8 | 10 | 1 | 829.47 | 0.681809485 | 1.719358354 | XN | HN | Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 isoform 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIRPB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 20328.16 | 1714250 | 246052.3 | 100922.7 | 124323.0772 | 174384.616 | 9610.337029 | 114380.5743 | 208488.0757 | 94303.10255 | 687825.5268 | 45292.81204 | 71656.15816 | 272330.9358 | 85752.63546 | 73564.78454 | 91821.50887 | 173724.4466 | 160040.6544 | 15608.57294 | 139930.5751 | 593999.2129 | 81014.7614 | 1006380.376 | 286071.734 | 286604.9491 | 174912.6088 | ||
| P21709 | 13 | 9 | 823.6 | 0.054064359 | 1.452862373 | HN | XN | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHA1 PE=1 SV=4 | 12269584 | 5910479 | 7688478 | 7456045 | 13114543.71 | 8450186.448 | 6371924.774 | 12239245.16 | 6276551.974 | 17531612.18 | 12505369.6 | 6085845.785 | 9624077.562 | 14715535.38 | 7848937.159 | 20436223.36 | 13757384.28 | 13319202.44 | 10040066.75 | 7506800.991 | 8582093.939 | 5842248.887 | 12224234.47 | 5244890.108 | 9819206.687 | 7534174.159 | 12927660.18 | ||
| P08174 | 12 | 10 | 823.38 | 0.038111105 | 2.087436837 | XA | HN | Complement decay-accelerating factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD55 PE=1 SV=4 | 10984079 | 82981843 | 80979723 | 24610649 | 25075928.77 | 31717274.2 | 19477839.73 | 29705011.44 | 35088786.68 | 9588867.378 | 16401190.18 | 22914677 | 15424070.72 | 13483591.56 | 25826594.08 | 13178661.24 | 21574372.31 | 24784714.05 | 18742614.91 | 24835942.97 | 20312313.66 | 34027257.23 | 23509749.34 | 67900927.6 | 20277985.8 | 27370778.13 | 23327626.26 | ||
| P19440;A6NGU5;B5MD39;Q14390;Q9BX51 | 16 | 5 | 822.5 | 0.356667477 | 1.299253 | XA | XN | Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GGT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5744448 | 3763494 | 4068686 | 3727267 | 2665105.415 | 6387447.421 | 7162257.693 | 6290895.193 | 4429186.606 | 5387812.796 | 8385131.546 | 6490396.299 | 2492058.78 | 7805089.09 | 1779882.878 | 2935447.476 | 3807396.903 | 4456222.568 | 3514635.555 | 3915555.918 | 5982581.781 | 2863485.468 | 3066082.683 | 1466387.64 | 2599584.978 | 4651811.22 | 5989276.777 | ||
| P08236 | 15 | 14 | 822.46 | 0.022731006 | 1.848971179 | XA | HN | Beta-glucuronidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GUSB PE=1 SV=2 | 11195225 | 15780020 | 37602580 | 23450818 | 11916805.83 | 22516628.22 | 44600034.83 | 36836900.96 | 39746793.5 | 7791229.739 | 12133317.44 | 16720385.89 | 37616310.8 | 6615532.227 | 12358062.85 | 7864241.436 | 21960347.49 | 8714290.098 | 15951258.91 | 9807274.555 | 12160174.25 | 12388407.62 | 23902143.16 | 10576325.16 | 13605063.75 | 26227418.4 | 12614245.33 | ||
| P35052 | 13 | 10 | 819.79 | 0.890527995 | 1.042037579 | XA | HN | Glypican-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 8232706 | 8934887 | 10244096 | 7370160 | 5794360.746 | 5851990.23 | 7518856.914 | 9044217.255 | 6492723.338 | 5438410.309 | 8647272.987 | 6624516.638 | 6175797.556 | 11371570.33 | 8311170.91 | 7851663.444 | 6774355.4 | 5486137.377 | 6730319.895 | 5684508.664 | 6719372.524 | 7191384.866 | 6493274.178 | 6297054.517 | 11304629 | 7096509.191 | 10203432.24 | ||
| P15291;O43286 | 10 | 9 | 818.75 | 0.611864683 | 1.23903019 | XA | HN | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=B4GALT1 PE=1 SV=5 | 24790768 | 7339359 | 9050979 | 14331007 | 9634938.411 | 6465221.497 | 8279544.514 | 13984952.04 | 7556605.222 | 7306240.726 | 6181339.199 | 6597797.934 | 6801732.01 | 7572769.222 | 10495655.95 | 18844643.61 | 10180613.79 | 7884342.781 | 6172089.814 | 9268527.994 | 11580401.19 | 7067110.741 | 12558901.79 | 4732547.358 | 18054814.49 | 12690756.84 | 12150332.08 | ||
| P68104;Q5VTE0 | 13 | 4 | 813.8 | 0.202542928 | 1.856828431 | XA | HN | Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1A1 PE=1 SV=1 | 11675922 | 3297846 | 5283032 | 26511325 | 4162619.712 | 9518740.606 | 8795151.89 | 24247496.69 | 7377172.171 | 7076062.791 | 2411268.354 | 14248094.41 | 6299293.183 | 2486591.497 | 2048756.878 | 11348922.98 | 3992723.865 | 4411724.754 | 3850502.092 | 6143171.41 | 15326260.78 | 9647554.151 | 13888976.42 | 1524325.472 | 4481056.59 | 5325376.532 | 3024065.251 | ||
| P30086 | 9 | 9 | 810.27 | 0.809750211 | 1.349280459 | HN | XN | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PEBP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 14515615 | 26271209 | 21427178 | 22348949 | 6716739.394 | 29024062.31 | 39735095.46 | 22748975.7 | 46201293.93 | 20580827.35 | 45263301.19 | 60898713.62 | 29885733.78 | 48767681.25 | 8219733.329 | 7680564.268 | 11241359.8 | 11597020.4 | 25422917.55 | 20446818 | 27294496.56 | 33286493.19 | 10929930.1 | 22032783.86 | 14358922.28 | 18198798.55 | 8965970.846 | ||
| Q9HBB8 | 6 | 6 | 807.23 | 0.625448486 | 1.223390779 | HN | XA | Cadherin-related family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDHR5 PE=1 SV=3 | 16921015 | 14556250 | 11189320 | 12623478 | 6188190.226 | 11674683.18 | 12135760.51 | 9500167.813 | 17226056.49 | 17714820.63 | 18084048.75 | 10760338.14 | 23010336.03 | 28290884.85 | 8130095.688 | 8149659.702 | 10105012.58 | 12792824.53 | 12393402.32 | 12385371.51 | 13046009.31 | 9522932.139 | 10756375.43 | 12668330.64 | 13027836.26 | 14364368.18 | 16349917.46 | ||
| Q16706 | 20 | 18 | 803.99 | 0.538720729 | 1.248220269 | XA | XN | Alpha-mannosidase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5211646 | 1457959 | 1913338 | 3773389 | 2826926.538 | 3326980.911 | 3813869.17 | 3755479.507 | 3308259.872 | 1340991.442 | 931513.6768 | 3809528.744 | 3281143.128 | 1068627.003 | 2292921.214 | 4400679.02 | 8137123.838 | 1830872.163 | 2077653.826 | 1861019.316 | 1977021.161 | 2221553.288 | 3650916.641 | 1486462.262 | 3751670.366 | 3438211.937 | 3079291.281 | ||
| P43652 | 18 | 14 | 802.33 | 0.531869726 | 1.348236322 | XN | XA | Afamin OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFM PE=1 SV=1 | 1.57E+08 | 1.1E+08 | 1.65E+08 | 1.83E+08 | 103722668.2 | 254554242 | 218988924.9 | 228873264.4 | 199108211.5 | 430140419.4 | 142139740.9 | 135790388.7 | 130573243.8 | 443613105.7 | 102826249.2 | 118162809.5 | 261876430.1 | 373384245.9 | 285642088.6 | 219377110.2 | 355608973 | 283813042.8 | 135117659.7 | 96783673.08 | 149558734.3 | 294745589.2 | 364438866.1 | ||
| Q15113 | 9 | 7 | 802.26 | 0.434379411 | 1.266620701 | HN | XA | Procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCOLCE PE=1 SV=2 | 74948920 | 27674289 | 26614820 | 41996313 | 46811762.16 | 23481911.8 | 20242789.39 | 34810518.38 | 21156736.67 | 78644657.11 | 42910941.39 | 29017495.4 | 38744950.03 | 44282152.53 | 21574046.82 | 82255363.33 | 36642608.83 | 28381389.05 | 25794018.35 | 34284298.64 | 31093733.33 | 27860975 | 31745476.52 | 48807425.92 | 47650047.6 | 30835043.37 | 44097576.8 | ||
| P22314 | 15 | 11 | 797.12 | 0.099467843 | 2.019641246 | XA | HN | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 2672494 | 675975.9 | 2205584 | 8547131 | 988785.5118 | 2098282.903 | 2270740.947 | 5090343.643 | 2513007.186 | 1627429.037 | 794647.923 | 2658356.91 | 1878648.241 | 765872.047 | 1665976.432 | 2959503.925 | 543209.3256 | 505936.4218 | 1252722.66 | 897712.2285 | 1623779.791 | 1039962.327 | 2872787.968 | 769651.2211 | 2333672.249 | 1208510.49 | 1660136.469 | ||
| P31947 | 12 | 7 | 796.78 | 0.717775333 | 3.042173068 | XA | XN | 14-3-3 protein sigma OS=Homo sapiens GN=SFN PE=1 SV=1 | 336405.1 | 154644.3 | 120523.6 | 330291 | 101578.2188 | 1050662.288 | 1729053.329 | 5988803.858 | 7096306.439 | 1702047.756 | 749718.02 | 4288150.836 | 1882961.824 | 177717.3554 | 259869.4791 | 1057901.135 | 144765.6415 | 332566.8805 | 1908490.284 | 1123508.217 | 765453.2204 | 668678.5036 | 175373.722 | 204403.4829 | 192126.5988 | 160628.5899 | 359294.6899 | ||
| O75891 | 14 | 7 | 793.7 | 0.002776417 | 2.944285626 | XA | HN | Cytosolic 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH1L1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3060595 | 534134.8 | 1576230 | 5847917 | 892781.7586 | 2247025.23 | 1739226.811 | 3755615.633 | 1691563.588 | 759727.3108 | 596247.0394 | 1259715.312 | 2040917.538 | 486227.4181 | 562255.4273 | 788898.4532 | 476526.6328 | 279151.439 | 938553.6926 | 554598.0705 | 1243585.656 | 654006.3473 | 1749202.423 | 774363.562 | 1154291.464 | 829408.3251 | 829939.1873 | ||
| Q8IYS5 | 9 | 9 | 793.63 | 0.426895294 | 1.255311792 | XN | XA | Osteoclast-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=OSCAR PE=2 SV=3 | 88093617 | 92064891 | 55231931 | 1.34E+08 | 56385021.2 | 115941502.4 | 53692468.78 | 121394797.4 | 76131721.13 | 161661621.1 | 167637333.8 | 54487352.96 | 88768806.54 | 119630515.8 | 54585213.53 | 56711191.2 | 55875117.48 | 96332149.71 | 114818046.1 | 116169441.1 | 127364490.3 | 46834932.55 | 114990187.1 | 68901111.19 | 130609500.8 | 142491533.4 | 133749535.1 | ||
| P43251 | 11 | 10 | 789.62 | 0.289149895 | 1.403247518 | HN | XN | Biotinidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=BTD PE=1 SV=2 | 11083011 | 32065617 | 19917494 | 7360949 | 17728834.71 | 11206644.96 | 18750086.52 | 10817653.42 | 18823049.45 | 18552482.84 | 27021725.99 | 28584706.44 | 21748241.66 | 26427121.37 | 22865801.53 | 5884461.401 | 25726819.22 | 13844920.93 | 12287224.65 | 12210296.31 | 11112091.63 | 14717053.74 | 14249335.35 | 29452342.6 | 13403946.6 | 12790785.83 | 15644814.73 | ||
| Q9BYE9 | 17 | 12 | 782.23 | 0.26711219 | 1.273811567 | HN | XA | Cadherin-related family member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDHR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 8703702 | 15856087 | 16700774 | 12337303 | 14305901.02 | 5287138.366 | 5077181.3 | 6510180.292 | 7278633.465 | 10595552.23 | 9584889.643 | 7929301.647 | 11960338.4 | 22022615.48 | 13249148.24 | 17749927.57 | 10130582.19 | 14040789.29 | 7298052.275 | 8996285.606 | 5325069.328 | 6507061.901 | 11890581.56 | 19704939.07 | 14174272.53 | 10064885.56 | 9541879.616 | ||
| P55000 | 5 | 4 | 779.3 | 0.934116708 | 1.045658158 | XN | HN | Secreted Ly-6/uPAR-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLURP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3.12E+08 | 5.86E+08 | 5.52E+08 | 6.56E+08 | 763410918.7 | 421026806.8 | 210582673.8 | 434752481.6 | 289186224.7 | 160283527.6 | 399361934.7 | 169325240.4 | 682146460.6 | 450594542.8 | 480416835.4 | 495093795.7 | 544530965.5 | 761544041.2 | 307823211.6 | 414855098.1 | 326100167 | 508931814 | 414570645 | 1126985323 | 500792589.4 | 410054074.4 | 322359746.1 | ||
| Q6S8J3;A5A3E0;P0CG38;P0CG39;Q9BYX7 | 11 | 2 | 775.76 | 0.372983474 | 2.868132777 | XA | HN | POTE ankyrin domain family member E OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEE PE=1 SV=3 | 997647.3 | 333865.5 | 253050.5 | 29078.13 | 52200.52442 | 29565.8372 | 32143.53667 | 26583.79921 | 43168.96755 | 139165.422 | 38653.91888 | 196441.6164 | 22117.29818 | 12544.79882 | 80282.23276 | 18800.32413 | 88876.65735 | 29763.75631 | 19056.1456 | 36713.04225 | 18200.19395 | 20731.31849 | 36898.38419 | 413963.4067 | 12307.01231 | 43665.43268 | 81887.49701 | ||
| Q14508 | 6 | 6 | 773.84 | 0.483805922 | 1.212614087 | XN | HN | WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WFDC2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.75E+08 | 4.19E+08 | 2.29E+08 | 1.73E+08 | 77922809.37 | 277060960.7 | 555741175.5 | 142135938.8 | 869812956.3 | 136773031.8 | 728130415.5 | 58351531.03 | 539496504.1 | 310244635.7 | 180545465.8 | 74351340.43 | 128530247.1 | 277389920.7 | 193948619 | 383984718 | 384475442.9 | 230966977.6 | 189506405.5 | 675296641.4 | 347847346.9 | 391178318.8 | 154071569.9 | ||
| Q92859 | 17 | 14 | 772.59 | 0.895042244 | 1.03125361 | XA | HN | Neogenin OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6356383 | 10479097 | 6164055 | 4747391 | 7256373.532 | 6308602.406 | 7209505.695 | 5988808.759 | 9614536.88 | 5677193.658 | 7719929.678 | 7584172.934 | 9040714.947 | 6879851.163 | 6178843.086 | 2375966.907 | 8166229.239 | 8558459.043 | 6374053.489 | 5231758.759 | 6899972.108 | 6074072.516 | 7059511.911 | 10157106.03 | 7071442.369 | 7710066.359 | 6061702.378 | ||
| Q9H2M3 | 14 | 8 | 770.11 | 0.135131233 | 1.69242737 | XA | HN | S-methylmethionine--homocysteine S-methyltransferase BHMT2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BHMT2 PE=1 SV=1 | 5462280 | 6903613 | 3515223 | 12283758 | 1025339.158 | 4704344.058 | 6292794.681 | 4423112.333 | 7877168.668 | 5032377.74 | 3485002.29 | 7728892.243 | 3990478.921 | 1184188.343 | 1443364.04 | 2139746.664 | 4234902.422 | 1774274.225 | 8624806.87 | 3183377.542 | 7017444.405 | 4566657.438 | 4108919.401 | 4606707.431 | 10922252.14 | 3652073.457 | 2287371.008 | ||
| P23526 | 16 | 12 | 768.28 | 0.311900483 | 1.68819829 | XA | HN | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 3073287 | 1065955 | 1935885 | 2869293 | 1680206.058 | 10732107.5 | 8508435.966 | 7192190.253 | 5149255.466 | 7276001.262 | 1935264.73 | 4972708.743 | 2849034.515 | 2580320.755 | 1506201.201 | 485145.8904 | 2102110.208 | 1294194.33 | 5120785.459 | 2835984.793 | 5046668.016 | 5380607.077 | 1884931.358 | 1860628.219 | 1963900.677 | 2440604.693 | 2069200.112 | ||
| P30530 | 13 | 10 | 765.92 | 0.097665128 | 1.363561114 | XN | HN | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO OS=Homo sapiens GN=AXL PE=1 SV=3 | 76229582 | 1.32E+08 | 1.22E+08 | 85251984 | 42511090.94 | 88801748.85 | 144342326 | 77794007.06 | 146717426.9 | 39331580.44 | 162868459.5 | 51919828.26 | 112212461.5 | 75867933.61 | 40894569.85 | 15772062.61 | 102978186.3 | 85632295.33 | 121231902 | 96568349.61 | 107155193 | 75313032.63 | 77872915.69 | 141593017 | 83787861.56 | 121374681.7 | 112520465.2 | ||
| P06280 | 12 | 8 | 759.51 | 0.354503897 | 1.312145746 | XA | XN | Alpha-galactosidase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLA PE=1 SV=1 | 7794165 | 10805636 | 18024847 | 9332937 | 7756152.877 | 11972455.22 | 16177018.37 | 8535722.11 | 10725272.42 | 7795813.412 | 8055558.837 | 5511343.433 | 19430779.91 | 17828005.46 | 5751338.684 | 7133158.156 | 17715879.93 | 9235227.805 | 8389560.049 | 7261518.969 | 9547062.756 | 7990972.495 | 7758729.602 | 8164812.418 | 8157242.623 | 11866835.94 | 7931080.473 | ||
| P13489 | 11 | 10 | 759.46 | 0.291257596 | 1.356723298 | HN | XN | Ribonuclease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4069129 | 3128311 | 2863070 | 4872534 | 3493861.856 | 4491616.202 | 2949170.865 | 4065539.996 | 3119207.701 | 6649016.866 | 3250413.089 | 5939690.725 | 2982198.105 | 4207515.806 | 3716970.489 | 5504824.674 | 2204224.544 | 1296908.806 | 3467276.189 | 2906920.97 | 3691334.581 | 2732198.949 | 2951409.974 | 4045810.959 | 2447088.364 | 1709076.273 | 2400434.678 | ||
| Q13421 | 15 | 12 | 759.25 | 0.980545662 | 1.485394174 | HN | XN | Mesothelin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSLN PE=1 SV=2 | 9336175 | 10370185 | 7482350 | 9419074 | 40498815.02 | 2529266.582 | 4757249.793 | 5854463.006 | 4449554.218 | 7263291.915 | 2948421.084 | 4629787.02 | 7556981.846 | 3979615.021 | 6948990.509 | 48984525.14 | 10799061.81 | 7764626.744 | 7869359.893 | 2845647.396 | 8464196.23 | 7257185.084 | 9847420.523 | 7465705.039 | 7459812.201 | 8797491.853 | 7904651.229 | ||
| Q13228 | 15 | 12 | 759.05 | 0.099981552 | 1.511694384 | XA | HN | Selenium-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SELENBP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4297913 | 11058664 | 11543517 | 5183880 | 6425656.237 | 11306144.57 | 13522239.12 | 9481690.56 | 16439063.46 | 5431928.582 | 6746788.644 | 11671785.19 | 9381534.515 | 9838807.584 | 5110407.747 | 3377895.57 | 3484333.339 | 4002029.506 | 5726427.304 | 5886031.949 | 7345588.661 | 8070781.286 | 6086870.932 | 13386746.18 | 5786033.967 | 5765350.845 | 3980127.057 | ||
| P55285 | 20 | 13 | 753.45 | 0.586795698 | 1.198284647 | XA | XN | Cadherin-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH6 PE=1 SV=1 | 12977851 | 13735794 | 11837064 | 12894238 | 23893677.62 | 5963528.968 | 4732451.689 | 13463658.67 | 5196646.543 | 9761780.195 | 12536701.69 | 6353190.571 | 7940169.304 | 9181283.634 | 8899662.972 | 20737380.4 | 14894843.71 | 11284473.55 | 4540990.125 | 4750529.157 | 5649436.278 | 6416436.634 | 19131151.07 | 16750548.67 | 11580957.3 | 7281617.861 | 11268984.15 | ||
| P08123 | 10 | 7 | 747.77 | 0.38264279 | 1.334679628 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A2 PE=1 SV=7 | 9550421 | 4325117 | 2999687 | 5513718 | 5464217.036 | 4791594.437 | 3515171.044 | 3021575.498 | 2848043.795 | 4138210.57 | 2751659.861 | 4572990.823 | 2358167.435 | 2755060.718 | 4308590.292 | 15391061.41 | 4533648.101 | 2888342.015 | 4331966.888 | 8113551.657 | 1917324.733 | 1872028.832 | 3016389.297 | 2199189.067 | 1432643.709 | 5675238.351 | 4181907.388 | ||
| O96009 | 8 | 3 | 746.65 | 0.035894022 | 1.945924 | HN | XN | Napsin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAPSA PE=1 SV=1 | 19491899 | 11928715 | 61956998 | 10726874 | 21071568.03 | 8001073.151 | 11596607.53 | 23215566.18 | 6684568.901 | 29006426.84 | 13371712.46 | 31423008.25 | 18390420.98 | 32221487.37 | 17813968.82 | 26616367.2 | 18569401.03 | 8973024.45 | 8681193.547 | 4992515.327 | 12519849.45 | 5338774.878 | 24967811.92 | 5229576.777 | 11189380.64 | 15996763.06 | 12005762.04 | ||
| P32119 | 10 | 7 | 741.67 | 0.742407181 | 1.519628783 | HN | XA | Peroxiredoxin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX2 PE=1 SV=5 | 13443931 | 6154659 | 7145273 | 22376432 | 7776729.867 | 15654817.12 | 13262311.35 | 17197403.36 | 13948088.29 | 28318780.19 | 10163062.89 | 72870528.98 | 13158370.82 | 7445756.962 | 5297356.238 | 7727455.748 | 17761963.14 | 14991966.17 | 34822326.32 | 9891601.965 | 24197548.83 | 16240317.04 | 10338851.06 | 6520502.984 | 7628824.342 | 6942108.65 | 6120730.653 | ||
| Q96IU4 | 8 | 7 | 741.21 | 0.257382003 | 1.995430298 | HN | XN | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 14B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD14B PE=1 SV=1 | 10886901 | 12647024 | 20974584 | 22847106 | 33560491.3 | 10320494.14 | 7999129.641 | 10984669.01 | 7509701.48 | 18053548.66 | 5866885.596 | 13545311.7 | 3914097.451 | 10437578.28 | 25407723.9 | 65719469.65 | 12981632.41 | 17738482.96 | 6268903.296 | 7021664.164 | 10766019.21 | 11161793.77 | 14166062.47 | 4870722.631 | 11419619.09 | 9509378.024 | 11847056.03 | ||
| Q9HB40 | 14 | 10 | 740.98 | 0.057201354 | 1.522380629 | XA | XN | Retinoid-inducible serine carboxypeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCPEP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 4832524 | 4295568 | 10714556 | 9810028 | 3086870.246 | 6828552.028 | 9080653.298 | 5601955.209 | 6103955.49 | 2567478.974 | 2652997.305 | 2808083.583 | 6809849.227 | 5694725.768 | 3550427.045 | 7662112.241 | 5027492.408 | 3619368.196 | 3278870.173 | 3766269.558 | 5092808.564 | 3411234.046 | 5504824.454 | 2588376.271 | 5042376.557 | 7427106.262 | 3533056.502 | ||
| P11021 | 17 | 9 | 740.61 | 0.939660157 | 1.172526339 | HN | XN | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA5 PE=1 SV=2 | 5128224 | 4164540 | 3820750 | 2659642 | 2402021.529 | 5769534.213 | 7207544.932 | 6945392.413 | 8601641.222 | 4387107.375 | 4467556.195 | 17441489.64 | 8398927.366 | 2907688.465 | 2882235.003 | 3263508.034 | 4892290.767 | 3431229.378 | 11601038.74 | 6127947.083 | 3981773.396 | 5626169.812 | 3341976.003 | 2548593.261 | 4290284.773 | 3082830.994 | 3809503.226 | ||
| O75309 | 10 | 9 | 739.71 | 0.128581619 | 1.299955595 | HN | XN | Cadherin-16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH16 PE=1 SV=1 | 8394449 | 5761332 | 5954653 | 9846426 | 9542005.532 | 4460912.616 | 4341685.819 | 6809334.223 | 4784601.675 | 10957139.34 | 6596692.58 | 6601611.92 | 6325072.933 | 6790369.218 | 7181990.729 | 12173668.42 | 7719812.819 | 8884109.739 | 4057800.814 | 3775206.532 | 4815461.978 | 5438373.211 | 8898689.5 | 7744442.21 | 8278887.079 | 5152393.517 | 8171798.364 | ||
| O43490 | 9 | 9 | 739.54 | 0.844712359 | 1.119928933 | HN | XA | Prominin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 8442986 | 1873085 | 1756548 | 1597321 | 1637152.893 | 3843795.663 | 3423379.66 | 4090712.36 | 2651802.126 | 1895313.835 | 6753943.053 | 7194344.708 | 2482586.339 | 4565361.523 | 2206730.98 | 1990564.559 | 1921303.175 | 3822564.582 | 5142728.748 | 3461814.279 | 4220026.656 | 1518775.298 | 1530549.847 | 4050255.971 | 2100154.311 | 5085451.671 | 4064122.712 | ||
| P40189 | 13 | 11 | 739.25 | 0.625399231 | 1.151358237 | XN | XA | Interleukin-6 receptor subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL6ST PE=1 SV=2 | 7332193 | 9424667 | 6653689 | 8009700 | 5655203.776 | 10736870.73 | 8619462.495 | 6179948.314 | 8008401.645 | 7056013.965 | 16877084.41 | 5707607.984 | 12405313.52 | 11565233.02 | 5690774.976 | 3466779.345 | 7144920.758 | 10515296.51 | 9812652.884 | 7965161.612 | 9492982.42 | 7262582.258 | 7340770.081 | 12671888.1 | 9675942.156 | 8192249.159 | 8894844.956 | ||
| P07900;Q14568 | 22 | 5 | 739.17 | 0.110128497 | 1.733882782 | XA | XN | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA1 PE=1 SV=5 | 1242324 | 450695.1 | 602740.9 | 2257139 | 384725.7158 | 1373507.942 | 1316230.267 | 2042202.361 | 924577.9501 | 907588.3682 | 636516.4011 | 762941.7519 | 1006318.304 | 213674.4513 | 481279.7007 | 1376014.679 | 278698.5906 | 491385.1202 | 692455.3531 | 467172.255 | 1074363.881 | 842864.1324 | 949220.6211 | 470216.4653 | 771926.8538 | 404800.8641 | 437048.2169 | ||
| Q03403 | 7 | 6 | 734.4 | 0.058188727 | 1.709061776 | XN | XA | Trefoil factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFF2 PE=1 SV=2 | 3.6E+08 | 6.03E+08 | 3.33E+08 | 2.4E+08 | 302372932.9 | 1055836542 | 414362709.6 | 314924538.3 | 472258543.4 | 228204887 | 666478385.6 | 133647256.4 | 826178294.8 | 623414394.6 | 283875116.7 | 326137125.8 | 533848488 | 861518862.8 | 753362617.4 | 1211235217 | 1269616024 | 916066470.2 | 355057744.8 | 913362478 | 550625913.2 | 608225047 | 422278627.1 | ||
| Q8N6Q3 | 12 | 9 | 727.26 | 0.829227254 | 1.464820028 | XA | XN | CD177 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD177 PE=1 SV=2 | 7250819 | 52421238 | 3509985 | 4977402 | 7470922.175 | 12197890.88 | 6368047.171 | 11492587.9 | 14400975.75 | 7141898.115 | 7579387.956 | 3881305.541 | 24797593.56 | 8683421.172 | 12549400.76 | 3138983.686 | 6608984.602 | 13892935.2 | 20236871.05 | 5366961.818 | 4356270.546 | 11684806.84 | 8051929.055 | 11605398.82 | 3292386.382 | 7835830.584 | 9552222.914 | ||
| Q7Z3B1 | 10 | 7 | 725.33 | 0.567950665 | 1.129671101 | XA | HN | Neuronal growth regulator 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEGR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 14029016 | 28022944 | 24580514 | 23745804 | 27832112.33 | 22309135.15 | 17807688.41 | 17311502.41 | 22577606.91 | 15496813.22 | 29663496.97 | 12437982.4 | 27462819.26 | 19676208.73 | 9946339.53 | 19693981.53 | 22018969.75 | 19067135.05 | 15058098.53 | 18219691.18 | 14198630.72 | 26848381.3 | 20574057.2 | 41655143.71 | 22086152.94 | 19684394.44 | 17476096.89 | ||
| P04220 | 11 | 1 | 723.55 | 0.075090313 | 2.20778509 | XA | XN | Ig mu heavy chain disease protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 35635.71 | 376711.6 | 231840.7 | 124439.8 | 57541.7643 | 544470.2691 | 268800.5006 | 55980.81136 | 323775.6856 | 14781.4714 | 530019.7079 | 16150.81074 | 88961.86465 | 4181.848822 | 16283.9626 | 15435.92003 | 22352.56712 | 323534.5 | 428755.823 | 28095.69672 | 53008.07607 | 71887.51098 | 146788.4667 | 7456.9387 | 121097.849 | 55078.69134 | 2411.291682 | ||
| P78380 | 9 | 7 | 721.34 | 0.520968857 | 1.493840899 | XN | HN | Oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=OLR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 15078904 | 10152244 | 8463090 | 11024494 | 19884342.16 | 13070099.05 | 9788341.911 | 7503758.784 | 12257340.22 | 12289530.7 | 8234886.835 | 6023023.146 | 15043085 | 5966486.109 | 5411578.592 | 10973811.92 | 16914661 | 11139152.2 | 6913510.201 | 11995268.04 | 10556648.65 | 7264048.401 | 37883335.74 | 6416281.185 | 7672009.956 | 15846420.5 | 32880186.58 | ||
| Q12913 | 14 | 10 | 721.25 | 0.720842138 | 1.382298268 | HN | XA | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase eta OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRJ PE=1 SV=3 | 8576669 | 5728258 | 3780078 | 6656612 | 2320947.181 | 4912950.238 | 6851197.799 | 4725178.54 | 7399270.168 | 5968645.275 | 19792204.96 | 6144633.914 | 14642191.25 | 7426404.193 | 3295170.273 | 3460741.892 | 2724550.63 | 6975159.014 | 3837239.19 | 6093343.768 | 7670956.363 | 4044175.532 | 5549651.432 | 7133298.989 | 5612508.123 | 5972890.209 | 7299065.323 | ||
| Q07507 | 9 | 6 | 720.51 | 0.550354746 | 1.358284623 | XA | XN | Dermatopontin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPT PE=2 SV=2 | 31890986 | 40471144 | 65951694 | 59948921 | 123762008.8 | 36030866.35 | 25771332.18 | 29091003.35 | 25071640.21 | 32540263.34 | 37430577.33 | 20717354.22 | 31525101.15 | 54938237.46 | 48623235.08 | 89372112.02 | 35278498.76 | 39512635.69 | 25458762.88 | 28952447 | 21902627.81 | 32336120.09 | 40737268.77 | 65786692.03 | 35358021.48 | 29207496.55 | 42718455.03 | ||
| P19801 | 18 | 12 | 720.35 | 0.000862352 | 2.564702161 | XA | HN | Amiloride-sensitive amine oxidase [copper-containing] OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 10550361 | 4375728 | 5464946 | 2719354 | 11358794.77 | 5436726.969 | 3900475.31 | 4107271.231 | 2685322.026 | 1615072.61 | 1156147.701 | 2665100.575 | 2054915.817 | 1452244.231 | 3013209.942 | 1622386.826 | 2689185.053 | 3460725.391 | 1838520.266 | 2596711.307 | 1968224.111 | 1427660.08 | 5007835.321 | 1973166.04 | 4941559.284 | 2066703.031 | 1203050.075 | ||
| P68133;P62736;P63267;P68032 | 11 | 1 | 716.52 | 0.241370147 | 1.607552016 | XA | XN | Actin, alpha skeletal muscle OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 23455035 | 8161252 | 17743781 | 28157996 | 9790248.853 | 21803766.69 | 26714099.14 | 42920810.53 | 23735014.19 | 33474810.5 | 16469395.88 | 41492921.45 | 17125237.1 | 23513835.74 | 10255607.17 | 6462567.834 | 11226214.19 | 9461688.09 | 13616877.78 | 15551238.93 | 16509630.72 | 19550768.17 | 19029573.18 | 8031430.734 | 12691961.57 | 10615604.66 | 10359649.51 | ||
| P15151 | 8 | 4 | 714.17 | 0.446317774 | 1.417952557 | HN | XA | Poliovirus receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVR PE=1 SV=2 | 22636354 | 14189545 | 9331972 | 10078231 | 6524194.999 | 13895819.84 | 16333065.62 | 10522119.8 | 21748435.14 | 17032649.85 | 39586763.57 | 19338723.15 | 17049765.01 | 34393026.81 | 11162432.65 | 4791680.685 | 20092189.27 | 14165133.25 | 23448823.05 | 18722718 | 15569367.93 | 8958568.724 | 15654944.95 | 24212735.73 | 12255807.47 | 13234423.59 | 17925872.47 | ||
| Q9UBX5 | 14 | 11 | 713.87 | 0.244318617 | 1.434065852 | HN | XA | Fibulin-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN5 PE=1 SV=1 | 63737594 | 41965915 | 48770582 | 79767698 | 46955555.05 | 25506078.72 | 28912350.56 | 26403802.31 | 28299118.72 | 81377313.35 | 82791534.81 | 28946702.54 | 49884347.62 | 43628016.61 | 46133079.01 | 138437962.4 | 37548717.3 | 50995038.39 | 35170302.51 | 45765974.14 | 39009885.96 | 32176566.71 | 51142430.9 | 90430394.11 | 53267881.52 | 45003454.27 | 48832132.8 | ||
| P34059 | 10 | 6 | 713.71 | 0.346446199 | 1.523933791 | XA | XN | N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALNS PE=1 SV=1 | 2198288 | 5740744 | 9100118 | 3385290 | 1995172.892 | 5208347.79 | 11766822.74 | 5754519.444 | 7604699.662 | 2050082.218 | 4840306.73 | 3869000.606 | 11458079.27 | 5125554.146 | 4304193.606 | 1879954.064 | 3418736.801 | 3135968.22 | 2078270.394 | 3144308.413 | 6174594.791 | 2065998.401 | 6176548.51 | 3944795.432 | 2270600.101 | 6182533.121 | 2579341.845 | ||
| P19320 | 11 | 9 | 712.61 | 0.898127442 | 1.243542419 | XA | HN | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCAM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 4080260 | 22630086 | 25853647 | 12386019 | 9540355.037 | 9055222.865 | 4639288.449 | 4889087.289 | 7213131.144 | 13171416.45 | 4611124.456 | 8074641.138 | 3946281.266 | 6752981.219 | 14808370.89 | 10531288.54 | 13250178.93 | 5500018.931 | 5839230.298 | 7191567.583 | 4433503.274 | 14287107.72 | 11044494.3 | 14985045.24 | 7930205.054 | 11111190.65 | 7536258.297 | ||
| Q9BRK5 | 12 | 11 | 709.74 | 0.549938341 | 1.166139832 | XA | HN | 45 kDa calcium-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDF4 PE=1 SV=1 | 9991905 | 6054055 | 6695653 | 7526809 | 4673334.391 | 3436189.623 | 5374128.594 | 8834863.618 | 6087005.594 | 2177153.15 | 3929004.423 | 6498558.181 | 5185643.329 | 4654790.991 | 5740058.89 | 10041319.26 | 3922855.229 | 8165288.836 | 2817666.193 | 6016307.404 | 4594437.078 | 4479332.899 | 7533108.857 | 4641880.18 | 9175403.111 | 6116397.655 | 6456206.967 | ||
| P05937;P22676 | 12 | 8 | 709.51 | 0.288162214 | 1.803412619 | HN | XN | Calbindin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 13328160 | 4714981 | 4281370 | 20643578 | 4881477.696 | 3552633.027 | 4864142.396 | 6712110.478 | 4349734.547 | 17415398.43 | 37564119.4 | 9924112.217 | 12904606.19 | 19493101.94 | 7430131.513 | 4167815.987 | 3917523.262 | 3767040.909 | 4079977.49 | 4394086.04 | 7898342.535 | 5705985.857 | 4139714.926 | 12161126.64 | 4806445.843 | 10475771.27 | 10984792.09 | ||
| P80188 | 11 | 9 | 699.4 | 0.952704979 | 1.786442055 | XA | HN | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 22053655 | 14826234 | 43211777 | 2588391 | 2787891.235 | 96498055.69 | 180971683.5 | 35120439.29 | 126703906.5 | 51632741.72 | 31518691.42 | 63287099.48 | 36905524.4 | 16712590 | 55125577.73 | 10710313.61 | 18492252.55 | 9362230.645 | 108472637.1 | 42073856.43 | 15354588.65 | 49160988.51 | 7663230.884 | 59822957.19 | 34124588.3 | 32235697.77 | 14197065.61 | ||
| P17931 | 5 | 5 | 698.8 | 0.092953068 | 2.236459682 | HN | XN | Galectin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS3 PE=1 SV=5 | 4655523 | 1003811 | 1258836 | 4348887 | 2736215.34 | 3040423.755 | 3673922.861 | 5151964.33 | 2738206.906 | 20196160 | 10730373.84 | 6340085.846 | 3943485.583 | 2993259.213 | 1856883.886 | 4861805.691 | 2693974.624 | 2920125.394 | 4858526.49 | 3301333.292 | 2847859.84 | 2384528.21 | 2622966.332 | 1203468.005 | 2872883.025 | 3038226.612 | 2149516.622 | ||
| P23470 | 11 | 9 | 698.73 | 0.116662563 | 1.346439032 | XA | XN | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRG PE=1 SV=4 | 5925703 | 14032025 | 13533778 | 8105877 | 15497680.17 | 7625689.71 | 4997806.322 | 6493786.422 | 5893442.95 | 7889848.583 | 8662407.432 | 9363733.663 | 7246600.112 | 6854402.815 | 10719711.4 | 9564122.192 | 10366823.81 | 8407296.547 | 5737766.012 | 7478301.803 | 5866590.608 | 6373524.677 | 8568038.263 | 6674916.506 | 6817585.452 | 6873681.656 | 6589548.157 | ||
| P53990 | 11 | 6 | 695.86 | 0.571430852 | 1.320099494 | XA | XN | IST1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=IST1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3447260 | 2641614 | 1972077 | 2238475 | 1966810.211 | 4497965.397 | 5817306.681 | 5745776.828 | 3800965.11 | 2332445.841 | 9436442.727 | 2577647.186 | 2955449.485 | 6693341.697 | 2095891.978 | 866956.3781 | 1628288.799 | 2159961.444 | 3287817.009 | 3544113.85 | 2570478.336 | 2864709.96 | 1668953.592 | 1748442.37 | 1715210.484 | 2948793.985 | 3989228.938 | ||
| P00918 | 10 | 6 | 694.89 | 0.031350266 | 1.849486907 | XA | XN | Carbonic anhydrase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 6917750 | 2787159 | 6350774 | 13995412 | 3043804.119 | 5416217.815 | 8566137.997 | 6935514.68 | 5581558.225 | 5871319.957 | 6635231.022 | 9667593.507 | 3493967.173 | 4255928.577 | 3524897.141 | 2532269.35 | 4331244.437 | 4545600.422 | 2806455.139 | 3085934.156 | 4372181.894 | 5727452.762 | 4687502.021 | 1570398.28 | 3487819.133 | 3089448.392 | 3394894.952 | ||
| Q14914 | 11 | 5 | 694.02 | 0.298922319 | 1.448996057 | XA | XN | Prostaglandin reductase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTGR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 8045835 | 2570848 | 4809479 | 15196860 | 2440403.793 | 3554746.594 | 8707613.786 | 8178968.682 | 8628690.05 | 8021636.64 | 5677638.242 | 6486974.407 | 9168240.048 | 7609197.551 | 3436936.247 | 3051255.687 | 3609458.661 | 3383052.673 | 2172316.368 | 3759670.562 | 14417266.44 | 7155578.561 | 4381314.07 | 1625913.036 | 3376486.576 | 2593299.34 | 3398495.942 | ||
| P10643 | 11 | 8 | 692.35 | 0.664124617 | 1.053416514 | XA | XN | Complement component C7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C7 PE=1 SV=2 | 10808091 | 17198963 | 11257209 | 10248301 | 4534697.695 | 11295444.5 | 15782034.4 | 8853647.92 | 16566974.23 | 4581465.448 | 28549766.44 | 6839869.067 | 23579249.16 | 11813031.78 | 9061237.859 | 5297966.058 | 5235960.429 | 6696840.388 | 7242156.082 | 15856155.77 | 7785632.465 | 9215229.961 | 10221485.41 | 20944192.32 | 10790790.5 | 9601688.676 | 9485341.344 | ||
| P35579 | 30 | 11 | 692.34 | 0.194913096 | 2.151176649 | XA | HN | Myosin-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH9 PE=1 SV=4 | 501971.5 | 1050428 | 888095.7 | 744015.8 | 1420913.959 | 4680403.843 | 4514312.939 | 1812983.411 | 4332526.84 | 750493.1116 | 990933.2659 | 988855.0886 | 1299535.658 | 513990.8269 | 1780606.067 | 1119273.183 | 1059593.803 | 768692.1439 | 1963039.797 | 1812703.046 | 743380.4273 | 2062544.785 | 1398340.097 | 1603714.373 | 909887.1456 | 1059195.638 | 661902.8786 | ||
| P18428 | 6 | 5 | 691.18 | 0.40539183 | 1.414214696 | XA | HN | Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LBP PE=1 SV=3 | 6659076 | 1942758 | 2471196 | 3216419 | 4143140.617 | 2243606.877 | 914435.2931 | 2419267.192 | 2051932.457 | 1750352.766 | 377918.4528 | 2212418.959 | 914148.0051 | 384853.8084 | 2580067.48 | 4364400.219 | 3527299.437 | 2317023.831 | 2872678.647 | 1193191.937 | 2116695.841 | 1557146.912 | 2005277.896 | 129006.816 | 4108059.948 | 2603697.581 | 2678636.19 | ||
| Q9H3G5 | 12 | 10 | 691.16 | 0.115269422 | 2.032269517 | XA | HN | Probable serine carboxypeptidase CPVL OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPVL PE=1 SV=2 | 2451515 | 4770233 | 3175479 | 15405039 | 13261541 | 6544117.845 | 7297765.68 | 5724747.237 | 7047916.875 | 1665208.422 | 1657871.176 | 2838222.182 | 3872533.852 | 981306.6171 | 4053631.415 | 6937449.939 | 5612268.495 | 4699246.711 | 2786251.909 | 5758013.984 | 6705658.122 | 1981119.852 | 6430408.542 | 821462.4744 | 9104522.337 | 11837561.68 | 6156246.191 | ||
| O14498 | 10 | 7 | 689.25 | 0.009859521 | 1.518069726 | XA | HN | Immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ISLR PE=1 SV=1 | 34749111 | 24541654 | 36742698 | 33991111 | 30035321.38 | 34998747.46 | 25465397.93 | 34906134.83 | 24872420.67 | 24504727.91 | 13380863.34 | 13207018.03 | 12483405.33 | 18174992.02 | 18020277.64 | 31514154.24 | 26978199.98 | 26380446.67 | 24478112.36 | 25110214.37 | 18140815.67 | 19493476.28 | 28265554.85 | 9347365.014 | 26174131.71 | 25704534.57 | 28245611.79 | ||
| P34931 | 14 | 1 | 688.58 | 0.158168183 | 1.913227364 | HN | XA | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1L PE=1 SV=2 | 101991.4 | 126336.5 | 63251.8 | 63810.69 | 293843.4675 | 871.1902004 | 1147.825708 | 27279.70486 | 7064.690842 | 123208.3415 | 149983.8886 | 26657.91606 | 165662.268 | 64646.81422 | 404882.1342 | 296917.9708 | 45696.04323 | 34048.142 | 124733.866 | 231579.8813 | 25074.55803 | 16158.10834 | 4583.518802 | 177573.5332 | 35706.12452 | 58857.9167 | 34147.23846 | ||
| Q12794 | 7 | 6 | 688.43 | 0.141105122 | 1.450424449 | XA | HN | Hyaluronidase-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HYAL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 63056458 | 29817677 | 51292604 | 40395006 | 26802117.46 | 47484610.96 | 40077159.15 | 54268017.5 | 38538460.23 | 29145829.91 | 18638308.81 | 21498583.77 | 38738203.45 | 35357281.64 | 20888252.86 | 33434263.44 | 48490412.37 | 23889880.61 | 28379542.53 | 21841720.46 | 40874521.87 | 32205553.54 | 44934873.07 | 7213281.208 | 42557017.77 | 40124442.91 | 50882871.27 | ||
| P51884 | 10 | 7 | 688.37 | 0.61434283 | 1.660973785 | XA | XN | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 10957849 | 54335844 | 42365680 | 16665081 | 55456935.02 | 11361873.19 | 7356861.464 | 13479469.49 | 12853342.87 | 7070270.195 | 7282339.04 | 12994249.21 | 5358672.394 | 19445534.92 | 44269101.83 | 41077908.19 | 43514517.39 | 16719077.46 | 10727081.88 | 18194726.96 | 5926604.589 | 13771342.97 | 29352398.97 | 11328263.74 | 19571662.7 | 10686268.28 | 15803771.4 | ||
| O43895 | 16 | 10 | 673.08 | 0.000141337 | 2.319292734 | XN | XA | Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=XPNPEP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 35541950 | 21678617 | 11524698 | 38917744 | 14596074.6 | 28561539.38 | 18877627.93 | 23773591.28 | 21004531.31 | 39189431.63 | 79869221.82 | 23487010.07 | 31104135.58 | 40366580.01 | 28041129.38 | 21838727.09 | 68126683.07 | 74055422.25 | 51599138.15 | 60764397.71 | 62570030.77 | 53615713.1 | 49870883.36 | 42835091.27 | 63341833.84 | 67801563.85 | 45034841.91 | ||
| Q96DA0 | 9 | 8 | 672.98 | 0.34794323 | 1.387593363 | XA | XN | Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZG16B PE=1 SV=3 | 1.42E+08 | 1.74E+08 | 1.05E+08 | 2.07E+08 | 237911809.9 | 116300280.2 | 58649912.7 | 175266523.3 | 96639624.23 | 122315974.2 | 95893392.11 | 58108520.78 | 57930232.45 | 269199269 | 88055542.58 | 170979221.9 | 158497569.4 | 89342599.94 | 110550934.8 | 147696476.6 | 95198996.45 | 78403708.13 | 106816419.7 | 56782537.86 | 140678000.3 | 82298195.07 | 128536446 | ||
| Q9Y646 | 14 | 9 | 672.5 | 0.112465489 | 1.426238222 | XA | XN | Carboxypeptidase Q OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPQ PE=1 SV=1 | 13315086 | 10615322 | 23183394 | 15707724 | 7750122.967 | 14945161.95 | 17926048.14 | 17996785.72 | 28614842.06 | 7897044.484 | 17718080.49 | 11211477.15 | 29497666.52 | 13919633.1 | 7370723.156 | 5047694.698 | 9889718.278 | 3938179.91 | 8966194.208 | 8969892.329 | 12964429.94 | 7564954.047 | 15739130.23 | 14430090.97 | 13366644.44 | 13601063.46 | 9607575.259 | ||
| Q14766 | 10 | 9 | 670.37 | 0.56486376 | 1.166999614 | XN | XA | Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTBP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 3342932 | 3623658 | 3670552 | 2528759 | 4191403.111 | 2787472.833 | 1813527.488 | 2172327.162 | 1475679.571 | 3332490.453 | 4414413.004 | 916327.3508 | 3081938.921 | 3535962.433 | 3372994.686 | 3712063.01 | 2713308.062 | 4355729.199 | 2325803.345 | 3414658.804 | 3114944.256 | 2822717.082 | 3382745.709 | 5324316.124 | 3050811.228 | 3290175.6 | 3156382.907 | ||
| P17936 | 8 | 6 | 667.68 | 0.339470524 | 1.405140698 | HN | XA | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP3 PE=1 SV=2 | 74938171 | 40602809 | 47621570 | 84632399 | 49475030.6 | 30672624.05 | 30277446.15 | 36969745.37 | 27068175.93 | 76529210.59 | 59076056.39 | 31863286.17 | 44514316.02 | 50653380.36 | 31901203.24 | 189038345.7 | 49641553.33 | 60114509.14 | 48178655.8 | 79897713.17 | 43927914.54 | 35261874.39 | 55877507.72 | 100794017.8 | 54233562.13 | 53682355.44 | 61311405.23 | ||
| P08238 | 20 | 1 | 666.31 | 0.441448464 | 1.874365346 | XA | XN | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 94357.09 | 85053.91 | 55930.32 | 6312.566 | 87161.66132 | 124469.487 | 146294.3401 | 323859.0819 | 164131.5279 | 43479.38256 | 57500.94643 | 105798.5071 | 92072.69769 | 49027.63476 | 107878.9881 | 178284.826 | 29638.38767 | 26504.5867 | 69826.42632 | 30378.83094 | 56206.64481 | 67307.75518 | 181158.3779 | 43993.57543 | 82745.83947 | 9760.33615 | 38855.9343 | ||
| O43278 | 18 | 13 | 665.38 | 0.084127311 | 1.390505289 | HN | XA | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 12088389 | 4212203 | 3567821 | 4074619 | 5037607.929 | 6144655.739 | 6953474.846 | 6481247.818 | 5886091.87 | 13392690.57 | 10186515.07 | 5871694.136 | 9403490.288 | 10799998.26 | 5000201.405 | 4812488.349 | 8451564.97 | 7788961.464 | 7232670.83 | 6411069.752 | 6410956.587 | 5262788.024 | 6536541.73 | 8875270.773 | 7427525.928 | 6132920.81 | 7669436.285 | ||
| P24855 | 6 | 4 | 662.84 | 0.692644633 | 1.319301009 | XA | HN | Deoxyribonuclease-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNASE1 PE=1 SV=1 | 17230173 | 83033397 | 28797841 | 10303399 | 12080156.04 | 35209569.23 | 47569526.37 | 25436970.16 | 119534576.6 | 10851787.46 | 35651020.2 | 102404762.3 | 26959409.02 | 37194058.62 | 15248417.21 | 10059698.27 | 16242892.59 | 32809555.28 | 25250927.96 | 35008203.75 | 30175732.12 | 36031839.08 | 19948447.93 | 53846929.72 | 34977575.41 | 35626081.42 | 21078290.94 | ||
| Q16610 | 14 | 12 | 662.28 | 0.301078583 | 2.006751822 | XN | HN | Extracellular matrix protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2487016 | 3831640 | 2924237 | 2543544 | 2209129.06 | 5411840.461 | 15799833.76 | 11819628.6 | 8171594.489 | 4326085.935 | 9343024.194 | 7310364.855 | 5895089.367 | 2388427.25 | 1474537.526 | 1429935.928 | 1689855.509 | 2181254.498 | 31750754.93 | 10187184.56 | 7239144.405 | 6239640.4 | 2167697.638 | 5038452.887 | 2532918.172 | 4665618.533 | 2499064.663 | ||
| P05067 | 17 | 14 | 661.13 | 0.52930471 | 1.119125627 | XN | HN | Amyloid beta A4 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=APP PE=1 SV=3 | 22526190 | 17370887 | 13297713 | 16085385 | 14678732.98 | 13762966.91 | 14624427.88 | 13414939.82 | 20828300.48 | 11339819.92 | 15161719.51 | 7977905.596 | 22005436.02 | 12075871.02 | 17172773.97 | 15026087.69 | 12949130.83 | 23472407.12 | 12620478.99 | 16489545.19 | 13387542.12 | 12903005.63 | 15582869.66 | 24458148.35 | 17418097.17 | 22360747.59 | 18302507.71 | ||
| P36955 | 12 | 9 | 660.53 | 0.138761383 | 1.322165871 | XA | XN | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 4924048 | 4292157 | 6348476 | 4926630 | 10063573.03 | 4740834.308 | 4544426.676 | 4910195.037 | 5432720.054 | 5112729.786 | 3263673.561 | 8635966.009 | 5930806.235 | 4015886.723 | 4190161.186 | 6737755.462 | 4114765.639 | 4027121.623 | 2790303.325 | 4086102.702 | 3733722.332 | 2163060.397 | 4775984.168 | 2359549.748 | 6729444.114 | 5531778.33 | 5785247.377 | ||
| P63104 | 11 | 6 | 659.65 | 0.521649945 | 1.434835731 | XA | XN | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAZ PE=1 SV=1 | 2810576 | 1503537 | 2387901 | 3456324 | 2057095.157 | 4809306.95 | 4721519.368 | 7485679.466 | 7990038.051 | 3403471.001 | 4678266.085 | 7974764.996 | 3920714.496 | 2323272.907 | 2531598.139 | 1408802.736 | 1875788.089 | 2286192.031 | 2615913.214 | 3070259.879 | 4161731.049 | 3802743.955 | 2180619.57 | 2907387.018 | 2823875.189 | 2372064.202 | 2007034.839 | ||
| Q16651 | 5 | 4 | 658.91 | 0.64617817 | 1.09193194 | XA | XN | Prostasin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRSS8 PE=1 SV=1 | 14169238 | 21551656 | 18989533 | 19461345 | 20830623.57 | 15437609.97 | 19537501.23 | 25213348.22 | 22055034.8 | 13407450.68 | 33822002.67 | 10995793.53 | 10226667.9 | 52432884.38 | 10728843.14 | 10050263.7 | 21468691.05 | 12940923.47 | 14444531.8 | 20185417.83 | 20846856.56 | 25947818.1 | 12230123.33 | 14637201.79 | 9669528.27 | 22849997.28 | 21511727.37 | ||
| Q9NQ38 | 21 | 12 | 657.63 | 0.275044894 | 1.719502524 | XA | HN | Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINK5 PE=1 SV=2 | 2113917 | 5021635 | 5936975 | 3656969 | 4053615.513 | 13669869.61 | 17999417.98 | 17292411.44 | 12734614.36 | 4321024.988 | 10495571.42 | 7202802.982 | 11140307.39 | 2360105.13 | 4161053.638 | 3531727.124 | 2419659.786 | 2334774.926 | 7699772.977 | 15873075.48 | 3380906.781 | 5696161.831 | 2591170.228 | 6558058.528 | 2852368.67 | 3391335.588 | 2760147.957 | ||
| P41222 | 8 | 7 | 657.44 | 0.778723162 | 1.976848894 | XA | HN | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTGDS PE=1 SV=1 | 89822900 | 2.27E+09 | 1.59E+09 | 1.89E+08 | 421790117.6 | 217532854.3 | 155823477.7 | 126903090.7 | 286956868 | 133639361.8 | 112673528 | 444064134.8 | 127158802.9 | 181274769.1 | 816214743.2 | 282368684.7 | 315493039.7 | 291836593.5 | 93986630.47 | 220700237.4 | 106246884.4 | 318615146.6 | 248997765.5 | 1431771257 | 189750528.7 | 314007699.7 | 217291533.2 | ||
| Q92692 | 15 | 8 | 657.35 | 0.198655078 | 1.306823207 | HN | XN | Poliovirus receptor-related protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVRL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 29618615 | 20621667 | 33078121 | 35356685 | 37687427.45 | 21500810.57 | 24782660.05 | 30109117.25 | 13564100.55 | 33653715.75 | 49259481.24 | 19591496.23 | 36432794.65 | 31695608.67 | 24619845.82 | 59295341.14 | 33519236.6 | 28596971.58 | 17586251.78 | 36609121.56 | 15501113.91 | 18519545.27 | 35369244.24 | 17676687.72 | 36651830.37 | 29733770.87 | 34668678.76 | ||
| P01591 | 8 | 6 | 655.45 | 0.242016872 | 1.362989456 | XN | HN | Immunoglobulin J chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGJ PE=1 SV=4 | 70155994 | 31833310 | 27631782 | 31698709 | 34246519.69 | 37982842.82 | 70296310.7 | 46631609.2 | 34683014.51 | 27048762.2 | 63214642.64 | 64801428.15 | 49692371.82 | 28669465.66 | 28317553.41 | 19076891.77 | 16170145.01 | 36051759.91 | 38171515.13 | 64265996.23 | 48872157.27 | 32922453.82 | 39434400.01 | 48407709.95 | 65351065.6 | 92803750.12 | 23705077.17 | ||
| P08727 | 13 | 4 | 655.34 | 0.644439311 | 1.81895388 | HN | XN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT19 PE=1 SV=4 | 304604.9 | 38511.26 | 122922.8 | 373679.4 | 241226.1955 | 367671.8707 | 129424.9597 | 91824.32873 | 306233.426 | 256300.4259 | 145753.9851 | 716069.3717 | 158336.0836 | 42224.56377 | 358064.6574 | 1368690.262 | 158257.2083 | 116192.267 | 428408.8786 | 136175.4106 | 100560.3268 | 396087.7314 | 94713.87708 | 410017.0569 | 103605.5223 | 97733.05019 | 57861.97359 | ||
| P08473 | 16 | 12 | 654.99 | 0.315479194 | 1.478412625 | HN | XA | Neprilysin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MME PE=1 SV=2 | 24754738 | 16290540 | 21618933 | 27770519 | 17447865.45 | 17231773.4 | 18331262.51 | 18551704.18 | 17124066.46 | 46870883.19 | 49002617.05 | 18986077.87 | 31128416.46 | 46043673.1 | 10753046.09 | 13725556.96 | 26098979.44 | 22206091.73 | 18222902.79 | 44609655.34 | 23361612.32 | 17476482.85 | 19874922.15 | 22332061.95 | 15253992.58 | 31885270.28 | 28697089.22 | ||
| P13727 | 9 | 5 | 650.67 | 0.663059818 | 1.166501391 | HN | XA | Bone marrow proteoglycan OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRG2 PE=1 SV=2 | 16022182 | 23892284 | 13511498 | 8419289 | 23482470.49 | 9337633.442 | 12239477.7 | 13903840.62 | 15530118.99 | 21751968.42 | 25315021.16 | 9982061.778 | 11458707.17 | 13268049.65 | 18230469.59 | 23922351.57 | 21096645.01 | 14014118.68 | 14163036.58 | 19016489.04 | 19219709.73 | 15884920.18 | 13395228.45 | 29317100.77 | 20484962.7 | 6529539.822 | 8124411.222 | ||
| Q99715 | 23 | 11 | 647.87 | 0.78596041 | 1.142985643 | HN | XA | Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL12A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 19819451 | 16139730 | 10035203 | 9192095 | 9867370.48 | 8015925.679 | 17622857.51 | 33665336.25 | 15091632.69 | 18240572.91 | 41820272.64 | 20811499.55 | 19817976.6 | 14044657.06 | 9389379.83 | 15072986.33 | 10612899.84 | 9578647.424 | 17198684.7 | 32277640.44 | 20517556.39 | 13623167.66 | 12850113.26 | 16066683.14 | 12686291.57 | 12024767.54 | 12332894 | ||
| P17900 | 9 | 6 | 646.02 | 0.942805287 | 1.719502218 | XA | XN | Ganglioside GM2 activator OS=Homo sapiens GN=GM2A PE=1 SV=4 | 16935657 | 67877016 | 1.21E+08 | 33810490 | 294433488.2 | 25099096.96 | 9477254.292 | 20752369.72 | 9916892.431 | 39968948.07 | 6169979.219 | 27962313.91 | 10132948.25 | 45305163.82 | 159389728.2 | 140154406.2 | 79042391.43 | 40372610.3 | 20402208.25 | 11142830.28 | 27731073.67 | 60331082.08 | 67687623.36 | 51389797.06 | 31236263.51 | 41003020.7 | 37847670.62 | ||
| P06865 | 15 | 8 | 644.9 | 0.610445593 | 1.141420745 | XA | XN | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEXA PE=1 SV=2 | 7153871 | 5244035 | 7305704 | 5332702 | 4002394.363 | 5923643.991 | 6728364.897 | 4732988.801 | 5647533.287 | 4877505.98 | 6974128.681 | 4372419.956 | 9504087.818 | 10919159.55 | 2603724.222 | 2243467.724 | 4167298.28 | 4251286.045 | 5164164.928 | 5648334.955 | 5323868.498 | 3291645.838 | 4319335.562 | 6206235.615 | 5950179.863 | 5097625.93 | 4618278.647 | ||
| Q9H6X2 | 11 | 8 | 641.57 | 0.053663103 | 1.879992268 | HN | XN | Anthrax toxin receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANTXR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2882327 | 4980751 | 4127623 | 4259827 | 10646123.77 | 2125787.753 | 1743762.409 | 2444613.065 | 1768407.547 | 13301429.28 | 4082065.397 | 5066458.393 | 1865825.846 | 4204823.27 | 6652703.302 | 5099750.989 | 8516941.587 | 5594345.733 | 4693921.708 | 2481354.323 | 2161589.45 | 4398680.328 | 3359424.89 | 4276045.54 | 3172318.184 | 1850775.372 | 2533851.617 | ||
| P02792 | 7 | 5 | 641.52 | 0.221997446 | 1.245210542 | XN | XA | Ferritin light chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTL PE=1 SV=2 | 6657234 | 5827094 | 11231207 | 10014255 | 4149882.406 | 6223782.22 | 9451921.027 | 6558030.67 | 4696588.651 | 7949711.555 | 3846475.295 | 3389222.652 | 7346824.095 | 11035240.2 | 7700750.613 | 5329568.619 | 7707047.34 | 11126581.68 | 7864226.6 | 4980453.559 | 11931417.78 | 10439450.06 | 9178329.79 | 10196713.94 | 7740001.274 | 9089825.303 | 9281671.38 | ||
| O95865 | 8 | 4 | 639.74 | 0.776740421 | 1.229673409 | XN | HN | N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDAH2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.16E+08 | 77533128 | 1.82E+08 | 1.06E+08 | 78703302.56 | 192360366.4 | 369671586.9 | 221416167.5 | 213608747.5 | 270420398.6 | 202819563.8 | 142987702.5 | 147260851.9 | 150290542.5 | 47634991.38 | 81288303.65 | 132091729.2 | 187808466.2 | 231253031.7 | 204213830 | 240318020.1 | 293746394 | 117852014.3 | 48030846.18 | 90498755 | 236404950.5 | 213238280.6 | ||
| P17342 | 14 | 11 | 638.46 | 0.162856945 | 1.308423022 | XA | HN | Atrial natriuretic peptide receptor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPR3 PE=1 SV=2 | 4218064 | 3267826 | 2829598 | 2768417 | 2259870.776 | 4069759.094 | 3590760.499 | 4064370.82 | 1821559.391 | 1794844.773 | 2773561.73 | 1704078.139 | 2308720.995 | 2132083.249 | 1854718.565 | 1582777.602 | 2626482.998 | 5302919.449 | 2494901.927 | 3628424.946 | 1766482.356 | 2946007.769 | 2074975.13 | 2242265.464 | 5721825.673 | 4573220.194 | 2910462.88 | ||
| Q06481 | 15 | 10 | 634.07 | 0.594139558 | 1.272372701 | XN | HN | Amyloid-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APLP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 4709025 | 2647606 | 1694170 | 2338406 | 2785444.212 | 2537727.307 | 1932706.483 | 3546636.632 | 2563494.68 | 2028079.967 | 3464637.518 | 1356139.299 | 2939397.083 | 3136919.399 | 3012908.781 | 2539685.318 | 2570899.963 | 2926781.073 | 1996035.968 | 6790129.992 | 1928181.54 | 2056875.079 | 2946046.479 | 2850881.728 | 2374370.317 | 3228153.319 | 6335031.617 | ||
| Q14982 | 8 | 4 | 633.9 | 0.287642222 | 1.545360765 | XA | HN | Opioid-binding protein/cell adhesion molecule OS=Homo sapiens GN=OPCML PE=1 SV=1 | 2154431 | 10324285 | 4039756 | 1845089 | 2587360.579 | 5394052.87 | 7481203.994 | 2748455.833 | 11288564.88 | 1341800.333 | 6115124.895 | 2198036.732 | 5474581.881 | 3988353.7 | 3565297.121 | 884170.1939 | 3662555.156 | 3742265.822 | 4011788.172 | 3753194.463 | 4388942.81 | 5264730.767 | 2756226.303 | 10589965.49 | 4112540.394 | 4421016.789 | 3079016.251 | ||
| P02545 | 18 | 14 | 632.34 | 0.270771586 | 1.912563865 | XA | HN | Prelamin-A/C OS=Homo sapiens GN=LMNA PE=1 SV=1 | 1224131 | 2167031 | 735878.7 | 1656082 | 1022471.45 | 3997509.33 | 4873436.177 | 5100277.834 | 4297505.639 | 1558254.634 | 642580.1271 | 3874246.636 | 1949271.701 | 695548.2229 | 1050728.882 | 1478429.069 | 1003759.678 | 857500.1932 | 6776723.929 | 2718874.219 | 973143.6561 | 5752199.374 | 561911.5977 | 1589950.167 | 1155859.828 | 814765.6228 | 559202.1381 | ||
| P26038 | 24 | 11 | 623.89 | 0.174660187 | 1.646564424 | XA | XN | Moesin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSN PE=1 SV=3 | 1604441 | 447779.8 | 844703.6 | 1230809 | 3302714.746 | 1049921.026 | 2015931.271 | 1494992.026 | 2086840.503 | 1505427.494 | 2411837.771 | 1145039.294 | 2098281.309 | 1068027.915 | 2224481.76 | 942564.4255 | 620222.4569 | 711148.9031 | 519471.9368 | 1183844.72 | 669924.2216 | 1539380.243 | 713893.245 | 878977.3815 | 942065.7224 | 813438.233 | 1289008.772 | ||
| Q8NDA2 | 23 | 12 | 622.74 | 0.337897839 | 1.375345332 | HN | XA | Hemicentin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HMCN2 PE=2 SV=2 | 5633784 | 6960847 | 6786508 | 3816904 | 4213788.167 | 4995878.444 | 2841564.629 | 5481983.729 | 3094653.54 | 4448263.962 | 4967604.647 | 2809829.031 | 3921708.051 | 10110286.14 | 6271642.959 | 4364860.729 | 13092836.25 | 10288732.68 | 3026274.953 | 5628332.112 | 3831697.985 | 5157289.569 | 8052659.11 | 9854867.369 | 8532459.157 | 6628686.758 | 7871089.196 | ||
| Q9H8L6 | 6 | 4 | 616.99 | 0.891172884 | 1.129863744 | XA | HN | Multimerin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMRN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 97723961 | 1.13E+08 | 73208867 | 1.2E+08 | 106166623.6 | 56836545.31 | 20528778.72 | 89533622.71 | 53703579.36 | 68775803.05 | 67183654.08 | 43609027.39 | 36893615.84 | 91293838.61 | 58878916.05 | 69103000.9 | 130386443.3 | 81145448.61 | 78196905.94 | 54206294.88 | 71847380.52 | 66212366.42 | 115438294.6 | 42181318.76 | 74839774.28 | 72570033.95 | 125282714.2 | ||
| Q5JS37 | 10 | 8 | 616.46 | 0.502034088 | 1.334127212 | HN | XN | NHL repeat-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NHLRC3 PE=2 SV=1 | 3173311 | 6523225 | 10387703 | 5507255 | 8184901.026 | 6170372.844 | 5718749.17 | 6989204.464 | 6606452.387 | 3506844.575 | 7470605.593 | 3825959.477 | 15491968.82 | 12723595.4 | 5972698.475 | 5082637.107 | 9304241.004 | 6064004.476 | 4819400.07 | 3572312.996 | 8891471.107 | 4126177.066 | 6742274.689 | 8070091.563 | 5174272.026 | 6862181.753 | 3792743.337 | ||
| P07384 | 17 | 13 | 616.05 | 0.92973022 | 3.540606621 | XN | HN | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 250437.8 | 236782.9 | 421816 | 528459.7 | 308741.1218 | 597717.4747 | 738945.1836 | 2376120.128 | 904558.0453 | 2424499.003 | 638837.2862 | 908882.5114 | 486334.2192 | 218444.6243 | 289830.5592 | 1050508.514 | 168555.1794 | 161546.358 | 19015737.57 | 935779.511 | 719090.564 | 395199.0348 | 251913.4889 | 458277.8909 | 239342.6959 | 293662.627 | 164778.5281 | ||
| P04040 | 10 | 9 | 614.17 | 0.040955354 | 4.968760717 | XA | XN | Catalase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAT PE=1 SV=3 | 408763.4 | 215118.9 | 151433.8 | 1306015 | 254561.6348 | 1895998.411 | 4249031.309 | 1152616.173 | 3968680.742 | 382417.4525 | 409094.6291 | 5953423.974 | 885424.4965 | 477566.8948 | 1417199.301 | 237087.2872 | 1047851.832 | 513673.1593 | 547525.1114 | 202179.7728 | 261727.875 | 566662.9452 | 351343.1819 | 148988.0134 | 294418.2825 | 221184.4295 | 143518.0926 | ||
| P00915 | 9 | 9 | 613.16 | 0.150943556 | 2.738625099 | HN | XN | Carbonic anhydrase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6360390 | 5362434 | 7928724 | 6821576 | 16381605.4 | 7653294.059 | 4829595.852 | 7057760.402 | 11870482.68 | 8628118.207 | 5985092.19 | 75883704.71 | 6769062.816 | 5824630.627 | 9469135.291 | 3932826.951 | 25760423.19 | 9777403.023 | 9639120.686 | 8371407.81 | 5761319.251 | 4231938.001 | 7395181.69 | 5364373.8 | 4322011.553 | 6471452.751 | 3956596.809 | ||
| P29401 | 14 | 11 | 612.44 | 0.259769584 | 1.6183706 | XA | XN | Transketolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TKT PE=1 SV=3 | 2058206 | 442990 | 667774 | 1899709 | 1193477.77 | 2238983.211 | 4474321.658 | 4189770.69 | 4841260.777 | 6014761.709 | 737623.7586 | 3480333.62 | 684671.4376 | 406609.4175 | 6055095.532 | 830384.6908 | 517057.7166 | 189194.2227 | 7370088.172 | 432494.6269 | 859626.143 | 613865.6706 | 826855.6858 | 274468.6958 | 2315835.555 | 534582.9042 | 370114.202 | ||
| Q8TDQ0 | 9 | 6 | 611.1 | 0.067203695 | 1.373191594 | XN | HN | Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HAVCR2 PE=1 SV=3 | 51612178 | 74745117 | 53893349 | 69460115 | 45377651.94 | 83222423.34 | 80179393.04 | 67807591.51 | 84762093.79 | 20862799.03 | 112688519.3 | 19806776.89 | 88896263.99 | 78009172.58 | 28141924.63 | 12299597.94 | 51878537.53 | 73617252.8 | 73296234.2 | 99954680.99 | 91694884.02 | 63638751.8 | 50843591.95 | 92303838.3 | 48986117.69 | 75623201.5 | 71305612.61 | ||
| P15586 | 13 | 9 | 610.98 | 0.914591176 | 1.194307997 | XA | HN | N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNS PE=1 SV=3 | 10341085 | 43248408 | 36708974 | 9937623 | 14624272.16 | 13198796.03 | 18610993.67 | 10123169.76 | 26979079.98 | 7556015.404 | 21107719.02 | 18122565.89 | 21776613.77 | 18359223.84 | 21093305.81 | 10921115.69 | 14030363.12 | 20906619.44 | 8520228.832 | 20410083.18 | 14132500.19 | 13784395.74 | 14242893.37 | 35957397.75 | 13565117.84 | 22565712.16 | 15039770.11 | ||
| P50897 | 6 | 5 | 609.41 | 0.566708647 | 1.260366819 | XA | XN | Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3672757 | 2429301 | 3489340 | 6524037 | 3850223.58 | 3721417.687 | 3441357.61 | 3811687.59 | 1285980.993 | 4599452.786 | 1662272.408 | 2765579.457 | 1682109.075 | 2386103.426 | 1927378.126 | 6686001.37 | 4664392.021 | 4914916.775 | 3958652.981 | 1695028.111 | 3798293.199 | 1965278.981 | 2613513.38 | 1125527.395 | 4122749.049 | 3268815.846 | 3020969.683 | ||
| P08779 | 16 | 3 | 608.62 | 0.423778437 | 5.020519463 | XA | HN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT16 PE=1 SV=4 | 26489.46 | 13053.02 | 17320.61 | 26719.57 | 7074.914339 | 1170318.845 | 123009.6451 | 27608.05854 | 402419.9916 | 57519.09982 | 0 | 93541.45311 | 16456.75375 | 24872.85248 | 24824.33347 | 86099.91844 | 48914.82596 | 9090.768677 | 108630.2128 | 10972.97779 | 7126.155032 | 381293.0651 | 38257.47819 | 3606.649727 | 16102.95166 | 28316.43495 | 11197.90182 | ||
| P56537 | 7 | 7 | 608.56 | 0.196040449 | 1.815317178 | HN | XN | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EIF6 PE=1 SV=1 | 6953262 | 5095081 | 5807643 | 5305503 | 3724727.49 | 3164170.729 | 11697452.13 | 3509849.746 | 6507967.89 | 6204686.232 | 3950287.427 | 11095100.16 | 4493507.851 | 9738034.083 | 6416879.492 | 30737178.64 | 4511593.891 | 4859840.575 | 4276953.858 | 2224695.093 | 3710175.329 | 4686804.198 | 4600564.771 | 7815384.28 | 8255258.547 | 4477384.159 | 5127865.075 | ||
| Q15904 | 8 | 5 | 608.32 | 0.722745433 | 1.207814697 | HN | XN | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6AP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 16632787 | 7896143 | 11830474 | 18506070 | 10203001.89 | 3251497.515 | 9221621.083 | 13077494.07 | 7783009.092 | 4915253.005 | 19670723.42 | 7584596.924 | 11429183.18 | 9825366.829 | 10040449.81 | 22950670.16 | 4790881.699 | 9276366.098 | 2687443.724 | 7236671.906 | 8386302.333 | 4647407.671 | 10312937.96 | 11690207.36 | 16620339.74 | 10929153.43 | 10683995.54 | ||
| Q00796 | 9 | 7 | 605.95 | 0.070583091 | 1.631106888 | XA | XN | Sorbitol dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SORD PE=1 SV=4 | 5513058 | 8767468 | 10469133 | 14521628 | 20525557.6 | 6936017.663 | 5753121.699 | 10739625.93 | 4947089.544 | 5179244.805 | 3612137.273 | 4591145.721 | 5028317.492 | 5336261.126 | 7835140.047 | 15569623.42 | 7097025.994 | 5000745.754 | 5763343.309 | 3307298.175 | 5638074.547 | 5445091.639 | 9491921.803 | 6390540.156 | 8069468.406 | 4886948.509 | 5064285.226 | ||
| O00560 | 9 | 7 | 604.25 | 0.014143244 | 2.106930882 | XN | XA | Syntenin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDCBP PE=1 SV=1 | 1.53E+08 | 84877567 | 1.5E+08 | 1.26E+08 | 58421807.48 | 82056405.2 | 104168417.6 | 112865293.7 | 105696325.4 | 208291918.1 | 137055892.8 | 79499912.79 | 137046727.6 | 330019775.9 | 54314211.39 | 173070288 | 182279362.3 | 241839206.6 | 261674214.3 | 182170268.7 | 363954634.3 | 278979489.9 | 137865837 | 78616625.24 | 185280125.9 | 220232752.6 | 348449038.2 | ||
| Q9UHG2 | 7 | 5 | 602.17 | 0.79621799 | 1.201183097 | XN | HN | ProSAAS OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCSK1N PE=1 SV=1 | 4372888 | 3748431 | 3606613 | 3904767 | 2617535.237 | 1823054.405 | 4521084.208 | 3208221.066 | 5250560.367 | 1609620.005 | 8162218.061 | 1694991.899 | 4997781.685 | 2873190.428 | 3387092.226 | 5224746.775 | 1440414.291 | 2038769.498 | 961472.8964 | 8523946.428 | 2828671.704 | 1716874.761 | 4570797.909 | 6975078.465 | 4937786.954 | 1618325.371 | 5618818.708 | ||
| Q9NR99 | 23 | 12 | 602.07 | 0.538742295 | 1.109056379 | XN | HN | Matrix-remodeling-associated protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MXRA5 PE=2 SV=3 | 3584219 | 2613285 | 2635520 | 3314196 | 2813322.877 | 3220039.718 | 3557828.456 | 3212455.205 | 3677603.741 | 2401643.803 | 3451784.781 | 1422907.559 | 4580264.133 | 2443518.977 | 3948458.59 | 3344002.765 | 2556754.458 | 2815786.298 | 3716301.36 | 3255319.437 | 2876261.98 | 2047775.331 | 2869660.39 | 4868934.091 | 3847716.904 | 3079864.443 | 3344005.923 | ||
| O95171 | 16 | 13 | 596.79 | 0.544774232 | 1.488811037 | XN | HN | Sciellin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCEL PE=1 SV=2 | 782014.8 | 617018.6 | 574561.4 | 655415 | 260402.0209 | 1417592.347 | 6825005.217 | 3284557.279 | 2608382.972 | 2907671.463 | 1930663.701 | 1751538.756 | 2173948.042 | 1414706.802 | 1005026.81 | 531080.0716 | 494321.5324 | 989950.798 | 5206830.332 | 3505345.571 | 1967617.757 | 2597040.844 | 788545.4275 | 2571354.287 | 564077.1079 | 1551298.924 | 898569.6273 | ||
| Q6UX73 | 12 | 6 | 596.12 | 0.643843628 | 1.333190773 | HN | XA | UPF0764 protein C16orf89 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C16orf89 PE=1 SV=2 | 4037604 | 5754000 | 6428269 | 4029792 | 4416270.572 | 2716858.271 | 2017887.78 | 1691166.19 | 1858461.826 | 13658490.61 | 2731130.686 | 5258470.735 | 3483962.314 | 2917803.075 | 9118253.437 | 1615468.98 | 3561088.445 | 1584380.859 | 2460103.484 | 1061792.014 | 1154317.486 | 2086637.034 | 9833880.477 | 1699655.071 | 3671684.659 | 3504204.702 | 8019981.755 | ||
| P10619 | 12 | 10 | 594.71 | 0.100637369 | 1.413073964 | HN | XN | Lysosomal protective protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSA PE=1 SV=2 | 14671063 | 15683988 | 46196044 | 18785209 | 12233047.61 | 15544477.68 | 22612473.29 | 21567491.18 | 18078620.2 | 15323451.85 | 20733012.42 | 27603414.38 | 29949935.23 | 26120088.3 | 16096029.13 | 27802834.69 | 17603316.64 | 11480791.22 | 12657588.03 | 10473056.93 | 21621547.7 | 9746416.783 | 14947882.51 | 15236738.29 | 14533052.3 | 25867956.91 | 11294236.69 | ||
| P24298 | 9 | 6 | 593.72 | 0.031315814 | 3.734604759 | XA | HN | Alanine aminotransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPT PE=1 SV=3 | 605666.6 | 347620.9 | 372170.6 | 675084.6 | 157411.8133 | 3213261.3 | 2070506.946 | 2450101.928 | 1384443.736 | 596611.5642 | 253991.1848 | 288186.6199 | 494914.321 | 261388.7609 | 321347.8589 | 139355.3786 | 319219.1264 | 344385.9355 | 905164.4554 | 719095.8522 | 1556885.841 | 1674315.361 | 647656.4401 | 376313.8242 | 547292.382 | 271584.8993 | 235622.694 | ||
| P61769 | 5 | 4 | 593.38 | 0.251920659 | 3.384331608 | HN | XN | Beta-2-microglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=B2M PE=1 SV=1 | 70940246 | 1.19E+08 | 1.36E+08 | 84267645 | 404992985.2 | 108617941.9 | 125366601.3 | 79674752.65 | 131359861.8 | 43120193.48 | 177983830.2 | 36443527.54 | 242153095.2 | 131405809.5 | 249860956.2 | 1712441564 | 140494581.4 | 153542793 | 42748473.91 | 114584060.2 | 78588987.81 | 80668222.71 | 83362749.32 | 95190665.13 | 123497654.6 | 146937692.5 | 87602176.34 | ||
| P12273 | 8 | 5 | 592.87 | 0.372475022 | 1.5534604 | XA | XN | Prolactin-inducible protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PIP PE=1 SV=1 | 51503991 | 50893938 | 47923022 | 47792341 | 72571445.16 | 23023676.67 | 11548968.53 | 53296595.82 | 36952539.64 | 85006789.97 | 49871827.29 | 8069386.309 | 66062770.77 | 49149398 | 15775480.75 | 10043749.73 | 38781343.48 | 29188081.1 | 14710183.18 | 23333570.51 | 16178999.71 | 24165341.8 | 20238423.9 | 59339710.78 | 23457423.65 | 37028957.5 | 36144492.1 | ||
| P08185 | 11 | 9 | 591.72 | 0.099190112 | 1.623097986 | HN | XN | Corticosteroid-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA6 PE=1 SV=1 | 13212151 | 38530890 | 38002679 | 9630360 | 48613634.02 | 21879430.27 | 26917515.92 | 18276865.84 | 17421577.7 | 22211337.53 | 24878331.93 | 39262218.01 | 46824436 | 30841426.75 | 20657430.57 | 14123938.01 | 51901847.82 | 31053088.65 | 37683202.59 | 15231008.87 | 19112341.54 | 29154325.25 | 16401095.38 | 20061121.85 | 9521896.346 | 9579670.612 | 16845630.77 | ||
| P01033 | 7 | 5 | 590.91 | 0.438602131 | 1.704349574 | XA | XN | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TIMP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2654833 | 2296294 | 2736019 | 4826204 | 19520879.44 | 708345.7751 | 871142.2892 | 2651267.23 | 1160074.969 | 4396061.481 | 1114479.274 | 1740254.495 | 1149034.99 | 5516483.897 | 5407977.912 | 5779499.511 | 4105778.047 | 5631713.144 | 1983607.297 | 930121.4112 | 584101.5345 | 893771.5253 | 1752571.503 | 3224136.243 | 4472448.442 | 4485808.043 | 3631992.706 | ||
| P19012 | 16 | 1 | 590.69 | 0.206010078 | 1.71910881 | HN | XN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT15 PE=1 SV=3 | 2045894 | 1786422 | 6523554 | 1291462 | 2849804.007 | 220031.4885 | 407352.7744 | 1240445.936 | 672524.4517 | 1869416.528 | 6772686.467 | 930639.2368 | 2816789.375 | 5393969.854 | 519653.6761 | 2193181.887 | 5737063.307 | 642605.7216 | 16151.20488 | 466499.6971 | 441016.4565 | 472440.8516 | 1045432.166 | 8953907.864 | 1790707.597 | 1494033.079 | 953496.3361 | ||
| P11047 | 16 | 8 | 589.48 | 0.81980013 | 1.017296206 | XA | HN | Laminin subunit gamma-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 2553168 | 4213438 | 2979655 | 1400141 | 2025680.457 | 2115590.772 | 1859875.401 | 1839544.876 | 3630810.84 | 1311580.294 | 4864280.255 | 927846.7653 | 4351550.343 | 4128180.092 | 2004406.549 | 1367144.606 | 1605815.451 | 1672546.927 | 1647278.075 | 1662038.547 | 2193387.479 | 2820146.33 | 2292657.759 | 5353068.508 | 2260378.339 | 2722441.595 | 1661351.721 | ||
| P09525 | 12 | 12 | 588.4 | 0.31657331 | 1.224342041 | HN | XN | Annexin A4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA4 PE=1 SV=4 | 2513261 | 3691036 | 4560845 | 4820051 | 4916959.079 | 3412590.723 | 3375288.453 | 2977574.86 | 2939876.085 | 4600232.891 | 5653338.309 | 3928498.691 | 2039756.253 | 3009923.512 | 2731332.039 | 5722753.116 | 3508601.908 | 4170025.728 | 6722989.265 | 2355974.617 | 3309759.696 | 3460484.215 | 2866305.75 | 2513087.543 | 2379518.538 | 2710687.982 | 2565655.446 | ||
| P54652 | 10 | 1 | 587.81 | 4.52E-05 | 4.118028774 | XA | XN | Heat shock-related 70 kDa protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 86258.66 | 41907.21 | 121019.6 | 59340.77 | 76948.56058 | 37655.02001 | 56038.39456 | 141574.6651 | 62066.70264 | 16434.09529 | 3865.886854 | 47247.73055 | 8205.544861 | 14391.72847 | 40835.78935 | 40821.98303 | 21444.30515 | 20771.77887 | 27899.32611 | 16313.93508 | 16042.39569 | 9750.291691 | 15262.36398 | 7677.509182 | 18265.59002 | 30783.18839 | 23815.20916 | ||
| B9A064;P0CG04 | 9 | 3 | 586.17 | 0.99714795 | 1.222960908 | XA | XN | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 28443370 | 1.67E+08 | 44717542 | 67449554 | 120446748.6 | 24882642.64 | 27714168.76 | 55123680.57 | 24398576.14 | 72226878.03 | 22536293.27 | 75701230 | 41338322.1 | 33340987.15 | 47040503.87 | 80611024.19 | 55855693.95 | 47534550.98 | 61850339.93 | 41106301.92 | 35869718.43 | 36533691.86 | 59503492.84 | 92100771.25 | 47827943.34 | 49441358.11 | 33658216.93 | ||
| P61106;P61018;Q96DA2 | 9 | 7 | 583.93 | 0.122398028 | 1.313089303 | HN | XN | Ras-related protein Rab-14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB14 PE=1 SV=4 | 3040596 | 2421135 | 1834481 | 1968840 | 1962250.248 | 1318654.19 | 1321240.087 | 2785673.981 | 1404056.934 | 3723360.905 | 2583919.493 | 1820746.58 | 1875744.091 | 2552855.799 | 1696734.352 | 1956083.863 | 2035957.357 | 2252679.243 | 2968248.585 | 1727515.259 | 1486110.017 | 1513862.18 | 1141563.92 | 1521752.187 | 1555347.031 | 1854427.606 | 1841750.227 | ||
| Q9Y653 | 6 | 4 | 583.58 | 0.187842843 | 1.492918528 | XN | HN | G-protein coupled receptor 56 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPR56 PE=1 SV=2 | 10360650 | 5208525 | 5887351 | 6344317 | 4294125.389 | 4970276.958 | 5403357.371 | 9117426.856 | 7003607.832 | 4040142.901 | 3462000.545 | 3963089.38 | 4064756.627 | 3116203.87 | 3273052.869 | 7509102.124 | 7305867.052 | 10263208.25 | 6857062.124 | 9794904.123 | 7467074.897 | 4194355.447 | 8155235.725 | 2004211.398 | 10507833.85 | 9484752.844 | 11697894.09 | ||
| P16112 | 11 | 8 | 583.13 | 0.051243204 | 1.721844609 | XN | HN | Aggrecan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACAN PE=1 SV=2 | 1702674 | 2684760 | 2135485 | 1131553 | 810114.2454 | 3270192.393 | 3338091.832 | 2227140.031 | 3910555.324 | 1029638.545 | 4007784.667 | 660514.7848 | 3416041.149 | 2279971.01 | 752774.0201 | 311690.5073 | 1904605.264 | 1848508.604 | 1978620.326 | 3640465.029 | 3008983.656 | 2570351.418 | 2159586.442 | 6336651.133 | 2635300.141 | 3648291.872 | 1935483.021 | ||
| P10153 | 4 | 4 | 583.07 | 0.529925632 | 1.362194583 | HN | XA | Non-secretory ribonuclease OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE2 PE=1 SV=2 | 5.06E+08 | 8.39E+08 | 8.76E+08 | 5.45E+08 | 480337082.7 | 313268175.3 | 328446222.6 | 226026845.7 | 458459004.5 | 539729615.8 | 1641852352 | 251937684.4 | 1021514911 | 311025284.6 | 618207967.7 | 304282200.4 | 659238319.6 | 882260883.8 | 364120713.3 | 373145748.9 | 418415540.6 | 848455289.2 | 474558687.5 | 1432334078 | 570534750.1 | 710964590.4 | 755574128.4 | ||
| P61970 | 6 | 5 | 582.9 | 0.000314537 | 1.559669927 | XA | XN | Nuclear transport factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUTF2 PE=1 SV=1 | 54361242 | 51077971 | 72628714 | 62716812 | 54750756.52 | 77506528.41 | 68108426.79 | 52715601.42 | 59649275.47 | 33485342.9 | 46675708.72 | 28061440.92 | 44825674.51 | 57088858.82 | 39144257.13 | 29677072.16 | 43142211.31 | 65340651.44 | 35608989.53 | 48010629.98 | 42678978.83 | 35160477.04 | 37934662.56 | 25746697.62 | 40848149.28 | 44603761.43 | 44300261.97 | ||
| P07996 | 18 | 12 | 582.64 | 0.011171814 | 1.64755518 | XA | HN | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 7993883 | 7542143 | 6541735 | 2785520 | 5726538.918 | 4173920.99 | 5140794.171 | 4999262.552 | 4396802.154 | 2371110.548 | 2747587.903 | 1862574.467 | 4117631.487 | 3073897.073 | 5197117.222 | 4357519.486 | 3710266.195 | 2485785.204 | 4583712.069 | 3970700.03 | 2971213.22 | 2352672.332 | 3353142.62 | 3794322.18 | 5689651.805 | 5992691.454 | 5101382.587 | ||
| Q9HBR0 | 13 | 9 | 581.23 | 0.303121065 | 1.312783056 | HN | XA | Putative sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC38A10 PE=1 SV=2 | 2560278 | 1312092 | 779202.3 | 1987595 | 1242183.087 | 958449.7311 | 1398453.272 | 1816707.539 | 1138773.322 | 2438250.829 | 1785655.805 | 861075.7748 | 3687393.215 | 1916250.241 | 1050520.259 | 2445389.899 | 1481559.821 | 1654413.673 | 961849.9666 | 1876970.634 | 2289142.537 | 1488309.423 | 2209726.788 | 1087751.28 | 2476522.967 | 2237180.84 | 2203161.112 | ||
| O95954 | 10 | 6 | 578.85 | 0.124091363 | 2.959461631 | XA | HN | Formimidoyltransferase-cyclodeaminase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTCD PE=1 SV=2 | 2178992 | 277780.8 | 1427028 | 7106735 | 169304.3799 | 1705009.428 | 1474010.856 | 3947552.161 | 2075482.449 | 605585.1374 | 522619.6587 | 1000700.378 | 2023196.905 | 275337.1494 | 481635.9652 | 1554718.521 | 185491.1754 | 230985.3554 | 501888.8629 | 915843.5831 | 994162.6659 | 447068.2835 | 2654257.325 | 214844.3116 | 764085.8303 | 961268.6943 | 1004935.972 | ||
| Q6P531 | 5 | 4 | 578.77 | 0.348915267 | 1.329030459 | XA | HN | Gamma-glutamyltransferase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GGT6 PE=2 SV=2 | 30251668 | 9276402 | 13666101 | 19942572 | 9758279.081 | 13129825.39 | 14219049.27 | 19681939.61 | 11356637.26 | 10652507.81 | 6034984.664 | 10573060.81 | 10721273.53 | 5989099.158 | 11856318.11 | 18812320.46 | 15243981.91 | 16421371.23 | 12760677.93 | 13312802.21 | 13130730.59 | 10267599.73 | 17902116.59 | 4949042.173 | 24191549.2 | 14430500.07 | 20974284.69 | ||
| P11117 | 13 | 12 | 572.93 | 0.786319867 | 1.349959318 | HN | XN | Lysosomal acid phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 10407545 | 17023880 | 23220572 | 7617134 | 4058902.7 | 17308177.8 | 30922899.67 | 15724395.03 | 31273439.46 | 6730005.346 | 26605654.63 | 39729151.97 | 28301125.65 | 27191638.5 | 8076115.008 | 6765607.448 | 7714990.987 | 7692409.443 | 12836050.09 | 8550416.078 | 16126218.31 | 11778822.99 | 4773211.815 | 13006229.91 | 9760678.665 | 21962370.64 | 18844138.37 | ||
| Q9UNW1 | 9 | 6 | 571.27 | 0.005012184 | 1.85033033 | XA | HN | Multiple inositol polyphosphate phosphatase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MINPP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 6578922 | 2291965 | 2687532 | 4142104 | 3241827.644 | 3351922.77 | 3008047.481 | 5377896.587 | 2995387.739 | 1075003.834 | 821869.2369 | 2105307.534 | 2109777.468 | 2081299.715 | 2227645.098 | 2258410.141 | 2947827.223 | 2572639.62 | 2823494.51 | 3648549.771 | 3059232.583 | 2205274.322 | 3338162.865 | 1323661.545 | 4757330.969 | 3143683.001 | 3472280.619 | ||
| O15230 | 18 | 11 | 571.21 | 0.87980732 | 1.180725056 | XA | XN | Laminin subunit alpha-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMA5 PE=1 SV=8 | 6343530 | 2031044 | 2763698 | 3243797 | 4242270.71 | 2066019.017 | 1792608.941 | 2319567.398 | 1276350.333 | 2771811.387 | 2664433.969 | 1006977.336 | 1853796.547 | 3055892.712 | 2036743.322 | 4455989.165 | 1994465.754 | 3754868.228 | 2939530.814 | 2027145.965 | 2143338.785 | 1635018.619 | 1649948.687 | 3682222.319 | 2151128.36 | 2427962.598 | 3430882.756 | ||
| P05362 | 12 | 10 | 568.69 | 0.155979581 | 1.917749567 | HN | XA | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ICAM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5204557 | 4085940 | 2380775 | 2149660 | 2851518.619 | 1862884.583 | 6296676.531 | 4142896.322 | 3326514.348 | 14456227.47 | 5530831.687 | 4447009.096 | 8416947.381 | 12158157.34 | 2914456.916 | 1210696.155 | 5378397.018 | 7433313.921 | 5392981.212 | 6364461.909 | 6404269.125 | 4577672.229 | 2607305.159 | 10925652.33 | 2428489.027 | 6143021.178 | 3882105.441 | ||
| Q9UKR3 | 11 | 9 | 568.51 | 0.833683214 | 1.078561649 | XA | XN | Kallikrein-13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK13 PE=1 SV=1 | 4594498 | 6597691 | 5290200 | 5144964 | 9582069.714 | 7677142.839 | 24086315.41 | 20119013.74 | 17431047 | 13518365.15 | 8724880.676 | 11664067.31 | 11560543.89 | 5993775.315 | 5765933.031 | 33665056.86 | 4572550.001 | 3397516.912 | 24076680.03 | 26822594.78 | 6835014.791 | 13323217.34 | 5411314.75 | 6062660.637 | 4143111.118 | 3324336.034 | 3201993.934 | ||
| P15924 | 39 | 17 | 567.5 | 0.231455054 | 1.366021306 | XN | XA | Desmoplakin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSP PE=1 SV=3 | 59665388 | 42643924 | 24098455 | 40524770 | 21843862.05 | 22504667.21 | 35999899.6 | 15945634.85 | 51607928.74 | 55892690.6 | 25935097.52 | 34674410.41 | 18191162.13 | 28901829.08 | 42913254.68 | 92032461.15 | 36985336.15 | 28801324.31 | 32131514.02 | 28981434.78 | 56291499.47 | 53574740.61 | 87313233.47 | 36152933.89 | 47890809.11 | 45706131.63 | 42028377.84 | ||
| P08195 | 11 | 8 | 567.36 | 0.149201454 | 1.751584475 | HN | XN | 4F2 cell-surface antigen heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC3A2 PE=1 SV=3 | 10206584 | 9908797 | 10458724 | 6819140 | 7344457.663 | 5982262.379 | 5366726.641 | 7060487.691 | 7234591.916 | 8360096.689 | 4851638.123 | 21429618.46 | 5410250.851 | 25741340.43 | 6864513.185 | 5630827.944 | 6446720.979 | 4338745.068 | 4034533.13 | 5131100.433 | 6055880.441 | 5658771.114 | 6758265.614 | 4337275.186 | 6399363.576 | 5020469.17 | 7457584.783 | ||
| Q15375 | 12 | 6 | 561.66 | 0.159211193 | 1.368105301 | XN | HN | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHA7 PE=1 SV=3 | 3164188 | 4605915 | 3193178 | 3325290 | 3624681.838 | 3393767.98 | 2343740.618 | 2412063.349 | 2968044.783 | 2680631.056 | 3950373.379 | 1606721.369 | 3613455.8 | 3147470.163 | 2006750.36 | 1092282.673 | 3347610.919 | 2722561.512 | 2198497.525 | 3621927.619 | 2577083.381 | 3511781.42 | 2825964.833 | 8084136.565 | 3095879.549 | 4069069.863 | 3079832.847 | ||
| P21266 | 9 | 7 | 560.36 | 0.055923035 | 2.177204063 | XA | XN | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTM3 PE=1 SV=3 | 3572032 | 983321.7 | 3901135 | 6918781 | 3526391.379 | 1198100.055 | 2544093.947 | 3890119.553 | 1198515.705 | 2267708.601 | 3339516.651 | 3125460.943 | 1665208.141 | 3350325.716 | 954201.9731 | 6789346.673 | 899586.9583 | 1337276.251 | 404404.5869 | 1510431.684 | 1606792.391 | 676546.3098 | 1007736.261 | 891403.2433 | 3145150.713 | 1902574.951 | 1592622.399 | ||
| P07686 | 15 | 10 | 560.16 | 0.352591389 | 1.329741434 | XA | XN | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEXB PE=1 SV=3 | 4157419 | 4656859 | 9815492 | 5427620 | 4690583.526 | 6745019.016 | 9049704.575 | 5600137.011 | 6448230.193 | 4203750.559 | 6460464.069 | 3939054.038 | 14075465.58 | 8799056.992 | 4137951.221 | 1707376.068 | 4791636.127 | 3603716.423 | 4241329.264 | 3603774.278 | 6818225.677 | 4527434.713 | 3997235.904 | 5925328.179 | 4215540.154 | 5981993.896 | 3247084.102 | ||
| Q8N4F0 | 6 | 4 | 560.12 | 0.813007714 | 2.315270243 | HN | XN | BPI fold-containing family B member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BPIFB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 4540232 | 1168219 | 4675200 | 14178321 | 860172.7164 | 390675.1311 | 286944.2815 | 2306198.846 | 2374395.493 | 763454.7392 | 368979.3083 | 278178.0283 | 688523.656 | 38828087.17 | 2608045.844 | 2765187.604 | 151383.5383 | 4290273.642 | 1495393.393 | 1216111.333 | 1064010.217 | 658460.4957 | 2330374.469 | 799528.2076 | 3996515.344 | 4574693.947 | 5781193.722 | ||
| P08246 | 6 | 5 | 559.97 | 0.22998041 | 4.951221491 | XA | HN | Neutrophil elastase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ELANE PE=1 SV=1 | 2454072 | 1474312 | 1084606 | 1322765 | 577402.9817 | 23061654.26 | 18802839.59 | 2649705.377 | 16500209.62 | 2452489.779 | 1429384.228 | 2106900.788 | 1454984.418 | 859113.4594 | 2559664.502 | 915090.1553 | 940052.3707 | 1001675.649 | 32789971.75 | 2267071.602 | 793433.4425 | 3030975.055 | 645760.2468 | 1968500.518 | 1213432.069 | 756364.9941 | 717418.7255 | ||
| P50395 | 9 | 4 | 559.4 | 0.092290246 | 1.682693897 | XA | HN | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=GDI2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1734834 | 433241.4 | 989201.8 | 1514340 | 643420.2107 | 2244553.495 | 2024047.392 | 2439839.661 | 1670487.503 | 1379228.548 | 594990.305 | 1088165.352 | 872619.5555 | 1455724.548 | 1105474.331 | 389439.1494 | 611824.2759 | 640654.4157 | 961822.8563 | 791231.6483 | 1655670.671 | 941494.6102 | 877427.3284 | 770712.2893 | 1143533.37 | 675063.5681 | 890312.8223 | ||
| Q969P0 | 7 | 3 | 557.35 | 0.585319397 | 1.219703377 | XN | XA | Immunoglobulin superfamily member 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGSF8 PE=1 SV=1 | 23276694 | 15194082 | 14509307 | 26077771 | 26216908.62 | 10932805.83 | 18879627.47 | 16736697.55 | 8795049.404 | 22797839.85 | 29740713.41 | 8360779.432 | 21960213.53 | 19081436.25 | 21218358.24 | 31571953.52 | 16257926.54 | 20181042.33 | 9546382.776 | 29378071.16 | 12817686.28 | 14263501.4 | 26526376.68 | 41272885.83 | 20769203.68 | 19419592.34 | 21913767.46 | ||
| P98088 | 15 | 9 | 555.76 | 0.081200553 | 1.908640235 | HN | XA | Mucin-5AC (Fragments) OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC5AC PE=1 SV=3 | 247479.3 | 442905.7 | 584341.1 | 299696.3 | 646426.579 | 212601.9615 | 2085443.481 | 338586.4263 | 250235.1621 | 1820885.006 | 1235239.427 | 1922109.181 | 772653.1027 | 695788.6711 | 991481.8753 | 1780726.33 | 242705.9417 | 287202.8504 | 639430.4122 | 987724.1477 | 526523.513 | 840074.8293 | 399334.6029 | 1544053.019 | 741713.1447 | 609325.641 | 436825.0525 | ||
| P17050 | 9 | 9 | 555.12 | 0.147876203 | 1.630490281 | XA | XN | Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAGA PE=1 SV=2 | 2420418 | 5891900 | 17358290 | 6641020 | 4560730.828 | 6246366.211 | 7115804.188 | 6399915.366 | 7185857.476 | 2771485.385 | 2528667.988 | 9378353.059 | 6851859.056 | 4517174.069 | 6953181.644 | 5056969.114 | 6787300.029 | 4281835.288 | 1842599.208 | 2879105.246 | 3918016.123 | 3917414.8 | 7154799.406 | 5853887.14 | 4860705.37 | 5010050.78 | 3705207.899 | ||
| P22392;O60361 | 10 | 4 | 555.02 | 0.804384203 | 2.336906137 | XN | HN | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B OS=Homo sapiens GN=NME2 PE=1 SV=1 | 534811.1 | 70100.58 | 187260.1 | 726778.8 | 318887.3108 | 421718.9154 | 554799.197 | 1741250.911 | 684618.9146 | 1605845.072 | 236074.3413 | 786243.2832 | 123035.0137 | 132291.1887 | 341407.0371 | 376150.9282 | 163938.2662 | 286907.0696 | 7382391.705 | 234636.4448 | 548485.0869 | 350103.7759 | 234785.6948 | 70083.09343 | 291843.0673 | 212203.9699 | 144358.9098 | ||
| P18510 | 5 | 2 | 554.04 | 0.870247445 | 1.520502497 | XN | HN | Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL1RN PE=1 SV=1 | 290090.3 | 224404.9 | 352090.1 | 791414.1 | 387075.9553 | 1907597.956 | 5188256.407 | 4621365.088 | 6564722.005 | 3635960.071 | 4844048.719 | 3614419.437 | 2360633.167 | 291570.005 | 143573.0976 | 225522.0983 | 325272.1268 | 405902.3126 | 16241716.35 | 3888107.487 | 1265541.71 | 1441849.395 | 241210.3022 | 147243.8956 | 239941.6072 | 292237.0966 | 337404.7514 | ||
| P13797 | 16 | 8 | 549.96 | 0.218935737 | 1.872526121 | XA | XN | Plastin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLS3 PE=1 SV=4 | 655044.4 | 102844.2 | 171930.3 | 1083484 | 268552.6441 | 289372.0364 | 448593.3169 | 975818.208 | 597809.4396 | 1051898.597 | 484448.8722 | 789391.2264 | 353880.3209 | 201921.5302 | 152946.3784 | 303506.7295 | 223464.9472 | 161817.4802 | 813495.363 | 227209.6156 | 369222.1217 | 298965.164 | 143446.1071 | 174112.4047 | 169711.5812 | 85953.47742 | 170959.7932 | ||
| Q8WWA0 | 8 | 5 | 548.81 | 0.188336296 | 7.500937378 | XA | HN | Intelectin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITLN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3798856 | 1635759 | 3990669 | 53018625 | 1939159.827 | 810783.5403 | 543756.1489 | 998799.2648 | 1410957.324 | 557495.4204 | 1126839.714 | 1543165.886 | 801889.1219 | 719852.7471 | 811006.7442 | 1751632.994 | 597375.1182 | 1175922.049 | 505309.5725 | 1999255.89 | 14102501.33 | 973850.5902 | 664764.5738 | 1244706.25 | 787112.9049 | 1873649.964 | 1125197.536 | ||
| Q8WVN6 | 3 | 3 | 543.18 | 0.49255634 | 1.383806652 | XA | XN | Secreted and transmembrane protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SECTM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 62813136 | 1.93E+08 | 1.05E+08 | 1.07E+08 | 122125418.9 | 105900192.2 | 395756131.9 | 96620763.74 | 207222861.7 | 110304065.1 | 208256166.1 | 84897313.39 | 98227780.12 | 126270765.7 | 98010390.88 | 65020728 | 191627806.7 | 85057298.11 | 150574869.5 | 95059212.88 | 50867865.71 | 102902731.5 | 75906577.17 | 173770032.9 | 104246443.9 | 118238037.1 | 136296057.8 | ||
| Q9Y2S2 | 8 | 6 | 542.37 | 0.240015471 | 1.651333335 | XA | HN | Lambda-crystallin homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRYL1 PE=1 SV=3 | 12630161 | 1063720 | 6115582 | 11818043 | 3468171.959 | 4791242.652 | 6781734.992 | 9189461.394 | 5063105.026 | 4180338.13 | 9229007.235 | 8141609.797 | 3215931.115 | 1621749.024 | 1481434.463 | 1670447.667 | 4612137.519 | 2739485.965 | 6970224.926 | 2662829.013 | 5038369.456 | 3512149.429 | 9159789.824 | 3393853.803 | 3881495.522 | 5973787.862 | 3714870.435 | ||
| Q96FE7 | 7 | 4 | 539.38 | 0.110628367 | 1.660190614 | XN | HN | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase-interacting protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PIK3IP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.66E+08 | 6.58E+08 | 7.12E+08 | 2.07E+08 | 199777437.4 | 479778292.1 | 929097592.6 | 309878440.3 | 1181404406 | 93898519.41 | 903376215.4 | 163193393.8 | 585020265.1 | 364434045.9 | 240680812.6 | 55854666.92 | 322739381 | 764586616.9 | 351352341.5 | 933355951.4 | 625934297.5 | 495897178.6 | 382034634.7 | 1192026565 | 536927057.8 | 888071939 | 394747302.4 | ||
| P06744 | 12 | 9 | 538.41 | 0.001659484 | 2.651387966 | XA | XN | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPI PE=1 SV=4 | 4517588 | 1111114 | 3293216 | 7513023 | 1983713.279 | 2169453.247 | 3013875.77 | 4962468.848 | 2730260.695 | 1834567.624 | 1227374.144 | 1967291.149 | 1153837.804 | 517428.8221 | 2939179.66 | 1674408.284 | 892171.9208 | 594606.2284 | 819103.4401 | 635035.8874 | 1398729.897 | 717658.2064 | 3024686.425 | 934480.3814 | 2553081.433 | 781090.3682 | 939277.7686 | ||
| Q99497 | 8 | 6 | 537.05 | 0.221554136 | 1.727598601 | HN | XN | Protein DJ-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PARK7 PE=1 SV=2 | 8548629 | 2937280 | 2841632 | 8768769 | 4805926.528 | 5972029.687 | 6990050.668 | 7921350.065 | 3596439.556 | 16235672.27 | 7218949.123 | 9679947.647 | 3746798.697 | 10245266.35 | 3288407.561 | 1909019.083 | 3257192.339 | 5969795.508 | 5873872.023 | 2807235.475 | 4814973.092 | 5391862.92 | 4931908.068 | 2330840.859 | 2772671.904 | 2947194.291 | 3757537.238 | ||
| P14780 | 12 | 7 | 535.22 | 0.976987956 | 1.200366937 | HN | XN | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP9 PE=1 SV=3 | 2346036 | 4120436 | 1947536 | 1362927 | 913981.9421 | 1145498.326 | 1817068.353 | 945202.7737 | 2120309.302 | 3298890.236 | 918751.2461 | 1468510.143 | 421975.629 | 1634701.874 | 4003384.507 | 3693705.823 | 1796029.4 | 1948210.855 | 2211897.369 | 1284846.942 | 1066164.155 | 1557154.135 | 2654653.89 | 1673429.663 | 2412473.036 | 1574901.224 | 1546392.384 | ||
| Q8N2S1 | 12 | 9 | 535.06 | 0.854528848 | 1.079692958 | HN | XA | Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTBP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 7026057 | 9122809 | 9464631 | 12156525 | 10578849.54 | 6532728.016 | 6098208.629 | 5266555.283 | 5614321.733 | 6075574.053 | 15642184.26 | 3654952.181 | 6765486.682 | 9106106.994 | 10664490.45 | 10613518.82 | 6539544.055 | 8525618.596 | 5571603.13 | 8355685.356 | 8016714.391 | 6125581.805 | 10711173.64 | 11430476.56 | 8387680.526 | 9494816.415 | 8974164.319 | ||
| P08758 | 6 | 5 | 533.22 | 0.037702526 | 1.663087053 | XA | XN | Annexin A5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA5 PE=1 SV=2 | 1112255 | 841203.8 | 1211537 | 908808 | 1202008.962 | 1750945.176 | 2405433.985 | 1509782.752 | 1575903.734 | 1274388.936 | 2832092.561 | 1633511.908 | 822747.2329 | 889842.4134 | 1096829.37 | 849684.0346 | 593447.5812 | 681083.1679 | 1143604.383 | 909204.4185 | 739422.6489 | 1081263.749 | 482840.6037 | 439250.7353 | 1128520.556 | 708362.6808 | 894423.4425 | ||
| P20711 | 11 | 6 | 533 | 0.074152832 | 2.145904825 | XA | HN | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDC PE=1 SV=2 | 3563414 | 1264215 | 3480186 | 6034647 | 787124.3173 | 5765367.224 | 3557906.4 | 8210918.31 | 4215205.284 | 2761817.581 | 1441332.36 | 3561767.043 | 3408436.949 | 1396621.219 | 1606933.073 | 980516.9387 | 1142591.451 | 885733.1551 | 2629431.225 | 1863039.118 | 3897651.55 | 4662620.241 | 5416033.767 | 1439287.539 | 3047309.355 | 1377839.766 | 1588596.452 | ||
| P42785 | 9 | 7 | 531.43 | 0.875475657 | 1.051177746 | HN | XA | Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRCP PE=1 SV=1 | 10195170 | 9405768 | 11185540 | 9706981 | 9720250.248 | 12107555.87 | 11065949.66 | 10865963.07 | 10014651.21 | 9543350.73 | 8681194.005 | 5889689.412 | 21255191.38 | 17594669.23 | 7461415.212 | 9643825.317 | 8830769.471 | 10192138.62 | 11925378.41 | 10113630.31 | 8946379.231 | 11592675.07 | 12386948.69 | 9423667.597 | 11858579.05 | 8844656.974 | 13387403.8 | ||
| P40925 | 11 | 9 | 528.64 | 0.122699236 | 1.686664631 | XA | XN | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=MDH1 PE=1 SV=4 | 5902896 | 2029823 | 3312445 | 6854248 | 1668322.911 | 8375943.183 | 9670229.673 | 7305259.879 | 5748879.085 | 7431000.043 | 2203323.789 | 6073094.845 | 1979820.757 | 4286239.25 | 2427973.183 | 1639106.434 | 1875217.315 | 2736209.801 | 3477575.894 | 2734411.896 | 5960551.253 | 4906275.374 | 4399634.524 | 1170452.188 | 2623719.281 | 2370612.091 | 2515724.459 | ||
| Q15274 | 7 | 6 | 527.99 | 0.234072447 | 1.341777635 | XA | HN | Nicotinate-nucleotide pyrophosphorylase [carboxylating] OS=Homo sapiens GN=QPRT PE=1 SV=3 | 2821536 | 2356398 | 2458827 | 2746671 | 4979409.024 | 7024375.902 | 4650623.592 | 4880881.444 | 3776692.582 | 4726067.57 | 3409508.239 | 3172356.517 | 1763495.051 | 4368797.146 | 2786784.769 | 1843328.705 | 2907318.117 | 1625421.539 | 5189603.968 | 1901153.62 | 4656846.194 | 3983684.196 | 4091153.327 | 701176.7943 | 1798782.021 | 2569205.537 | 1715125.646 | ||
| Q08345 | 18 | 14 | 527.26 | 0.357493866 | 1.228733251 | XA | XN | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 12302894 | 7198012 | 5856697 | 8498401 | 6432252.262 | 9364612.656 | 7880569.25 | 9640390.334 | 8392704.728 | 6588608.653 | 12654002.24 | 6525485.514 | 10070784.19 | 9738733.429 | 5390783.499 | 3510143.115 | 7022475.428 | 8136640.176 | 6618238.848 | 7481354.982 | 6801758.699 | 6220655.181 | 6784957.055 | 2023314.434 | 7933147.026 | 9335916.204 | 8300200.327 | ||
| Q08257 | 10 | 8 | 525.7 | 0.247000705 | 1.661986831 | XA | XN | Quinone oxidoreductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRYZ PE=1 SV=1 | 8043734 | 2431052 | 1548599 | 9660201 | 3084099.625 | 12078917.93 | 7871166.479 | 6836301.304 | 6839650.04 | 5657527.988 | 7313002.819 | 5487447.041 | 4264582.63 | 4763372.366 | 2732501.341 | 1993528.26 | 3283128.134 | 2874570.005 | 6274559.062 | 3950517.03 | 7421978.254 | 3136721.06 | 3437493.417 | 1921333.354 | 3898730.79 | 2859529.377 | 2234025.433 | ||
| P55072 | 10 | 7 | 522.65 | 0.251832931 | 1.85819352 | XA | XN | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCP PE=1 SV=4 | 1364225 | 246964.7 | 748157.7 | 2783882 | 368729.5869 | 1255944.157 | 1633527.105 | 2574221.077 | 1441981.98 | 1302835.196 | 660433.6186 | 1428854.9 | 1232629.781 | 551550.07 | 874112.5648 | 593874.5196 | 197684.0138 | 381099.5643 | 1144630.978 | 445496.4623 | 1341788.467 | 763628.637 | 972121.0287 | 247011.9593 | 772616.3422 | 495988.8478 | 499354.5505 | ||
| Q8TB96 | 10 | 10 | 520.02 | 0.828452124 | 1.117881135 | HN | XN | T-cell immunomodulatory protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITFG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 13960744 | 5649086 | 5347378 | 5932335 | 6217639.781 | 7511246.057 | 6901940.016 | 6454534.712 | 5804127.445 | 8779064.832 | 10522395.2 | 10229445.91 | 7185745.437 | 6794874.13 | 4164805.733 | 4266739.63 | 5683755.807 | 8251397.539 | 6096781.823 | 6732068.252 | 6200634.572 | 4069372.802 | 5586145.33 | 7679925.545 | 7021086.502 | 6451068.234 | 9094248.871 | ||
| Q6PCB0 | 9 | 7 | 517.64 | 0.87823781 | 1.120984033 | XA | XN | von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VWA1 PE=2 SV=1 | 7947277 | 2640425 | 7341759 | 3904068 | 2301535.202 | 1672520.341 | 2738727.855 | 4820372.957 | 3070124.309 | 2376680.872 | 2370940.274 | 2237769.508 | 2756750.262 | 3497293.963 | 4213852.573 | 8254628.251 | 3804620.231 | 3239839.344 | 1296586.289 | 3480788.092 | 2749468.34 | 1728915 | 7016376.659 | 1988875.963 | 4515813.52 | 4288788.012 | 5438695.935 | ||
| Q5IJ48 | 9 | 7 | 517.28 | 0.319513312 | 1.484493241 | HN | XA | Crumbs homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2873815 | 1365172 | 606714.8 | 1649753 | 929896.0588 | 1159737.745 | 1616932.432 | 1892014.772 | 2219541.312 | 1823246.642 | 4504619.449 | 2418673.45 | 3411503.971 | 3963545.066 | 1241513.402 | 697693.943 | 1651969.891 | 1535642.337 | 1967523.024 | 2279420.543 | 1867008.242 | 1270340.053 | 1864568.426 | 2114591.302 | 1735092.264 | 2309722.575 | 1099084.999 | ||
| Q6UWP8 | 7 | 5 | 517.22 | 0.813077365 | 1.055958488 | XN | HN | Suprabasin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SBSN PE=2 SV=1 | 1525847 | 1986066 | 1677205 | 75103.36 | 1559055.557 | 1642747.197 | 2027559.699 | 4676232.606 | 3123890.225 | 1428661.52 | 1514214 | 3266374.914 | 2939887.21 | 1483699.53 | 910086.3441 | 1636143.125 | 3802395.71 | 1172570.675 | 1934090.132 | 4451968.722 | 2418519.809 | 3003051.339 | 1949056.257 | 2652369.787 | 500816.4841 | 1051484.405 | 1208548.341 | ||
| P05787 | 15 | 2 | 516.15 | 0.06766622 | 5.662599323 | HN | XN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT8 PE=1 SV=7 | 343635.2 | 17858.8 | 181621 | 826270 | 168218.2965 | 94720.62163 | 66902.65452 | 133135.672 | 364736.5486 | 36122.79936 | 249348.1661 | 1233341.976 | 106584.8414 | 16804.78471 | 423721.1144 | 1711919.924 | 296187.5238 | 68109.14506 | 46582.93867 | 10465.32738 | 43521.88716 | 11473.81904 | 153089.3175 | 45886.82992 | 317603.5156 | 52715.42466 | 50151.91073 | ||
| P15531 | 8 | 3 | 513.46 | 0.735794504 | 1.791566547 | XN | XA | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=NME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 110977.9 | 3834.641 | 86497.82 | 295699.9 | 125755.9243 | 61323.50204 | 153565.8824 | 221460.7205 | 87495.97846 | 314645.4046 | 38644.23236 | 215375.8305 | 62592.02902 | 42798.10138 | 98057.16374 | 468136.6656 | 34184.22015 | 62696.94412 | 1135174.484 | 32587.06334 | 152996.4285 | 66875.34447 | 80736.10799 | 171514.2111 | 50568.39894 | 169046.2217 | 194733.8706 | ||
| Q9HD89 | 5 | 4 | 512.96 | 0.380139704 | 1.400784544 | XN | XA | Resistin OS=Homo sapiens GN=RETN PE=2 SV=1 | 7721774 | 21181650 | 37405028 | 3750258 | 22045363.72 | 27286994.39 | 8128337.405 | 17498529.37 | 12491656.23 | 19585777.55 | 26465653.71 | 4586395.449 | 19018728.67 | 13806627.24 | 8004109.674 | 29717217.88 | 14256556.5 | 33901271.39 | 16575396.47 | 7137542.18 | 27676752.85 | 45369627.91 | 25071695.2 | 30589937.44 | 29780592.57 | 12179745.15 | 26255710.15 | ||
| P29279 | 9 | 7 | 510.52 | 0.510728554 | 1.278425993 | HN | XA | Connective tissue growth factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTGF PE=1 SV=2 | 7251009 | 4892268 | 4852790 | 10877135 | 7936441.712 | 4095452.255 | 2424680.019 | 3953009.451 | 2639566.709 | 5925057.771 | 7145544.21 | 3227489.769 | 4687155.442 | 5444951.232 | 3824783.575 | 17570455.62 | 6653070.028 | 8065099.106 | 5380564.08 | 6578788.614 | 4507057.867 | 3460207.29 | 5082008.9 | 8600920.703 | 7474409.137 | 5621329.452 | 6915756.439 | ||
| P01036 | 8 | 3 | 510.39 | 0.705186375 | 2.202254505 | HN | XA | Cystatin-S OS=Homo sapiens GN=CST4 PE=1 SV=3 | 2822749 | 12735106 | 5944129 | 7529066 | 7653505.463 | 3460523.271 | 4586082.641 | 3263620.918 | 1978990.084 | 2839390.733 | 2058369.383 | 1923075.133 | 6386901.537 | 42679952.88 | 11371509.79 | 29261618.81 | 10841853.66 | 2692294.009 | 3783604.222 | 2242471.003 | 1814341.71 | 8291287.503 | 10734383 | 19023504.35 | 5719679.952 | 3115362.486 | 13184962.44 | ||
| P15311 | 21 | 5 | 509.71 | 0.336417854 | 1.328956269 | XA | XN | Ezrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=EZR PE=1 SV=4 | 1031229 | 333010 | 551990.1 | 838420.3 | 528792.782 | 478110.8313 | 868126.5845 | 1135087.158 | 937669.7275 | 1491527.05 | 890363.5542 | 758799.5739 | 815175.1644 | 825806.007 | 449352.7575 | 611747.0762 | 257941.9906 | 283889.5106 | 349872.7807 | 449418.6652 | 383848.7665 | 331072.0016 | 304896.9811 | 1299087.028 | 992592.955 | 317166.7892 | 615428.0777 | ||
| Q9HCN6 | 4 | 4 | 504.23 | 0.598739449 | 1.074954862 | XN | XA | Platelet glycoprotein VI OS=Homo sapiens GN=GP6 PE=1 SV=4 | 31266355 | 32067852 | 25972761 | 23828106 | 18229339.5 | 24608732.89 | 21231211.45 | 30395087.13 | 31068584.35 | 27056595.34 | 87561687.3 | 11129045.09 | 38731546.82 | 28393732.42 | 9114033.523 | 8334853.612 | 18400545.67 | 25804595.54 | 32485729.42 | 27732216.3 | 37195175.94 | 30459129.04 | 13217975.68 | 41093805.65 | 23478408.68 | 32237964.28 | 18656953.86 | ||
| P19021 | 16 | 12 | 502.78 | 0.330680479 | 1.178459579 | XN | XA | Peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAM PE=1 SV=2 | 7328575 | 4621184 | 3002430 | 5107714 | 3821516.728 | 4790148.58 | 3667535.371 | 3513297.048 | 4744427.554 | 3672930.18 | 4468706.347 | 3571009.19 | 5005553.114 | 2628545.719 | 4845111.673 | 5538528.144 | 5127787.355 | 6580685.298 | 4051184.502 | 6261641.122 | 5209879.249 | 3298017.704 | 4870732.696 | 4805086.667 | 6320129.097 | 5835968.96 | 7189080.892 | ||
| P23528 | 10 | 5 | 502.65 | 0.849632389 | 1.162951203 | HN | XA | Cofilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFL1 PE=1 SV=3 | 6293882 | 3071008 | 4221188 | 8909531 | 2230757.229 | 5585894.435 | 5754978.715 | 7685100.221 | 5484516.029 | 11575129.75 | 3675488.169 | 10266411.86 | 4696098.302 | 8921873.068 | 3572516.22 | 8473609.875 | 2673006.035 | 3405928.095 | 4255390.584 | 7006682.996 | 11412562.5 | 9789141.898 | 4534456.577 | 1151493.611 | 4530001.587 | 3496820.699 | 4727763.865 | ||
| P15328 | 9 | 8 | 502.59 | 0.52933628 | 1.241408455 | XA | XN | Folate receptor alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=FOLR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1.1E+08 | 36371084 | 23034792 | 59613206 | 26346177.22 | 48075406.16 | 42253322.27 | 47061426.37 | 43933979.29 | 53571048.77 | 38793090.53 | 34860403.3 | 75811939.84 | 48549099.61 | 34948523.92 | 31407750.71 | 31749295.31 | 73225379.78 | 44172861 | 50783910.52 | 39919309.27 | 41516597.32 | 37963110.26 | 13381867.4 | 27194574.35 | 35778187.33 | 61289066.36 | ||
| P49189 | 10 | 7 | 500.42 | 0.244180337 | 1.868687245 | HN | XA | 4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH9A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 5802617 | 4611129 | 7553630 | 5393113 | 5315976.048 | 5554572.314 | 5722278.736 | 5737059.114 | 4583699.377 | 16665397.63 | 25188198.65 | 7229368.178 | 14432798.83 | 9541730.134 | 2882747.52 | 5622563.972 | 6334590.736 | 6049127.201 | 4387136.964 | 14572007.27 | 7902332.59 | 6037254.148 | 2877569.175 | 7070670.165 | 3302474.702 | 21691345.61 | 6608111.811 | ||
| P29323 | 14 | 10 | 499.44 | 0.539552651 | 1.130487939 | XA | HN | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHB2 PE=1 SV=5 | 1922093 | 3426618 | 2370592 | 1257430 | 1039952.047 | 2111041.421 | 2889095.984 | 2513357.662 | 2361962.333 | 839038.1958 | 4243627.815 | 1542374.062 | 3757786.556 | 2378403.224 | 1537063.99 | 567297.6087 | 1343738.543 | 1386738.502 | 2121068.385 | 2083559.06 | 1998967.274 | 1551140.381 | 1896836.018 | 3684248.147 | 1228709.141 | 1717834.468 | 1522083.832 | ||
| Q96J84 | 6 | 4 | 498.26 | 0.46612088 | 1.373000672 | XN | XA | Kin of IRRE-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIRREL PE=1 SV=2 | 5174359 | 3733840 | 2520572 | 2788146 | 2970256.94 | 4302852.322 | 4588542.962 | 3247619.114 | 4694198.156 | 6065041.012 | 5602085.173 | 2468688.597 | 5420987.511 | 3452522.408 | 2144316.512 | 1316669.032 | 4540851.412 | 3770795.744 | 6622422.152 | 4866314.005 | 2860215.145 | 13481370.06 | 2108819.395 | 5696109.047 | 3540093.577 | 3828212.643 | 3706458.804 | ||
| Q8WUM4 | 11 | 10 | 497.86 | 0.044844753 | 2.50444627 | XA | XN | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6IP PE=1 SV=1 | 1823165 | 581025.6 | 1205299 | 1402252 | 1068639.93 | 8917852.809 | 1593022.16 | 2220441.486 | 986796.0007 | 785213.0105 | 1293505.042 | 1674656.199 | 755700.7223 | 1798392.43 | 461386.2199 | 950787.6538 | 413794.9222 | 588091.3216 | 959218.5372 | 842475.2175 | 766616.2556 | 474228.3791 | 562417.0834 | 460070.7908 | 1054797.921 | 1047239.032 | 1738275.075 | ||
| P49747 | 8 | 5 | 494.67 | 0.186127374 | 1.311063664 | HN | XA | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMP PE=1 SV=2 | 28771746 | 14728794 | 12968937 | 15496444 | 12418367.3 | 12819917.33 | 8629205.151 | 11475803.26 | 7629949.866 | 29640701.85 | 24624913.9 | 9421016.964 | 12304487.01 | 18485764.27 | 10994718.84 | 15012807.09 | 17175643.32 | 26143144.91 | 15969761.35 | 19852038.7 | 20363837.51 | 10871126.45 | 27777013.81 | 16154826.94 | 17133188.8 | 14227562.36 | 16158982.21 | ||
| P08311 | 11 | 3 | 489.81 | 0.316783878 | 12.44907949 | XA | HN | Cathepsin G OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSG PE=1 SV=2 | 373139.4 | 596482.6 | 680395 | 392645.4 | 201271.6997 | 39206517.39 | 51733674.48 | 10328284.18 | 20033255.79 | 3692834.11 | 821010.7805 | 1622097.281 | 366821.6832 | 502138.3624 | 1474654.169 | 668734.5136 | 323547.8232 | 452241.688 | 65506825.12 | 806780.3173 | 342101.3883 | 3795948.467 | 336607.9546 | 257565.9083 | 842887.8314 | 413366.4003 | 361441.592 | ||
| P02763 | 8 | 5 | 489.66 | 0.47041767 | 1.708979926 | HN | XN | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ORM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1956845 | 6413668 | 13581790 | 4880789 | 30935274.09 | 1919121.784 | 1379237.488 | 3817757.627 | 2305160.697 | 8126027.69 | 1631951.456 | 37208848.85 | 2097325.368 | 3929866.332 | 6057861.973 | 18828920.27 | 11968178.57 | 9517646.663 | 3807776.016 | 2624794.655 | 3645386.033 | 4105016.607 | 4502561.46 | 27539321.04 | 2703987.914 | 4621064.206 | 4593915.553 | ||
| P13284 | 4 | 2 | 489.2 | 0.134464817 | 1.599391329 | XA | HN | Gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=IFI30 PE=1 SV=3 | 608467.4 | 2657689 | 3273154 | 1399341 | 1551381.577 | 1240969.748 | 1255758.706 | 646506.6556 | 1233727.386 | 409975.4867 | 727437.9893 | 893313.5182 | 555371.2141 | 1227653.332 | 1228603.421 | 817663.8826 | 1607538.624 | 1202612.826 | 756641.2292 | 857905.7056 | 1477922.691 | 960179.7871 | 2049831.526 | 1580357.327 | 984958.2978 | 1959504.622 | 1852447.017 | ||
| P37802 | 9 | 8 | 489.12 | 0.492829406 | 1.410333819 | HN | XN | Transgelin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAGLN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 3421431 | 1358556 | 1165399 | 3956688 | 963405.2894 | 1548200.617 | 2723690.348 | 4401452.67 | 3049611.106 | 5297363.122 | 2761551.04 | 4771575.447 | 3257577.944 | 2099188.782 | 1299887.677 | 2398497.141 | 1112009.939 | 1383125.422 | 2870709.938 | 1600827.372 | 3451671.387 | 2537694.019 | 1875405.465 | 1245951.437 | 1314680.16 | 1226328.166 | 1163970.144 | ||
| Q9NY97 | 9 | 7 | 488.53 | 0.03481936 | 1.469107398 | XA | HN | UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=B3GNT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 4182418 | 2135626 | 2336307 | 3985233 | 2068685.403 | 2879617.526 | 2326077.945 | 4173383.735 | 3055480.852 | 1783397.079 | 1529340.147 | 1609579.931 | 2354342.322 | 1592490.379 | 1905418.639 | 2527246.15 | 2533469.062 | 2640444.288 | 2116607.943 | 2037330.769 | 2646166.401 | 2009924.191 | 2935238.557 | 1676016.649 | 4758085.326 | 3174681.917 | 4420910.945 | ||
| Q01459 | 8 | 6 | 487.74 | 0.260961935 | 1.353831966 | XA | XN | Di-N-acetylchitobiase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTBS PE=1 SV=1 | 3069967 | 8308159 | 10503266 | 3738345 | 5671863.891 | 3585831.932 | 4463745.409 | 5046762.937 | 7357512.753 | 3348616.511 | 5329891.922 | 4259956.302 | 4286157.899 | 3468340.031 | 6073975.468 | 3175001.183 | 4190405.371 | 7160906.149 | 2700030.373 | 5036161.306 | 3977962.342 | 4772665.162 | 2471105.47 | 6910229.975 | 2080104.569 | 5494707.038 | 4778507.507 | ||
| Q9Y490 | 13 | 4 | 487.32 | 0.407695844 | 1.861409238 | HN | XN | Talin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 427493.1 | 90924.47 | 241785.1 | 186840.7 | 385028.0769 | 334350.714 | 262825.9193 | 176319.3934 | 902789.7821 | 1169850.001 | 311875.0234 | 562658.1669 | 126862.485 | 300769.9961 | 862807.2311 | 1081581.577 | 200895.6783 | 74564.11204 | 921840.444 | 196863.8504 | 180711.8748 | 206200.7146 | 276553.5784 | 180791.1723 | 93338.73161 | 356496.0136 | 107801.5498 | ||
| O75874 | 14 | 9 | 484.54 | 0.045012853 | 1.812545796 | XA | HN | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=IDH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2496102 | 2216807 | 1917331 | 2182927 | 1708674.524 | 3938421.699 | 5715545.987 | 3143318.352 | 2519886.884 | 1616875.607 | 1350660.432 | 1735966.071 | 543520.3922 | 2778462.668 | 2696400.327 | 812048.2719 | 1213880.859 | 1507834.006 | 1648033.378 | 743094.4204 | 5853637.603 | 2610091.901 | 1853006.731 | 353069.9654 | 1619552.35 | 1239350.691 | 684464.667 | ||
| Q01973 | 9 | 7 | 483.87 | 0.921470733 | 1.024608368 | XA | XN | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ROR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 10805466 | 8344688 | 9937527 | 16593335 | 9446204.362 | 5370050.497 | 3238792.875 | 9857278.286 | 5291702.652 | 12511076.88 | 9468145.905 | 8453116.137 | 5896429.562 | 6786021.297 | 5039959.782 | 10229644.15 | 10100296.86 | 9483124.118 | 7042776.783 | 9037561.155 | 7637655.472 | 9028730.596 | 8726763.372 | 11348334.35 | 7435804.957 | 7180084.116 | 9552724.864 | ||
| P49221 | 14 | 11 | 483.59 | 0.630790773 | 5.058621614 | HN | XN | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGM4 PE=1 SV=2 | 702732.4 | 1046645 | 1021489 | 1403408 | 918619.1206 | 697614.4485 | 776812.7599 | 1141822.001 | 1023821.198 | 324990.529 | 992899.4317 | 603252.2302 | 745735.6775 | 384737.5784 | 26698918.79 | 386458.9136 | 696605.0181 | 679941.0326 | 580050.0054 | 621463.4452 | 533305.7692 | 795724.6723 | 450381.939 | 1223658.494 | 630985.9607 | 684240.8051 | 709858.097 | ||
| Q99519 | 7 | 6 | 483.39 | 0.484526898 | 1.182748605 | HN | XN | Sialidase-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEU1 PE=1 SV=1 | 10895284 | 8316306 | 18373973 | 7815918 | 10885448.04 | 7072341.355 | 6799861.618 | 12656887.09 | 5113176.663 | 10289970.71 | 6524680.493 | 11147468.07 | 7478855.059 | 10315582.37 | 11608227.56 | 19020718.4 | 14383846.87 | 7646817.753 | 6456226.555 | 6177316.589 | 8428976.71 | 5441559.628 | 23764854.65 | 5683326.077 | 9794578.517 | 9006276.272 | 8456594.058 | ||
| P25940 | 14 | 6 | 479.44 | 0.507084004 | 1.232312682 | XA | HN | Collagen alpha-3(V) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL5A3 PE=1 SV=3 | 3199888 | 5073458 | 4904300 | 3135079 | 2525206.83 | 7093951.25 | 6565691.78 | 4392539.6 | 8974916.186 | 4962084.752 | 6162947.431 | 2517320.857 | 7958641.881 | 4758107.869 | 3013011.165 | 1103352.176 | 2839339.676 | 3903857.564 | 4367612.524 | 4289428.528 | 4265964.915 | 2735497.909 | 2137892.023 | 7325794.184 | 5593457.492 | 5498397.264 | 2240729.455 | ||
| Q8IV08 | 9 | 5 | 479.23 | 0.669076901 | 1.220746416 | XA | HN | Phospholipase D3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLD3 PE=1 SV=1 | 20843899 | 8418193 | 20083918 | 23914082 | 9794537.857 | 11998586.42 | 12305644.45 | 20225779.58 | 10149436.92 | 10412859.18 | 10242216.76 | 9524433.985 | 14183704.86 | 14779765.71 | 9195891.134 | 17748722.56 | 20135691.04 | 6604469.263 | 6588466.67 | 6578953.32 | 11672355.64 | 9734550.25 | 28256943.46 | 7755243.571 | 21227042.17 | 18157028.46 | 21270185.31 | ||
| P55957 | 5 | 4 | 478.6 | 0.442946487 | 1.405177929 | HN | XA | BH3-interacting domain death agonist OS=Homo sapiens GN=BID PE=1 SV=1 | 2750494 | 723775.9 | 989631.7 | 2284066 | 1243236.071 | 1161911.742 | 779888.2423 | 1888637.147 | 815856.3292 | 1403681.995 | 2064244.054 | 770601.6403 | 1232184.797 | 2039467.625 | 1130140.628 | 6224816.326 | 1249018.091 | 1643777.134 | 2229544.6 | 1629869.322 | 1479178.087 | 1136581.64 | 1391970.097 | 1496757.579 | 1803669.727 | 1987646.747 | 1264853.914 | ||
| P12429 | 11 | 8 | 478.43 | 0.057984344 | 4.624756553 | XA | HN | Annexin A3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA3 PE=1 SV=3 | 101428.1 | 152982.7 | 334534 | 370424.6 | 399399.8839 | 1274662.843 | 3582815.703 | 1265678.466 | 3315108.736 | 183316.8469 | 485661.6106 | 490580.7861 | 456907.9979 | 54093.69108 | 337932.4698 | 93511.24338 | 52152.17649 | 180460.1556 | 2573251.289 | 110801.2571 | 152833.4163 | 718122.9794 | 108775.951 | 46370.16475 | 158777.5923 | 65186.71792 | 187368.1388 | ||
| P48745 | 5 | 4 | 478.11 | 0.591118118 | 1.302504399 | HN | XA | Protein NOV homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOV PE=1 SV=1 | 8792928 | 13214960 | 15507912 | 18700703 | 16589786.86 | 11335975.87 | 9127042.404 | 7128966.146 | 10956330.94 | 6475716.675 | 15530883.7 | 4133292.878 | 9762136.326 | 17062739.49 | 23171615.7 | 26829697.24 | 16903565.18 | 25170215.51 | 10131913.1 | 16638352.06 | 11638871.59 | 11098015.77 | 15743725.24 | 25612154.17 | 12221098.26 | 15318694.46 | 18479478.39 | ||
| P13929;P09104 | 9 | 1 | 476.6 | 0.121387169 | 3.438985591 | XA | XN | Beta-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO3 PE=1 SV=4 | 52819.88 | 25316.84 | 29045.2 | 14451.94 | 52816.6696 | 2660.506624 | 43598.40974 | 142676.4734 | 713478.7024 | 57848.30422 | 158514.7048 | 346144.7664 | 26019.81635 | 94853.52034 | 44637.59829 | 61046.9673 | 83111.34848 | 170480.6526 | 36582.54503 | 48958.77986 | 48860.80897 | 14823.50907 | 23160.8947 | 28014.32413 | 26794.74412 | 36860.03956 | 49078.73427 | ||
| Q14019 | 8 | 4 | 476.52 | 0.799666091 | 1.369814497 | HN | XN | Coactosin-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COTL1 PE=1 SV=3 | 9571302 | 4764259 | 4072104 | 5762225 | 2287446.532 | 13295109.45 | 15478173.33 | 13858414.59 | 7057207.642 | 8129122.128 | 10268362.38 | 9870067.59 | 11478278.66 | 6104395.129 | 2218213.755 | 26616072.37 | 3574984.88 | 4063777.397 | 7645958.109 | 6592668.161 | 11060517.6 | 12069828.14 | 7196583.933 | 4553084.538 | 3902991.388 | 4254782.236 | 2821704.613 | ||
| P42330;P52895;Q04828 | 7 | 4 | 475.71 | 0.003794948 | 2.964041427 | XA | HN | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1C3 PE=1 SV=4 | 3664160 | 745151.8 | 1896833 | 5839212 | 1314640.701 | 3190250.993 | 2870115.357 | 5655678.654 | 4162343.987 | 1086543.996 | 752531.2524 | 1176037.672 | 1969948.231 | 534984.0673 | 812228.8931 | 1798134.645 | 1021380.912 | 746313.0081 | 1242439.166 | 940902.1888 | 2247210.451 | 1327761.342 | 3156573.551 | 357960.6072 | 1879770.757 | 891871.2208 | 1141750.364 | ||
| Q03405 | 7 | 6 | 472.26 | 0.827365942 | 1.188580453 | HN | XN | Urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLAUR PE=1 SV=1 | 2379139 | 4926534 | 3944047 | 2401062 | 2776585.561 | 6384520.4 | 6058880.474 | 4504211.456 | 6895348.76 | 3315260.593 | 6509559 | 13453556.24 | 3384194.55 | 2361985.069 | 4318009.781 | 4710009.779 | 3493146.046 | 5873109.224 | 4471369.234 | 8764762.33 | 3366913.478 | 2887254.217 | 3516534.543 | 6652845.935 | 2901799.658 | 3561154.232 | 3772713.946 | ||
| Q93099 | 11 | 9 | 472.21 | 0.217262807 | 1.822353146 | XA | HN | Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=HGD PE=1 SV=2 | 2632692 | 757451.7 | 1593172 | 3139345 | 903527.5722 | 5960848.398 | 3051062.039 | 4394167.249 | 3432716.784 | 1267444.66 | 549646.9588 | 1855507.685 | 4041560.399 | 432329.2426 | 1486158.287 | 1189659.017 | 1766144.367 | 1604727.623 | 2926799.141 | 2165179.398 | 4683337.18 | 4186137.365 | 1169222.529 | 407854.1159 | 1353779.661 | 1535696.145 | 1443332.016 | ||
| Q9UHI8 | 7 | 5 | 470.08 | 0.668890526 | 1.992665895 | HN | XN | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTS1 PE=1 SV=4 | 3689480 | 1878475 | 3922826 | 9151264 | 4428145.236 | 2297768.939 | 2304223.983 | 2796035.584 | 1628006.681 | 5011029.216 | 1514830.98 | 1737448.584 | 2950959.123 | 3026183.623 | 3763712.228 | 36793051.89 | 4110156.527 | 4356628.459 | 3196573.316 | 2614456.152 | 2591789.693 | 3945739.671 | 5530140.138 | 2655670.074 | 5307256.312 | 2463351.691 | 3443446.402 | ||
| P00338 | 11 | 5 | 469.4 | 0.203254707 | 1.662861428 | HN | XN | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHA PE=1 SV=2 | 594395.7 | 805806.4 | 1027362 | 1169671 | 485954.1531 | 1468263.392 | 1947040.992 | 1805539.405 | 2266190.952 | 3555918.713 | 681456.0999 | 1406128.515 | 1501271.717 | 1234822.821 | 1682812.477 | 358215.4848 | 567782.2084 | 981473.8369 | 1347668.691 | 546555.7004 | 918338.5804 | 1379114.4 | 886080.5562 | 377315.4826 | 552766.9227 | 470669.1884 | 719854.496 | ||
| P55268 | 14 | 9 | 468.26 | 0.494002822 | 1.266845203 | HN | XA | Laminin subunit beta-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2755658 | 2190094 | 2077641 | 2936311 | 3992619.243 | 1612829.572 | 839941.5255 | 2250731.966 | 1161799.251 | 1935471.074 | 3146371.574 | 1018807.185 | 2357531.565 | 3584116.16 | 2733768.577 | 5440975.089 | 2295770.381 | 2593051.74 | 1229440.89 | 1424210.591 | 1385242.001 | 1185641.008 | 3417043.715 | 3287022.794 | 2501395.488 | 2871250.667 | 3038307.649 | ||
| P17858 | 9 | 5 | 466.97 | 0.011998713 | 2.81302432 | XA | HN | 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFKL PE=1 SV=6 | 978256.8 | 180608.1 | 641485.6 | 2627866 | 702317.8278 | 676226.1244 | 433026.2416 | 1241435.712 | 621465.4725 | 260698.905 | 261098.0355 | 410480.9219 | 488060.992 | 173167.3 | 454945.0166 | 491878.7649 | 125429.4207 | 214659.3657 | 294555.5343 | 161584.2884 | 637749.6845 | 168805.505 | 683272.4589 | 138574.8817 | 526994.1296 | 314143.5615 | 608782.8429 | ||
| A6NI73 | 5 | 4 | 466.25 | 0.927512547 | 1.013940187 | XN | HN | Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily A member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LILRA5 PE=1 SV=1 | 3431740 | 2549664 | 3299493 | 4363741 | 2595639.635 | 9594621.124 | 4678919.386 | 5043899.984 | 5007745.318 | 5313821.782 | 7119856.081 | 4130279.576 | 7329159.778 | 5054761.947 | 1942789.504 | 2094810.283 | 4528820.758 | 2784412.955 | 5266334.451 | 6105141.306 | 4365508.256 | 5270849.268 | 2360028.278 | 2995472.491 | 5674598.657 | 4274000.814 | 4548550.754 | ||
| O00244 | 5 | 4 | 466.18 | 0.622513035 | 3.383579334 | HN | XN | Copper transport protein ATOX1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATOX1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1042669 | 981407 | 1448404 | 2843453 | 7918630.251 | 590068.7762 | 689726.8321 | 1197434.49 | 360459.237 | 1822401.782 | 1063796.798 | 610556.6946 | 409897.5658 | 1054436.239 | 2929286.331 | 26009523.2 | 1880840.911 | 1376381.128 | 848493.5891 | 838701.3478 | 1147883.928 | 1085282.733 | 2664745.415 | 963931.9706 | 1586137.528 | 809407.791 | 1037017.421 | ||
| O60701 | 12 | 7 | 466.1 | 0.86481637 | 1.301873518 | XN | HN | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=UGDH PE=1 SV=1 | 2968203 | 684335.7 | 1191371 | 1214513 | 599430.5531 | 1539454.344 | 2997570.334 | 4015922.127 | 1548737.359 | 2849566.157 | 1941463.441 | 2379337.985 | 1739987.539 | 1159304.501 | 879561.5026 | 1065056.735 | 572333.0206 | 1032451.97 | 6267531.878 | 1255046.327 | 2955925.514 | 2159802.812 | 1292149.62 | 1079767.614 | 871161.4261 | 756002.1933 | 1092909.886 | ||
| Q9UKU6 | 14 | 12 | 463.41 | 0.096425286 | 1.740395754 | XA | HN | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-degrading ectoenzyme OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRHDE PE=2 SV=1 | 2415771 | 3338990 | 2271209 | 1036009 | 1319982.387 | 3313101.913 | 2901733.391 | 1810513.899 | 6595533.167 | 1175648.392 | 1385016.42 | 1581527.672 | 3302690.68 | 1509013.667 | 1029369.122 | 1571404.707 | 2049898.842 | 761613.0179 | 2527886.004 | 1361531.532 | 1724672.896 | 965885.8399 | 1000649.584 | 1168667.521 | 2546569.402 | 2902796.785 | 2725054.557 | ||
| P62937 | 7 | 3 | 461.87 | 0.092708675 | 1.619757014 | XA | HN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPIA PE=1 SV=2 | 3705580 | 1483113 | 2271232 | 5371701 | 1796573.492 | 1737322.362 | 3455113.079 | 5277653.101 | 2510310.506 | 1446086.177 | 1428835.914 | 4604166.853 | 1537376.055 | 1463279.332 | 1158221.928 | 2468485.912 | 1032920.252 | 1905529.076 | 950821.0317 | 1371297.729 | 3521893.677 | 2255431.799 | 3728473.856 | 804537.7291 | 1912120.249 | 1576370.953 | 2334399.1 | ||
| P13716 | 7 | 7 | 461.52 | 0.073906188 | 2.287228217 | XN | HN | Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALAD PE=1 SV=1 | 2580804 | 2002600 | 1463444 | 1879003 | 2638960.254 | 3992136.59 | 4403374.933 | 4317252.28 | 3023403.498 | 2098280.741 | 955486.2474 | 4363543.914 | 2225562.557 | 822178.6403 | 992739.1002 | 1188702.437 | 1382696.862 | 1692809.977 | 3880196.194 | 8356171.49 | 3352315.807 | 3138360.1 | 1462234.824 | 1473853.788 | 916919.8151 | 1640165.722 | 11739585.37 | ||
| P06731;P13688;P40199 | 7 | 6 | 460.34 | 0.933719472 | 4.208009161 | XN | HN | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEACAM5 PE=1 SV=3 | 334355.9 | 113524.2 | 173866.6 | 70112.63 | 723446.4475 | 485356.6018 | 1137243.751 | 387196.0911 | 489077.6073 | 551127.1387 | 409542.6936 | 504276.1801 | 200661.6391 | 128878.2176 | 293614.7015 | 669493.7742 | 632158.4684 | 148387.0694 | 12603830.81 | 522605.8733 | 167118.8968 | 533833.5997 | 87095.67274 | 226449.4155 | 309762.4006 | 240878.3113 | 196950.0617 | ||
| Q86UD1 | 9 | 6 | 456.09 | 0.326967956 | 1.517491683 | XA | HN | Out at first protein homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=OAF PE=2 SV=1 | 9762640 | 3352939 | 2588923 | 5902735 | 2596742.618 | 2662434.621 | 2306175.905 | 7028011.301 | 2823731.184 | 2835078.195 | 1279856.991 | 2573340.905 | 2919792.714 | 998182.1584 | 1981252.814 | 4824510.914 | 4315246.996 | 3989078.337 | 2840965.594 | 3851419.825 | 4161666.91 | 3090652.665 | 5176628.853 | 738941.146 | 3659458.642 | 3932506.439 | 5274049.308 | ||
| P62258 | 11 | 7 | 455.32 | 0.84418443 | 1.225333224 | XA | XN | 14-3-3 protein epsilon OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAE PE=1 SV=1 | 2409803 | 903572.1 | 1188020 | 1524799 | 1113608.422 | 3253839.322 | 3358928.419 | 3452005.912 | 3176847.203 | 2654859.828 | 4693972.191 | 3160156.068 | 2682038.111 | 2004279.346 | 1574793.554 | 1599748.295 | 686402.2504 | 1118803.049 | 1618744.849 | 1529482.75 | 2877894.034 | 3034255.61 | 1836631.997 | 1515958.713 | 1208650.017 | 1453488.858 | 1558265.78 | ||
| P02511 | 7 | 6 | 454.72 | 0.684791168 | 1.6598811 | XA | HN | Alpha-crystallin B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRYAB PE=1 SV=2 | 8091011 | 555355.5 | 1598856 | 10796936 | 632229.9963 | 3929109.514 | 4146847.318 | 5136193.412 | 3783581.972 | 1894018.695 | 3638647.09 | 3833048.873 | 6366557.955 | 798202.8364 | 1798586.718 | 2765098.709 | 1202783.882 | 999977.5658 | 1943551.475 | 2177070.93 | 4959070.702 | 6709843.75 | 2340376.251 | 1046093.709 | 3809879.196 | 1621009.416 | 2034281.817 | ||
| Q16661 | 6 | 5 | 454.33 | 0.469596628 | 21.23953163 | HN | XN | Guanylate cyclase activator 2B OS=Homo sapiens GN=GUCA2B PE=1 SV=1 | 9942562 | 7856036 | 17295622 | 18165463 | 70809743.93 | 5919797.643 | 7747821.565 | 5039518.033 | 8306043.85 | 5214986.713 | 10286542.52 | 8760183.444 | 10635454.51 | 11379506.52 | 13671974.56 | 1506160882 | 6934128.974 | 5376642.903 | 5926051.845 | 7745551.001 | 6158678.345 | 5248203.867 | 10962542.47 | 10715322.12 | 14134230.38 | 6086780.435 | 7337851.849 | ||
| Q02413 | 10 | 6 | 454.3 | 0.054127678 | 1.687582167 | XA | XN | Desmoglein-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1006193 | 946126.9 | 1184656 | 2127760 | 1544277.539 | 787154.744 | 854574.5476 | 1782692.656 | 1737308.458 | 1898557.298 | 242934.7384 | 968601.3992 | 536486.2153 | 470365.0613 | 1105663.706 | 1121993.588 | 1456567.467 | 762813.3006 | 736431.6135 | 443351.8553 | 346522.0241 | 410633.7451 | 1999103.224 | 1544953.945 | 473950.0918 | 510331.3485 | 628151.0991 | ||
| P05109 | 11 | 8 | 454.29 | 0.980319209 | 3.5814282 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A8 PE=1 SV=1 | 2966862 | 3682990 | 2420657 | 2726474 | 2421607.965 | 43627040.77 | 124606697.3 | 54993733.5 | 88157240.08 | 12229665.42 | 24008653.65 | 36886217.21 | 43964628.03 | 4219509.901 | 19596396.77 | 3111181.351 | 2926716.367 | 4038090.566 | 459720046.8 | 24000292.5 | 14325586.91 | 19352281.09 | 1666093.094 | 2705134.09 | 13189155.72 | 2712544.038 | 3056689.014 | ||
| O75340 | 7 | 6 | 453.76 | 0.305308092 | 1.573170502 | XA | XN | Programmed cell death protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6 PE=1 SV=1 | 2640811 | 1350264 | 874733.7 | 1855942 | 808639.1224 | 2115545.187 | 2465404.327 | 3891282.205 | 2416462.978 | 2433230.606 | 5240440.718 | 1948000.531 | 867452.3182 | 1923690.308 | 580877.3954 | 969651.9493 | 753422.9591 | 903082.1592 | 1882860.193 | 1455949.165 | 1665064.682 | 951304.1954 | 859948.3921 | 1004377.578 | 1084688.91 | 1244884.852 | 1559178.461 | ||
| O95154 | 7 | 5 | 453.74 | 0.103722708 | 2.331062583 | XA | HN | Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR7A3 PE=1 SV=2 | 3484619 | 978732.8 | 2573971 | 10308599 | 717310.1206 | 3681564.26 | 3463464.024 | 8101567.673 | 2763547.529 | 1960773.646 | 1081983.109 | 3149281.436 | 2882983.979 | 854665.0575 | 906010.5946 | 2769097.104 | 829215.4895 | 1041067.939 | 1832136.722 | 1629663.232 | 2643077.789 | 1428341.581 | 3869101.629 | 585500.6776 | 2558622.611 | 2621833.167 | 1714116.641 | ||
| O95998 | 5 | 4 | 453.29 | 0.73690215 | 1.228304003 | HN | XA | Interleukin-18-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL18BP PE=1 SV=2 | 29840193 | 23690999 | 16559136 | 23678433 | 13070586.07 | 39821795.51 | 41535730.72 | 23783221.21 | 37210388.16 | 48432308.4 | 88339765.66 | 14389756.59 | 48757819.19 | 32091874.96 | 12891134.04 | 7620381.99 | 21631585.17 | 31927041.43 | 38408666.35 | 30717462.39 | 41331496.38 | 22887987.41 | 18751502.73 | 30585310.89 | 27510982.09 | 43213322.25 | 34847780.52 | ||
| O43240 | 7 | 7 | 451.71 | 0.689309388 | 1.938302507 | XA | HN | Kallikrein-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK10 PE=1 SV=3 | 1468147 | 498852.1 | 2166195 | 591387.9 | 539933.5305 | 2718171.908 | 5981271.225 | 9537272.845 | 2235488.619 | 2109187.285 | 1112832.019 | 3927241.89 | 1130938.982 | 1299775.395 | 505810.2421 | 1465268.067 | 728659.2857 | 998255.0993 | 10044308.14 | 4231636.8 | 1961708.852 | 2890630.98 | 1043168.304 | 560022.2404 | 640201.5989 | 655291.5329 | 1336834.573 | ||
| P26927 | 12 | 5 | 448.99 | 0.360045615 | 1.232191737 | XA | XN | Hepatocyte growth factor-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MST1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2979208 | 1532582 | 2056482 | 2177441 | 2152594.005 | 3320665.655 | 1676885.194 | 2059126.136 | 1647533.886 | 1923538.943 | 3273606.676 | 810055.5328 | 2449018.748 | 2958077.916 | 1224295.415 | 1851666.002 | 1362130.86 | 1218783.724 | 1264234.028 | 1364058.573 | 2214138.724 | 1476756.016 | 1281764.999 | 2319604.78 | 2329190.177 | 1753289.224 | 1905622.747 | ||
| P52758 | 7 | 6 | 448.21 | 0.721742243 | 1.108575878 | XA | HN | Ribonuclease UK114 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRSP12 PE=1 SV=1 | 2515310 | 2926400 | 3895335 | 3007851 | 1889113.147 | 9332350.718 | 13509246.05 | 5137621.374 | 11493749.82 | 3773782.072 | 6453039.324 | 18344707.5 | 8341690.069 | 2616020.431 | 2917061.562 | 1611970.595 | 2320408.471 | 2068140.517 | 4475741.681 | 4839132.892 | 7691222.7 | 10512769.44 | 2677029.412 | 6755702.256 | 2744645.353 | 6481478.601 | 3536022.029 | ||
| P00739 | 9 | 1 | 448.1 | 0.250789863 | 61.19518202 | XN | XA | Haptoglobin-related protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPR PE=1 SV=2 | 0 | 0 | 4537.818 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.186502321 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 891.4736104 | 1446.920983 | 0 | 115.7276239 | 26382.35415 | 11839.41362 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11872.50936 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 265892.7133 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P04275 | 12 | 4 | 446.66 | 0.002383947 | 1.863325371 | XA | HN | von Willebrand factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=VWF PE=1 SV=4 | 1791510 | 1176201 | 1588739 | 4119885 | 1273017.336 | 1425635.541 | 1401344.693 | 1926735.331 | 1965974.96 | 402575.5238 | 924717.0931 | 984191.3268 | 1272058.758 | 1490820.776 | 1012293.224 | 836567.3226 | 1240556.193 | 782077.1887 | 820564.297 | 878081.73 | 1069967.535 | 542695.4359 | 1444996.76 | 779809.9819 | 1665929.376 | 1065443.388 | 967942.3679 | ||
| Q9UBQ7 | 8 | 8 | 445.58 | 0.02484682 | 2.203329707 | XA | HN | Glyoxylate reductase/hydroxypyruvate reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRHPR PE=1 SV=1 | 3604272 | 1071460 | 1979141 | 6966829 | 1056775.618 | 2892369.196 | 3885221.429 | 5231889.68 | 2639809.294 | 2451787.506 | 1528168.675 | 2586165.558 | 1304417.883 | 870252.5148 | 1199421.786 | 1785516.177 | 736785.1814 | 848142.3477 | 1509619.167 | 801071.8872 | 3008611.876 | 2018843.99 | 3147055.686 | 683874.6471 | 1615364.778 | 1441912.52 | 942081.6222 | ||
| Q8NFT8 | 4 | 4 | 444.3 | 0.728903433 | 1.203585674 | XN | XA | Delta and Notch-like epidermal growth factor-related receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNER PE=1 SV=1 | 3163399 | 3941938 | 2110462 | 2828092 | 1610353.843 | 4117239.779 | 3037949.016 | 3128405.103 | 3267241.114 | 1087215.832 | 6202379.502 | 1788217.21 | 9688210.244 | 4390785.216 | 1573468.591 | 513864.1705 | 3325525.152 | 3211924.245 | 2476967.288 | 5666326.237 | 3382762.745 | 2229978.617 | 2061486.438 | 8931584.39 | 2586318.304 | 3092868.369 | 2315351.165 | ||
| O15240 | 6 | 6 | 444.23 | 0.175182214 | 1.518436893 | HN | XA | Neurosecretory protein VGF OS=Homo sapiens GN=VGF PE=1 SV=2 | 1688214 | 873245.7 | 1104283 | 1561621 | 1405933.294 | 1446794.201 | 1759963.142 | 1881565.524 | 1579803.695 | 2811728.895 | 3033564.685 | 875568.8134 | 1864929.551 | 1832462.252 | 2680964.969 | 3968299.182 | 802768.9955 | 2327083.651 | 1425111.039 | 1485092.438 | 2143686.854 | 1724911.617 | 2419112.583 | 2258658.85 | 2091342.787 | 1548789.095 | 1498942.697 | ||
| Q99969 | 5 | 4 | 443 | 0.46895215 | 1.237332494 | XN | HN | Retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RARRES2 PE=1 SV=1 | 11773793 | 6019027 | 3344328 | 5402411 | 6576292.997 | 4967760.591 | 5278306.301 | 6309722.391 | 3477039.991 | 2089323.274 | 1863493.336 | 4141835.477 | 7102821.764 | 890673.1719 | 5579570.042 | 11431198.05 | 7044180.305 | 7562342.938 | 11335593.51 | 3579424.538 | 5570001.381 | 3378599.945 | 8938443.305 | 2282075.731 | 11465285.38 | 6111314.378 | 6366750.851 | ||
| Q9BYF1 | 10 | 6 | 442.2 | 0.261778208 | 1.859725385 | HN | XA | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACE2 PE=1 SV=2 | 3038861 | 1338961 | 1888911 | 1224618 | 972129.5466 | 1569538.272 | 1096958.332 | 1238543.556 | 887923.0541 | 1527866.713 | 3599812.811 | 1058024.566 | 1071937.156 | 7780793.555 | 1650705.315 | 5193488.251 | 1442244.75 | 1328472.168 | 1351446.705 | 816979.6549 | 1424043.399 | 1794422.976 | 2629554.169 | 552057.984 | 1661148.366 | 1605697.094 | 3311216.231 | ||
| Q9GZX9 | 4 | 3 | 441.81 | 0.85106495 | 1.07238993 | XN | XA | Twisted gastrulation protein homolog 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TWSG1 PE=2 SV=1 | 52352737 | 30113332 | 37504504 | 70943545 | 50023041.86 | 34605750.93 | 24639743.71 | 44245676.44 | 27902292.61 | 50790414.58 | 49199457.13 | 24786054.2 | 28904462.48 | 49061929.53 | 22510823.12 | 63663077.87 | 43801660.2 | 53376697.94 | 35356367.18 | 58768306 | 32179030.01 | 27840715.71 | 34718296.87 | 52594762.89 | 48479130.71 | 50659388.85 | 58687612.29 | ||
| P32926 | 9 | 8 | 441.69 | 0.130800281 | 2.049205712 | XA | XN | Desmoglein-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSG3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1989776 | 1560959 | 2492417 | 2847896 | 1882222.927 | 2275782.657 | 5748579.921 | 7654760.965 | 9510654.319 | 11008396.59 | 3899011.334 | 8023440.328 | 2939920.313 | 2401108.265 | 1585554.275 | 3164171.341 | 1144319.503 | 910439.334 | 4457169.302 | 3493622.349 | 1481469.145 | 1182765.005 | 1528006.457 | 1621260.326 | 1471443.991 | 1002379.673 | 1311634.522 | ||
| Q8TF66 | 8 | 5 | 441.42 | 0.010852764 | 1.66208555 | XA | HN | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRRC15 PE=1 SV=2 | 9112159 | 4427939 | 4205688 | 2198800 | 2855032.353 | 5086465.158 | 3121601.928 | 5224775.962 | 3898001.796 | 2779576.244 | 3136207.436 | 1429696.433 | 2982393.209 | 1347450.581 | 1942163.041 | 2182482.922 | 5029744.825 | 3314928.525 | 2699934.736 | 4860453.351 | 3875839.757 | 2786250.942 | 5381226.607 | 5001753.079 | 4542599.914 | 4446985.714 | 3797149.005 | ||
| P68371;A6NKZ8;A6NNZ2;P04350;Q13509;Q13885;Q9BUF5;Q9BVA1 | 11 | 1 | 440.67 | 0.329319705 | 2.946277159 | XA | HN | Tubulin beta-4B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB4B PE=1 SV=1 | 26146.35 | 8158.963 | 6481.67 | 388452.8 | 22378.07832 | 29481.56389 | 53661.13159 | 194244.3026 | 24059.03752 | 4878.407675 | 17553.78241 | 8166.249023 | 52021.20637 | 4033.345205 | 14285.61244 | 123279.8469 | 20382.85392 | 10997.15723 | 169802.5417 | 16314.37912 | 34991.49959 | 28442.05563 | 15641.69469 | 12120.08141 | 4203.999057 | 22922.38801 | 15000.30131 | ||
| P01625;P06314 | 5 | 1 | 439.93 | 0.21519179 | 1.600698593 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-IV region Len OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=2 | 24258494 | 1.28E+08 | 80476321 | 57006632 | 75083369.91 | 44151033.01 | 59269078.73 | 39753705.43 | 25242773.55 | 46406101.21 | 16784290.23 | 62597892.91 | 67683435.74 | 53986029.62 | 52341600.8 | 60252212.19 | 28378165.22 | 36531324.19 | 44780647.12 | 36992601.81 | 31873560.5 | 54713482.13 | 38035561.34 | 42299504.42 | 26637031.55 | 36006437.01 | 21744172.3 | ||
| P54826 | 5 | 4 | 439.92 | 0.324644483 | 1.272546315 | HN | XA | Growth arrest-specific protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5319892 | 2572649 | 1762957 | 2470539 | 2192642.063 | 1646241.498 | 1425301.398 | 2497441.218 | 1867669.209 | 4304009.451 | 2862445.138 | 1800059.199 | 2907550.357 | 4163160.974 | 1539992.136 | 2202336.143 | 3004587.004 | 4900527.893 | 2437702.558 | 2775900.974 | 3619385.178 | 2171111.165 | 2315602.48 | 1686278.647 | 2572729.476 | 3648845.199 | 4071964.554 | ||
| Q9UIB8 | 5 | 4 | 439.1 | 0.698255411 | 1.124592995 | XN | XA | SLAM family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD84 PE=1 SV=1 | 6355693 | 11455667 | 5868943 | 2677642 | 8873014.504 | 5064814.435 | 8859933.679 | 4842664.712 | 10597873.33 | 9630153.617 | 10268565.31 | 4145529.24 | 6422003.294 | 5855445.285 | 4184654.365 | 2463813.478 | 12882793.9 | 10266289.32 | 11871511.37 | 5740230.897 | 8425385.019 | 7491016.164 | 4135186.924 | 12263936.69 | 6470425.527 | 7613088.89 | 8633705.183 | ||
| P04118 | 5 | 5 | 438.44 | 0.147142752 | 2.257612155 | HN | XN | Colipase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLPS PE=1 SV=2 | 3805325 | 1390525 | 1092447 | 1208972 | 1791136.324 | 278692.2622 | 1749451.585 | 428456.6721 | 409500.4832 | 1161251.613 | 2786476.259 | 2516250.891 | 623064.0477 | 2497851.541 | 2109084.585 | 8570839.106 | 1252059.008 | 758135.1757 | 652539.412 | 820901.6663 | 538760.2939 | 912515.6296 | 2228189.255 | 996384.2098 | 1236163.027 | 540104.2208 | 1941067.153 | ||
| P30044 | 7 | 6 | 437.76 | 0.284448856 | 1.545639246 | HN | XN | Peroxiredoxin-5, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX5 PE=1 SV=4 | 4022489 | 765427.4 | 2114689 | 6216612 | 2005131.983 | 2467083.616 | 3295512.846 | 1833158.48 | 2456236.947 | 4766487.567 | 4036746.123 | 5776525.041 | 1744826.61 | 2989222.726 | 1430739.416 | 3698104.8 | 1263417.455 | 1986351.616 | 1582620.881 | 990931.9375 | 3648062.503 | 2693709.2 | 2194764.347 | 902288.4051 | 2461372.544 | 1539519.995 | 1903214.538 | ||
| P20138 | 7 | 5 | 437.61 | 0.969899324 | 1.063843675 | HN | XN | Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD33 PE=1 SV=2 | 1970307 | 2799209 | 694731.9 | 367028.3 | 999768.11 | 1812603.823 | 3133921.708 | 1230136.181 | 2874352.646 | 3077240.511 | 4382193.209 | 1325507.227 | 792077.9312 | 903586.1986 | 1016407.552 | 593057.7076 | 2905186.611 | 1411571.506 | 3163995.226 | 1801044.485 | 2711749.156 | 1226627.775 | 765701.6837 | 1392614.591 | 1146530.499 | 2152721.618 | 1061232.378 | ||
| P00746 | 9 | 7 | 436.67 | 0.198711065 | 2.018114566 | XA | XN | Complement factor D OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFD PE=1 SV=5 | 1367207 | 318265.8 | 1164351 | 1426265 | 4176344.39 | 1322579.21 | 1602528.991 | 1611504.056 | 724191.0001 | 819872.7248 | 316589.2994 | 2305730.809 | 829082.3538 | 271734.0275 | 1182278.676 | 4117349.22 | 1149474.521 | 502407.8744 | 421833.3652 | 1060752.867 | 757559.6297 | 226913.364 | 880096.3795 | 302229.6584 | 883551.5189 | 1293637.552 | 968498.6696 | ||
| P17174 | 9 | 5 | 435.97 | 0.332197819 | 1.774398274 | XA | XN | Aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=GOT1 PE=1 SV=3 | 2411978 | 2708870 | 2720312 | 3108486 | 1352136.064 | 3606079.241 | 14270635.81 | 6078496.184 | 7850070.531 | 2298227.64 | 5649789.411 | 8405006.155 | 4706470.279 | 6179879.484 | 1410276.751 | 720998.6748 | 1108279.152 | 1222093.005 | 6554310.005 | 2616118.673 | 3324517.073 | 4367924.234 | 1967231.007 | 983992.6288 | 2361003.254 | 1655773.093 | 1026606.701 | ||
| P01617;P06309 | 4 | 2 | 435.91 | 0.034885768 | 1.837036487 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-II region TEW OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1.06E+08 | 1.71E+08 | 1.47E+08 | 1.88E+08 | 182000515.6 | 46892487.51 | 74267667.35 | 77236341.44 | 59439017.87 | 51557555.79 | 18878860.78 | 86246531.94 | 53424645.07 | 52619338.95 | 106831385.9 | 87928222.32 | 47666744.75 | 67343780 | 46285293.17 | 22824975.89 | 30128154.59 | 69635414.72 | 76449664.66 | 207331013.9 | 51297777.46 | 38647346.89 | 51316947.88 | ||
| Q99988 | 6 | 4 | 435.28 | 0.571659464 | 1.606079156 | HN | XA | Growth/differentiation factor 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GDF15 PE=1 SV=3 | 14979108 | 7062814 | 9342053 | 17034565 | 32388211.93 | 6882051.379 | 7061612.474 | 35648769.91 | 17017188.23 | 55053473.05 | 2242499.229 | 4706487.151 | 12112811.86 | 16808319.76 | 17296682.09 | 67242365.57 | 10173329.98 | 51126397.11 | 25358772.42 | 17822022.42 | 23488618.5 | 31676935.78 | 13619387.82 | 11227696.99 | 34585308.74 | 19119680.4 | 16768741.33 | ||
| Q08629;Q9BQ16 | 9 | 7 | 434.18 | 0.088441185 | 1.966084625 | XN | HN | Testican-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPOCK1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1614558 | 1622482 | 1178288 | 3088791 | 1051309.622 | 1031014.17 | 463275.2504 | 1785889.336 | 322141.5869 | 495400.1616 | 259760.3491 | 659031.1426 | 796222.4738 | 474260.9031 | 691034.5443 | 917342.9189 | 1254729.808 | 1656590.304 | 1069648.049 | 2445262.544 | 1124447.229 | 537291.5133 | 2220584.576 | 526768.4393 | 2105243.183 | 2313502.274 | 1821658.4 | ||
| P32004 | 17 | 12 | 434.14 | 0.356733244 | 1.22062074 | XA | XN | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=L1CAM PE=1 SV=2 | 3184746 | 1469646 | 2022143 | 2943279 | 1885962.011 | 2040271.858 | 1690068.473 | 1682192.397 | 2150022.447 | 890184.8926 | 992489.6915 | 1498182.945 | 2420568.538 | 818690.6198 | 1656386.721 | 2784622.601 | 2571670.657 | 2675712.065 | 2552921.228 | 1578709.617 | 1347715.131 | 992507.7801 | 2239485.62 | 1537134.654 | 1609953.746 | 2270073.778 | 1493328.731 | ||
| P19652 | 8 | 5 | 431.77 | 0.025066912 | 3.016863384 | HN | XN | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ORM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 990356.8 | 2782664 | 2572427 | 1745311 | 10796733.74 | 1153241.288 | 792278.9953 | 1329177.3 | 1003987.481 | 2475384.044 | 2472545.889 | 3398376.24 | 4120916.318 | 2244251.657 | 4287676.918 | 33607425.63 | 3781676.454 | 7021715.097 | 1344987.894 | 2453717.794 | 1559672.933 | 5487802.551 | 1884474.247 | 2027533.641 | 3108485.294 | 1571384.863 | 1580449.135 | ||
| P04632 | 9 | 5 | 431.53 | 0.603684322 | 1.88013628 | XN | HN | Calpain small subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPNS1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1022065 | 563831.7 | 422624.5 | 973819.1 | 603574.3407 | 1285104.841 | 1605310.879 | 4121775.863 | 1884161.809 | 3366182.658 | 662378.1063 | 1475032.28 | 1275297.252 | 404007.2044 | 550280.8775 | 639590.0509 | 352684.459 | 480517.3661 | 12645854.81 | 725172.1624 | 870294.5345 | 1150093.136 | 341634.3643 | 323917.1547 | 469746.5642 | 346490.7897 | 435275.1533 | ||
| O75071 | 6 | 4 | 430.63 | 0.612199842 | 1.169943793 | HN | XA | EF-hand domain-containing protein KIAA0494 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA0494 PE=1 SV=1 | 6784671 | 3917591 | 4921022 | 8882879 | 5571440.848 | 4005948.574 | 2967856.834 | 5319384.248 | 3939173.932 | 4969242.221 | 6034531.957 | 2491044.332 | 7769329.918 | 7368892.359 | 4376637.03 | 9198497.949 | 5275226.316 | 6696657.076 | 3409057.483 | 4998362.453 | 6411552.659 | 5381973.673 | 5317628.849 | 6476884.618 | 5264841.47 | 5885484.486 | 5443662.988 | ||
| P62805 | 7 | 6 | 430.06 | 0.659414964 | 4.073517181 | XA | HN | Histone H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H4A PE=1 SV=2 | 1109889 | 186042.2 | 122714 | 269346.8 | 276160.4157 | 16854040.01 | 11861333.64 | 9025596.576 | 18008172.23 | 4832239.397 | 1020720.345 | 1871636.514 | 594040.5681 | 192351.8796 | 3210105.051 | 1854374.898 | 341727.6203 | 250730.9208 | 32363125.55 | 1070632.199 | 345353.4417 | 2388191.914 | 343935.6324 | 72661.41467 | 474088.6372 | 578581.303 | 520353.9272 | ||
| Q8N307 | 6 | 5 | 429.89 | 0.173034972 | 1.504676478 | XA | HN | Mucin-20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC20 PE=1 SV=3 | 6564472 | 16929857 | 17110285 | 13233904 | 5375678.101 | 6177876.057 | 7442850.528 | 10653601.88 | 14894737.73 | 2876054.562 | 8083633.224 | 5889918.221 | 11807641.64 | 3653665.572 | 10336646.66 | 9246388.511 | 5393384.998 | 8097660.168 | 2742892.339 | 4814612.867 | 3580044.653 | 5295783.71 | 11833742.73 | 20413127.31 | 10143969.03 | 7005982.385 | 4859178.727 | ||
| P08263;Q16772 | 11 | 1 | 428.95 | 0.186334577 | 1.911082802 | XA | HN | Glutathione S-transferase A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 851091.8 | 350813.3 | 830201.2 | 1798037 | 172198.0925 | 1249972.181 | 1234150.55 | 1378430.998 | 1299101.528 | 878024.7234 | 560181.5988 | 1029835.054 | 517477.2514 | 484708.2277 | 362853.4605 | 360326.3185 | 227249.9233 | 374528.9354 | 586305.1582 | 560262.0087 | 1181984.5 | 1017138.628 | 1120669.735 | 159845.032 | 687149.6123 | 397097.6542 | 475084.6896 | ||
| P01037 | 5 | 2 | 427.21 | 0.977456311 | 5.520509702 | HN | XA | Cystatin-SN OS=Homo sapiens GN=CST1 PE=1 SV=3 | 236193.7 | 102812.1 | 256874.2 | 264455.9 | 615274.7393 | 39311.28935 | 120626.2584 | 116083.4234 | 68370.73897 | 18348.51238 | 177362.5253 | 12324.65723 | 183245.08 | 125823.5497 | 276773.3573 | 8879711.266 | 180734.1997 | 193017.5704 | 36956.22017 | 304286.4784 | 71710.19096 | 29726.00819 | 212391.9202 | 738201.1114 | 371503.163 | 115643.6881 | 148502.7421 | ||
| Q8NHP8 | 11 | 8 | 426.09 | 0.059217253 | 1.305011931 | XA | XN | Putative phospholipase B-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLBD2 PE=1 SV=2 | 5725412 | 3775674 | 6593183 | 5508356 | 5197423.057 | 4577846.999 | 3434209.454 | 3878804.057 | 4605225.382 | 4816985.57 | 3405931.619 | 3643083.716 | 6800789.788 | 4896394.487 | 5066697.415 | 3072847.53 | 4601360.241 | 3869625.475 | 3165521.396 | 2597000.585 | 3337905.327 | 4904506.221 | 5591883.515 | 2815078.383 | 3224177.266 | 3695557.11 | 3845180.534 | ||
| Q86UN3 | 10 | 4 | 425.62 | 0.779469788 | 1.295053206 | XN | HN | Reticulon-4 receptor-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RTN4RL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1978214 | 2201161 | 3118689 | 1169397 | 1194563.243 | 3800068.507 | 3641395.005 | 3697534.733 | 5147513.684 | 1742788.575 | 5031149.082 | 3015692.601 | 2736023.198 | 2669169.538 | 2421422.583 | 607151.1198 | 2041252.118 | 1334075.967 | 6986791.996 | 3900691.811 | 3168562.092 | 6594792.487 | 2150568.657 | 775578.465 | 1110535.365 | 1579976.196 | 1704000.715 | ||
| Q8NHJ6 | 6 | 4 | 424.18 | 0.27717151 | 1.356415523 | XA | XN | Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LILRB4 PE=1 SV=3 | 7975708 | 4982720 | 6065337 | 6861906 | 6346638.425 | 5392067.818 | 5309087.873 | 9703592.412 | 2891609.827 | 3590327.054 | 3453575.148 | 2771838.979 | 2988405.177 | 2587652.533 | 6956631.219 | 8792440.419 | 6398167.776 | 10443353.43 | 2336625.814 | 3711778.26 | 3536366.104 | 3824300.078 | 6224129.062 | 4270764.91 | 8251653.718 | 4810894.552 | 3971287.322 | ||
| P07741 | 6 | 4 | 424.03 | 0.631845527 | 1.513329951 | XA | XN | Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=APRT PE=1 SV=2 | 879207.7 | 233119.7 | 502066 | 2062921 | 345677.3762 | 635345.6884 | 906291.9058 | 1188766.435 | 233610.0478 | 684228.4065 | 555496.6621 | 840269.5735 | 522042.2502 | 339211.3622 | 369056.3872 | 1202118.785 | 506735.1879 | 246132.5789 | 489792.4187 | 310524.3341 | 1011189.386 | 462495.6208 | 729415.0041 | 314446.9872 | 583706.1939 | 447542.6133 | 267862.2689 | ||
| Q96P63 | 8 | 6 | 421.61 | 0.511694133 | 2.299637807 | XA | HN | Serpin B12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB12 PE=1 SV=1 | 815613.7 | 1027203 | 448611.8 | 2093159 | 487955.5011 | 3428379.03 | 8066450.036 | 6443329.896 | 10670577.12 | 1695097.942 | 2696570.55 | 2977012.353 | 3151182.96 | 653287.3249 | 477705.6818 | 1909394.958 | 335805.4851 | 663313.601 | 7335210.403 | 2475174.834 | 1704534.826 | 3144265.137 | 612657.5605 | 1218402.652 | 1096402.985 | 838622.0122 | 768000.2963 | ||
| P08138 | 5 | 5 | 420.9 | 0.115106204 | 2.40813194 | XA | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NGFR PE=1 SV=1 | 2634655 | 8969762 | 7578369 | 2137094 | 1823296.812 | 6369865.727 | 18007692.08 | 2656415.068 | 23833413.89 | 1690511.059 | 4614502.258 | 3166935.804 | 3320322.356 | 2328837.298 | 2233030.649 | 2035553.407 | 3753790.451 | 7590116.55 | 3453659.798 | 9554643.029 | 6637818.397 | 3673201.714 | 3710649.74 | 8239195.72 | 3346876.844 | 21971893.91 | 5163285.207 | ||
| P08519 | 6 | 4 | 419.73 | 0.381964197 | 1.16366882 | XA | HN | Apolipoprotein(a) OS=Homo sapiens GN=LPA PE=1 SV=1 | 17384399 | 14887008 | 17763706 | 20712935 | 18307304.26 | 59099132.97 | 33157729.11 | 20225567.65 | 18284192.12 | 16379862.81 | 82785637.62 | 9571350.498 | 15281286.83 | 28152860.68 | 3561780.929 | 3910642.425 | 11881699.67 | 17379118.45 | 16909824.54 | 71272408.95 | 24944333.17 | 20039536.75 | 5814650.323 | 12912654.18 | 8707494.228 | 25753920.9 | 28485247.45 | ||
| P35241 | 16 | 5 | 418.9 | 0.813901284 | 1.516895679 | HN | XN | Radixin OS=Homo sapiens GN=RDX PE=1 SV=1 | 7130082 | 6153166 | 5073703 | 12550992 | 9329893.604 | 3677285.563 | 2199726.801 | 3394243.309 | 2412339.822 | 5218870.068 | 2591906.185 | 5221134.965 | 2860232.666 | 3833909.4 | 10253309.16 | 30376794.45 | 5308898.089 | 5173751.314 | 6441453.812 | 3947145.188 | 3075381.252 | 4937788.661 | 5566129.988 | 4075696.832 | 10184925.9 | 3787824.058 | 4683508.03 | ||
| Q15223 | 6 | 3 | 417.46 | 0.900862287 | 1.083221268 | XN | XA | Poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVRL1 PE=1 SV=3 | 5756807 | 7573110 | 6908295 | 4819845 | 3046358.019 | 6229207.139 | 7072852.335 | 5135951.04 | 9124129.835 | 4562539.877 | 12629943.82 | 7043056.973 | 8188527.65 | 9109393.891 | 4163699.361 | 1376774.296 | 6285256.566 | 5469321.066 | 6132452.276 | 8386552.072 | 12321289.64 | 5118535.757 | 3400835.523 | 8472201.754 | 4610123.485 | 6877081.003 | 4980125.661 | ||
| Q9BUT1 | 3 | 2 | 417.41 | 0.086358686 | 2.562479091 | XA | HN | 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase type 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BDH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 4987159 | 1307714 | 2193382 | 9854417 | 1290931.164 | 6237555.915 | 1443047.631 | 7585059.739 | 1868896.44 | 1530785.089 | 1167318.417 | 2421866.794 | 1600290.769 | 1413741.657 | 835306.5371 | 1670342.641 | 1612635.518 | 2096380.969 | 4227491.614 | 1616934.964 | 4065759.435 | 3979322.63 | 3238834.803 | 611972.3977 | 1951597.375 | 1502710.85 | 1370760.201 | ||
| P13598 | 4 | 3 | 417.25 | 0.33407049 | 1.331895594 | XN | XA | Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ICAM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 26462322 | 17703445 | 21725859 | 23559155 | 23158268.39 | 25809439.02 | 14957374.46 | 18038265.16 | 12848600.17 | 53146047.11 | 26550304.52 | 18399643.54 | 35378170.85 | 19486204.18 | 18240327.36 | 8788657.534 | 22533684.93 | 25871113.34 | 37001939.42 | 36634122.49 | 40071585.16 | 23880150.02 | 22687607.7 | 17455704.94 | 21133731.99 | 29538605.23 | 17015267.69 | ||
| Q14574 | 6 | 4 | 415.58 | 0.160108045 | 1.771967979 | XA | HN | Desmocollin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSC3 PE=1 SV=3 | 2894862 | 819012.9 | 1787656 | 4881866 | 982352.8626 | 793683.6255 | 1282141.766 | 3219124.86 | 2101866.114 | 624123.7576 | 2602238.472 | 1028784.582 | 1732680.143 | 856104.4563 | 892646.5526 | 669642.064 | 1285110.043 | 897216.7562 | 644665.6889 | 413594.3647 | 601701.4213 | 496080.5565 | 1103530.141 | 3069413.727 | 1941644.228 | 1424012.298 | 1974459.055 | ||
| P61626 | 8 | 7 | 415.1 | 0.273834337 | 2.06582705 | XA | XN | Lysozyme C OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYZ PE=1 SV=1 | 15405079 | 9596704 | 20215340 | 11221602 | 11696204.89 | 72875600.85 | 80336382.93 | 32384352.74 | 82040283.79 | 79788597.45 | 11017069.38 | 33826075.34 | 10372117.18 | 11065629.37 | 12418614.13 | 12814580.87 | 11643670.01 | 10973601.6 | 24707260.18 | 13110283.02 | 16956333.59 | 26209341.01 | 19577164.05 | 6134610.798 | 13375487.91 | 21511425.53 | 20954231.52 | ||
| P62158 | 6 | 5 | 414.59 | 0.817077117 | 1.16886525 | XA | HN | Calmodulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6834427 | 4342141 | 3695579 | 8439387 | 4577902.966 | 13708755.71 | 15480293.21 | 14391192.04 | 16985228.63 | 9068886.596 | 16564597.49 | 12121637.31 | 8924175.018 | 12650647.32 | 3554508.181 | 2394092.971 | 3650667.054 | 6746667.841 | 7778164.03 | 14356253.55 | 15438867.96 | 13383401.69 | 3954814.238 | 8220105.485 | 4911552.226 | 5836468.539 | 4404391.331 | ||
| O00462 | 9 | 8 | 414.32 | 0.652928562 | 1.106456086 | HN | XA | Beta-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MANBA PE=1 SV=3 | 2067295 | 1621032 | 1123427 | 902695.4 | 752729.7121 | 2282884.738 | 2595571.853 | 1085264.203 | 2382916.056 | 971304.3497 | 2778290.041 | 958795.1491 | 5733186.115 | 2782662.385 | 732600.2149 | 360746.0613 | 540379.0346 | 1532873.584 | 1661773.954 | 2526327.873 | 1945012.891 | 1357711.429 | 920305.6257 | 2704164.346 | 1384405.387 | 1561040.77 | 1644675.568 | ||
| Q6UY11 | 5 | 4 | 410.76 | 0.086864923 | 1.419302446 | XN | HN | Protein delta homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DLK2 PE=2 SV=1 | 4680381 | 2950482 | 2977834 | 6433549 | 3948432.857 | 4410817.512 | 3477640.614 | 3139181.336 | 3483864.911 | 4245561.981 | 5099391.589 | 1377783.77 | 3469397.376 | 4460049.216 | 1977365.286 | 1881300.38 | 2965860.608 | 5065310.965 | 4945452.148 | 5721190.533 | 4069160.423 | 2604408.09 | 4694636.122 | 8037003.659 | 3673188.614 | 4023063.73 | 5580262.045 | ||
| P10599 | 7 | 5 | 410.05 | 0.701441617 | 1.451843634 | XA | HN | Thioredoxin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TXN PE=1 SV=3 | 9419799 | 5345811 | 8149808 | 9110886 | 2755230.095 | 34499029.36 | 60080081.95 | 28457388.15 | 39516722.78 | 13260580.91 | 36815641.6 | 30576336.53 | 30677915.65 | 8602445.57 | 3826277.181 | 2096807.514 | 4542385.617 | 5521726.538 | 13734183.17 | 38656540.28 | 20090344.66 | 27342153.08 | 6502223.079 | 11439138.06 | 5677165.285 | 8274975.934 | 4839005.542 | ||
| P58499 | 8 | 4 | 409.11 | 0.392842759 | 1.231042389 | XA | XN | Protein FAM3B OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM3B PE=1 SV=2 | 5595821 | 5042325 | 3499539 | 4038090 | 3574460.685 | 6104971.269 | 4437417.348 | 5208890.385 | 7291584.514 | 8723078.202 | 5207594.027 | 4259470.487 | 6568250.305 | 5576318.226 | 2946987.988 | 1971049.432 | 3182964.621 | 2645872.813 | 3289317.519 | 3499618.435 | 4292974.51 | 3353226.27 | 2168031.292 | 5046160.338 | 7836545.571 | 2968910.653 | 3931532.943 | ||
| P31944 | 7 | 6 | 408.4 | 0.027085605 | 5.984138648 | XA | HN | Caspase-14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CASP14 PE=1 SV=2 | 275501.4 | 245947.4 | 185259.3 | 592993.6 | 251081.6342 | 471825.7083 | 6020743.646 | 1456198.894 | 2841876.606 | 355501.1323 | 357167.931 | 332546.2192 | 183482.057 | 211286.9141 | 166192.8098 | 260199.413 | 86653.74674 | 109326.4294 | 465092.9219 | 198224.3002 | 258574.5687 | 1435763.989 | 177710.1961 | 123991.8754 | 212971.2054 | 357647.3468 | 151096.5821 | ||
| P15941 | 6 | 6 | 408.37 | 0.988907721 | 1.077611762 | HN | XN | Mucin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 27863481 | 10546501 | 15130682 | 12153598 | 6253604.847 | 12676130.46 | 21690515.55 | 15818369.41 | 24744985.54 | 15901046.22 | 38498614.45 | 15961153.13 | 20299873.1 | 27034042.33 | 7694086.787 | 7676555.122 | 8085429.392 | 15308500.99 | 11784563.79 | 24322993.6 | 18833427.58 | 12339397.18 | 9595755.882 | 16792541.97 | 10968112.25 | 20877255.06 | 19676741.25 | ||
| Q14126 | 17 | 14 | 407.79 | 0.927682327 | 1.106752184 | HN | XN | Desmoglein-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSG2 PE=1 SV=2 | 11913240 | 7544201 | 7356720 | 10102657 | 6544145.843 | 7421436.667 | 7948228.062 | 5779405.547 | 8701790.192 | 10779948.46 | 16781794.82 | 6023610.361 | 12335983.51 | 7279818.763 | 7730835.785 | 4354468.59 | 7147597.254 | 4971800.476 | 6662573.257 | 7426278.308 | 6960603.876 | 4724813.217 | 8323855.678 | 11935541.06 | 6864622.531 | 9761068.272 | 7280291.627 | ||
| Q8TDL5 | 11 | 6 | 407.5 | 0.793064105 | 1.386841196 | XA | HN | BPI fold-containing family B member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BPIFB1 PE=2 SV=1 | 12910185 | 2264270 | 5918224 | 21812245 | 2607862.153 | 10022405.03 | 16210147.38 | 18678228.37 | 10417995.23 | 20118043.14 | 4026052.99 | 10816470.62 | 7843205.405 | 6321952.73 | 5919633.552 | 7870457.108 | 4329985.544 | 5467327.513 | 10386727.13 | 5305556.587 | 15649541.37 | 10767416.29 | 11029839.79 | 1854020.132 | 9239284.819 | 7604481.307 | 6364054.47 | ||
| Q92520 | 9 | 3 | 405.81 | 0.134984803 | 1.328622258 | XA | XN | Protein FAM3C OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM3C PE=1 SV=1 | 4544417 | 4239478 | 3939427 | 3855609 | 4556560.878 | 5219323.107 | 5130504.204 | 5280121.433 | 7624291.865 | 1802950.355 | 7691243.348 | 2811571.746 | 6967001.031 | 4325386.861 | 2860998.183 | 2583806.571 | 3608770.022 | 3723558.965 | 2025864.473 | 4794078.592 | 3218578.363 | 2664989.701 | 3391301.595 | 4713153.966 | 4213429.949 | 4445457.999 | 3943493.392 | ||
| P54753 | 13 | 9 | 405.57 | 0.694128949 | 1.148562047 | XN | HN | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 3268729 | 7176321 | 6488199 | 4612982 | 4199233.896 | 5351405.682 | 5616475.674 | 4402508.955 | 3954858.733 | 3687331.086 | 9254061.393 | 2371110.842 | 6554758.963 | 4878278.083 | 5421486.179 | 3222986.805 | 4433545.403 | 4862540.33 | 5614537.357 | 5893410.754 | 2938066.118 | 4496859.119 | 3899771.104 | 6906123.824 | 4281589.46 | 6113083.139 | 11181316.57 | ||
| Q12841 | 9 | 7 | 405.19 | 0.455459648 | 1.22194935 | HN | XN | Follistatin-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FSTL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3140838 | 1952525 | 1315174 | 2982174 | 2486993.356 | 1196269.954 | 1211317.507 | 1709380.257 | 1956120.903 | 1181756.455 | 2245238.664 | 2939372.163 | 2009564.984 | 1856528.514 | 2071425.985 | 2090664.24 | 1751795.635 | 3459133.745 | 1542002.731 | 2202529.581 | 1674955.612 | 1055912.61 | 1123645.116 | 2040294.401 | 2229532.419 | 1939721.268 | 2235835.911 | ||
| Q9NZZ3 | 3 | 2 | 403.65 | 0.592317726 | 1.335663012 | HN | XN | Charged multivesicular body protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP5 PE=1 SV=1 | 7247509 | 4044898 | 4271264 | 4529198 | 3027783.494 | 4586997.882 | 5334544.031 | 8647598.193 | 5338824.931 | 3705187.033 | 12026730.27 | 7554195.22 | 6468719.032 | 8971796.686 | 1521696.733 | 1078251.399 | 3717647.54 | 4050000.763 | 3275836.125 | 6885105.344 | 5954289.234 | 2834722.362 | 2504548.26 | 3556048.754 | 2644769.795 | 4337210.092 | 4763915.508 | ||
| O43570 | 5 | 4 | 402.79 | 0.031094983 | 1.671233358 | XA | XN | Carbonic anhydrase 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CA12 PE=1 SV=1 | 3217464 | 2933185 | 2397468 | 4032821 | 1739127.087 | 2776826.061 | 2037293.282 | 2466985.415 | 4496813.903 | 1243191.926 | 1193131.49 | 3918096.039 | 2399142.415 | 1161354.665 | 2013908.523 | 3346331.45 | 2371279.113 | 1595309.042 | 2854001.256 | 697699.475 | 1107264.002 | 853432.8701 | 2591848.999 | 809800.5018 | 2270922.769 | 1968106.122 | 2462926.484 | ||
| Q15485 | 8 | 6 | 401.58 | 0.922266323 | 1.372160696 | XA | XN | Ficolin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 5387504 | 3407904 | 15961668 | 30869625 | 11026872.3 | 4931647.474 | 15998722.94 | 12188038.38 | 1724268.512 | 2172672.763 | 5250246.733 | 3424892.858 | 8297353.384 | 6224050.688 | 14289915.33 | 36282907.24 | 5742631.457 | 7837786.361 | 4421040.786 | 9790877.85 | 4854349.328 | 5889006.501 | 7516031.426 | 17617028.89 | 4849457.592 | 8912824.429 | 10117578.12 | ||
| P40197 | 12 | 9 | 401.52 | 0.529201422 | 1.173988202 | XA | HN | Platelet glycoprotein V OS=Homo sapiens GN=GP5 PE=1 SV=1 | 5233764 | 4056524 | 2448890 | 4523291 | 2808408.43 | 2726095.988 | 1902648 | 4001456.896 | 3688643.742 | 4396423.471 | 1147176.218 | 3832953.559 | 1411186.999 | 1375049.906 | 2580225.739 | 4384492.366 | 4337578.88 | 3272593.759 | 3278664.513 | 3136214.592 | 5007166.227 | 3871389.74 | 4817653.736 | 1500714.961 | 3882899.983 | 1888244.517 | 2210822.704 | ||
| P80370 | 7 | 5 | 401.39 | 0.807474602 | 1.112898361 | HN | XA | Protein delta homolog 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DLK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 28792120 | 60484616 | 61765744 | 56746240 | 36143881.26 | 37599705.48 | 24784819.96 | 45963090.71 | 34653667.97 | 15910353 | 27908120.85 | 11894679.68 | 37048673.17 | 96806551.85 | 18865896.34 | 51104801.26 | 55024283.86 | 116054726.4 | 45863819.2 | 60234694.17 | 61328578.07 | 50104551.92 | 31856718.84 | 85213667.26 | 46573025.46 | 24244493.58 | 20824396.15 | ||
| P13591 | 9 | 7 | 400.13 | 0.692069911 | 1.27385264 | XA | HN | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCAM1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1839473 | 7376825 | 5732486 | 1739418 | 7637653.231 | 4118729.123 | 3477180.806 | 2720660.852 | 5993187.538 | 2687927.811 | 3603062.163 | 2755773.221 | 3300030.235 | 4069424.703 | 6727974.085 | 1874571.234 | 3190377.677 | 3690634.783 | 2883110.775 | 3218383.866 | 4066837.838 | 6098735.836 | 3365948.327 | 8655779.897 | 3132664.848 | 3234568.306 | 2783469.175 | ||
| P34913 | 9 | 6 | 399.18 | 0.000999224 | 4.03428469 | XA | HN | Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHX2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2370421 | 732419.3 | 887685.6 | 3922649 | 1731683.279 | 3522389.842 | 2787456.826 | 4377232.422 | 2387898.605 | 1211482.691 | 330969.49 | 1498429.635 | 263536.0256 | 798896.6756 | 592043.4506 | 431837.8194 | 343355.1144 | 161137.8774 | 88397.34595 | 231914.8745 | 1777195.743 | 1367177.577 | 889956.0805 | 344056.6605 | 1242301.394 | 955729.163 | 267073.0607 | ||
| Q14117 | 8 | 5 | 397.86 | 0.015340449 | 2.757065922 | XA | HN | Dihydropyrimidinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPYS PE=1 SV=1 | 545694.4 | 271002.1 | 518662.5 | 1668183 | 121766.6432 | 775574.4176 | 755972.4939 | 1171135.678 | 1076347.73 | 205295.4612 | 176479.9858 | 361132.9277 | 546338.3639 | 358211.7875 | 311390.5391 | 203431.6024 | 214733.0344 | 127220.499 | 329995.0914 | 170628.2898 | 434953.1516 | 655952.2872 | 519191.2313 | 323888.6752 | 493660.71 | 222123.1722 | 183672.3749 | ||
| P04424 | 6 | 5 | 396.13 | 0.025154203 | 3.69166774 | XA | HN | Argininosuccinate lyase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASL PE=1 SV=4 | 379303.6 | 273951.8 | 506174.2 | 1999722 | 363372.4133 | 3064994.106 | 2207794.602 | 3586480.792 | 1376397.755 | 845984.2561 | 120497.1004 | 1111466.578 | 245597.067 | 277517.2108 | 472869.9004 | 155290.2007 | 251201.6035 | 246398.8645 | 823804.9001 | 851829.7676 | 1985831.898 | 2271971.33 | 849079.2221 | 408364.2945 | 501417.0033 | 391965.9957 | 179928.9822 | ||
| Q9UMR5 | 4 | 4 | 394.46 | 0.196609982 | 1.266748584 | XA | HN | Lysosomal thioesterase PPT2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPT2 PE=1 SV=4 | 15069132 | 7862925 | 8474176 | 12525852 | 9017027.851 | 9190471.418 | 8380153.826 | 15768861.9 | 7848229.561 | 15169544.11 | 4407176.132 | 11642131.62 | 7822970.75 | 7614771.951 | 4745011.19 | 6661274.48 | 9699844.163 | 6551019.488 | 9372042.391 | 7672416.948 | 12785679.57 | 8445803.81 | 11918933.88 | 6302371.997 | 6910564.824 | 11027731.5 | 12344844.1 | ||
| P08637 | 6 | 3 | 393.78 | 0.590492886 | 1.948051133 | XA | HN | Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCGR3A PE=1 SV=2 | 2987409 | 10133369 | 18439389 | 2639159 | 2192363.101 | 17811488.15 | 10318665.27 | 5136049.598 | 34146609.93 | 6513203.203 | 5746275.028 | 10442550.71 | 7962811.471 | 5674730.199 | 2445650.46 | 900745.0615 | 5578636.351 | 8021730.576 | 23695150.65 | 2807455.212 | 9346391.683 | 14233669.65 | 1469025.777 | 7453413.952 | 1217038.217 | 10330554.92 | 10211869.22 | ||
| P07998 | 4 | 4 | 392.8 | 0.64993309 | 1.119255838 | XN | XA | Ribonuclease pancreatic OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE1 PE=1 SV=4 | 12708235 | 32735526 | 15757521 | 14200018 | 13968150.54 | 9490158.23 | 9515291.796 | 9573491.116 | 46069420.98 | 12587630.28 | 20268005.72 | 27703414.11 | 29664283.05 | 15275089.83 | 18876200.51 | 23877531.3 | 14227158.91 | 15987656.92 | 8523358.293 | 22543853.07 | 18466459.69 | 20251183.3 | 9633424.641 | 48629915.6 | 12384391.97 | 24333481.54 | 18811826.18 | ||
| P20774 | 7 | 6 | 392.62 | 0.547682209 | 3.097287513 | HN | XN | Mimecan OS=Homo sapiens GN=OGN PE=1 SV=1 | 97645.96 | 497495.7 | 451186.3 | 158982.6 | 2110789.611 | 224919.4006 | 104287.0617 | 156306.6422 | 86021.51696 | 300928.3736 | 88349.66179 | 363399.5818 | 70831.11299 | 78603.12956 | 764600.3364 | 3300208.064 | 350265.1847 | 185653.1411 | 215775.9474 | 256798.1002 | 100590.7416 | 306269.5846 | 298522.2988 | 335011.9251 | 148109.3583 | 57934.55205 | 57651.28643 | ||
| P16035 | 10 | 7 | 390 | 0.746614177 | 1.142639447 | HN | XA | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TIMP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 6381416 | 3612859 | 1188850 | 3275798 | 2942640.586 | 2997885.051 | 3540170.25 | 4757890.103 | 3371192.262 | 4843699.734 | 3960360.768 | 1827939.26 | 6013029.23 | 5152100.437 | 3405037.914 | 2390780.213 | 3177215.629 | 5872799.159 | 5107103.911 | 4651219.711 | 2936685.377 | 4016726.174 | 4196557.547 | 1975974.616 | 3282382.941 | 2552941.011 | 4796036.733 | ||
| P30043 | 5 | 4 | 388.52 | 0.751456829 | 1.193387815 | HN | XN | Flavin reductase (NADPH) OS=Homo sapiens GN=BLVRB PE=1 SV=3 | 2421958 | 2798149 | 4041417 | 4778345 | 7144971.891 | 2597355.199 | 1779809.9 | 5134688.211 | 3014748.836 | 2318714.465 | 1243073.943 | 13277517.64 | 1398798.194 | 1147713.894 | 3627090.039 | 2607302.461 | 4836578.441 | 5013773.304 | 4014386.824 | 3692390.237 | 3157661.496 | 3709070.999 | 8645685.907 | 1560389.099 | 1198932.652 | 1882217.316 | 1861843.441 | ||
| P54289 | 11 | 9 | 388.33 | 0.083752106 | 1.436236065 | XA | XN | Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CACNA2D1 PE=1 SV=3 | 2985700 | 3646553 | 2464780 | 2380137 | 3698658.4 | 1735738.863 | 1682407.215 | 1713503.228 | 1580091.351 | 1805066.666 | 1997714.597 | 1472327.517 | 1929401.07 | 2435130.633 | 2884423.729 | 1850630.093 | 1708033.992 | 2927717.588 | 1199543.288 | 1668278.055 | 1946573.437 | 2226501.141 | 1606700.884 | 522705.1698 | 1685324.1 | 2180408.341 | 2203499.555 | ||
| P16070 | 6 | 3 | 388.22 | 0.057766416 | 2.187999991 | XA | HN | CD44 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD44 PE=1 SV=3 | 6873276 | 22128241 | 17033998 | 5707987 | 4708973.616 | 19125462.11 | 36058083.05 | 12703650.51 | 59589326.49 | 6736018.95 | 20756105.86 | 9397690.538 | 13960535 | 6229709.844 | 2667645.382 | 3180182.784 | 8427451.243 | 12707273.84 | 16867233.94 | 36329114.09 | 25407298.7 | 9663132.162 | 9876613.367 | 23259005.11 | 10870480.12 | 36865623.11 | 9459079.058 | ||
| P22223 | 10 | 7 | 387.65 | 0.903821807 | 1.395452492 | XA | XN | Cadherin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 2587797 | 2466887 | 5424464 | 11396917 | 4530815.97 | 1229037.353 | 608751.228 | 2624018.561 | 1513278.297 | 5576707.214 | 1348933.368 | 3517840.325 | 1520663.061 | 1175316.34 | 2411833.086 | 1540144.335 | 3400689.238 | 2754039.201 | 944091.1494 | 2063350.766 | 3663147.164 | 2686137.937 | 5160972.881 | 2336992.427 | 1703483.679 | 2104035.152 | 2543140.774 | ||
| Q5JZY3 | 8 | 4 | 385.6 | 0.427155745 | 1.424411525 | HN | XA | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHA10 PE=2 SV=1 | 973949.5 | 1228224 | 1234713 | 1912648 | 1091795.838 | 883182.6546 | 812797.839 | 1415500.649 | 820127.8 | 1225332.726 | 1334714.389 | 1202012.479 | 3487972.808 | 922452.2306 | 2884524.082 | 2140183.101 | 757025.5165 | 821117.2913 | 738240.9767 | 1641257.802 | 1393508.753 | 1576995.627 | 925906.1504 | 1787411.112 | 1184855.36 | 786779.2251 | 1412594.774 | ||
| P61916 | 8 | 5 | 385.19 | 0.498204946 | 1.324238804 | HN | XN | Epididymal secretory protein E1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPC2 PE=1 SV=1 | 16070635 | 21861743 | 14554105 | 9054750 | 14596598.33 | 22180511.84 | 24783673.08 | 17007117.84 | 23376773.25 | 32285601.96 | 27966767.95 | 6467150.397 | 25336759.36 | 25162883.99 | 22047531.18 | 12501358.95 | 11854147.48 | 16811890.74 | 10436893.87 | 17475956.47 | 13190865.29 | 12525757.07 | 20205053.16 | 17854473.96 | 11120162.56 | 16686122.59 | 16759664.99 | ||
| Q7Z7G0 | 8 | 6 | 385.14 | 0.398223939 | 1.204706011 | XN | XA | Target of Nesh-SH3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABI3BP PE=1 SV=1 | 5362281 | 4249411 | 3750264 | 5717621 | 2803152.786 | 5638051.198 | 5614526.095 | 4536886.207 | 8546143.986 | 6981950.399 | 5036865.531 | 4000464.352 | 3727653.459 | 8418537.202 | 5786956.516 | 7558834.629 | 5330984.874 | 6949335.241 | 5585258.63 | 4449236.448 | 5218197.607 | 9244261.538 | 7440634.929 | 3484699.184 | 9021725.511 | 5079636.481 | 6155858.07 | ||
| P26842 | 5 | 5 | 384.62 | 0.057788441 | 1.587854728 | XN | HN | CD27 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD27 PE=1 SV=2 | 42233317 | 1.33E+08 | 78470163 | 63970200 | 58502761.92 | 97470321.96 | 86255289.77 | 68268989.3 | 72710193.44 | 31434799.53 | 99753559.28 | 38182459.62 | 61862266.87 | 60816802.78 | 70623385.92 | 16659803.99 | 41435522.82 | 90095692.54 | 69664952.32 | 139700286.5 | 78709432.98 | 54570433.18 | 62761850.72 | 183728523 | 57617697.66 | 87623013.07 | 76802094.15 | ||
| P04196 | 10 | 7 | 383.82 | 0.355992062 | 1.512938724 | XA | XN | Histidine-rich glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRG PE=1 SV=1 | 2066103 | 3254500 | 1900829 | 6631720 | 4219220.552 | 1508505.535 | 1984385.866 | 2393297.655 | 1537406.107 | 1603104.095 | 700062.6299 | 3060539.687 | 1288585.652 | 798973.1235 | 4235706.488 | 3718870.024 | 3051125.856 | 2390962.061 | 2104447.426 | 1054585.664 | 954135.3513 | 1545801.591 | 2582420.012 | 1958619.969 | 2960765.165 | 1612492.737 | 2078681.993 | ||
| Q6P9A2 | 11 | 9 | 382.63 | 0.308024516 | 1.295666664 | XA | HN | Putative polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-like protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALNTL4 PE=2 SV=2 | 4484329 | 1507487 | 1533387 | 2049148 | 2045875.215 | 2722965.672 | 2582883.662 | 3995240.352 | 2393419.072 | 1895124.533 | 1225931.971 | 1715917.095 | 3883364.49 | 908396.3028 | 2062890.549 | 2293090.742 | 2418526.017 | 1591151.065 | 1872720.236 | 1608899.653 | 1604234.111 | 974667.2006 | 2303878.544 | 1651034.478 | 3554043.399 | 2387959.156 | 2624335.55 | ||
| Q03591 | 7 | 1 | 381.25 | 0.451756847 | 1.657132712 | XN | XA | Complement factor H-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFHR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 11976.63 | 0 | 60979.03 | 74876.92 | 217167.8428 | 140202.4204 | 137342.4381 | 202911.9293 | 72713.55027 | 125980.2339 | 57532.46532 | 112688.3038 | 19338.75338 | 50232.10343 | 163849.2006 | 225343.6801 | 119412.6307 | 417274.3565 | 246486.5882 | 399591.3444 | 263561.5157 | 7882.587531 | 29795.33518 | 2219.760754 | 263211.7209 | 166390.569 | 142391.3765 | ||
| O95460 | 4 | 3 | 381.19 | 0.225826104 | 2.405356991 | HN | XA | Matrilin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MATN4 PE=1 SV=3 | 4908514 | 7762764 | 10167368 | 5716875 | 5925102.074 | 5685529.465 | 7049403.378 | 10723947.55 | 10711576.99 | 4131627.358 | 11504480.64 | 1770111.873 | 16330363.85 | 54020800.69 | 23075831 | 15678136.04 | 10143171.86 | 28475834.64 | 4546713.927 | 11810197.94 | 5556018.987 | 3356021.94 | 7051017.173 | 10997486.48 | 11652751.79 | 9172764.701 | 16827863.4 | ||
| O75787 | 6 | 5 | 380.4 | 0.806939216 | 1.334797654 | XA | HN | Renin receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6AP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 11237389 | 1924742 | 4208981 | 11884176 | 1316300.475 | 957415.6486 | 2268520.002 | 6202128.446 | 4498887.41 | 1862453.161 | 1840543.523 | 2036694.221 | 1289273.1 | 1577327.077 | 3619151.392 | 14293860.71 | 2074962.752 | 4743027.143 | 2424821.747 | 2696402.929 | 4046828.393 | 1640666.492 | 9784914.085 | 328356.7512 | 9025521.754 | 4717498.228 | 6370745.881 | ||
| P09564 | 3 | 3 | 380.28 | 0.62999122 | 1.088237995 | XN | XA | T-cell antigen CD7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD7 PE=1 SV=1 | 59458787 | 52518128 | 32428630 | 67915572 | 30554470.09 | 81147197.26 | 179194585.8 | 78728901.91 | 69780003.14 | 125001417.6 | 114254542.3 | 71611343.58 | 109244131.5 | 65060752.58 | 28266561.67 | 18669233.17 | 56412662.37 | 73118634.66 | 86272215.33 | 82429255.04 | 66296191.41 | 117359282.5 | 50556497.59 | 77045801.26 | 81477150.6 | 75982796.53 | 71814104.57 | ||
| O43653 | 3 | 2 | 379.49 | 0.062374693 | 5.294785665 | XN | HN | Prostate stem cell antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSCA PE=1 SV=1 | 206002.5 | 21957143 | 309081.8 | 13647187 | 13903078.63 | 210887.0363 | 22635334.51 | 9027158.528 | 413650.8253 | 527181.4858 | 376138.5412 | 455919.2679 | 326614.026 | 30673641.22 | 435734.2433 | 4305982.992 | 219458.9085 | 186945.8942 | 296833.6002 | 86131067.45 | 36891508.33 | 10728595.42 | 949034.6473 | 747711.8889 | 17376082.02 | 18392290.86 | 27081666.37 | ||
| P02748 | 11 | 8 | 378.18 | 0.056845307 | 1.820335172 | XA | XN | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 2847025 | 875342.8 | 1108323 | 647947.2 | 1451633.405 | 1554032.964 | 1415980.386 | 1152997.049 | 1236299.192 | 2527876.818 | 756710.9407 | 902288.8102 | 1218130.827 | 364005.9783 | 1074540.405 | 644701.8723 | 925260.3656 | 548566.295 | 868693.2471 | 644691.9243 | 625474.955 | 900383.6483 | 621386.1521 | 121830.3998 | 658542.0403 | 1271700.056 | 1038570.853 | ||
| P07737 | 7 | 4 | 377.59 | 0.094132622 | 4.499537593 | HN | XN | Profilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4813380 | 1767476 | 2668887 | 5649409 | 3574935.603 | 6292732.929 | 7657575.697 | 7915659.609 | 5933567.582 | 6360730.352 | 7405207.443 | 8774335.514 | 7212044.338 | 6187813.488 | 6843243.538 | 103059187.6 | 2412735.228 | 2397969.072 | 3221967.659 | 2880519.705 | 8467831.85 | 3996257.974 | 3317033.021 | 2817195.863 | 3959650.309 | 2326775.723 | 2494712.09 | ||
| P27482;P02585 | 7 | 5 | 377.48 | 0.826286816 | 1.204741525 | XA | XN | Calmodulin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALML3 PE=1 SV=2 | 743447.3 | 7434319 | 6845301 | 1154194 | 6914718.99 | 2865395.912 | 3243422.765 | 4137078.616 | 6659589.908 | 4312892.394 | 4022934.791 | 12416473.59 | 3873108.29 | 4158113.883 | 2729409.556 | 1735639.512 | 3209357.166 | 3195598.661 | 3301928.014 | 6382944.34 | 4915404.631 | 3527932.133 | 2655878.821 | 3388038.98 | 823000.7502 | 6682463.116 | 1522449.443 | ||
| O75144 | 4 | 3 | 375.64 | 0.018898474 | 1.63162568 | XA | HN | ICOS ligand OS=Homo sapiens GN=ICOSLG PE=1 SV=2 | 22776107 | 38146298 | 27218941 | 28132712 | 8426180.841 | 21251931.4 | 31522593.58 | 32855863.65 | 36724825.67 | 9046523.151 | 25122501.01 | 12418668.45 | 22106080.2 | 22043012.04 | 13067348.18 | 5353494.387 | 12143198.49 | 30115921.39 | 24623521.96 | 32315255.59 | 22711220.51 | 20135613.13 | 27309909.92 | 29618146.11 | 24392930.15 | 28424863.29 | 20231279.22 | ||
| Q99523 | 9 | 4 | 375.32 | 0.27941025 | 1.265135173 | XA | HN | Sortilin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SORT1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1608608 | 1068241 | 843347.5 | 825858.1 | 987746.0105 | 1336641.126 | 1438760.084 | 1564655.218 | 2229005.364 | 739660.261 | 2238247.073 | 908530.1962 | 1518611.546 | 1476950.754 | 589688.5319 | 340792.0131 | 802756.8796 | 793134.9421 | 1522394.199 | 1230756.491 | 1488328.079 | 917726.0315 | 573257.21 | 1310350.974 | 1322027.966 | 878700.9292 | 967435.3785 | ||
| Q9H665 | 5 | 3 | 375.14 | 0.239056053 | 1.478993594 | XN | XA | IGF-like family receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFLR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 7221864 | 8082139 | 9386383 | 5537159 | 5260508.532 | 11549443.19 | 13163367.88 | 8045832.815 | 14485177.41 | 5888233.971 | 28068472.75 | 3562168.752 | 13462104.11 | 11810468.61 | 4030239.381 | 3751132.539 | 4866713.646 | 16435883.12 | 11440645.2 | 21256112.9 | 13376626.51 | 8449178.07 | 4274122.568 | 21167842.78 | 10918014.99 | 20214558.5 | 11262810.65 | ||
| Q9NPF0 | 6 | 4 | 374.69 | 0.613592217 | 1.56812442 | HN | XA | CD320 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD320 PE=1 SV=1 | 1474345 | 5555128 | 1767683 | 713556.5 | 743781.6429 | 3578333.459 | 3253186.235 | 1031858.148 | 5350663.911 | 652155.331 | 9428057.638 | 243610.9008 | 13890606.96 | 3301086.629 | 2600611.707 | 249468.5457 | 1499562.467 | 4936423.517 | 1833127.921 | 4930313.293 | 2452945.406 | 2146832.104 | 4405496.793 | 4388665.558 | 1649807.659 | 3215549.394 | 3149747.348 | ||
| P02533 | 12 | 1 | 374.44 | 0.0267414 | 1.937163823 | HN | XA | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 3231093 | 7987703 | 2935401 | 2109351 | 7376241.651 | 4587307.188 | 3654035.188 | 3288659.901 | 3709052.734 | 10149110.46 | 9476763.305 | 11771587.04 | 5834690.573 | 6421994.488 | 4372872.155 | 17858855.93 | 6243964.293 | 3184854.601 | 5201749.619 | 3570547.979 | 5427340.099 | 6910141.429 | 5274973.045 | 9580541.672 | 5278025.134 | 13365519.62 | 3861279.898 | ||
| Q09328 | 14 | 10 | 371.55 | 0.244846671 | 1.416891093 | XA | HN | Alpha-1,6-mannosylglycoprotein 6-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=MGAT5 PE=1 SV=1 | 2471324 | 996064.6 | 892240.3 | 2261717 | 1331073.709 | 1907776.094 | 1489616.353 | 2211656.705 | 1222001.127 | 661278.8192 | 511796.8761 | 574563.5438 | 1048513.122 | 502770.3252 | 1836808 | 2425217.116 | 1776518.528 | 1096271.321 | 1444467.175 | 1420079.023 | 1202979.696 | 687287.405 | 1634048.239 | 289220.5176 | 2754681.547 | 1573835.807 | 1564455.965 | ||
| P20160 | 7 | 7 | 371.52 | 0.483954607 | 3.768950869 | XA | HN | Azurocidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=AZU1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1185974 | 814536 | 1074801 | 1878712 | 1036605.401 | 26465068.2 | 19874829.07 | 2535494.331 | 14314258.82 | 3845837.089 | 1726584.448 | 1607179.855 | 1499090.729 | 1109770.538 | 4142742.48 | 2383426.631 | 1151789.562 | 888893.107 | 37490271.09 | 962647.2403 | 897595.885 | 4523266.232 | 1033125.087 | 1275589.242 | 1780692.27 | 1022361.705 | 1154536.848 | ||
| Q7Z4W1 | 6 | 6 | 371.26 | 0.543346799 | 1.336089015 | XA | HN | L-xylulose reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCXR PE=1 SV=2 | 3097552 | 1110369 | 2489355 | 6832094 | 1342824.259 | 4556118.553 | 2110585.552 | 5100083.271 | 2088592.842 | 3506656.927 | 1708002.77 | 3324326.325 | 2627693.473 | 1810830.042 | 1859874.153 | 1972611.473 | 2503431.195 | 2187816.584 | 3925401.01 | 2689414.826 | 5077535.709 | 5295873.383 | 1707548.928 | 2757941.557 | 2282820.884 | 2890638.225 | 1751685.253 | ||
| O00754 | 8 | 4 | 370.72 | 0.368825304 | 1.729687888 | XA | XN | Lysosomal alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 182187.6 | 421984.5 | 1670061 | 222574.6 | 150230.1767 | 494378.2935 | 1213668.913 | 604910.2754 | 968075.3278 | 334957.5086 | 263415.235 | 501416.1725 | 1283330.786 | 473111.6788 | 666949.9407 | 284453.5942 | 597922.7916 | 140349.094 | 120824.5813 | 123076.5813 | 353974.477 | 277086.2697 | 965661.8324 | 218703.9215 | 829406.7243 | 314984.5725 | 223529.8991 | ||
| Q9P121 | 7 | 3 | 369.94 | 0.266578794 | 1.730297813 | XA | HN | Neurotrimin OS=Homo sapiens GN=NTM PE=1 SV=1 | 605436.8 | 5287189 | 1621202 | 290645.6 | 604646.3785 | 2070523.794 | 2985422.047 | 1092566.325 | 4565028.524 | 770473.5311 | 3065207.43 | 598303.6428 | 1781515.694 | 1601546.297 | 1354552.375 | 242671.5394 | 731858.0963 | 905530.237 | 1567460.637 | 1491059.072 | 1927104.701 | 1866782.045 | 1294795.248 | 5860494.118 | 1567547.504 | 1740117.277 | 1061817.54 | ||
| P01619 | 8 | 3 | 369.84 | 0.18268357 | 1.388746546 | HN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-III region B6 OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 16708738 | 23058972 | 17581585 | 20608202 | 28731716.73 | 8613744.307 | 13405545.31 | 13956704.42 | 8312436.092 | 15920865.35 | 18113705.44 | 29933056.55 | 18858039.35 | 20428351 | 44685163.8 | 28629779.93 | 19171856.33 | 13928864.67 | 19269122.73 | 11804778.63 | 14830073.41 | 28654790.97 | 24477799.46 | 48017474.63 | 25278941.95 | 12962193.03 | 20250623.72 | ||
| P13987 | 6 | 5 | 367.58 | 0.735914374 | 1.496538345 | XA | HN | CD59 glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD59 PE=1 SV=1 | 1.1E+08 | 4.11E+08 | 2.6E+08 | 24781339 | 83403862.45 | 164917438.1 | 243805351.2 | 121325612.8 | 347062126.1 | 86038548.75 | 167951400.2 | 116927270.1 | 129562484.3 | 104949279.6 | 203502794.4 | 64992513.25 | 110831047.5 | 195933890.3 | 90295347.63 | 205849032.4 | 127570682.1 | 155953381.6 | 111790027.1 | 373766995.8 | 77790300.19 | 217099131.3 | 139824648.2 | ||
| Q9BZG9 | 4 | 4 | 365.67 | 0.242610364 | 1.398068575 | HN | XN | Ly-6/neurotoxin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYNX1 PE=1 SV=3 | 3.86E+08 | 1.55E+08 | 2.24E+08 | 3.51E+08 | 221382597.6 | 194516895.1 | 149295482.1 | 234304450.8 | 97408506.14 | 239328916.5 | 142724238.5 | 201167276.1 | 138424414.6 | 302776035.2 | 208913372.7 | 532482123.2 | 233116152.5 | 210642022.8 | 236126825.6 | 143442735.8 | 142002795.7 | 133199695.1 | 195785788.8 | 53445334.67 | 314428386.9 | 149525841.7 | 212490502.2 | ||
| P07307 | 4 | 4 | 364.42 | 0.130685381 | 1.58578077 | XN | XA | Asialoglycoprotein receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASGR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2584460 | 2294760 | 2582832 | 3343607 | 5404132.011 | 4591636.507 | 3148377.639 | 2062932.49 | 2162629.378 | 5636405.268 | 8442744.299 | 1875582.516 | 4996443.762 | 4611326.729 | 4614487.169 | 4814298.96 | 4507028.381 | 1372143.741 | 4129423.352 | 4583472.772 | 4233137.854 | 4852602.246 | 2100813.421 | 9748577.971 | 7058400.598 | 4073839.117 | 3899688.673 | ||
| P35754 | 4 | 4 | 363.56 | 0.357693779 | 2.903836144 | HN | XN | Glutaredoxin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLRX PE=1 SV=2 | 2825075 | 1391463 | 3140061 | 5095143 | 2556533.341 | 3926996.792 | 3965548.401 | 3583437.656 | 2737586.129 | 3350046.82 | 3793692.61 | 2690139.377 | 2943019.577 | 5142376.019 | 2588342.063 | 47775246.41 | 1908683.2 | 2539161.235 | 3883514.614 | 2574668.062 | 3766852.673 | 3592085.52 | 2061065.445 | 2798327.158 | 2199654.11 | 1559686.501 | 2610568.545 | ||
| Q5ZPR3 | 2 | 2 | 362.22 | 0.463012807 | 1.21931264 | XN | XA | CD276 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD276 PE=1 SV=1 | 1312416 | 1908084 | 933798 | 952945.5 | 836764.2664 | 2028544.346 | 3034281.173 | 1515872.692 | 4101668.794 | 2400136.062 | 2626351.518 | 767000.2332 | 2254812.134 | 1998763.558 | 1957356.703 | 736375.7993 | 1473176.358 | 3029269.158 | 2466166.453 | 3032266.429 | 1891047.875 | 1619271.216 | 1196730.303 | 3549229.749 | 1352463.408 | 2443619.07 | 2719515.593 | ||
| P30047 | 6 | 3 | 361.89 | 0.25854793 | 2.52227028 | HN | XN | GTP cyclohydrolase 1 feedback regulatory protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GCHFR PE=1 SV=3 | 3905857 | 3408773 | 4515129 | 8286063 | 5924498.94 | 4675162.451 | 3737184.989 | 5039912.24 | 1884207.405 | 4913341.227 | 1543079.943 | 3095712.676 | 2901567.408 | 2728019.687 | 5578494.636 | 37418303.87 | 4883883.603 | 10512170.69 | 3426611.461 | 2591028.617 | 2961467.162 | 3083473.353 | 3106752.331 | 3166237.832 | 2573336.284 | 2239144.92 | 6021928.084 | ||
| O75083 | 9 | 7 | 360.09 | 0.311471708 | 1.529984339 | XA | XN | WD repeat-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR1 PE=1 SV=4 | 2014143 | 828830.4 | 1353722 | 4285052 | 495329.0742 | 1553363.788 | 1702786.205 | 3007848.367 | 1639202.403 | 2162935.63 | 742439.1021 | 2890302.882 | 1216557.985 | 751276.7125 | 738748.3172 | 1629037.233 | 855688.2195 | 682148.1845 | 579564.4614 | 1209413.335 | 2569627.122 | 1122260.293 | 1969281.928 | 554608.7394 | 1578976.207 | 887034.5762 | 562206.559 | ||
| P36896 | 3 | 2 | 359.45 | 0.079108102 | 1.320898612 | XN | XA | Activin receptor type-1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACVR1B PE=1 SV=1 | 38208604 | 28526778 | 18263581 | 33265857 | 25503870.06 | 37959383.42 | 32755847.96 | 38766033.83 | 33714989.6 | 31096523.65 | 54140559.62 | 27072345.56 | 35038313.61 | 58115125.64 | 19195745.43 | 21484286.76 | 38550235.59 | 32623716.69 | 39758530.58 | 47443503.15 | 47887028.04 | 43284022.69 | 33757127.91 | 46339986.1 | 33093597 | 50981268.12 | 36506532.49 | ||
| P35443 | 6 | 5 | 359.04 | 0.167055293 | 1.558884226 | XN | XA | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 1798476 | 3259368 | 3959392 | 2121162 | 2221313.632 | 1893088.488 | 1846908.725 | 1684540.182 | 2219136.95 | 910034.1814 | 6255210.263 | 1280480.715 | 4076179.397 | 3563272.163 | 1842811.416 | 1305066.592 | 2567567.564 | 4952703.772 | 2196383.865 | 5625202.918 | 3811311.051 | 2234556.437 | 3010003.26 | 5103946.954 | 2223296.348 | 5116731.715 | 3420412.946 | ||
| Q5VY43 | 6 | 6 | 358.81 | 0.536449677 | 1.195686861 | HN | XA | Platelet endothelial aggregation receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PEAR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1642750 | 695543.8 | 632736.8 | 257488.2 | 651369.2242 | 372675.8595 | 313727.7127 | 520800.2916 | 338595.1867 | 381717.2751 | 849547.8914 | 181360.7487 | 283729.2706 | 692595.7898 | 482332.7798 | 1253755.163 | 1273105.76 | 1089278.385 | 618786.8659 | 517595.8685 | 848066.5905 | 542028.6638 | 947708.9124 | 949470.5542 | 481973.5758 | 706096.7522 | 727946.7109 | ||
| P24821 | 8 | 7 | 358.19 | 0.826113569 | 1.219333281 | HN | XA | Tenascin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNC PE=1 SV=3 | 270496.9 | 3177145 | 1468300 | 388295.6 | 1466793.314 | 1318392.299 | 809385.6308 | 316663.5609 | 1093681.856 | 320531.6169 | 691148.6822 | 383990.547 | 404156.6107 | 887549.9532 | 890579.0768 | 389376.6001 | 5756177.508 | 2846783.12 | 4230373.096 | 495636.4205 | 475965.3724 | 660231.0935 | 846309.8506 | 1703870.238 | 1015771.573 | 1334733.384 | 1100294.635 | ||
| P09466 | 5 | 5 | 357.42 | 0.452535469 | 32.59662862 | XN | XA | Glycodelin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAEP PE=1 SV=2 | 55559.24 | 59346.47 | 53623.96 | 51545.77 | 10544.27299 | 29909.42382 | 130980.1245 | 611773.6005 | 86995.14026 | 5249082.61 | 237126.8634 | 2595805.153 | 41347.13841 | 72130.50573 | 103200.2788 | 37625.25246 | 43224.10998 | 39443.83576 | 34633586.97 | 253205.0809 | 65710.77063 | 28095.8834 | 50256.10589 | 237203.3582 | 41679.76333 | 88836.71918 | 140812.2543 | ||
| P01616 | 2 | 1 | 357.19 | 0.230026189 | 2.009262537 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-II region MIL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 15200859 | 10833992 | 8930106 | 15325736 | 35249692.79 | 3445831.509 | 7079177.677 | 8197388.192 | 3673877.792 | 5765677.899 | 2383727.54 | 8417021.071 | 3211809.107 | 6223649.789 | 10080303.55 | 8812174.427 | 3808501.761 | 5016675.969 | 5593543.674 | 6346469.566 | 2677859.52 | 23633585.69 | 7475038.084 | 24005917.15 | 5352196.674 | 3678710.897 | 5513684.062 | ||
| P40121 | 9 | 6 | 356.86 | 0.603172437 | 1.732794676 | HN | XA | Macrophage-capping protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPG PE=1 SV=2 | 3930643 | 1125421 | 1415840 | 7142006 | 1855217.406 | 1466969.28 | 2867564.848 | 3714120 | 2398337.293 | 7395886.303 | 3512468.664 | 4942401.524 | 2700663.08 | 2699374.469 | 1631923.825 | 19320198.51 | 1474580.469 | 1229815.03 | 3636046.657 | 2514960.896 | 7952856.447 | 2519638.702 | 2556585.382 | 1041967.716 | 3112300.646 | 1627163.495 | 2481828.495 | ||
| Q92956 | 4 | 4 | 354.18 | 0.219631666 | 1.433039996 | XN | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF14 PE=1 SV=3 | 5795315 | 17340448 | 7521336 | 13024126 | 4475742.985 | 16917936.23 | 24202368.06 | 7772576.897 | 20904503.92 | 4790119.511 | 27050994.56 | 2334944.757 | 13618433.22 | 10226547.65 | 6542727.29 | 3126858.402 | 7000556.542 | 13818797.78 | 6925265.963 | 18830537.62 | 13406911.41 | 11536645.72 | 9705759.251 | 30048867.57 | 8248737.624 | 19294440.92 | 8841174.85 | ||
| P27797 | 9 | 7 | 353.42 | 0.155616625 | 1.394140449 | XA | XN | Calreticulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALR PE=1 SV=1 | 7032431 | 9223082 | 5446072 | 2432919 | 9963666.27 | 9554607.644 | 4886381.564 | 6725002.42 | 6883645.863 | 6702295.414 | 6309735.395 | 5440554.64 | 4912890.988 | 5013590.827 | 6551454.115 | 3606667.424 | 4295313.518 | 4055451.265 | 9283532.861 | 4324476.763 | 3316542.174 | 3502710.814 | 5160385.201 | 9774543.913 | 2615491.696 | 3018962.572 | 3581221.254 | ||
| P52209 | 8 | 7 | 353.17 | 0.173925869 | 1.867312408 | XA | XN | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGD PE=1 SV=3 | 539087.1 | 395893.8 | 764975.8 | 285253.9 | 327879.7134 | 943815.6938 | 1724270.271 | 2219050.694 | 2477524.179 | 1315218.019 | 161901.9515 | 1901359.646 | 373827.0647 | 165869.1258 | 641437.774 | 188297.3115 | 234359.905 | 299625.874 | 1665324.831 | 482857.5799 | 838120.2155 | 441844.4363 | 217237.7351 | 96592.50204 | 300502.1387 | 154772.3367 | 985464.9132 | ||
| Q15847 | 2 | 1 | 353.14 | 0.326943479 | 1.614290744 | XN | XA | Adipose most abundant gene transcript 2 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=APM2 PE=1 SV=1 | 4742797 | 1292877 | 1494311 | 7937715 | 1749337.357 | 4666870.588 | 5587665.24 | 5922445.399 | 2349633.823 | 6575306.689 | 6012921.963 | 7431293.609 | 4025568.763 | 5613359.018 | 2352732.468 | 11616521.13 | 2594345.218 | 3075167.378 | 5092514.088 | 4902373.186 | 17730341.09 | 13614050.88 | 4741867.48 | 2882456.371 | 3100910.748 | 2263983.908 | 3372148.055 | ||
| Q9UBP4 | 7 | 7 | 352.93 | 0.088647752 | 1.934474752 | HN | XN | Dickkopf-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DKK3 PE=1 SV=2 | 894075.4 | 1440585 | 1766108 | 432911.9 | 1726915.547 | 1065488.799 | 1245747.215 | 748080.9458 | 1860705.904 | 779944.3881 | 1403157.153 | 2418933.535 | 1262342.046 | 1383267.508 | 1289792.973 | 5185349.939 | 1067333.172 | 812033.9575 | 630526.8314 | 714670.5639 | 780201.4363 | 514738.4948 | 990392.5688 | 1119075.683 | 1036357.776 | 1266325.187 | 1013029.785 | ||
| P02679 | 9 | 8 | 352.74 | 0.167448996 | 2.183218878 | HN | XN | Fibrinogen gamma chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGG PE=1 SV=3 | 4038710 | 1446765 | 2264905 | 1884100 | 2836477.369 | 2751577.083 | 1981892.054 | 3099437.783 | 3838602.574 | 4350251.541 | 1189695.017 | 15635153.14 | 1488765.505 | 2016065.708 | 2147403.899 | 3896530.335 | 2173177.715 | 1107187.187 | 2337575.612 | 1522871.362 | 1315673.849 | 1101752.5 | 1572539.164 | 1280874.209 | 2938471.209 | 1635818.522 | 1869696.577 | ||
| Q9UL46 | 6 | 4 | 352.6 | 0.422237005 | 2.102580967 | XA | HN | Proteasome activator complex subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSME2 PE=1 SV=4 | 537723.3 | 56005.07 | 125148.8 | 1312930 | 80377.41089 | 434853.7083 | 298314.0074 | 829162.9527 | 460370.3425 | 333798.7199 | 85680.23068 | 368904.3786 | 235716.8942 | 44974.3559 | 238681.081 | 402971.4442 | 82317.95501 | 173531.3155 | 163421.9205 | 95457.98767 | 495712.7587 | 713945.6802 | 298558.3909 | 113845.844 | 308455.2358 | 115541.6191 | 108299.7528 | ||
| P01621 | 5 | 1 | 349.74 | 0.52189564 | 2.685140068 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-III region NG9 (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 204497.1 | 2250543 | 6067998 | 399127 | 880867.484 | 284046.4163 | 163360.1809 | 259064.7985 | 150285.106 | 732109.9482 | 140729.7006 | 249242.457 | 204893.5797 | 164449.1081 | 804083.8975 | 437327.0806 | 1124464.266 | 324967.3964 | 320329.4675 | 48222.5649 | 95221.51333 | 299055.5136 | 426585.7399 | 1735945.358 | 536948.5027 | 292016.6773 | 215594.0381 | ||
| Q96FV2 | 5 | 5 | 349.55 | 0.006633984 | 1.992561202 | XA | XN | Secernin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCRN2 PE=2 SV=3 | 626114.3 | 584007.8 | 1156583 | 1756551 | 715518.5458 | 1293419.175 | 1179542.763 | 1558504.484 | 657192.0767 | 413889.1894 | 513240.6401 | 1501343.39 | 766371.2269 | 449798.5473 | 639729.8893 | 820703.4206 | 1066920.026 | 462667.6149 | 484260.9181 | 496132.8942 | 798316.4249 | 829900.5041 | 640324.3141 | 366894.2529 | 419056.3151 | 416148.4284 | 330466.9539 | ||
| Q53FA7 | 6 | 2 | 349.35 | 0.026016532 | 1.92536473 | XA | HN | Quinone oxidoreductase PIG3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TP53I3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1879333 | 1021723 | 711105.8 | 1592470 | 1024309.618 | 1158489.197 | 2275619.229 | 2395844.302 | 1184467.316 | 964648.1241 | 356569.3888 | 790828.9326 | 316298.9013 | 644822.9538 | 1436627.593 | 1315997.638 | 608657.8301 | 443913.516 | 2051222.968 | 687221.8475 | 983959.7801 | 690607.5315 | 1984607.627 | 1567381.128 | 1139035.516 | 353955.8793 | 701717.5078 | ||
| P31150 | 6 | 1 | 349.08 | 1.48E-05 | 2.312737663 | XA | XN | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=GDI1 PE=1 SV=2 | 98867.35 | 53721.16 | 108088 | 104098.8 | 196537.4692 | 133999.6084 | 130342.1746 | 131969.3179 | 131197.8527 | 49564.71933 | 91043.54378 | 71235.09334 | 78145.92601 | 83275.88322 | 70792.39637 | 49286.54831 | 54185.14697 | 88963.13283 | 31460.28718 | 48511.47739 | 39714.04415 | 52565.38033 | 52284.30246 | 68029.09731 | 74769.40923 | 58883.20449 | 44576.25842 | ||
| Q8N271 | 11 | 8 | 348.96 | 0.895076298 | 1.068322442 | HN | XA | Prominin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROM2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1255660 | 999013.6 | 453395.4 | 736973.4 | 865299.2711 | 1214905.554 | 1906929.4 | 2073481.652 | 1470547.067 | 2136631.217 | 1257377.037 | 1508308.057 | 882123.2545 | 1759934.09 | 627084.7858 | 1315677.836 | 1437811.553 | 801178.5321 | 2257967.963 | 1292314.117 | 915476.805 | 1836239.843 | 1156259.272 | 493810.2054 | 1390687.673 | 1110936.334 | 1085995.814 | ||
| P35908 | 10 | 1 | 347.7 | 0.14257342 | 2.386257904 | XA | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 66993.91 | 74582.15 | 109139.8 | 14735.73 | 68776.99218 | 460125.1493 | 143104.614 | 71789.59339 | 101175.3385 | 24461.9846 | 88363.83493 | 63028.38944 | 40226.53899 | 53741.54073 | 40577.91334 | 45021.45444 | 52909.2243 | 57009.97354 | 67041.70079 | 110638.8029 | 53882.62949 | 81751.14704 | 78119.19232 | 94500.10454 | 119191.2532 | 80927.12841 | 30465.90329 | ||
| Q13477 | 7 | 5 | 347.59 | 0.943672453 | 1.081348146 | HN | XA | Mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MADCAM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6848779 | 8158248 | 6457633 | 7421269 | 3008186.329 | 11588500.38 | 11655744.13 | 7963094.902 | 8716544.825 | 7483258.355 | 16780076.82 | 7773654.775 | 13909115.49 | 6704252.329 | 4096220.905 | 2197317.953 | 8016704.757 | 10699659.48 | 7615856.112 | 13653105.54 | 9981051.426 | 8428411.336 | 4289290.122 | 12406947.52 | 6057478.336 | 8305723.499 | 5632685.898 | ||
| Q6UXG3 | 6 | 2 | 347.35 | 0.975373285 | 1.198771064 | HN | XA | CMRF35-like molecule 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD300LG PE=1 SV=2 | 27419274 | 39891064 | 21358089 | 16893416 | 21796461.1 | 39228250.21 | 34330145.06 | 25518107.69 | 37453767.63 | 37527643.02 | 81457030.78 | 10426512.74 | 63092121.47 | 46815643.41 | 21032284.32 | 7962404.251 | 20459275.31 | 27569071.24 | 18872597.14 | 33652102.58 | 39819215.22 | 34472486.03 | 31040612.2 | 28697887.79 | 18196408.55 | 41237563.14 | 24836220.98 | ||
| P07437 | 10 | 1 | 347.03 | 0.116283942 | 4.459823974 | XA | XN | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 47445.52 | 11389.05 | 86729.41 | 1018180 | 53382.74186 | 66117.81986 | 75194.48349 | 126082.0548 | 149535.4214 | 39831.94488 | 77669.38059 | 115524.096 | 40650.56432 | 3482.963225 | 59084.65629 | 98449.61693 | 11040.34928 | 63400.46885 | 44562.57608 | 5095.849617 | 14655.25463 | 3080.619494 | 66670.8859 | 90068.54392 | 30760.72662 | 47470.75748 | 64029.66834 | ||
| Q8IZF2 | 12 | 10 | 346.73 | 0.853969476 | 1.0632002 | XA | XN | Probable G-protein coupled receptor 116 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPR116 PE=1 SV=3 | 4406663 | 2824585 | 3945187 | 4565978 | 3512572.16 | 4597165.438 | 3354859.27 | 2390230.426 | 2470245.142 | 3062404.98 | 5094018.058 | 2583354.433 | 3278014.792 | 3978143.723 | 3415813.403 | 3081165.807 | 3885568.599 | 3474006.639 | 3936094.51 | 3178066.149 | 3806004.099 | 2771249.983 | 2866724.319 | 4381348.584 | 3480779.11 | 2791226.862 | 2949792.619 | ||
| P24592 | 4 | 4 | 345.91 | 0.661998099 | 1.277456143 | HN | XA | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP6 PE=1 SV=1 | 7060211 | 3597581 | 2825242 | 2123076 | 5008421.557 | 3012210.235 | 2468780.67 | 3934315.164 | 8222318.245 | 1271476.055 | 1472377.009 | 3654368.465 | 2429844.467 | 612576.9527 | 2755454.034 | 26036677.07 | 5575870.982 | 5056805.603 | 3999467.962 | 4252642.911 | 5370622.122 | 3449154.647 | 9010838.199 | 730215.2787 | 6071480.856 | 4208447.517 | 7671980.276 | ||
| P40926 | 5 | 4 | 345.54 | 0.083238668 | 4.755162611 | HN | XA | Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=MDH2 PE=1 SV=3 | 465343.4 | 131066.1 | 47024 | 536648.9 | 217399.4271 | 184401.5737 | 357278.9177 | 369461.5983 | 252865.864 | 3248976.467 | 1815521.106 | 4072899.609 | 675982.917 | 1556235.939 | 302799.1077 | 104234.6477 | 179800.7886 | 223850.1316 | 2129579.602 | 61380.7962 | 159221.6253 | 206010.5693 | 206131.5262 | 695587.0474 | 334425.5052 | 116610.6971 | 199624.8926 | ||
| Q96AP7 | 4 | 4 | 342.39 | 0.638137653 | 1.220885827 | XA | XN | Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule OS=Homo sapiens GN=ESAM PE=1 SV=1 | 2015147 | 6304522 | 7387708 | 5576216 | 4186798.243 | 3497544.663 | 8019744.319 | 4002820.529 | 9151943.019 | 2742531.569 | 7403122.974 | 2501507.538 | 5924044.806 | 4252058.624 | 9255110.585 | 4135336.365 | 3744785.013 | 3235626.075 | 2275594.542 | 4285514.493 | 2826639.431 | 5557024.2 | 2941092.337 | 9565794.949 | 5436683.216 | 4659523.805 | 3522676.451 | ||
| P08133 | 16 | 9 | 341.94 | 0.366199814 | 1.440967302 | XA | XN | Annexin A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA6 PE=1 SV=3 | 1951008 | 5863529 | 11170190 | 3443982 | 2226363.902 | 3140146.741 | 5518285.083 | 3029330.876 | 5663964.916 | 2363846.85 | 6681379.031 | 2516681.01 | 3304001.608 | 2719532.902 | 5442061.755 | 3161043.824 | 2120664.375 | 2646877.749 | 4137386.391 | 3533913.541 | 2667081.676 | 2914090.437 | 2164588.339 | 5483317.086 | 2597247.412 | 3031286.158 | 2622895.945 | ||
| A0M8Q6 | 4 | 1 | 341.13 | 0.373755176 | 1.623200382 | HN | XA | Ig lambda-7 chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLC7 PE=1 SV=2 | 749464.2 | 498611.4 | 921097.5 | 197846.5 | 2159005.419 | 1279031.042 | 1524255.889 | 847985.0232 | 1641283.406 | 1915446.414 | 2081788.841 | 5520099.504 | 596491.1128 | 1086919.798 | 1645694.73 | 813396.7193 | 897475.9228 | 1380210.45 | 1413302.778 | 2987041.461 | 864477.5294 | 281870.3823 | 961699.7449 | 1415580.191 | 1027982.913 | 1379814.525 | 1452462.571 | ||
| P02452 | 11 | 6 | 339.85 | 0.904730868 | 1.236132739 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 249732.7 | 393905.7 | 518475.4 | 159994.8 | 612682.7054 | 140675.6475 | 378053.4832 | 86773.00838 | 266752.47 | 97575.45208 | 411807.5184 | 169014.2976 | 180361.9589 | 196824.5228 | 319227.0899 | 1358529.327 | 146668.4686 | 200965.9468 | 80846.63302 | 211837.2662 | 121899.8726 | 183081.4439 | 452692.9074 | 735030.9844 | 218528.0641 | 243502.4133 | 245010.6248 | ||
| Q6XQN6 | 9 | 4 | 338.99 | 0.030346861 | 1.622227385 | HN | XA | Nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAPRT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 12504148 | 4062713 | 4567467 | 6951842 | 4942142.45 | 6189802.428 | 9066412.163 | 8370882.352 | 7052900.55 | 21148077.69 | 14818643.02 | 5499245.446 | 15136939.6 | 11886596.94 | 7840401.942 | 14070070.51 | 6573744.524 | 6375645.268 | 14086313.51 | 10676357.24 | 7180763.292 | 11956141.41 | 11843171.76 | 10268585.52 | 8920624.053 | 7158415.125 | 10814887.67 | ||
| Q8WVQ1 | 9 | 8 | 338.12 | 0.604490389 | 1.12139322 | XA | HN | Soluble calcium-activated nucleotidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CANT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3468221 | 1816464 | 2177719 | 2483202 | 2340484.009 | 2562892.509 | 2683589.132 | 3676389.52 | 2584988.046 | 1609839.292 | 2183154.916 | 1547164.953 | 4588197.93 | 2408612.454 | 1809563.187 | 1594784.554 | 2372229.23 | 3104656.381 | 2042433.203 | 2588023.652 | 2635326.313 | 1124631.754 | 2852174.974 | 1286062.79 | 3071321.325 | 3648699.105 | 2974423.935 | ||
| Q14894 | 5 | 4 | 337.65 | 0.170712779 | 2.080431633 | XA | XN | Thiomorpholine-carboxylate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRYM PE=1 SV=1 | 1737118 | 1553738 | 2124526 | 5966515 | 694274.9584 | 5697638.194 | 5917059.523 | 2687981.333 | 5393344.412 | 5650226.112 | 2782633.081 | 3708329.727 | 3105853.468 | 4093649.199 | 2010926.176 | 584400.3075 | 1286734.505 | 1307403.433 | 1433384.748 | 1590478.958 | 2615255.06 | 3324464.201 | 1560885.403 | 1115854.89 | 934835.6733 | 1523742.287 | 1173023.999 | ||
| P35321 | 5 | 2 | 336.75 | 0.858248253 | 1.605969066 | XN | XA | Cornifin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR1A PE=1 SV=2 | 535814 | 294105.9 | 236872.8 | 306964.2 | 239748.0795 | 4969762.177 | 10496118.51 | 8430496.404 | 8906265.488 | 1567150.106 | 18846096.05 | 14051173.34 | 7225182.089 | 453434.8857 | 359077.3134 | 768761.1553 | 186696.0783 | 251343.9155 | 6428813.45 | 24016000.34 | 4736492.416 | 17300642.44 | 518645.042 | 792358.3343 | 818209.8923 | 312725.7752 | 347380.6458 | ||
| P12277 | 4 | 3 | 335.89 | 0.243833814 | 1.763770471 | XA | XN | Creatine kinase B-type OS=Homo sapiens GN=CKB PE=1 SV=1 | 1071214 | 757139.1 | 1826080 | 3874341 | 2795952.368 | 268386.0543 | 495983.8471 | 1522638.875 | 1103503.138 | 1534487.706 | 665314.8557 | 845554.4797 | 565125.0961 | 929904.4368 | 1011926.885 | 2441989.985 | 385235.0387 | 1197230.968 | 335079.2061 | 342369.6601 | 306931.3149 | 348266.5002 | 1387263.602 | 601955.564 | 2863083.866 | 792505.6967 | 798634.8277 | ||
| P01040 | 6 | 5 | 335.8 | 0.858692609 | 1.933811722 | XA | HN | Cystatin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSTA PE=1 SV=1 | 1253226 | 3706902 | 2741574 | 1626177 | 1430120.968 | 7296881.881 | 52959508.89 | 13700225.64 | 31899859.13 | 2309520.06 | 21840852.16 | 15154648.65 | 9638146.45 | 2041400.068 | 3350638.741 | 2228284.45 | 1534793.801 | 2204626.006 | 2795196.882 | 54269499.5 | 5698441.691 | 13793546.39 | 2345969.963 | 6643614.236 | 3663671.768 | 3316305.623 | 1374346.549 | ||
| Q8N126 | 6 | 4 | 335.53 | 0.846238938 | 1.344678538 | HN | XN | Cell adhesion molecule 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CADM3 PE=1 SV=1 | 615946.5 | 4608169 | 2492988 | 1321269 | 3974211.607 | 660445.5865 | 331613.7525 | 839994.145 | 673016.6529 | 1507851.332 | 565954.8948 | 814021.6141 | 668670.3543 | 1491694.242 | 3136775.867 | 4960073.105 | 1590305.592 | 990346.3529 | 678902.0061 | 475927.6276 | 633777.6109 | 1974650.38 | 1912527.627 | 2619112.402 | 1061467.006 | 1346852.904 | 991542.8611 | ||
| Q9UL52 | 6 | 5 | 334.09 | 0.921183342 | 2.3863214 | XN | HN | Transmembrane protease serine 11E OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMPRSS11E PE=1 SV=2 | 124036.3 | 133270.3 | 454192.6 | 139031.1 | 537743.8871 | 307060.5849 | 6965194.786 | 1482242.577 | 836002.7651 | 1167727.363 | 866344.6661 | 1573747.901 | 1671999.149 | 241671.927 | 378723.8624 | 159076.8304 | 288768.8091 | 367742.8996 | 4269978.25 | 6534715.362 | 457477.6885 | 3660492.226 | 132279.8086 | 442635.2139 | 198323.7328 | 208501.1906 | 121661.9177 | ||
| Q8WZ42 | 162 | 47 | 333.97 | 0.314770457 | 1.235858928 | XN | XA | Titin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTN PE=1 SV=4 | 87043924 | 1.24E+08 | 92441285 | 62122557 | 78344350.11 | 84109835.9 | 78287349.48 | 63755191.49 | 106645835.8 | 113957943 | 120112101.8 | 140628684.6 | 84913484.62 | 76890210.79 | 80722533.92 | 44963631.57 | 93038600.04 | 125507941.9 | 132206940.3 | 94089014.79 | 85897908.04 | 75321862.6 | 113295476.8 | 153667720.6 | 75213718.01 | 128397701.1 | 101526721.3 | ||
| Q9NZV1 | 10 | 7 | 333.02 | 0.026346848 | 1.406642899 | HN | XN | Cysteine-rich motor neuron 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRIM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3565650 | 1474736 | 2158232 | 1417542 | 1458033.924 | 1743658.137 | 2190794.968 | 1984532.776 | 2136472.364 | 3285604.364 | 2482859.558 | 1655824.128 | 2318088.553 | 1805266.696 | 2033908.799 | 1537861.132 | 1785487.406 | 2342138.18 | 1895271.528 | 1563220.756 | 1319115.028 | 865865.208 | 1500298.091 | 1363254.888 | 1432562.415 | 2220052.301 | 1523319.995 | ||
| O43488 | 7 | 1 | 332.29 | 0.001388191 | 8.675013979 | XA | HN | Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR7A2 PE=1 SV=3 | 225310.8 | 1240692 | 201878.4 | 2286349 | 69876.6661 | 251655.7164 | 403190.158 | 1280564.361 | 279806.8458 | 84345.49949 | 17998.74533 | 194389.3118 | 74866.52209 | 3224.989014 | 62960.66587 | 163688.4736 | 92544.70582 | 25210.40558 | 160612.2166 | 63254.98898 | 114795.6978 | 293057.2598 | 349314.2626 | 32836.89391 | 250777.6834 | 83757.76577 | 109794.1319 | ||
| P09417 | 4 | 3 | 331.94 | 0.210174973 | 2.152629715 | XA | XN | Dihydropteridine reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=QDPR PE=1 SV=2 | 1038195 | 540501 | 752918.5 | 833127.3 | 108640.0728 | 1692656.84 | 3921092.131 | 2147731.23 | 1072712.923 | 635221.2961 | 908424.7849 | 1187666.511 | 1467010.744 | 704391.3548 | 489103.0995 | 460861.3245 | 407179.403 | 686657.3316 | 1555685.606 | 391177.042 | 1158860.134 | 835555.5189 | 511084.524 | 91675.79796 | 395262.5921 | 359247.6914 | 326001.5875 | ||
| P20062 | 7 | 4 | 331.93 | 0.015178944 | 1.603500672 | XN | HN | Transcobalamin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 1369022 | 1753165 | 1277675 | 1129586 | 616513.2079 | 1411768.789 | 1813287.633 | 1133222.072 | 800943.1665 | 234390.073 | 1280958.716 | 745988.1695 | 2114136.881 | 1034226.266 | 502474.8776 | 446483.3657 | 511387.5512 | 527062.6215 | 832795.3157 | 1594490.913 | 1610190.97 | 882698.0291 | 1180735.035 | 1679973.336 | 1005994.863 | 1958562.395 | 1115827.628 | ||
| Q5D862 | 7 | 5 | 330.97 | 0.079898691 | 12.76098339 | XA | HN | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 26104.3 | 12452.13 | 14509.04 | 10182.74 | 6800.16569 | 33806.00129 | 377902.1844 | 720775.0713 | 56885.09769 | 3098.510865 | 25690.18424 | 11810.58971 | 10379.36558 | 13685.99834 | 12648.63179 | 7886.174709 | 9891.699329 | 3601.610279 | 3629.566469 | 133221.6314 | 64251.72853 | 246605.2242 | 11755.57033 | 6214.611729 | 24423.18139 | 19908.60323 | 10763.77549 | ||
| Q13308 | 7 | 5 | 330.69 | 0.434534987 | 1.40503261 | XN | XA | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTK7 PE=1 SV=2 | 1106079 | 797388.5 | 776826.1 | 676557 | 547359.6 | 1162087.8 | 1250972.3 | 1235240.519 | 1219296.158 | 1342350.48 | 1440802.721 | 1153308.264 | 1733446.41 | 849711.1635 | 654197.8303 | 585342.1066 | 970527.422 | 1113834.702 | 1553992.817 | 1317534.95 | 913762.4434 | 3876124.821 | 810178.4672 | 843153.9594 | 1104334.291 | 1023127.404 | 882466.2687 | ||
| Q9UNN8 | 5 | 5 | 330.6 | 0.047589978 | 1.628746601 | XA | HN | Endothelial protein C receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROCR PE=1 SV=1 | 96922828 | 1.31E+08 | 94176133 | 68551787 | 42540771.53 | 96787620.25 | 135770846.3 | 256402154.1 | 124659598.7 | 46770888.28 | 110146572.2 | 57201183.7 | 96518978.44 | 58411798.54 | 49325636.78 | 64614681.1 | 92045536.64 | 67690770.17 | 78353185.88 | 94890788.94 | 87316417.41 | 75142678.04 | 75963852.57 | 94746150.27 | 112058959.2 | 121435499.7 | 112147905.9 | ||
| O95497 | 6 | 3 | 329.76 | 0.18027042 | 1.566032321 | XN | HN | Pantetheinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VNN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 274384.6 | 381823.5 | 543644.5 | 48176.52 | 454718.152 | 454628.0963 | 469567.9755 | 795499.0731 | 509093.4123 | 257901.4709 | 188101.4551 | 764136.0203 | 272458.7434 | 207034.0806 | 1086932.998 | 143380.5201 | 117281.6351 | 331516.2568 | 889421.9313 | 999887.919 | 337404.9772 | 734080.2533 | 430323.3367 | 663840.8746 | 623588.8608 | 236371.7559 | 360640.7921 | ||
| P18136;P18135 | 5 | 1 | 327.82 | 0.319054754 | 1.330157681 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-III region HIC OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=2 | 228471.5 | 504681.4 | 253381.7 | 576903.2 | 390744.7027 | 502054.548 | 266671.0627 | 246567.0503 | 366644.9909 | 164225.2589 | 146957.5371 | 88540.77104 | 537732.9908 | 245750.6806 | 428691.8648 | 655351.3804 | 457502.3236 | 969705.328 | 471231.2587 | 602528.6033 | 372162.3402 | 434255.6921 | 373351.051 | 543149.1806 | 935280.1576 | 282544.3258 | 423063.2744 | ||
| Q86V85 | 5 | 4 | 327.59 | 0.970522183 | 1.096525727 | XA | XN | Integral membrane protein GPR180 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPR180 PE=2 SV=1 | 3417192 | 2484209 | 6905744 | 3215649 | 1783743.55 | 1840930.652 | 1448597.531 | 2499855.706 | 1634094.348 | 3353643.529 | 3965083.011 | 1398133.339 | 1918749.17 | 2875770.756 | 3141074.637 | 2037265.53 | 1661657.926 | 2681190.677 | 1355172.116 | 1709848.247 | 2576429.522 | 1160478.385 | 2439825.743 | 3410556.808 | 3745290.841 | 3120306.558 | 3491142.672 | ||
| Q9Y624 | 7 | 5 | 327.36 | 0.80785214 | 1.025528301 | XN | XA | Junctional adhesion molecule A OS=Homo sapiens GN=F11R PE=1 SV=1 | 3792438 | 3444572 | 4227567 | 2938643 | 1987923.627 | 2745807.876 | 4309249.9 | 3225434.671 | 4272987.62 | 3145191.107 | 8243861.038 | 2059967.3 | 6088221.024 | 3919815.771 | 1880721.2 | 1947889.363 | 2013069.058 | 1857589.526 | 2279245.604 | 3077712.257 | 2987798.424 | 2389538.143 | 3415286.303 | 7823912.89 | 3705393.971 | 3806895.53 | 2248803.534 | ||
| Q53RD9 | 10 | 7 | 326.65 | 0.386868422 | 1.346674009 | XA | XN | Fibulin-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN7 PE=2 SV=1 | 13741647 | 6518100 | 10918902 | 13109587 | 13353469.15 | 6870631.282 | 4275145.858 | 8746765.452 | 3648025.463 | 10438689.06 | 2037648.281 | 4442739.99 | 5394661.493 | 3702828.825 | 5982899.389 | 18199618.63 | 8948019.669 | 4920330.895 | 5406327.967 | 5778857.128 | 7092377.657 | 4357519.148 | 11274955.88 | 3657757.462 | 9994229.886 | 7056848.986 | 5664663.5 | ||
| Q8NI32 | 2 | 2 | 326.03 | 0.80409312 | 1.400560684 | HN | XA | Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPD6B PE=2 SV=1 | 1149919 | 204054.8 | 291351.8 | 40970.56 | 375276.3578 | 494521.8903 | 417319.5801 | 615138.3624 | 351227.5377 | 74580.51323 | 75852.95031 | 203471.3815 | 1782031.353 | 190414.5582 | 463725.7021 | 929152.4478 | 757328.8625 | 1041343.727 | 230452.168 | 436311.893 | 347232.4979 | 1291741.29 | 409588.7198 | 124620.1714 | 1203552.928 | 406492.4153 | 601286.2523 | ||
| Q99574 | 9 | 8 | 325.99 | 0.660600321 | 1.23289621 | HN | XN | Neuroserpin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINI1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2661951 | 3481843 | 2729822 | 3289602 | 4898575.482 | 3861542.247 | 3274597.01 | 3641272.007 | 3224964.611 | 2803614.176 | 7044401.311 | 5671152.854 | 4198200.032 | 6277635.829 | 2052674.419 | 2256946.295 | 1679689.811 | 1399889.734 | 2078138.787 | 4427811.396 | 2460533.657 | 3586496.942 | 1938074.576 | 2767251.618 | 5176234.586 | 2378318.874 | 2265010.502 | ||
| Q14651 | 7 | 1 | 325.61 | 0.84228875 | 1.444891568 | XN | HN | Plastin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 151023.4 | 11292.2 | 35234.81 | 177594 | 40493.77853 | 86915.43502 | 67541.63961 | 132661.8408 | 38899.95484 | 4546.27113 | 66904.57587 | 60572.31987 | 101454.9274 | 78933.15201 | 46728.23364 | 97883.13538 | 34744.96912 | 51728.55079 | 52637.87214 | 40576.47019 | 323702.9757 | 113245.4585 | 88406.54726 | 7893.808013 | 94872.90353 | 25485.44575 | 38471.50167 | ||
| Q7Z5N4 | 10 | 4 | 323.46 | 0.912680008 | 1.140632201 | HN | XN | Protein sidekick-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1824004 | 2022165 | 695879.6 | 1372556 | 486742.1459 | 1589619.092 | 1579113.564 | 1494398.314 | 1825774.347 | 551937.8194 | 3099174.882 | 2357687.636 | 2514914.989 | 2225861.845 | 1055579.539 | 221486.6083 | 1347448.31 | 714286.7015 | 1432589.187 | 1567333.666 | 1475061.369 | 1231835.998 | 769324.0307 | 1845234.479 | 1326412.209 | 1509792.068 | 1193793.985 | ||
| Q01518 | 10 | 5 | 323.08 | 0.824090922 | 1.276575723 | HN | XN | Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAP1 PE=1 SV=5 | 1834765 | 740789.6 | 907004.4 | 1840195 | 559214.2934 | 1827332.279 | 1790756.941 | 2450151.12 | 1664768.328 | 3660850.663 | 1159329.075 | 3023255.634 | 745873.6381 | 899435.1475 | 2555287.009 | 1161328.973 | 1587148.943 | 706046.475 | 891953.5615 | 1170841.885 | 2146024.103 | 1244129.177 | 1381908.421 | 1806213.742 | 2057167.496 | 837419.1144 | 605068.0946 | ||
| P24593 | 4 | 3 | 322.76 | 0.70166893 | 1.091302595 | XA | HN | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP5 PE=1 SV=1 | 1944432 | 454428.9 | 572609.6 | 672328.1 | 971661.4022 | 399415.5095 | 551608.7287 | 863044.2277 | 918691.8565 | 559065.8576 | 496304.6287 | 376406.2656 | 275722.8207 | 312531.0144 | 1263633.379 | 1771508.794 | 857343.9504 | 820922.9542 | 609642.264 | 590136.5508 | 609430.317 | 338839.8554 | 1083818.993 | 783876.8191 | 1082870.92 | 1129187.355 | 1067694.83 | ||
| Q9H159 | 5 | 2 | 321.74 | 0.914381767 | 1.107969283 | XN | XA | Cadherin-19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH19 PE=2 SV=1 | 1870219 | 1064726 | 945959.1 | 995216.4 | 1339810.565 | 820622.0673 | 1018990.388 | 1198384.386 | 937426.4779 | 2865814.915 | 1438524.49 | 856269.1795 | 762169.492 | 1191292.189 | 810186.7241 | 747783.3639 | 1356137.318 | 1173849.907 | 1102703.99 | 873049.6851 | 1902043.697 | 1130096.754 | 1597990.926 | 1967707.067 | 633056.341 | 1002256.157 | 1082802.376 | ||
| P09619 | 6 | 3 | 320.87 | 0.454967107 | 1.348750378 | XN | HN | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDGFRB PE=1 SV=1 | 1306130 | 1997214 | 1349784 | 600973.6 | 989617.576 | 1256876.447 | 1354493.222 | 3577315.176 | 1606709.181 | 1653211.228 | 2375669.319 | 997612.0134 | 1093460.046 | 1430433.706 | 1027919.168 | 501951.5368 | 2031255.727 | 1765673.99 | 2015516.22 | 4541413.165 | 1659527.484 | 1592419.865 | 1187649.505 | 2596653.055 | 985525.5361 | 1723363.689 | 1066041.961 | ||
| Q96DG6 | 12 | 8 | 320.58 | 0.023721206 | 2.246273374 | XA | HN | Carboxymethylenebutenolidase homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=CMBL PE=1 SV=1 | 2010624 | 489666.7 | 1173504 | 2130991 | 618296.364 | 2605559.176 | 2583643.31 | 3714776.595 | 1863137.56 | 777801.6195 | 1026233.069 | 1332170.092 | 1103920.231 | 843541.7609 | 293469.4271 | 951662.869 | 794804.4862 | 529159.8761 | 770637.3545 | 2924121.707 | 1185692.443 | 1544837.381 | 1924014.355 | 953644.4928 | 1530114.003 | 858821.2364 | 1497208.765 | ||
| P60022 | 2 | 2 | 320.02 | 0.582545969 | 1.282403271 | XN | XA | Beta-defensin 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DEFB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2.25E+08 | 1.57E+08 | 1.18E+08 | 2.28E+08 | 178564393.4 | 198239158.8 | 67954443.35 | 170268896.5 | 206331808.2 | 200234335.9 | 150626039.2 | 91697978 | 266736235.3 | 327527682.4 | 103776998.8 | 207989926.5 | 79267788.88 | 241711121.5 | 154099649.5 | 268198676.8 | 265694061 | 131671502 | 209062182.3 | 75750056.95 | 200498342.5 | 320441712.1 | 361341045.2 | ||
| P31949 | 5 | 2 | 319.4 | 0.963344545 | 1.608990737 | XN | XA | Protein S100-A11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A11 PE=1 SV=2 | 1391437 | 1104851 | 1307414 | 2672485 | 2111481.768 | 4006970.534 | 7450678.545 | 13319204.47 | 11674748.58 | 18514513.28 | 8439737.283 | 4662089.927 | 5731620.661 | 1339570.419 | 2571646.602 | 2390872.351 | 1406142.688 | 1825479.434 | 51528182.18 | 4432965.31 | 3868161.589 | 5135984.825 | 1394948.039 | 1660837.508 | 2328811.351 | 899560.1414 | 1218319.439 | ||
| Q13822 | 7 | 7 | 318.94 | 0.65188477 | 1.318665228 | XA | XN | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENPP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 811684.8 | 1208250 | 430259.6 | 202153.5 | 275749.6505 | 807669.1043 | 570352.2601 | 512264.8038 | 1275968.27 | 326363.859 | 1215825.862 | 260133.182 | 1614182.174 | 303022.1441 | 488216.318 | 93533.05761 | 635450.894 | 411729.0365 | 598870.4727 | 676714.029 | 522820.5702 | 471695.3867 | 457554.204 | 461605.273 | 649149.2475 | 432719.1383 | 350478.4004 | ||
| P46940 | 11 | 5 | 318.88 | 0.286697411 | 1.811636228 | XA | HN | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IQGAP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 142842.8 | 107875.7 | 49692.66 | 449137.7 | 130231.8514 | 412349.5586 | 367275.8243 | 673712.6745 | 1146753.511 | 243818.2783 | 133330.9031 | 242698.0173 | 531003.8216 | 231424.8969 | 327056.2305 | 140588.8728 | 45734.84115 | 25189.04969 | 1309195.379 | 130152.2598 | 41047.41083 | 194971.5514 | 140625.1148 | 75834.28333 | 161710.7767 | 39247.12981 | 60463.96313 | ||
| Q5VUB5 | 4 | 4 | 318.18 | 0.981519806 | 1.047314104 | HN | XN | Protein FAM171A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM171A1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2005291 | 1124818 | 1019545 | 1365403 | 1452498.93 | 1080740.265 | 615657.4949 | 1238151.12 | 573216.2798 | 1247268.83 | 407337.4125 | 414925.5829 | 836873.7929 | 1338988.278 | 1405771.092 | 1924468.039 | 1559887.518 | 1539693.163 | 825647.2697 | 1263482.203 | 1262060.746 | 1194581.056 | 1467012.647 | 494323.6537 | 1417227.706 | 1028927.156 | 1239681.275 | ||
| P19971 | 5 | 4 | 317.44 | 0.869632029 | 1.055887287 | XN | XA | Thymidine phosphorylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TYMP PE=1 SV=2 | 478255.5 | 1028151 | 742988.9 | 588430.2 | 290596.3699 | 161808.718 | 1122111.227 | 378798.2409 | 532441.2679 | 1025811.291 | 1306504.283 | 138333.3668 | 489538.269 | 237933.6693 | 1173454.916 | 793640.7284 | 308628.6108 | 138598.4904 | 2115291.687 | 225338.0798 | 166418.0698 | 127486.6822 | 662345.8781 | 1125875.872 | 626289.6304 | 369416.0017 | 202640.3662 | ||
| P12814 | 12 | 1 | 316.69 | 0.465902302 | 1.55196782 | XA | XN | Alpha-actinin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 25277.88 | 23433.11 | 3630.767 | 56707.7 | 1695.06708 | 90687.92209 | 49259.99367 | 33798.6129 | 101952.5041 | 23493.15663 | 59089.9697 | 65834.94915 | 14666.77267 | 25911.98691 | 99485.61561 | 0 | 13424.35317 | 0 | 62224.66186 | 0 | 22462.26863 | 32439.98775 | 8081.231764 | 18143.62384 | 32635.30294 | 19318.70605 | 53696.52113 | ||
| P01612 | 4 | 2 | 316.22 | 0.741091245 | 1.891477317 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region Mev OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 32918180 | 7655270 | 8269247 | 3317685 | 6073614.589 | 1387774.395 | 1698665.494 | 1582098.752 | 2872595.899 | 3961718.578 | 1318867.662 | 5779623.25 | 3043756.372 | 1852025.836 | 9431323.139 | 2611480.259 | 4741579.156 | 2034101.346 | 2049982.015 | 1731582.078 | 2564118.336 | 2788064.376 | 4333882.792 | 16169423.13 | 4942858.944 | 1591532.026 | 3672890.249 | ||
| P20827 | 5 | 3 | 315.5 | 0.298454003 | 1.237140822 | XA | HN | Ephrin-A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFNA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5687657 | 3955552 | 2392768 | 3453290 | 1761118.544 | 3077331.364 | 2823895.698 | 3817492.679 | 3645263.324 | 1667596.495 | 4441947.916 | 2000346.601 | 5076718.801 | 2615808.86 | 1909613.105 | 1293430.806 | 2386609.875 | 3353993.748 | 2629441.292 | 4538610.798 | 4734704.886 | 2022295.078 | 3515886.523 | 1926165.75 | 3545848.065 | 2706603.49 | 4304604.487 | ||
| P49419 | 9 | 6 | 313.61 | 0.946098311 | 1.14898777 | XA | HN | Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH7A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 2019880 | 1702852 | 816876.5 | 4256437 | 604553.8341 | 3082827.358 | 1715439.583 | 2350972.314 | 1547718.428 | 2165018.748 | 1278057.135 | 2960592.161 | 3138423.484 | 1642570.514 | 1608659.511 | 929933.304 | 970611.4711 | 1057003.273 | 3975350.956 | 1631007.948 | 2840074.69 | 2139298.376 | 1233352.077 | 1693877.801 | 612487.4429 | 1696943.89 | 1093432.617 | ||
| Q8NBS9 | 8 | 5 | 313.31 | 0.529615885 | 1.917519193 | HN | XN | Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TXNDC5 PE=1 SV=2 | 2007659 | 966706.1 | 1434344 | 2457558 | 2522449.281 | 597763.232 | 1151704.045 | 1127713.7 | 713744.1432 | 973891.3728 | 933941.2082 | 1116076.801 | 624068.863 | 696650.5182 | 1811261.924 | 11074756.2 | 1045298.701 | 893798.2622 | 218536.2228 | 519236.5801 | 712210.9679 | 750381.2247 | 2209175.388 | 951339.6704 | 1993600.452 | 1252228.522 | 1390449.761 | ||
| P07237 | 11 | 6 | 313.27 | 0.278726129 | 2.166993119 | XA | XN | Protein disulfide-isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=P4HB PE=1 SV=3 | 343631.9 | 130100 | 178166.9 | 206398.4 | 175118.0748 | 264471.1868 | 523671.0805 | 1255068.938 | 1518617.841 | 598374.8077 | 574844.1872 | 1227580.49 | 683771.661 | 264773.5814 | 154536.7818 | 151742.1089 | 158017.6812 | 218396.8829 | 421147.9242 | 112756.1877 | 155459.4975 | 264067.1222 | 134603.7695 | 185697.0646 | 423046.2889 | 133247.2839 | 290537.3964 | ||
| Q8NCC3 | 7 | 5 | 312.78 | 0.124005219 | 1.351850931 | XA | XN | Group XV phospholipase A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLA2G15 PE=1 SV=2 | 3392772 | 3365204 | 6192313 | 4356599 | 4127731.789 | 3557588.894 | 3479660.484 | 3862094.239 | 2387729.713 | 3779181.799 | 1895170.918 | 3310553.835 | 3714429.092 | 7544820.566 | 3978355.492 | 4229772.502 | 2914303.909 | 2406779.51 | 1601251.756 | 2633258.012 | 3836405.91 | 3123669.966 | 4168714.235 | 1272288.418 | 3009822.031 | 4029726.053 | 2009421.286 | ||
| O95678 | 14 | 3 | 312.43 | 0.090084895 | 3.612715178 | XN | XA | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 75 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT75 PE=1 SV=2 | 2409897 | 1357628 | 632585.3 | 1182216 | 2725163.385 | 3357109.166 | 2325156.593 | 1996342.668 | 721069.1842 | 8644363.036 | 4444989.151 | 2105457.391 | 1053580.808 | 9441878.778 | 1174462.959 | 936741.0175 | 10110644.5 | 13252777.33 | 8903509.518 | 3010922.307 | 4623523.219 | 9964641.917 | 1947687.992 | 845430.3029 | 1160533.335 | 7513494.005 | 22388496.91 | ||
| Q92817 | 32 | 11 | 312.22 | 0.010104888 | 1.840388036 | XN | XA | Envoplakin OS=Homo sapiens GN=EVPL PE=1 SV=3 | 7295843 | 18502827 | 17206644 | 11900263 | 12295772.02 | 30264873.72 | 24041457.15 | 17460886.15 | 40776802.2 | 17394213.89 | 29878456.42 | 65482432.49 | 49330724.01 | 29164193 | 23898981.73 | 14793238.31 | 28010652.1 | 36697743.32 | 48257381.31 | 54694792.06 | 27388119.55 | 35872501.41 | 25216547.64 | 48351583.96 | 43067658.22 | 23076501.22 | 24876139.48 | ||
| P50995 | 10 | 5 | 312.13 | 0.250324657 | 2.901125632 | XN | HN | Annexin A11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA11 PE=1 SV=1 | 3461363 | 2708863 | 2491658 | 1679526 | 3476791.327 | 2743254.996 | 2582990.636 | 4693702.826 | 2160554.566 | 2724914.161 | 4977732.617 | 2858695.559 | 1904559.135 | 1494428.518 | 1702517.356 | 1326160.871 | 1982232.675 | 3379230.801 | 4453392.319 | 14244726.04 | 2318488.74 | 2179268.281 | 1918786.331 | 2806612.407 | 1295833.731 | 2893324.019 | 32731094.44 | ||
| Q16819 | 4 | 4 | 311.17 | 0.143430406 | 19.27026851 | HN | XA | Meprin A subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=MEP1A PE=1 SV=2 | 124821.9 | 254958.3 | 286169.6 | 127300.6 | 506349.6849 | 103964.1603 | 77532.13953 | 130150.8554 | 93923.50038 | 295085.4872 | 187602.3858 | 239786.6018 | 183191.8108 | 214926.2444 | 300495.6521 | 30921792.77 | 282015.5155 | 234201.4095 | 96557.70465 | 57196.9276 | 232894.8124 | 208230.3851 | 180730.5079 | 419795.6408 | 205248.5177 | 228028.1476 | 251348.6369 | ||
| O60888 | 5 | 4 | 309.58 | 0.564173186 | 1.136642813 | XN | XA | Protein CutA OS=Homo sapiens GN=CUTA PE=1 SV=2 | 2256336 | 2616123 | 1830283 | 2105699 | 2588700.605 | 5230883.564 | 3475545.903 | 2598521.303 | 6748480.027 | 1301687.242 | 4340867.814 | 1130061.103 | 6889479.012 | 5064335.908 | 3399666.253 | 1704978.116 | 2661542.218 | 3983682.239 | 4674008.831 | 4842998.592 | 3299777.855 | 3472387.015 | 2494642.454 | 4413452.355 | 4854463.121 | 2517307.383 | 2905744.72 | ||
| P22352 | 7 | 6 | 308.39 | 0.388212155 | 1.156986161 | XA | HN | Glutathione peroxidase 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPX3 PE=1 SV=2 | 19341141 | 34146619 | 26214407 | 15154927 | 12931763.72 | 23599405.54 | 28961911.75 | 19521856.09 | 30084636.06 | 9293228.111 | 40455805.39 | 13598008.63 | 44861253.33 | 21952686.93 | 10879836.24 | 5937897.436 | 11450909.46 | 23038981.53 | 19447626.48 | 21532596.7 | 19683119.68 | 12598120.2 | 17852248.58 | 41715622.42 | 24358802.54 | 22864922.41 | 14457351.47 | ||
| P11684 | 3 | 3 | 307.72 | 0.429755697 | 2.33786283 | HN | XA | Uteroglobin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCGB1A1 PE=1 SV=1 | 4551073 | 14026178 | 7434851 | 15721978 | 26156236.71 | 906314.3285 | 495968.8243 | 934383.724 | 342108.105 | 7615043.801 | 809862.3813 | 6499422.249 | 956895.7863 | 16847906.01 | 57703163.78 | 49845069.18 | 14948556.12 | 9754938.774 | 491189.7811 | 730343.1383 | 831158.6527 | 1223908.223 | 16035086.89 | 16811755.28 | 27280883.86 | 22867019.42 | 25535568.75 | ||
| Q9NQ36 | 5 | 4 | 307.51 | 0.33964878 | 1.889404903 | XA | XN | Signal peptide, CUB and EGF-like domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCUBE2 PE=2 SV=2 | 7161440 | 60858535 | 68504558 | 27608534 | 61903923.32 | 28626702.66 | 11291777.43 | 13607762.79 | 14184831.92 | 5698136.946 | 19862947.27 | 8425966.995 | 7163960.353 | 12847336.57 | 53713448.6 | 21220190.55 | 24654417.3 | 33938718.56 | 7017706.836 | 11430988.81 | 7994649.143 | 10259312.47 | 26162008.04 | 24616287.19 | 17691077.5 | 28817135.83 | 21482043.98 | ||
| O95980 | 5 | 3 | 307.43 | 0.506318998 | 1.186897639 | XA | HN | Reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs OS=Homo sapiens GN=RECK PE=1 SV=1 | 1272143 | 454706.9 | 383005.7 | 717180.1 | 414108.6902 | 751611.5076 | 718821.7444 | 799327.92 | 490129.1559 | 472772.0456 | 146089.8953 | 513704.9356 | 806960.1372 | 74806.12402 | 630691.8157 | 752061.383 | 645048.968 | 1013932.406 | 875216.7258 | 592009.4881 | 819252.7683 | 510548.6634 | 549567.3125 | 149949.6128 | 644606.0602 | 833640.7075 | 667307.1754 | ||
| P01620;P01623 | 5 | 1 | 306.38 | 0.369516963 | 1.443210976 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-III region SIE OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 5021421 | 6326164 | 7794791 | 10867444 | 11268228.16 | 3833402.285 | 2621619.789 | 4070407.941 | 2055840.937 | 5137878.145 | 3957647.307 | 14638643.67 | 5593645.528 | 5572115.126 | 9193071.631 | 11770640.47 | 4785678.202 | 3197180.272 | 10054353.37 | 3896008.075 | 4774429.64 | 9738232.179 | 8145236.569 | 21518750.4 | 8645473.59 | 3718352.675 | 7239522.938 | ||
| P04080 | 5 | 4 | 306.08 | 0.76525386 | 1.97786639 | XA | XN | Cystatin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSTB PE=1 SV=2 | 2357539 | 1402689 | 1245295 | 2454616 | 1440701.761 | 6217925.048 | 15603585.24 | 38781770.06 | 35259420.39 | 25873211.57 | 22857723.06 | 27529318.95 | 18128542.01 | 1704404.481 | 1723580.529 | 3899094.347 | 941317.686 | 1215838.074 | 22098456.99 | 12619599.86 | 6240285.358 | 3122122.3 | 1724742.662 | 1927353.513 | 2327094.388 | 1661777.348 | 1246523.978 | ||
| P09936 | 4 | 3 | 305.82 | 0.551898981 | 1.343747945 | HN | XN | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UCHL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1593648 | 429404 | 747461.3 | 1012983 | 693026.7097 | 229526.4906 | 524881.6228 | 1052406.6 | 225665.3511 | 1383737.419 | 941779.3989 | 1029355.223 | 229291.248 | 604230.2808 | 334342.4573 | 1537284.276 | 240987.628 | 460754.9808 | 201135.8791 | 303288.8009 | 479966.7586 | 380582.2842 | 1056784.39 | 186670.4009 | 1556193.831 | 322077.557 | 545317.4012 | ||
| Q5JRA6 | 13 | 9 | 305.3 | 0.312844336 | 1.257464767 | HN | XN | Melanoma inhibitory activity protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MIA3 PE=1 SV=1 | 2660248 | 2065989 | 2307397 | 2466481 | 3871711.061 | 1620545.556 | 1649760.416 | 2550042.363 | 2110578.15 | 2008607.38 | 3370609.011 | 1350005.084 | 1861792.883 | 3264277.613 | 1765860.996 | 3855265.197 | 2137353.509 | 2832846.775 | 671431.7795 | 1773963.559 | 1708435.535 | 1783036.68 | 2717015.948 | 2558031.751 | 2097220.91 | 2037617.452 | 2503940.12 | ||
| O75015 | 5 | 2 | 303.96 | 0.347108795 | 1.58867828 | XN | HN | Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCGR3B PE=1 SV=2 | 139561.3 | 1456471 | 2064310 | 509558.3 | 241707.5043 | 1779487.281 | 1713256.252 | 1627458.07 | 578603.3902 | 2907018.92 | 160736.1831 | 761995.9625 | 252250.2166 | 653243.7699 | 256504.4167 | 153178.2997 | 624821.0806 | 1246411.509 | 3741604.049 | 1849797.691 | 684513.6667 | 1870118.057 | 769800.2509 | 271285.4371 | 583072.614 | 486793.6108 | 889436.1906 | ||
| Q9UBR2 | 11 | 9 | 303.72 | 0.06269932 | 1.946269079 | HN | XN | Cathepsin Z OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSZ PE=1 SV=1 | 1673169 | 2145623 | 4950793 | 1239711 | 3932759.246 | 1500030.928 | 2128097.81 | 1264330.99 | 2123986.796 | 1655319.51 | 1564181.451 | 3467507.459 | 3524002.943 | 2626918.7 | 4279441.655 | 8272919.86 | 2650085.013 | 1265642.993 | 1095118.456 | 1215117.853 | 1391616.107 | 1532860.901 | 2253383.076 | 2924156.894 | 1711772.486 | 1728950.852 | 1204560.844 | ||
| O95274 | 6 | 4 | 303.55 | 0.876419587 | 1.491896035 | XA | HN | Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPD3 PE=1 SV=2 | 588946.4 | 1272356 | 809747.7 | 372895.3 | 590190.1465 | 3960756.376 | 7361347.933 | 2922386.989 | 9765819.732 | 3966898.357 | 4068475.576 | 2322695.834 | 5101153.63 | 620876.8663 | 548424.147 | 361966.3696 | 549538.0218 | 989712.0886 | 7144407.421 | 6058375.106 | 1534438.098 | 2688650.069 | 681198.9729 | 1794597.313 | 528735.4728 | 910318.5428 | 746446.81 | ||
| P13639 | 11 | 6 | 302.57 | 0.24083789 | 2.025114476 | XA | HN | Elongation factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF2 PE=1 SV=4 | 1673654 | 319615.2 | 1100174 | 3343504 | 267629.8423 | 1467143.292 | 1379187.56 | 3119262.543 | 1518631.944 | 917176.6176 | 586512.3268 | 1235505.266 | 1290123.755 | 207618.728 | 440684.8913 | 1695496.07 | 273780.0093 | 359522.3048 | 729722.1709 | 572912.0118 | 1840755.778 | 545551.1868 | 2628118.61 | 154976.4953 | 1317289.238 | 828006.3841 | 586740.7759 | ||
| Q9UEF7 | 10 | 6 | 302.31 | 0.302138099 | 3.721160506 | HN | XN | Klotho OS=Homo sapiens GN=KL PE=1 SV=2 | 20155372 | 26461218 | 63325868 | 44285587 | 151836266.4 | 9372525.11 | 19966676.61 | 23566747.08 | 7175082.902 | 38299049.97 | 19188730.1 | 24928681.41 | 6285269.534 | 20708592.77 | 76681557.86 | 485791900.8 | 75767222.19 | 14888967.31 | 11094467.92 | 8618838.767 | 9618430.858 | 18074024.44 | 77677004.57 | 7161952.364 | 20594610.85 | 21198375.72 | 30882230.29 | ||
| P17813 | 5 | 4 | 301.42 | 0.227769088 | 1.260545573 | HN | XA | Endoglin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENG PE=1 SV=2 | 5148305 | 4841642 | 4902606 | 3814414 | 4057829.584 | 4621400.237 | 4602089.642 | 3975140.41 | 4899245.494 | 6793655.131 | 7154227.551 | 6470645.423 | 6227644.969 | 6866761.579 | 2457853.747 | 5262352.527 | 4388969.526 | 5887149.531 | 5131975.535 | 5692684.983 | 4996050.773 | 4439857.883 | 5297398.3 | 9105943.03 | 4175839.427 | 5156481.44 | 4497165.64 | ||
| P16930 | 9 | 7 | 301.41 | 0.796832605 | 1.288471478 | XA | XN | Fumarylacetoacetase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAH PE=1 SV=2 | 888246.9 | 706194.8 | 1077727 | 1109276 | 323288.9188 | 2148618.833 | 3001280.415 | 1458683.429 | 1570752.375 | 1212879.989 | 1858572.661 | 1282723.572 | 2996947.228 | 1262810.081 | 829515.0137 | 690292.7133 | 588089.6272 | 697900.7597 | 871060.0328 | 1009692.85 | 1506262.139 | 1661805.575 | 1181193.907 | 1543661.81 | 631730.425 | 589466.5484 | 538957.1068 | ||
| P20151 | 5 | 3 | 300.54 | 0.643856987 | 1.368707768 | HN | XN | Kallikrein-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK2 PE=2 SV=1 | 554706.2 | 1073715 | 519183.5 | 1873425 | 7176985.12 | 118655.288 | 66836.58712 | 58241.61258 | 77283.26605 | 871304.4773 | 140427.7949 | 95693.26556 | 90930.67735 | 1387564.769 | 1675059.799 | 2867411.967 | 810091.2219 | 4810829.805 | 188927.7835 | 338499.089 | 195463.6886 | 187286.4598 | 981916.9683 | 968084.3148 | 2794358.837 | 2482835.598 | 1177481.806 | ||
| Q96PX8 | 4 | 4 | 299.99 | 0.003065584 | 1.370346212 | XA | HN | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLITRK1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5463227 | 5142488 | 5843362 | 4966067 | 4730797.516 | 4820639.231 | 5006638.545 | 5027458.791 | 5043731.817 | 2415679.717 | 4543014.148 | 5271681.656 | 2965385.301 | 5333401.811 | 3937093.182 | 2725386.633 | 3132699.05 | 3276226.615 | 3605762.844 | 3503587.872 | 3825061.026 | 5164950.564 | 3953471.941 | 5474121.083 | 4282225.84 | 4157818.314 | 4716831.935 | ||
| Q9BVM4 | 3 | 3 | 299.44 | 0.89923426 | 1.069319505 | HN | XN | Gamma-glutamylaminecyclotransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2LD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 10791724 | 2564853 | 5649717 | 7910759 | 2792853.433 | 4825231.19 | 5806634.57 | 6501269.738 | 2990074.41 | 5206447.253 | 6895931.844 | 4131380.51 | 7314124.394 | 6635735.676 | 5311629.282 | 7586516.362 | 2938071.707 | 4436317.117 | 3850017.572 | 4442208.932 | 5390883.192 | 5745548.047 | 5631021.347 | 5265717.223 | 8491979.404 | 3096702.001 | 5271215.268 | ||
| P33151 | 8 | 5 | 298.86 | 0.934639507 | 1.378723224 | HN | XN | Cadherin-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH5 PE=1 SV=5 | 609971.6 | 1359960 | 2812275 | 1994531 | 3793918.767 | 476777.3928 | 670556.415 | 486208.7006 | 310552.1974 | 400289.0935 | 843669.1452 | 521264.1961 | 651286.2085 | 1075738.933 | 2320717.094 | 4411189.734 | 1959142.928 | 999069.5326 | 696017.6628 | 1667988.505 | 905427.6484 | 1289721.661 | 995631.3773 | 1038216.658 | 573548.8287 | 1161425.649 | 1233307.866 | ||
| A6ND91 | 6 | 3 | 298.36 | 0.431633398 | 2.076159077 | XA | HN | Putative L-aspartate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASPDH PE=2 SV=2 | 580789.7 | 43834.4 | 340596.1 | 983534.9 | 63793.59452 | 1075808.46 | 928102.645 | 1066305.457 | 303937.1053 | 641031.5099 | 180673.6888 | 391901.9531 | 717298.8917 | 136211.9329 | 142130.5716 | 78355.21292 | 60384.36558 | 246563.6911 | 422636.3033 | 310029.7344 | 799952.1784 | 813614.9746 | 400846.4074 | 196054.2961 | 104620.6139 | 105063.6614 | 150117.0917 | ||
| P54108 | 6 | 5 | 298.08 | 0.930236895 | 1.775503268 | XN | HN | Cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRISP3 PE=1 SV=1 | 935183 | 690321.4 | 2703093 | 1358552 | 546207.9291 | 6427038.844 | 10186018.23 | 9378707.367 | 5930094.961 | 4238323.584 | 7750628.166 | 3757869.229 | 6243530.401 | 1439961.391 | 779320.4141 | 321664.4724 | 820612.7944 | 3105110.989 | 23278505.5 | 17435626.62 | 1191275.424 | 2310615.088 | 830653.044 | 2240665.577 | 655102.5663 | 1552114.416 | 1030976.325 | ||
| P09237 | 7 | 5 | 297.89 | 0.972092653 | 1.192622675 | XA | HN | Matrilysin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP7 PE=1 SV=1 | 10490940 | 2408579 | 1217784 | 7505638 | 3147586.07 | 1075382.284 | 1172562.942 | 5155452.368 | 1346233.423 | 1976878.582 | 1449842.375 | 2355545.056 | 1438557.59 | 3184534.069 | 4449597.235 | 3969734.696 | 6130502.87 | 3151063.419 | 3812481.663 | 2449230.305 | 2783336.997 | 1678752.878 | 1358303.074 | 691806.3301 | 3345331.318 | 4252182.067 | 8962472.316 | ||
| Q06278 | 9 | 8 | 297.67 | 0.009018758 | 2.969749588 | XA | XN | Aldehyde oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AOX1 PE=2 SV=2 | 1010328 | 166998.1 | 1036184 | 2118115 | 802074.1135 | 1113724.88 | 368869.9114 | 1212327.229 | 344214.9321 | 65396.77193 | 105913.7541 | 491432.5029 | 1319056.475 | 123668.7715 | 354619.8504 | 334171.6811 | 283107.7535 | 79777.38723 | 255636.1739 | 174964.1629 | 231958.7594 | 618650.5769 | 267687.1228 | 170518.5761 | 472294.3882 | 367133.1929 | 193185.7706 | ||
| Q08334 | 6 | 5 | 297.5 | 0.399188858 | 1.242101175 | XN | HN | Interleukin-10 receptor subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL10RB PE=1 SV=2 | 4956105 | 4839419 | 2796074 | 2992869 | 2275808.732 | 9443437.94 | 7599201.034 | 5356769.822 | 9253435.465 | 3464024.923 | 9543470.361 | 2582823.161 | 9675793.662 | 5824345.721 | 3324288.014 | 243106.6319 | 3616580.612 | 5449742.831 | 6308535.614 | 5927875.601 | 5073847.649 | 4877630.678 | 2870345.534 | 12933481.98 | 6830282.344 | 5439027.664 | 4048823.243 | ||
| P07711 | 5 | 4 | 295.47 | 0.274111419 | 1.385420016 | XA | XN | Cathepsin L1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2499273 | 3439802 | 2375988 | 4918195 | 5369041.215 | 5975018.695 | 3135360.387 | 2084726.118 | 3592799.33 | 1735323.867 | 2475660.046 | 942446.3132 | 4775980.56 | 4078191.512 | 3919451.378 | 3979262.417 | 1948446.843 | 3406963.191 | 1941920.983 | 1799681.939 | 2271994.74 | 3030486.905 | 3482265.62 | 3189333.475 | 3517289.568 | 2367989.088 | 2500178.782 | ||
| P22528 | 5 | 2 | 294.09 | 0.905927962 | 1.352816333 | XN | HN | Cornifin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR1B PE=1 SV=2 | 429043.6 | 782849.1 | 488584.5 | 3455423 | 3959261.713 | 30166617.57 | 74327338.45 | 82733051.66 | 88624345 | 9767030.825 | 81802649.43 | 82764271.74 | 43737331.17 | 288615.226 | 2176152.855 | 882957.3628 | 1554036.031 | 449578.6036 | 25500589.33 | 111067013.5 | 45692479.99 | 112791499.7 | 1195552.91 | 1876404.649 | 890847.4137 | 607040.0318 | 2628346.379 | ||
| Q9GZM7 | 10 | 7 | 292.97 | 0.163600104 | 1.201300829 | XN | HN | Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=TINAGL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 4136987 | 3439909 | 3279161 | 5413362 | 4427227.738 | 3998416.696 | 2866514.498 | 4027290.697 | 3342598.609 | 2535097.073 | 3825198.71 | 2174735.592 | 3797727.898 | 2236377.975 | 3391004.458 | 4816729.767 | 3749517.291 | 3227558.471 | 3894436.45 | 4359258.01 | 3011721.537 | 2575898.585 | 3834074.477 | 5499705.148 | 3948263.478 | 4508336.618 | 4111747.175 | ||
| P00736 | 7 | 3 | 291.94 | 0.196107801 | 1.467680522 | XA | HN | Complement C1r subcomponent OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1R PE=1 SV=2 | 1243716 | 347948.7 | 360653.6 | 413308.8 | 203197.2852 | 797901.1603 | 739180.4851 | 971833.5001 | 892888.6454 | 59652.84976 | 211997.006 | 467963.8649 | 1929137.52 | 151893.4207 | 345957.5687 | 154597.5286 | 573485.5421 | 173385.3708 | 214794.3758 | 672810.4851 | 325680.4174 | 213741.2109 | 595161.843 | 64734.07801 | 904905.4159 | 444920.7736 | 912355.4107 | ||
| P04433 | 3 | 2 | 291.67 | 0.64205242 | 1.441914801 | HN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-III region VG (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 3200684 | 2589698 | 3035438 | 8902182 | 6947518.368 | 2321592.507 | 1549374.201 | 2859851.078 | 2182703.438 | 3765661.143 | 1548415.094 | 6455515.11 | 3903814.293 | 5046819.805 | 3427752.85 | 19148077.37 | 4182951.6 | 953527.4431 | 6527084.89 | 2443826.877 | 3450088.046 | 5672119.026 | 3980513.519 | 13384260.5 | 2835736.842 | 2777310.323 | 3683172.587 | ||
| P31151;Q86SG5 | 6 | 6 | 290.27 | 0.986315742 | 1.895934958 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A7 PE=1 SV=4 | 683147.1 | 723397.4 | 712061.7 | 774531.9 | 1050051.868 | 2398630.091 | 2755312.14 | 2720712.165 | 22458260.4 | 5893269.835 | 2232398.764 | 5203609.64 | 2873951.318 | 667582.7077 | 464727.8431 | 1176892.832 | 1142197.065 | 652274.2597 | 14326649.2 | 1784032.274 | 3747339.611 | 15665702.66 | 475881.3278 | 820820.1391 | 537707.5505 | 598614.5288 | 543822.3863 | ||
| Q6PK18 | 7 | 5 | 289.43 | 0.359634515 | 1.46187021 | HN | XN | PKHD domain-containing transmembrane protein C17orf101 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C17orf101 PE=2 SV=2 | 1360559 | 2792621 | 1367684 | 1483376 | 1257869.906 | 1095691.594 | 1074433.491 | 1156949.459 | 1580676.126 | 1936163.868 | 1338536.471 | 3924195.345 | 987180.1856 | 1358281.78 | 2880529.117 | 733388.0146 | 889353.4218 | 739622.6463 | 860597.1312 | 1242486.198 | 770654.1436 | 984405.4993 | 1214819.1 | 1080633.72 | 1802643.657 | 1020328.239 | 1138728.97 | ||
| Q92597 | 4 | 4 | 288.79 | 0.012051082 | 4.357793845 | XA | XN | Protein NDRG1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NDRG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 281783.3 | 18814.32 | 140403.1 | 1201875 | 158967.1912 | 211717.8501 | 239589.241 | 448209.853 | 171558.2412 | 77016.25836 | 22562.04508 | 269307.3898 | 47046.05004 | 20571.67599 | 94900.32698 | 92753.31214 | 32013.34492 | 62574.67001 | 45514.76753 | 41136.06493 | 93489.03475 | 82380.36227 | 210054.2635 | 6793.210883 | 65972.56345 | 49349.57407 | 64569.96985 | ||
| P02743 | 6 | 5 | 288.15 | 0.80414074 | 1.339333132 | HN | XN | Serum amyloid P-component OS=Homo sapiens GN=APCS PE=1 SV=2 | 9944611 | 16385139 | 23248110 | 16575910 | 26163351.9 | 12826611.63 | 13148086.51 | 8137261.597 | 16279270.79 | 3406361.678 | 12826290.17 | 5093819.619 | 10823637.97 | 13335078.8 | 28351242.45 | 76693446.02 | 7376135.73 | 12857033.11 | 7979498.899 | 9932141.782 | 6644309.112 | 15350272.46 | 12320326.55 | 11573149.57 | 20984136.49 | 18616305.55 | 24098419.52 | ||
| Q496F6 | 4 | 2 | 286.96 | 0.572423987 | 1.376655478 | HN | XA | CMRF35-like molecule 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD300E PE=1 SV=2 | 439379.9 | 760131.3 | 564958.9 | 63892.17 | 385261.2322 | 1119694.138 | 832340.762 | 622229.5951 | 1490014.616 | 1760346.281 | 1394436.434 | 300523.2327 | 1589105.613 | 1089993.73 | 722060.1771 | 192366.2477 | 721800.4451 | 871876.9691 | 1243888.31 | 890637.5329 | 679551.2112 | 829634.5033 | 239431.2135 | 928349.265 | 248166.8188 | 1533995.453 | 1165864.655 | ||
| O00764 | 4 | 3 | 285.13 | 0.144243255 | 2.872688249 | XA | HN | Pyridoxal kinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDXK PE=1 SV=1 | 1623594 | 284806.1 | 1284782 | 3825386 | 799349.6019 | 227808.2861 | 725750.6992 | 2206432.071 | 842157.8349 | 370754.9227 | 282082.8597 | 321524.6078 | 413150.7144 | 558136.2483 | 580448.4529 | 712636.149 | 366103.7244 | 509798.354 | 164782.3259 | 280507.592 | 620464.4341 | 819608.2074 | 2238272.412 | 156464.5222 | 2408374.049 | 457176.5578 | 716565.6089 | ||
| P18669;P15259;Q8N0Y7 | 6 | 4 | 284.04 | 0.058167569 | 1.89095982 | XA | HN | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGAM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4492168 | 2455042 | 3961106 | 6172859 | 2033590.69 | 7870399.177 | 9733181.35 | 8929723.285 | 9047998.917 | 3439480.858 | 2966212.063 | 5142142.394 | 2201546.123 | 4490709.353 | 3991675.253 | 1485117.259 | 2556821.279 | 2651324.787 | 4183943.01 | 3279231.68 | 6146041.419 | 4838799.829 | 3720453.708 | 835064.5155 | 3378760.271 | 2701621.433 | 3265294.377 | ||
| Q9H0W9 | 7 | 6 | 283.23 | 0.309922521 | 1.62032295 | XA | HN | Ester hydrolase C11orf54 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C11orf54 PE=1 SV=1 | 1754298 | 7491461 | 4569534 | 2859306 | 2862553.224 | 11957392.04 | 14606409.63 | 7169007.621 | 10140428.57 | 4382935.589 | 6909479.316 | 10036056.89 | 7121733.591 | 2455770.958 | 2139083.355 | 1961732.324 | 2274532.391 | 1853090.321 | 5523331.581 | 3526537.43 | 8969646.525 | 8156135.084 | 3527653.678 | 5677367.866 | 3024112.115 | 4238947.152 | 2031484.882 | ||
| P13671 | 5 | 4 | 282.74 | 0.095017816 | 1.970884863 | XA | HN | Complement component C6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C6 PE=1 SV=3 | 3014607 | 6230190 | 1695111 | 1060229 | 686365.8241 | 948642.1241 | 1616036.479 | 1599225.17 | 1370085.64 | 400694.6342 | 983460.359 | 962268.6099 | 656272.0732 | 1044885.593 | 1657595.473 | 555552.7403 | 1459309.085 | 1524789.907 | 694041.4637 | 1093461.449 | 1002694.468 | 1012677.213 | 914007.9118 | 2056508.095 | 1815820.495 | 1727017.394 | 922371.4684 | ||
| P19957 | 3 | 3 | 282.45 | 0.156395281 | 2.099750624 | XN | XA | Elafin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PI3 PE=1 SV=3 | 513581.5 | 215476.9 | 840195.1 | 97301.21 | 199649.4809 | 344189.2542 | 167842.5165 | 11566492.83 | 14726818.77 | 2815196.378 | 11516722.85 | 3639573.93 | 9944514.563 | 241702.1759 | 822228.6312 | 561876.3135 | 340296.8053 | 217309.124 | 5875747.205 | 25180486.18 | 17384031.15 | 6273967.608 | 734167.876 | 1052474.22 | 480049.4903 | 1961866.376 | 1260309.865 | ||
| P02652 | 5 | 2 | 282.27 | 0.92160666 | 1.166206546 | HN | XN | Apolipoprotein A-II OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1624133 | 692861.5 | 1281693 | 3565840 | 2050503.903 | 1173859.486 | 1605610.739 | 1096758.124 | 2014533.564 | 1736961.201 | 1412556.06 | 4585772.787 | 1310708.592 | 1304708.083 | 1505469.617 | 772619.221 | 1353257.689 | 1881774.803 | 739521.915 | 1751358.269 | 1010181.71 | 1735486.537 | 2052169.753 | 1518499.271 | 1615868.084 | 1247042.677 | 1932803.531 | ||
| O60235 | 4 | 3 | 282.11 | 0.134877262 | 4.114945364 | XA | HN | Transmembrane protease serine 11D OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMPRSS11D PE=1 SV=1 | 480694.4 | 486854.8 | 597938.3 | 360405 | 1191272.697 | 3735920.459 | 9608418.6 | 1252724.083 | 2864478.047 | 303853.6014 | 623353.8001 | 1140145.001 | 1313007.185 | 438541.1659 | 253273.613 | 152929.2935 | 312351.9367 | 463511.4954 | 3493189.336 | 5044010.207 | 443767.9598 | 2574332.936 | 257075.3823 | 186558.8555 | 302398.2034 | 337132.9567 | 321880.8801 | ||
| P05981 | 6 | 2 | 281.93 | 0.348131815 | 1.471464671 | XA | XN | Serine protease hepsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPN PE=1 SV=1 | 126778.2 | 140002.1 | 153055.2 | 480297.9 | 209888.4723 | 110638.0214 | 219387.9474 | 429325.7941 | 127517.5255 | 41237.95989 | 143189.7275 | 148766.2548 | 139768.4344 | 112742.7161 | 189059.5579 | 930398.8892 | 87238.32826 | 114211.1821 | 114427.0936 | 99135.53148 | 39048.21358 | 63816.78676 | 253995.7815 | 57176.22839 | 405389.8566 | 120549.1993 | 203538.5296 | ||
| P18206 | 11 | 6 | 281.62 | 0.511691253 | 1.374205359 | XN | HN | Vinculin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCL PE=1 SV=4 | 706839.1 | 551092.5 | 502482.9 | 916915.3 | 735744.3532 | 1734770.205 | 2100435.53 | 2038202.887 | 1516791.47 | 1281394.236 | 370251.1845 | 1920667.661 | 945352.7288 | 351671.1065 | 1236806.764 | 1341292.982 | 293620.0077 | 315028.7893 | 4379438.46 | 1026919.078 | 972290.2947 | 1626464.278 | 448811.0923 | 733140.5085 | 1040812.447 | 316606.5828 | 526233.0697 | ||
| O43598 | 5 | 4 | 281.5 | 0.793077718 | 1.266738605 | XN | XA | Deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphate N-glycosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=RCL PE=1 SV=1 | 551234.7 | 200445.3 | 486121.2 | 424473.7 | 308727.5142 | 859218.0573 | 625846.842 | 873776.3893 | 273415.3535 | 689645.7709 | 1492664.313 | 785104.065 | 677355.2611 | 717373.0817 | 248659.5872 | 472414.8137 | 286779.1761 | 271051.1456 | 874322.4448 | 424883.1554 | 1173119.799 | 1361309.592 | 732324.9779 | 293395.473 | 389627.1652 | 326081.1167 | 256062.2871 | ||
| Q92876 | 5 | 5 | 281.16 | 0.554472723 | 2.983171353 | XA | HN | Kallikrein-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK6 PE=1 SV=1 | 277343.1 | 146945.5 | 49084.84 | 194518.1 | 201129.7017 | 2216448.804 | 3403268.654 | 2369401.854 | 4285543.398 | 1037631.519 | 821003.663 | 1311751.217 | 551529.8055 | 90429.54623 | 263102.5524 | 108308.2811 | 101605.2118 | 120581.5465 | 6686607.896 | 773066.0656 | 495621.75 | 2505588.025 | 634107.7421 | 209827.1493 | 113023.8938 | 257694.7481 | 168057.3331 | ||
| P12955 | 7 | 4 | 279.32 | 0.557354789 | 1.501843165 | XA | XN | Xaa-Pro dipeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PEPD PE=1 SV=3 | 996070.6 | 437021.2 | 767339.7 | 835045.6 | 179296.6652 | 1621904.918 | 2198350.625 | 910023.2663 | 496611.0393 | 780765.6073 | 848103.5507 | 1062028.691 | 1727041.17 | 1049743.392 | 236704.8312 | 136928.9969 | 467037.8549 | 228689.7885 | 589059.999 | 427096.275 | 1464738.897 | 429995.8621 | 1052295.709 | 381638.5862 | 419658.8823 | 508945.6213 | 347439.0562 | ||
| O75351 | 11 | 5 | 279.07 | 0.553807161 | 1.342867888 | XA | XN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4B OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS4B PE=1 SV=2 | 1251999 | 590067.3 | 341867.6 | 296856.1 | 353437.9972 | 613108.582 | 1125852.664 | 1342895.964 | 697131.4892 | 661198.3387 | 1773573.193 | 797744.2899 | 277863.1932 | 754131.8331 | 202197.4301 | 1007416.544 | 206357.8579 | 300989.7819 | 732635.5175 | 418895.0259 | 677245.4171 | 288500.7865 | 300845.2788 | 129163.3786 | 309771.4453 | 744474.7416 | 1323164.796 | ||
| P23284 | 11 | 9 | 278.78 | 0.11198087 | 1.354287338 | XA | HN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPIB PE=1 SV=2 | 3394476 | 4558362 | 2790380 | 1882447 | 2087768.336 | 3927858.411 | 3354156.89 | 3529889.645 | 2860928.952 | 2522801.695 | 2423764.864 | 2167436.755 | 2627708.268 | 2088098.325 | 1884395.438 | 4128492.555 | 1953285.689 | 1164315.005 | 2033290.056 | 3314271.286 | 2281029.451 | 1514100.286 | 2291870.539 | 798077.9676 | 3813865.516 | 2169722.444 | 2937409.915 | ||
| P49788 | 7 | 4 | 277.4 | 0.520143593 | 2.568889614 | XN | HN | Retinoic acid receptor responder protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RARRES1 PE=2 SV=2 | 1289577 | 266020 | 1180548 | 374482 | 378526.9731 | 305497.7651 | 258233.2631 | 183784.2616 | 468311.4053 | 103601.7586 | 79309.98744 | 140617.3545 | 219513.1972 | 601635.1271 | 477336.9691 | 1292032.703 | 812197.6759 | 324661.992 | 133485.5225 | 315098.1569 | 577198.4816 | 80658.96371 | 241033.3774 | 4003625.77 | 2023544.747 | 2627367.221 | 404320.0757 | ||
| P01594 | 4 | 2 | 276.85 | 0.327489243 | 1.849692739 | XN | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region AU OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1435778 | 2133433 | 700877.7 | 1099472 | 3351550.909 | 273857.8438 | 1291645.848 | 280355.5338 | 272698.5708 | 1058056.571 | 296936.846 | 1580001.145 | 2733679.253 | 567130.0827 | 1926528.586 | 410459.239 | 815920.7164 | 739140.5624 | 893468.3253 | 2217280.592 | 2500878.771 | 699878.9876 | 3048955.23 | 6292332.553 | 1773856.372 | 297931.7173 | 1008833.609 | ||
| P00995 | 4 | 2 | 275.98 | 0.619933636 | 1.348746546 | XA | HN | Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINK1 PE=1 SV=2 | 8366943 | 21825558 | 32250020 | 9934502 | 8207027.369 | 1937494.699 | 40098738.31 | 3982215.018 | 36493939.87 | 6393436.105 | 23958392.68 | 4600872.944 | 17931211.58 | 8150167.429 | 3100957.133 | 32820835.92 | 7616657.934 | 16351920.79 | 5921047.884 | 26110226.18 | 10103937.91 | 15546371.51 | 18165673.31 | 18811025.87 | 10656025.88 | 21439799.88 | 20065323.89 | ||
| P36980 | 5 | 1 | 275.7 | 0.486601509 | 3.10249213 | HN | XN | Complement factor H-related protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFHR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 87909.45 | 66968.5 | 98785.8 | 62155.89 | 275620.0648 | 233466.2908 | 329759.1 | 93228.9906 | 265965.155 | 182195.852 | 15448.09688 | 82519.11867 | 417689.4056 | 64104.63469 | 6340.401421 | 1963977.448 | 23197.21294 | 53642.47053 | 99971.56789 | 30432.7619 | 256276.4003 | 88183.47026 | 43033.56979 | 59329.39465 | 27803.02341 | 178560.0424 | 121847.8892 | ||
| P01767 | 6 | 3 | 275.53 | 0.678736248 | 1.205282889 | XN | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region BUT OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1476432 | 2230955 | 1947653 | 2805565 | 6182238.014 | 2995029.315 | 3627442.323 | 3050117.427 | 2979674.242 | 2599067.575 | 2619180.267 | 4780049.509 | 2232958.911 | 1063600.998 | 3009836.091 | 1435294.73 | 2792697.078 | 2637443.046 | 4994325.816 | 2731564.833 | 2607552.032 | 1664316.8 | 4269121.64 | 3327271.443 | 2346319.71 | 4910086.097 | 1076000.695 | ||
| Q9UBX7 | 6 | 4 | 274.75 | 0.227841102 | 2.307178466 | XN | HN | Kallikrein-11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK11 PE=1 SV=2 | 106935 | 605691 | 355310.6 | 258721.4 | 711418.6198 | 290068.9449 | 1002399.542 | 651905.6066 | 1039158.563 | 728260.9944 | 241597.1682 | 292562.3684 | 369057.1429 | 273897.2702 | 566217.5421 | 56357.21628 | 162584.0073 | 231827.1213 | 1594104.997 | 2034754.287 | 116396.376 | 353071.8657 | 752246.7607 | 1089034.977 | 258842.4271 | 322687.6814 | 221268.6073 | ||
| P08729 | 10 | 2 | 273.85 | 0.914238542 | 1.808657869 | XA | XN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT7 PE=1 SV=5 | 119622.9 | 32693.83 | 8691.065 | 84759.34 | 44514.10779 | 1753508.446 | 444853.903 | 44618.47542 | 1605553.823 | 69501.54174 | 146866.2933 | 508559.5708 | 225659.8598 | 32790.02213 | 163364.0175 | 1144198.802 | 102354.3198 | 23090.3652 | 457234.2087 | 152691.2339 | 16788.48676 | 1314198.121 | 72440.81711 | 53595.90299 | 136557.3048 | 24653.81064 | 60175.53906 | ||
| P07108 | 5 | 4 | 273.65 | 0.32199955 | 1.423561589 | XA | XN | Acyl-CoA-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DBI PE=1 SV=2 | 8445858 | 3616931 | 3499258 | 10159968 | 4849863.107 | 7176950.4 | 16903963.26 | 13837515 | 9080492.03 | 4590048.72 | 10365738.19 | 7743075.555 | 8094034.68 | 5694363.709 | 4156843.083 | 5473234.671 | 5044345.267 | 4642562.942 | 6422329.875 | 9726526.175 | 10236620.44 | 8056880.798 | 2206309.078 | 6556887.947 | 4194009.156 | 4617524.031 | 2473564.558 | ||
| O95971 | 3 | 3 | 272.94 | 0.188712155 | 1.403230458 | XA | HN | CD160 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD160 PE=2 SV=1 | 894999.4 | 1199560 | 1263705 | 1093873 | 615645.5083 | 1025140.811 | 3061432.405 | 916265.9311 | 817177.2335 | 644621.3858 | 1643132.086 | 764158.0558 | 880465.5925 | 891351.2519 | 649785.0518 | 700280.7313 | 820371.002 | 764930.3533 | 1607407.698 | 847043.9096 | 744659.8881 | 732689.7897 | 468012.2031 | 758481.7218 | 789448.3709 | 851341.7989 | 1002312.215 | ||
| Q6W4X9 | 8 | 7 | 272.87 | 0.148357238 | 3.24975441 | HN | XN | Mucin-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC6 PE=1 SV=3 | 919944.1 | 154421.9 | 217231.8 | 90584.78 | 153922.0453 | 107975.4339 | 137406.9762 | 1974146.774 | 255229.1857 | 865404.1509 | 330862.578 | 1266004.809 | 974062.8204 | 478071.6437 | 32571.99398 | 86315.40776 | 387499.2402 | 169523.2142 | 345581.1743 | 256508.9503 | 163459.7719 | 56704.41587 | 36279.75464 | 51279.00447 | 237073.777 | 164847.5296 | 100777.2397 | ||
| Q9BQ51 | 4 | 4 | 270.8 | 0.572173434 | 1.18201836 | XN | XA | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD1LG2 PE=1 SV=2 | 9882264 | 8511814 | 7564295 | 7688382 | 5295863.145 | 12017120.01 | 12653060.78 | 10647529.06 | 10795804.58 | 14581125.06 | 15277200.32 | 6458548.105 | 8654399.184 | 14417176.57 | 3691057.297 | 1261793.765 | 13162353.93 | 11181171.26 | 19171592.29 | 10699433.77 | 17755764.11 | 10704460.22 | 6636845.519 | 9162642.65 | 6228235.01 | 10524187.01 | 9654751.523 | ||
| O76070 | 5 | 4 | 270.12 | 0.983697371 | 1.881264888 | XN | XA | Gamma-synuclein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SNCG PE=1 SV=2 | 605762.6 | 278504.8 | 229422.4 | 498353.9 | 407071.8191 | 436871.452 | 274023.9689 | 1960429.132 | 253013.0645 | 916944.8209 | 2016393.95 | 547316.825 | 188596.0853 | 315625.3257 | 150889.1677 | 1132185.442 | 222524.6839 | 403070.5707 | 533504.2748 | 1464241.997 | 5792699.764 | 194794.0039 | 135637.9861 | 327099.5482 | 206658.5591 | 247167.1751 | 398141.4675 | ||
| Q9H6B4 | 6 | 3 | 270.09 | 0.126283879 | 1.481271811 | XA | HN | CXADR-like membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLMP PE=1 SV=1 | 1492928 | 3983087 | 4472533 | 4073725 | 7720641.197 | 5281068.228 | 2398701.924 | 5955246.599 | 4049478.658 | 1092354.079 | 852126.4244 | 3836948.056 | 3538241.345 | 255407.6406 | 5010785.055 | 5107992.822 | 3588298.553 | 3335114.492 | 4904828.769 | 8300083.156 | 2448126.882 | 4956026.216 | 4885759.574 | 3764290.122 | 2390677.243 | 3075172.915 | 2939037.251 | ||
| Q9BRT3 | 4 | 1 | 270.06 | 0.671384835 | 1.241684583 | HN | XN | Migration and invasion enhancer 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MIEN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1882786 | 1096745 | 1047652 | 1388199 | 2194253.862 | 2117243.467 | 1055593.956 | 1707365.694 | 1361758.55 | 1586901.318 | 1241411.273 | 1122165.815 | 1868335.964 | 2938752.281 | 1096908.562 | 812628.6842 | 3665335.38 | 2778143.246 | 2701233.844 | 1637161.539 | 1523549.756 | 1945722.371 | 691335.8431 | 910709.527 | 1465320.175 | 1046587.341 | 1858515.679 | ||
| Q13591 | 7 | 3 | 268.66 | 0.170378802 | 1.412486469 | HN | XN | Semaphorin-5A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMA5A PE=1 SV=3 | 1125781 | 1250432 | 1034469 | 1361871 | 887062.3216 | 456863.9749 | 449741.6133 | 757303.2165 | 531800.8497 | 507423.312 | 469153.0929 | 1097805.812 | 803904.6223 | 537587.6625 | 876901.519 | 1286603.322 | 1367374.031 | 1223664.147 | 537431.6866 | 968976.0591 | 685372.1731 | 158380.5851 | 535043.6147 | 185027.6904 | 717424.9469 | 831778.6593 | 1164986.382 | ||
| Q9NRX4 | 3 | 3 | 268.55 | 0.154291191 | 1.517773696 | XA | XN | 14 kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHPT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 8044410 | 4140785 | 6762564 | 3808919 | 11420786.44 | 3375142.679 | 5709824.442 | 5883249.683 | 7171498.474 | 1701928.004 | 1781625.459 | 5462480.749 | 4267927.801 | 2654864.256 | 2949285.932 | 10597287.71 | 7979400.334 | 6795607.292 | 2887906.235 | 2907792.754 | 3630056.752 | 2552075.309 | 11332076.12 | 1445677.751 | 3970422.395 | 4206917.958 | 4172197.079 | ||
| O00401 | 7 | 5 | 268.38 | 0.119898424 | 2.220783828 | XA | HN | Neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=WASL PE=1 SV=2 | 822730 | 189644.3 | 424608.6 | 1756500 | 212216.9811 | 691578.8863 | 735842.2679 | 1885824.138 | 614727.5554 | 274456.0252 | 245794.4602 | 559392.7525 | 790331.3329 | 294645.7495 | 205998.0257 | 282321.8261 | 199553.3719 | 449796.8416 | 222250.1492 | 265509.465 | 774333.726 | 1074761.203 | 708689.5998 | 146870.6693 | 248294.0684 | 375161.4812 | 387402.5126 | ||
| P14625 | 6 | 4 | 268.36 | 0.595506765 | 3.262104237 | XN | HN | Endoplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90B1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1291000 | 91138.86 | 304080.5 | 252176.2 | 89944.8707 | 130868.5908 | 224111.9748 | 686276.3588 | 459481.8724 | 107477.5049 | 101863.6819 | 240548.2652 | 216594.1945 | 67831.1444 | 196864.6448 | 506012.949 | 179865.4695 | 133203.3208 | 101821.5659 | 1708917.89 | 170929.0766 | 166229.2684 | 36622.7004 | 54648.4253 | 1023249.295 | 138020.6399 | 2309095.533 | ||
| P48061 | 4 | 4 | 268.1 | 0.016627557 | 1.920379498 | XN | HN | Stromal cell-derived factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CXCL12 PE=1 SV=1 | 43739608 | 13657679 | 12887951 | 24454696 | 31988429.29 | 23798839.86 | 21000566.91 | 29071838.03 | 20960893.54 | 6130320.346 | 3273450.194 | 4908279.857 | 6912605.052 | 5038694.852 | 10096399.46 | 29913011 | 23621047.92 | 32531082.77 | 27806200.55 | 27019380.8 | 32848093.1 | 22686411.84 | 29308300.75 | 4334577.627 | 18648043.9 | 25771349.34 | 46679893.64 | ||
| P00390 | 7 | 4 | 266.04 | 0.376751078 | 1.21053146 | HN | XN | Glutathione reductase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSR PE=1 SV=2 | 443423.3 | 294783.9 | 345728.3 | 414897.7 | 452055.0603 | 796773.8917 | 1047606.935 | 722412.8783 | 699670.1539 | 995567.181 | 1147316.843 | 560501.256 | 1028447.997 | 758132.5243 | 402282.8604 | 100628.0061 | 195437.4462 | 216146.3769 | 2145083.767 | 191634.0861 | 459677.6642 | 525715.4172 | 258256.9874 | 87401.52564 | 278028.0368 | 283992.1486 | 234745.713 | ||
| Q6UXB4 | 6 | 2 | 265.75 | 0.515129892 | 1.446129382 | HN | XN | C-type lectin domain family 4 member G OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC4G PE=1 SV=1 | 1161653 | 2963526 | 711279.7 | 3209591 | 2415992.935 | 2482863 | 2259847.595 | 2134244.877 | 1957116.379 | 1323188.803 | 5701047.252 | 779045.0038 | 7562978.454 | 1781654.75 | 1010050.6 | 742508.595 | 922528.8008 | 867992.6743 | 2010887.573 | 1683657.202 | 1360118.016 | 3189143.613 | 671519.5233 | 1852152.546 | 893125.2577 | 2164945.072 | 482296.1162 | ||
| P03950 | 4 | 3 | 265.31 | 0.241879105 | 1.223574913 | XA | HN | Angiogenin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANG PE=1 SV=1 | 1742713 | 1717955 | 1669625 | 1948645 | 1551084.604 | 1787994.507 | 1193428.188 | 2192003.382 | 1066850.256 | 774617.9172 | 448820.1024 | 725452.6011 | 1062073.555 | 443277.7885 | 1684463.947 | 2725404.326 | 2645334.163 | 1643713.097 | 1624445.954 | 1507704.882 | 1630510.89 | 1410941.126 | 1903204.854 | 469786.3045 | 2126461.973 | 2341544.514 | 1619523.205 | ||
| P11766 | 6 | 3 | 265.12 | 0.445822086 | 1.389309903 | XA | XN | Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADH5 PE=1 SV=4 | 1559278 | 636295.5 | 367525.3 | 1627458 | 544032.1979 | 1026002.495 | 928152.875 | 1997292.176 | 887177.4517 | 1595151.326 | 885608.8388 | 2185410.286 | 825907.1268 | 386834.1103 | 254410.9717 | 998631.2398 | 349435.991 | 245664.8182 | 824024.9028 | 548258.684 | 1348371.364 | 555596.2926 | 1264254.854 | 150737.4836 | 724339.8735 | 1044351.686 | 430690.4811 | ||
| Q9Y5Y7 | 5 | 3 | 264.43 | 0.69497684 | 2.735636008 | XA | HN | Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYVE1 PE=1 SV=2 | 31182.89 | 4324544 | 1377736 | 182503.3 | 1143144.117 | 372729.8774 | 224315.5693 | 122793.1204 | 366517.4785 | 170142.9122 | 76250.38831 | 499124.5862 | 96631.41709 | 178635.9146 | 788370.2614 | 387722.0135 | 483258.3965 | 297404.2186 | 76143.57378 | 275036.8955 | 116295.1526 | 642618.5259 | 633469.6838 | 675199.6477 | 126480.7035 | 254616.1172 | 236682.5676 | ||
| P09228 | 6 | 2 | 264.09 | 0.540501992 | 2.010892685 | HN | XA | Cystatin-SA OS=Homo sapiens GN=CST2 PE=1 SV=1 | 61901.13 | 84361.32 | 236378.6 | 18794.96 | 3620.291974 | 5382.830732 | 12189.50769 | 17801.43374 | 6418.505907 | 9170.404197 | 41405.99826 | 9568.437294 | 20303.73802 | 562850.6043 | 60441.18068 | 156228.8156 | 38595.45895 | 0 | 14064.50129 | 3434.468105 | 13066.56815 | 53891.87811 | 63944.13998 | 111291.2346 | 315697.7372 | 118509.8346 | 168508.1382 | ||
| Q13835 | 12 | 9 | 263.85 | 0.266249444 | 1.534117496 | XN | XA | Plakophilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1975562 | 1505054 | 1355599 | 1365652 | 1532681.526 | 2013000.507 | 3348623.371 | 5036929.663 | 2602037.852 | 3723444.825 | 2337695.431 | 2573845.621 | 3534912.156 | 3794126.68 | 2334647.734 | 1924975.592 | 1896272.879 | 1414308.999 | 11073810.29 | 3403740.415 | 2269248.245 | 2691471.486 | 2316249.061 | 2079507.603 | 2355402.952 | 1877652.188 | 3743059.196 | ||
| Q86Y46 | 10 | 1 | 262.9 | 0.557430633 | 1.960387205 | XN | HN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 2150744 | 1667694 | 3355480 | 2970173 | 4430652.346 | 517925.9693 | 723082.88 | 1381149.775 | 361813.509 | 845422.7407 | 1238908.559 | 1575514.789 | 454605.0515 | 609547.2877 | 3670279.739 | 2375432.854 | 603675.4871 | 865202.6855 | 1491341.791 | 898908.4827 | 1047363.345 | 590993.1522 | 1769301.318 | 12360933.79 | 2350747.801 | 766102.2039 | 2716681.787 | ||
| Q06323 | 9 | 6 | 262.07 | 0.586771328 | 1.446858389 | XA | HN | Proteasome activator complex subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2406895 | 490200.6 | 772277.8 | 3880651 | 772845.7692 | 1871812.038 | 1726624.848 | 3868360.103 | 1562780.11 | 2575252.486 | 801116.6542 | 2926608.988 | 1282175.499 | 526870.1463 | 705724.7721 | 1700584.689 | 655672.7451 | 819184.1075 | 1914369.173 | 1351052.466 | 3601087.633 | 2500047.339 | 1552683.975 | 358853.209 | 1205091.347 | 939944.6741 | 682880.9661 | ||
| Q02747 | 3 | 3 | 261.98 | 0.893251816 | 2.459488685 | HN | XN | Guanylin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GUCA2A PE=1 SV=2 | 52311530 | 1.61E+08 | 1.07E+08 | 1.16E+08 | 146630809.3 | 45678095.01 | 65391101.27 | 30683872.92 | 49576141.52 | 31014119.21 | 39707499.92 | 49330617.25 | 62529366.13 | 95546487.26 | 103373543 | 1145076928 | 66977721.87 | 43819199.26 | 55456452.67 | 65370589 | 37456947.31 | 79986879.1 | 91894087.18 | 158199495.6 | 81369677.55 | 36152036.28 | 59851999.52 | ||
| P11586 | 10 | 7 | 260.88 | 0.864553934 | 1.090647756 | XN | HN | C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=MTHFD1 PE=1 SV=3 | 963215.8 | 1071456 | 805222.2 | 2110468 | 649438.5671 | 1935128.927 | 2327949.045 | 1796686.845 | 1771527.689 | 2750998.246 | 2124656.367 | 1071989.431 | 1642820.724 | 1710214.52 | 1025932.056 | 502889.3013 | 1104699.654 | 1043049.694 | 3073391.109 | 2056751.05 | 1243166.059 | 1129939.599 | 953454.5657 | 1722120.703 | 836768.1204 | 1462643.444 | 1675373.936 | ||
| Q9H6S3 | 9 | 7 | 260.74 | 0.047140629 | 2.122637277 | XA | HN | Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPS8L2 PE=1 SV=2 | 974870.7 | 352406.6 | 612598.2 | 1911970 | 309753.8354 | 641153.8807 | 1016309.207 | 1757094.028 | 952882.5148 | 234486.8505 | 604400.6073 | 335566.5826 | 424591.1866 | 623311.1268 | 626317.0712 | 597922.9298 | 334990.5734 | 236546.0353 | 369661.076 | 229797.6355 | 413473.6205 | 535116.9203 | 334640.7807 | 862170.8695 | 1038957.552 | 376842.5722 | 1108031.965 | ||
| P11279 | 5 | 4 | 259.96 | 0.636967001 | 1.177817358 | XN | HN | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 969343 | 2939626 | 3300367 | 585518 | 821090.5166 | 1877547.118 | 3752808.504 | 1502249.1 | 2187777.482 | 745408.2454 | 2614592.318 | 1162042.461 | 3012747.448 | 3783771.286 | 1770196.967 | 464909.7525 | 724764.8165 | 1719122.416 | 1504818.528 | 1051607.76 | 2864985.569 | 1415557.316 | 1919358.991 | 4043718.977 | 1090088.024 | 2695938.785 | 2256124.845 | ||
| P04216 | 4 | 3 | 259.73 | 0.968995768 | 1.329142322 | HN | XA | Thy-1 membrane glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=THY1 PE=1 SV=2 | 842313 | 518104.9 | 384836.4 | 359048.7 | 316051.637 | 824536.8423 | 898995.7886 | 516780.6085 | 749932.8094 | 868223.6295 | 3634757.047 | 496050.2747 | 320793.5854 | 457989.6777 | 202678.8803 | 308272.0046 | 460589.4113 | 442103.7049 | 450112.3122 | 1186306.592 | 904828.121 | 524614.134 | 494047.484 | 219059.2601 | 331337.3408 | 692732.9894 | 739197.3164 | ||
| P54727 | 5 | 3 | 259.44 | 0.745271073 | 1.3642777 | HN | XN | UV excision repair protein RAD23 homolog B OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAD23B PE=1 SV=1 | 808361.8 | 141401.8 | 265000 | 1571744 | 185534.0739 | 597180.6265 | 638753.2556 | 1050846.04 | 679189.9104 | 1369570.658 | 629331.048 | 1492953.261 | 491394.0882 | 391777.0293 | 247940.8382 | 1579896.036 | 309726.5197 | 405179.6517 | 354615.7348 | 347644.6721 | 1512543.256 | 567852.231 | 457269.6354 | 736914.6241 | 597937.8879 | 223151.7362 | 272716.1239 | ||
| P04206 | 4 | 1 | 259.03 | 0.739220187 | 1.301162417 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-III region GOL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 354842.7 | 1609545 | 3007590 | 1426134 | 1478096.029 | 427785.2368 | 610246.6891 | 923689.0351 | 201631.1089 | 129285.5572 | 247749.2247 | 659867.046 | 703728.9001 | 775095.7223 | 1478703.891 | 3413651.662 | 802696.7852 | 632490.7535 | 521901.3841 | 307669.8261 | 184056.0224 | 1761129.037 | 797142.1225 | 2675828.647 | 586657.2336 | 203350.4003 | 678104.1633 | ||
| P09958 | 8 | 5 | 257.25 | 0.591265011 | 1.297401536 | XA | HN | Furin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FURIN PE=1 SV=2 | 2061399 | 460855.5 | 375304.4 | 1133389 | 381014.7112 | 918538.0229 | 710796.2334 | 727686.0329 | 755069.4742 | 771758.5095 | 202665.0289 | 652393.2507 | 946539.7351 | 138371.4538 | 315828.5313 | 721196.8428 | 983963.2055 | 1066607.909 | 911299.1921 | 998059.1936 | 998770.203 | 544767.0754 | 624324.3014 | 411003.9072 | 625651.4793 | 937783.6299 | 131728.0047 | ||
| Q9H444 | 4 | 4 | 257.07 | 0.453905427 | 1.695434946 | HN | XA | Charged multivesicular body protein 4b OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP4B PE=1 SV=1 | 1850006 | 777580 | 583641.2 | 678491.7 | 396333.8249 | 808253.3543 | 1475964.146 | 2175141.155 | 1060886.303 | 2011189.491 | 4870402.232 | 2656000.331 | 1984544.255 | 2526231.163 | 875517.6097 | 316691.0817 | 596119.0008 | 789244.3719 | 1660244.875 | 1613736.213 | 1309634.773 | 922315.0424 | 698620.7722 | 697345.625 | 604738.831 | 1134137.502 | 1297393.607 | ||
| P09871 | 8 | 2 | 256.69 | 0.126111975 | 1.487956459 | HN | XA | Complement C1s subcomponent OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1S PE=1 SV=1 | 98.06624 | 10873.54 | 7268.887 | 72622.71 | 241908.5639 | 11506.1795 | 8819.837959 | 45558.87932 | 20744.77276 | 44177.51909 | 31087.75838 | 80551.11898 | 59673.51358 | 30532.53572 | 95840.61729 | 89598.28347 | 166290.0819 | 26299.65343 | 18932.14794 | 16411.0659 | 14480.10202 | 27289.73396 | 5301.536353 | 431679.706 | 36233.45998 | 21240.88689 | 11439.87376 | ||
| Q9NR34 | 8 | 6 | 256.49 | 0.175171204 | 1.705317698 | XA | HN | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase IC OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN1C1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1722295 | 717168.4 | 1053536 | 1952617 | 433741.2292 | 509038.0467 | 977929.6551 | 1049028.469 | 652400.2155 | 332057.8498 | 807981.9291 | 631798.3667 | 572604.8254 | 204739.5744 | 691613.3023 | 1349452.638 | 439366.6687 | 287724.5985 | 562795.3835 | 589203.7767 | 462472.77 | 215866.6949 | 1191404.596 | 173719.5575 | 1804142.807 | 1081115.854 | 866535.6367 | ||
| P19827 | 7 | 2 | 256 | 0.39629847 | 1.414131375 | XA | XN | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 131460.8 | 1190137 | 871284.1 | 470782.3 | 722227.0704 | 635609.0219 | 1029978.456 | 579800.84 | 550469.1793 | 559697.4673 | 713857.2385 | 411604.2185 | 580067.5038 | 1166095.313 | 632507.7076 | 397114.0472 | 425255.0872 | 516250.7744 | 486284.5383 | 284700.8788 | 242002.3055 | 433283.3097 | 421935.4427 | 1107944.053 | 550873.5599 | 414780.1945 | 429606.4399 | ||
| P07148 | 6 | 4 | 255.12 | 0.697742672 | 1.33736934 | XA | HN | Fatty acid-binding protein, liver OS=Homo sapiens GN=FABP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 573394.8 | 594573.3 | 754403 | 1211506 | 168211.4334 | 1426611.423 | 2722107.637 | 1407729.503 | 1109472.087 | 1389050.039 | 1308173.979 | 1369015.646 | 863338.1927 | 1049911.858 | 584670.9791 | 234525.258 | 401440.2272 | 253319.3673 | 1085601.893 | 554276.5359 | 1137597.44 | 2500777.649 | 1067485.287 | 1418009.349 | 517127.4229 | 832420.6753 | 259697.4164 | ||
| P04155 | 3 | 3 | 255.05 | 0.118725269 | 1.858999227 | XN | XA | Trefoil factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFF1 PE=1 SV=1 | 20482294 | 19635442 | 18358641 | 5522332 | 11551093.84 | 19985107.91 | 10308954.82 | 7263755.147 | 19958114.6 | 10843559.64 | 29748132.44 | 8128465.976 | 64122725.49 | 18301947.56 | 11700163.56 | 24776544.36 | 16371535.43 | 31125489.28 | 24864359.3 | 43590837.08 | 39601092.15 | 26641570.98 | 13385103.14 | 16786891.77 | 33269638.19 | 41770746.52 | 7458859.337 | ||
| P19823 | 9 | 6 | 253.98 | 0.157254548 | 1.401588646 | HN | XN | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2412904 | 1532214 | 1607614 | 3450319 | 1958832.292 | 3243211.449 | 3310900.158 | 2180988.689 | 2487479.268 | 2820050.574 | 2891468.296 | 4699893.001 | 3735266.554 | 1418471.848 | 1458390.745 | 3307475.054 | 2364908.615 | 2302073.596 | 2258255.306 | 2968294.453 | 2216895.988 | 1670094.712 | 1541028.332 | 2056669.09 | 1644611.133 | 1947789.516 | 1531835.77 | ||
| Q99983 | 3 | 3 | 253.96 | 0.23739729 | 1.416418378 | XA | HN | Osteomodulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=OMD PE=1 SV=1 | 1647902 | 1788254 | 2291064 | 1335564 | 2196818.117 | 1426703.319 | 713233.6031 | 2986570.102 | 1749449.257 | 1351305.709 | 575505.5895 | 470093.165 | 515749.9767 | 1375064.341 | 2617955.163 | 920554.2397 | 1644671.787 | 1920902.761 | 396360.7616 | 1485489.574 | 1550970.271 | 1513853.298 | 1740775.278 | 328961.0472 | 2328929.546 | 1401172.851 | 1369421.054 | ||
| Q9NQR4 | 5 | 5 | 253.71 | 0.43717668 | 1.287359605 | XA | XN | Omega-amidase NIT2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NIT2 PE=1 SV=1 | 3307362 | 1384032 | 1090392 | 2838309 | 1361507.57 | 3785895.292 | 4535351.021 | 4035165.199 | 3614243.644 | 3665413.322 | 2392772.635 | 5949300.514 | 1977610.191 | 1993244.085 | 861520.3304 | 905408.9097 | 1248500.268 | 1240593.207 | 5393755.063 | 1462790.776 | 4042865.782 | 2586163.1 | 1848993.595 | 785145.7304 | 1504840.581 | 1537543.398 | 997192.941 | ||
| P31946 | 7 | 2 | 250.95 | 0.773556773 | 1.345241553 | XA | XN | 14-3-3 protein beta/alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAB PE=1 SV=3 | 827860.3 | 192793.2 | 385995 | 788437.1 | 206189.5685 | 831544.782 | 1050821.127 | 1444359.211 | 998297.346 | 724150.0353 | 1161552.942 | 1328956.39 | 663419.6009 | 503816.1365 | 752375.2792 | 154206.1223 | 154907.9249 | 368011.4064 | 223538.8133 | 428234.2947 | 1171768.003 | 730778.2381 | 796055.6518 | 395804.5151 | 411697.6008 | 499947.4879 | 342242.2127 | ||
| O75936 | 6 | 6 | 250.87 | 0.387333203 | 1.865222148 | XA | HN | Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=BBOX1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2214531 | 408655.7 | 1366007 | 4440085 | 204881.7057 | 1582283.154 | 1833977.833 | 3232499.48 | 1781190.821 | 1699279.909 | 743035.3503 | 2109835.546 | 1364129.631 | 846440.9655 | 672610.354 | 796718.3436 | 472006.6701 | 444510.6651 | 674495.8693 | 1413633.877 | 1889920.965 | 789401.6824 | 2014267.189 | 350386.7886 | 1149976.277 | 798366.2953 | 709650.7062 | ||
| Q7Z4R8 | 3 | 3 | 249.04 | 0.342906368 | 1.245695708 | XN | HN | UPF0669 protein C6orf120 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C6orf120 PE=1 SV=1 | 4745877 | 6547971 | 6120481 | 5069128 | 3089279.703 | 7457949.626 | 6005434.877 | 5774259.181 | 7875958.203 | 2705470.094 | 7467342.596 | 3713963.483 | 6421816.048 | 6401556.336 | 5709840.218 | 1541417.679 | 8387446.874 | 8726305.077 | 6775309.841 | 9417097.068 | 11895976.21 | 5414913.369 | 5036325.036 | 6164520.238 | 3969244.237 | 7682181.407 | 7268538.185 | ||
| Q68D85 | 4 | 3 | 247.67 | 0.277962544 | 1.23401399 | XN | XA | Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 ligand 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCR3LG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3625510 | 1247446 | 1077468 | 2087084 | 1586961.362 | 2047668.109 | 1852894.785 | 2201219.171 | 2213991.88 | 3582978.092 | 2460693.325 | 2223624.545 | 2896758.008 | 3215621.048 | 1073465.41 | 2126442.868 | 2380022.09 | 2058222.016 | 2183372.039 | 2938974.641 | 2874640.823 | 1247815.344 | 2102449.078 | 2408134.364 | 2163726.977 | 2788111.889 | 3431287.254 | ||
| P04066 | 6 | 5 | 246.3 | 0.076337117 | 1.591915467 | XA | XN | Tissue alpha-L-fucosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FUCA1 PE=1 SV=4 | 2337414 | 1672531 | 4288662 | 2113390 | 4207996.974 | 2746790.787 | 2120524.053 | 1534603.382 | 2792642.254 | 2103126.573 | 1203571.476 | 2102093.971 | 5508895.164 | 3189843.85 | 1801623.855 | 2320379.135 | 3267094.507 | 838489.4078 | 1398801.691 | 756365.5391 | 1564263.696 | 860566.5284 | 2109166.755 | 1831784.33 | 3824547.16 | 1646283.596 | 967905.5077 | ||
| Q96KN2 | 6 | 6 | 246.15 | 0.005094453 | 2.187565534 | HN | XA | Beta-Ala-His dipeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNDP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 164875.9 | 447157.8 | 469388.8 | 190644.8 | 800786.4362 | 364178.579 | 224879.7383 | 156686.9574 | 358277.1629 | 551749.8785 | 495589.3894 | 1260012.34 | 270622.8603 | 634967.9145 | 615834.6613 | 442229.6346 | 1866144.24 | 812473.8855 | 633918.5893 | 631672.8818 | 1287658.39 | 414565.2397 | 681181.7633 | 1133157.54 | 422655.8097 | 567831.675 | 543322.5697 | ||
| P15814 | 3 | 3 | 245.99 | 0.902409346 | 1.519911699 | XA | HN | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 5706675 | 22916506 | 2137840 | 10611620 | 35153795.27 | 47301422.64 | 6753642.171 | 6306905.964 | 5122963.68 | 23306701.69 | 17208679.44 | 6144582.083 | 2337498.138 | 12658884.23 | 6670422.111 | 7322546.442 | 12021974.31 | 5762672.816 | 8448357.719 | 29397011.42 | 5196758.466 | 4255578.929 | 6714465.484 | 22763403.63 | 7803484.822 | 9302329.967 | 5637359.929 | ||
| P30613 | 9 | 4 | 243.99 | 0.167412515 | 1.848920067 | XA | HN | Pyruvate kinase isozymes R/L OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKLR PE=1 SV=2 | 599801.2 | 138423.5 | 327798.7 | 573419.9 | 189079.8928 | 490564.2063 | 565307.1989 | 840731.6736 | 272439.825 | 572813.0836 | 99614.51862 | 392723.2047 | 91852.38094 | 102585.5284 | 347418.5303 | 158166.5212 | 243518.4886 | 153416.4205 | 450608.1071 | 287541.268 | 335838.8929 | 1002617.007 | 303570.7747 | 34733.73977 | 124930.6294 | 171827.8384 | 282530.5558 | ||
| P27824 | 8 | 7 | 243.59 | 0.440580522 | 1.941315824 | XA | XN | Calnexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CANX PE=1 SV=2 | 787895.9 | 1731049 | 1582028 | 927839.9 | 8435550.52 | 556082.0568 | 469451.0345 | 818682.7406 | 844927.5753 | 1219543.847 | 586588.0812 | 2241975.851 | 676514.0151 | 705039.4319 | 1635766.365 | 1752354.967 | 2404187.37 | 1419123.032 | 763793.3768 | 548749.1931 | 739730.2133 | 798889.2026 | 1943622.614 | 1076601.559 | 637005.7877 | 961901.268 | 850612.9913 | ||
| P02675 | 8 | 6 | 243.54 | 0.003464499 | 3.087853529 | XA | XN | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 3819433 | 5094343 | 3560043 | 5353567 | 5093210.826 | 3134837.287 | 2447187.523 | 5828585.98 | 2530145.559 | 3502048.996 | 438905.6488 | 7539414.887 | 479699.26 | 999402.4022 | 4732626.529 | 2292389.048 | 1524806.089 | 877184.3189 | 2920013.711 | 920491.073 | 683870.1071 | 319623.7625 | 1759430.832 | 1412270.953 | 2518903.86 | 889986.4019 | 512942.6662 | ||
| P01624 | 3 | 1 | 243.39 | 0.432637263 | 1.373443245 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-III region POM OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2359235 | 3335993 | 4309173 | 2268758 | 3645040.489 | 2677016.93 | 3108131.229 | 2053813.634 | 2042759.499 | 4703657.006 | 2704079.521 | 4067898.723 | 1855520.855 | 3020593.931 | 2740145.85 | 2997560.008 | 1710749.4 | 2177221.23 | 3222555.504 | 6743036.97 | 2270229.621 | 6013448.233 | 6868094.122 | 3881011.999 | 2397014.93 | 2739029.417 | 1300305.436 | ||
| P05783 | 11 | 4 | 242.18 | 0.372448296 | 1.550404386 | HN | XA | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 18 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT18 PE=1 SV=2 | 110390.5 | 56756.67 | 165542.9 | 379351.4 | 56523.57551 | 445743.5327 | 453843.954 | 339221.1148 | 762173.4349 | 169027.449 | 1316156.554 | 311395.7045 | 726004.3419 | 272990.2684 | 196574.4809 | 1040909.092 | 164630.2118 | 96229.7858 | 317634.3849 | 297256.1699 | 321895.6273 | 473229.2274 | 630143.6988 | 308849.958 | 369278.955 | 483740.9364 | 208214.1661 | ||
| Q08188 | 8 | 6 | 242.06 | 0.865372082 | 3.403423767 | XA | HN | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase E OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGM3 PE=1 SV=4 | 21075.27 | 27208.77 | 19187.48 | 12049.54 | 7738.728041 | 71311.09084 | 2365948.944 | 761124.7937 | 988994.2717 | 104510.583 | 302706.8749 | 74594.38977 | 143214.9086 | 29714.86461 | 26976.13329 | 487611.5266 | 28607.55656 | 58045.13192 | 1229065.449 | 395696.1494 | 113937.7496 | 185235.2883 | 32208.54869 | 50769.74696 | 26470.70677 | 34133.21448 | 244506.4164 | ||
| P12724 | 3 | 3 | 242 | 0.741446578 | 2.100267462 | XN | HN | Eosinophil cationic protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1497401 | 1238947 | 487060.3 | 697740.8 | 1526483.724 | 6909741.154 | 3320391.721 | 1915117.628 | 2686943.713 | 2285915.31 | 1090246.811 | 1064170.031 | 940838.7224 | 1291022.705 | 729164.9065 | 3235255.521 | 1127076.343 | 1011582.24 | 17949960.41 | 821496.3243 | 672924.3767 | 1074270.869 | 1494372.128 | 834374.0639 | 1499647.632 | 1092102.921 | 1392340.611 | ||
| Q04695 | 9 | 1 | 241.55 | 0.12818278 | 1.73809191 | XN | HN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT17 PE=1 SV=2 | 385492.3 | 239877.8 | 161131.6 | 80296.39 | 74082.12629 | 532236.3244 | 318514.6589 | 107356.2458 | 356529.5752 | 71165.65721 | 289994.0901 | 121970.0022 | 459755.9795 | 374705.3258 | 138654.9939 | 38678.27395 | 151833.8557 | 123854.3761 | 393728.9148 | 196717.3298 | 331899.7133 | 850709.1584 | 263081.4964 | 423448.0838 | 263672.6668 | 174356.1866 | 179873.8072 | ||
| Q14703 | 3 | 3 | 241.28 | 0.199540763 | 1.939291619 | XA | HN | Membrane-bound transcription factor site-1 protease OS=Homo sapiens GN=MBTPS1 PE=1 SV=1 | 961225.9 | 303794.8 | 292579.4 | 784670.6 | 249589.069 | 229330.4076 | 263289.3088 | 774498.8306 | 783219.903 | 176929.9232 | 190898.3479 | 103975.5575 | 484132.8541 | 82015.77247 | 365353.8703 | 335749.9419 | 438972.1405 | 215731.3636 | 292615.5372 | 369019.6377 | 339580.0156 | 82656.80817 | 539267.7593 | 35874.51932 | 670747.9699 | 479272.9475 | 655507.2457 | ||
| P04208 | 3 | 1 | 241.24 | 0.356104815 | 1.764041828 | HN | XN | Ig lambda chain V-I region WAH OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 457771.5 | 1033971 | 882972.4 | 1296580 | 912823.6603 | 501663.7496 | 335042.5379 | 332683.8019 | 227627.1492 | 1784293.306 | 419041.6912 | 544404.1269 | 136046.1286 | 1100779.264 | 1430534.286 | 1517213.31 | 1236314.977 | 743477.6073 | 623621.7818 | 493191.734 | 578991.9529 | 532815.9089 | 1072874.035 | 681967.3981 | 423448.4982 | 245734.5113 | 399447.9313 | ||
| O14798 | 2 | 2 | 241.12 | 0.264194585 | 1.76622702 | XA | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10C OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF10C PE=1 SV=3 | 389020.1 | 2023023 | 1054604 | 409742.2 | 229114.0611 | 1415726.893 | 1839804.456 | 692782.6036 | 4796855.914 | 535429.2459 | 1715789.423 | 490145.8923 | 1140737.013 | 920427.3645 | 563622.1482 | 82079.26344 | 486736.8063 | 1340809.271 | 559485.5629 | 1579326.961 | 984273.7605 | 1405232.821 | 1054008.976 | 2416310.285 | 1196723.654 | 1949444.135 | 565337.1019 | ||
| P51693 | 3 | 3 | 240.02 | 0.035251504 | 1.993414259 | XN | XA | Amyloid-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APLP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 415607.5 | 339747.7 | 145966.3 | 355724.2 | 263702.5005 | 320287.9388 | 326343.0208 | 296292.5599 | 357619.5482 | 583574.0075 | 681395.8658 | 141435.1118 | 783750.8179 | 701776.8399 | 289088.9981 | 268516.5402 | 217348.4643 | 353591.8334 | 349906.5586 | 914021.9013 | 1136636.957 | 380336.5217 | 374175.298 | 945107.861 | 371442.3423 | 713849.5735 | 438524.9715 | ||
| O75503 | 7 | 4 | 239.8 | 0.962932056 | 1.078393901 | HN | XN | Ceroid-lipofuscinosis neuronal protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLN5 PE=1 SV=2 | 2990763 | 4250229 | 3172097 | 2515840 | 2837926.739 | 2856167.102 | 3904468.891 | 2687752.353 | 2687158.276 | 2604908.438 | 4468840.09 | 2064451.059 | 3141652.499 | 7736840.408 | 2106297.62 | 2327863.528 | 2037134.357 | 2844865.585 | 3183931.852 | 3368563.403 | 2785221.406 | 2752298.386 | 2044022.521 | 2430951.045 | 3324585.074 | 3459134.609 | 3851791.96 | ||
| Q8N1N4 | 10 | 5 | 236.71 | 0.742124328 | 1.717452895 | XA | XN | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT78 PE=2 SV=2 | 171217.6 | 156230.8 | 416285.1 | 112097.2 | 76012.31601 | 1315388.07 | 726112.706 | 232570.0216 | 1118961.334 | 399710.571 | 349301.1551 | 637854.4892 | 246185.3944 | 308706.0492 | 364735.7681 | 221602.0227 | 153058.2908 | 94844.24368 | 237484.5218 | 106535.3664 | 222246.2009 | 711789.681 | 303962.4415 | 415215.4542 | 71791.47417 | 248275.193 | 200891.1249 | ||
| P82980 | 5 | 5 | 236.42 | 0.598895469 | 1.514880288 | HN | XN | Retinol-binding protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBP5 PE=1 SV=3 | 1159069 | 477312.8 | 543762.4 | 1092233 | 275479.8426 | 2010786.129 | 1743741.041 | 1977331.987 | 784382.8135 | 2872955.92 | 2057525.887 | 1751804.145 | 1877397.162 | 1637836.336 | 363461.4259 | 528055.2549 | 719636.6117 | 606739.9088 | 757355.7551 | 1608402.551 | 1440994.203 | 1338725.233 | 953553.3834 | 439929.66 | 566090.3915 | 470544.3681 | 620043.9033 | ||
| Q5R3I4 | 8 | 5 | 236.42 | 0.631581013 | 2.017139525 | XA | XN | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 38 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTC38 PE=1 SV=1 | 1244388 | 285854.2 | 436598.9 | 1401153 | 103123.8509 | 1935415.859 | 8412919.826 | 1970851.661 | 3478235.935 | 781350.0725 | 6487280.827 | 3207491.937 | 431944.7092 | 374778.65 | 343979.6788 | 336382.9667 | 415004.1244 | 231570.2833 | 483405.0554 | 2028623.536 | 985758.8907 | 2144904.98 | 852485.7435 | 1283439.083 | 349608.8381 | 434630.2367 | 989552.2866 | ||
| Q16849 | 3 | 2 | 235.92 | 0.207368666 | 1.499629268 | XN | HN | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase-like N OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRN PE=1 SV=1 | 747044.4 | 2457684 | 2703550 | 859210.4 | 926518.3198 | 1714382.343 | 2748381.963 | 919027.464 | 3104763.204 | 406667.2659 | 1936245.627 | 676652.9738 | 2016708.113 | 1402766.903 | 1479462.032 | 806026.9426 | 1265473.128 | 837534.6774 | 2502324.055 | 1879905.44 | 983306.1969 | 1148232.976 | 1152575.924 | 4063517.577 | 1387278.661 | 1890850.526 | 1229301.027 | ||
| O43405 | 7 | 3 | 235.1 | 0.92169092 | 1.344289329 | HN | XN | Cochlin OS=Homo sapiens GN=COCH PE=1 SV=1 | 64850.58 | 144199.7 | 168166.6 | 161004.7 | 485307.0589 | 378765.6833 | 115678.2333 | 98539.88425 | 430627.1802 | 90395.7394 | 207936.5212 | 52065.01121 | 244801.7129 | 182509.2828 | 465066.2195 | 790349.2929 | 199902.7598 | 198518.005 | 254141.1058 | 274464.7166 | 99682.36382 | 299832.506 | 107117.8271 | 301524.5362 | 204131.4069 | 127228.1118 | 140672.9678 | ||
| P50053 | 7 | 5 | 234.84 | 0.003658566 | 1.856103323 | XA | HN | Ketohexokinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=KHK PE=1 SV=1 | 4527510 | 4738396 | 3979500 | 4715687 | 2684846.525 | 6456477.286 | 4078266.027 | 3603325.02 | 5062519.693 | 2231003.019 | 2349946.11 | 4578681.601 | 2563238.213 | 1563560.434 | 1785242.351 | 2201445.256 | 2131130.16 | 2063591.85 | 3423788.871 | 2871851.445 | 5584992.832 | 3902618.962 | 7075842.382 | 1489140.182 | 2953801.915 | 2059202.671 | 2325567.532 | ||
| P31997 | 4 | 3 | 233.81 | 0.273677192 | 1.911879725 | XN | HN | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEACAM8 PE=1 SV=2 | 205157.9 | 920235.4 | 636223.1 | 349284.2 | 140148.7568 | 1008599.51 | 2028572.261 | 594131.0831 | 2385400.219 | 381110.4053 | 1398443.27 | 190261.5402 | 1596306.463 | 1301664.957 | 268016.8985 | 103829.483 | 265523.7033 | 826019.4212 | 756623.5305 | 1496388.865 | 588058.1 | 1023862.329 | 204213.5329 | 3141303.057 | 3134397.116 | 1215871.175 | 543729.5987 | ||
| Q96HD9 | 5 | 5 | 233.55 | 0.061421262 | 1.763946111 | XA | HN | Aspartoacylase-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACY3 PE=1 SV=1 | 700984 | 520896.4 | 754930.8 | 555183.9 | 1010567.771 | 1412270.935 | 1770387.342 | 1680514.299 | 1498317.537 | 595405.3601 | 684402.5566 | 1137495.516 | 1253199.582 | 345365.085 | 461881.8802 | 440345.1049 | 362210.9701 | 334408.0095 | 609594.9199 | 372407.8827 | 1275273.174 | 755139.9163 | 446140.2206 | 1972578.435 | 487649.6428 | 298612.5177 | 328315.277 | ||
| Q2TV78 | 7 | 1 | 231.38 | 0.851401341 | 1.682913788 | HN | XN | Putative macrophage-stimulating protein MSTP9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MST1P9 PE=5 SV=2 | 4860999 | 2650848 | 3803937 | 6185461 | 2875281.495 | 2006562.471 | 2256071.049 | 2060448.837 | 467826.2413 | 1870769.975 | 3331224.59 | 1634505.729 | 713625.9121 | 1518786.205 | 3624990.683 | 22679147.15 | 797880.2413 | 1169682.407 | 1819611.525 | 922489.6412 | 1138989.525 | 952909.1482 | 3711801.724 | 4572566.48 | 5366276.807 | 1626248.486 | 2077179.019 | ||
| P19438 | 4 | 3 | 230.59 | 0.67994366 | 1.311393643 | XA | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF1A PE=1 SV=1 | 203809.7 | 887712.6 | 1035104 | 189846.5 | 450400.4343 | 753477.3823 | 603819.7175 | 240181.0555 | 681750.8623 | 195850.073 | 827057.6386 | 504613.9796 | 387226.5559 | 348098.0742 | 720560.2901 | 268601.4836 | 239835.7896 | 356048.7461 | 194800.8146 | 501318.8427 | 391889.9741 | 389996.2305 | 248138.4829 | 1114758.129 | 250950.4959 | 550754.4497 | 365886.4199 | ||
| P01781;P01782 | 4 | 3 | 230.4 | 0.427686754 | 1.239169248 | XA | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region GAL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 4316981 | 9255759 | 4936391 | 6630518 | 9969068.116 | 9123124.852 | 6379204.218 | 5011825.767 | 7083444.778 | 5572318.437 | 4108674.124 | 8221281.564 | 4768443.885 | 3851699.218 | 6404475.997 | 2611279.272 | 5190908.342 | 9874432.672 | 7107839.896 | 8899301.227 | 6074465.9 | 5529327.089 | 13488682.94 | 10202210.3 | 3480756.244 | 3688530.072 | 3754726.139 | ||
| P10645 | 4 | 3 | 229.4 | 0.861381563 | 1.118663939 | XN | XA | Chromogranin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHGA PE=1 SV=7 | 3704938 | 8560414 | 7137480 | 6252486 | 11298510.6 | 10297843.42 | 10311796.6 | 4258946.601 | 12413057.47 | 6976382.45 | 9370807.915 | 5988068.517 | 9944441.737 | 8024856.33 | 8937348.895 | 12440461.02 | 5965711.217 | 10963123.17 | 6060312.963 | 17472408.21 | 10906539.41 | 7582640.195 | 3153763.842 | 15083027.82 | 8076731.305 | 8326747.482 | 6382375.976 | ||
| P30046;A6NHG4 | 6 | 5 | 229.34 | 0.852362641 | 1.178669234 | HN | XN | D-dopachrome decarboxylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDT PE=1 SV=3 | 9036698 | 2083228 | 3417846 | 5494280 | 2139241.893 | 5632458.407 | 7313303.318 | 6440363.264 | 4506530.607 | 9034909.638 | 7678438.685 | 8530731.461 | 8449266.505 | 5205770.23 | 2645897.181 | 1474684.077 | 2562019.969 | 3016422.746 | 5711053.631 | 3152820.15 | 9881328.683 | 8196535.276 | 3551570.435 | 3259791.756 | 2597638.674 | 1993820.189 | 2886805.436 | ||
| Q9NZT1 | 4 | 2 | 228.98 | 0.331347091 | 3.646566031 | XA | HN | Calmodulin-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALML5 PE=1 SV=2 | 256794.5 | 75655.71 | 136636.5 | 466850.7 | 426018.2677 | 733400.6684 | 4804386.54 | 1272815.624 | 4143600.793 | 718415.4155 | 722403.206 | 802657.5154 | 573610.3422 | 94987.07371 | 122721.0217 | 177075.7556 | 73730.86069 | 91866.60413 | 2589417.503 | 1117386.496 | 452564.2977 | 1372077.748 | 118025.5422 | 118098.2648 | 277362.5555 | 310998.3764 | 67410.08794 | ||
| Q9NQ84 | 6 | 3 | 228.85 | 0.145580356 | 1.547043613 | XA | XN | G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member C OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPRC5C PE=1 SV=2 | 2610956 | 1341280 | 1234863 | 540367.6 | 1216611.789 | 1297714.364 | 2097707.894 | 1047713.619 | 1395506.347 | 575647.4226 | 2093672.628 | 1227320.16 | 1000277.434 | 1878242.056 | 672159.26 | 241980.1671 | 566583.8429 | 784315.4289 | 1438111.018 | 1132933.75 | 746004.7886 | 399691.6558 | 974848.2835 | 423307.8968 | 773701.8778 | 930552.5639 | 1443524.084 | ||
| P01779;P01770 | 2 | 1 | 227.93 | 0.38304991 | 1.14837155 | XA | XN | Ig heavy chain V-III region TUR OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1097186 | 1737507 | 1266506 | 1454818 | 1606709.982 | 2023770.258 | 1550122.831 | 1585290.624 | 1739219.519 | 1282927.33 | 1293389.971 | 2786544.31 | 1848114.869 | 740674.7681 | 1391917.181 | 789226.2087 | 1051788.591 | 1858285.813 | 2220988.108 | 1996126.246 | 2164482.329 | 1686789.593 | 101365.3929 | 1795103.267 | 742406.4587 | 1060028.314 | 477118.2781 | ||
| P02656 | 3 | 2 | 227.55 | 0.676022604 | 32.00629819 | XA | HN | Apolipoprotein C-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOC3 PE=1 SV=1 | 282551.2 | 112614.4 | 318502.4 | 331628.2 | 257352.8605 | 82357831.5 | 279854069.6 | 20382540.3 | 5089977.426 | 2701794.973 | 2806433.253 | 595976.2805 | 646979.3547 | 663288.3069 | 978389.8314 | 2732059.593 | 194214.3839 | 834317.8763 | 65891545.78 | 5550092.96 | 360647.1077 | 9298495.648 | 409357.6669 | 745591.1029 | 290775.52 | 265677.7491 | 2864337.39 | ||
| O00584 | 4 | 3 | 226.9 | 0.630582103 | 1.745953008 | XA | XN | Ribonuclease T2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASET2 PE=1 SV=2 | 66685.06 | 274350.6 | 757329 | 153804 | 1121588.981 | 192570.141 | 394558.5556 | 154749.2866 | 346242.542 | 71056.54894 | 282304.8338 | 58317.68778 | 346795.2527 | 119087.7772 | 513929.8506 | 779541.0142 | 263756.886 | 165086.0201 | 129732.1758 | 150467.1276 | 112003.3371 | 217293.3359 | 264316.8023 | 147245.7262 | 419441.7337 | 326062.338 | 216238.909 | ||
| P22735 | 5 | 3 | 226.64 | 0.445587218 | 2.960365408 | XN | HN | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase K OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGM1 PE=1 SV=4 | 1229642 | 395248.2 | 86571.04 | 181423.6 | 2088575.822 | 4369090.749 | 2426978.465 | 4268256.264 | 2948082.886 | 2908496.06 | 449666.3706 | 4192210.723 | 1429687.836 | 141693.2385 | 123898.4348 | 841341.2078 | 58445.06319 | 25095.02392 | 21542196.36 | 2551558.419 | 866298.1088 | 3974428.766 | 113530.4214 | 249571.4303 | 65755.36263 | 133152.3912 | 612005.6516 | ||
| P21926 | 4 | 3 | 225.32 | 0.841536646 | 1.119621965 | XA | XN | CD9 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD9 PE=1 SV=4 | 2640038 | 925382.6 | 885182.9 | 2019085 | 2615767.49 | 3023694.041 | 2440841.165 | 2225842.981 | 1941514.126 | 1727631.734 | 2671881.107 | 1418615.626 | 2172669.078 | 3589163.179 | 1226822.954 | 825371.8006 | 1418459.485 | 1869413.805 | 2569029.567 | 2741184.349 | 1931418.828 | 1596999.499 | 1165100.272 | 1525338.47 | 1293461.875 | 2122482.775 | 1772545.341 | ||
| O00182;Q3B8N2;Q6DKI2 | 3 | 2 | 222.92 | 0.092228799 | 1.815362928 | XA | XN | Galectin-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS9 PE=1 SV=2 | 438675.2 | 153883.2 | 185931 | 471219.6 | 489288.0882 | 304841.4595 | 509113.6892 | 566912.8688 | 152343.7339 | 153187.702 | 158319.8265 | 43822.78444 | 852797.9848 | 217978.616 | 164583.5472 | 265362.6518 | 201592.3584 | 397906.3066 | 609735.2081 | 157211.6107 | 63558.02205 | 83120.21495 | 106468.6814 | 74024.7255 | 380373.3983 | 184903.8686 | 143113.7098 | ||
| P24158 | 4 | 4 | 222.83 | 0.601434219 | 1.647352405 | XA | XN | Myeloblastin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRTN3 PE=1 SV=3 | 13876035 | 4452756 | 2443427 | 4882079 | 3952302.212 | 32687677.4 | 18889165.52 | 11705310.03 | 20833063.24 | 29377198.08 | 3178205.656 | 14290039.51 | 6193395.697 | 5001312.921 | 5293435.044 | 5037705.625 | 7120358.489 | 6093710.948 | 21145049.81 | 5036117.222 | 5850907.287 | 8482575.766 | 5254587.131 | 2171579.565 | 7786486.695 | 6455818.388 | 6849961.078 | ||
| Q9BZR6 | 4 | 4 | 222.82 | 0.770440847 | 1.085387651 | XN | HN | Reticulon-4 receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=RTN4R PE=1 SV=1 | 652252.8 | 309747.2 | 553569.1 | 538245.1 | 767918.5897 | 457195.8202 | 373630.7613 | 636967.5775 | 294797.9498 | 693879.2991 | 599451.0428 | 191712.5012 | 262015.9264 | 146222.7963 | 553594.8338 | 859667.2451 | 673103.6229 | 528148.2977 | 624225.4274 | 593791.0147 | 410487.9815 | 721555.0713 | 528321.0382 | 405386.852 | 199250.3285 | 521400.1477 | 888287.7776 | ||
| Q9BTY2 | 6 | 3 | 222.78 | 0.063346788 | 1.594482765 | XA | XN | Plasma alpha-L-fucosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FUCA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 683278.1 | 1107655 | 1945098 | 598768.3 | 1212067.145 | 686792.6663 | 821796.0205 | 831915.5601 | 912124.5034 | 1081096.002 | 606944.1624 | 1029710.966 | 1690209.823 | 1132220.469 | 750587.924 | 474830.5471 | 1279208.038 | 295739.0237 | 933790.0183 | 389407.5627 | 170544.6204 | 410381.7409 | 730173.7213 | 477440.1001 | 1532917.037 | 539942.8377 | 334116.7425 | ||
| Q24JP5 | 8 | 7 | 222.1 | 0.306563656 | 1.966524043 | XA | HN | Transmembrane protein 132A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMEM132A PE=2 SV=1 | 1889984 | 517351.9 | 529287.1 | 882944.4 | 380564.0676 | 3568586.778 | 3768863.11 | 1748630.636 | 1064010.532 | 334879.074 | 374350.5533 | 696503.3438 | 1282952.73 | 1035449.61 | 1304897.431 | 1048268.102 | 835783.1837 | 384168.5091 | 1814507.798 | 741283.8548 | 916172.4175 | 457394.4482 | 394535.4461 | 550313.6347 | 1454125.715 | 563702.7501 | 2100365.754 | ||
| P03973 | 5 | 5 | 221.49 | 0.586264956 | 2.039421296 | XN | XA | Antileukoproteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLPI PE=1 SV=2 | 2485586 | 1116452 | 1477014 | 1008615 | 1057648.543 | 4593646.994 | 7523985.271 | 8062765.784 | 3168351.654 | 23807123.66 | 3137022.407 | 1822175.112 | 3424669.862 | 842747.0448 | 1588000.701 | 1609384.659 | 2810203.194 | 2075418.985 | 15448919.75 | 28710505.8 | 3502942.336 | 4583392.714 | 2395015.289 | 1020256.485 | 1893654.08 | 2459823.495 | 2175736.526 | ||
| P67936 | 10 | 2 | 221.3 | 0.74587525 | 1.593601459 | XA | HN | Tropomyosin alpha-4 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPM4 PE=1 SV=3 | 14350.16 | 10562.46 | 37536.33 | 54365.86 | 6892.47652 | 978765.8852 | 700465.1459 | 589183.8411 | 388457.9354 | 242954.5387 | 486529.3582 | 651232.0828 | 260680.2207 | 8716.37952 | 17987.30342 | 1026.097466 | 1725.139154 | 73989.21445 | 1155490.35 | 364500.5639 | 148971.0834 | 912471.016 | 13622.39575 | 16213.19109 | 20521.70689 | 6561.185134 | 34979.09364 | ||
| P80748 | 2 | 2 | 220.34 | 0.372989978 | 1.510123112 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-III region LOI OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1743518 | 3168871 | 2361011 | 2067639 | 5529097.494 | 2405839.151 | 733377.4209 | 2250981.027 | 1046191.678 | 6746652.475 | 2806585.487 | 4231891.482 | 1723521.445 | 698512.3643 | 6096010.425 | 2738061.039 | 5175397.542 | 1958845.088 | 2927086.786 | 3851648.689 | 1346868.582 | 3472627.568 | 3921129.369 | 4486234.641 | 2733205.944 | 2034714.648 | 2044421.015 | ||
| P12259 | 11 | 6 | 219.85 | 0.892000897 | 1.12793574 | XN | XA | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 900414.8 | 2403758 | 2154837 | 2437864 | 2385119.914 | 1758930.971 | 2897876.689 | 2563594.983 | 2250300.067 | 1591262.804 | 5067215.916 | 917268.7331 | 3948499.39 | 2871451.169 | 1869278.722 | 921542.3833 | 1718949.543 | 2435067.345 | 1316345.927 | 3150850.23 | 3487028.019 | 2230113.279 | 1937287.926 | 4708515.788 | 2226525.272 | 2101947.418 | 1121158.856 | ||
| Q96C23 | 7 | 4 | 219.03 | 0.257255093 | 1.613316559 | HN | XA | Aldose 1-epimerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALM PE=1 SV=1 | 729712 | 760455.5 | 655866.8 | 1133459 | 656732.9327 | 381718.0128 | 943728.8677 | 417805.5286 | 742330.3855 | 1469917.349 | 584334.3861 | 2706660.274 | 603843.3231 | 1521776.353 | 1016987.241 | 1053620.15 | 957766.0343 | 445505.6958 | 1674585.147 | 638075.3183 | 1161362.91 | 1408471.851 | 673675.5909 | 822963.5827 | 288620.0304 | 640559.6346 | 535256.9332 | ||
| O00592 | 5 | 4 | 218.55 | 0.473991351 | 1.228640214 | XN | XA | Podocalyxin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PODXL PE=1 SV=2 | 14424980 | 6870238 | 4293392 | 3613530 | 4009093.148 | 4162132.922 | 4743052.72 | 4883634.45 | 6024654.273 | 6494342.679 | 10997922.97 | 5496127.585 | 5647742.658 | 9703737.204 | 4761121.728 | 3522541.821 | 5109540.508 | 5851931.672 | 6152104.25 | 7144182.276 | 7465944.205 | 5432763.814 | 13234271.15 | 3659028.45 | 4366261.462 | 7068402.399 | 10625330.06 | ||
| Q9H008 | 2 | 2 | 217.88 | 0.397916036 | 1.691613172 | XA | HN | Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LHPP PE=1 SV=2 | 149868.6 | 105722.8 | 99643.6 | 336949.7 | 53937.4152 | 560347.0835 | 399935.2036 | 225284.5399 | 423405.1144 | 95937.28737 | 146818.5561 | 72582.85912 | 475936.3292 | 122475.6056 | 116733.2499 | 182644.6842 | 42700.62457 | 136388.6499 | 783098.8075 | 121259.082 | 153001.1104 | 486533.1138 | 110607.641 | 85432.39521 | 155493.1939 | 85383.58865 | 93088.9133 | ||
| P13473 | 4 | 2 | 217.7 | 0.989883376 | 1.078117878 | HN | XA | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 597448.5 | 756997.7 | 640818.2 | 413210.5 | 666285.5724 | 1573631.483 | 1384716.924 | 855486.4548 | 1805667.474 | 518463.3576 | 1094781.557 | 544942.4421 | 2113782.686 | 2035835.28 | 1307448.413 | 321307.9449 | 510859.0114 | 926019.429 | 1091676.48 | 1025333.761 | 966662.5775 | 803039.0047 | 234475.1212 | 1250687.696 | 966432.152 | 1275070.753 | 1140764.546 | ||
| Q9UNZ2 | 4 | 4 | 215.67 | 0.819496415 | 1.024059963 | XA | XN | NSFL1 cofactor p47 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NSFL1C PE=1 SV=2 | 95111.29 | 295738.8 | 352454.9 | 190849.8 | 70195.04732 | 240488.0498 | 1155866.761 | 661864.5292 | 525101.8262 | 264729.8034 | 883768.9217 | 395493.1818 | 739635.1252 | 253482.1754 | 420221.8022 | 174807.037 | 200565.5957 | 218474.4978 | 190110.4656 | 517036.9272 | 400780.4594 | 557787.4776 | 158337.3379 | 616719.1234 | 323283.3276 | 553915.5447 | 185409.108 | ||
| P30153 | 3 | 2 | 214.1 | 0.019611519 | 4.183821732 | XA | HN | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 65 kDa regulatory subunit A alpha isoform OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPP2R1A PE=1 SV=4 | 135050.2 | 12658.86 | 84426.01 | 441817.1 | 38416.06112 | 65602.10013 | 79424.21505 | 266339.8456 | 161756.8967 | 54783.35394 | 24474.52676 | 49491.5888 | 50790.9206 | 12194.18759 | 31451.22615 | 61502.48121 | 5207.49712 | 17357.09487 | 18769.96713 | 14160.12111 | 43360.51075 | 10112.73526 | 120742.4932 | 1654.131134 | 71709.86225 | 41603.28605 | 29644.87182 | ||
| P04070 | 7 | 5 | 214.05 | 0.699975402 | 1.37470916 | HN | XN | Vitamin K-dependent protein C OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROC PE=1 SV=1 | 2794119 | 1510026 | 1466321 | 2201166 | 1690708.888 | 1356480.064 | 1157958.775 | 1743724.559 | 1477267.104 | 1072346.25 | 1329652.422 | 1113007.556 | 1388836.16 | 709783.7393 | 2070339.027 | 6953843.15 | 1896625.186 | 2272477.003 | 1208888.385 | 929535.8424 | 1387775.884 | 1082923.656 | 1854143.541 | 691997.1281 | 2464048.566 | 1767560.07 | 2293773.748 | ||
| Q8WUT4 | 5 | 3 | 213.71 | 0.121414822 | 1.486262417 | XA | XN | Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRRN4 PE=1 SV=3 | 1187177 | 1395580 | 2643241 | 1452000 | 724077.2543 | 1642342.261 | 1907694.047 | 1504319.896 | 1109558.208 | 1790658.564 | 618149.5796 | 953377.8623 | 1371182.731 | 2527071.868 | 520043.7552 | 585875.7585 | 704791.6378 | 1015850.809 | 1027381.61 | 663326.2453 | 406748.6447 | 607646.9141 | 1154585.549 | 1244439.727 | 1128283.697 | 1426918.652 | 1468256.276 | ||
| Q9NU53 | 4 | 3 | 213.13 | 0.807027263 | 1.139801589 | HN | XN | Glycoprotein integral membrane protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GINM1 PE=2 SV=1 | 1197335 | 2377823 | 1545422 | 1594708 | 1035519.666 | 1355327.013 | 965908.2815 | 1285667.769 | 1180917.769 | 1441804.882 | 2697129.877 | 1087927.042 | 2369898.069 | 1748267.484 | 981830.0842 | 710866.9023 | 1696146.709 | 1321804.459 | 1202458.743 | 1731194.98 | 808354.432 | 1587436.043 | 1137434.303 | 2399789.402 | 1220171.683 | 1418939.067 | 825907.5286 | ||
| Q9Y625 | 4 | 1 | 212.89 | 0.195468796 | 1.394431958 | XA | HN | Glypican-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPC6 PE=1 SV=1 | 67253.19 | 8700.415 | 12775.9 | 17236.29 | 5926.897194 | 21982.99093 | 22865.41084 | 70247.21469 | 5952.160343 | 630.6163405 | 8572.41384 | 1533.140319 | 0 | 7893.543422 | 17429.48323 | 12462.84047 | 32777.28867 | 85751.11595 | 24771.66682 | 5507.214084 | 22608.68338 | 6318.967643 | 44053.60683 | 2009.917692 | 66948.90776 | 13304.77739 | 32047.24142 | ||
| P36952 | 7 | 6 | 212.61 | 0.611746498 | 2.349831856 | HN | XA | Serpin B5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB5 PE=1 SV=2 | 268405.2 | 146885.8 | 288120.1 | 134555.6 | 148037.8151 | 191096.8443 | 682850.9972 | 1049035.756 | 1225862.867 | 6660200.055 | 636419.7572 | 1062519.788 | 188333.6402 | 263317.1492 | 283815.6356 | 106417.8446 | 225544.3377 | 289635.9817 | 1154190.882 | 436572.4147 | 436836.6281 | 5122303.77 | 713699.6716 | 271542.1312 | 286908.6683 | 246769.0108 | 208778.5035 | ||
| Q13145 | 4 | 4 | 212.54 | 0.185759809 | 1.307530223 | XN | XA | BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=BAMBI PE=1 SV=1 | 6120136 | 8655354 | 4778838 | 7503511 | 4730583.705 | 8397212.694 | 8243609.863 | 6576105.039 | 10879584.12 | 3715421.913 | 20943732.73 | 1393672.586 | 10718850.93 | 9182292.631 | 5218025.247 | 2982072.971 | 6175542.713 | 7381216.188 | 6302747.103 | 11576814.04 | 9206669.371 | 6734922.794 | 6724741.833 | 15840243.29 | 9505019.66 | 10670951.72 | 9584434.173 | ||
| P60953 | 5 | 4 | 210.69 | 0.655479027 | 1.262702674 | XA | XN | Cell division control protein 42 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDC42 PE=1 SV=2 | 2087047 | 486860 | 730437.4 | 1245525 | 610208.5493 | 969700.3307 | 1250229.064 | 1809178.586 | 994647.5004 | 1445349.619 | 1785997.305 | 1577402.174 | 466506.7101 | 1949693.586 | 747527.2031 | 1069890.949 | 513620.3736 | 618483.0479 | 613369.7025 | 755931.7076 | 1205637.43 | 1271399.913 | 1227864.936 | 408875.9781 | 801174.0111 | 676996.2844 | 1103858.301 | ||
| P32320 | 2 | 2 | 210.68 | 0.398973157 | 1.386248376 | XA | HN | Cytidine deaminase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDA PE=1 SV=2 | 76621.09 | 375299.9 | 382463.2 | 178474.3 | 270020.0601 | 2078659.243 | 2180359.768 | 1093549.802 | 1655183.039 | 812507.2745 | 664528.5346 | 2949672.933 | 391038.2713 | 237161.0838 | 59215.4036 | 105963.7706 | 649748.6419 | 110788.2062 | 3197755.349 | 1545639.642 | 64792.55359 | 1252444.235 | 14752.26021 | 48884.56663 | 73551.44488 | 237634.4784 | 186664.3927 | ||
| P09972 | 5 | 1 | 210.58 | 0.857076888 | 1.517889473 | XN | XA | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase C OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOC PE=1 SV=2 | 246063.2 | 82662.73 | 179251.4 | 249713.6 | 107679.776 | 478462.7641 | 702078.3298 | 1055126.74 | 1127653.178 | 2879134.389 | 431943.7421 | 812254.9568 | 291830.2936 | 395835.4952 | 221254.5789 | 138348.0159 | 41816.53134 | 63195.49713 | 4626094.985 | 416558.2526 | 305923.9928 | 280583.5608 | 12644.37641 | 140923.549 | 359800.6608 | 174105.7121 | 102051.5 | ||
| Q9BUP0 | 5 | 1 | 210.19 | 0.282830386 | 1.798146194 | XA | HN | EF-hand domain-containing protein D1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFHD1 PE=1 SV=1 | 151514 | 17662.07 | 27338.44 | 70796.86 | 42233.2465 | 105497.0426 | 183365.7561 | 311685.1971 | 38037.0474 | 127367.9093 | 0 | 171642.7791 | 10374.63389 | 29865.24652 | 5135.449991 | 57888.61281 | 44076.97168 | 80930.14599 | 110959.1784 | 57640.91153 | 307075.6092 | 169213.1844 | 12839.12941 | 4587.569362 | 16141.95556 | 166246.4665 | 18465.21515 | ||
| P02814 | 2 | 2 | 210.13 | 0.261612399 | 2.025490119 | HN | XA | Submaxillary gland androgen-regulated protein 3B OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMR3B PE=1 SV=2 | 11501228 | 16553265 | 9904218 | 32840875 | 25838438.09 | 4194160.643 | 4170690.645 | 9454164.961 | 2641356.061 | 8097676.107 | 41013677.67 | 12370365.5 | 21096931.58 | 45008813.41 | 18228031.9 | 76458255.58 | 11453455.46 | 3454439.451 | 8018722.722 | 30609862.42 | 9086415.911 | 8180881.384 | 27550460.71 | 21850006.22 | 13795199.16 | 8136672.418 | 16638907.62 | ||
| P00441 | 5 | 4 | 209.91 | 0.205400343 | 1.318541386 | HN | XA | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4953506 | 24312099 | 18906224 | 11306436 | 21671742.22 | 7612415.2 | 5475836.478 | 5758460.668 | 9315269.562 | 10642411.26 | 11624444.52 | 9938643.313 | 10437877.95 | 23046580.51 | 22302886.42 | 21146499.66 | 19508500.59 | 15484535.76 | 7781094.754 | 9247198.804 | 8615690.158 | 11734182.68 | 22224491.69 | 27346856.68 | 18352771.09 | 22975744.92 | 14731030.49 | ||
| O94760 | 7 | 5 | 209.89 | 0.136593328 | 1.421922623 | XA | XN | N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDAH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 4626360 | 2713198 | 4632576 | 4542676 | 6203178.331 | 2025201.182 | 3480667.37 | 3951140.579 | 2246149.535 | 4577348.991 | 3006315.062 | 7659660.549 | 2439524.39 | 4303070.953 | 2522013.671 | 3731882.646 | 2216812.441 | 2552857.489 | 2286338.73 | 2021992.283 | 3069347.258 | 3521550.774 | 1718531.139 | 4262001.027 | 2990589.264 | 1662937.557 | 2674180.95 | ||
| O95841 | 11 | 4 | 209.15 | 0.811064276 | 1.226724872 | XA | HN | Angiopoietin-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANGPTL1 PE=2 SV=1 | 1743425 | 473056.2 | 947234.6 | 1742949 | 469237.9981 | 2217269.252 | 2477933.022 | 2401501.778 | 1948689.369 | 961607.7522 | 1543344.914 | 3195162.261 | 1671634.468 | 883338.5031 | 839905.651 | 882527.6874 | 1065712.189 | 712700.663 | 543631.857 | 1004528.453 | 1957300.099 | 1197706.27 | 1121594.069 | 2112002.428 | 1606721.308 | 1787892.701 | 1210820.147 | ||
| P35326 | 4 | 1 | 209.13 | 0.84689914 | 1.792274245 | XN | HN | Small proline-rich protein 2A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR2A PE=2 SV=1 | 1380500 | 1181524 | 849081.4 | 2026702 | 8081110.505 | 4681526.727 | 8560000.191 | 19434990.34 | 28321170.59 | 3620460.913 | 16247609.55 | 13090647.21 | 4573510.801 | 1833630.622 | 2892276.224 | 1435846.548 | 926806.156 | 1999261.309 | 10352868.39 | 18921962.5 | 9025872.293 | 36633758.54 | 984809.1944 | 1306426.887 | 1771643.249 | 2766763.875 | 1791808.785 | ||
| Q86SQ4 | 9 | 5 | 209.12 | 0.585585759 | 1.261704491 | XA | XN | G-protein coupled receptor 126 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPR126 PE=1 SV=3 | 1353508 | 411404.9 | 559495.3 | 454298.3 | 383359.5035 | 432253.5477 | 588454.5443 | 426228.734 | 316518.4333 | 300903.5825 | 645092.1421 | 336381.3325 | 674235.0245 | 812572.3854 | 211905.3727 | 187897.4852 | 410616.9945 | 993109.5246 | 754538.2226 | 404746.997 | 605379.4566 | 199010.5281 | 202670.2304 | 184419.5731 | 437296.0031 | 664350.8096 | 451451.3728 | ||
| Q9UBG0 | 8 | 5 | 208.9 | 0.423119304 | 1.9237977 | XA | XN | C-type mannose receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRC2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1600026 | 1393655 | 1645429 | 1605045 | 9778239.899 | 3573277.331 | 13442256.95 | 2014831.827 | 1694535.04 | 968872.1775 | 2650395.229 | 1135839.835 | 2458150.753 | 2213801.334 | 1848149.634 | 5242876.145 | 1808256.94 | 1617048.879 | 2699448.482 | 2213177.307 | 1523937.428 | 1264518.772 | 1955324.37 | 3894650.158 | 1710638.915 | 1809558.768 | 2030180.188 | ||
| P22532;P35325;Q9BYE4 | 5 | 1 | 208.83 | 0.928016398 | 1.314252989 | XN | HN | Small proline-rich protein 2D OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR2D PE=2 SV=2 | 1351471 | 403438.1 | 346520.4 | 307349.1 | 351519.8077 | 1738772.734 | 3001415.064 | 10692355.18 | 19574589.92 | 9328610.633 | 9227590.281 | 6100198.538 | 8401869.191 | 204563.4363 | 431847.4643 | 180289.6994 | 247060.2348 | 514924.9175 | 10261976.96 | 7441053.25 | 4663065.17 | 20792305.21 | 262741.6291 | 684424.3798 | 490885.2968 | 560895.9781 | 364372.951 | ||
| Q6ZN80 | 6 | 1 | 208.38 | 0.216264811 | 1.501690213 | XA | HN | Putative maltase-glucoamylase-like protein FLJ16351 OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 74390.8 | 133706.7 | 128811.6 | 127875.8 | 47543.22077 | 29430.99196 | 51904.81865 | 81263.3399 | 61934.32711 | 51249.54843 | 38499.23432 | 82405.67074 | 38796.37954 | 47203.64924 | 113014.2958 | 45060.50121 | 49377.4286 | 25081.42375 | 35489.12098 | 29244.3926 | 58583.27172 | 54643.24909 | 62508.57763 | 154543.8268 | 57156.24996 | 50405.1522 | 40566.50349 | ||
| Q92563 | 6 | 4 | 208.26 | 0.227454194 | 1.493118002 | XN | HN | Testican-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPOCK2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1620959 | 648294.7 | 806239.7 | 1026832 | 332813.7533 | 689768.3185 | 687628.6456 | 1145976.291 | 605800.6368 | 460914.409 | 690405.6595 | 386943.4697 | 745067.8592 | 726026.1978 | 758742.5211 | 1183991.496 | 737645.09 | 1669441.71 | 1209480.557 | 2128914.073 | 965628.0279 | 573750.7732 | 969905.051 | 388292.6919 | 1840233.555 | 1094595.796 | 1817321.243 | ||
| Q05707 | 10 | 5 | 208.14 | 0.035928018 | 1.706728981 | XA | HN | Collagen alpha-1(XIV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL14A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 382493.2 | 421365.2 | 360328.5 | 303100.2 | 672684.3554 | 250711.6473 | 738265.1562 | 355494.638 | 1063467.896 | 78415.11828 | 294201.263 | 273971.0664 | 409021.9097 | 254277.8313 | 492120.528 | 354992.6371 | 293696.0841 | 213997.8115 | 357951.4429 | 458122.3012 | 368424.9601 | 560697.4645 | 276429.2044 | 878389.0672 | 547437.7693 | 544087.7403 | 294213.698 | ||
| P01602 | 3 | 2 | 208.06 | 0.562314438 | 1.58917282 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region HK102 (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGKV1-5 PE=4 SV=1 | 286186.1 | 209719.5 | 273823.7 | 668115.5 | 887503.4164 | 528745.4023 | 387661.316 | 495614.038 | 620618.2573 | 193068.5522 | 110622.6317 | 2039296.978 | 872484.2903 | 158155.2903 | 591159.6882 | 178567.656 | 830753.3827 | 365841.2648 | 1158009.474 | 1192559.101 | 439519.528 | 1919363.14 | 1095034.182 | 390798.7646 | 205125.6528 | 309673.8246 | 215511.0223 | ||
| Q9NQS3 | 5 | 3 | 207.44 | 0.174956428 | 2.147503723 | HN | XA | Poliovirus receptor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVRL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 3647085 | 2585592 | 1447104 | 1119144 | 1802437.327 | 3222402.94 | 2948527.112 | 2291188.885 | 2962057.43 | 7082506.97 | 5869280.768 | 1437387.68 | 5701004.853 | 6050233.227 | 1721247.631 | 237338.2525 | 8492668.338 | 10708257.03 | 6426536.218 | 4926658.719 | 6577462.835 | 4802537.696 | 2393407.856 | 6414505.14 | 2859690.784 | 4013279.969 | 5359886.164 | ||
| Q96B86;Q6NW40;Q6ZVN8 | 6 | 4 | 207.09 | 0.04221767 | 1.787802828 | XN | XA | Repulsive guidance molecule A OS=Homo sapiens GN=RGMA PE=1 SV=3 | 2645689 | 1742347 | 2301696 | 4908904 | 2974801.883 | 2387066.419 | 2766260.533 | 2540008.047 | 2075134.543 | 6297413.64 | 2600896.168 | 1985911.385 | 2078325.496 | 6813482.73 | 1974938.264 | 9424569.643 | 4327141.256 | 4181416.723 | 4490821.514 | 2116035.077 | 8858004.218 | 5026956.273 | 3618698.018 | 3407719.183 | 6001888.779 | 4690228.957 | 5308181.058 | ||
| P28838 | 9 | 7 | 206.73 | 0.978046135 | 1.092056186 | HN | XA | Cytosol aminopeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAP3 PE=1 SV=3 | 8269119 | 6462640 | 5061080 | 11333169 | 6752286.476 | 4601464.173 | 3025301.95 | 5486288.104 | 5814360.354 | 12839269.8 | 2801120.232 | 6393109.744 | 3192478.96 | 4329870.737 | 8320204.865 | 9716304.933 | 7924330.745 | 6518337.091 | 5587584.675 | 5385048.415 | 5173014.673 | 5772114.941 | 14959006.32 | 5994336.422 | 4890472.602 | 4087072.525 | 7412432.577 | ||
| P36871 | 6 | 5 | 206.32 | 0.666758199 | 1.213230404 | HN | XA | Phosphoglucomutase-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGM1 PE=1 SV=3 | 4707272 | 11711642 | 12318570 | 6668880 | 12718165.87 | 8533834.335 | 6760657.628 | 4715447.93 | 9529215.881 | 17476703.2 | 9474383.69 | 8987477.634 | 7518026.616 | 11004775.58 | 18200076.18 | 4299333.61 | 9894248.34 | 7368919.906 | 8051600.499 | 4585883.566 | 6456954.354 | 5278169.694 | 5224892.014 | 22776303.45 | 9794814.499 | 8703443.451 | 12959361.74 | ||
| Q16822 | 5 | 1 | 206.17 | 0.055429061 | 2.534770207 | XN | XA | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase [GTP], mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCK2 PE=1 SV=3 | 97373.25 | 47699.9 | 87436.96 | 54.58766 | 18932.79194 | 65152.71294 | 61330.80968 | 51633.14435 | 476391.5787 | 158544.5503 | 145130.4076 | 348167.9939 | 135012.0953 | 70536.59199 | 108731.6897 | 136686.8555 | 273281.3936 | 63845.35379 | 174834.5119 | 291260.361 | 460676.019 | 240289.8723 | 180813.9201 | 266334.9531 | 19581.25587 | 425972.3149 | 236753.1551 | ||
| Q15848 | 4 | 3 | 205.01 | 0.955964109 | 1.634808746 | HN | XN | Adiponectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADIPOQ PE=1 SV=1 | 283535 | 1017170 | 1021064 | 1727376 | 2478144.715 | 192830.1034 | 152055.6924 | 282538.1589 | 83952.01786 | 381142.2562 | 189757.4052 | 660181.3433 | 63303.90943 | 417506.3852 | 1056861.006 | 6238421.92 | 985067.9712 | 276641.2214 | 227308.398 | 1045951.167 | 61430.58793 | 368375.6166 | 1851504.566 | 601486.3506 | 109760.0424 | 492547.6985 | 1523032.979 | ||
| P15104 | 5 | 5 | 204.91 | 0.692248932 | 2.602005985 | XA | HN | Glutamine synthetase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLUL PE=1 SV=4 | 58352.8 | 187903.8 | 63135.66 | 238294.7 | 210238.0698 | 1335792.366 | 3441430.279 | 1868344.758 | 3449744.779 | 327843.7329 | 586153.1853 | 1761355.088 | 676394.6086 | 106186.1323 | 222683.0784 | 323185.9471 | 70030.001 | 97272.09374 | 5868916.073 | 605870.339 | 302549.9291 | 1040869.159 | 399471.7569 | 91781.66115 | 184078.3725 | 34396.20342 | 28765.26527 | ||
| P01611 | 4 | 1 | 203.6 | 0.744699528 | 1.284689097 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region Wes OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2012523 | 1200676 | 814450.3 | 991634.9 | 1943269.237 | 343589.5982 | 1551386.316 | 852951.465 | 503544.5005 | 1470053.918 | 426457.058 | 1943453.116 | 1471776.432 | 1200010.334 | 1727621.011 | 1234426.308 | 1776339.693 | 587995.2589 | 609172.1475 | 859590.4476 | 192735.2459 | 819486.5071 | 2563832.166 | 5780307.696 | 1035300.108 | 575494.3094 | 685928.4388 | ||
| Q9Y6Q6 | 4 | 3 | 202.74 | 0.508037809 | 1.24930515 | XN | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF11A PE=1 SV=1 | 1418099 | 2695678 | 2188310 | 939108.7 | 1135927.295 | 1598741.621 | 1724913.642 | 1789237.538 | 1086334.398 | 729399.1282 | 2678421.036 | 799588.2192 | 1293560.904 | 1751110.736 | 2125508.806 | 1271970.383 | 1797301.865 | 1698741.901 | 1370995.779 | 3671684.991 | 1075932.181 | 1196409.633 | 1785207.693 | 3059205.435 | 1292945.48 | 1988156.087 | 2231637.373 | ||
| Q6GTX8 | 5 | 2 | 202.57 | 0.584131226 | 1.049780186 | HN | XA | Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAIR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 251502.2 | 486013.5 | 574529.5 | 159985.5 | 447116.7008 | 425814.0667 | 709305.5636 | 284730.4545 | 2016330.86 | 1032479.775 | 857822.9249 | 539993.3536 | 280008.6311 | 742293.4324 | 336186.0503 | 442188.7954 | 637519.1866 | 753425.4426 | 841371.1863 | 820472.0282 | 472867.1538 | 687322.3754 | 306957.241 | 549470.792 | 332870.516 | 866375.9437 | 604926.0005 | ||
| Q92928;Q9H0U4 | 4 | 1 | 201.82 | 0.016527908 | 4.795421014 | XA | XN | Putative Ras-related protein Rab-1C OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB1C PE=5 SV=2 | 30262.81 | 16386.3 | 18947.39 | 54361.97 | 13939.12959 | 3772.824511 | 4733.760219 | 28640.86574 | 9524.847561 | 1846.05677 | 3106.031442 | 10802.69184 | 1395.771961 | 4900.114662 | 12764.61468 | 51508.93774 | 2618.92333 | 8809.929723 | 614.6488149 | 0 | 821.6134573 | 2419.05279 | 11172.77351 | 23.83099632 | 3475.619112 | 10657.52042 | 8469.590891 | ||
| Q9NZH0 | 2 | 2 | 201.77 | 0.229217073 | 1.390776853 | XA | XN | G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member B OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPRC5B PE=2 SV=2 | 1697826 | 756558.1 | 1546498 | 517371.8 | 1440968.867 | 1041741.963 | 1633070.506 | 1348584.485 | 982539.5262 | 620787.1048 | 1578930.31 | 851411.5728 | 959278.5697 | 1410168.559 | 368523.6109 | 760756.4111 | 476745.741 | 1470990.303 | 1676795.246 | 655070.5173 | 966531.3368 | 292480.2437 | 564084.0102 | 709442.7132 | 559221.9396 | 1086800.483 | 1373770.965 | ||
| Q8WW52 | 5 | 3 | 201.48 | 0.669735579 | 1.538189008 | HN | XN | Protein FAM151A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM151A PE=2 SV=2 | 1355784 | 1530209 | 3390760 | 463586.6 | 790178.9105 | 456247.1302 | 852688.1954 | 581554.9809 | 628247.2089 | 976585.651 | 2176826.514 | 725470.7678 | 509396.0127 | 4775162.842 | 1313355.678 | 471992.1399 | 898107.7314 | 606440.5106 | 513713.103 | 489849.2837 | 1611874.656 | 448476.2943 | 1349216.98 | 331037.9421 | 700510.3895 | 1088968.997 | 1562456.136 | ||
| Q07954 | 15 | 6 | 201.47 | 0.002178376 | 1.965945234 | XA | HN | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1231168 | 743447.4 | 901583.6 | 459304.1 | 765505.5481 | 983489.7946 | 769069.1619 | 705100.9398 | 836031.5267 | 157894.408 | 729347.5813 | 460509.751 | 436250.1827 | 314233.1384 | 482472.4862 | 209386.782 | 408199.6773 | 563103.0273 | 444782.8878 | 1004187.669 | 389927.2577 | 317800.1596 | 687395.6647 | 1010950.223 | 919951.8933 | 731643.6017 | 698756.2224 | ||
| Q9ULV1 | 1 | 1 | 200.46 | 0.084384742 | 1.577493143 | XA | HN | Frizzled-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD4 PE=1 SV=2 | 21305653 | 32173936 | 32247686 | 20992616 | 14727135.38 | 48340482.34 | 43213268.24 | 19984992.53 | 47047873.77 | 12683648.63 | 24956100.88 | 11421687.19 | 41286494.01 | 29940199.61 | 9630934.196 | 5728486.672 | 21575485.37 | 20295099.53 | 20809816.46 | 42306833.25 | 29149252.88 | 20216267.46 | 15777330.45 | 23880389.18 | 15705984.89 | 33962815.58 | 14567723.91 | ||
| Q9NQ79 | 6 | 5 | 200.06 | 0.662490065 | 2.048959732 | XN | HN | Cartilage acidic protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRTAC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3756476 | 1262346 | 1434804 | 1337628 | 697046.3146 | 2748719.681 | 7158444.132 | 6501593.334 | 3965547.761 | 1789154.044 | 3180853.94 | 3039474.192 | 4300551.487 | 1534022.755 | 1514141.812 | 607839.8098 | 926921.6361 | 1458715.587 | 21785910.67 | 2829734.695 | 3256807.938 | 3682531.986 | 1528397.912 | 616878.9974 | 1319164.105 | 1583922.005 | 998495.3182 | ||
| P05534 | 5 | 1 | 199.86 | 0.57428112 | 1.786578376 | XA | XN | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A-24 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-A PE=1 SV=2 | 1640894 | 405390 | 603599.8 | 1996291 | 500832.0158 | 95723.13434 | 178084.3575 | 1879899.983 | 646967.4272 | 233522.1731 | 174210.1536 | 226782.3484 | 79492.18849 | 582705.6769 | 531782.871 | 1604165.584 | 1136054.067 | 974924.9678 | 586716.6337 | 328158.0233 | 343197.9406 | 123226.9443 | 915457.2121 | 76756.40176 | 535015.8074 | 286872.3005 | 1253147.947 | ||
| Q8N114 | 3 | 3 | 199.76 | 0.032164539 | 2.174406544 | XA | HN | Protein shisa-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHISA5 PE=2 SV=1 | 10296454 | 86828325 | 71717611 | 30707655 | 20640146.58 | 32158420.36 | 71218359.02 | 16689136.45 | 89539636.13 | 7142471.93 | 21756699.44 | 5143695.433 | 27546534.91 | 25770658.11 | 25456643.21 | 10247150.74 | 19624407.66 | 54972909.51 | 18756877.02 | 51752817.07 | 34947618.71 | 33372457.04 | 39603822.48 | 58491329.35 | 36746484.52 | 66570502.68 | 28908150.9 | ||
| Q13126 | 5 | 3 | 198.77 | 0.671160874 | 1.634674173 | XN | HN | S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine phosphorylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MTAP PE=1 SV=2 | 412673.9 | 67238.65 | 128899.1 | 844318.8 | 137180.0151 | 561190.3498 | 571681.1737 | 1080314.984 | 680596.4274 | 948313.8034 | 284323.9014 | 453645.2407 | 389610.0066 | 82114.51335 | 148961.7591 | 354346.037 | 93103.12671 | 322068.443 | 1642659.941 | 279947.5247 | 1568918.329 | 428389.857 | 267314.8822 | 324688.4648 | 195658.4098 | 154919.5927 | 166556.566 | ||
| P01614 | 3 | 1 | 198.55 | 0.518827224 | 1.166399584 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-II region Cum OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 573079 | 681318.7 | 441168.7 | 310538.5 | 357609.6367 | 98345.12256 | 84162.40132 | 99014.04723 | 86654.22874 | 123447.5157 | 55340.04159 | 333632.4879 | 81267.56118 | 214510.4588 | 1011399.066 | 355796.0182 | 196020.4336 | 296802.193 | 73192.50305 | 160542.5562 | 70597.77122 | 84787.49798 | 247685.7788 | 1344690.017 | 193916.9967 | 33386.03112 | 133357.3405 | ||
| P32754 | 7 | 6 | 198.49 | 0.320050157 | 1.592391567 | XA | HN | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPD PE=1 SV=2 | 1000417 | 335854 | 474391.7 | 1512896 | 114515.9309 | 1521346.832 | 1368547.624 | 1122711.233 | 853200.2786 | 464202.2212 | 677799.3297 | 878559.0243 | 2061370.849 | 278918.3615 | 230819.3967 | 138420.5241 | 201909.8168 | 282723.1684 | 945669.6318 | 308244.5968 | 747191.1804 | 1728237.548 | 803459.5084 | 321372.7851 | 310669.5452 | 207366.4416 | 126773.2512 | ||
| P98172 | 4 | 2 | 198.38 | 0.022650084 | 2.451302267 | XA | HN | Ephrin-B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFNB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 392467.8 | 4183208 | 3005809 | 1184639 | 1175091.962 | 1658777.064 | 2284362.408 | 955071.3253 | 3470976.684 | 294442.8404 | 981099.026 | 492779.8416 | 935314.5518 | 642466.2786 | 1280985.418 | 722181.6995 | 782158.4916 | 1338235.067 | 505351.755 | 1006351.905 | 597208.2582 | 1114779.554 | 1032832.921 | 2096258.509 | 707293.2417 | 1198846.508 | 913309.9311 | ||
| P07333 | 4 | 3 | 198.09 | 0.721853658 | 1.188966058 | XN | HN | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSF1R PE=1 SV=2 | 1194194 | 2169924 | 1424279 | 761228.9 | 783800.3093 | 1736288.393 | 1919194.224 | 1138656.741 | 2418798.44 | 717808.4984 | 3028371.812 | 749468.4882 | 1687092.737 | 1444320.785 | 928851.3399 | 1222458.146 | 1959149.106 | 1708649.529 | 2209690.567 | 1841000.3 | 3677268.254 | 671599.2217 | 1690331.487 | 1539722.102 | 913120.9063 | 2046249.196 | 1398058.232 | ||
| Q9UHD9 | 3 | 1 | 197.91 | 0.851197945 | 1.144169259 | HN | XN | Ubiquilin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBQLN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 157150 | 70565.95 | 127794 | 193311.2 | 114497.7522 | 128738.4283 | 579703.5941 | 227008.0994 | 247845.2627 | 47981.65237 | 439621.1607 | 208449.295 | 427975.9708 | 289621.2315 | 165401.6416 | 248566.5478 | 113652.3839 | 133222.7141 | 54096.8682 | 133868.3271 | 230193.7564 | 113404.5589 | 125256.5958 | 658071.937 | 166461.7828 | 145952.7101 | 185792.8649 | ||
| Q9NP79 | 4 | 3 | 197.84 | 0.207655655 | 1.629543052 | XA | XN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein VTA1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1786057 | 489652.6 | 476938.5 | 792341 | 450919.3973 | 531017.532 | 962525.8335 | 1477033.341 | 652178.9093 | 600293.2967 | 2974205.661 | 1106185.98 | 320306.3891 | 582738.7515 | 95793.29712 | 301746.4128 | 120698.1303 | 212776.3579 | 549660.2412 | 376322.3751 | 573955.0089 | 204952.4824 | 335636.2037 | 146074.8897 | 350354.6057 | 997641.4362 | 1140740.263 | ||
| Q8N339;P02795;P04732;P13640;P80297 | 2 | 2 | 197.33 | 0.084717602 | 2.330667119 | XN | XA | Metallothionein-1M OS=Homo sapiens GN=MT1M PE=2 SV=2 | 274789.4 | 177900.1 | 53961.24 | 151019.5 | 26011.27392 | 273462.7437 | 79114.05897 | 120624.8029 | 577186.7435 | 210049.3295 | 600083.0903 | 52602.58894 | 746376.9749 | 395289.4753 | 254025.3579 | 56937.66575 | 33196.50761 | 194873.6736 | 200700.7518 | 530647.2378 | 404186.7201 | 915816.4606 | 164645.3089 | 1016752.56 | 175246.5992 | 330653.4241 | 302890.6211 | ||
| O95445 | 5 | 3 | 197.16 | 0.286855345 | 1.449195714 | XA | XN | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 317278.9 | 1291745 | 1352425 | 686942.6 | 1320006.929 | 961454.746 | 684211.584 | 635409.9949 | 627051.6073 | 202221.69 | 632616.9739 | 274751.7375 | 641047.7535 | 1463961.236 | 863018.2769 | 806232.9174 | 520970.9907 | 705733.8359 | 352248.274 | 477633.4028 | 405541.094 | 869494.909 | 976459.1158 | 775491.6027 | 706920.2692 | 362683.4122 | 508629.3366 | ||
| Q8IUK5 | 6 | 6 | 196.94 | 0.046135843 | 1.333848348 | XA | XN | Plexin domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLXDC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2281504 | 1754582 | 1810992 | 1862074 | 1409681.81 | 1892977.333 | 2061301.169 | 2174433.717 | 3105046.199 | 798438.9736 | 1829242.949 | 1507559.887 | 1741201.039 | 1726772.058 | 1915746.901 | 1101380.537 | 1783656.156 | 1725109.81 | 1233533.723 | 1921476.885 | 1434611.625 | 1864505.529 | 1014821.819 | 1973752.841 | 945524.9069 | 1877640.88 | 1493261.89 | ||
| Q03167 | 4 | 2 | 195.82 | 0.491384057 | 1.227933354 | HN | XA | Transforming growth factor beta receptor type 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBR3 PE=1 SV=3 | 7389127 | 3053571 | 3198778 | 8189227 | 2852407.432 | 3112447.264 | 3224687.418 | 3625406.277 | 3143682.468 | 4039445.613 | 6910293.505 | 2413703.967 | 7604745.256 | 7284450.193 | 3352983.752 | 7035106.327 | 3789518.387 | 3972535.425 | 2891618.368 | 4331048.227 | 6078184.467 | 2308558.264 | 5973393.633 | 7556549.799 | 5228346.948 | 4156895.913 | 5325458.033 | ||
| Q8TCD5 | 5 | 4 | 195.44 | 0.016243972 | 2.127244987 | XA | HN | 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase, cytosolic type OS=Homo sapiens GN=NT5C PE=1 SV=2 | 987458.1 | 710969 | 1213042 | 3343622 | 931998.2931 | 728535.1367 | 1490346.161 | 1449488.338 | 974635.7952 | 244625.8671 | 352131.2966 | 451272.0953 | 369559.0198 | 813250.1445 | 1012313.083 | 1229928.528 | 646534.5955 | 441613.5828 | 604268.4336 | 1343706.849 | 1552075.587 | 367969.8303 | 274905.36 | 275966.9264 | 860403.0507 | 569240.5212 | 825434.2652 | ||
| Q8NES3 | 2 | 1 | 193.93 | 0.803003723 | 1.005745397 | XN | XA | Beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase lunatic fringe OS=Homo sapiens GN=LFNG PE=1 SV=2 | 1270482 | 2613589 | 420228.8 | 5007476 | 999115.0496 | 1250656.684 | 1266227.494 | 1124533.775 | 1779459.863 | 274357.1651 | 6680083.097 | 295568.3502 | 1509969.565 | 898769.1743 | 1109976.953 | 3375189.949 | 860401.2458 | 798220.5122 | 472741.2848 | 2014555.886 | 575810.0927 | 357243.269 | 1331572.901 | 6629715.489 | 2262033.859 | 1291779.12 | 886701.4104 | ||
| Q96C19 | 6 | 1 | 193.38 | 0.579909104 | 1.311226022 | HN | XA | EF-hand domain-containing protein D2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFHD2 PE=1 SV=1 | 8655.661 | 0 | 14148.53 | 37433.51 | 12389.1335 | 22242.6932 | 23687.86703 | 59890.16573 | 22527.10449 | 6668.939803 | 15856.01844 | 3733.84299 | 34173.50295 | 5316.67481 | 125185.9292 | 50068.02454 | 15482.40254 | 7037.872251 | 5083.435471 | 27315.02378 | 78429.71863 | 17743.25256 | 7081.728317 | 32637.1789 | 12234.6462 | 11041.96501 | 39672.4137 | ||
| P61604 | 5 | 2 | 193 | 0.045895601 | 2.378340224 | HN | XN | 10 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPE1 PE=1 SV=2 | 579152.8 | 97235.9 | 1440142 | 1060360 | 649459.3057 | 616205.0882 | 441942.752 | 290723.7101 | 296615.4514 | 2102926.154 | 817872.5391 | 2632010.421 | 458823.4085 | 414908.3888 | 1273845.859 | 617161.2918 | 656515.5944 | 767297.1577 | 701964.6421 | 476678.5394 | 261990.3189 | 357132.1431 | 638862.1934 | 673631.1053 | 391376.4746 | 292705.7372 | 301523.9855 | ||
| P29373 | 2 | 2 | 192.78 | 0.506725505 | 1.693983437 | XA | XN | Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRABP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 282997 | 923285.4 | 505446.3 | 325536.7 | 313449.0663 | 607987.4104 | 1431237.253 | 1359364.703 | 2686996.806 | 648027.535 | 910013.3596 | 1383620.99 | 660943.1908 | 262861.7323 | 306995.1631 | 561675.7234 | 271117.8638 | 496233.3621 | 653911.5524 | 463360.1286 | 574716.3147 | 437278.5048 | 408237.3817 | 956043.4325 | 587809.053 | 437384.4072 | 461414.543 | ||
| Q96L46 | 5 | 2 | 192.38 | 0.748256066 | 4.497248314 | XN | HN | Calpain small subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPNS2 PE=2 SV=2 | 408059.4 | 187714.5 | 200282.1 | 365110.8 | 78354.49028 | 1050297.141 | 3442841.303 | 7202179.019 | 2828132.077 | 1025236.443 | 1330981.908 | 1679958.102 | 485339.0497 | 335989.9257 | 225336.0762 | 211003.8571 | 214545.8333 | 250649.5352 | 20388767.35 | 1792505.591 | 1438980.641 | 930805.277 | 224315.9832 | 467092.0611 | 243538.7846 | 164351.0207 | 249479.5053 | ||
| Q96HE7 | 7 | 4 | 192.34 | 0.542354725 | 2.060650781 | XA | XN | ERO1-like protein alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERO1L PE=1 SV=2 | 41209.8 | 26121.43 | 15931.9 | 70282.8 | 15987.78501 | 218612.6844 | 420226.6567 | 1463053.149 | 872660.8252 | 736552.2068 | 590369.8206 | 1095588.807 | 228958.3686 | 81654.93577 | 82281.12636 | 7961.941807 | 45661.55245 | 17151.71127 | 1058430.515 | 182363.1684 | 135287.9308 | 27523.82122 | 13834.1875 | 27477.67002 | 37577.96463 | 30565.52875 | 12713.03878 | ||
| O60613 | 4 | 4 | 192.19 | 0.892935369 | 1.117292021 | XN | HN | 15 kDa selenoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEP15 PE=1 SV=3 | 2049654 | 642984.2 | 441107.1 | 833502.4 | 504059.1473 | 437082.5709 | 656146.5012 | 784677.8855 | 744005.1334 | 856479.9092 | 596731.1753 | 667916.2947 | 824084.3715 | 501415.817 | 425429.449 | 1456529.066 | 656342.5611 | 635077.3235 | 554194.1947 | 532766.3325 | 1027827.663 | 591230.828 | 992560.214 | 326412.4484 | 967419.4654 | 1222278.475 | 1181790.224 | ||
| Q96I82 | 3 | 3 | 191.96 | 0.406701186 | 1.461560903 | HN | XN | Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KAZALD1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1162414 | 340274.1 | 857679.2 | 2470904 | 320507.6439 | 96469.6174 | 114505.222 | 128298.7865 | 51025.27171 | 825335.0553 | 398091.92 | 135583.4968 | 460634.0485 | 469477.5152 | 1111248.844 | 2395986.224 | 227884.4541 | 1090526.841 | 810568.4031 | 461515.3199 | 146451.571 | 163089.63 | 300563.002 | 672478.8451 | 340241.635 | 549422.3241 | 1423593.954 | ||
| P99999 | 5 | 4 | 191.72 | 0.952277031 | 1.63781792 | HN | XA | Cytochrome c OS=Homo sapiens GN=CYCS PE=1 SV=2 | 406931.1 | 190976.9 | 302737 | 313907.7 | 137249.0175 | 686133.8015 | 3553782.459 | 3886286.464 | 2402593.244 | 3076324.907 | 6860046.947 | 6931426.008 | 1972528.271 | 129156.9309 | 235536.5701 | 82664.03119 | 119388.112 | 51184.12323 | 2501729.735 | 7087993.423 | 1754746.649 | 2878358.319 | 113881.2317 | 116154.1195 | 66009.97778 | 916672.4079 | 33054.63308 | ||
| Q969H8 | 3 | 2 | 190.49 | 0.440878403 | 3.467258799 | HN | XN | UPF0556 protein C19orf10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C19orf10 PE=1 SV=1 | 55762.8 | 964178.5 | 964407 | 119245.8 | 2083936.121 | 90616.4236 | 111501.4934 | 104915.6105 | 99680.96703 | 185968.4931 | 245397.0904 | 155722.7678 | 83717.92723 | 232370.0571 | 2623237.603 | 2010891.388 | 198774.9811 | 133646.1853 | 93973.75056 | 83359.93421 | 37644.32463 | 127446.6216 | 277144.787 | 321812.7309 | 133052.6219 | 382249.0403 | 236217.3632 | ||
| Q969Z4 | 4 | 4 | 190.31 | 0.238216865 | 1.367909178 | HN | XA | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 19L OS=Homo sapiens GN=RELT PE=1 SV=1 | 37478800 | 11841039 | 18645353 | 36356442 | 19802141.88 | 9971968.509 | 8394898.837 | 17709460.75 | 10058544.58 | 34244898.06 | 20366965.78 | 12660714.98 | 13380341.12 | 37782624.17 | 14074330.18 | 43090962.6 | 29681500.04 | 27616030.11 | 14924345.04 | 20265287.49 | 16332897.04 | 15169736.09 | 25494051.1 | 27035587.94 | 28493033.96 | 21362846.07 | 25413203.19 | ||
| P47756 | 9 | 7 | 189.7 | 0.906459534 | 1.276397529 | HN | XA | F-actin-capping protein subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPZB PE=1 SV=4 | 950527.6 | 407836.6 | 431810.7 | 981148 | 1703981.646 | 1464243.007 | 1121402.148 | 1555361.632 | 1114339.659 | 2929530.662 | 1179517.209 | 1454085.401 | 782619.2842 | 1177007.729 | 735709.8647 | 395140.4607 | 425907.9645 | 3340660.328 | 2679085.883 | 786494.7633 | 1524591.483 | 1512812.259 | 430168.9031 | 669024.0558 | 692666.1017 | 1464462.486 | 1722085.641 | ||
| P10768 | 4 | 4 | 189.51 | 9.83E-05 | 2.261437625 | XA | XN | S-formylglutathione hydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ESD PE=1 SV=2 | 2156455 | 1393787 | 924387.3 | 2895142 | 1235525.993 | 1569747.838 | 1842903.551 | 1238741.167 | 1218002.792 | 1081141.005 | 909548.0098 | 1415209.376 | 523587.5379 | 905298.6373 | 1340419.926 | 753884.5183 | 635118.0363 | 633973.1071 | 900804.1614 | 684289.7139 | 737453.8156 | 718662.5352 | 796203.2167 | 414917.9076 | 987337.5155 | 720334.8984 | 440655.8761 | ||
| Q8N3J6 | 4 | 3 | 189.36 | 0.201768942 | 1.474364383 | XN | HN | Cell adhesion molecule 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CADM2 PE=2 SV=1 | 401626.8 | 2800688 | 1812740 | 478796.2 | 968726.3951 | 883993.6625 | 900558.8236 | 675431.7762 | 1621300.589 | 383685.6815 | 655768.7909 | 582867.4462 | 1139550.79 | 886452.0735 | 1084935.547 | 163343.4562 | 1183467.32 | 1182447.021 | 632633.5522 | 1130745.606 | 1258402.028 | 1220866.737 | 1327435.208 | 2211806.117 | 799375.3812 | 1263363.368 | 862970.0567 | ||
| Q9H756 | 2 | 2 | 189.24 | 0.904180386 | 1.132096318 | XA | XN | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRRC19 PE=2 SV=1 | 1496146 | 2953497 | 2271793 | 1408288 | 1060113.125 | 4439332.719 | 4529961.818 | 2507283.522 | 4926194.851 | 1388234.39 | 4781504.555 | 2753951.67 | 6458233.798 | 3875425.542 | 1912480.694 | 586829.0102 | 1400929.184 | 1788832.476 | 2047864.245 | 2524830.637 | 2800114.24 | 2638940.085 | 1569716.456 | 4656141.084 | 2211707.467 | 2459607.765 | 1697467.169 | ||
| P01777 | 2 | 1 | 186.93 | 0.158053562 | 9.02069011 | XN | XA | Ig heavy chain V-III region TEI OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 13499.93 | 21419.63 | 1412.227 | 71736.49 | 49541.77664 | 279632.9577 | 32605.71572 | 41412.87968 | 22767.59369 | 88577.28057 | 112441.3828 | 89678.98471 | 172215.0654 | 69221.35783 | 33034.50671 | 38330.79428 | 47833.46823 | 2831705.868 | 32266.25392 | 1839053.443 | 11728.45246 | 787936.8961 | 29821.63544 | 120770.5615 | 25503.81949 | 21047.45635 | 1949183.451 | ||
| Q9BUJ0 | 3 | 2 | 186.86 | 0.204840623 | 1.962211886 | XA | HN | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 14A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD14A PE=2 SV=2 | 218393.7 | 54448.71 | 27954.73 | 381855.9 | 26679.32798 | 104358.1908 | 133339.7328 | 210557.3076 | 143318.6458 | 19258.56813 | 27674.17822 | 39851.90108 | 54864.68638 | 13377.77404 | 51007.78477 | 195890.304 | 85802.9336 | 175251.3629 | 72656.89465 | 45858.70354 | 103861.3534 | 46865.9937 | 138563.8287 | 47294.67603 | 227060.2863 | 47278.64488 | 224255.7366 | ||
| P35221 | 14 | 2 | 186.56 | 0.284755235 | 1.7103886 | XN | HN | Catenin alpha-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTNNA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 41945.07 | 37572.21 | 10420.15 | 19288.73 | 7363.982859 | 40428.38999 | 42293.05521 | 98340.79199 | 79926.12461 | 100408.7069 | 8135.301814 | 36714.61618 | 16454.44126 | 41551.33305 | 29076.38316 | 10508.96685 | 15298.23665 | 11464.47905 | 128477.1057 | 83227.10297 | 19391.51927 | 64296.94602 | 49533.58696 | 32329.65983 | 10045.53252 | 38785.73395 | 35054.89913 | ||
| Q96RM1 | 5 | 2 | 186.38 | 0.062532791 | 2.199122713 | HN | XN | Small proline-rich protein 2F OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR2F PE=2 SV=1 | 189240.4 | 853912.6 | 657515.3 | 328717.8 | 460136.4966 | 109170.2518 | 55676.06356 | 113148.9005 | 308354.2666 | 515407.9915 | 1690109.773 | 131047.752 | 712885.1628 | 247055.2881 | 527926.4639 | 331503.1879 | 1036246.979 | 579858.2969 | 382169.2112 | 114276.589 | 173668.1385 | 1245572.673 | 100792.1596 | 30442.37809 | 197553.4822 | 231654.0306 | 148572.9337 | ||
| P01598 | 4 | 1 | 186.35 | 0.837613757 | 22.87145414 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region EU OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 355436.9584 | 304.6214404 | 6397.435023 | 17588.07931 | 6582.327291 | 0 | 0 | 6005.534361 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4014.803483 | 0 | 6935.308705 | 0 | 3043.27711 | 14511.18971 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6799.121265 | ||
| Q99878;P04908;P0C0S8;P16104;P20671;Q16777;Q6FI13;Q7L7L0;Q93077;Q96KK5;Q96QV6;Q9BTM1 | 6 | 3 | 185.85 | 0.616678602 | 2.267377524 | XA | XN | Histone H2A type 1-J OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H2AJ PE=1 SV=3 | 1123871 | 267214.8 | 776005.3 | 4410307 | 588620.194 | 24443070.62 | 10928567.74 | 35278579.71 | 14115738.38 | 13638690.56 | 2101294.257 | 9893965.256 | 2169967.966 | 137846.8268 | 9950771.855 | 2566164.855 | 406624.6503 | 477348.5141 | 26581034.28 | 1384775.528 | 470237.1519 | 5660857.267 | 1399439.226 | 320392.8976 | 1470488.925 | 1868878.452 | 1389404.88 | ||
| P81172 | 1 | 1 | 185.67 | 0.118758356 | 2.235060517 | HN | XN | Hepcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HAMP PE=1 SV=2 | 16031260 | 6507267 | 3053163 | 13016278 | 37921538.37 | 2167813.191 | 2479305.093 | 4690498.267 | 1536752.005 | 28914056.74 | 2716593.558 | 6479808.642 | 5162844.906 | 10629486.08 | 11448212.88 | 56121650.75 | 3746112.255 | 9651671.832 | 2316504.879 | 314389.7806 | 54043.3175 | 219976.4287 | 9979490.816 | 21126572.5 | 6995656.369 | 13028866.96 | 6307579.867 | ||
| P01743 | 3 | 2 | 185.62 | 0.933811391 | 1.02627339 | HN | XA | Ig heavy chain V-I region HG3 OS=Homo sapiens PE=4 SV=1 | 1938434 | 3072593 | 1389002 | 2505769 | 1683423.294 | 3051460.298 | 1731870.225 | 2502165.931 | 1698399.346 | 1799109.184 | 2049441.501 | 5235987.419 | 3009277.135 | 1060108.484 | 1563587.151 | 892729.1007 | 2123957.133 | 2353172.267 | 2283741.394 | 2754880.652 | 1583829.279 | 3228460.015 | 2584624.996 | 2721265.694 | 1150390.338 | 1976996.404 | 1347365.427 | ||
| P05120 | 6 | 6 | 185.6 | 0.728500191 | 1.232954617 | XA | HN | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1783841 | 408975.4 | 594464.3 | 795218.8 | 882607.058 | 1200118.537 | 862652.0132 | 1135873.705 | 1313238.346 | 623578.5173 | 844625.1541 | 1162771.514 | 1030421.315 | 436498.5995 | 1060499.525 | 705645.9091 | 491988.759 | 924846.6507 | 2754733.777 | 631456.4039 | 404065.0023 | 530109.2927 | 1066374.721 | 619805.7451 | 897621.6727 | 536733.1263 | 1510488.442 | ||
| Q9NZ53 | 2 | 2 | 184.06 | 0.592301896 | 1.121466936 | XN | XA | Podocalyxin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PODXL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1249491 | 672989.5 | 486981.1 | 972587.5 | 613257.9906 | 893681.49 | 722375.5797 | 809473.5888 | 1141647.963 | 676889.6545 | 1407222.193 | 456398.9567 | 1270367.697 | 911165.0102 | 975713.6781 | 484722.8437 | 625896.2526 | 1078105.935 | 614200.2553 | 925801.2191 | 1091767.449 | 720854.1465 | 1016474.367 | 1084920.462 | 1000706.7 | 953884.2914 | 1072468.521 | ||
| Q8IWU5 | 3 | 2 | 183.85 | 0.69827884 | 1.289766369 | HN | XN | Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SULF2 PE=1 SV=1 | 958241.7 | 1073188 | 1242687 | 126919.7 | 513709.873 | 655489.718 | 2446093.907 | 1285199.838 | 3685790.243 | 1093359.819 | 2614933.994 | 1259273.27 | 3273105.605 | 1275884.028 | 1153181.518 | 727730.5456 | 615794.8317 | 563110.1039 | 551170.1696 | 1137268.865 | 840671.5178 | 654176.1985 | 1181366.033 | 2524737.902 | 129875.424 | 1646292.941 | 1085333.835 | ||
| P07951 | 7 | 1 | 183.84 | 0.867292846 | 1.62080754 | XA | XN | Tropomyosin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPM2 PE=1 SV=1 | 42237.21 | 7227.738 | 0 | 17926.13 | 1227.666716 | 97074.43185 | 263655.3413 | 51511.4711 | 119129.0063 | 124718.4557 | 0 | 99908.65677 | 18698.60801 | 47680.53204 | 51793.87407 | 9050.257466 | 16113.52955 | 15856.64935 | 85700.26192 | 93488.98417 | 36751.22561 | 119077.168 | 6416.033017 | 9777.134146 | 2716.748565 | 6963.928878 | 9287.567793 | ||
| P20618 | 2 | 2 | 183.7 | 0.020101498 | 32.64165973 | XA | HN | Proteasome subunit beta type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 89715.08 | 21992.45 | 56788.27 | 49725.57 | 40553.20898 | 2513739.568 | 5091629.182 | 596067.9257 | 195164.2194 | 13145.26363 | 14785.33875 | 22732.44404 | 30563.64293 | 7809.652894 | 39946.5564 | 46629.72034 | 35342.25915 | 54208.58322 | 985719.5348 | 27940.35752 | 50636.71072 | 118757.3999 | 37293.84215 | 2991.247241 | 26734.826 | 45125.5574 | 22227.98159 | ||
| P04156 | 3 | 2 | 183.62 | 0.335717018 | 1.170258356 | XA | XN | Major prion protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRNP PE=1 SV=1 | 43728112 | 34617174 | 30930838 | 54963502 | 45621561.34 | 42658803.91 | 32926950.5 | 40674110.87 | 35133005.78 | 22326989.07 | 45000819.86 | 18380578.46 | 56877182.96 | 36443400.98 | 22712621.56 | 43695643.97 | 23918895.97 | 39913168.5 | 38402313.1 | 45350160.36 | 32925764.74 | 17401289.13 | 25108146.8 | 61497568.06 | 29693531.95 | 37450040.74 | 20867172.29 | ||
| P36897 | 2 | 1 | 181.85 | 0.045318958 | 1.837282872 | XN | HN | TGF-beta receptor type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 385585 | 337069.7 | 326450.3 | 384939.2 | 122086.8586 | 783390.4447 | 785274.9246 | 705518.9936 | 678233.5342 | 167317.3834 | 648642.3759 | 102191.5026 | 585519.1351 | 237690.1931 | 144380.8119 | 93991.67781 | 228132.2931 | 345711.2352 | 585204.3631 | 780368.3893 | 597571.3194 | 458181.4866 | 200707.4217 | 615470.0425 | 185317.7782 | 924642.8748 | 344178.8895 | ||
| P04278 | 3 | 2 | 181.85 | 0.667704834 | 1.429419054 | HN | XN | Sex hormone-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHBG PE=1 SV=2 | 488686.3 | 646143.6 | 659613.9 | 384542.3 | 1170146.39 | 353196.2522 | 301863.7898 | 337868.9651 | 188924.4796 | 973990.4941 | 387943.817 | 403411.289 | 537393.0132 | 298226.2648 | 931715.3593 | 1924015.197 | 560717.6378 | 128633.3195 | 240546.1226 | 425450.7984 | 334507.7127 | 592150.9221 | 1053621.931 | 71112.71182 | 556915.0668 | 437639.6955 | 587736.3514 | ||
| Q99538 | 3 | 3 | 181.79 | 0.933848764 | 1.714350064 | HN | XN | Legumain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGMN PE=1 SV=1 | 666901.2 | 527135.2 | 980350.8 | 2114710 | 618120.8749 | 493613.4323 | 642737.4914 | 637587.6935 | 857650.0523 | 368111.2549 | 477811.7325 | 516444.2617 | 834067.2616 | 524777.1548 | 1121033.874 | 6245812.649 | 382378.6064 | 824320.6753 | 341939.9064 | 524882.9598 | 566219.3159 | 785611.2997 | 945966.5811 | 1033700.508 | 981736.3554 | 838330.0994 | 569974.1907 | ||
| Q14CN2 | 5 | 4 | 180.69 | 0.410709334 | 1.514642049 | HN | XA | Calcium-activated chloride channel regulator 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLCA4 PE=1 SV=2 | 164846.3 | 140129.5 | 236543 | 491038.8 | 314786.154 | 325126.7626 | 675124.5696 | 1600081.308 | 1151304.991 | 4414648.13 | 458415.7579 | 1857387.7 | 323372.159 | 86457.36049 | 189425.7574 | 74552.81572 | 141150.709 | 177721.2751 | 5000325.165 | 56974.45117 | 233039.3275 | 228650.63 | 108392.0519 | 84073.76002 | 105139.1467 | 239172.358 | 109019.0724 | ||
| P78504 | 9 | 2 | 180.25 | 0.582985106 | 1.085596923 | HN | XN | Protein jagged-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=JAG1 PE=1 SV=3 | 66739.36 | 36239.67 | 1327.192 | 41925.03 | 13151.79997 | 65565.6322 | 38856.74364 | 88679.32099 | 67359.46778 | 120050.1181 | 75036.94444 | 16341.00403 | 51104.1542 | 29542.69238 | 24253.57626 | 0 | 60478.58501 | 70835.8123 | 141754.4933 | 73468.18022 | 3404.225491 | 110.1991503 | 31898.142 | 0 | 70399.27391 | 58263.16527 | 33049.55323 | ||
| P00750 | 6 | 4 | 180.24 | 0.788753373 | 1.140976251 | HN | XA | Tissue-type plasminogen activator OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLAT PE=1 SV=1 | 1171282 | 28756.56 | 359591 | 253829.9 | 106311.1351 | 35177.86988 | 49816.5804 | 33484.10895 | 67035.62429 | 7378.469005 | 3378.263238 | 47492.81757 | 65922.20707 | 1531.966968 | 552696.0461 | 498222.6862 | 605446.0793 | 620011.8651 | 63389.66496 | 81711.5195 | 141263.4409 | 2860.139017 | 272299.0213 | 18798.14407 | 725999.7686 | 581299.1636 | 373087.8453 | ||
| Q8WVV5;Q7KYR7 | 5 | 4 | 180.12 | 0.635347435 | 1.576296396 | HN | XA | Butyrophilin subfamily 2 member A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BTN2A2 PE=2 SV=2 | 1868601 | 2492091 | 2336845 | 1215070 | 1164990.587 | 1429456.485 | 1713040.384 | 1176895.586 | 3159741.283 | 2553748.575 | 1377418.532 | 9040247.461 | 1409408.562 | 3250703.768 | 1148499.979 | 615216.8901 | 3197562.261 | 3505511.706 | 2579054.246 | 1764952.917 | 1984525.021 | 1632618.182 | 1306497.443 | 2668572.555 | 1470827.921 | 2191731.914 | 1907736.467 | ||
| Q9UGN4 | 3 | 2 | 179.96 | 0.347529189 | 1.272905718 | XN | XA | CMRF35-like molecule 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD300A PE=1 SV=2 | 3232407 | 4935544 | 5488537 | 5008772 | 1847884.249 | 4134118.9 | 5090412.759 | 4016048.437 | 6549900.265 | 5021606.765 | 7411234.871 | 2271932.859 | 7344803.628 | 8000024.545 | 2311888.372 | 1954042.658 | 3326132.286 | 4289978.56 | 7956936.744 | 5524449.905 | 3545248.045 | 5416964.276 | 3883487.116 | 9617976.544 | 4802057.739 | 6622161.545 | 3933430.939 | ||
| Q8N0V5;Q06430;Q8NFS9 | 6 | 4 | 179.92 | 0.904517644 | 1.2990924 | XA | XN | N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase, isoform A OS=Homo sapiens GN=GCNT2 PE=2 SV=1 | 887642.2 | 74615.05 | 124089.9 | 413954.5 | 365315.1709 | 423161.3398 | 433677.0869 | 1019138.422 | 384158.878 | 436613.2395 | 437754.2028 | 332650.4767 | 159804.1901 | 52686.3349 | 198573.0473 | 555506.0023 | 519534.3128 | 850392.4029 | 460801.0467 | 302757.2148 | 255528.346 | 189248.4423 | 363178.0359 | 83423.92997 | 685607.1247 | 371448.9631 | 463879.9752 | ||
| Q9NPY3 | 5 | 2 | 178.75 | 0.969829249 | 1.174707659 | HN | XN | Complement component C1q receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD93 PE=1 SV=3 | 15495.07 | 21031.69 | 221496.5 | 291654.8 | 422986.6507 | 105761.2657 | 157971.5868 | 95642.51263 | 94913.87122 | 96730.75949 | 66788.59805 | 32851.9454 | 33162.54181 | 108508.8507 | 195770.2542 | 552224.1845 | 254692.2933 | 90839.73174 | 17400.39233 | 46806.03033 | 46967.91392 | 85017.12505 | 314308.3261 | 320197.2439 | 158042.6041 | 107939.1685 | 121981.1304 | ||
| Q92743 | 2 | 2 | 178.1 | 0.070184556 | 1.65264195 | XN | HN | Serine protease HTRA1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HTRA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 613027.9 | 316309 | 428966.6 | 383202.7 | 478099.4075 | 196250.7692 | 193753.4213 | 158541.2741 | 118494.1751 | 83990.77685 | 447342.1962 | 97940.64553 | 57025.17526 | 239788.6586 | 377504.5041 | 620943.4409 | 353231.5048 | 346852.2377 | 312997.1424 | 600769.9124 | 539835.2284 | 231602.1512 | 692941.1233 | 660645.1331 | 493885.8282 | 492006.9344 | 312872.2404 | ||
| Q8NFQ8 | 4 | 3 | 177.64 | 0.534995094 | 2.38994716 | HN | XN | Torsin-1A-interacting protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TOR1AIP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 126491.9 | 102420.3 | 397024.9 | 323387.9 | 167980.974 | 28494.47757 | 37264.28658 | 160968.7828 | 78228.67477 | 31841.69716 | 8337.202061 | 123331.0873 | 13290.42664 | 45414.62039 | 179696.5384 | 1818093.596 | 62288.89557 | 61162.42367 | 34854.03786 | 56923.27684 | 26060.85366 | 27877.68634 | 393257.2088 | 30887.22996 | 229083.0176 | 124486.5547 | 57117.53999 | ||
| P14314 | 9 | 4 | 177.6 | 0.706969425 | 1.213817115 | HN | XN | Glucosidase 2 subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRKCSH PE=1 SV=2 | 910730.1 | 388783.7 | 397238 | 607825.3 | 361785.2276 | 355348.5351 | 611569.2359 | 639111.3557 | 493101.4775 | 707704.8588 | 1330391.474 | 423908.0547 | 655679.4981 | 678200.1959 | 491756.4444 | 195774.1747 | 543700.2888 | 712675.2892 | 345131.0229 | 367445.921 | 387401.3627 | 387947.8575 | 471596.8604 | 1024144.041 | 735492.9369 | 488603.85 | 520947.0941 | ||
| P61019;Q8WUD1 | 3 | 3 | 177.27 | 0.60579164 | 1.325690451 | HN | XA | Ras-related protein Rab-2A OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB2A PE=1 SV=1 | 41740.27 | 108063.3 | 68348.26 | 201122 | 247484.1612 | 135870.8598 | 192954.7154 | 429399.9842 | 191243.2224 | 323387.9843 | 476424.4972 | 386570.7623 | 159357.3577 | 253944.8013 | 126686.158 | 256033.8061 | 83369.07025 | 76841.96241 | 428886.4137 | 116308.3876 | 225945.9844 | 376764.793 | 128162.9292 | 145778.4183 | 198102.9959 | 136579.9104 | 82545.74258 | ||
| P29400 | 7 | 2 | 176.95 | 0.63632197 | 2.401191963 | XN | HN | Collagen alpha-5(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A5 PE=1 SV=2 | 194549 | 320864.5 | 241543.2 | 885959.9 | 282203.3383 | 188179.5774 | 155462.4729 | 90408.56233 | 75585.71488 | 270354.2368 | 475192.9386 | 335434.4454 | 87694.44202 | 102356.1379 | 191149.196 | 153220.7723 | 95651.47705 | 172673.3417 | 357956.99 | 1412100.264 | 82693.08111 | 1423880.9 | 666182.7449 | 48102.21926 | 73511.87596 | 268989.0764 | 189772.9519 | ||
| Q6UY14 | 5 | 4 | 176.39 | 0.201885235 | 1.560881427 | HN | XA | ADAMTS-like protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTSL4 PE=1 SV=2 | 728678.8 | 823608.4 | 1069263 | 2722342 | 1395313.755 | 914558.8032 | 1706459.052 | 1111369.633 | 1359345.392 | 2214680.086 | 2606108.011 | 1890029.558 | 2051789.184 | 1689446.576 | 1488649.227 | 4729795.764 | 804694.3358 | 991499.4537 | 980320.8028 | 1928051.554 | 792167.7649 | 826742.5775 | 2141691.767 | 1788951.166 | 1511959.552 | 664905.5129 | 2769819.951 | ||
| O43155 | 8 | 8 | 175.91 | 0.331966021 | 1.274054727 | XA | HN | Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLRT2 PE=1 SV=1 | 4265710 | 3640795 | 3415117 | 1789527 | 1213240.375 | 3238878.221 | 4761761.801 | 4392769.065 | 4578399.362 | 2031651.572 | 2029472.516 | 2485024.808 | 3448661.603 | 1454424.472 | 2821546.726 | 6237344.81 | 1918764.96 | 2137357.496 | 2406043.118 | 2887741.302 | 3745063.901 | 3107012.55 | 5297083.313 | 2285561.444 | 3103425.161 | 3024224.421 | 3304768.393 | ||
| P61158;Q9C0K3;Q9P1U1 | 8 | 6 | 175.82 | 0.176401304 | 2.195023472 | XA | XN | Actin-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTR3 PE=1 SV=3 | 1337808 | 337055.4 | 396149.2 | 2388143 | 222433.1101 | 1391774.476 | 1154833.56 | 2887228.177 | 1204610.354 | 1301046.35 | 515920.9676 | 850479.0965 | 1182008.71 | 564357.2008 | 695795.2374 | 464382.7306 | 250915.5098 | 260457.2532 | 817778.2131 | 405324.2443 | 967170.4936 | 391374.541 | 796887.6067 | 135465.5963 | 751261.1846 | 493455.7232 | 398418.5575 | ||
| P55286 | 6 | 4 | 175.52 | 0.744319224 | 1.063031419 | XA | HN | Cadherin-8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH8 PE=1 SV=2 | 490486.8 | 598771.2 | 426409.6 | 701003 | 1235435.532 | 719485.5749 | 439568.6603 | 788720.3831 | 492605.9079 | 1132141.477 | 290604.7485 | 338952.6579 | 268066.9526 | 513969.6471 | 892546.9626 | 766192.6158 | 906855.1698 | 433767.1623 | 392177.5588 | 160842.2137 | 462811.8298 | 289634.6556 | 1678381.127 | 707306.328 | 538820.8253 | 427550.2709 | 1010372.431 | ||
| Q6B0K9 | 3 | 2 | 175.29 | 0.232096135 | 3.447600671 | XN | HN | Hemoglobin subunit mu OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBM PE=2 SV=1 | 420489 | 123728.5 | 368194 | 1487916 | 31810.92442 | 71961.03141 | 3153.871454 | 253652.6543 | 56731.59928 | 2239.82621 | 56715.24648 | 5447.598834 | 31432.14618 | 130643.4542 | 37800.85813 | 118782.9429 | 267826.125 | 421062.7431 | 52406.56521 | 62099.85365 | 229111.3647 | 9365.946971 | 980910.5168 | 189729.0091 | 459468.9973 | 873731.6873 | 838834.8423 | ||
| P06311 | 2 | 2 | 175.07 | 0.753600385 | 1.109473703 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-III region IARC/BL41 OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 4518123 | 5856808 | 3442567 | 7811153 | 9513040.595 | 6760706.779 | 7227776.615 | 8186474.899 | 4484500.301 | 6812562.664 | 4188648.417 | 6103842.155 | 3762845.726 | 5847568.606 | 4002230.63 | 8147955.077 | 4080132.529 | 9152023.609 | 5745896.676 | 5287252.288 | 6938050.649 | 5514638.111 | 5382087.481 | 9356534.534 | 4745178.669 | 5324809.776 | 4700248.4 | ||
| P01130 | 10 | 7 | 173.98 | 0.319475982 | 1.345899224 | XN | XA | Low-density lipoprotein receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDLR PE=1 SV=1 | 3522289 | 7099563 | 6095718 | 5545952 | 3182297.544 | 9117651.461 | 3600115.064 | 3313059.073 | 6643805.161 | 3378648.123 | 9303732.822 | 1908719.178 | 3418673.942 | 8310725.449 | 3793576.912 | 1394532.851 | 6317498.498 | 11504570.61 | 4782379.555 | 11935135.86 | 10059593.73 | 8366094.146 | 4211420.419 | 10411272.79 | 2845426.091 | 5932252.439 | 6221702.088 | ||
| Q96FQ6 | 3 | 3 | 173.09 | 0.748882875 | 2.630276597 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A16 PE=1 SV=1 | 65401.94 | 16021.36 | 52309.75 | 21566.83 | 26117.85439 | 105827.3303 | 414534.4866 | 1247800.411 | 375038.5462 | 491174.0929 | 203121.8691 | 242115.7828 | 86856.92548 | 124110.5463 | 18.20319488 | 94235.68352 | 31964.34505 | 32959.25525 | 2901399.543 | 165091.8773 | 142190.5247 | 144523.9378 | 20244.06072 | 8739.254497 | 9670.808298 | 32522.63501 | 12222.87846 | ||
| P01258 | 3 | 3 | 173.06 | 0.23900116 | 1.508960353 | HN | XN | Calcitonin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALCA PE=1 SV=2 | 1390740 | 901029.5 | 923609.1 | 937428.1 | 541951.2642 | 490711.6112 | 1207978.654 | 1215182.488 | 1502621.359 | 2150251.883 | 4324826.949 | 1446142.221 | 1135643.818 | 402907.4559 | 840559.0381 | 841393.7568 | 637077.0477 | 796035.0432 | 542823.9961 | 351583.8231 | 496673.3395 | 488625.7795 | 3844946.237 | 593674.9744 | 1078237.378 | 465122.7273 | 471756.1506 | ||
| P48637 | 8 | 5 | 172.2 | 0.01983981 | 1.983882195 | XA | HN | Glutathione synthetase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSS PE=1 SV=1 | 1003808 | 2050763 | 3222096 | 2952798 | 1334971.746 | 4485165.586 | 2691796.507 | 1246509.77 | 1914572.627 | 1136266.852 | 1890792.318 | 1001399.629 | 1207976.329 | 715825.2101 | 1745924.952 | 575122.6571 | 1014523.144 | 1248319.495 | 1947326.123 | 660519.421 | 735435.8903 | 2951545.47 | 1133221.374 | 2035278.053 | 1413609.722 | 838494.9057 | 1345326.048 | ||
| P45877 | 4 | 3 | 171.83 | 0.017355648 | 1.854787687 | XA | HN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase C OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPIC PE=1 SV=1 | 884452.1 | 629043.1 | 601947.7 | 784833.3 | 293271.1256 | 973751.6812 | 1063714.387 | 987701.2411 | 966021.6756 | 147997.3324 | 491068.2528 | 238910.2761 | 1015142.183 | 440129.0618 | 349534.0462 | 551708.0857 | 191484.5123 | 447642.8358 | 253893.0597 | 631903.2467 | 479868.1153 | 307783.7459 | 769015.6821 | 358013.9687 | 909103.7047 | 496873.0347 | 733322.4162 | ||
| P27348 | 7 | 1 | 171.73 | 0.150051464 | 1.833016562 | XA | XN | 14-3-3 protein theta OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAQ PE=1 SV=1 | 121183.4 | 52277.79 | 88847.52 | 311780.9 | 69318.96002 | 183767.1191 | 134225.4487 | 234816.652 | 270191.3583 | 35226.77699 | 110861.1535 | 126957.865 | 164657.9819 | 51158.90024 | 171574.7892 | 125460.9364 | 63770.73002 | 159318.949 | 60438.91803 | 59563.46952 | 99600.07316 | 61764.65762 | 105320.4663 | 98870.67117 | 122707.4753 | 91206.97647 | 100525.0744 | ||
| P46952 | 6 | 4 | 171.65 | 0.545035628 | 1.420734074 | XN | HN | 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=HAAO PE=1 SV=2 | 358566.2 | 149997.3 | 152886.3 | 354308.3 | 69695.37985 | 613806.2486 | 359290.8752 | 533940.5312 | 440829.9591 | 174986.9664 | 457265.9896 | 328588.9444 | 574547.0493 | 367497.2731 | 57849.4062 | 96586.90839 | 110396.8006 | 136862.0886 | 449355.4499 | 213900.9974 | 413510.2418 | 1172599.887 | 202110.6102 | 379747.916 | 141950.2135 | 207268.2484 | 93753.79373 | ||
| P32189;Q14409 | 6 | 2 | 170.98 | 0.014978537 | 2.287995737 | XA | HN | Glycerol kinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GK PE=1 SV=3 | 264241.1 | 96897.31 | 134819.4 | 323587.6 | 84045.12157 | 514651.5677 | 503697.5493 | 312332.4692 | 419990.2997 | 165339.4462 | 163313.9572 | 132084.9476 | 115131.529 | 78379.12131 | 125098.867 | 123133.2299 | 156501.8115 | 101099.002 | 229753.4445 | 86393.33108 | 148995.4997 | 135851.9338 | 264047.8509 | 160544.388 | 115970.4225 | 69918.58886 | 91495.00929 | ||
| Q9UP38 | 4 | 1 | 170.53 | 0.335186009 | 1.272569595 | XN | XA | Frizzled-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1049792 | 709817.8 | 620917.2 | 543881 | 985558.8668 | 414175.8457 | 249532.8707 | 446211.7409 | 305979.1937 | 500830.6658 | 787642.6367 | 293834.4172 | 628231.968 | 1168165.668 | 521477.8091 | 850511.4827 | 591358.0608 | 1143322.448 | 493270.6528 | 941500.7542 | 611050.73 | 400192.6453 | 915914.6924 | 702207.395 | 709795.7593 | 755154.5207 | 1248448.233 | ||
| P25787 | 4 | 4 | 170.4 | 0.422279329 | 1.058184774 | XA | HN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 392325.7 | 567869.4 | 361500.5 | 536045 | 407410.8252 | 467077.8555 | 742448.8175 | 671109.867 | 674596.2893 | 491755.302 | 520324.1151 | 979082.5707 | 569842.6613 | 438570.8592 | 257250.7452 | 473247.5135 | 412844.935 | 412414.5391 | 1948570.527 | 261900.1911 | 324637.7105 | 693681.5105 | 401866.6423 | 157972.4138 | 357999.7678 | 232042.747 | 305290.2158 | ||
| Q14002 | 2 | 2 | 170.35 | 0.595888517 | 1.267537524 | XN | XA | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEACAM7 PE=1 SV=1 | 69858.93 | 176544.9 | 34329.45 | 31537.13 | 93949.91607 | 155157.8768 | 511028.8436 | 387436.1129 | 716844.599 | 1000988.945 | 60937.6477 | 931063.8359 | 235292.6127 | 28508.78285 | 40059.82173 | 55712.29747 | 58296.39879 | 93802.18225 | 2122857.524 | 233275.1118 | 57600.74626 | 175811.5339 | 32544.45703 | 54913.59919 | 19810.82039 | 8505.775943 | 53713.8815 | ||
| P60903 | 2 | 2 | 169.44 | 0.839633593 | 2.812248738 | XA | HN | Protein S100-A10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A10 PE=1 SV=2 | 178401.4 | 30166.69 | 59846.15 | 330392.4 | 177101.5686 | 518005.4318 | 3254509.397 | 8920272.334 | 1651970.138 | 989707.8878 | 555443.7449 | 2585262.878 | 566108.9473 | 151506.3791 | 195230.9469 | 126247.5565 | 60620.82028 | 146587.8069 | 3824059.072 | 682874.5866 | 675554.8144 | 730167.7196 | 68048.22727 | 483124.513 | 42942.22228 | 93373.39545 | 67055.18308 | ||
| Q15181 | 5 | 3 | 168.35 | 0.784678141 | 1.597715991 | XA | HN | Inorganic pyrophosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1240236 | 39871.1 | 155264.2 | 1361974 | 125247.4394 | 421737.3768 | 655154.5369 | 1235648.407 | 402925.8992 | 646805.3051 | 174218.5698 | 1165397.267 | 255820.3688 | 102588.9394 | 121371.973 | 493547.4501 | 260096.5457 | 308977.502 | 649093.7465 | 242741.5251 | 1373450.366 | 1203765.385 | 905898.3656 | 72471.79513 | 301252.4667 | 226653.2534 | 224105.1223 | ||
| P00748 | 4 | 3 | 168.33 | 0.260689307 | 2.160359324 | XA | XN | Coagulation factor XII OS=Homo sapiens GN=F12 PE=1 SV=3 | 2091270 | 347950.1 | 785516.3 | 1147703 | 1323737.668 | 168973.972 | 284094.4422 | 1200028.199 | 146508.8515 | 422911.4489 | 322712.0256 | 237657.8504 | 239302.0868 | 764953.5068 | 214085.8464 | 1060056.345 | 569120.4019 | 285710.6602 | 218484.1612 | 236317.2799 | 253781.9811 | 130052.9981 | 415571.3586 | 207145.6331 | 452370.2922 | 824298.3396 | 731670.5011 | ||
| Q99536 | 4 | 4 | 168.17 | 0.025149089 | 2.859150949 | XA | HN | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VAT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 499893.8 | 219485.2 | 364427.3 | 1433108 | 130982.1327 | 795035.7675 | 866996.1082 | 1506445.9 | 626384.7549 | 592108.9947 | 157113.0549 | 309394.6711 | 237259.9609 | 215532.6053 | 208763.1701 | 143897.6791 | 269966.4223 | 119345.5161 | 609448.3432 | 706749.199 | 560838.6537 | 652787.4238 | 303333.9687 | 151625.4695 | 187991.2634 | 167564.822 | 351000.3572 | ||
| Q07654 | 4 | 4 | 167.48 | 0.604283452 | 1.170906944 | XA | HN | Trefoil factor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFF3 PE=1 SV=1 | 9106912 | 23408129 | 32454567 | 25996601 | 15082102.5 | 14314646.12 | 15760040.61 | 9294822.413 | 20381261.8 | 13687004.1 | 22950048.44 | 7376506.719 | 13591946.13 | 8996803.714 | 24210482.94 | 35197559.3 | 4969535.629 | 10618968.42 | 13421048.35 | 16712763.67 | 6380815.702 | 11783484.02 | 17777478.77 | 39066938.62 | 15835682.24 | 13537505.99 | 10809350.91 | ||
| Q06418 | 2 | 1 | 166.79 | 0.683870075 | 1.019778709 | XN | XA | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TYRO3 PE=1 SV=1 | 729375.4 | 448186.5 | 326709.2 | 528483.6 | 209609.2498 | 578841.2091 | 543254.8387 | 602173.6564 | 1096129.39 | 723674.9907 | 1006144.019 | 644815.7834 | 840179.9609 | 657680.1874 | 236229.36 | 29064.06746 | 457461.2311 | 486446.671 | 463078.9079 | 612663.5736 | 592511.678 | 336099.7601 | 734062.4624 | 858489.2543 | 495227.8856 | 595346.4865 | 475418.0345 | ||
| P48643 | 7 | 3 | 166.56 | 0.634941265 | 1.082902836 | XN | HN | T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT5 PE=1 SV=1 | 1786104 | 820584.8 | 713443.1 | 1416575 | 950465.4687 | 1139859.846 | 724760.08 | 1297015.93 | 1306773.293 | 927098.5038 | 781044.084 | 756615.8768 | 1780378.39 | 806954.8006 | 1374391.26 | 1157381.534 | 945136.638 | 1349373.844 | 1012825.74 | 1202250.127 | 1374899.107 | 969233.8198 | 1115363.051 | 1327450.039 | 1296379.408 | 1071355.961 | 1327562.976 | ||
| P61586;P08134 | 4 | 2 | 166.28 | 0.88867161 | 1.411386104 | XA | XN | Transforming protein RhoA OS=Homo sapiens GN=RHOA PE=1 SV=1 | 35133.3 | 37796.23 | 56319.28 | 388618.2 | 50992.77065 | 29414.40421 | 34199.16654 | 64215.80189 | 43709.67047 | 35263.65311 | 63761.1896 | 69589.44019 | 19801.95043 | 45309.02766 | 27370.50042 | 235395.6258 | 47046.11213 | 27273.69487 | 24206.73961 | 30570.52136 | 31283.58252 | 33762.65804 | 91242.45848 | 42284.15 | 139359.1136 | 107206.928 | 24673.73352 | ||
| P50991 | 6 | 3 | 165.97 | 0.232486352 | 3.01995902 | XA | HN | T-complex protein 1 subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 171889.2 | 15323 | 147022.9 | 315856.3 | 26154.61427 | 280355.6134 | 223546.946 | 383555.7566 | 89945.85599 | 106597.3987 | 16523.12327 | 50790.93712 | 110363.6873 | 20231.28009 | 37492.11746 | 161496.5848 | 31633.17614 | 12445.40586 | 40965.26899 | 56929.22665 | 159889.3253 | 72730.089 | 170042.373 | 0 | 61500.87124 | 36998.46317 | 16300.7197 | ||
| Q9BX67 | 5 | 3 | 165.64 | 0.651680235 | 1.131460269 | XA | HN | Junctional adhesion molecule C OS=Homo sapiens GN=JAM3 PE=1 SV=1 | 18419381 | 9020579 | 13246327 | 15433505 | 8068267.431 | 14569389.93 | 15221200.69 | 14365680.75 | 11897141.56 | 14783380.08 | 8513431.359 | 7419075.302 | 5581165.11 | 15551200.97 | 11288518.05 | 8769654.2 | 14999771.27 | 19364855 | 11952239.17 | 9220692.068 | 19238845.92 | 18518767.07 | 15667776.42 | 5142142.027 | 8060208.027 | 13487014.33 | 18339217.29 | ||
| Q15365 | 6 | 1 | 165.51 | 0.67747122 | 1.43593309 | XA | HN | Poly(rC)-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCBP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 568730.8 | 45966.26 | 102121.4 | 603156.3 | 59994.8084 | 408694.8104 | 757910.6125 | 1497315.656 | 535121.0073 | 1544983.624 | 186684.725 | 593795.7747 | 163654.011 | 121430.2483 | 128136.7679 | 234365.4052 | 108915.0994 | 106909.7092 | 1414610.991 | 289290.2853 | 1149785.512 | 471444.9706 | 494446.4683 | 112550.8154 | 119866.4109 | 246724.8865 | 127942.7533 | ||
| P78325 | 3 | 1 | 165.27 | 0.629129127 | 1.228019474 | HN | XA | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAM8 PE=1 SV=2 | 1515774 | 1797428 | 1980479 | 6890942 | 2893988.671 | 669766.3141 | 1620419.388 | 710323.4108 | 779008.1809 | 4683503.419 | 2403117.744 | 1017084.847 | 1874843.431 | 455004.0677 | 1992624.542 | 6561168.605 | 1678098.574 | 2492703.927 | 2303744.265 | 2878694.202 | 1535720.529 | 2749649.344 | 1160970.987 | 7506510.003 | 1473716.85 | 1705622.788 | 1687284.564 | ||
| Q9Y617 | 5 | 4 | 164.24 | 0.149579829 | 3.066008957 | XA | HN | Phosphoserine aminotransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSAT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 423384.5 | 69594.32 | 251368.4 | 232679.4 | 18690.50325 | 141127.3222 | 489967.78 | 691842.3971 | 78669.36284 | 229687.8124 | 13699.31751 | 101753.919 | 72830.28707 | 129276.0169 | 37541.63429 | 22536.72644 | 76508.0648 | 98069.99668 | 61189.53818 | 19839.24766 | 274689.8109 | 87001.9909 | 693715.4722 | 26549.62666 | 32821.99618 | 79551.34515 | 108816.8186 | ||
| P05387 | 2 | 2 | 163.91 | 0.777377579 | 1.45750447 | HN | XA | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPLP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 495345.4 | 159247 | 154550.2 | 617967.2 | 342805.7494 | 525248.5961 | 1429361.578 | 1996960.796 | 777873.7712 | 3140520.361 | 1746805.143 | 2122088.751 | 762817.687 | 258082.8692 | 375038.2529 | 595295.8756 | 210745.0502 | 261452.8055 | 724852.3614 | 1750693.088 | 1522238.832 | 1138887.335 | 387848.6403 | 1428142.854 | 301750.0186 | 261953.29 | 347263.6767 | ||
| P30501 | 5 | 1 | 163.9 | 0.923822243 | 17.99268644 | HN | XN | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, Cw-2 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-C PE=1 SV=1 | 14375.2 | 158315.8 | 8793.105 | 7780.322 | 8866.011917 | 101016.22 | 36.98827109 | 3204.927653 | 9451.317698 | 105295.0111 | 2345657.22 | 23260.99243 | 169304.9463 | 3.259002752 | 23799.29311 | 0 | 5319.155515 | 7800.423918 | 40603.61948 | 21888.85201 | 7893.295155 | 22.31301497 | 32125.58029 | 26591.2879 | 8218.255878 | 11594.47077 | 36.2050285 | ||
| P01763 | 3 | 2 | 163.74 | 0.322901491 | 1.315535345 | XA | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region WEA OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2506314 | 9168898 | 8374421 | 7461030 | 8890779.876 | 7994304.983 | 4727085.752 | 6610457.836 | 5330694.367 | 5736303.434 | 2937081.552 | 7174355.486 | 3236399.28 | 2200673.38 | 5386439.436 | 6255081.401 | 7833721.714 | 5657539.285 | 7171074.742 | 11722335.29 | 4583853.707 | 4671814.261 | 5695385.979 | 6395525.535 | 5858605.615 | 5022870.684 | 3526463.515 | ||
| P60900 | 3 | 2 | 163.04 | 0.307438405 | 1.819940019 | XN | HN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA6 PE=1 SV=1 | 550927.1 | 239173.7 | 108835.4 | 107672 | 220906.8799 | 345551.4097 | 550898.1671 | 366469.2825 | 516056.1564 | 127319.1067 | 307513.365 | 508220.9401 | 375510.9787 | 96756.37363 | 139962.3819 | 22532.2815 | 77732.76255 | 173772.7105 | 1633918.16 | 340673.7879 | 315362.7798 | 298226.1113 | 134146.5597 | 45409.48641 | 92572.51086 | 380710.188 | 88234.73034 | ||
| P55103 | 3 | 3 | 162.66 | 0.203475869 | 12.97830664 | HN | XN | Inhibin beta C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=INHBC PE=1 SV=1 | 62672.33 | 20160.39 | 529755.6 | 88804.82 | 1002232.437 | 16734.41455 | 6486.837257 | 52322.31613 | 7798.935507 | 13831.91713 | 54977.09569 | 191126.5653 | 17497.92711 | 291022.0945 | 427712.9443 | 8397091.972 | 1889050.646 | 83979.93407 | 29525.65123 | 44087.641 | 45133.98928 | 18269.29026 | 57308.88028 | 31609.48229 | 76109.24549 | 380862.9812 | 192884.3744 | ||
| P54803 | 7 | 6 | 162.51 | 0.444782142 | 1.562597045 | XA | XN | Galactocerebrosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALC PE=1 SV=2 | 612609.8 | 543727.2 | 4354588 | 474090.4 | 1009523.039 | 731337.97 | 762571.0459 | 539833.6546 | 794719.04 | 444559.198 | 231582.627 | 941104.9131 | 387909.959 | 171326.9178 | 861203.6733 | 1882292.732 | 894482.5107 | 575121.3956 | 853389.2201 | 484781.9161 | 995766.8678 | 144363.9534 | 1270635.5 | 38593.50645 | 1126625.072 | 641947.8386 | 730225.8656 | ||
| P36543 | 5 | 3 | 161.33 | 0.069069959 | 1.654763726 | XA | XN | V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6V1E1 PE=1 SV=1 | 390475.3 | 169873.8 | 427249.1 | 466415.8 | 309258.6805 | 118039.2591 | 257378.9027 | 349552.9477 | 200416.8455 | 225597.7028 | 230556.2011 | 542482.2151 | 106876.941 | 350131.2876 | 233479.9469 | 161165.0522 | 195871.3965 | 219055.263 | 77345.03199 | 50049.19116 | 123039.5502 | 177219.2981 | 307499.4606 | 87153.92396 | 263214.3246 | 381128.6626 | 158150.8729 | ||
| Q15762 | 2 | 2 | 160.85 | 0.125894858 | 1.643204061 | XN | HN | CD226 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD226 PE=1 SV=2 | 284162.6 | 746179.3 | 567061.6 | 365374.4 | 286883.2025 | 199744.0953 | 307695.5026 | 244525.0101 | 263827.0983 | 281899.5884 | 526337.4178 | 187225.2162 | 258052.3158 | 301869.309 | 272149.0757 | 32418.17518 | 179246.1874 | 276121.6575 | 357699.9415 | 280821.202 | 576419.291 | 303570.4917 | 307272.7578 | 1116580.219 | 207853.7933 | 330313.2827 | 324010.5106 | ||
| P62888 | 3 | 3 | 160.52 | 0.229638052 | 2.753571688 | XN | HN | 60S ribosomal protein L30 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPL30 PE=1 SV=2 | 25943.31 | 12198.33 | 42863.95 | 125793.4 | 596880.8451 | 160320.732 | 369302.0259 | 941318.1842 | 318650.3942 | 759132.422 | 10209.3016 | 257560.555 | 42656.2641 | 9285.636822 | 30965.15539 | 29281.69818 | 9873.560108 | 39589.96276 | 2816987.284 | 82427.86443 | 48925.60341 | 57237.98437 | 32136.46824 | 122029.6317 | 59192.19571 | 25693.1513 | 28139.99082 | ||
| Q9Y281 | 4 | 1 | 159.17 | 0.355396 | 2.074353138 | HN | XN | Cofilin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 46133.93 | 4646.476 | 25177.56 | 128280.8 | 3190.494744 | 82009.68315 | 74370.34537 | 88352.37541 | 35825.93562 | 240815.719 | 41218.78931 | 158373.1543 | 60097.87915 | 41576.49432 | 7127.12709 | 31649.85639 | 7731.221554 | 7531.758968 | 11836.61521 | 13178.17532 | 71768.67347 | 88623.29535 | 47044.36478 | 0 | 28659.73189 | 13397.9541 | 12868.48796 | ||
| Q66K79 | 4 | 3 | 158.8 | 0.125295106 | 1.587658061 | XN | XA | Carboxypeptidase Z OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPZ PE=1 SV=2 | 824871.8 | 1103710 | 729601 | 950402.6 | 326131.5792 | 692644.814 | 687893.1195 | 702479.9297 | 477459.5068 | 552353.725 | 850522.7809 | 336045.7025 | 715687.8877 | 1852164.229 | 811988.6563 | 489101.1496 | 863346.5968 | 1032405.017 | 705454.683 | 974047.8285 | 1030452.049 | 585538.6999 | 913889.5262 | 1183682.318 | 2387410.213 | 724908.7091 | 1806764.002 | ||
| Q8N436 | 3 | 2 | 158.8 | 0.576322053 | 1.406318473 | XN | HN | Inactive carboxypeptidase-like protein X2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPXM2 PE=2 SV=3 | 282065.8 | 110750.9 | 113948.7 | 405265.3 | 96071.91768 | 93109.28898 | 37857.36403 | 141740.8245 | 125470.9753 | 124579.2809 | 72815.74782 | 25547.00917 | 106953.2885 | 98561.5822 | 77296.98362 | 308265.6244 | 120183.5057 | 83661.37017 | 101106.2231 | 185809.8795 | 176221.0314 | 146103.5328 | 178578.7142 | 17843.86153 | 333716.3256 | 173433.3349 | 118628.5957 | ||
| P10646 | 4 | 4 | 158.68 | 0.586598243 | 1.237500171 | XA | HN | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFPI PE=1 SV=1 | 596206.9 | 1369725 | 964059.7 | 651252.2 | 1231924.241 | 596280.4437 | 1071628.946 | 469541.4872 | 977637.2949 | 646852.3095 | 1078362.36 | 590322.5064 | 642940.2914 | 634696.5558 | 763446.6469 | 879552.7561 | 612800.2314 | 557697.019 | 649913.845 | 1024582.478 | 330253.0681 | 706068.0455 | 733793.4137 | 1589017.682 | 777441.6368 | 1287968.131 | 627954.5033 | ||
| Q99816 | 4 | 3 | 158.38 | 0.418315192 | 1.213368352 | XA | HN | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 671216.7 | 317151.9 | 250658.4 | 265276.1 | 246061.2356 | 361509.3761 | 436823.7218 | 518398.2053 | 405985.434 | 308696.7557 | 796723.2211 | 322599.3912 | 243944.8675 | 592352.119 | 190812.5005 | 99688.06888 | 98316.96435 | 209212.9365 | 515522.4297 | 357459.3989 | 264000.5755 | 68499.6431 | 217093.2612 | 96800.18645 | 234138.8418 | 473876.2188 | 719050.2296 | ||
| P16066 | 5 | 4 | 157.65 | 0.90228738 | 1.145288764 | XA | XN | Atrial natriuretic peptide receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2668314 | 970758.2 | 938309 | 3349878 | 1017825.586 | 858505.2691 | 1085273.972 | 1244135.891 | 1037280.676 | 2117474.258 | 1476923.118 | 833044.9289 | 1703059.072 | 1022737.157 | 1038838.65 | 1367267.562 | 945868.2423 | 1521501.393 | 1121083.789 | 979006.7365 | 850099.5162 | 791550.0058 | 2231739.245 | 846445.1493 | 1441402.412 | 1217804.416 | 2020397.517 | ||
| Q13443 | 6 | 3 | 157.21 | 0.954759682 | 1.344082878 | XA | HN | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAM9 PE=1 SV=1 | 2182495 | 354723.4 | 243170.2 | 988979 | 363022.3145 | 2478802.628 | 1210058.73 | 710458.6712 | 1709047.959 | 684132.8824 | 1226182.023 | 821198.9011 | 828625.6099 | 1120124.515 | 640354.3218 | 886463.3705 | 542381.7078 | 869678.0062 | 980263.0844 | 699781.1076 | 601334.8687 | 2474955.362 | 968502.4531 | 670609.8737 | 918658.0038 | 555635.6132 | 1061492.479 | ||
| P62942 | 2 | 1 | 157.07 | 0.199144911 | 1.939591585 | XA | HN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FKBP1A PE=1 SV=2 | 150704.8 | 63663.13 | 102901.5 | 202727.6 | 119298.6913 | 1137894.829 | 373790.2378 | 256247.2609 | 341969.9258 | 132992.0953 | 45605.81869 | 548768.7061 | 142665.0733 | 141829.0258 | 136017.6745 | 59739.63351 | 91084.03887 | 118708.6903 | 48347.4446 | 156854.04 | 266195.6484 | 672799.1967 | 65227.1064 | 59119.51696 | 119150.6439 | 9252.484749 | 111514.6106 | ||
| Q9P2T1 | 5 | 3 | 156.78 | 0.024877439 | 1.820131231 | XA | HN | GMP reductase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GMPR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 402239.5 | 258210.3 | 355102.7 | 501708.2 | 209168.7947 | 698677.9698 | 1175422.219 | 542709.9214 | 374964.4748 | 290893.4648 | 173731.3904 | 373401.0731 | 272014.5903 | 99482.86653 | 530851.4448 | 242957.7343 | 212995.9459 | 286022.211 | 502074.4096 | 485378.8523 | 663725.2937 | 315726.2804 | 443560.7483 | 941924.99 | 348862.1984 | 310875.8396 | 265582.9799 | ||
| P02462 | 7 | 2 | 156.01 | 0.975610954 | 1.837749856 | XA | HN | Collagen alpha-1(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 9946309 | 6991186 | 2387516 | 2307010 | 3423280.871 | 60156162.95 | 86364015.05 | 35985156.16 | 36793252.05 | 26464321.92 | 31389685.71 | 6501529.046 | 16315339.07 | 8733135.148 | 18315386.84 | 4527799.958 | 8504147.467 | 12212282.74 | 21785728.58 | 72909543.16 | 12323611.79 | 30279035.83 | 5074774.169 | 8169925.205 | 3168823.039 | 7101856.213 | 32268945.67 | ||
| A8MT79 | 4 | 1 | 155.74 | 0.294092893 | 1.552184412 | XA | HN | Putative zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein-like 1 OS=Homo sapiens PE=5 SV=2 | 362443.9 | 307106.7 | 209822.7 | 92863.7 | 51128.67579 | 51605.20691 | 84847.84212 | 44275.43541 | 42638.72508 | 49535.19912 | 81330.33799 | 27074.95253 | 258828.6066 | 71559.59674 | 6732.249395 | 163202.5592 | 77848.76487 | 67099.56519 | 87819.26605 | 116843.8248 | 185188.5958 | 122549.8726 | 225219.4124 | 64268.96048 | 92400.47974 | 67920.26543 | 95534.36264 | ||
| P51606 | 6 | 3 | 155.4 | 0.325342389 | 1.966073145 | XA | XN | N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=RENBP PE=1 SV=2 | 327186.7 | 42899.51 | 225220.2 | 471431.4 | 61405.59502 | 270634.351 | 350870.4742 | 410618.4367 | 121869.3397 | 209141.866 | 154784.3363 | 253376.128 | 266331.8563 | 426545.6651 | 160335.3501 | 93351.83421 | 107169.7126 | 42229.05719 | 130747.7027 | 63752.66114 | 170526.1921 | 106245.0446 | 172125.9416 | 102044.0905 | 120321.7734 | 214296.807 | 80698.24062 | ||
| P15907 | 8 | 3 | 154.45 | 0.769233298 | 1.302152094 | XA | HN | Beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ST6GAL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1551138 | 458199 | 489991.3 | 149111.2 | 1049941.026 | 728837.3072 | 600629.3067 | 1010036.461 | 268637.7365 | 857810.7072 | 109733.5703 | 497172.7166 | 306398.2068 | 315364.5127 | 487565.7616 | 600854.4072 | 1038572.262 | 629680.1782 | 1412463.874 | 463523.3112 | 395573.6082 | 521319.8178 | 1008371.352 | 173514.5184 | 376889.4789 | 383898.3951 | 1319110.544 | ||
| P01780 | 1 | 1 | 154.43 | 0.518011563 | 1.514211269 | XA | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region JON OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 237895.3 | 1152474 | 504338 | 110729.3 | 735656.4811 | 421000.0445 | 260492.9102 | 937754.895 | 226437.9749 | 260443.5537 | 227517.9614 | 605384.4599 | 188869.2289 | 136748.4378 | 323573.4433 | 88430.50902 | 615674.0911 | 582512.033 | 343266.156 | 967277.7927 | 410618.2928 | 258050.3039 | 355736.4126 | 408009.4242 | 258829.1866 | 177756.7924 | 117421.298 | ||
| P40227 | 7 | 5 | 153.85 | 0.201425944 | 1.475654034 | XA | HN | T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 1182470 | 540559.9 | 421774 | 1467594 | 960361.8553 | 447251.215 | 575041.3519 | 1170972.573 | 563631.4631 | 720010.7329 | 208322.6713 | 541010.9523 | 434651.6611 | 259561.298 | 990195.5228 | 399586.8647 | 1061086.149 | 352630.4208 | 2061849.873 | 417135.6801 | 555159.029 | 414937.1297 | 872066.4671 | 1042765.535 | 656309.2861 | 483104.8789 | 523800.1295 | ||
| P61457 | 4 | 2 | 153.57 | 0.722014212 | 1.21664632 | XA | HN | Pterin-4-alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCBD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 97571.2 | 51123.15 | 66062.21 | 191491.6 | 17495.25434 | 371459.4371 | 329773.2956 | 221923.0679 | 231566.719 | 162444.1166 | 302334.5137 | 73973.07538 | 447876.2036 | 130731.5909 | 78189.38942 | 6735.026919 | 21076.67586 | 74030.33311 | 406819.3768 | 145603.0763 | 348564.525 | 187281.2858 | 95952.69076 | 119117.9314 | 31312.59491 | 53763.18542 | 30078.10035 | ||
| O94772 | 3 | 1 | 153.33 | 0.716961373 | 1.30016139 | HN | XA | Lymphocyte antigen 6H OS=Homo sapiens GN=LY6H PE=2 SV=1 | 1238628 | 3175899 | 2687414 | 1915558 | 4496406.113 | 1973110.933 | 1413828.446 | 952032.9119 | 1167964.036 | 1390475.367 | 1481152.562 | 1174786.212 | 1594950.322 | 2895815.318 | 5066772.903 | 6907929.714 | 2649702.585 | 1568578.208 | 1233881.109 | 1637058.999 | 1421785.733 | 2147727.605 | 3026407.638 | 3270830.323 | 1920570.258 | 2012587.246 | 2623208.265 | ||
| P16422 | 3 | 2 | 152.79 | 0.564811916 | 1.236730589 | XA | HN | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPCAM PE=1 SV=2 | 1475182 | 415576.4 | 446522.4 | 1113892 | 425003.7401 | 863753.7745 | 859335.6958 | 692368.2711 | 795374.016 | 1393747.62 | 474407.6246 | 620524.5571 | 407629.1409 | 467559.3919 | 307729.5296 | 625276.8907 | 675689.2966 | 757873.9395 | 636222.3732 | 672510.3582 | 766439.2565 | 822700.0047 | 532951.1425 | 222139.814 | 818023.2506 | 790957.5125 | 683446.2612 | ||
| P25815 | 3 | 2 | 152.53 | 0.657761714 | 1.799097595 | XN | HN | Protein S100-P OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100P PE=1 SV=2 | 1272104 | 286677 | 351852.3 | 653341.1 | 301796.2042 | 5981333.064 | 5958466.8 | 2189105.411 | 4074111.989 | 4262788.017 | 3744455.177 | 6243513.395 | 688330.83 | 817974.816 | 969724.2335 | 1727161.081 | 367468.2049 | 455068.7734 | 4469359.904 | 973954.9684 | 19926711.43 | 2099346.898 | 2870662.817 | 749180.4524 | 1202927.529 | 1804597.695 | 583535.2538 | ||
| P47755 | 4 | 2 | 152.32 | 0.481198328 | 1.285970069 | XN | HN | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPZA2 PE=1 SV=3 | 637417.3 | 233704.6 | 409521.1 | 569495.1 | 206645.8069 | 1145589.168 | 910688.5538 | 1089378.377 | 474398.7997 | 1542365.702 | 368334.268 | 813462.0458 | 437164.9143 | 358578.7147 | 226976.7547 | 126818.2279 | 475472.8883 | 264238.4383 | 1198961.543 | 606650.5504 | 1315008.346 | 977233.9797 | 424093.786 | 351299.7051 | 334571.264 | 448472.5132 | 276418.002 | ||
| Q9UMX0 | 2 | 1 | 151.99 | 0.543143041 | 1.082350419 | HN | XA | Ubiquilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBQLN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 33864.11 | 0 | 44354.65 | 61947.11 | 2731.591906 | 22826.03363 | 55397.22415 | 45369.09051 | 34577.93305 | 33855.52723 | 100115.5088 | 6877.974365 | 76431.74102 | 30856.06249 | 37115.32037 | 5495.098131 | 18032.28475 | 17081.2772 | 16776.44002 | 5402.381273 | 33080.26413 | 17805.44724 | 12597.16868 | 96881.89876 | 21154.78644 | 60689.95903 | 38027.2325 | ||
| P52823 | 4 | 3 | 151.83 | 0.175245199 | 2.205231149 | XN | HN | Stanniocalcin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 488530.1 | 124424.2 | 264109.5 | 301963.5 | 178339.9782 | 177075.9625 | 119026.8611 | 261346.6563 | 97464.81227 | 158447.378 | 87447.90345 | 80510.22206 | 173114.6627 | 194996.1348 | 276217.3405 | 346191.8059 | 223287.5235 | 321729.3358 | 475950.7815 | 539365.4776 | 224762.7397 | 532287.5632 | 235647.9631 | 48436.41274 | 412308.3583 | 214085.7268 | 1423168.149 | ||
| P37837 | 6 | 3 | 151.68 | 0.765228936 | 1.43012453 | XA | HN | Transaldolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TALDO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 99521.28 | 182660.7 | 84465.71 | 60140.99 | 102186.4799 | 298645.4357 | 752915.1709 | 458594.0309 | 1278569.853 | 575421.8285 | 421891.2191 | 527588.0988 | 191187.5434 | 118170.0427 | 137455.9217 | 74963.79198 | 87071.54523 | 186117.6679 | 1884371.75 | 151798.6837 | 239562.6338 | 80138.67614 | 237442.0266 | 85888.25912 | 136622.1531 | 57810.31666 | 71853.51861 | ||
| P12821 | 8 | 4 | 151.43 | 0.258373551 | 1.53089861 | HN | XN | Angiotensin-converting enzyme OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACE PE=1 SV=1 | 411979.8 | 486082.1 | 838536 | 607743.2 | 632857.4632 | 485701.4754 | 307902.9167 | 532930.3135 | 315543.6244 | 893010.3564 | 538460.617 | 770082.2599 | 233837.5302 | 1971157.726 | 422931.5896 | 815978.7611 | 473763.563 | 850732.4487 | 825724.7501 | 719914.9802 | 599667.0983 | 320870.1648 | 317611.8053 | 174216.8007 | 445159.7645 | 452960.5371 | 696726.1341 | ||
| P28332 | 6 | 5 | 151 | 0.048664438 | 2.344324466 | XA | XN | Alcohol dehydrogenase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADH6 PE=2 SV=2 | 1561678 | 423501.3 | 466684.8 | 2865503 | 319483.9235 | 1454630.107 | 1708853.007 | 2186025.294 | 2384555.35 | 985004.2836 | 175954.5865 | 1439234.381 | 948996.2987 | 351652.6272 | 353167.559 | 361438.0764 | 584096.2778 | 567486.0804 | 894876.6943 | 536295.6062 | 1271354.015 | 795524.0079 | 872551.1085 | 160359.6241 | 545594.3693 | 276551.0873 | 350419.4795 | ||
| O15393 | 5 | 2 | 150.88 | 0.153237225 | 1.353244979 | XN | XA | Transmembrane protease serine 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMPRSS2 PE=1 SV=3 | 11479763 | 4476192 | 4780417 | 6210282 | 6068485.908 | 5105904.932 | 5144270.717 | 10373363.13 | 4388606.085 | 9299335.109 | 9199714.135 | 7652608.712 | 11506293.57 | 12589830.57 | 2923931.747 | 9678296.645 | 8020036.784 | 5571030.42 | 7999359.411 | 8643028.68 | 8917585.108 | 10110649.75 | 11326852.26 | 4645187.594 | 12316257.41 | 7080821.984 | 7485388.675 | ||
| Q13873 | 5 | 3 | 150.34 | 0.582806561 | 1.30208179 | XA | HN | Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BMPR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 457098.1 | 1659583 | 886933.7 | 342781.1 | 456662.2489 | 1645833.806 | 1969345.137 | 667490.496 | 2591719.135 | 217355.8382 | 1373647.923 | 390489.5537 | 1526675.081 | 1004046.964 | 661924.3221 | 307114.1878 | 643857.1851 | 2075178.034 | 548383.0635 | 1558714.154 | 1012324.455 | 1540040.856 | 709620.1898 | 2500464.454 | 982108.4118 | 543567.7849 | 635587.3648 | ||
| P10912 | 5 | 2 | 150.21 | 0.145675875 | 1.615621089 | XA | HN | Growth hormone receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=GHR PE=1 SV=1 | 428936.8 | 844268.4 | 56896.75 | 513360.1 | 759168.2253 | 385933.8203 | 226715.3093 | 798329.3843 | 400755.4583 | 140028.1006 | 214583.284 | 62764.97164 | 276667.4986 | 546284.5662 | 84266.64502 | 135817.2407 | 692159.8707 | 579729.573 | 309697.9741 | 604039.954 | 550630.7437 | 283308.7184 | 277356.9198 | 1094401.116 | 401765.1099 | 329927.0622 | 427735.0814 | ||
| O43633 | 6 | 1 | 149.87 | 0.858889716 | 1.601970013 | HN | XA | Charged multivesicular body protein 2a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP2A PE=1 SV=1 | 358485.5 | 78048.54 | 26249.37 | 111215.4 | 47572.46462 | 138386.1817 | 365304.8366 | 263311.0395 | 87192.81834 | 327045.7132 | 1161635.273 | 250628.3972 | 171155.8957 | 267746.5132 | 47409.63542 | 5900.364516 | 107828.0248 | 24783.37179 | 106404.8143 | 305502.4737 | 227432.7857 | 98830.05527 | 111607.1633 | 52295.74268 | 123583.7004 | 234215.8581 | 287996.4517 | ||
| P09758 | 3 | 2 | 149.59 | 0.576340435 | 1.283384085 | XA | XN | Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TACSTD2 PE=1 SV=3 | 94307.12 | 162373.8 | 153273.9 | 52874.51 | 64051.29354 | 146624.7928 | 150677.5612 | 273700.0318 | 296686.9128 | 224772.3414 | 125532.2097 | 153747.0266 | 116186.0216 | 45656.54903 | 73161.80096 | 71425.58226 | 109193.9649 | 190735.1869 | 277574.819 | 121468.9867 | 110583.9468 | 127371.63 | 50988.43331 | 145351.396 | 22760.15285 | 156611.5998 | 73923.91622 | ||
| P28066 | 4 | 4 | 148.77 | 0.334981968 | 1.949734842 | XN | HN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 61289.97 | 17118.74 | 40997.44 | 163054.4 | 267756.4922 | 218495.9782 | 300831.9337 | 254039.3189 | 343768.9158 | 272629.5741 | 124340.8734 | 228782.4492 | 237178.385 | 59595.43739 | 87048.35092 | 6739.306116 | 6246.746139 | 17843.96002 | 1066116.064 | 295696.7684 | 221101.5016 | 133368.8509 | 72618.40704 | 32845.59054 | 125826.9887 | 37889.93433 | 43049.93249 | ||
| P49763 | 3 | 2 | 148.77 | 0.901701745 | 1.226855318 | HN | XA | Placenta growth factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGF PE=1 SV=2 | 1410223 | 1068161 | 1759077 | 2050758 | 1807135.354 | 900521.6207 | 366305.6974 | 946238.7632 | 477829.2737 | 893843.3282 | 852776.2233 | 229073.4358 | 732973.3241 | 1861491.071 | 1205056.283 | 2917370.19 | 1572006.476 | 2968577.119 | 760170.2579 | 1230673.958 | 1141180.979 | 728797.3999 | 1307647.146 | 1728371.821 | 1109615.565 | 1229947.254 | 1704098.032 | ||
| P20333 | 5 | 4 | 148.72 | 0.974729358 | 1.07746101 | XA | XN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF1B PE=1 SV=3 | 965591.1 | 1508075 | 1161576 | 2381537 | 1467935.147 | 1191761.91 | 627857.5789 | 1140240.53 | 486713.6488 | 1071189.544 | 2052890.648 | 625888.7891 | 1319382.346 | 870803.8198 | 1313399.441 | 708374.1755 | 913217.3715 | 1407444.426 | 1068217.567 | 1223553.179 | 445381.312 | 1115291.395 | 971696.3912 | 1733228.172 | 765353.2884 | 1535251.48 | 1287440.447 | ||
| P48551 | 3 | 2 | 148.68 | 0.70834251 | 1.432969495 | HN | XN | Interferon alpha/beta receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IFNAR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 738828.9 | 1605153 | 1636027 | 961989.8 | 3125857.865 | 551561.4898 | 249428.5999 | 770224.1861 | 425134.0568 | 994000.7475 | 348397.5103 | 558721.2366 | 403868.2095 | 1746255.766 | 2163358.667 | 1267825.394 | 1848455.368 | 1686956.756 | 776535.2387 | 822112.8733 | 398600.7351 | 1357967.569 | 990177.2027 | 1056140.535 | 392361.0183 | 1174258.809 | 720662.6309 | ||
| Q16832 | 6 | 5 | 148.34 | 0.357781864 | 1.228088856 | HN | XN | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2858119 | 3883298 | 3466922 | 3621094 | 4620358.324 | 2443700.895 | 2290573.293 | 2742350.399 | 1840898.107 | 2837628.948 | 2289234.33 | 1810142.396 | 2413566.036 | 2227288.279 | 4010984.896 | 3953043.864 | 5184192.942 | 3433250.573 | 2465147.64 | 2438794.556 | 2020738.579 | 2786998.519 | 1786125.801 | 3039100.348 | 2841168.914 | 2924493.41 | 2626825.436 | ||
| P09486 | 2 | 1 | 148.1 | 0.982232516 | 1.097307803 | XN | XA | SPARC OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPARC PE=1 SV=1 | 622055.7 | 240642.8 | 250160.2 | 455737.5 | 327798.3356 | 169173.4848 | 354688.7031 | 386352.4657 | 677328.0344 | 537915.7147 | 522304.6528 | 377521.7846 | 601072.2458 | 749901.6102 | 203820.388 | 122640.1819 | 168474.5882 | 522506.4795 | 90259.02713 | 730374.7127 | 651437.0131 | 182449.7493 | 339859.3104 | 266956.1301 | 229444.6209 | 442096.1306 | 890074.8559 | ||
| P34096 | 4 | 4 | 147.95 | 0.345643207 | 1.446804894 | XA | HN | Ribonuclease 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE4 PE=1 SV=3 | 1108425 | 801458.3 | 518730.9 | 898996.3 | 2033164.315 | 527105.6638 | 327076.3292 | 888602.6219 | 319039.2647 | 231575.3637 | 67289.53911 | 306009.899 | 588448.787 | 825140.8699 | 601173.0915 | 688018.1063 | 640051.2958 | 1182631.471 | 646505.4854 | 569564.8535 | 494491.0787 | 332483.675 | 741661.2518 | 331203.2612 | 658225.9749 | 860470.2873 | 843421.1338 | ||
| A6NL28 | 3 | 1 | 147.85 | 0.535196017 | 2.215970255 | XA | XN | Putative tropomyosin alpha-3 chain-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=5 SV=2 | 21984.26 | 8929.103 | 13541.02 | 30521.4 | 26550.77154 | 332509.917 | 232173.5015 | 164010.1978 | 264480.5269 | 141524.1407 | 84422.45491 | 139857.6948 | 61071.324 | 18312.96168 | 50462.68531 | 2248.52938 | 9782.188885 | 13651.81814 | 143553.0043 | 86515.47495 | 51078.84329 | 142700.5872 | 9584.413344 | 17988.94456 | 23321.73886 | 5395.803238 | 13866.32941 | ||
| Q9UBV8 | 3 | 2 | 147.62 | 0.362119556 | 1.515197144 | XA | XN | Peflin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PEF1 PE=1 SV=1 | 259345.6 | 90568.72 | 42218.53 | 95222.62 | 134322.3916 | 103621.5414 | 101257.8061 | 204631.9378 | 86153.47975 | 145770.6659 | 299559.4755 | 84290.5295 | 53832.55786 | 265503.8917 | 46621.84041 | 39440.21885 | 39889.19786 | 48777.29434 | 169175.7232 | 36274.30989 | 76613.83856 | 32586.39038 | 44295.76979 | 74444.3835 | 69772.11268 | 89199.53079 | 145061.8936 | ||
| P62834;A6NIZ1;P61224 | 3 | 1 | 147.48 | 0.072915054 | 1.820023852 | HN | XN | Ras-related protein Rap-1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAP1A PE=1 SV=1 | 151314.7 | 56126.28 | 58411.93 | 122756.2 | 90534.52999 | 107130.9168 | 111703.6877 | 170142.0491 | 106294.3853 | 257557.8042 | 241772.0408 | 101766.6275 | 97814.68482 | 220168.2563 | 94366.91748 | 334219.5211 | 57955.05393 | 119719.778 | 75802.76876 | 87676.53832 | 76016.94153 | 112506.7485 | 90137.60239 | 47008.06386 | 157868.6447 | 65436.49365 | 125634.4916 | ||
| Q16851 | 6 | 3 | 147.42 | 0.126172159 | 3.286486595 | XA | HN | UTP--glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=UGP2 PE=1 SV=5 | 251973.3 | 9063.664 | 108870.6 | 692708.9 | 101116.3827 | 447415.5944 | 463589.6478 | 814741.4201 | 333903.3483 | 160907.5068 | 56953.21282 | 221283.2319 | 170694.1307 | 10756.23453 | 205796.1379 | 81564.50163 | 36363.56472 | 36480.49893 | 73450.10937 | 74590.24993 | 181478.6047 | 89108.67404 | 310473.3484 | 50805.12599 | 203891.8572 | 105845.4616 | 37048.03425 | ||
| P21333 | 15 | 4 | 147.34 | 0.321222413 | 1.545347871 | HN | XN | Filamin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLNA PE=1 SV=4 | 666966.5 | 644211.8 | 351807 | 780627 | 699512.4621 | 772719.1165 | 828193.3006 | 470622.1812 | 861355.8149 | 959409.3552 | 492179.3396 | 602172.4309 | 453475.475 | 457745.0046 | 822070.8385 | 2440546.102 | 425493.6838 | 1304873.687 | 677526.2624 | 330683.8862 | 323379.2851 | 484757.9645 | 582535.8745 | 761064.2969 | 972195.1935 | 433911.3182 | 583573.432 | ||
| P38606 | 4 | 2 | 147.27 | 0.065492688 | 2.10449274 | XA | XN | V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6V1A PE=1 SV=2 | 1022479 | 285515.3 | 345741.4 | 944684.6 | 236101.9889 | 331652.9463 | 532108.7056 | 815556.1137 | 328923.6596 | 736152.8851 | 482771.7513 | 742644.3312 | 254632.1101 | 753923.4589 | 197534.7528 | 316545.6128 | 102231.5981 | 117350.1391 | 159468.4194 | 110909.1502 | 254747.0889 | 196620.4226 | 637688.6254 | 147595.8129 | 319489.9024 | 277520.6709 | 197114.7011 | ||
| Q14332 | 4 | 1 | 146.56 | 0.286273127 | 1.863752757 | XN | XA | Frizzled-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD2 PE=2 SV=1 | 239779.9 | 56414.32 | 137226.4 | 128669.2 | 69731.1025 | 83673.43323 | 114325.6651 | 111713.5587 | 63926.17549 | 212913.6859 | 80734.5158 | 110150.8443 | 120694.8096 | 120314.6327 | 120504.6265 | 249812.0375 | 130462.933 | 182805.0758 | 745504.3547 | 132073.6615 | 116817.4355 | 78882.62414 | 140244.7798 | 98144.99667 | 170041.4598 | 331625.8761 | 60593.2023 | ||
| Q16363 | 5 | 2 | 146.51 | 0.053571728 | 1.441587359 | XN | HN | Laminin subunit alpha-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMA4 PE=1 SV=4 | 2033456 | 1276639 | 1174858 | 2735038 | 2241221.739 | 3513600.84 | 2347646.018 | 3021972.88 | 2621931.863 | 3352447.416 | 2948467.19 | 897848.4069 | 2231140.018 | 2135953.969 | 865125.1021 | 1683715.356 | 2236054.204 | 3233505.018 | 3156860.478 | 3952740.113 | 3802850.517 | 2219698.671 | 2380339.743 | 3318857.826 | 2512074.713 | 3200801.698 | 3688193.105 | ||
| P52565 | 4 | 2 | 146.41 | 0.45203799 | 1.14538119 | XA | XN | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARHGDIA PE=1 SV=3 | 1635840 | 1193794 | 1974101 | 2598097 | 3246176.204 | 3517532.632 | 6662431.264 | 2337135.677 | 2547654.629 | 2058273.352 | 3591347.392 | 8587015.46 | 4188557.515 | 1904429.659 | 469045.4236 | 682642.562 | 894887.9666 | 688159.9667 | 1612451.031 | 2715596.518 | 3465361.963 | 2985317.44 | 4143246.51 | 1828055.18 | 1287442.66 | 3646423.984 | 765192.4853 | ||
| P15428 | 2 | 2 | 145.93 | 0.513581378 | 3.000401672 | XN | XA | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)] OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPGD PE=1 SV=1 | 237212.8 | 16377.13 | 31856.23 | 166320.1 | 81601.70461 | 37119.79804 | 77589.03093 | 139962.6398 | 60327.07249 | 76408.44 | 161039.7727 | 177924.1081 | 43177.55598 | 160616.8094 | 79318.46591 | 838615.2378 | 103157.7272 | 20931.55695 | 189331.2836 | 41812.97189 | 1676667.981 | 61108.22973 | 183108.6361 | 51054.26849 | 108479.4431 | 202089.2075 | 31788.3189 | ||
| P06753;P09493 | 8 | 3 | 145.44 | 0.874870703 | 1.393959997 | XA | XN | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPM3 PE=1 SV=1 | 24605.12 | 53698.88 | 39611.24 | 33140.33 | 162981.2716 | 356928.2656 | 350990.5716 | 125489.1414 | 231460.5014 | 280598.7845 | 74815.44441 | 272150.048 | 108779.0828 | 53809.96545 | 106147.658 | 95613.73237 | 39212.70247 | 110259.0027 | 225333.2515 | 182867.1325 | 60104.25091 | 242077.9609 | 38513.64685 | 50700.80759 | 60460.70425 | 43690.94014 | 85451.37185 | ||
| P11362 | 5 | 3 | 145.19 | 0.624503119 | 1.179722238 | XA | HN | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGFR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 2224443 | 3711455 | 3723463 | 2515495 | 2348729.057 | 3220417.393 | 4260238.99 | 2576911.836 | 8672047.476 | 1942049.387 | 4331390.984 | 2055496.264 | 4527449.498 | 4147361.801 | 2220908.597 | 2872489.799 | 2986573.199 | 3103593.603 | 2806338.975 | 4703816.871 | 3031907.299 | 2396772.635 | 4108365.996 | 5512974.685 | 2908028.423 | 4803365.62 | 2605759.364 | ||
| P01601 | 3 | 1 | 144.58 | 0.97992493 | 1.179986002 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region HK101 (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens PE=4 SV=1 | 445596.8 | 617466.4 | 801357 | 482123 | 1528268.43 | 638607.5754 | 405407.566 | 362146.2266 | 172782.4448 | 793861.6167 | 144825.079 | 1462286.02 | 182847.8551 | 724363.0472 | 429333.2141 | 698970.9422 | 879422.4024 | 391621.8642 | 1430297.725 | 453795.2086 | 560634.2489 | 369832.301 | 234257.4367 | 2205463.822 | 456536.1839 | 418276.0398 | 306262.175 | ||
| Q9GZP0 | 5 | 3 | 144.45 | 0.401687759 | 1.542838554 | XN | HN | Platelet-derived growth factor D OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDGFD PE=1 SV=1 | 604156.9 | 403457.3 | 390705.2 | 567488.3 | 125750.1759 | 143435.1088 | 217492.1133 | 154436.0715 | 203498.3005 | 41758.61546 | 47311.74697 | 120073.29 | 310557.0342 | 42273.10139 | 323788.7428 | 325074.4944 | 269958.8742 | 578143.2874 | 440044.7763 | 391857.4031 | 269681.8795 | 221485.0219 | 392325.1717 | 14379.23201 | 600040.8179 | 319366.1326 | 527430.323 | ||
| Q6IS14;P63241;Q9GZV4 | 4 | 4 | 144.32 | 0.714809541 | 2.144567769 | HN | XN | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=EIF5AL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5147563 | 9863668 | 9093769 | 4296071 | 2513407.35 | 3291021.26 | 5928791.598 | 2827936.74 | 10891028.29 | 3889194.964 | 5042797.798 | 48341493.14 | 3780253.858 | 9339399.972 | 4849076.725 | 1204791.146 | 4907435.247 | 19588429.78 | 5020101.913 | 5365702.437 | 9904680.495 | 3320724.156 | 6364668.341 | 4617617.973 | 3518528.197 | 5833522.164 | 3123553.317 | ||
| O15031 | 10 | 4 | 144.26 | 0.731517363 | 1.535700244 | HN | XA | Plexin-B2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLXNB2 PE=1 SV=3 | 530830.3 | 327513.5 | 275912.5 | 136704.8 | 118284.9037 | 335371.5569 | 509351.2876 | 396028.4376 | 279521.2835 | 380984.2801 | 162815.5767 | 1985206.987 | 343945.8689 | 572262.8816 | 134001.4715 | 322407.8973 | 246542.359 | 319980.9846 | 558401.9891 | 378595.4999 | 276566.3361 | 309709.9419 | 544828.6538 | 277518.9274 | 272961.181 | 271084.4361 | 355008.4315 | ||
| O00757 | 2 | 1 | 144.25 | 0.894663261 | 1.241628943 | HN | XN | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase isozyme 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 458327.3 | 508251.7 | 428658.4 | 151602.5 | 262974.7318 | 1417398.061 | 2140511.13 | 882759.7762 | 865539.4976 | 428156.4121 | 1269921.824 | 917505.2793 | 1830747.375 | 949630.0481 | 397141.7477 | 353158.16 | 427791.1704 | 558247.337 | 464037.9648 | 602535.3457 | 781085.238 | 1089162.996 | 775977.182 | 408560.8789 | 373790.4543 | 661015.0003 | 588143.1695 | ||
| Q9UGB7 | 3 | 2 | 143.85 | 0.267139906 | 1.797755362 | XA | HN | Inositol oxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MIOX PE=1 SV=1 | 638234.7 | 155580.4 | 339829.5 | 892554.5 | 108617.5396 | 842334.5221 | 653472.9165 | 797297.1721 | 503155.432 | 433894.7946 | 366179.3768 | 270456.2205 | 591993.2688 | 274113.1501 | 168314.8251 | 108403.6272 | 211628.7589 | 317923.5099 | 709119.1291 | 280660.5381 | 605090.0306 | 525542.6172 | 611464.0431 | 253017.3203 | 173934.4955 | 200449.8607 | 178247.0226 | ||
| P17661 | 8 | 2 | 143.78 | 0.85031485 | 1.462176324 | HN | XN | Desmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DES PE=1 SV=3 | 63215.93 | 39376.97 | 45413.33 | 95533.31 | 19712.01073 | 8088.665078 | 5411.381916 | 6337.388053 | 16238.14982 | 36912.89399 | 2721.315664 | 206095.2937 | 2527.102165 | 43207.88036 | 41848.52139 | 14083.34438 | 19313.05079 | 2092.255652 | 19680.43186 | 6606.003445 | 22501.71808 | 15316.18274 | 104700.6403 | 12340.08288 | 49564.124 | 9079.06547 | 12439.64743 | ||
| P61981 | 8 | 3 | 143.58 | 0.272013336 | 1.491920908 | XA | HN | 14-3-3 protein gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAG PE=1 SV=2 | 158567.1 | 73420.93 | 196565.5 | 405045.6 | 104613.7145 | 225395.4468 | 286318.0895 | 244784.238 | 262095.3106 | 172836.8443 | 155869.0332 | 225868.8219 | 183582.8552 | 127199.6669 | 112900.6963 | 117268.0774 | 116043.7263 | 100031.9346 | 75102.79911 | 97242.98394 | 229670.1223 | 312200.3096 | 127416.3965 | 253521.4722 | 149478.9921 | 90979.89899 | 149784.5168 | ||
| Q86X29 | 6 | 3 | 143.46 | 0.497534125 | 1.777861742 | XA | XN | Lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=LSR PE=1 SV=4 | 438645.9 | 1860344 | 775793.8 | 608217.8 | 4112835.717 | 663565.0776 | 302862.315 | 1014847.646 | 752147.5362 | 1823648.196 | 412221.0003 | 230998.8394 | 548845.4071 | 1154144.299 | 689528.286 | 856967.0926 | 564420.9066 | 1675253.556 | 482798.9937 | 498952.5386 | 784371.1664 | 468080.9635 | 564576.1033 | 1500852.375 | 871560.5246 | 349149.0663 | 402087.1592 | ||
| Q6ZVX7 | 3 | 2 | 142.11 | 0.562054184 | 1.633557807 | XA | XN | Non-specific cytotoxic cell receptor protein 1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCCRP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 343309 | 182526.6 | 130639.5 | 185084.8 | 122899.1454 | 397596.5685 | 2869500.269 | 3315789.291 | 2528152.894 | 1140077.518 | 700192.4916 | 2125423.622 | 1518077.367 | 114697.1475 | 119604.5506 | 134239.9984 | 194019.5509 | 203408.5802 | 3683225.968 | 1294469.478 | 346620.57 | 150766.8463 | 185758.7393 | 235784.2434 | 179704.6926 | 49730.50402 | 41763.60397 | ||
| P49368 | 8 | 4 | 141.76 | 0.484985849 | 1.865899122 | XA | XN | T-complex protein 1 subunit gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT3 PE=1 SV=4 | 469113.9 | 23515.87 | 149597.5 | 659616.7 | 75072.58642 | 241658.3893 | 306701.4748 | 664881.3858 | 292643.8475 | 182528.7712 | 72451.98883 | 394518.3711 | 219613.5036 | 50922.26767 | 229779.9623 | 265558.9116 | 80801.53388 | 121147.4853 | 170533.1524 | 86590.7689 | 333971.2429 | 182953.8848 | 375580.5283 | 53585.07131 | 169201.6942 | 89820.03047 | 82756.91281 | ||
| P41218 | 8 | 4 | 140.86 | 0.355175541 | 4.537879857 | XA | XN | Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=MNDA PE=1 SV=1 | 56153.98 | 10534.73 | 11738.67 | 43777.3 | 39812.17354 | 349142.4629 | 881793.8253 | 52329.28614 | 427291.3707 | 18256.63765 | 70140.9291 | 80218.62255 | 39412.35478 | 24881.78616 | 86205.02183 | 24528.98431 | 89020.30272 | 34376.79402 | 27668.50765 | 68167.47315 | 22359.76703 | 59344.03003 | 5374.172167 | 52510.24384 | 88886.3136 | 44859.09221 | 43484.2958 | ||
| Q9P0M6;O75367 | 6 | 1 | 140.86 | 0.765289124 | 24.59526255 | XA | HN | Core histone macro-H2A.2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=H2AFY2 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 0 | 148.3752 | 99.07396 | 0 | 267009.6674 | 38126.44846 | 5274.296479 | 107281.6567 | 1291.927775 | 0 | 163.0010379 | 100.947045 | 0 | 14176.10302 | 1013.945163 | 246.7597036 | 0 | 105802.7011 | 39.45632671 | 3616.929428 | 3742.319092 | 105.8788878 | 0 | 0 | 11.95058822 | 71.2058852 | ||
| Q9BXN2 | 2 | 2 | 140.79 | 0.340273999 | 1.425981378 | XA | HN | C-type lectin domain family 7 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC7A PE=1 SV=1 | 561084.8 | 1696939 | 1223714 | 865530.6 | 260189.59 | 1163006.114 | 1630984.512 | 799938.0725 | 2107402.591 | 411794.0206 | 1912012.632 | 564829.2177 | 1121458.416 | 1132768.404 | 418507.6245 | 208464.0483 | 425246.6846 | 1034178.77 | 925855.8088 | 1851122.541 | 506950.7219 | 599376.9424 | 507797.3542 | 2213569.281 | 934832.4313 | 1780011.083 | 680456.2154 | ||
| P00533 | 5 | 4 | 140.6 | 0.971450301 | 1.406307293 | HN | XA | Epidermal growth factor receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=EGFR PE=1 SV=2 | 778079.6 | 715473 | 739269.2 | 739774.2 | 1481196.731 | 738579.4385 | 1055825.113 | 1070888.622 | 740846.2859 | 609976.3806 | 687619.394 | 1092298.932 | 289312.7189 | 704158.2824 | 1274365.219 | 4993793.979 | 1162303.587 | 520912.8993 | 841853.6731 | 1139047.796 | 732312.6908 | 889748.7541 | 2293135.086 | 736115.4911 | 851612.882 | 381873.5689 | 1439479.311 | ||
| P55083 | 4 | 3 | 140.57 | 0.290930978 | 1.404905151 | XA | XN | Microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFAP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 4027588 | 1431217 | 1942056 | 2776688 | 1158710.847 | 1283789.689 | 1362031.067 | 2755641.842 | 1215737.558 | 1092181.343 | 831174.6503 | 991895.1257 | 1348927.976 | 1396559.026 | 2362018.165 | 3145983.168 | 1806872.6 | 1266822.162 | 968664.3448 | 943326.6731 | 1218257.096 | 940839.259 | 2568057.925 | 1843232.359 | 1635001.963 | 1289639.264 | 1372107.23 | ||
| O14732 | 2 | 2 | 140.22 | 0.096991777 | 4.127761473 | XA | HN | Inositol monophosphatase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IMPA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 107282.4 | 22047.04 | 52083.38 | 194073.1 | 2148.683854 | 164525.8981 | 128082.9109 | 159308.738 | 125974.0012 | 47704.75689 | 4593.895272 | 28658.59395 | 71347.43918 | 44214.85885 | 6225.577311 | 14713.53031 | 4643.540973 | 9385.529853 | 145215.3916 | 100800.7818 | 78738.25135 | 139425.4215 | 21731.77522 | 6350.792701 | 3990.037016 | 12159.53539 | 19395.44746 | ||
| Q9NY15 | 5 | 2 | 140.07 | 0.843498043 | 1.124175323 | XA | XN | Stabilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STAB1 PE=1 SV=3 | 163499.3 | 187023.6 | 230606.6 | 490336.8 | 353782.2897 | 325390.0435 | 277360.6021 | 86014.39159 | 190573.5802 | 43069.27188 | 372652.6613 | 43249.11945 | 208027.0507 | 251432.1836 | 215482.6732 | 454399.6928 | 297768.4496 | 333592.1079 | 71034.69797 | 292989.6035 | 300013.6471 | 85534.04601 | 216299.6663 | 292017.4789 | 201572.3357 | 274268.6373 | 316294.5645 | ||
| Q8IWA5 | 9 | 3 | 139.97 | 0.356977354 | 1.704383773 | XA | HN | Choline transporter-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC44A2 PE=1 SV=3 | 210337 | 166763.5 | 190294.1 | 28178.43 | 315665.4513 | 881756.8854 | 253022.052 | 58688.17981 | 310135.7676 | 308985.8095 | 449966.4392 | 202639.5634 | 30860.79558 | 212072.6313 | 62298.47729 | 5313.601165 | 36606.25311 | 108097.7796 | 459564.0112 | 331907.6927 | 127622.3877 | 224450.6768 | 360104.8645 | 48997.83239 | 12543.77037 | 209180.4643 | 553753.1802 | ||
| P78417 | 5 | 5 | 139.94 | 0.316194969 | 1.699498919 | XA | XN | Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 967516.5 | 812790.8 | 822742.4 | 1100424 | 375331.2303 | 2295425.81 | 2857730.991 | 1579643.973 | 2168731.823 | 2207694.395 | 2075052.036 | 2148108.834 | 1430708.331 | 1144182.942 | 776741.9559 | 232298.7313 | 627748.9423 | 454655.1439 | 1769262.725 | 688865.6852 | 1251934.981 | 553010.2865 | 889510.6267 | 765463.0309 | 924631.5097 | 504779.0412 | 290286.3006 | ||
| P04430 | 2 | 1 | 139.57 | 0.058381432 | 1.456221411 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region BAN OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 10514186 | 9962486 | 10443929 | 8075957 | 15397574.13 | 10645052.18 | 6734632.124 | 8714096.036 | 7961540.522 | 4533842.279 | 2429474.255 | 5678277.708 | 5674073.316 | 15832968.05 | 7175737.622 | 6315213.873 | 4272039.985 | 8827387.484 | 13642228.7 | 5601972.406 | 4096053.968 | 9664086.545 | 5930749.125 | 9727826.8 | 9118153.606 | 5794895.622 | 9984643.162 | ||
| Q9BVK6 | 3 | 1 | 139.42 | 0.772371877 | 1.685720502 | XA | XN | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMED9 PE=1 SV=2 | 123434.4 | 263834.9 | 387937.2 | 320943 | 644108.9567 | 116766.2638 | 35155.63309 | 165669.8674 | 59369.84342 | 154626.7594 | 52302.77803 | 189317.095 | 34142.70082 | 194938.7653 | 234066.3752 | 394200.5098 | 258660.5331 | 192233.3037 | 93871.4297 | 97982.55048 | 66876.13353 | 122194.9678 | 177192.4763 | 212409.6664 | 204379.6628 | 129930.1383 | 151136.3178 | ||
| P69891;P69892 | 3 | 2 | 139.2 | 0.711248545 | 9.924375688 | HN | XN | Hemoglobin subunit gamma-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 41151.99 | 47159.85 | 3742.018 | 82281.34 | 276777.7724 | 23946.3984 | 16327.79348 | 69629.65591 | 368713.1293 | 1954.888412 | 26652.28105 | 2574592.971 | 39236.554 | 39879.86947 | 28825.53802 | 22948.91795 | 138063.415 | 33354.23345 | 54728.51181 | 41598.77307 | 11611.91153 | 22761.23372 | 32388.6517 | 44976.87768 | 43732.75672 | 22193.54773 | 18772.6171 | ||
| O95084 | 3 | 3 | 139.18 | 0.841562984 | 1.41618357 | XA | HN | Serine protease 23 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRSS23 PE=1 SV=1 | 1177279 | 948044.9 | 3276121 | 3083777 | 392527.3815 | 416285.2969 | 323123.2171 | 1184618.544 | 573968.394 | 905439.3108 | 872962.2567 | 1027537.746 | 1313813.148 | 1026155.469 | 346953.0351 | 1236573.549 | 591008.7314 | 712233.3876 | 294600.1895 | 1705200.432 | 881154.1631 | 350660.1725 | 948005.1686 | 396427.2398 | 1462301.044 | 1316325.661 | 686301.3427 | ||
| P14555 | 2 | 2 | 138.87 | 0.986509769 | 1.250031778 | XN | HN | Phospholipase A2, membrane associated OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLA2G2A PE=1 SV=2 | 220918.8 | 139898.7 | 186349.1 | 875154.4 | 1518089.547 | 142437.5709 | 296613.751 | 274479.6066 | 145380.9686 | 109382.4308 | 168353.6385 | 426145.7689 | 108469.4459 | 190789.1937 | 267681.3388 | 499582.1392 | 356425.6553 | 959924.3245 | 291521.6954 | 177196.8282 | 99618.18839 | 189489.9 | 74822.67742 | 1113173.227 | 339784.6081 | 1360650.457 | 212282.9282 | ||
| O00337 | 3 | 2 | 138.31 | 0.403656916 | 1.399381306 | XA | HN | Sodium/nucleoside cotransporter 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC28A1 PE=2 SV=2 | 533701.6 | 4111090 | 1098764 | 892049.3 | 573090.5467 | 2467587.707 | 6495121.82 | 605075.8422 | 5352337.923 | 692578.9754 | 4134495.417 | 380835.2276 | 3041238.955 | 3803012.073 | 1101959.104 | 179527.9633 | 895843.6815 | 1583795.541 | 1492234.907 | 3257826.952 | 1102140.558 | 1537518.496 | 1415068.832 | 5200102.44 | 1550774.447 | 4615330.495 | 1622013.932 | ||
| Q9Y5Z4 | 2 | 1 | 138.07 | 0.229085621 | 2.061550231 | HN | XN | Heme-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 137535.2 | 115366.5 | 101295.6 | 99957.83 | 183767.3061 | 252638.9034 | 535632.0019 | 488040.809 | 858097.1469 | 992959.3064 | 670572.4124 | 174088.4547 | 576697.6214 | 471960.3107 | 131758.037 | 139762.1626 | 211819.4965 | 662197.3072 | 231964.9632 | 262180.5634 | 277760.1373 | 203703.9288 | 287148.266 | 222249.9272 | 106330.6764 | 111825.1006 | 252556.4817 | ||
| P29034 | 6 | 3 | 137.23 | 0.73419814 | 1.736110518 | XN | XA | Protein S100-A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A2 PE=1 SV=3 | 52590.81 | 173442 | 69974.13 | 219308.2 | 71821.42349 | 89795.90927 | 248089.9196 | 516674.7915 | 639522.5625 | 1283222.639 | 74926.64329 | 338830.2097 | 146308.9839 | 69396.87279 | 72749.40237 | 96657.98167 | 13532.72534 | 78072.70214 | 2734586.555 | 188907.1555 | 281690.3279 | 205700.9018 | 54338.62994 | 7661.624899 | 45526.92742 | 43295.0093 | 51520.47976 | ||
| Q5UCC4 | 3 | 1 | 137.1 | 0.722657505 | 1.105229522 | XN | XA | ER membrane protein complex subunit 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EMC10 PE=1 SV=1 | 196521.3 | 404193.6 | 326086.9 | 459871.7 | 737192.7688 | 449147.6627 | 529857.907 | 423510.5136 | 468469.7796 | 385158.6423 | 378583.1429 | 352567.1823 | 387638.1797 | 376288.3994 | 277565.5005 | 1125021.667 | 689532.3975 | 312867.4574 | 367982.0296 | 355270.0191 | 441141.6337 | 488234.5369 | 370809.4363 | 652109.1036 | 510884.3103 | 664973.3355 | 563824.163 | ||
| P49913 | 6 | 4 | 137.07 | 0.422917013 | 1.310994702 | HN | XN | Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAMP PE=1 SV=1 | 718511.8 | 993218.7 | 962769.8 | 568824.9 | 598643.091 | 851762.9116 | 913727.5406 | 793524.5217 | 1082920.32 | 1904898.537 | 1367290.927 | 464792.6601 | 739132.8608 | 473821.5975 | 1147989.254 | 919593.4419 | 588958.5543 | 704165.2468 | 772898.4493 | 484060.623 | 597822.2107 | 966118.8748 | 438612.7181 | 892938.5013 | 806908.0475 | 525432.1764 | 854397.3126 | ||
| P01609 | 4 | 2 | 135.82 | 0.706846527 | 1.203417663 | HN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region Scw OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 8589891 | 10495893 | 4284453 | 1197017 | 4259471.693 | 2273426.265 | 4123875.867 | 3134382.802 | 5783033.291 | 6971228.951 | 2298995.427 | 4208664.888 | 3460784.11 | 2192334.898 | 22213901.02 | 3421060.656 | 4238153.094 | 4115470.94 | 6911563.577 | 2592947.3 | 2645979.724 | 8788793.147 | 3692538.084 | 6960715.629 | 6031064.841 | 4911213.951 | 9159003.711 | ||
| P16234 | 5 | 2 | 135.63 | 0.896877697 | 1.13197899 | XN | HN | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDGFRA PE=1 SV=1 | 2138128 | 2967717 | 2251833 | 1729488 | 1669773.509 | 2285775.84 | 2713513.92 | 1714676.017 | 3266258.413 | 2037197.895 | 2481373.787 | 1857138.941 | 1978836.199 | 2268191.143 | 2273248.895 | 1542631.806 | 2364380.491 | 2345617.257 | 2714499.244 | 2364446.19 | 2860541.7 | 2289798.678 | 1052015.047 | 4339788.343 | 1182793.604 | 2761646.673 | 2110301.991 | ||
| Q9Y376 | 6 | 3 | 135.56 | 0.606747854 | 1.714191774 | HN | XN | Calcium-binding protein 39 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAB39 PE=1 SV=1 | 421923.5 | 74489.45 | 125143 | 304266.3 | 44315.30906 | 262146.5753 | 270864.7133 | 471415.3307 | 255676.555 | 690121.369 | 719752.6261 | 286791.9821 | 232453.8675 | 475679.0994 | 130194.3088 | 122876.5204 | 58691.07499 | 66421.78696 | 470991.71 | 258262.0411 | 231581.938 | 137751.6096 | 76853.28688 | 57542.40101 | 110750.0171 | 113626.8732 | 166135.625 | ||
| P00568 | 4 | 3 | 135.53 | 0.159392879 | 1.713034038 | XN | XA | Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1282134 | 751865 | 1622098 | 1756642 | 619343.2762 | 1048553.29 | 1324284.863 | 757767.3671 | 667799.5524 | 1211953.797 | 1026617.392 | 739824.7234 | 577436.2268 | 3055350.3 | 998311.6137 | 1542771.294 | 1508740.56 | 1535621.307 | 1475942.489 | 812519.8597 | 2694110.725 | 3278689.564 | 1911060.64 | 478859.8259 | 1889448.99 | 1727802.666 | 2571523.868 | ||
| O95633 | 4 | 4 | 135.33 | 0.011918682 | 1.551030917 | XA | HN | Follistatin-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FSTL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 1123978 | 880189.7 | 720757.9 | 2240375 | 1009273.489 | 1216624.573 | 1212544.142 | 1220619.698 | 704373.0987 | 600851.0917 | 1080514.011 | 390663.4586 | 601716.3776 | 818420.4454 | 920524.4385 | 573618.2269 | 479855.4953 | 1193107.26 | 912002.7488 | 995554.5003 | 800525.345 | 960682.6563 | 894677.246 | 1090940.382 | 1097670.303 | 1058757.894 | 1215280.383 | ||
| Q92954 | 7 | 2 | 134.73 | 0.589967297 | 1.088888297 | XA | HN | Proteoglycan 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRG4 PE=1 SV=2 | 7850.608 | 268356 | 236456.1 | 83866.19 | 90081.93427 | 23436.90981 | 89298.2527 | 22609.76424 | 117682.0313 | 8054.587882 | 96719.74125 | 8997.934189 | 20906.98714 | 27336.06153 | 188572.832 | 292777.9127 | 71566.19899 | 148000.9139 | 27378.6796 | 90037.75342 | 63679.89478 | 60308.53729 | 87666.10146 | 179768.8581 | 93879.84642 | 148360.7074 | 125299.1866 | ||
| P05413 | 5 | 4 | 134.61 | 0.194580589 | 2.417373545 | HN | XN | Fatty acid-binding protein, heart OS=Homo sapiens GN=FABP3 PE=1 SV=4 | 144185.4 | 479956.3 | 300249.4 | 284211.5 | 156118.1648 | 546083.3473 | 665257.3464 | 272680.3794 | 346159.5477 | 276739.4672 | 901015.2898 | 270018.3638 | 860628.2505 | 419901.2694 | 278472.0085 | 2393283.7 | 284803.2494 | 124561.8323 | 142240.5704 | 217773.0358 | 220970.3052 | 377850.4511 | 348003.9743 | 390200.3885 | 366073.4813 | 172353.1181 | 167731.0877 | ||
| O75084 | 4 | 1 | 134.53 | 0.559171755 | 1.102628393 | XN | HN | Frizzled-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD7 PE=2 SV=2 | 119076.1 | 93375.32 | 127771.8 | 92653.57 | 240668.1729 | 192889.7879 | 102219.7367 | 127838.6995 | 210669.0029 | 166834.9401 | 283200.7376 | 11269.60983 | 162037.1418 | 132893.8327 | 130066.001 | 73658.89256 | 144421.8807 | 113708.555 | 122016.153 | 176669.2573 | 121950.6625 | 76643.59815 | 167755.7632 | 155609.5313 | 249728.5687 | 166356.1836 | 106372.6566 | ||
| Q9BS26 | 5 | 3 | 134.27 | 0.875142704 | 1.2813379 | XN | XA | Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 44 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERP44 PE=1 SV=1 | 653334 | 293820.3 | 790744.1 | 1239250 | 743263.9628 | 517841.7072 | 862764.8971 | 970575.5609 | 1160205.967 | 848354.5145 | 230670.754 | 457649.3554 | 460990.3837 | 779537.3501 | 746538.7878 | 1562511.029 | 1498888.644 | 1297763.895 | 1217042.048 | 577039.5634 | 978641.169 | 2863091.39 | 1402881.686 | 293819.3174 | 632839.5096 | 654487.3797 | 646537.6579 | ||
| Q9UBN7 | 3 | 2 | 133.44 | 0.019626491 | 5.595060576 | HN | XN | Histone deacetylase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HDAC6 PE=1 SV=2 | 404278.5 | 254830.4 | 384491.8 | 837592.1 | 761393.9862 | 159645.4764 | 233981.5356 | 292711.7296 | 109756.3323 | 71280.05268 | 38245.03085 | 92804.78816 | 82700.24509 | 157666.2001 | 219329.5576 | 3888888.886 | 487087.4326 | 184511.1148 | 96149.24347 | 45559.68296 | 68164.02815 | 97944.23204 | 360274.5693 | 30960.84649 | 63311.5586 | 52772.3868 | 118278.4236 | ||
| Q9UBD6 | 5 | 3 | 132.97 | 0.142389096 | 1.786617723 | XA | HN | Ammonium transporter Rh type C OS=Homo sapiens GN=RHCG PE=1 SV=1 | 785701.7 | 385812.1 | 153356.3 | 110023 | 245883.2593 | 787991.3652 | 425984.1654 | 472843.9081 | 281081.7696 | 92867.54142 | 299922.3051 | 517593.3373 | 178834.8186 | 333157.8855 | 122316.2563 | 56479.13031 | 88625.68746 | 352429.2133 | 619941.7962 | 180355.0346 | 352532.2316 | 131793.7992 | 118617.4274 | 99157.73627 | 70012.56141 | 177397.5872 | 428010.4185 | ||
| Q96S96 | 4 | 2 | 132.44 | 0.502734703 | 1.709775718 | XA | HN | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PEBP4 PE=1 SV=3 | 11302.02 | 2170255 | 164503.5 | 49673.87 | 215819.5087 | 103294.2127 | 174645.6144 | 134052.7022 | 627544.0221 | 136618.9506 | 113645.5738 | 547963.8774 | 444889.009 | 119328.2406 | 256538.8947 | 92844.21336 | 255517.6854 | 168074.2243 | 6660.359053 | 286921.5361 | 30777.00785 | 27213.56354 | 291454.8433 | 1093456.116 | 573934.5129 | 59156.48535 | 36526.19758 | ||
| P01880 | 4 | 2 | 132.43 | 0.903162104 | 1.328078391 | HN | XA | Ig delta chain C region OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGHD PE=1 SV=2 | 24496.63 | 437972.7 | 141460 | 243777 | 370066.2156 | 787356.3673 | 50445.71279 | 537083.592 | 477661.3379 | 326189.6223 | 75300.71864 | 1962273.347 | 69976.23874 | 170934.3403 | 107709.047 | 654948.8142 | 406160.4727 | 304132.4881 | 58214.42682 | 882556.1492 | 17233.81813 | 88740.48419 | 69921.42584 | 219863.3783 | 424266.0154 | 1059472.204 | 847075.7098 | ||
| P20933 | 3 | 3 | 130.96 | 0.043518152 | 2.106033173 | XA | HN | N(4)-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGA PE=1 SV=2 | 386162.5 | 641101.9 | 580937.1 | 418145.2 | 306462.3876 | 788189.0176 | 980746.1925 | 256033.0872 | 1247523.817 | 119381.8433 | 415149.2554 | 270870.5584 | 515786.4056 | 397460.559 | 180351.2974 | 58538.6298 | 269516.1457 | 434489.8638 | 1450663.561 | 395752.41 | 271442.9161 | 264805.1876 | 132604.0439 | 421921.2705 | 368769.5592 | 487597.0481 | 290888.2419 | ||
| P30443;P30455 | 6 | 1 | 130.79 | 0.00450868 | 1.988849294 | XN | HN | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A-1 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-A PE=1 SV=1 | 940898 | 559503.5 | 396144 | 332886.5 | 370772.5591 | 935775.52 | 556956.9549 | 560786.4206 | 598907.3107 | 93299.46167 | 95409.25413 | 135650.249 | 524317.4791 | 156486.8941 | 558066.7098 | 404493.2049 | 499422.3634 | 609981.8942 | 874301.7988 | 702510.6014 | 918160.957 | 587592.6454 | 585500.0041 | 311556.6151 | 804225.155 | 565947.0209 | 770148.0779 | ||
| Q8NC42 | 3 | 2 | 130.4 | 0.94269394 | 1.106216525 | HN | XN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF149 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNF149 PE=2 SV=2 | 238947.6 | 782865.9 | 477499.2 | 152320.6 | 182167.2177 | 663243.0728 | 901697.6406 | 435829.2623 | 725633.0763 | 495400.0938 | 1347012.115 | 209211.1785 | 1101583.052 | 717313.4794 | 337957.3028 | 76917.82427 | 459383.1653 | 266764.2584 | 364755.416 | 562587.6026 | 451812.1812 | 331682.1551 | 270583.4088 | 1078491.645 | 494385.9311 | 657500.1077 | 318546.5228 | ||
| Q15366;P57721 | 6 | 2 | 130.06 | 0.165602063 | 1.677307296 | HN | XN | Poly(rC)-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 750128.9 | 716189.7 | 693342.6 | 1015470 | 484982.2053 | 301992.2082 | 554599.2955 | 278916.2272 | 406679.0033 | 817518.7279 | 1663543.85 | 1055154.783 | 1048335.602 | 2027681.185 | 412130.5918 | 626934.6582 | 481058.3726 | 443305.4705 | 711259.5702 | 545520.284 | 489891.2714 | 385149.9512 | 751474.4721 | 66210.07249 | 585777.5163 | 874166.7734 | 703306.2675 | ||
| O60279 | 6 | 3 | 129.93 | 0.812975377 | 1.164541974 | XA | XN | Sushi domain-containing protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SUSD5 PE=1 SV=3 | 137253.9 | 831270.5 | 1254062 | 464810.2 | 1131747.743 | 385959.8548 | 371213.9752 | 303839.328 | 402684.576 | 141286.1427 | 857897.7246 | 229847.6455 | 284523.3781 | 379964.1301 | 694438.5532 | 892199.8182 | 524582.2271 | 951900.7257 | 227001.8042 | 413960.8045 | 179733.115 | 164532.6908 | 574501.59 | 1486836.582 | 379918.5069 | 816718.9672 | 293208.0013 | ||
| Q7Z3S9 | 2 | 1 | 129.91 | 0.066669449 | 3.975984177 | XN | HN | Notch homolog 2 N-terminal-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOTCH2NL PE=1 SV=1 | 1231169 | 32960.69 | 20479.14 | 150850.3 | 2753.431261 | 19348.32548 | 12794.18421 | 12678.65271 | 123101.4153 | 5347.668507 | 119554.0148 | 31.70912681 | 5849.458528 | 24375.01789 | 42578.42498 | 530.634069 | 21466.32595 | 263263.0079 | 6593.38549 | 371626.6383 | 30368.24728 | 76231.18535 | 695939.8148 | 170027.5928 | 27168.57861 | 349848.0437 | 192582.0078 | ||
| Q58FF8 | 6 | 2 | 129.56 | 0.918126484 | 1.406601928 | XN | XA | Putative heat shock protein HSP 90-beta 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB2P PE=1 SV=2 | 137141.5 | 293948.7 | 769836.5 | 117562 | 572801.5224 | 17553.27004 | 196356.1407 | 226317.6103 | 167527.0278 | 47802.03849 | 519212.3452 | 130358.8545 | 57728.40868 | 60618.33745 | 1462645.246 | 108414.1702 | 344257.242 | 284605.023 | 490435.1265 | 80578.5974 | 60591.08591 | 99217.09685 | 382220.4839 | 1741240.132 | 282872.0867 | 290247.7431 | 87758.18823 | ||
| Q8WWZ8 | 6 | 5 | 129.16 | 0.254440555 | 1.423504686 | XN | XA | Oncoprotein-induced transcript 3 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=OIT3 PE=1 SV=2 | 938255.7 | 438798.6 | 304058.3 | 368241.9 | 480975.0035 | 382580.1096 | 350286.0802 | 426151.1958 | 366363.6996 | 1403615.27 | 599035.79 | 241963.8187 | 704068.739 | 730598.2789 | 215297.9873 | 191892.3641 | 381307.0405 | 738754.6368 | 519392.5625 | 775079.7833 | 1008441.556 | 579161.5159 | 392549.4754 | 872256.3908 | 461895.2647 | 575030.2244 | 589516.2288 | ||
| Q8NFU3 | 4 | 3 | 129.02 | 0.810423918 | 1.152333462 | HN | XA | Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase/rhodanese-like domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSTD1 PE=1 SV=3 | 823151.8 | 323197.4 | 457336.7 | 622007 | 386488.6172 | 1560447.404 | 714798.8539 | 698350.5521 | 529066.1149 | 106500.6244 | 411334.6315 | 426996.3867 | 432449.5453 | 424412.338 | 517977.4438 | 3497269.712 | 533426.8321 | 695972.3841 | 925845.0263 | 1050170.448 | 912884.8555 | 436226.7968 | 357681.3496 | 159481.7599 | 474512.0592 | 976306.9317 | 1225228.541 | ||
| P36957 | 4 | 1 | 128.96 | 0.509536844 | 1.746395673 | XN | XA | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=DLST PE=1 SV=4 | 76946.05 | 110345.5 | 161524.7 | 82408.46 | 55494.62052 | 63333.87744 | 197460.2607 | 84866.20367 | 228203.1683 | 192375.4375 | 209733.4427 | 277883.1473 | 85782.95997 | 190949.993 | 47675.66 | 77308.41411 | 82375.72984 | 147214.4117 | 57361.24673 | 408062.4605 | 156577.686 | 88239.60651 | 106288.3796 | 535986.8622 | 174680.4947 | 278459.1231 | 46541.36559 | ||
| Q8N474 | 5 | 3 | 128.89 | 0.496883413 | 1.40782261 | XA | HN | Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SFRP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1773212 | 688923.3 | 591207.2 | 1060991 | 895463.0141 | 796950.4641 | 195743.1064 | 789802.5618 | 361485.6117 | 441340.3184 | 211553.7776 | 287984.7005 | 317176.6189 | 552201.7455 | 442308.61 | 1224106.469 | 839299.8905 | 765476.6737 | 724262.5158 | 468712.2412 | 496620.2828 | 283067.716 | 930217.2868 | 245593.0107 | 826721.9617 | 650736.8606 | 1133453.052 | ||
| Q14956 | 3 | 2 | 128.81 | 0.633275123 | 1.222365353 | XA | HN | Transmembrane glycoprotein NMB OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPNMB PE=1 SV=2 | 111149.8 | 413417.5 | 183254.1 | 130053.9 | 278459.6825 | 409858.5019 | 345635.866 | 193073.6182 | 458224.1449 | 125575.194 | 175184.3697 | 144963.0635 | 484709.7451 | 271301.2966 | 271178.7743 | 125915.4341 | 151861.6658 | 313445.4354 | 213220.6691 | 158410.6781 | 236581.3653 | 176176.703 | 231484.7516 | 323318.3105 | 356877.7729 | 241581.0443 | 264263.7621 | ||
| P17213 | 9 | 7 | 128.42 | 0.550573673 | 5.498241046 | XN | HN | Bactericidal permeability-increasing protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=BPI PE=1 SV=4 | 276575.3 | 178123.7 | 219035.4 | 103640 | 78134.625 | 1558999.312 | 1250232.586 | 255216.2791 | 783910.5187 | 133479.3404 | 271839.9222 | 309610.5178 | 198745.6358 | 208406.3175 | 236600.7792 | 157644.8815 | 183413.7689 | 123939.2642 | 8469149.352 | 205925.3435 | 103203.766 | 311585.3863 | 237044.1807 | 165021.1688 | 200372.6685 | 206555.8223 | 128176.894 | ||
| O95490 | 4 | 2 | 127.8 | 0.486338266 | 1.095722968 | XA | XN | Latrophilin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LPHN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 210113.7 | 28482.76 | 182614.9 | 174661.8 | 123073.9916 | 76075.65222 | 26891.75641 | 133811.1435 | 39441.55191 | 0 | 67961.12583 | 36519.92897 | 129567.2194 | 73960.6013 | 120592.1574 | 261921.0093 | 109755.4055 | 132633.5534 | 67404.88934 | 71431.34434 | 77868.52954 | 93564.44927 | 128906.6423 | 228425.7072 | 141433.8847 | 43575.73958 | 55617.66513 | ||
| P28072 | 4 | 1 | 127.35 | 0.353175693 | 2.725058733 | XN | HN | Proteasome subunit beta type-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB6 PE=1 SV=4 | 44731.09 | 17254.71 | 34601.22 | 30455.12 | 15777.53585 | 142982.8055 | 147369.6982 | 56340.14281 | 67069.40111 | 31064.75836 | 24374.8901 | 3355.672131 | 150224.5283 | 19041.47394 | 28490.67163 | 26083.59345 | 14487.28356 | 31482.38034 | 378905.5291 | 67661.0408 | 75716.95612 | 146342.1235 | 47227.34577 | 971.5090035 | 48114.1884 | 41825.92513 | 88703.99348 | ||
| Q5DX21 | 2 | 1 | 127.27 | 0.150458294 | 1.739287941 | XN | XA | Immunoglobulin superfamily member 11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGSF11 PE=2 SV=3 | 1051169 | 408134.3 | 478086.3 | 17909.61 | 434992.9711 | 799466.1294 | 751768.5713 | 718471.2219 | 528230.8077 | 579219.3059 | 1715399.399 | 256935.5889 | 1828804.987 | 1664845.331 | 837007.5757 | 313712.3334 | 721177.4696 | 646634.7883 | 689176.0763 | 727046.1679 | 1221521.998 | 430335.1336 | 1126415.216 | 2086705.628 | 648255.8463 | 1336720.455 | 757646.8295 | ||
| P35609 | 10 | 1 | 126.9 | 0.771463763 | 1.579158125 | HN | XA | Alpha-actinin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTN2 PE=1 SV=1 | 143084.3 | 90318.15 | 77089.91 | 184091.7 | 524252.5644 | 230655.5422 | 348342.7314 | 188088.4411 | 649778.5156 | 650429.8691 | 270429.7778 | 713314.5221 | 69166.60768 | 375336.8487 | 75093.10393 | 1220846.288 | 347526.2699 | 124215.1194 | 224885.1241 | 249986.1795 | 233065.7294 | 826225.2889 | 116514.8183 | 1050385.71 | 224692.5311 | 541166.3246 | 49899.78843 | ||
| P18054 | 4 | 2 | 126.49 | 0.229377397 | 4.454345854 | XN | HN | Arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, 12S-type OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALOX12 PE=1 SV=4 | 31452.07 | 34597.49 | 32671.54 | 16919.76 | 15928.7008 | 5967.302835 | 73573.22869 | 29250.46523 | 22036.99757 | 26185.65548 | 11483.35503 | 24889.26556 | 16096.54411 | 15332.30944 | 55660.51668 | 4034.222234 | 3687.854096 | 14560.62954 | 559154.5607 | 22034.36739 | 8498.549406 | 20214.89592 | 13842.40522 | 46084.96581 | 56432.98663 | 12793.40245 | 26781.11784 | ||
| Q9UBI6 | 3 | 2 | 125.78 | 0.321164746 | 1.683781867 | XA | XN | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNG12 PE=1 SV=3 | 1030889 | 486372.6 | 822983.8 | 1339811 | 336594.0989 | 672573.1747 | 1428354.071 | 2120246.994 | 1176627.98 | 1153026.707 | 2323725.722 | 1482906.008 | 871096.097 | 1190536.716 | 412859.6245 | 266508.9968 | 241739.088 | 461988.0441 | 406767.1886 | 710957.7604 | 644170.6823 | 311177.0471 | 583851.1399 | 541231.4736 | 793775.5311 | 605389.4229 | 993934.317 | ||
| Q7Z3Y7 | 4 | 1 | 125.54 | 0.315931381 | 1.559978061 | HN | XN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 28 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT28 PE=1 SV=2 | 1046566 | 3731711 | 1940832 | 2836565 | 5525922.604 | 1668355.137 | 1747399.382 | 3128670.228 | 2376897.799 | 2616479.097 | 2215946.933 | 8043534.076 | 2058106.729 | 1270862.485 | 1412158.75 | 2379044.633 | 4537150.416 | 1774943.822 | 1629356.017 | 1712504.888 | 1648047.89 | 2916081.956 | 1702964.563 | 2433925.59 | 968278.5383 | 2244940.186 | 1608385.588 | ||
| P50990 | 4 | 3 | 124.85 | 0.147047581 | 1.727509095 | XA | XN | T-complex protein 1 subunit theta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT8 PE=1 SV=4 | 538629.1 | 313808.7 | 578404.6 | 686166.6 | 326464.6372 | 639432.3186 | 786706.3004 | 711972.6039 | 507276.6489 | 869746.9682 | 933537.18 | 538731.8533 | 758401.0754 | 725352.3384 | 202799.8685 | 202936.0712 | 72497.46313 | 146654.8357 | 269501.2449 | 499800.9177 | 422250.0419 | 260623.7934 | 204495.1245 | 297491.6438 | 560203.4798 | 307502.6562 | 123910.9869 | ||
| P04434 | 5 | 2 | 124.73 | 0.319895232 | 1.954396706 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-III region VH (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens PE=4 SV=1 | 595567.2 | 573227.5 | 178273.1 | 109338.4 | 1013233.639 | 166715.0703 | 60097.73007 | 541535.7879 | 225754.3113 | 216864.0793 | 82725.70896 | 668486.3726 | 126197.4011 | 195141.1004 | 598420.6548 | 185129.9153 | 127831.9604 | 69637.03043 | 307527.9717 | 63510.20283 | 204819.2139 | 104268.2609 | 162996.5786 | 488146.6155 | 333965.0153 | 61470.71754 | 45577.76331 | ||
| P59666;P59665 | 3 | 2 | 124.65 | 0.561680698 | 1.945665755 | HN | XN | Neutrophil defensin 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DEFA3 PE=1 SV=1 | 1470665 | 2375149 | 1267770 | 390446.3 | 2354643.009 | 44674848.56 | 33869542.01 | 7070340.921 | 25000017.4 | 77224752.12 | 3355122.214 | 20635872.53 | 3144887.209 | 4860801.6 | 27760207.34 | 8876936.761 | 6127053.254 | 944634.7323 | 46649430.36 | 1450422.33 | 1092608.246 | 7593079.563 | 1365689.064 | 2283112.594 | 11469661.24 | 2703331.721 | 3993147.705 | ||
| Q14247 | 7 | 5 | 124.38 | 0.730252952 | 1.080165475 | XA | HN | Src substrate cortactin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTTN PE=1 SV=2 | 2391652 | 4871479 | 3475371 | 2097972 | 2669905.959 | 3741421.441 | 2914536.045 | 2689160.948 | 2634242.591 | 2593283.564 | 1453547.448 | 3391519.671 | 2532870.965 | 1580908.621 | 4217039.495 | 3607467.618 | 2736694.081 | 3332529.212 | 1535881.779 | 2347140.528 | 3395482.421 | 4345320.822 | 3380972.23 | 4767861.766 | 1768837.956 | 2687613.152 | 1291972.29 | ||
| Q9Y334 | 5 | 2 | 123.78 | 0.543289421 | 1.29486569 | XN | HN | von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VWA7 PE=2 SV=4 | 976774.7 | 249145.9 | 621055.7 | 453161.6 | 619371.72 | 579565.3104 | 557276.1923 | 585813.4063 | 721705.7803 | 365597.3554 | 807356.6152 | 1389660.596 | 699055.9466 | 770079.8804 | 255178.8083 | 294501.2046 | 388670.3608 | 200797.5901 | 1063246.481 | 679867.4106 | 592376.9568 | 272388.0314 | 553140.3572 | 499690.0832 | 876956.0105 | 1830302.672 | 327650.8638 | ||
| P01596 | 2 | 1 | 123.67 | 0.609705703 | Infinity | HN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region CAR OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45575.38705 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9878.864773 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q5XKE5 | 10 | 1 | 123.6 | 0.031016213 | 1.637656661 | HN | XA | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 79 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT79 PE=1 SV=2 | 406987 | 347484.1 | 457822.2 | 280409.1 | 906240.6557 | 346105.6517 | 419624.4727 | 223423.8386 | 457116.1248 | 973938.7903 | 587599.3674 | 969979.1912 | 564627.0135 | 416131.2527 | 760781.0947 | 1153345.983 | 511657.9864 | 359078.3255 | 485092.1464 | 259736.5178 | 454203.6014 | 349251.0828 | 411227.2378 | 327818.5933 | 1082126.496 | 390059.3142 | 445265.6665 | ||
| Q5VW32 | 5 | 3 | 123.52 | 0.09522227 | 1.745933296 | XA | HN | BRO1 domain-containing protein BROX OS=Homo sapiens GN=BROX PE=1 SV=1 | 161266.1 | 49505.95 | 71362.59 | 65781.48 | 54716.60941 | 81377.32857 | 144379.5337 | 222993.4077 | 101032.7277 | 62813.23618 | 266956.4678 | 24939.01996 | 40589.19748 | 75020.79092 | 23377.94294 | 15775.01854 | 26398.37564 | 9635.175181 | 95174.83394 | 34840.05727 | 83673.85133 | 7797.578644 | 39927.22531 | 15890.87634 | 63562.84683 | 130340.4176 | 220743.2543 | ||
| P01768 | 4 | 1 | 122.74 | 0.16403905 | 1.939205189 | XN | XA | Ig heavy chain V-III region CAM OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 144379.6 | 471293.6 | 31334.46 | 338165.5 | 598036.8302 | 434987.7915 | 521816.1643 | 57215.28065 | 33166.48348 | 202853.5753 | 294161.2692 | 1129220.08 | 128333.4921 | 84030.08766 | 386100.1434 | 283973.848 | 320488.5599 | 215660.8803 | 472253.8767 | 342373.4437 | 369854.9585 | 219360.2097 | 2123602.986 | 552964.3356 | 331587.9055 | 534208.7181 | 154670.5584 | ||
| Q9H2A2 | 2 | 2 | 122.63 | 0.573480489 | 1.886238403 | XA | HN | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 8 member A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH8A1 PE=1 SV=1 | 287833.3 | 33278.84 | 151487.8 | 648826.4 | 5519.043693 | 360620.4874 | 314672.6094 | 567413.2497 | 195617.8734 | 195256.4169 | 248134.7277 | 104500.7656 | 402449.1611 | 136312.1964 | 62796.61093 | 88131.05374 | 63839.66096 | 58571.64431 | 133906.7932 | 202396.6292 | 406871.4112 | 322888.4584 | 383800.6654 | 117676.6625 | 181186.3588 | 196709.1045 | 98444.27514 | ||
| O60704 | 8 | 5 | 122.41 | 0.289689722 | 1.371070414 | XA | HN | Protein-tyrosine sulfotransferase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPST2 PE=1 SV=1 | 608410.6 | 413159.6 | 1196831 | 1106219 | 579575.5355 | 432408.6459 | 236080.7468 | 634730.101 | 1111133.391 | 305316.4628 | 524273.7854 | 396358.7195 | 403175.056 | 272272.1137 | 240020.9273 | 1883620.465 | 285175.3376 | 298265.1527 | 101082.9133 | 259031.4631 | 300453.4208 | 160688.2411 | 910670.6487 | 299458.2435 | 1231976.191 | 951808.5338 | 516575.4479 | ||
| Q86YD3 | 1 | 1 | 122.35 | 0.774835177 | 1.183329468 | HN | XA | Transmembrane protein 25 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMEM25 PE=1 SV=1 | 1523167 | 264504.9 | 473780.9 | 889650.6 | 319481.9178 | 497310.2183 | 387029.2838 | 582677.6967 | 489070.7046 | 1093479.423 | 1066373.605 | 347935.2587 | 1008211.426 | 821369.8703 | 145862.0461 | 500345.5686 | 582152.1709 | 855813.1655 | 634799.126 | 455736.2721 | 649162.4282 | 703838.1251 | 722258.2482 | 343794.9292 | 575529.0148 | 739356.601 | 773130.4216 | ||
| Q9Y287 | 3 | 3 | 121.99 | 0.264607143 | 1.301160758 | XA | XN | Integral membrane protein 2B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITM2B PE=1 SV=1 | 1047691 | 589160 | 332881.5 | 467501.8 | 970559.3113 | 493114.097 | 567953.7196 | 776591.2769 | 737479.8985 | 540573.6637 | 430048.2909 | 718491.0244 | 539346.4914 | 854134.467 | 222609.5261 | 427891.2079 | 276987.0048 | 589353.3162 | 686110.0895 | 377889.5393 | 291302.734 | 220274.8872 | 498333.699 | 177725.2439 | 589738.49 | 627251.0927 | 1129524.442 | ||
| P61204;P84077;P84085 | 3 | 1 | 121.74 | 0.0730488 | 1.555371394 | XA | HN | ADP-ribosylation factor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARF3 PE=1 SV=2 | 300052.4 | 130067.3 | 99413.28 | 294230.5 | 142956.5536 | 294644.1444 | 215636.4298 | 372926.4936 | 292789.8994 | 240355.6598 | 238382.7896 | 214664.3848 | 70477.78207 | 184183.8025 | 83719.48062 | 87673.34225 | 75176.0618 | 182990.703 | 175524.7985 | 167764.4598 | 227989.0494 | 191605.3646 | 112530.4521 | 109223.68 | 93360.52003 | 121232.6132 | 184576.2767 | ||
| O60635 | 1 | 1 | 121.68 | 0.60477195 | 1.141199247 | XA | XN | Tetraspanin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSPAN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 6011698 | 4506888 | 4894691 | 1782954 | 3101693.973 | 4231458.479 | 3290880.955 | 3687406.731 | 3734077.917 | 2286698.136 | 5683780.247 | 6251526.968 | 3577964.832 | 6646763.939 | 1131973.345 | 961794.3746 | 1815335.456 | 3788345.591 | 5072394.694 | 5153166.234 | 4929729.638 | 1415100.213 | 1348600.731 | 1677500.97 | 2615803.437 | 4336456.277 | 4332576.062 | ||
| Q9UKZ9 | 5 | 1 | 121.67 | 0.855252161 | 1.21363731 | HN | XN | Procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCOLCE2 PE=1 SV=1 | 678547.1 | 73661.81 | 292486.9 | 759926.7 | 832970.5787 | 270747.9835 | 331762.9891 | 490687.8001 | 166948.8503 | 172095.7127 | 3806.10493 | 321756.6123 | 610553.7463 | 797660.1265 | 310958.5185 | 1129079.095 | 304225.6912 | 442695.966 | 175636.847 | 169699.6527 | 241431.588 | 310553.7169 | 445061.3782 | 720402.1927 | 596797.3846 | 116692.4473 | 596092.7489 | ||
| P52907 | 3 | 1 | 121.58 | 0.866091427 | 1.603534435 | XN | HN | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPZA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 426354.7 | 90880.26 | 123131.7 | 402077.3 | 29276.49744 | 1054516.913 | 1198347.912 | 1520226.134 | 1756106.722 | 2380105.68 | 470748.9631 | 900593.726 | 436048.4493 | 265335.2938 | 500583.917 | 132559.1424 | 188821.3589 | 215838.9524 | 4957795.513 | 507681.8532 | 1291733.463 | 649106.7878 | 326560.4649 | 162725.17 | 492168.3877 | 248823.037 | 167828.3917 | ||
| P01714 | 3 | 2 | 120.68 | 0.180905706 | 1.510232399 | XA | HN | Ig lambda chain V-III region SH OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2158096 | 3590382 | 3435621 | 3221679 | 4106887.666 | 1164252.292 | 2347101.363 | 1484638.547 | 1136010.778 | 2210607.599 | 1156301.573 | 2318677.425 | 1447655.224 | 946294.491 | 1724674.699 | 2975446.621 | 915112.8951 | 1299391.592 | 1909832.048 | 2197561.532 | 827627.6685 | 1222178.969 | 1777728.965 | 2264376.509 | 1805436.515 | 2174572.121 | 2989115.951 | ||
| Q9NZD2 | 5 | 4 | 120.48 | 0.783049411 | 2.448334919 | XN | XA | Glycolipid transfer protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLTP PE=1 SV=3 | 98169.43 | 61875.65 | 88829.97 | 88711.17 | 56665.87106 | 68221.96099 | 108701.707 | 412690.217 | 205758.5453 | 1180704.954 | 186661.5298 | 230623.6232 | 124861.8128 | 111479.3136 | 34488.39162 | 94034.62117 | 86126.60395 | 125707.8782 | 2181272.645 | 160558.948 | 172684.5004 | 28286.98021 | 30248.92661 | 78434.55006 | 74908.66057 | 47527.24127 | 138676.7858 | ||
| O00461 | 4 | 4 | 120.28 | 0.388989202 | 1.879756449 | XN | XA | Golgi integral membrane protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GOLIM4 PE=1 SV=1 | 1518256 | 1516688 | 1104555 | 1152885 | 833364.4374 | 960086.0545 | 1088422.911 | 1337841.323 | 970524.1542 | 1210367.754 | 1831366.499 | 3463210.877 | 1174916.485 | 2657692.416 | 1155775.164 | 1017183.099 | 1042004.959 | 1260555.3 | 1095992.039 | 6489788.501 | 2275725.395 | 636993.6737 | 1711965.078 | 661638.5357 | 946755.0368 | 1453166.737 | 4432752.298 | ||
| Q9BYJ0 | 3 | 3 | 120.03 | 0.337379114 | 1.361246973 | HN | XA | Fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGFBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 342753.9 | 433593 | 387995.4 | 674090.9 | 615465.9048 | 400456.7136 | 225500.9454 | 242741.1254 | 421991.094 | 489506.7778 | 686087.1575 | 417742.9814 | 441731.2952 | 291255.2984 | 607106.7762 | 1239725.428 | 539085.9819 | 385068.6483 | 543957.0333 | 480199.443 | 538538.6195 | 187976.3055 | 490787.2692 | 1193067.605 | 400692.1552 | 490744.949 | 535173.3981 | ||
| P16401 | 5 | 2 | 120.01 | 0.389747563 | 2.721418819 | XA | XN | Histone H1.5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H1B PE=1 SV=3 | 392637.3 | 278973.7 | 130903.3 | 24574.72 | 743908.7967 | 1355843.764 | 3386367.706 | 1776650.858 | 2225464.74 | 529847.3483 | 86182.56918 | 146900.9513 | 1466529.951 | 134250.6642 | 677932.5916 | 145699.66 | 124527.8341 | 534748.0143 | 1323426.853 | 580271.5754 | 64901.86546 | 302256.4522 | 355400.8038 | 130059.3208 | 170539.7219 | 106691.128 | 756873.9449 | ||
| P83593 | 3 | 2 | 119.76 | 0.695035022 | 2.645469168 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-IV region STH (Fragment) OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 222687.2 | 191964.7 | 187803.5 | 366692.2 | 2738657.982 | 76258.60064 | 77596.25904 | 134125.8813 | 72496.2509 | 165792.2391 | 89531.48041 | 76919.72963 | 188364.7169 | 173987.0758 | 320717.3882 | 1311403.811 | 109113.5069 | 183106.8069 | 63139.69411 | 163428.1515 | 291844.1205 | 124462.5709 | 110280.9695 | 442531.3438 | 127917.3121 | 68249.45487 | 145976.6227 | ||
| P01031 | 11 | 4 | 119.57 | 0.033821821 | 2.410804324 | XA | XN | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 1142725 | 1942157 | 1273295 | 521507.8 | 4183787.589 | 553197.3255 | 546796.3828 | 808991.3928 | 507771.3831 | 811566.7376 | 726068.8782 | 481248.6001 | 593277.9622 | 1854198.274 | 784900.5353 | 618578.5213 | 1202672.392 | 1140578.197 | 624002.4354 | 425471.9354 | 492051.1756 | 291216.5173 | 745731.442 | 489352.5019 | 401584.5997 | 593176.8717 | 699403.687 | ||
| Q10588 | 5 | 3 | 119.23 | 0.498715244 | 1.623141205 | XN | XA | ADP-ribosyl cyclase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BST1 PE=1 SV=2 | 229398.9 | 556188.3 | 298745.7 | 167938.6 | 113190.5096 | 142700.9646 | 427178.1819 | 199752.2527 | 423081.4575 | 170055.9713 | 336995.3675 | 964340.6522 | 261136.0947 | 445068.653 | 67328.66092 | 92161.67397 | 163011.0361 | 285103.775 | 207911.9848 | 345176.0475 | 272175.9361 | 170585.4559 | 239463.3929 | 1785110.907 | 191605.8136 | 332707.6753 | 607541.89 | ||
| P27930 | 6 | 2 | 119.23 | 0.752693733 | 1.166024834 | HN | XA | Interleukin-1 receptor type 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL1R2 PE=1 SV=1 | 477435.9 | 96788.82 | 115785.9 | 199907.1 | 172543.8658 | 164816.8874 | 153972.6304 | 240909.3683 | 248433.8382 | 163113.9442 | 295215.5119 | 215774.9617 | 306585.8052 | 320019.4125 | 273981.48 | 62837.50443 | 276203.5456 | 267427.2187 | 288110.491 | 221475.1719 | 128827.0198 | 220694.4824 | 94352.42665 | 316169.5476 | 298714.0001 | 277309.3006 | 93300.00178 | ||
| O00115 | 5 | 4 | 118.9 | 0.417518287 | 1.362602767 | HN | XN | Deoxyribonuclease-2-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNASE2 PE=1 SV=2 | 754501.3 | 2316815 | 2793290 | 1202645 | 575649.7529 | 837546.4054 | 1872269.663 | 806581.866 | 2079969.123 | 732362.0767 | 2833916.082 | 2455686.757 | 1979712.664 | 3168525.108 | 2135266.692 | 1554388.828 | 877839.8292 | 1275495.359 | 458760.0731 | 1422693.968 | 1251743.803 | 1172297.79 | 2178671.24 | 1781457.138 | 1245513.508 | 1663025.488 | 1311642.697 | ||
| P10721 | 8 | 2 | 118.79 | 0.477135621 | 1.176288594 | XN | HN | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIT PE=1 SV=1 | 1334773 | 1206620 | 389409.5 | 611148.7 | 430335.3126 | 513231.1872 | 619460.864 | 566005.9878 | 993858.5337 | 751861.4367 | 737631.5521 | 1126022.598 | 666525.405 | 1022012.515 | 646302.0719 | 236364.9947 | 567489.5243 | 549821.6766 | 1009533.527 | 814272.1104 | 945408.6921 | 522469.159 | 759989.4138 | 978966.1396 | 557269.1103 | 961888.3612 | 865564.1555 | ||
| Q8WU39 | 3 | 3 | 118.54 | 0.331942794 | 1.298209655 | XA | XN | Plasma cell-induced resident endoplasmic reticulum protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PACAP PE=1 SV=1 | 796707.5 | 704330.7 | 683450.3 | 865166.1 | 1449184.46 | 879597.5604 | 819768.1731 | 744180.4383 | 400685.4753 | 784308.0089 | 615875.9575 | 569192.7114 | 472469.4 | 448401.876 | 777452.3087 | 1912318.24 | 529035.7747 | 752423.7645 | 642719.0095 | 568153.8163 | 308824.3842 | 201091.4079 | 785580.5953 | 1014670.234 | 703503.2203 | 717742.2181 | 714020.8983 | ||
| O00499 | 7 | 5 | 118.37 | 0.066600449 | 1.879902845 | XA | HN | Myc box-dependent-interacting protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BIN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 769297.8 | 485597.7 | 1220365 | 1479666 | 190355.2544 | 503230.9343 | 650709.6702 | 603359.1109 | 312826.6868 | 358980.2297 | 363135.794 | 369805.599 | 440546.8138 | 202640.5867 | 207659.5533 | 587149.9925 | 185492.5333 | 590828.1152 | 200660.2595 | 455931.7202 | 490669.174 | 378217.2375 | 553768.8365 | 632489.1262 | 316248.9866 | 350711.1932 | 306618.5317 | ||
| Q9UM47 | 5 | 3 | 117.12 | 0.083510034 | 2.304307382 | HN | XA | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOTCH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 617595.8 | 386055.7 | 379209.2 | 149803.4 | 181594.6941 | 135969.849 | 347895.2444 | 127976.9558 | 223961.5127 | 520026.376 | 1183300.571 | 135093.6342 | 269224.8326 | 651831.878 | 362368.8728 | 2018513.891 | 301161.8887 | 434605.4367 | 223657.838 | 238161.4396 | 378222.4391 | 320263.1862 | 275354.9627 | 1181953.679 | 732202.9351 | 590737.1381 | 713173.5543 | ||
| Q969E1 | 2 | 2 | 116.6 | 0.532921222 | 1.290678393 | HN | XA | Liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LEAP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 356809.1 | 1293946 | 2321411 | 342985.1 | 305810.0769 | 160104.8608 | 271648.71 | 144354.7665 | 314300.2516 | 276463.2356 | 1159884.822 | 173673.299 | 400414.6095 | 1093460.308 | 1217077.672 | 1978592.453 | 296984.9846 | 516855.0714 | 175435.3053 | 380574.2468 | 363970.7887 | 823349.4724 | 392522.5965 | 1255583.704 | 406883.2807 | 1374387.37 | 765402.122 | ||
| Q9Y4C0 | 9 | 6 | 116.49 | 0.998625568 | 1.064354576 | HN | XN | Neurexin-3-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=NRXN3 PE=1 SV=4 | 2112682 | 2908819 | 2922219 | 1383589 | 2563334.065 | 2175013.082 | 2038941.525 | 1676753.179 | 2419590.072 | 863314.3551 | 2763834.663 | 4460135.955 | 1908866.823 | 2225785.994 | 2550412.809 | 2906149.551 | 1727005.086 | 1851814.98 | 1544325.211 | 2619421.212 | 2260967.524 | 1711052.545 | 2662173.265 | 2756653.827 | 2445824.459 | 2281598.851 | 1690011.875 | ||
| Q96MM7 | 7 | 3 | 116.46 | 0.176917341 | 1.906028144 | XN | HN | Heparan-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HS6ST2 PE=2 SV=2 | 764060 | 87351.25 | 71838.92 | 344837.2 | 233897.0822 | 634879.9071 | 313169.4543 | 275602.5162 | 239920.9487 | 432259.1883 | 116754.2237 | 238795.4226 | 260475.8928 | 701573.5499 | 123028.5945 | 195294.0691 | 320556.9312 | 299442.6011 | 926550.7817 | 1134750.797 | 639570.2485 | 179547.2229 | 164273.2835 | 166549.6708 | 557170.558 | 552076.1257 | 803258.95 | ||
| P54793 | 4 | 1 | 116.16 | 0.83852396 | 1.475120827 | HN | XA | Arylsulfatase F OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARSF PE=1 SV=4 | 149915.7 | 37177.95 | 175918.9 | 60927.15 | 33939.70092 | 37062.84515 | 76245.71317 | 295957.7476 | 160114.3773 | 310890.8347 | 165521.3288 | 494358.3098 | 268753.2657 | 15889.53604 | 63336.99044 | 65319.31809 | 69288.61734 | 61974.48753 | 76031.92947 | 28011.3764 | 414258.8361 | 48591.68743 | 290374.4861 | 38581.91607 | 41271.75375 | 100678.0936 | 114239.6303 | ||
| P23588 | 3 | 3 | 116.13 | 0.841214432 | 1.480880656 | HN | XN | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B OS=Homo sapiens GN=EIF4B PE=1 SV=2 | 205748.3 | 82763.7 | 251100.1 | 109834.7 | 1035752.959 | 557735.2132 | 355716.9292 | 231781.2366 | 230987.6581 | 251521.1062 | 975461.9668 | 1220748.732 | 591854.1116 | 208938.7687 | 62844.52912 | 58038.83448 | 542147.4056 | 141886.657 | 114479.4916 | 292348.5802 | 358040.2202 | 163217.7759 | 109604.1834 | 1040277.632 | 441799.6192 | 132877.1279 | 84538.87891 | ||
| Q6UXD5 | 6 | 4 | 115.8 | 0.022466626 | 1.516967831 | HN | XA | Seizure 6-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEZ6L2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2493551 | 2355078 | 1535380 | 2125266 | 2426375.785 | 2810160.392 | 2055605.972 | 2592894.101 | 1972303.96 | 3306911.081 | 4138241.642 | 1443984.792 | 4193388.035 | 3326826.808 | 3587583.166 | 4477166.569 | 2747538.861 | 3673858.727 | 2225376.8 | 2920208.944 | 2474940.165 | 2207550.26 | 2790403.374 | 4652971.855 | 3647798.158 | 1915254.357 | 2391816.644 | ||
| P16402 | 9 | 1 | 115.75 | 0.161418168 | 91.13073932 | XA | HN | Histone H1.3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H1D PE=1 SV=2 | 198.8297 | 665.701 | 197.545 | 1337995 | 2666.030433 | 378448.5693 | 344.4586607 | 545.5495347 | 375.5305147 | 162.9375728 | 1830.639596 | 3731.334013 | 139.2723279 | 128.3131034 | 11307.89137 | 101.2359642 | 243.4762626 | 1244.655533 | 3630.252854 | 10858.45389 | 5801.833339 | 504.5448924 | 6734.818805 | 1521.142824 | 30933.46238 | 2765.945443 | 9728.951954 | ||
| P41271 | 3 | 2 | 115.65 | 0.079661544 | 2.097833875 | HN | XN | Neuroblastoma suppressor of tumorigenicity 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NBL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1473035 | 900867.4 | 1991112 | 1827271 | 2397290.744 | 1067476.477 | 798902.8097 | 367209.1425 | 446962.6526 | 3333413.338 | 1617204.303 | 528810.6286 | 1071220.463 | 2378700.145 | 1821065.529 | 6763037.482 | 1458361.011 | 2893353.734 | 661451.8378 | 1022837.454 | 778838.6794 | 559414.1785 | 1345695.139 | 1751757.257 | 1742440.474 | 723582.2163 | 1836717.801 | ||
| Q9UN37 | 7 | 2 | 115.5 | 0.155071964 | 1.668495283 | XA | HN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4A OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS4A PE=1 SV=1 | 498578.2 | 153151.6 | 243073.7 | 433710 | 145240.5742 | 152408.6119 | 236323.7562 | 412350.4575 | 200351.8627 | 92873.52454 | 490365.3829 | 254896.8456 | 97440.59026 | 135600.9405 | 85788.77459 | 198917.8082 | 46899.9114 | 80701.85836 | 198128.7329 | 132204.877 | 299996.2936 | 75276.2919 | 69658.48159 | 14472.51897 | 208812.7644 | 309860.9447 | 362764.9861 | ||
| P17405 | 4 | 3 | 115.45 | 0.082786008 | 2.039455995 | XA | XN | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMPD1 PE=1 SV=4 | 892265.7 | 265300.7 | 781138.8 | 139410.3 | 573446.5832 | 441806.5702 | 699925.5088 | 772626.5071 | 420054.576 | 494860.9 | 221347.3565 | 203450.4144 | 262799.3389 | 559840.2664 | 349318.6283 | 1520407.973 | 539373.3359 | 158925.5936 | 261646.0054 | 204942.7104 | 325608.4542 | 235549.0063 | 357409.4481 | 53768.63867 | 242054.9571 | 347642.3429 | 416135.9078 | ||
| P01344 | 2 | 2 | 115.35 | 0.942863124 | 1.801377524 | HN | XN | Insulin-like growth factor II OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2 PE=1 SV=1 | 962529.6 | 742131.8 | 1002134 | 1722467 | 1117864.661 | 440051.4219 | 512849.5033 | 413093.7593 | 443179.5647 | 431946.1706 | 821996.3078 | 1266539.88 | 703414.1458 | 161589.326 | 618517.4132 | 7018947.538 | 424914.148 | 404728.4988 | 409541.762 | 848306.1501 | 536387.1153 | 276368.7414 | 755390.1374 | 1643890.61 | 928155.5936 | 465763.778 | 715934.8218 | ||
| P61978 | 5 | 3 | 115.27 | 0.189493267 | 3.630822088 | XA | XN | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K OS=Homo sapiens GN=HNRNPK PE=1 SV=1 | 243906.9 | 19687.08 | 31274.44 | 655623.6 | 322358.1793 | 568637.0182 | 1120561.293 | 1867774.384 | 1210069.904 | 426682.8233 | 32902.71121 | 635155.5311 | 598042.4675 | 29577.92452 | 600305.9797 | 680002.1465 | 93838.54482 | 92577.97668 | 255847.584 | 163695.2002 | 219676.5858 | 744739.9052 | 137173.5172 | 14662.79778 | 12511.51799 | 73982.53056 | 41215.94336 | ||
| Q9H0E2 | 4 | 1 | 115.16 | 0.005205541 | 2.020640029 | HN | XN | Toll-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TOLLIP PE=1 SV=1 | 108392.8 | 196942.4 | 230579.8 | 446920.3 | 343713.0609 | 139682.703 | 372047.5743 | 255606.1131 | 127212.158 | 393314.8949 | 478149.8116 | 592372.7362 | 707747.0358 | 566391.0209 | 190461.144 | 482363.5401 | 584691.6219 | 239781.2013 | 87541.48534 | 129268.3527 | 262777.2786 | 202421.3749 | 255077.1676 | 401802.2399 | 336549.8742 | 225898.7696 | 194669.1516 | ||
| Q9H1E1 | 3 | 2 | 115.07 | 0.156785557 | 7.101225515 | XN | HN | Ribonuclease 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE7 PE=1 SV=2 | 12990.03 | 66652.18 | 10462.32 | 86479.36 | 40030.3275 | 190506.2818 | 492194.3907 | 583111.4574 | 704845.1352 | 35985.09031 | 0 | 36758.06363 | 85053.80342 | 21497.14712 | 50227.83298 | 51292.0086 | 19371.90141 | 56236.65561 | 244062.2927 | 1362181.994 | 174017.4118 | 617730.3375 | 8504.481375 | 32735.39318 | 40116.34732 | 16426.55158 | 35261.76305 | ||
| P83110 | 2 | 2 | 114.79 | 0.060584001 | 3.616218783 | XN | XA | Serine protease HTRA3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HTRA3 PE=1 SV=2 | 27514.67 | 14814.12 | 28919.7 | 131109 | 59715.6243 | 76922.41179 | 51718.37685 | 55912.10482 | 33108.29044 | 131712.44 | 61909.71151 | 57830.06359 | 76771.6242 | 36042.335 | 110330.1382 | 319934.1201 | 38190.66469 | 55747.17747 | 949740.3498 | 32379.96881 | 60085.45218 | 139378.4109 | 79840.08095 | 157551.7733 | 175745.3944 | 85006.5957 | 55096.03253 | ||
| Q9UM07 | 6 | 1 | 114.45 | 0.106598632 | 4.183503577 | XA | XN | Protein-arginine deiminase type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PADI4 PE=1 SV=2 | 13091.06 | 8088.499 | 44010.06 | 7218.835 | 12305.26996 | 222042.6626 | 29679.44923 | 25855.49911 | 143502.5201 | 53008.7261 | 8992.099041 | 2860.224743 | 4536.000389 | 10612.28133 | 379106.1868 | 1171.751295 | 0 | 0 | 66959.48252 | 6215.721187 | 5934.774282 | 188.4397818 | 5410.510785 | 16624.109 | 12156.0747 | 4731.909693 | 2680.956007 | ||
| P13798 | 7 | 4 | 114.37 | 0.658440277 | 1.317117717 | HN | XN | Acylamino-acid-releasing enzyme OS=Homo sapiens GN=APEH PE=1 SV=4 | 97406.75 | 153514 | 178645.7 | 305721.8 | 159444.2657 | 715114.1029 | 474279.7259 | 413585.9489 | 637009.4415 | 211828.631 | 351149.9899 | 883473.413 | 537557.6185 | 376632.6887 | 105451.7781 | 447471.01 | 135328.2457 | 159414.5968 | 557753.0013 | 108095.4393 | 211865.1422 | 468532.133 | 147706.0852 | 526865.6233 | 157103.6329 | 143944.5869 | 113989.5043 | ||
| A6NL88 | 3 | 2 | 113.58 | 0.083511958 | 1.495739284 | XN | XA | Protein shisa-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHISA7 PE=2 SV=3 | 430488 | 422330.9 | 554485.1 | 495584.8 | 390487.0233 | 348736.0929 | 291262.3497 | 224927.0257 | 384584.2616 | 532605.5921 | 466983.0762 | 190019.6794 | 369184.4677 | 836799.5145 | 711372.9868 | 683818.3325 | 439600.9692 | 420214.5133 | 388058.848 | 356578.629 | 655433.9296 | 830272.3621 | 593920.9982 | 683524.1163 | 394305.5198 | 829947.5203 | 567191.0809 | ||
| Q9Y5F6 | 5 | 2 | 113.44 | 0.333077164 | 1.425795789 | XN | HN | Protocadherin gamma-C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHGC5 PE=2 SV=1 | 1004054 | 612331 | 348072.7 | 1673066 | 224588.4486 | 345286.3469 | 643936.2095 | 768377.8988 | 716008.0495 | 474998.1576 | 355991.1439 | 190242.5602 | 516528.6579 | 201017.6767 | 519177.8374 | 1548299.787 | 203222.0575 | 439599.9375 | 320824.5942 | 214476.5535 | 831575.0263 | 255475.4144 | 1452403.184 | 612214.4697 | 1160920.444 | 608018.5833 | 887568.1433 | ||
| Q6ISS4 | 4 | 3 | 113.22 | 0.60076185 | 1.545099381 | XN | XA | Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAIR2 PE=2 SV=1 | 96827.95 | 185956.3 | 234060.4 | 191657 | 121408.8382 | 147632.2448 | 300749.7691 | 521757.4036 | 282159.4463 | 100573.3595 | 1304480.3 | 132379.7264 | 269972.4142 | 147490.9172 | 373098.7571 | 78432.76348 | 186253.638 | 143092.131 | 283664.1491 | 848717.9508 | 173687.8476 | 163235.5454 | 148683.9695 | 370900.885 | 246575.9599 | 876168.3212 | 105585.706 | ||
| P48960 | 2 | 1 | 113.12 | 0.473821242 | 1.240315151 | XN | XA | CD97 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD97 PE=1 SV=4 | 298365.2 | 1231700 | 811287.3 | 1240568 | 707347.4465 | 704997.0778 | 423226.1495 | 509816.7816 | 723533.7514 | 472269.4197 | 726443.1542 | 75215.69352 | 1467183.778 | 671581.1493 | 865174.051 | 364307.6024 | 461442.6935 | 2156697.311 | 659911.6419 | 943323.5173 | 1084004.188 | 864790.4915 | 559758.9026 | 1961047.76 | 687160.8735 | 858839.5715 | 630302.9351 | ||
| O43157 | 8 | 3 | 112.9 | 0.151009252 | 1.447851704 | HN | XA | Plexin-B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLXNB1 PE=1 SV=3 | 319412.4 | 795176.4 | 870954.5 | 578192.7 | 814104.6096 | 483551.2098 | 465982.134 | 286356.3681 | 239396.5697 | 1093978.181 | 1338435.574 | 941433.5654 | 802650.5422 | 629367.1295 | 620941.3816 | 497013.9072 | 388202.3905 | 714585.3513 | 1146264.354 | 487733.4062 | 635331.8718 | 426581.6088 | 496894.5369 | 357560.5022 | 355671.9151 | 931441.3495 | 655876.0874 | ||
| Q99972 | 6 | 3 | 112.69 | 0.194707374 | 8.842695209 | XA | XN | Myocilin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYOC PE=1 SV=2 | 10433.74 | 401165.4 | 745720.2 | 74504.51 | 894009.4302 | 6352.588347 | 41269.14701 | 44885.34712 | 27802.1798 | 10900.44442 | 14402.07175 | 120610.3072 | 11044.80329 | 38740.78606 | 723134.0173 | 352068.7251 | 92966.28492 | 74062.1105 | 53951.72773 | 41370.34521 | 11708.2913 | 40563.05963 | 43260.22174 | 24097.04483 | 18434.90233 | 9321.885693 | 11303.59885 | ||
| P21583 | 4 | 3 | 112.39 | 0.938027759 | 1.073904704 | HN | XN | Kit ligand OS=Homo sapiens GN=KITLG PE=1 SV=1 | 212111.3 | 188361.1 | 93844.62 | 82534.02 | 338071.8481 | 55017.65582 | 231140.865 | 138564.922 | 191948.4694 | 83322.69933 | 116235.4989 | 52868.66816 | 422193.4201 | 206059.8773 | 195760.873 | 181205.7014 | 177600.8849 | 155668.2747 | 47307.04259 | 139853.5153 | 181236.9941 | 60707.503 | 109192.2917 | 348776.334 | 110945.9509 | 241575.6622 | 241835.8721 | ||
| Q9BXJ7 | 5 | 2 | 112.09 | 0.770905674 | 1.264033774 | XN | XA | Protein amnionless OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMN PE=1 SV=2 | 1220203 | 220549.9 | 790366.1 | 1591064 | 538175.2499 | 499196.084 | 357713.7354 | 999916.1649 | 461985.866 | 1113255.73 | 575576.7322 | 1314048.401 | 498513.0268 | 623541.2331 | 732676.4588 | 1354526.852 | 804966.5917 | 293063.5321 | 532645.8209 | 378818.647 | 1601691.819 | 1346706.353 | 1800847.983 | 217474.1113 | 1225955.409 | 737095.8726 | 601460.491 | ||
| P53801 | 2 | 1 | 111.77 | 0.258649276 | 1.248453196 | XN | XA | Pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1 protein-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTTG1IP PE=1 SV=1 | 8908131 | 7534818 | 7934418 | 8725574 | 7618321.538 | 8559215.175 | 7844398.092 | 7821903.147 | 8458198.141 | 9305255.606 | 11601334.94 | 6053385.526 | 13972605.18 | 14137041.16 | 4432111.67 | 9952719.576 | 8277277.633 | 10337587.44 | 8223466.149 | 9798251.114 | 9992927.945 | 6578552.874 | 10369930.68 | 14824372.02 | 10638779.64 | 11316818.07 | 9899579.887 | ||
| O75608 | 4 | 3 | 111.66 | 0.620667229 | 1.457179282 | HN | XN | Acyl-protein thioesterase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPLA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 488484.1 | 96851.65 | 242511.4 | 734483.6 | 878038.2651 | 346059.4669 | 526115.9715 | 673052.6168 | 369303.8118 | 1058679.485 | 219334.2532 | 109289.0444 | 228850.7945 | 406532.8221 | 467574.6192 | 1930121.52 | 393736.5199 | 342692.4574 | 1269057.17 | 169662.2793 | 513172.6761 | 297823.3096 | 416157.5541 | 284120.7116 | 254866.0591 | 73122.28381 | 260917.7864 | ||
| P38571 | 2 | 2 | 111.63 | 0.799751391 | 1.127244808 | XA | HN | Lysosomal acid lipase/cholesteryl ester hydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LIPA PE=1 SV=2 | 1256552 | 211685.7 | 824918.3 | 772615 | 1079360.834 | 883477.7148 | 494156.7317 | 1022087.608 | 575764.0523 | 1027868.097 | 171079.7677 | 826367.3389 | 284805.2895 | 516563.4947 | 691736.4094 | 1353640.203 | 941964.1897 | 502808.695 | 903160.4027 | 599012.9129 | 790677.8385 | 377814.9536 | 813858.4675 | 99160.30469 | 918516.6011 | 692884.1077 | 1124983.319 | ||
| P20810 | 4 | 3 | 111.54 | 0.773763127 | 1.613064244 | XA | XN | Calpastatin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAST PE=1 SV=4 | 62112.14 | 42315.38 | 45077.66 | 176714.5 | 60472.05158 | 92500.57407 | 240875.529 | 575276.9026 | 246544.0331 | 175562.6002 | 471908.0846 | 226192.9807 | 371179.4068 | 35869.43664 | 44485.8403 | 48051.61474 | 55535.41901 | 48852.03051 | 144666.2899 | 105058.8598 | 265033.8605 | 130225.5473 | 106846.3542 | 85152.92513 | 51984.00598 | 32868.36008 | 34039.40123 | ||
| P28161 | 3 | 1 | 111.36 | 0.037539469 | 1.99103105 | XA | XN | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 141741.9 | 49082.77 | 76483.26 | 123722.7 | 69619.30844 | 67964.88285 | 116067.3354 | 181334.6923 | 76113.60427 | 57803.21503 | 22786.38892 | 125891.0031 | 83811.78887 | 150707.7613 | 81503.25896 | 46155.45967 | 53390.81579 | 48648.3336 | 38416.84505 | 40917.7874 | 62029.07134 | 27570.06896 | 40957.94498 | 5172.115316 | 72573.23876 | 73784.22832 | 91675.85957 | ||
| O43175 | 5 | 3 | 111.32 | 0.354002658 | 1.330689796 | XA | XN | D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHGDH PE=1 SV=4 | 2507526 | 490175.3 | 1013099 | 1178025 | 454535.6433 | 1977887.011 | 446420.9488 | 1559605.11 | 830678.9372 | 339111.941 | 72520.84877 | 508535.4391 | 3956801.276 | 1003364.978 | 360333.4514 | 521364.5867 | 670460.0384 | 695860.0048 | 2092177.071 | 166507.389 | 911747.9191 | 653117.5835 | 1027371.368 | 1003494.683 | 346701.9181 | 965682.4864 | 692245.9265 | ||
| Q96BW5 | 5 | 4 | 111.32 | 0.884724466 | 1.155328155 | HN | XN | Phosphotriesterase-related protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTER PE=1 SV=1 | 1434634 | 377195.9 | 1965957 | 3315976 | 1301459.561 | 2646340.193 | 3150767.903 | 3378120.457 | 2788052.378 | 1224160.174 | 2568048.966 | 2275918.103 | 1662425.749 | 5160748.598 | 842627.6445 | 2991135.569 | 1716271.259 | 1924523.835 | 2512105.128 | 1068033.387 | 2274913.437 | 1118338.071 | 626037.066 | 1697196.045 | 2258674.78 | 3126306.359 | 2946166.509 | ||
| O15511 | 2 | 1 | 111.26 | 0.989033877 | 2.789622757 | XA | XN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARPC5 PE=1 SV=3 | 60527.66 | 0 | 21673.64 | 168401 | 23641.90573 | 120169.1538 | 126944.1548 | 260271.5548 | 103901.7147 | 147695.5006 | 26970.71395 | 136329.547 | 77140.57125 | 10675.87205 | 1452.118266 | 15023.06947 | 9224.526709 | 59628.06685 | 5670.141251 | 65065.90793 | 61866.67919 | 90438.11081 | 25395.47521 | 25418.12849 | 13958.7632 | 7139.301203 | 22484.95619 | ||
| Q12962 | 2 | 1 | 111.21 | 0.151087459 | 6.314925116 | XN | XA | Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAF10 PE=1 SV=1 | 12440.2 | 51071.89 | 36275.9 | 1477.119 | 0 | 0 | 63393.44222 | 6932.129375 | 81598.87987 | 2.29780532 | 798400.7733 | 11077.24767 | 223866.913 | 54786.33491 | 227698.814 | 0 | 11407.89477 | 107319.0328 | 10140.19355 | 333698.1474 | 210159.6756 | 30251.69149 | 152202.7019 | 533986.2465 | 57623.68667 | 249888.1304 | 20922.68316 | ||
| Q8N2G4 | 2 | 2 | 111.14 | 0.496899626 | 1.140490007 | XN | XA | Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 262502.2 | 388029.3 | 185323.3 | 181251.8 | 325508.9479 | 619234.9155 | 467943.1212 | 380614.0647 | 420953.9187 | 260539.5946 | 1004907.821 | 65547.26798 | 898446.3685 | 611923.6446 | 152023.8855 | 61074.43741 | 251991.6028 | 358895.557 | 502634.4324 | 399250.089 | 380333.0051 | 411365.1008 | 313183.4843 | 591198.0326 | 339660.0245 | 526014.7448 | 221696.7233 | ||
| P06310 | 3 | 2 | 111.08 | 0.820461464 | 1.587708916 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-II region RPMI 6410 OS=Homo sapiens PE=4 SV=1 | 589721.2 | 526575 | 88394.36 | 285449.3 | 694917.1322 | 196201.8976 | 80399.53855 | 88920.55356 | 32138.19496 | 385591.0617 | 132419.1387 | 237970.3394 | 48800.355 | 102940.7665 | 168015.6487 | 1321740.442 | 150358.9741 | 103109.7213 | 85177.66784 | 705233.5161 | 184728.427 | 62185.70815 | 172806.5777 | 2154542.126 | 118712.5749 | 415460.4019 | 201756.1057 | ||
| P34897 | 7 | 4 | 110.92 | 0.423190483 | 1.39522143 | HN | XA | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHMT2 PE=1 SV=3 | 14504605 | 49994122 | 34420562 | 14503593 | 41032974.16 | 15072297.84 | 12127502.5 | 15045362.23 | 11062510.85 | 24504367.68 | 13644810.22 | 20802056.17 | 11408678.31 | 30404135.4 | 76138919.44 | 64946808.36 | 23816185.81 | 24210166.49 | 17048388.74 | 13958052.02 | 17071566.22 | 28331897.02 | 41178367.9 | 34982055.65 | 39909791.38 | 29763777.29 | 30809934.57 | ||
| O60346 | 6 | 2 | 110.87 | 0.373041995 | 1.264868299 | HN | XN | PH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHLPP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 439123.1 | 134017 | 169844.7 | 210819.8 | 107713.0449 | 120795.238 | 162377.6057 | 53233.24844 | 47314.14157 | 146253.2794 | 141550.6789 | 147598.6953 | 154114.8163 | 165740.5814 | 208451.5577 | 279931.5791 | 145893.2329 | 204622.643 | 87751.66543 | 82702.37946 | 166863.0191 | 107391.7004 | 121576.8469 | 183035.6852 | 132826.2807 | 191966.1792 | 186220.6718 | ||
| P68036 | 5 | 3 | 110.66 | 0.011713646 | 3.762156557 | XN | XA | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 L3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBE2L3 PE=1 SV=1 | 21569330 | 16571967 | 23268704 | 8478521 | 3517328.94 | 28901574.54 | 36031145.82 | 14415715.72 | 26197194.86 | 46521982.21 | 97784472.07 | 136794383.7 | 48980520.33 | 82112810.32 | 15375705.08 | 22298144.13 | 59915170.02 | 17134862.64 | 24584057.19 | 46332779.39 | 45848887.23 | 28856095.24 | 43831535.94 | 324278749 | 105486568.8 | 25354616.43 | 28670203.26 | ||
| P35270 | 3 | 2 | 110.64 | 0.748066986 | 1.397760668 | XA | HN | Sepiapterin reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPR PE=1 SV=1 | 190852.9 | 7533.617 | 24491.9 | 208526 | 19873.25313 | 276217.982 | 178878.3093 | 274945.92 | 98059.20411 | 67573.00383 | 315124.7812 | 33381.78494 | 352990.5394 | 42751.29337 | 17355.72455 | 40363.9681 | 23331.3106 | 22433.80394 | 81724.62355 | 54648.90571 | 299552.0751 | 318876.1088 | 85432.5181 | 8000.044476 | 115397.3273 | 33470.0033 | 32672.30711 | ||
| Q9H461 | 4 | 3 | 110.45 | 0.221926152 | 1.263607856 | XN | XA | Frizzled-8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD8 PE=1 SV=1 | 3499877 | 3018303 | 1597837 | 1945850 | 1677101.523 | 2847904.716 | 2114329.76 | 2065515.543 | 2645549.256 | 3094851.985 | 4381668.12 | 2269518.029 | 2949548.604 | 2092865.026 | 1135849.546 | 2379391.464 | 2729987.998 | 2783701.594 | 3670808.747 | 4173434.347 | 3044559.858 | 2417071.988 | 3138570.889 | 2331443.35 | 2136114.807 | 2681466.608 | 3463238.528 | ||
| Q8IZA0 | 6 | 4 | 110.1 | 0.377560902 | 1.353162589 | XN | XA | Dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA0319L PE=1 SV=2 | 13511109 | 25480780 | 18555198 | 7683506 | 20875580.48 | 12180392.43 | 10814020.55 | 9755981.222 | 6856997.496 | 9492516.877 | 8377442.121 | 13548766.64 | 5753811.043 | 12895084.24 | 24113257.78 | 26157187.45 | 17342083.97 | 13299064.53 | 14044538.69 | 11908868.66 | 17459568.54 | 15945232.37 | 26210751.85 | 37650816.23 | 27163779.44 | 8857348.765 | 10869989.27 | ||
| P09382 | 4 | 4 | 110.03 | 0.133780011 | 5.874732513 | HN | XN | Galectin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 374295.9 | 265591.8 | 78567.51 | 238923.7 | 444357.9741 | 91377.91792 | 107906.6966 | 107647.4778 | 65451.00421 | 458756.9807 | 63306.813 | 292021.8391 | 110781.3863 | 165617.0083 | 249462.3445 | 4361733.044 | 106568.1803 | 127673.8074 | 28636.79518 | 58533.41594 | 152019.888 | 105759.6385 | 222495.623 | 69414.98338 | 119360.2989 | 100494.2735 | 153700.6882 | ||
| O14917 | 6 | 1 | 109.99 | 0.406026971 | 6.895651918 | XA | HN | Protocadherin-17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDH17 PE=2 SV=2 | 46405.66 | 48165.19 | 0 | 35882.85 | 580025.3317 | 61091.09628 | 45204.2556 | 105155.304 | 100771.1632 | 42424.99842 | 0.719543943 | 5565.389137 | 5573.679128 | 1477.804061 | 20114.12339 | 27360.13942 | 7567.946547 | 38226.17349 | 50054.16785 | 56594.5342 | 50608.42089 | 37191.76544 | 54496.96133 | 42175.67382 | 7294.935632 | 57693.75412 | 1022.91724 | ||
| Q6ZMJ2 | 3 | 1 | 109.98 | 0.171788543 | 2.068202416 | HN | XA | Scavenger receptor class A member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCARA5 PE=2 SV=1 | 110294.7 | 67818.95 | 62196.23 | 177414.4 | 207405.4414 | 34430.3845 | 66972.68412 | 72333.77596 | 45873.41691 | 115830.2695 | 116675.4092 | 50402.79784 | 125837.8009 | 170595.1826 | 166095.2598 | 674730.3351 | 54417.02251 | 272509.2123 | 118458.5341 | 91733.55965 | 112192.2659 | 31120.49527 | 83884.66839 | 87598.76844 | 164685.3226 | 132643.3113 | 154830.9708 | ||
| Q13442 | 2 | 1 | 109.53 | 0.278822199 | 4.735139582 | XA | HN | 28 kDa heat- and acid-stable phosphoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDAP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 34062.54 | 10952.96 | 15339.52 | 12281.18 | 2641.277022 | 19853.89407 | 69574.13935 | 690058.1512 | 29783.6541 | 6216.193286 | 64884.93908 | 5867.259724 | 1963.940019 | 6718.193412 | 9004.414178 | 7403.613192 | 34664.70076 | 50081.65243 | 53098.02218 | 115806.7254 | 289622.6712 | 113709.5524 | 76829.40122 | 680.2892528 | 5624.255614 | 58386.38179 | 35679.02285 | ||
| P78552 | 3 | 3 | 108.82 | 0.474229361 | 1.199560228 | HN | XN | Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL13RA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 760980.6 | 482956.8 | 458294.6 | 634894.3 | 603688.0305 | 419517.7942 | 351544.7473 | 574661.1861 | 385203.4851 | 702788.2658 | 349882.0178 | 266711.3952 | 452347.6763 | 614940.4268 | 584080.2738 | 645012.6327 | 609897.6453 | 775806.8276 | 447278.7161 | 395061.2062 | 394950.5174 | 474090.2743 | 722692.6646 | 662949.959 | 327519.7074 | 374750.4639 | 370123.7852 | ||
| P01622 | 3 | 1 | 108.66 | 0.417778972 | 1.357704376 | XN | HN | Ig kappa chain V-III region Ti OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1895814 | 2444349 | 2276817 | 2536341 | 3021226.271 | 1456089.728 | 1195910.949 | 962632.3584 | 883702.1698 | 1088825.969 | 511873.3063 | 1590977.625 | 581441.9521 | 640835.9126 | 3445671.261 | 2787743.659 | 1765025.099 | 1050445.38 | 1186122.225 | 1972855.749 | 998015.2146 | 641392.4986 | 4748758.048 | 3371924.08 | 2174066.4 | 961055.5362 | 2224367.26 | ||
| P06858 | 1 | 1 | 108.53 | 0.142617109 | 1.939573035 | XA | HN | Lipoprotein lipase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LPL PE=1 SV=1 | 167670.6 | 230513.3 | 118077.4 | 309521.9 | 86040.01787 | 68622.73322 | 97379.10103 | 166286.1244 | 199638.2439 | 17002.14077 | 34641.23419 | 32319.51633 | 67306.23624 | 56305.54896 | 157132.4023 | 174432.3499 | 129023.7206 | 76201.42996 | 53818.83375 | 95035.76665 | 63398.03254 | 105960.2298 | 197593.5688 | 5896.29114 | 100155.9106 | 278762.6475 | 186172.7715 | ||
| P14923 | 3 | 2 | 108.51 | 0.09141158 | 8.759723529 | XA | XN | Junction plakoglobin OS=Homo sapiens GN=JUP PE=1 SV=3 | 456.6862 | 0 | 3951.143 | 3480.689 | 1541.083763 | 24067.55921 | 29059.7816 | 386117.7228 | 114944.8987 | 10556.3267 | 11453.0496 | 20773.10433 | 217934.0692 | 475.8438309 | 729.8000181 | 13116.77011 | 691.4067186 | 853.6240542 | 44272.2225 | 1264.132734 | 156.586273 | 14723.78514 | 3681.910891 | 0 | 0 | 243.5260565 | 0 | ||
| P14854 | 1 | 1 | 108.24 | 0.191320295 | 2.274546863 | HN | XA | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=COX6B1 PE=1 SV=2 | 60343.76 | 9762.378 | 22212.79 | 81965.58 | 35317.92664 | 36024.12562 | 17488.96281 | 37487.72739 | 39866.11742 | 157909.6049 | 86933.44783 | 275715.4325 | 86943.01473 | 21002.91688 | 42492.15282 | 14474.95322 | 60761.76131 | 28180.23904 | 34906.30997 | 9099.938796 | 56194.3487 | 159790.4017 | 26662.39886 | 44295.21912 | 11572.43059 | 0 | 7796.777349 | ||
| P21281;P15313 | 5 | 2 | 108.21 | 0.487600962 | 1.773834016 | XA | XN | V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6V1B2 PE=1 SV=3 | 2771701 | 2149729 | 282805.9 | 2088584 | 412303.1115 | 829019.8118 | 1017008.04 | 2190886.771 | 878189.2921 | 1696493.505 | 3677914.577 | 1273278.868 | 875983.9621 | 1093871.255 | 1258780.142 | 438995.5955 | 393692.0404 | 193390.5645 | 538705.2394 | 399469.4457 | 1211799.932 | 1009447.552 | 1009962.505 | 1303530.004 | 620142.8224 | 647555.4783 | 374047.2314 | ||
| Q15846 | 3 | 2 | 107.58 | 0.619689098 | 2.595035433 | XN | XA | Clusterin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLUL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 93007.17 | 6702.398 | 49556.84 | 69061.66 | 23873.92302 | 0 | 12449.88206 | 19776.14519 | 42542.22178 | 5844.789942 | 19353.24192 | 41357.73009 | 100512.3906 | 42043.20225 | 61896.40457 | 64778.42513 | 90151.74575 | 21584.10633 | 55707.52356 | 123044.0013 | 137468.7051 | 74424.52529 | 77136.73023 | 0 | 39800.90883 | 204099.7726 | 110866.8512 | ||
| P22692 | 4 | 2 | 107.15 | 0.19915483 | 1.66909829 | HN | XA | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 816453.5 | 235267.4 | 386408.1 | 411553.7 | 359410.6861 | 228379.7498 | 306735.9921 | 290734.91 | 397768.6756 | 467795.0863 | 714243.279 | 423568.7687 | 608168.6849 | 150229.5591 | 1544295.371 | 791202.2181 | 467329.7274 | 562702.2296 | 251654.6493 | 379322.9983 | 332600.4069 | 418571.8209 | 502762.0068 | 285724.34 | 671930.0299 | 983483.041 | 501374.3084 | ||
| P07360 | 3 | 2 | 106.94 | 0.786320904 | 1.43258253 | HN | XN | Complement component C8 gamma chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=C8G PE=1 SV=3 | 466197.9 | 218319.8 | 399601.6 | 92250.77 | 76693.99802 | 42016.92094 | 43069.95189 | 77524.52252 | 66987.31711 | 164573.6872 | 79554.35599 | 371363.5613 | 211947.634 | 91501.84621 | 87620.14949 | 849773.049 | 69636.2986 | 55648.87378 | 288990.6018 | 165170.1274 | 169941.2277 | 112846.1835 | 243763.2585 | 43369.63379 | 137393.2077 | 146248.0522 | 75527.4774 | ||
| Q07020 | 2 | 2 | 106.51 | 0.165252331 | 1.51244176 | XN | XA | 60S ribosomal protein L18 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPL18 PE=1 SV=2 | 1182803 | 526667.9 | 271424.4 | 1086834 | 461439.1855 | 1102078.279 | 895760.6795 | 852526.2406 | 346927.7181 | 1610330.072 | 835039.1065 | 596481.2093 | 408502.4561 | 2488448.344 | 775717.5062 | 1629387.415 | 356935.119 | 666366.3155 | 1042012.215 | 1122189.173 | 1010998.447 | 1239821.948 | 1458469.569 | 1044704.722 | 773748.6724 | 634399.0688 | 1847036.549 | ||
| O43852 | 5 | 1 | 106.47 | 0.343273449 | 1.820400715 | HN | XN | Calumenin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALU PE=1 SV=2 | 117686.4 | 39695.93 | 80021.63 | 78137.56 | 11292.98382 | 29504.37078 | 66506.27871 | 64963.3831 | 76912.22305 | 118978.8814 | 147959.0136 | 39163.34045 | 57388.34293 | 60407.17905 | 50009.07261 | 313166.8446 | 21650.00803 | 74604.75989 | 14659.36773 | 98697.74049 | 26526.44645 | 10168.29136 | 68175.50817 | 70787.06709 | 46803.04463 | 89978.61467 | 59441.83174 | ||
| P07864 | 4 | 1 | 106.4 | 0.37490273 | 1.622408894 | XN | XA | L-lactate dehydrogenase C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHC PE=2 SV=4 | 554700.2 | 580551.7 | 62754.89 | 23421.36 | 105756.8617 | 81227.32143 | 126008.7313 | 67383.22185 | 81.81272209 | 0 | 547308.6555 | 192344.6545 | 165649.3569 | 832719.2313 | 90827.08302 | 0 | 315389.8224 | 344823.2061 | 118411.9292 | 348801.3222 | 614994.5494 | 376317.7309 | 293594.416 | 27511.40169 | 27774.505 | 320618.8493 | 470889.4411 | ||
| Q9H4M9 | 7 | 4 | 106.27 | 0.258531053 | 1.461303814 | XN | HN | EH domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EHD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3833775 | 2158491 | 1743423 | 1923745 | 2193531.117 | 5755321.386 | 7252600.96 | 2251061.346 | 5646113.39 | 1793243.461 | 1105628.579 | 2844034.179 | 4174547.794 | 1545315.893 | 1784264.329 | 4002727.849 | 5370025.765 | 1493797.904 | 8156433.05 | 2597452.274 | 4767654.009 | 3019985.576 | 3611318.523 | 1399908.09 | 5308312.326 | 3418762.378 | 2957448.611 | ||
| Q6UX71 | 5 | 2 | 106.05 | 0.966302283 | 1.276722323 | HN | XA | Plexin domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLXDC2 PE=1 SV=1 | 319786.1 | 563703.4 | 458515.9 | 157929.3 | 307993.3388 | 815308.2393 | 642158.0868 | 304192.7984 | 1008441.375 | 323784.2672 | 1902414.643 | 380878.457 | 1219544.237 | 1032337.865 | 364385.0963 | 51544.26492 | 287101.9977 | 282880.5441 | 307379.2742 | 540951.3462 | 394936.1327 | 463580.0511 | 273337.1099 | 1369549.384 | 502537.0184 | 770577.8135 | 238519.0357 | ||
| P31025;Q5VSP4 | 2 | 1 | 105.96 | 0.054363793 | 1.800834316 | XA | HN | Lipocalin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 912666.4 | 1051927 | 1606929 | 486060.6 | 2124353.847 | 680749.5859 | 646584.9501 | 628041.756 | 708631.5904 | 851719.7554 | 305121.5491 | 425290.0238 | 395693.1281 | 444800.9972 | 806522.5485 | 695554.4065 | 541669.7746 | 445764.7779 | 416186.3207 | 758465.2167 | 545566.5203 | 669175.494 | 477542.6412 | 1847457.769 | 958756.8482 | 657992.6732 | 1833941.916 | ||
| P15121;C9JRZ8 | 7 | 3 | 105.38 | 0.008353493 | 1.884764223 | HN | XN | Aldose reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 728599.3 | 406159.2 | 508998.3 | 1162174 | 303300.5998 | 325062.0225 | 722211.666 | 539669.3284 | 771044.252 | 774295.2145 | 952065.9984 | 355677.2454 | 811000.8841 | 734060.3062 | 628845.1712 | 713187.611 | 269044.6364 | 320141.1718 | 288940.3719 | 241910.1557 | 193197.2742 | 182746.1113 | 655224.6372 | 164838.5374 | 565061.6221 | 212077.8747 | 445082.2287 | ||
| Q58FG1 | 4 | 1 | 105 | 0.112499485 | 1.761495415 | XA | XN | Putative heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha A4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA4P PE=5 SV=1 | 969330 | 544819.2 | 656544.5 | 1012573 | 477084.8129 | 948609.2406 | 1128861.623 | 1107853.333 | 563139.3641 | 988976.1478 | 660584.136 | 1486436.05 | 408899.4541 | 215588.3469 | 321169.8513 | 29790.74074 | 390919.2322 | 528454.6488 | 401460.43 | 571717.7761 | 1075822.07 | 292085.7569 | 663730.0256 | 65575.52262 | 274335.454 | 501560.7667 | 359692.5529 | ||
| Q96EY5 | 2 | 1 | 104.88 | 0.93853875 | 1.540498718 | HN | XN | Multivesicular body subunit 12A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM125A PE=1 SV=1 | 360587.3 | 151959 | 162258.4 | 121979.2 | 66719.4633 | 126856.2431 | 231699.6088 | 267148.6617 | 228707.6667 | 292819.6872 | 1005898.538 | 171160.2145 | 233582.8606 | 631205.7311 | 102215.1248 | 31029.71733 | 50660.80545 | 53783.36573 | 187694.5968 | 173070.5914 | 209460.8971 | 31232.27368 | 105443.4686 | 107562.0934 | 139642.8688 | 207538.7465 | 508174.7721 | ||
| Q9UBR1 | 2 | 1 | 104.73 | 0.151640779 | 2.524490449 | XA | HN | Beta-ureidopropionase OS=Homo sapiens GN=UPB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 129807.8 | 55870.18 | 353951.4 | 279462.2 | 21744.56138 | 562442.5899 | 53923.46228 | 482965.7512 | 379221.564 | 46477.66292 | 95751.67673 | 297474.0765 | 291608.633 | 27572.59341 | 15461.28251 | 62483.01627 | 53210.77329 | 28715.75446 | 146930.7916 | 135038.6299 | 423402.0491 | 310192.6773 | 261102.5605 | 16895.84843 | 89514.68133 | 114852.3296 | 86099.35561 | ||
| Q9H9H4 | 2 | 1 | 104.63 | 0.831778853 | 1.665213143 | HN | XN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 37B OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS37B PE=1 SV=1 | 157242.6 | 46656.17 | 49230.2 | 101553.4 | 185203.295 | 39729.73346 | 162164.994 | 124461.2003 | 93165.85935 | 17536.41062 | 434667.3876 | 81706.42916 | 123774.1913 | 307006.9884 | 35930.36288 | 29347.27275 | 87535.88691 | 123252.096 | 77589.00174 | 123178.8411 | 55141.77166 | 38161.91558 | 99418.26499 | 41045.62312 | 66915.9745 | 88844.39727 | 154808.2413 | ||
| Q6ZMR3 | 4 | 2 | 103.72 | 0.98355563 | 1.066132047 | HN | XN | L-lactate dehydrogenase A-like 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHAL6A PE=2 SV=1 | 1849908 | 1559355 | 1918387 | 3520072 | 673834.4494 | 2657425.546 | 2033074.751 | 1372838.205 | 3026951.712 | 3502296.942 | 2213046.507 | 2118175.787 | 1338138.407 | 4234585.066 | 1208164.36 | 921396.2825 | 1672191.477 | 2304781.934 | 2529999.917 | 1832030.912 | 2472896.222 | 1497842.8 | 2409965.832 | 562138.6331 | 1760329.139 | 2633610.806 | 2603587.218 | ||
| P55259 | 4 | 3 | 102.81 | 0.815170892 | 1.78458626 | XN | XA | Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GP2 PE=2 SV=3 | 135448.2 | 135397.7 | 360843.2 | 161043.9 | 344607.4914 | 272834.152 | 177558.3221 | 69932.40847 | 319445.9229 | 79251.43161 | 263518.3313 | 68027.98831 | 289151.3108 | 626849.0839 | 296799.432 | 533241.7384 | 165694.7797 | 474949.3209 | 146819.8797 | 124302.0301 | 100194.4679 | 42501.94933 | 328022.0794 | 1491691.363 | 503993.9672 | 566684.9226 | 224115.1081 | ||
| Q9Y2G1 | 5 | 4 | 102.68 | 0.764380538 | 1.106989869 | XN | XA | Myelin gene regulatory factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRF PE=1 SV=3 | 1043827 | 694031.9 | 650980.7 | 673116.4 | 706798.1208 | 733590.6623 | 793309.6813 | 686887.5803 | 949142.5538 | 677390.9796 | 1925572.124 | 411866.6168 | 1244635.256 | 839221.0116 | 617749.0378 | 216183.3331 | 811727.9313 | 844704.4561 | 825065.3746 | 806212.1853 | 822671.1262 | 467199.5308 | 693516.1089 | 1227112.932 | 842600.2116 | 1061357.087 | 927570.0814 | ||
| Q9BRA2 | 3 | 3 | 102.33 | 0.860399828 | 1.198512268 | XA | XN | Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TXNDC17 PE=1 SV=1 | 279237.6 | 229607.5 | 228210.2 | 45501.14 | 22942.16503 | 551692.8611 | 824782.1209 | 493343.1174 | 726258.1665 | 156581.7007 | 460181.0106 | 1400683.612 | 294585.6372 | 365630.4104 | 106870.1833 | 26323.66801 | 89523.94775 | 61932.26262 | 1087902.954 | 255778.9645 | 490446.998 | 471778.2744 | 176791.2041 | 67719.40608 | 119599.2377 | 126608.1632 | 41539.17374 | ||
| Q9UP52 | 3 | 2 | 101.96 | 0.792471959 | 1.556689109 | XN | XA | Transferrin receptor protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 391079.5 | 813774.7 | 641557.1 | 655406.7 | 1077662.928 | 420335.7242 | 340710.9928 | 323037.7071 | 585201.198 | 525444.5112 | 384944.28 | 692802.8164 | 668057.7862 | 671288.136 | 2309693.592 | 1796116.556 | 310761.405 | 255899.3365 | 3603377.106 | 338042.1753 | 239913.4245 | 506316.9801 | 677384.1397 | 982972.5958 | 454789.6361 | 590392.3554 | 777509.3563 | ||
| P01700 | 2 | 1 | 101.81 | 0.271236594 | 1.384927906 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-I region HA OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 771788.2 | 704129.5 | 1569886 | 477165.7 | 1553303.186 | 427357.4346 | 307493.5552 | 298209.7879 | 267952.8741 | 1072472.118 | 388138.7414 | 1298926.933 | 284366.1464 | 1418652.349 | 1261166.222 | 945726.4181 | 1359554.516 | 803077.8862 | 677565.5748 | 585199.6538 | 629887.5747 | 1008809.113 | 624422.9166 | 1935809.273 | 682903.5459 | 574819.3961 | 1169559.651 | ||
| Q14954;P43627;P43632;Q14952 | 5 | 2 | 101.61 | 0.770744207 | 1.466496763 | XN | XA | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIR2DS1 PE=2 SV=1 | 364806 | 282675.9 | 611970.2 | 192974.7 | 107505.9198 | 383916.0901 | 531794.006 | 300351.1111 | 166525.2191 | 224495.2905 | 563650.8574 | 1233716.248 | 231744.8894 | 339963.6665 | 207647.0427 | 85852.71298 | 1060885.88 | 223387.0675 | 163944.3126 | 353863.5192 | 321959.9974 | 209159.4811 | 363038.6858 | 1557090.89 | 836254.9395 | 238574.4532 | 271308.692 | ||
| Q9Y3B3 | 2 | 2 | 101.46 | 0.044929747 | 2.484834958 | XA | HN | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMED7 PE=1 SV=2 | 52908.93 | 558530 | 366415.4 | 126082.6 | 133469.2746 | 182286.4518 | 134492.4178 | 107827.4102 | 217606.5764 | 25544.54766 | 52708.64321 | 52119.85574 | 65528.32486 | 138399.0342 | 128456.4591 | 55130.90877 | 105865.1027 | 132683.3302 | 88738.29124 | 68323.03256 | 61086.61454 | 126016.3045 | 95337.95498 | 580945.0263 | 228504.1838 | 99309.29663 | 84999.30419 | ||
| P55786 | 8 | 4 | 101.44 | 0.516197944 | 1.544155703 | XA | XN | Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPEPPS PE=1 SV=2 | 1380697 | 496655.1 | 724545.8 | 947773.4 | 251890.4965 | 729291.1054 | 1191007.491 | 1768042.703 | 3454855.131 | 1117485.88 | 995091.1156 | 676070.6699 | 1032055.896 | 385629.3417 | 451817.794 | 997787.6894 | 742403.4613 | 1315684.033 | 638088.668 | 451357.897 | 745688.8704 | 500463.3985 | 1498520.315 | 360813.4911 | 720125.743 | 1670086.813 | 502714.2462 | ||
| P05546 | 4 | 3 | 101.41 | 0.384646367 | 1.551137374 | XA | HN | Heparin cofactor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPIND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 352683.7 | 69151.52 | 180678.8 | 615184.9 | 258655.2703 | 68827.14688 | 164280.3608 | 172473.0675 | 125066.3236 | 191041.0937 | 60636.64547 | 258347.4168 | 122769.3645 | 56697.83834 | 180037.948 | 146696.6888 | 178559.9456 | 99103.01818 | 76554.43089 | 74533.01602 | 124370.5959 | 42863.4576 | 253668.1065 | 469601.468 | 148197.448 | 80879.06662 | 89408.22254 | ||
| Q14050 | 5 | 2 | 101.29 | 0.666625924 | 1.212152989 | HN | XA | Collagen alpha-3(IX) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL9A3 PE=2 SV=2 | 569004.3 | 1432877 | 299743 | 310648.8 | 219195.2062 | 277929.9277 | 237924.7779 | 347876.4112 | 269258.4397 | 616344.215 | 1492732.243 | 195762.4802 | 208991.3719 | 475357.7304 | 579131.2639 | 257548.5503 | 382932.5293 | 596728.8007 | 769029.1912 | 438923.0362 | 326687.7481 | 296466.66 | 407146.2506 | 555623.3826 | 630756.3081 | 329300.6667 | 403852.3833 | ||
| P80511 | 2 | 1 | 101.13 | 0.704973567 | 2.354602963 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A12 PE=1 SV=2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4959.517522 | 11910.40175 | 2025.195351 | 71121.30568 | 69266.74928 | 0 | 8106.306068 | 0 | 0 | 4025.967563 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 189350.0671 | 0 | 2312.313393 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P49720 | 2 | 1 | 100.47 | 0.060564069 | 4.112480931 | XN | HN | Proteasome subunit beta type-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 2669.304 | 11609.64 | 10207.46 | 25332.06 | 3279.09177 | 61112.83155 | 57173.71497 | 60314.06909 | 59743.1017 | 1694.232142 | 45.23182787 | 3485.145906 | 79659.48578 | 6603.123114 | 7839.915488 | 235.7043721 | 896.8460896 | 7458.523547 | 273170.0972 | 13850.29044 | 32286.20084 | 97402.66465 | 17950.0376 | 1068.217996 | 985.3005027 | 5127.723554 | 1971.040718 | ||
| Q9Y536 | 3 | 1 | 100.35 | 0.233348175 | 12.30563446 | HN | XN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A-like 4A/B/C OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPIAL4A PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1998.15 | 1138.045836 | 6135.790139 | 5777.393202 | 5281.716438 | 2437.694922 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2241.286333 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 202395.144 | 6465.268508 | 173.6836618 | 0 | 0 | 6452.962219 | 2688.943169 | 419.8218153 | 428.811038 | 0 | ||
| P10109 | 5 | 3 | 100.2 | 0.404388558 | 1.71284074 | HN | XA | Adrenodoxin, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=FDX1 PE=1 SV=1 | 847246.7 | 840310.7 | 654734.5 | 472771.8 | 1305066.492 | 514854.2354 | 2665544.692 | 3237676.573 | 1007745.395 | 1664050.634 | 3433462.841 | 6425607.852 | 1846906.121 | 904281.4076 | 2052633.59 | 1393772.613 | 579146.2053 | 1476514.316 | 1538895.11 | 4745902.195 | 2853101.16 | 2998229.089 | 2141891.932 | 1024903.519 | 519736.8605 | 164161.5329 | 1015608.564 | ||
| P58062 | 4 | 3 | 100.13 | 0.993549286 | 1.669751477 | XN | HN | Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINK7 PE=1 SV=1 | 233215.3 | 316502.2 | 213644.3 | 161741.9 | 332948.9492 | 3574379.291 | 3893902.297 | 6882311.645 | 3147244.246 | 481727.1199 | 6892558.353 | 2940850.404 | 5799595.587 | 184599.3194 | 388039.0313 | 411240.1193 | 386347.8276 | 188088.7728 | 14404473.5 | 7782634.165 | 738769.5958 | 5492618.297 | 236360.9783 | 272284.2654 | 193595.2164 | 156979.7201 | 231879.8039 | ||
| P29218 | 3 | 3 | 100.1 | 0.238088337 | 1.377904421 | XA | HN | Inositol monophosphatase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IMPA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 448501.1 | 276025.4 | 285183.5 | 506523.5 | 146591.3572 | 522380.4041 | 582528.8271 | 298386.8409 | 477351.4873 | 345541.4796 | 442546.5305 | 379288.4386 | 354778.9556 | 275886.5115 | 236469.9029 | 264977.6297 | 132836.9855 | 139312.4183 | 492366.9011 | 238617.8922 | 391735.6418 | 302035.1962 | 331766.7799 | 212077.7559 | 271002.296 | 375506.0597 | 344004.4048 | ||
| Q13621 | 9 | 5 | 100.09 | 0.188641447 | 1.603518031 | HN | XN | Solute carrier family 12 member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC12A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 239090.5 | 460225.4 | 470129.1 | 223872.8 | 673548.5719 | 599880.1444 | 250490.7509 | 233062.9924 | 260551.3383 | 129517.0754 | 555434.0429 | 661243.4022 | 251085.1219 | 670968.6223 | 525345.3952 | 389915.9171 | 194819.1425 | 175114.3864 | 215298.306 | 180768.5434 | 198592.1352 | 119184.975 | 320220.0999 | 309443.2156 | 339824.8051 | 257069.1977 | 275628.126 | ||
| Q7Z7H5 | 3 | 1 | 99.83 | 4.98E-05 | 4.175725714 | XN | XA | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMED4 PE=1 SV=1 | 135812.6 | 58328.94 | 114547.2 | 113343.5 | 40575.80163 | 152607.1945 | 298868.2927 | 196736.1471 | 110221.0837 | 888344.3229 | 268973.0887 | 170754.9283 | 305159.0772 | 1047785.111 | 260565.5502 | 752582.5144 | 303096.6984 | 390111.7978 | 391603.5945 | 198348.6946 | 571466.8903 | 591138.8268 | 529521.5993 | 295711.5887 | 1480334.824 | 593645.0436 | 446960.5192 | ||
| Q9P1F3 | 2 | 1 | 99.62 | 0.51629478 | 2.206984399 | HN | XN | Costars family protein ABRACL OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABRACL PE=1 SV=1 | 288128.9 | 101286.8 | 118934.8 | 230783.8 | 116588.2097 | 324169.1942 | 369530.0957 | 323056.5886 | 302325.0913 | 205143.6501 | 224918.0456 | 212779.0287 | 181806.4414 | 103731.4781 | 148583.6584 | 2047840.888 | 98522.43704 | 91651.04757 | 137512.0651 | 101068.9573 | 343169.9909 | 250305.3693 | 148685.2672 | 136917.9993 | 170659.0483 | 117432.8153 | 96287.50326 | ||
| Q92747;O15143 | 5 | 5 | 99.59 | 0.021322691 | 1.700906542 | HN | XN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARPC1A PE=1 SV=2 | 1238713 | 1712337 | 944157.9 | 2701297 | 1797865.818 | 2201222.029 | 1678574.836 | 2009220.807 | 1863161.262 | 1426453.656 | 2109550.084 | 854960.0074 | 2533822.984 | 3333235.848 | 2606910.232 | 2530285.769 | 1474875.514 | 2239231.239 | 1242751.768 | 1223311.453 | 1438268.743 | 985529.241 | 1242678.69 | 1197662.622 | 435288.2004 | 1864227.862 | 1605069.966 | ||
| P01605 | 3 | 1 | 99.47 | 0.074340114 | 1.500653659 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region Lay OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2017004 | 3160943 | 4229468 | 4828388 | 3352700.13 | 2170779.881 | 1799989.416 | 2534514.723 | 2975816.899 | 1975846.467 | 1069772.312 | 2874110.18 | 1509886.02 | 1475766.055 | 3054910.049 | 1556429.776 | 2776609.181 | 1745210.976 | 1397637.48 | 2750191.152 | 3082473.941 | 2521610.929 | 2196656.23 | 4863576.792 | 2092160.581 | 2167677.145 | 1326797.048 | ||
| P01717 | 1 | 1 | 99.47 | 0.417705871 | 1.296447519 | HN | XN | Ig lambda chain V-IV region Hil OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 3592447 | 6432466 | 3570282 | 3576598 | 3019947.896 | 5395887.918 | 3667771.9 | 3193234.793 | 3793157.218 | 6564936.565 | 2718583.617 | 10977315.32 | 4653464.285 | 1719550.159 | 5100962.226 | 4389155.474 | 6101690.007 | 4387105.314 | 3547771.102 | 4431304.622 | 2709684.513 | 1811976.822 | 3779038.835 | 10289933.43 | 3553534.743 | 4661846.968 | 1169131.8 | ||
| Q14847 | 5 | 2 | 99.34 | 0.827329477 | 1.242869109 | XN | XA | LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LASP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 199282.6 | 122249 | 142337.2 | 427476.9 | 34225.09474 | 67871.91985 | 198779.3608 | 244994.6355 | 185941.5772 | 201278.1715 | 73588.87076 | 383678.1797 | 282226.937 | 55722.88345 | 117066.9439 | 378644.5164 | 151927.5311 | 193680.0136 | 61847.65994 | 201269.6385 | 423994.1285 | 525820.3716 | 265704.4436 | 109365.8586 | 216430.2955 | 126777.2096 | 86163.68333 | ||
| P49773 | 2 | 2 | 99.27 | 0.600189247 | 1.66018625 | XA | XN | Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HINT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 338730.3 | 35818.45 | 367688.2 | 1898951 | 514467.614 | 366998.2869 | 998601.1136 | 1776103.61 | 765878.6064 | 698301.2404 | 244611.162 | 1665418.807 | 275724.127 | 217185.4917 | 94695.37084 | 1101236.709 | 161682.9256 | 265841.9843 | 66644.94856 | 58879.57276 | 347440.4867 | 706114.5722 | 1353311.279 | 163114.1994 | 740883.6461 | 302907.9071 | 515187.9598 | ||
| Q14697 | 7 | 3 | 99.23 | 0.031875855 | 2.848051366 | XA | HN | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Homo sapiens GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=3 | 213343.4 | 82828.02 | 149525.2 | 319536.7 | 115137.7716 | 261360.8119 | 958538.1638 | 367937.8265 | 188225.3823 | 18243.88971 | 17729.40222 | 11478.68104 | 114820.8034 | 46494.98208 | 164764.5862 | 304704.3907 | 111628.0121 | 142854.8491 | 111324.4793 | 88047.16942 | 143748.7591 | 13429.2049 | 192280.3132 | 49691.54791 | 437192.9417 | 141473.9578 | 160064.2302 | ||
| P54725 | 4 | 1 | 99.21 | 0.238496307 | 1.546031558 | HN | XN | UV excision repair protein RAD23 homolog A OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAD23A PE=1 SV=1 | 131405.3 | 17443.38 | 35491.19 | 188280.4 | 32317.33218 | 97701.27739 | 86955.98826 | 170872.6062 | 133527.5073 | 126224.3106 | 69713.67027 | 364370.4802 | 126291.1162 | 98529.16249 | 66839.91224 | 127082.5894 | 101460.0152 | 101830.1175 | 47241.88081 | 60753.32138 | 182863.414 | 222890.7962 | 97057.05803 | 5782.988022 | 53189.22228 | 47477.98162 | 47502.22516 | ||
| P06734 | 7 | 4 | 98.81 | 0.456688555 | 1.352527883 | XA | HN | Low affinity immunoglobulin epsilon Fc receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCER2 PE=1 SV=1 | 197565 | 1181078 | 468242.8 | 564879.3 | 78290.63411 | 924659.4889 | 254885.8606 | 68137.27551 | 915040.3942 | 138044.1123 | 1531792.524 | 71878.26282 | 154567.7258 | 149762.3765 | 137018.4305 | 174882.5318 | 47483.07349 | 1034632.346 | 257027.9585 | 1220294.729 | 326286.1993 | 176755.3305 | 289953.2762 | 764991.7713 | 161097.9048 | 126890.8454 | 250355.657 | ||
| P0DJD8;P0DJD7;P0DJD9 | 5 | 3 | 98.72 | 0.156620865 | 1.719094867 | XA | HN | Pepsin A-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGA3 PE=1 SV=1 | 46070515 | 1.36E+08 | 74058927 | 24490266 | 51576724.78 | 110975222.9 | 20765005.67 | 37673527.93 | 38228665.04 | 12160606.08 | 14867204.05 | 43581226.77 | 24736102.79 | 50181883.92 | 59287834.71 | 45224807.88 | 36523093.38 | 27681997.33 | 69570835.91 | 38212931.36 | 45121023.49 | 59051297.45 | 27422563.56 | 119758188.5 | 87192326.4 | 37487800.88 | 23029512.29 | ||
| P04062 | 4 | 4 | 98.65 | 0.601772862 | 1.123505764 | XA | XN | Glucosylceramidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GBA PE=1 SV=3 | 992135.7 | 533942.6 | 792204.9 | 883008.5 | 625210.4235 | 708838.9888 | 701428.1032 | 948154.3081 | 516992.392 | 675028.8757 | 439292.0166 | 264477.3767 | 439341.7213 | 855641.0991 | 840102.1339 | 1165894.458 | 998075.8533 | 777550.0958 | 769006.1398 | 501491.2515 | 756865.9588 | 669544.3365 | 785378.9361 | 94236.867 | 1083513.28 | 460112.3623 | 845032.4955 | ||
| P04207 | 3 | 1 | 98.34 | 0.481096208 | 3.540791586 | XA | HN | Ig kappa chain V-III region CLL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=2 | 249967.9 | 6681.398 | 3823.998 | 24386.81 | 23165.26463 | 22212.06666 | 947.959414 | 19189.49565 | 2607.471085 | 6658.226917 | 7481.32094 | 47785.17448 | 6483.503055 | 9173.521056 | 6134.129923 | 0 | 11170.58767 | 4803.781923 | 59168.27729 | 11177.10703 | 1616.272634 | 11144.70197 | 73060.6265 | 5397.992383 | 0 | 0 | 61815.77661 | ||
| Q9HBJ8 | 2 | 2 | 98.18 | 0.979561838 | 1.045698832 | HN | XN | Collectrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMEM27 PE=1 SV=1 | 2642176 | 394618.2 | 1683725 | 1290971 | 918734.3118 | 1129164.143 | 661441.2665 | 1098255.448 | 1074539.616 | 795555.1 | 1100018.011 | 618937.1511 | 1037748.188 | 1607688.183 | 1030141.395 | 1858145.333 | 370450.2013 | 2904761.116 | 373845.9841 | 789452.7355 | 855490.6465 | 1637371.144 | 1811227.829 | 367894.6605 | 2133342.393 | 1221308.877 | 1638656.455 | ||
| Q02388 | 16 | 5 | 98.06 | 0.592078073 | 1.132035962 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL7A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2373283 | 2421376 | 1525849 | 2590202 | 2864293.091 | 2893096.695 | 1667384.149 | 2238776.042 | 1820175.953 | 3116503.074 | 2648878.05 | 3989194.125 | 2033393.051 | 1933798.76 | 3117105.275 | 2517389.301 | 1869923.662 | 1720973.372 | 2421963.466 | 1110350.75 | 2794684.724 | 3328702.554 | 2650465.793 | 2489578.589 | 1807824.274 | 1902084.62 | 1765042.835 | ||
| Q14CN4 | 7 | 3 | 97.96 | 0.646765987 | 1.245001711 | HN | XA | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 72 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT72 PE=1 SV=2 | 1029334 | 617670.8 | 681170.2 | 283829.9 | 1248795.994 | 472707.759 | 285098.5529 | 255325.6167 | 317176.1763 | 556278.3147 | 603047.2354 | 988780.9956 | 234477.4627 | 920502.795 | 1023414.591 | 1429131.09 | 479388.437 | 227918.1416 | 720125.7375 | 236887.6284 | 371935.0609 | 443704.6153 | 1289418.544 | 834361.7343 | 969847.9642 | 483121.3484 | 1070430.4 | ||
| Q6NUS6 | 3 | 3 | 97.39 | 0.952730844 | 1.103064549 | HN | XN | Tectonic-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCTN3 PE=2 SV=2 | 298115.8 | 95224.89 | 131911.7 | 268102.5 | 75285.40842 | 160351.1101 | 161342.6902 | 152761.2823 | 160780.5602 | 151451.1379 | 209822.8772 | 47463.79681 | 338063.9559 | 365917.8629 | 105979.5949 | 49421.87913 | 166734.5959 | 217473.259 | 226706.3874 | 115631.4646 | 205696.9987 | 124804.9188 | 226441.1267 | 118495.1769 | 123370.4249 | 189124.4061 | 167673.1292 | ||
| P49184 | 2 | 2 | 97.2 | 0.767912145 | 1.702684656 | XA | HN | Deoxyribonuclease-1-like 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNASE1L1 PE=1 SV=1 | 517002.9 | 31676.01 | 118704.6 | 437522 | 30663.42389 | 253214.9673 | 423109.1323 | 256629.9297 | 549301.6597 | 122491.0441 | 247307.5452 | 110732.7547 | 449125.6996 | 66326.04278 | 155853.1627 | 159649.4847 | 124505.2695 | 101477.8296 | 176698.8625 | 119017.3168 | 201863.0775 | 126485.2288 | 453168.9194 | 43355.28076 | 211879.0476 | 256978.2925 | 269158.6516 | ||
| Q16698 | 3 | 1 | 96.94 | 0.2100318 | 1.776427426 | HN | XA | 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=DECR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 59067.18 | 2167.703 | 58288.53 | 6550.033 | 5253.264449 | 122137.2343 | 35773.21907 | 70059.0776 | 33430.71814 | 119187.4287 | 167034.0887 | 192788.6831 | 39415.09122 | 132362.3743 | 28337.91504 | 3480.552681 | 9131.855224 | 5912.943748 | 375532.5313 | 19954.91486 | 18664.5533 | 65185.44428 | 85.59739533 | 188.9976112 | 11634.80846 | 7129.504651 | 4614.213197 | ||
| P01610 | 4 | 2 | 96.93 | 0.508692908 | 1.367058394 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-I region WEA OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1361885 | 1591769 | 1081612 | 917666 | 3693341.24 | 925718.4017 | 459082.703 | 938738.7939 | 1788368.4 | 751631.0059 | 572475.2695 | 2133389.553 | 1546573.403 | 717651.3185 | 1987690.459 | 1600157.708 | 1428678.375 | 1516047.653 | 1374796.85 | 1020028.706 | 611224.6236 | 786937.0494 | 950162.0528 | 1767097.109 | 1173725.317 | 1145440.424 | 503167.5203 | ||
| Q5TZA2 | 24 | 4 | 96.81 | 0.801484417 | 2.023158777 | XN | HN | Rootletin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CROCC PE=1 SV=1 | 449471.7 | 406354.9 | 245306.6 | 255176.7 | 292014.679 | 6127421.625 | 7086765.625 | 5428762.822 | 3510162.834 | 286996.2834 | 7496812.706 | 6062235.71 | 1930007.329 | 324998.4399 | 374975.6344 | 144675.2728 | 104760.9679 | 676069.1802 | 397997.61 | 11750525.13 | 3499157.672 | 18041185.13 | 300349.7351 | 308825.4754 | 448023.2349 | 263249.7671 | 196747.4788 | ||
| Q9Y2T3 | 4 | 3 | 96.35 | 0.504163617 | 1.93874996 | XA | HN | Guanine deaminase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GDA PE=1 SV=1 | 103117.9 | 29278.39 | 111344.8 | 165242.6 | 64737.51469 | 287590.8586 | 629619.0918 | 400345.2934 | 54826.31875 | 175364.6672 | 84159.50519 | 106918.2481 | 21008.68428 | 209588.717 | 55955.05931 | 114207.8756 | 126869.9338 | 58140.20136 | 194843.9082 | 71104.39163 | 139853.3057 | 114314.028 | 68174.40945 | 221087.6348 | 76644.19864 | 43930.71599 | 97106.07498 | ||
| O60234 | 2 | 2 | 96.33 | 0.052195611 | 13.31977348 | HN | XN | Glia maturation factor gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=GMFG PE=1 SV=1 | 120539.1 | 52676.61 | 40449.56 | 30536.62 | 232650.3312 | 23206.17443 | 92043.12908 | 57627.67754 | 18582.92351 | 45886.04559 | 31606.80098 | 140102.902 | 223490.9294 | 52189.83264 | 69023.81673 | 2648621.507 | 10676.78957 | 28316.90037 | 37698.28556 | 26156.00353 | 2801.160614 | 77356.62397 | 19282.67487 | 17131.75681 | 15118.0148 | 24140.29422 | 24306.98685 | ||
| P0C7U0 | 3 | 1 | 95.33 | 0.169513643 | 1.481237083 | XA | HN | Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 28 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ELFN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 115055.2 | 110508.8 | 60751.12 | 71965.72 | 66398.2788 | 145268.7475 | 65470.68387 | 160446.5756 | 205423.592 | 7887.149246 | 141453.1087 | 89340.94387 | 50555.19607 | 165883.816 | 55003.50871 | 16465.84656 | 102017.2474 | 47374.59199 | 33522.49963 | 145289.874 | 87614.23612 | 33799.46532 | 53417.47558 | 70708.58144 | 66175.18561 | 141821.3319 | 56683.45977 | ||
| P07942 | 10 | 5 | 95.02 | 0.335715635 | 1.332872303 | XA | HN | Laminin subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 523452.3 | 1135687 | 592651.7 | 666350.4 | 710354.544 | 2068338.933 | 1183367.76 | 800350.2892 | 1426419.37 | 857052.2592 | 1091924.039 | 1614146.167 | 832067.5241 | 365323.093 | 776001.7255 | 354540.6257 | 452045.5613 | 489490.4924 | 1154160.389 | 2131407.357 | 1558237.407 | 834976.5679 | 584488.6132 | 762448.4633 | 460020.7032 | 738007.871 | 754379.8017 | ||
| P46926 | 3 | 1 | 94.73 | 0.188212221 | 2.480459402 | XA | HN | Glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNPDA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 73011.88 | 19180.78 | 10961.09 | 91180.33 | 53830.52983 | 184072.4643 | 366647.1657 | 269492.0387 | 102186.4807 | 28083.9426 | 6835.110443 | 49101.35606 | 150816.9907 | 52226.59596 | 34798.90263 | 39624.11138 | 44628.01531 | 65798.67051 | 183634.7677 | 63522.47153 | 167610.9559 | 262935.0207 | 69037.48131 | 90109.26542 | 45002.82586 | 39421.01871 | 38684.2729 | ||
| Q9UKK9 | 2 | 2 | 94.72 | 0.999623751 | 1.523794515 | XN | XA | ADP-sugar pyrophosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUDT5 PE=1 SV=1 | 158239.1 | 54950.63 | 73031.61 | 245474.8 | 63492.662 | 203924.7675 | 502690.2942 | 287926.752 | 382693.0622 | 227169.0733 | 345449.285 | 455361.9448 | 459325.4871 | 409082.391 | 40257.83102 | 28100.70212 | 59688.03598 | 267127.5745 | 355160.2886 | 60599.86951 | 165352.592 | 1815467.093 | 202456.7248 | 142282.234 | 101309.5699 | 82560.49342 | 80379.61117 | ||
| O60911 | 4 | 3 | 94.41 | 0.329681242 | 4.009600535 | XN | HN | Cathepsin L2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 54602.87 | 103899.2 | 48000.91 | 67108.97 | 36097.06566 | 540571.0965 | 915928.5466 | 455562.1054 | 175315.496 | 36010.8134 | 25952.3232 | 78237.73826 | 144412.2361 | 52480.40847 | 19716.26648 | 212713.5256 | 66786.42853 | 39843.96825 | 649164.7639 | 1279185.147 | 144328.8035 | 391320.4545 | 119513.5667 | 36641.23172 | 46419.12112 | 40752.03478 | 3781.148007 | ||
| O14908 | 3 | 1 | 93.95 | 0.990799249 | 7.097721341 | HN | XA | PDZ domain-containing protein GIPC1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GIPC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0 | 4496.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8535.613676 | 49412.34737 | 57560.68193 | 12950.98225 | 0 | 14107.47316 | 0 | 3182.979727 | 4507.695464 | 0 | 0 | 921573.7196 | 315.0766681 | 3964.111086 | 56122.22588 | 14887.65005 | 172243.1524 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 351.489918 | ||
| P60983 | 1 | 1 | 93.85 | 0.587150873 | 1.517769481 | XA | HN | Glia maturation factor beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=GMFB PE=1 SV=2 | 46626.27 | 47516.06 | 8794.338 | 104228.3 | 74714.05261 | 263080.4332 | 353889.2772 | 185721.4545 | 126591.5521 | 103973.839 | 107793.7259 | 16794.61041 | 309743.1477 | 92348.27227 | 30742.77507 | 97932.09623 | 3673.170728 | 34986.30254 | 254008.2573 | 79830.48881 | 164016.7876 | 463922.8505 | 25919.43669 | 88741.42691 | 29889.76368 | 39460.81671 | 18567.47567 | ||
| P35749 | 13 | 2 | 93.14 | 0.37472347 | 1.19807738 | XA | HN | Myosin-11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH11 PE=1 SV=3 | 3864254 | 2058958 | 3142901 | 3470769 | 1923210.136 | 2688895.796 | 3655072.109 | 3472518.201 | 2621804.275 | 3005743.499 | 1452285.085 | 1354686.456 | 1109777.127 | 3208604.212 | 2114109.173 | 2414983.344 | 3541112.437 | 4249987.874 | 3087702.716 | 2309983.838 | 3899453.42 | 3775258.348 | 3063586.473 | 1301226.34 | 1818929.471 | 2649365.658 | 4070889.518 | ||
| Q7Z7D3 | 2 | 2 | 93.09 | 0.939554964 | 1.432627599 | XA | HN | V-set domain-containing T-cell activation inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTCN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1424122 | 105213.4 | 1445177 | 1173477 | 71951.50463 | 81912.85242 | 389318.3849 | 1601423.982 | 656258.9979 | 60831.14018 | 470045.1595 | 348843.3236 | 906515.7624 | 702952.6561 | 611295.5093 | 1435766.317 | 152968.3328 | 161208.6515 | 207658.7667 | 352126.3957 | 286288.598 | 202753.1725 | 1227421.015 | 213084.0967 | 1483346.497 | 525274.9207 | 512417.5988 | ||
| P01225 | 2 | 2 | 92.77 | 0.551189583 | 2.199583339 | XA | HN | Follitropin subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=FSHB PE=1 SV=2 | 11370.27 | 337607.7 | 108264.2 | 33916.31 | 10533.16304 | 735764.5783 | 185699.4299 | 137910.6536 | 431840.5744 | 61271.58242 | 190635.3309 | 98424.00891 | 95564.03788 | 200123.1827 | 57437.54056 | 17733.1237 | 96382.96877 | 88466.5907 | 187886.2937 | 267003.1858 | 75862.60535 | 219258.6469 | 61438.82187 | 306402.9046 | 188407.5817 | 91044.7002 | 89568.76375 | ||
| Q9BXS4 | 1 | 1 | 92.24 | 0.330299118 | 1.424628501 | HN | XA | Transmembrane protein 59 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMEM59 PE=1 SV=1 | 202638.3 | 59128.95 | 183382.5 | 587630.2 | 362511.2515 | 265785.6045 | 287418.2907 | 335900.1677 | 174885.6751 | 325761.2078 | 231555.8828 | 154772.441 | 347125.1768 | 552047.9222 | 111479.3964 | 917680.6493 | 369903.7473 | 493235.2354 | 273940.4756 | 386248.4178 | 426929.4624 | 138452.8868 | 246767.3421 | 689311.0608 | 513649.2914 | 368462.7259 | 360874.5864 | ||
| P26447 | 4 | 1 | 92.12 | 0.346812805 | 1.357272549 | HN | XA | Protein S100-A4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A4 PE=1 SV=1 | 159058.2 | 59552.94 | 18122.99 | 67273.91 | 30434.83132 | 131849.2262 | 332804.0863 | 174559.4237 | 711561.0308 | 878115.2503 | 183329.9501 | 375696.9635 | 81729.01937 | 81053.36017 | 310499.0264 | 51152.44094 | 189671.349 | 136050.8762 | 1514204.722 | 92787.89103 | 152939.9822 | 48617.73954 | 17928.71374 | 11288.80843 | 117856.1325 | 48409.53981 | 90856.31892 | ||
| Q7Z3Z0 | 4 | 1 | 92.09 | 0.000285638 | 2.133015819 | XA | XN | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 25 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT25 PE=1 SV=1 | 327487.8 | 369663.4 | 388836.7 | 282967.2 | 189699.4758 | 336630.153 | 369465.1277 | 481044.762 | 243592.4644 | 114637.9994 | 215698.5768 | 198204.131 | 236507.0924 | 115421.593 | 217951.635 | 71144.27256 | 114440.9698 | 164832.0725 | 88504.27765 | 216273.9125 | 114494.7524 | 89468.36795 | 192298.3498 | 63534.44485 | 241393.4489 | 160846.8011 | 234669.4113 | ||
| Q7Z3Y8 | 3 | 1 | 92.07 | 0.355063985 | 1.489593077 | XN | XA | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT27 PE=1 SV=2 | 438006.3 | 505618.7 | 412351.8 | 455539.6 | 267876.9481 | 620002.4535 | 594575.24 | 286696.0863 | 335182.4322 | 277306.8115 | 1801999.827 | 172321.6566 | 1037761.598 | 414828.3328 | 209703.2995 | 77481.00421 | 368867.2329 | 987173.5889 | 455569.8488 | 755896.5474 | 868932.9832 | 449740.5262 | 397127.1854 | 929198.8588 | 350296.1397 | 1151306.254 | 474954.137 | ||
| Q04760 | 3 | 2 | 91.91 | 0.792572023 | 1.207239579 | HN | XN | Lactoylglutathione lyase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLO1 PE=1 SV=4 | 814350.8 | 226361 | 306842.1 | 269178.2 | 527105.4746 | 269712.5428 | 449911.6322 | 658022.5238 | 379128.8129 | 670349.697 | 636010.7018 | 331064.3923 | 316543.5311 | 484878.763 | 715657.3157 | 148846.6504 | 306575.2748 | 650201.2259 | 342480.0644 | 434011.2399 | 798641.9596 | 405634.9867 | 237322.2634 | 274909.1586 | 376291.3823 | 289397.3163 | 370128.6309 | ||
| Q6ZN66 | 7 | 1 | 91.83 | 0.914688592 | 5.51687582 | XA | HN | Guanylate-binding protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GBP6 PE=2 SV=1 | 886.9675 | 0 | 50.76092 | 42.80392 | 0 | 7857.917201 | 25643.90427 | 92871.41695 | 39995.50476 | 7157.057356 | 3246.708588 | 4330.792735 | 12656.69171 | 1860.726743 | 933.8788377 | 24.97013678 | 0.394564939 | 122.8453817 | 16785.69972 | 2044.636989 | 1132.040234 | 5052.333039 | 0 | 707.737865 | 1980.841372 | 533.4925006 | 3607.527627 | ||
| P01178 | 1 | 1 | 91.75 | 0.858479755 | 2.54554738 | HN | XA | Oxytocin-neurophysin 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=OXT PE=1 SV=1 | 306092.3 | 56449.05 | 214104.3 | 181278.5 | 259020.5365 | 194232.0258 | 153994.0286 | 231303.2462 | 222666.9255 | 295941.1393 | 227240.6247 | 42682.81472 | 202381.6171 | 77812.96156 | 99872.43887 | 2997932.863 | 207670.4744 | 479174.5913 | 617095.3337 | 174978.0148 | 99391.23182 | 180482.0306 | 424644.6562 | 289422.0963 | 206649.0234 | 169890.6822 | 180249.1413 | ||
| Q9BW04 | 4 | 4 | 91.69 | 0.382294942 | 1.202755214 | HN | XN | Specifically androgen-regulated gene protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SARG PE=1 SV=2 | 359614.1 | 290371.2 | 1071363 | 863355.5 | 496140.9404 | 282151.7433 | 648719.9431 | 1570802.409 | 469060.2528 | 507193.1749 | 882717.1915 | 1479031.075 | 692379.4565 | 990773.3321 | 752185.3441 | 568843.8233 | 344678.5726 | 289988.1033 | 65879.3992 | 1771107.596 | 799545.6425 | 995226.7188 | 780708.7053 | 225143.1583 | 234372.325 | 217470.3862 | 321281.3501 | ||
| Q9HCE6 | 7 | 3 | 91.53 | 0.055775846 | 3.067138382 | XA | HN | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 10-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARHGEF10L PE=1 SV=3 | 297468.6 | 21695.02 | 195995.8 | 800918.5 | 138222.2566 | 305265.9683 | 223969.6231 | 529191.7036 | 360235.758 | 45478.44722 | 30465.86567 | 129472.5394 | 200831.4606 | 20581.56406 | 122186.6834 | 195395.4772 | 67184.56042 | 125095.1406 | 54114.2368 | 82824.31177 | 133984.6677 | 44061.61511 | 421117.767 | 132202.5113 | 204559.3838 | 265309.6941 | 163043.5643 | ||
| Q9NVS9 | 4 | 3 | 91.33 | 0.119246867 | 2.756416401 | XA | HN | Pyridoxine-5'-phosphate oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PNPO PE=1 SV=1 | 1125970 | 52900.83 | 542479.5 | 2355949 | 264717.6437 | 559642.9878 | 751483.6294 | 1621290.93 | 592077.1398 | 221925.3946 | 351610.281 | 889220.4693 | 359465.4716 | 102147.3593 | 156221.2533 | 356402.4363 | 139304.7257 | 277593.8159 | 166704.0333 | 319959.44 | 1022655.09 | 559471.3617 | 375412.7619 | 365673.8814 | 505282.3287 | 306009.9536 | 288888.1258 | ||
| Q8IZJ3 | 9 | 5 | 91.23 | 0.24098583 | 1.284429347 | XN | HN | C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPAMD8 PE=1 SV=2 | 4124277 | 10020601 | 5518715 | 4828791 | 4954316.682 | 4398210.972 | 6466071.886 | 4764785.372 | 6395680.56 | 5213269.672 | 9982560.01 | 5323937.501 | 10690144.17 | 3921071.564 | 3267933.701 | 5968678.574 | 3089434.27 | 3959767.214 | 4291305.291 | 5439881.76 | 8538661.724 | 5928844.1 | 6071742.926 | 13150414.1 | 10693009.26 | 6222935.418 | 5704448.028 | ||
| P01229 | 2 | 1 | 90.97 | 0.666803785 | 1.545741803 | XN | HN | Lutropin subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=LHB PE=1 SV=3 | 654475.3 | 418239.7 | 1301330 | 2160042 | 1660032.177 | 1159652.691 | 3182203.864 | 1437086.223 | 6146097.218 | 1276326.931 | 1468804.233 | 1089429.375 | 5455246.7 | 1324199.712 | 517154.3658 | 1812411.446 | 1100316.057 | 518889.2487 | 984757.2094 | 8547635.061 | 3639995.625 | 385798.7752 | 1585378.659 | 2318238.607 | 2277453.974 | 932683.6801 | 1838353.234 | ||
| Q96MU8 | 5 | 4 | 90.87 | 0.114369957 | 1.823305282 | XN | HN | Kremen protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KREMEN1 PE=2 SV=3 | 780006.4 | 409660.6 | 756456.8 | 369910.5 | 1045597.407 | 1187838.614 | 793425.8601 | 618239.5516 | 894904.5745 | 345625.4864 | 863504.9157 | 225450.7539 | 904314.4889 | 1575716.243 | 114658.5713 | 841508.0882 | 440219.1157 | 765146.7862 | 1204155.923 | 3339820.26 | 1013546.117 | 619940.5231 | 490181.4798 | 1413940.645 | 480121.5773 | 795047.4508 | 1721912.29 | ||
| O60664 | 4 | 2 | 90.28 | 0.356430126 | 2.113882621 | XA | XN | Perilipin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLIN3 PE=1 SV=3 | 85769.98 | 31138.03 | 59782.2 | 92852.87 | 400107.6223 | 172530.1579 | 890359.5739 | 908284.4608 | 378970.1338 | 693382.8251 | 346710.1083 | 1053728.912 | 261090.7437 | 26944.50308 | 73522.35135 | 106134.7297 | 30612.39265 | 64934.92602 | 69057.38353 | 456525.2973 | 396154.806 | 325834.7271 | 67601.28792 | 24864.59701 | 45248.81499 | 18261.23342 | 25005.6428 | ||
| O00253 | 2 | 1 | 90.17 | 0.743517535 | 1.750596677 | XA | XN | Agouti-related protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGRP PE=1 SV=1 | 223299.6 | 39729.57 | 60286.26 | 0 | 24259.87927 | 87868.62862 | 51291.54782 | 250598.4043 | 104305.3742 | 31148.75941 | 35915.40303 | 24863.34147 | 75995.92748 | 8692.099524 | 31500.701 | 165337.7503 | 110550.8383 | 117835.6667 | 0 | 38016.29951 | 118281.7824 | 60197.74396 | 46932.11213 | 19818.84096 | 54008.39116 | 89092.52091 | 54425.08671 | ||
| P25788 | 5 | 1 | 89.79 | 0.360278947 | 1.102057497 | HN | XN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA3 PE=1 SV=2 | 57506.38 | 33986.57 | 30986.7 | 6214.914 | 38462.10028 | 97892.48614 | 199692.6022 | 145638.605 | 189524.4315 | 114667.7891 | 139184.0162 | 80853.95966 | 208393.2664 | 60763.68452 | 68110.53562 | 90806.25016 | 30394.19379 | 39789.6327 | 432348.4319 | 21536.86278 | 84315.60529 | 88452.30392 | 64978.2191 | 17782.18623 | 7920.411794 | 17815.89881 | 20675.73417 | ||
| Q9BTM9 | 2 | 1 | 89.33 | 0.897600986 | 1.718726835 | HN | XN | Ubiquitin-related modifier 1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=URM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 406726 | 706094.9 | 883797.7 | 530980.2 | 223914.4697 | 285885.4673 | 210015.2972 | 342000.3938 | 109625.3901 | 555066.3041 | 253471.7928 | 384252.5186 | 130390.1403 | 407089.6727 | 13959.39606 | 2194799.747 | 609398.7347 | 479907.6037 | 143237.9897 | 168392.7177 | 82082.75253 | 399602.854 | 315202.5418 | 387578.5158 | 528583.9897 | 395127.8629 | 505807.4637 | ||
| Q15833 | 10 | 2 | 89.07 | 0.518873397 | 1.382002538 | HN | XN | Syntaxin-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STXBP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 773091.8 | 864169 | 1142057 | 806384.5 | 551271.5064 | 907881.0813 | 1014703.299 | 906107.7661 | 1392359.84 | 545214.2498 | 1060110.487 | 4249699.684 | 714347.4649 | 677781.4056 | 595578.9793 | 195762.9303 | 712898.3454 | 746421.9374 | 1698260.465 | 1138236.174 | 710701.3708 | 309069.3868 | 675592.5532 | 1010455.846 | 608499.978 | 481393.0888 | 240293.3348 | ||
| Q9BWD1 | 3 | 3 | 88.89 | 0.403496961 | 2.850413856 | XA | HN | Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, cytosolic OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACAT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 841196.9 | 836265 | 866485.1 | 966914.4 | 4165771.115 | 19941108.26 | 18583470.06 | 5095205.339 | 8262601.983 | 4626909.325 | 727249.1574 | 2364166.429 | 1027072.706 | 421826.5216 | 1241773.456 | 8329190.789 | 1508956.739 | 647721.7871 | 26269769.02 | 4617674.873 | 1140458.043 | 2807144.076 | 5109656.649 | 864158.601 | 908145.1726 | 365287.097 | 610097.4883 | ||
| Q9P283 | 3 | 1 | 88.87 | 0.953760753 | 4.443965223 | XA | XN | Semaphorin-5B OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMA5B PE=2 SV=4 | 22247.67 | 1944783 | 143186.4 | 10800.63 | 1370715.902 | 125479.0918 | 10154.4073 | 12470.27352 | 0 | 140900.209 | 0 | 24722.09864 | 0 | 98451.73103 | 993535.223 | 42966.43456 | 933093.6046 | 461349.3494 | 26426.31468 | 37397.47526 | 92223.01264 | 104336.2803 | 385786.9633 | 121505.1133 | 0 | 13706.40381 | 37670.04637 | ||
| P84243;P68431;Q16695;Q6NXT2;Q71DI3 | 6 | 1 | 88.6 | 0.668110358 | 3.481814291 | XN | HN | Histone H3.3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=H3F3A PE=1 SV=2 | 4364.731 | 3587.406 | 3243.929 | 19924.36 | 13814.507 | 216956.3173 | 4080.721218 | 12995.28083 | 79296.32665 | 4292.680184 | 3609.627212 | 1876.53667 | 6499.851499 | 6719.343772 | 31447.1299 | 26560.58454 | 8604.163774 | 14925.05995 | 299266.2666 | 11156.97456 | 5753.502321 | 23504.75957 | 2721.820891 | 3003.816264 | 15991.28544 | 1297.952289 | 1275.000634 | ||
| P03951 | 4 | 2 | 88.29 | 0.170789349 | 1.490756546 | XA | HN | Coagulation factor XI OS=Homo sapiens GN=F11 PE=1 SV=1 | 443698 | 311903.5 | 322596.2 | 166613.4 | 285469.4163 | 186239.5161 | 181233.0234 | 222575.6353 | 115417.379 | 91326.96162 | 116836.1766 | 85235.5843 | 240755.7516 | 115259.2746 | 281154.6832 | 251562.1701 | 202958.9526 | 114649.6557 | 95534.85129 | 182472.2718 | 98636.38154 | 38839.46804 | 215745.7385 | 61623.08645 | 467363.2396 | 197400.8905 | 273930.5894 | ||
| O75347 | 3 | 2 | 87.81 | 0.839454255 | 1.268440122 | HN | XA | Tubulin-specific chaperone A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TBCA PE=1 SV=3 | 366791 | 58380.36 | 82755.91 | 110399.5 | 110422.4945 | 343097.3976 | 451522.1188 | 709818.9435 | 255004.7942 | 695438.5902 | 771336.1767 | 405554.6288 | 349265.4626 | 455207.1564 | 74532.88446 | 73810.41268 | 153696.1777 | 177281.6452 | 388494.8537 | 152958.2475 | 809949.8272 | 509453.3397 | 293925.3421 | 142922.6307 | 178148.0792 | 149773.6867 | 54075.13106 | ||
| Q16787 | 16 | 7 | 87.79 | 0.569588064 | 1.420171741 | XN | HN | Laminin subunit alpha-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMA3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1053218 | 4162279 | 2095475 | 289489.4 | 389051.1315 | 2768393.353 | 6714091.127 | 2051014.656 | 3683868.521 | 1745946.972 | 2496896.402 | 3763797.641 | 781991.9963 | 1722763.719 | 1742516.857 | 1225808.748 | 482263.2824 | 2481552.758 | 3192540.974 | 2291774.168 | 4219155.855 | 2306307.061 | 934145.4529 | 4206280.233 | 3508482.454 | 1300680.441 | 1393281.884 | ||
| Q9Y6W3 | 3 | 2 | 87.72 | 0.039020373 | 1.792028849 | XA | HN | Calpain-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPN7 PE=1 SV=1 | 130979.4 | 50159.73 | 79231.41 | 64485.57 | 60581.74867 | 78450.14658 | 96721.68223 | 98445.9091 | 68530.76146 | 17266.59469 | 77407.08691 | 29940.86523 | 34923.27582 | 148948.4314 | 16912.49426 | 44930.45286 | 16589.98361 | 19093.44152 | 70967.09904 | 47403.81696 | 47968.48191 | 19507.83421 | 24728.33075 | 30536.59511 | 117602.6887 | 88348.86563 | 250571.7478 | ||
| P51149 | 3 | 3 | 87.52 | 0.321883871 | 2.000840289 | HN | XN | Ras-related protein Rab-7a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB7A PE=1 SV=1 | 308222.6 | 127871.2 | 145848.9 | 172120.1 | 52601.92381 | 137544.1642 | 256595.599 | 238226.6331 | 190590.1452 | 461103.5751 | 680623.0454 | 326709.0995 | 165785.6519 | 503685.0743 | 146700.9767 | 86519.47432 | 80951.31891 | 66825.29862 | 234545.9105 | 96656.08184 | 230097.4254 | 138685.1741 | 95511.27114 | 63168.71061 | 71581.06654 | 178826.3414 | 149850.8462 | ||
| Q9HC56 | 2 | 1 | 87.35 | 0.084001707 | 2.040651339 | HN | XA | Protocadherin-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDH9 PE=1 SV=2 | 65626.91 | 26441.52 | 37097.73 | 104150.8 | 63043.93675 | 37433.83261 | 15107.34229 | 24696.83632 | 48997.16638 | 140694.1587 | 192489.2159 | 31359.36825 | 79417.15246 | 63732.33516 | 57044.72581 | 59113.70278 | 199221.4203 | 39299.26305 | 59225.69677 | 37471.89997 | 44748.86669 | 116842.7657 | 114881.2455 | 162881.2728 | 23539.27336 | 88400.94204 | 59687.10537 | ||
| Q11201 | 2 | 1 | 87.3 | 0.072813614 | 2.689131713 | XA | HN | CMP-N-acetylneuraminate-beta-galactosamide-alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ST3GAL1 PE=2 SV=1 | 131581.1 | 28498.95 | 30052.46 | 87374.04 | 33260.56153 | 38712.21539 | 43039.6004 | 43500.32644 | 44343.54341 | 0 | 7982.476892 | 28138.66664 | 233.4680186 | 16716.52462 | 35121.34601 | 51576.48223 | 31764.36737 | 7097.865021 | 15826.91731 | 15589.31956 | 15504.59762 | 5251.352639 | 41030.44155 | 6718.912389 | 81605.42783 | 37990.59013 | 32841.61485 | ||
| O75531 | 4 | 3 | 87.27 | 0.164725384 | 5.970034974 | HN | XN | Barrier-to-autointegration factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=BANF1 PE=1 SV=1 | 291611.3 | 332344.2 | 471473.4 | 986187.3 | 318101.1028 | 49227.05989 | 158287.7726 | 278749.4645 | 167902.2825 | 10759.26642 | 135750.98 | 1057846.531 | 81436.83356 | 224250.3932 | 418306.4088 | 4334527.261 | 195247.741 | 195932.8114 | 71884.53554 | 56512.05396 | 73416.91572 | 70779.62332 | 265074.8991 | 282614.4075 | 149893.2314 | 27851.13158 | 116549.29 | ||
| Q13162 | 3 | 1 | 87.15 | 0.672975868 | 11.32654129 | XN | HN | Peroxiredoxin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX4 PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4646.966 | 10429.25414 | 0 | 16639.99979 | 21083.008 | 59005.93436 | 0 | 3593.377576 | 5538.763401 | 7860.291357 | 0 | 6318.743578 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 248455.5937 | 0 | 6143.759519 | 0 | 0 | 9435.64333 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P22607 | 6 | 3 | 87.11 | 0.675534315 | 1.473070306 | HN | XN | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGFR3 PE=1 SV=1 | 682854.9 | 384846 | 630945.1 | 493059.4 | 463688.311 | 940932.2493 | 1400076.397 | 542526.5503 | 1509899.928 | 456445.428 | 1186891.595 | 3888172.576 | 465755.8363 | 297352.9114 | 519824.7609 | 173433.8642 | 353874.7594 | 561071.4041 | 876131.506 | 833828.6707 | 535871.8486 | 580979.8599 | 249984.628 | 452840.6345 | 435497.6245 | 492256.451 | 907473.6452 | ||
| Q04917 | 6 | 1 | 87.02 | 0.086538544 | 3.373574155 | HN | XA | 14-3-3 protein eta OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAH PE=1 SV=4 | 92001.52 | 644770.6 | 122763.7 | 111985.9 | 286529.8253 | 95087.75095 | 157113.0794 | 194913.319 | 223589.3747 | 454501.5527 | 712510.2024 | 212634.9327 | 226293.7577 | 423294.8924 | 468896.5106 | 3493473.792 | 370830.1917 | 144362.743 | 119120.2232 | 242959.0778 | 170982.0187 | 347429.7889 | 468159.4944 | 2743235.601 | 453189.4468 | 198916.8054 | 144464.9956 | ||
| P05026 | 3 | 2 | 86.77 | 0.989938869 | 1.03969416 | HN | XN | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP1B1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1742742 | 768072.1 | 1288662 | 930752.2 | 543824.5519 | 814373.8056 | 1005947.311 | 1120463.706 | 913803.3837 | 1144324.298 | 1574942.72 | 941911.8381 | 1531249.569 | 1538532.304 | 534259.2278 | 395443.5302 | 886931.0444 | 830852.1275 | 775815.3506 | 1173015.094 | 1046960.772 | 498292.5326 | 1105634.302 | 605833.9194 | 1117272.876 | 906836.0781 | 1790728.936 | ||
| P18827 | 1 | 1 | 86.7 | 0.041084098 | 8.555178104 | XA | HN | Syndecan-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 130072.3 | 1356087 | 599722.2 | 346423.3 | 460466.9863 | 635956.2158 | 4186117.523 | 792459.5028 | 14088491.18 | 71639.70087 | 123647.8602 | 163474.4823 | 718356.9354 | 205141.2102 | 352518.6616 | 300165.4713 | 394500.9239 | 311738.3696 | 80750.07244 | 505578.9112 | 479787.9652 | 389558.756 | 418362.6775 | 2264006.457 | 629010.1471 | 2322129.703 | 516590.0419 | ||
| Q9UPN3 | 42 | 9 | 86.65 | 0.339008216 | 1.155300689 | XA | HN | Microtubule-actin cross-linking factor 1, isoforms 1/2/3/5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MACF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 3784220 | 5322891 | 5255617 | 4440168 | 5220461.324 | 5404042.602 | 5124252.715 | 2924138.832 | 4224666.672 | 2183549.962 | 2624497.068 | 4080665.403 | 2143362.982 | 2621665.876 | 7736721.528 | 8418282.245 | 3451331.38 | 2834818.412 | 3089827.383 | 6800085.207 | 3485559.701 | 3768757.54 | 4617505.758 | 2698990.624 | 3477578.839 | 3223152.969 | 5604328.897 | ||
| P10586 | 10 | 6 | 85.94 | 0.916409657 | 1.15640827 | HN | XA | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRF PE=1 SV=2 | 963862 | 1452924 | 1666056 | 827528.8 | 866429.1079 | 1656548.588 | 2018931.316 | 1107762.55 | 1901701.221 | 925953.1075 | 2810429.566 | 2481168.168 | 2206630.598 | 1816979.573 | 1463467.566 | 560712.4301 | 1077978.709 | 1067543.034 | 1239336.841 | 2416367.712 | 1104676.474 | 698536.5808 | 935214.8789 | 2376005.248 | 1566477.128 | 1535919.703 | 1714492.334 | ||
| P55017 | 3 | 2 | 85.89 | 0.78182912 | 1.969946625 | HN | XA | Solute carrier family 12 member 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC12A3 PE=1 SV=3 | 669573.9 | 39330.58 | 11517.01 | 30379.97 | 87798.56072 | 134014.2817 | 194735.5152 | 92422.63303 | 112266.2157 | 1322243.044 | 51850.24025 | 206696.931 | 177922.5988 | 688015.903 | 40887.61025 | 16618.17122 | 163098.0895 | 35510.41742 | 295122.5932 | 41495.87473 | 432860.9032 | 72135.1237 | 22408.4405 | 19929.25855 | 19106.04144 | 177757.3862 | 408427.7347 | ||
| O75631 | 4 | 2 | 85.76 | 0.195192724 | 1.948273024 | XN | XA | Uroplakin-3a OS=Homo sapiens GN=UPK3A PE=1 SV=3 | 591010.1 | 183475.8 | 49838.63 | 422694.7 | 460133.7709 | 416982.6754 | 481161.3193 | 267115.7953 | 247460.5831 | 466118.3002 | 147685.3907 | 172962.9201 | 248512.7407 | 804478.2582 | 452106.758 | 1107061.178 | 337378.5491 | 358351.8887 | 746685.9929 | 1057063.644 | 639352.4433 | 312724.6826 | 230738.4225 | 1639056.734 | 225494.1108 | 320516.756 | 906732.1678 | ||
| O75629 | 2 | 1 | 85.61 | 0.972303905 | 1.048764451 | HN | XA | Protein CREG1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CREG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2200364 | 1662191 | 2637732 | 4297559 | 1888864.501 | 2584821.13 | 1709785.646 | 2830563.204 | 2707706.847 | 2670331.507 | 859047.6408 | 3201217.194 | 5507228.886 | 1781350.289 | 3446264.125 | 2224714.971 | 1801908.163 | 2125680.676 | 3299588.595 | 1702487.03 | 2847344.909 | 3341571.422 | 3156798.551 | 1226095.763 | 2417668.053 | 2703554.106 | 2327372.964 | ||
| P43628;P43629;P43631;Q14943;Q14953 | 4 | 1 | 85.59 | 0.01859422 | 4.55143013 | XA | XN | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIR2DL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 11990.95 | 77359.6 | 39416.69 | 44415.38 | 45980.23521 | 234885.6646 | 347352.8054 | 69798.96191 | 39099.06884 | 39649.52064 | 40259.87935 | 190184.2368 | 39291.71098 | 17398.20661 | 38367.00852 | 47427.37926 | 10831.62355 | 28795.65796 | 36881.6769 | 10139.93994 | 7800.472152 | 26764.01051 | 25708.89612 | 16492.31151 | 29600.81408 | 25254.01905 | 21360.78851 | ||
| Q10567 | 5 | 2 | 85.54 | 0.026693041 | 2.314923059 | XN | HN | AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AP1B1 PE=1 SV=2 | 123650.9 | 65394.85 | 64511.22 | 238153.8 | 568680.1783 | 520650.1346 | 219342.7442 | 613625.513 | 339108.263 | 249635.9957 | 19329.1406 | 228742.3666 | 117800.5295 | 116750.2584 | 96503.00885 | 92371.62014 | 124294.3433 | 175478.7094 | 491495.4121 | 369590.8953 | 310769.264 | 178115.3994 | 215852.5517 | 240390.0681 | 146362.3759 | 358447.9976 | 515279.4241 | ||
| Q9UBX1 | 6 | 4 | 85.4 | 0.210879123 | 1.708976304 | XN | HN | Cathepsin F OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSF PE=1 SV=1 | 368660.2 | 167690.1 | 283371.1 | 407570 | 209376.5994 | 197943.4621 | 224569.6119 | 312399.2058 | 67258.35374 | 89833.00449 | 48651.94017 | 92475.70288 | 194981.1567 | 66922.73939 | 103641.9284 | 254842.1697 | 211427.3078 | 270166.5679 | 343353.2772 | 138193.3196 | 310275.1718 | 310148.4554 | 269411.7059 | 20647.1885 | 331575.2843 | 170780.1505 | 383582.6238 | ||
| Q13011 | 2 | 1 | 84.85 | 0.138287884 | 3.20004629 | HN | XA | Delta(3,5)-Delta(2,4)-dienoyl-CoA isomerase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 34802.74 | 4833.872 | 9865.795 | 35208.82 | 158518.0385 | 34105.65035 | 89616.05412 | 32832.04913 | 15111.26044 | 44342.77704 | 202740.3453 | 514524.3198 | 148704.2227 | 189386.629 | 11104.3242 | 11412.78522 | 180769.3784 | 24696.10879 | 429695.7889 | 23537.93181 | 0 | 75722.8379 | 143564.027 | 929.9554869 | 10393.11805 | 4270.068848 | 8513.994625 | ||
| Q9HBT6 | 4 | 3 | 84.39 | 0.02697329 | 2.202827682 | HN | XA | Cadherin-20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH20 PE=2 SV=2 | 3345015 | 1935191 | 1272064 | 2821875 | 1094177.399 | 2573066.72 | 4056570.535 | 791748.2898 | 3370994.257 | 8674344.44 | 10490967.16 | 5282544.479 | 4626058.076 | 7661011.636 | 2851714.971 | 1302496.52 | 2648202.726 | 3296322.962 | 6990570.764 | 3014579.281 | 4692648.637 | 2992453.941 | 1676556.753 | 2512711.823 | 4204920.084 | 4464610.305 | 4744152.465 | ||
| P12036 | 12 | 3 | 84.39 | 0.624872678 | 1.663123444 | HN | XN | Neurofilament heavy polypeptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEFH PE=1 SV=4 | 5875828 | 2979543 | 1725973 | 281770.2 | 3437247.763 | 4423134.346 | 2483707.766 | 513424.6281 | 405334.408 | 6702973.637 | 346805.5273 | 4456221.823 | 3483528.629 | 3493579.571 | 430955.6404 | 529601.7316 | 4329753.657 | 3167979.78 | 376793.385 | 2663251.585 | 562650.0918 | 2379416.82 | 3639199.422 | 175760.3115 | 2391162.656 | 506400.5059 | 3504643.813 | ||
| Q9Y5Y6 | 4 | 1 | 84.3 | 0.523896651 | 1.655802489 | XA | HN | Suppressor of tumorigenicity 14 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ST14 PE=1 SV=2 | 1193132 | 173160.6 | 61687.6 | 466773.3 | 161861.2406 | 384779.4151 | 401546.3681 | 454493.9275 | 746733.3356 | 338911.5691 | 199131.7262 | 215599.4405 | 772433.5812 | 168882.4552 | 242168.9326 | 201644.7838 | 191229.7004 | 112419.4394 | 276407.7399 | 404844.5557 | 310911.2862 | 125982.9748 | 243627.9968 | 111351.7953 | 381490.4028 | 346331.5169 | 451484.4617 | ||
| Q14764 | 8 | 4 | 84.28 | 0.79990598 | 1.720736212 | HN | XN | Major vault protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MVP PE=1 SV=4 | 361515.7 | 19963.45 | 141801.9 | 469906.7 | 122902.4107 | 361249.4685 | 243504.4119 | 602201.9705 | 143286.243 | 635276.7222 | 43076.52767 | 533519.9252 | 38762.32357 | 859072.8679 | 50222.33041 | 129816.694 | 13426.19367 | 518203.0461 | 130437.6334 | 173518.5717 | 308363.842 | 153382.2037 | 189351.3923 | 28651.81704 | 59744.91482 | 288489.9664 | 307693.0964 | ||
| Q15109 | 3 | 3 | 84.08 | 0.930837009 | 1.117729582 | HN | XA | Advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGER PE=1 SV=1 | 10698379 | 11207847 | 7387992 | 21562599 | 12000718.44 | 9553275.704 | 14525847.09 | 8707559.731 | 12037045.97 | 10017207.89 | 11223834.86 | 6714946.633 | 21533342.22 | 9474523.179 | 10433552.56 | 27955794.83 | 10008627.53 | 12996704.3 | 11897555.29 | 8417204.368 | 16110866.23 | 14070326.88 | 11662996.27 | 18127069.82 | 11086854.47 | 10957898.13 | 6865015.017 | ||
| O14737 | 2 | 1 | 84.04 | 0.641826882 | 1.484651954 | XA | XN | Programmed cell death protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD5 PE=1 SV=3 | 131163.5 | 22833.87 | 38498.65 | 47960.3 | 6464.601462 | 71285.94293 | 119462.2614 | 172189.646 | 93527.03417 | 39633.72002 | 108913.0844 | 170366.6924 | 11639.296 | 30854.70326 | 24498.38243 | 44415.673 | 26453.34682 | 20888.66824 | 44213.08803 | 43814.89169 | 120069.4357 | 82654.60987 | 75323.75845 | 11011.96026 | 14476.77736 | 55757.17193 | 26449.82491 | ||
| Q9BQR3 | 3 | 2 | 83.91 | 0.955395885 | 1.525649463 | XN | HN | Serine protease 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRSS27 PE=1 SV=1 | 72730.16 | 56431.78 | 55381.44 | 75823.56 | 48577.68423 | 175531.4992 | 764717.4805 | 650847.0645 | 766990.0379 | 691601.446 | 742033.9461 | 350854.3744 | 288890.4126 | 40803.43929 | 97564.06656 | 21512.45717 | 158080.1619 | 92338.67904 | 2273108.837 | 619435.8539 | 220299.0208 | 210828.5457 | 30733.46557 | 113530.9808 | 140918.0654 | 61749.6577 | 118619.0807 | ||
| Q9P2B2 | 8 | 4 | 83.84 | 0.153913278 | 1.414034194 | XN | HN | Prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTGFRN PE=1 SV=2 | 862427 | 1707930 | 1714771 | 522488.4 | 919483.3324 | 1296528.505 | 1862418.467 | 706282.1403 | 2025967.183 | 696921.9258 | 1932446.584 | 811908.2431 | 1096949.13 | 1290847.267 | 1761428.204 | 521565.7675 | 1178769.904 | 1119816.65 | 720303.0688 | 1627994.208 | 1749515.64 | 1447333.646 | 1622346.276 | 2148279.765 | 1526366.149 | 2346379.742 | 1532501.785 | ||
| P28908 | 3 | 3 | 83.47 | 0.219872173 | 1.448815771 | XN | XA | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF8 PE=1 SV=1 | 187222.5 | 683458.5 | 135956.4 | 36902.46 | 106220.2708 | 172951.916 | 86006.75338 | 157442.1131 | 40404.57569 | 65179.788 | 312280.3275 | 298912.3384 | 146670.9258 | 166585.0137 | 111079.8043 | 28656.95375 | 136640.6604 | 353369.5601 | 229106.7804 | 351323.8223 | 212971.7862 | 310670.3393 | 85538.26247 | 486706.6342 | 118882.4671 | 358079.9714 | 174337.4336 | ||
| Q86VP6 | 2 | 2 | 83.45 | 0.29336545 | 1.689539338 | XN | XA | Cullin-associated NEDD8-dissociated protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAND1 PE=1 SV=2 | 903017.3 | 714753.5 | 717511.9 | 657826.5 | 272703.7217 | 1036985.115 | 295951.2248 | 343933.2558 | 308792.4565 | 407610.0085 | 1278492.149 | 230469.5679 | 575298.8062 | 621956.0808 | 3037038.377 | 206075.4097 | 403920.8791 | 469694.7631 | 771046.8404 | 910516.1004 | 507712.898 | 875629.2274 | 648572.262 | 825669.6365 | 495930.0929 | 3196400.051 | 641096.4583 | ||
| Q9Y219 | 2 | 1 | 83.4 | 0.883968244 | 2.565075175 | XN | HN | Protein jagged-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=JAG2 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 33499.24 | 60875.08 | 64063.81 | 164441.4956 | 503579.9516 | 1488976.629 | 1100190.549 | 802513.4554 | 26279.07547 | 844952.9993 | 920784.9332 | 440785.8964 | 15393.30798 | 24514.00531 | 28183.54519 | 43603.86959 | 12458.51819 | 24756.75437 | 2618467.608 | 606034.3013 | 2573815.296 | 125912.2045 | 22278.45113 | 29741.7073 | 26305.32809 | 18458.06085 | ||
| O75348 | 3 | 3 | 83.11 | 0.618800152 | 1.365676707 | XA | XN | V-type proton ATPase subunit G 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6V1G1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1599170 | 670064.5 | 804354.8 | 1320811 | 443950.2563 | 850117.9983 | 1880800.409 | 1410566.663 | 2834956.156 | 1037456.737 | 2293816.581 | 1389370.735 | 1295242.293 | 1314122.873 | 594095.4968 | 635398.8667 | 417278.6453 | 859217.9606 | 406871.8229 | 1132299.015 | 1026660.228 | 553337.5384 | 1106810.42 | 922807.4987 | 956194.0007 | 1279982.275 | 1266273.451 | ||
| P23083 | 3 | 2 | 82.98 | 0.45588579 | 1.684372044 | XA | HN | Ig heavy chain V-I region V35 OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1220164 | 6933349 | 1818138 | 1884435 | 10825657.74 | 1596662.067 | 5793503.066 | 3595015.986 | 825812.4086 | 3109535.789 | 854650.0995 | 1812865.506 | 1124305.85 | 2480722.554 | 3759916.423 | 547126.6519 | 4809052.039 | 1979923.861 | 5088558.312 | 5803033.653 | 3147179.511 | 1552744.586 | 997647.7343 | 1953495.893 | 2861021.691 | 3051189.32 | 2882572.398 | ||
| P15848 | 7 | 3 | 82.77 | 0.266276998 | 1.307474875 | HN | XN | Arylsulfatase B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARSB PE=1 SV=1 | 511724.9 | 533839.9 | 766435 | 613312.5 | 637015.7553 | 476380.9444 | 633026.8748 | 687660.3483 | 683619.3395 | 673035.4009 | 635855.0237 | 923369.2738 | 1448024.699 | 339175.81 | 232398.088 | 219326.6822 | 664956.0267 | 479518.9183 | 712732.6343 | 345152.0227 | 863114.2437 | 348684.1055 | 775280.4625 | 162369.8603 | 199782.7361 | 602806.4814 | 285119.7772 | ||
| P27105 | 4 | 3 | 82.62 | 0.976767094 | 1.150715153 | XA | XN | Erythrocyte band 7 integral membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=STOM PE=1 SV=3 | 1090924 | 301405.9 | 627107.9 | 145301.3 | 413400.0679 | 773718.5976 | 991623.8589 | 554246.4352 | 342046.269 | 559099.1537 | 993657.4319 | 555468.2248 | 673318.4288 | 856221.1293 | 309065.2878 | 236724.0894 | 340520.953 | 256340.4677 | 687083.154 | 729038.3238 | 534775.3615 | 461114.1387 | 436772.55 | 253995.6598 | 472652.2756 | 470398.4359 | 507663.9347 | ||
| P35475 | 3 | 2 | 82.49 | 0.440069046 | 1.274815348 | XA | HN | Alpha-L-iduronidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=IDUA PE=1 SV=2 | 331781.2 | 240260.5 | 336498.1 | 372063.9 | 148428.6083 | 477695.6632 | 375343.1874 | 465182.7277 | 184071.3203 | 375097.0613 | 182592.5143 | 398736.2545 | 607984.7786 | 153233.0473 | 229403.807 | 132128.7786 | 89260.87612 | 130974.4463 | 369583.5531 | 434774.2054 | 448261.5488 | 231832.8204 | 343561.4192 | 41731.58769 | 143701.3679 | 286185.3023 | 197582.4944 | ||
| P54819 | 2 | 1 | 82.47 | 0.631230954 | 1.730942942 | HN | XA | Adenylate kinase 2, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=AK2 PE=1 SV=2 | 30322.16 | 267.802 | 2141.19 | 41947.36 | 19282.7459 | 15102.34014 | 4563.785294 | 14753.06973 | 18108.68102 | 122.9220782 | 29328.74311 | 17766.98798 | 38401.65201 | 31821.16587 | 60973.44008 | 41704.20216 | 10258.90375 | 23186.32475 | 87524.14465 | 10444.73296 | 7102.737546 | 23944.96975 | 12243.23372 | 15022.15497 | 39392.63298 | 7295.578338 | 7778.743456 | ||
| Q9NPR2 | 6 | 4 | 82.22 | 0.976918504 | 1.050548412 | XN | XA | Semaphorin-4B OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMA4B PE=1 SV=3 | 665145.5 | 195134.4 | 421631 | 507732.7 | 333777.9132 | 351483.3225 | 411312.8345 | 580820.1052 | 278104.4771 | 392207.6109 | 679435.4038 | 323626.6108 | 237654.9559 | 733605.6146 | 328647.4534 | 281514.3653 | 457792.9054 | 410047.9775 | 262868.4415 | 593657.2466 | 438305.9365 | 157826.4014 | 434940.2448 | 481332.9332 | 506642.9078 | 440471.648 | 618407.5508 | ||
| Q9H299 | 1 | 1 | 82.13 | 0.290486935 | 1.457464838 | XA | XN | SH3 domain-binding glutamic acid-rich-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SH3BGRL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 1683021 | 7425417 | 6832639 | 3359500 | 5026783.524 | 2910795.288 | 2431765.383 | 4113479.847 | 7254928.597 | 3216237.333 | 1506736.481 | 4558826.527 | 1432117.032 | 1815439.33 | 1296892.641 | 11968756.58 | 4039703.364 | 2316395.318 | 5256000.684 | 2754052.009 | 1693112.622 | 4018732.017 | 2270326.723 | 5560863.112 | 1706841.937 | 2470625.501 | 2426782.963 | ||
| Q9HCY8 | 3 | 1 | 81.91 | 0.568909751 | 2.149477023 | XN | HN | Protein S100-A14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A14 PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 2552.076 | 16442.52 | 1531.619 | 26777.95107 | 34747.64747 | 135139.5902 | 399851.4485 | 259795.4298 | 167128.7797 | 64345.33985 | 122578.1657 | 62347.11645 | 10158.20276 | 19734.84493 | 4206.611144 | 17562.75502 | 5622.578431 | 831477.5278 | 52669.99035 | 22278.32603 | 27504.57179 | 11803.3292 | 9623.571563 | 12544.22581 | 28026.22133 | 22245.9573 | ||
| Q96CN7 | 2 | 2 | 81.86 | 0.278099901 | 3.177267139 | XA | HN | Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ISOC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 29750.45 | 419.139 | 25998.91 | 216816.2 | 29916.54642 | 67748.94814 | 58907.67196 | 111399.6831 | 42629.01454 | 562.4561364 | 4602.435081 | 28566.70616 | 31680.45666 | 64602.36864 | 16215.4445 | 28507.00227 | 3033.660219 | 5905.097613 | 65671.23751 | 14143.96171 | 13069.41398 | 79204.03801 | 44312.2404 | 2100.731206 | 28117.80203 | 11249.55508 | 10118.44723 | ||
| Q9NP55 | 1 | 1 | 81.63 | 0.596547127 | 10.27467442 | HN | XN | BPI fold-containing family A member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BPIFA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 13408.39 | 0 | 6569.719 | 4376.863 | 181562.9037 | 44236.20988 | 0 | 7501.105871 | 0 | 485910.7325 | 454574.6504 | 0 | 11771.66759 | 22353.49931 | 22309.92342 | 779542.2521 | 0 | 4988.201761 | 0 | 0 | 14220.2666 | 1426.064842 | 0 | 96195.42485 | 14974.65848 | 35874.31665 | 10691.98166 | ||
| Q96CX2 | 3 | 1 | 81.61 | 0.194202472 | 2.113973414 | HN | XA | BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KCTD12 PE=1 SV=1 | 128446.6 | 60272.17 | 74114.74 | 51930.58 | 85409.30782 | 20659.78487 | 35837.93744 | 45123.15712 | 20645.29949 | 98024.30435 | 78506.56387 | 87683.28679 | 37370.30872 | 46413.70116 | 158305.0295 | 366801.1433 | 179054.8693 | 52264.08315 | 15635.95222 | 288803.68 | 4705.03554 | 32997.63197 | 92740.76822 | 110386.2571 | 43683.36036 | 33617.95377 | 101947.1837 | ||
| Q6FHJ7 | 7 | 3 | 81.61 | 0.236912284 | 1.382566593 | XA | HN | Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SFRP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 347432.4 | 877351.7 | 605251.8 | 339863.1 | 585848.2364 | 690584.1692 | 1000131.925 | 284200.0702 | 1116529.939 | 163093.1311 | 1416216.723 | 379527.4549 | 490049.8816 | 496208.4228 | 224999.989 | 87061.08878 | 361387.4763 | 610686.7119 | 332500.3838 | 993430.4799 | 606773.1512 | 585032.1819 | 252392.4344 | 887378.6471 | 394613.0107 | 523153.2584 | 313357.8715 | ||
| O15144 | 2 | 2 | 81.35 | 0.539497751 | 2.001454043 | XA | HN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARPC2 PE=1 SV=1 | 360410.2 | 49913.04 | 150668.9 | 430509.9 | 6916.534829 | 334163.587 | 326205.2962 | 584035.9354 | 254041.4492 | 200313.7279 | 107695.281 | 220686.7559 | 139756.27 | 83609.25325 | 238666.2341 | 85355.27542 | 62108.74178 | 109333.9254 | 290091.2149 | 142098.5298 | 355729.635 | 178372.927 | 391891.1848 | 0 | 185500.6777 | 80608.19704 | 102270.651 | ||
| Q6DKI7 | 1 | 1 | 81.33 | 0.699595719 | 1.08397955 | XN | HN | Transmembrane protein PVRIG OS=Homo sapiens GN=PVRIG PE=2 SV=1 | 1212383 | 1253954 | 800788.8 | 893010.9 | 213377.708 | 1150535.789 | 1948094.463 | 1068391.919 | 1119849.057 | 1111535.009 | 2291632.3 | 827136.3824 | 1703461.05 | 1332174.535 | 199982.8102 | 240302.8195 | 494867.9585 | 749476.6502 | 1679237.797 | 1926440.579 | 962740.6402 | 1307542.663 | 401732.1369 | 1259694.735 | 620485.9642 | 874535.298 | 669824.506 | ||
| P14174 | 3 | 1 | 81.01 | 0.005443738 | 1.967842001 | XA | XN | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=MIF PE=1 SV=4 | 4208458 | 2235357 | 5472499 | 8090896 | 4295244.115 | 5321289.353 | 5496992.62 | 6984882.131 | 2322149.466 | 2482882.1 | 3992848.788 | 3107606.273 | 824484.8736 | 1129406.354 | 4242566.903 | 3749037.012 | 1388620.492 | 1684817.924 | 2762437.676 | 2312574.508 | 1820425.589 | 3154848.393 | 3705066.717 | 1269179.216 | 3253858.463 | 1913936.522 | 2384570.915 | ||
| P01699 | 3 | 2 | 80.96 | 0.399798708 | 1.938281804 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-I region VOR OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1490396 | 2254032 | 1848883 | 1050966 | 2219606.157 | 1395077.539 | 1226520.579 | 1182723.374 | 525219.5595 | 2137844.011 | 1527078.809 | 1833411.825 | 1200200.602 | 1488605.51 | 3187205.377 | 11989076.7 | 1173453.647 | 1035696.357 | 1768198.466 | 1114949.198 | 1422167.441 | 2306795.031 | 2787999.024 | 3769543.607 | 2213974.579 | 640707.5801 | 1186036.13 | ||
| P63000;P15153 | 4 | 2 | 80.49 | 0.162238113 | 1.919256808 | XA | XN | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 665463.4 | 184963 | 250828.7 | 285389.9 | 139426.5413 | 204415.6283 | 486095.2333 | 554599.7833 | 250422.2972 | 337643.2351 | 753532.1204 | 245689.4555 | 117283.5774 | 762572.0182 | 79719.67415 | 61611.1494 | 100901.9283 | 112601.987 | 249886.4312 | 223096.2364 | 237851.1147 | 120756.2841 | 265395.4042 | 40018.59401 | 82589.41558 | 136071.4272 | 218696.8497 | ||
| P30085 | 2 | 2 | 80.05 | 0.426847341 | 1.404600467 | XA | HN | UMP-CMP kinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CMPK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 345208 | 55973.44 | 136443.1 | 322326 | 44906.89257 | 316062.7118 | 400891.2903 | 353838.7105 | 174901.441 | 197774.2922 | 165381.1044 | 677032.5784 | 147816.7134 | 83494.92959 | 33203.74491 | 115844.1484 | 49503.24949 | 61026.39096 | 247297.4388 | 90202.44647 | 597158.1818 | 146597.4652 | 182407.4488 | 32351.29071 | 104488.1425 | 75034.56329 | 93350.90218 | ||
| Q9UKY0 | 2 | 2 | 79.77 | 0.050071546 | 1.559362943 | XN | XA | Prion-like protein doppel OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRND PE=1 SV=2 | 584228.5 | 603394.3 | 328192.5 | 412537.9 | 305231.3261 | 570551.967 | 656920.5619 | 420695.1794 | 307806.749 | 505204.8942 | 924396.4072 | 472829.7087 | 723621.1703 | 652533.7555 | 306228.957 | 397966.9173 | 358878.9322 | 489132.1392 | 643429.3464 | 1343150.191 | 577681.2084 | 360571.9538 | 606742.7874 | 1041414.761 | 569868.5326 | 585958.0767 | 804226.107 | ||
| Q14376 | 3 | 2 | 79.48 | 0.779669776 | 1.817790996 | XA | HN | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALE PE=1 SV=2 | 106851.8 | 10960.53 | 196609.6 | 395667.8 | 1564.243763 | 80544.18568 | 97254.00727 | 173818.7148 | 96782.02861 | 57353.10668 | 26549.90638 | 149759.7765 | 100816.7939 | 48962.16766 | 22392.64994 | 193542.6561 | 16961.50384 | 21827.69455 | 16970.14002 | 27124.01778 | 82236.57517 | 43571.04683 | 265588.5909 | 1828.050975 | 174375.1569 | 64293.27797 | 32015.17034 | ||
| P40313 | 1 | 1 | 79.27 | 0.644484027 | 1.341962672 | HN | XA | Chymotrypsin-like protease CTRL-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTRL PE=2 SV=1 | 11744.6 | 14642.27 | 61786.14 | 34342.8 | 28374.47227 | 12713.14825 | 12126.97559 | 13545.01669 | 55175.51044 | 70173.29047 | 42256.32408 | 17967.74427 | 79694.85468 | 21624.76558 | 23861.40914 | 27587.67019 | 36449.802 | 8428.170928 | 26757.21114 | 120028.3355 | 22755.99259 | 17988.62358 | 18021.35692 | 52194.73382 | 10575.54319 | 19185.89926 | 7301.194344 | ||
| Q96GW7 | 9 | 4 | 79.22 | 0.693914514 | 1.397471118 | XN | XA | Brevican core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=BCAN PE=1 SV=2 | 298106.5 | 625133.1 | 450854.3 | 772513.8 | 654607.1619 | 308940.1914 | 476957.2321 | 287524.4087 | 564405.695 | 609587.9752 | 866982.014 | 226443.4474 | 692109.716 | 390468.3693 | 1535237.061 | 956424.7042 | 339026.6788 | 255426.3716 | 437107.5149 | 411394.5465 | 330709.2101 | 524600.782 | 632512.4473 | 1877757.627 | 1183992.827 | 445411.6924 | 359946.9447 | ||
| P60660 | 2 | 1 | 79.17 | 0.141609839 | 1.784085829 | HN | XN | Myosin light polypeptide 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYL6 PE=1 SV=2 | 447631 | 173147.6 | 302045 | 832016.6 | 168781.0954 | 203659.814 | 308796.0934 | 646195.7681 | 342878.3982 | 744514.3452 | 162123.0577 | 1004874.716 | 332836.1407 | 284606.2294 | 402875.1487 | 263369.1495 | 144314.5335 | 218582.8881 | 147744.1902 | 132842.0639 | 351339.0206 | 140174.3613 | 325796.7833 | 322728.4429 | 238044.3455 | 147270.9747 | 188412.4161 | ||
| P14136 | 10 | 1 | 78.84 | 0.412843461 | 2.057765076 | HN | XN | Glial fibrillary acidic protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GFAP PE=1 SV=1 | 591334.3 | 118750 | 216544.4 | 1320047 | 181190.3386 | 272802.6006 | 574827.7177 | 60075.01083 | 67512.10303 | 85467.15767 | 23008.10728 | 2745762.214 | 61236.17316 | 18690.88929 | 277083.1511 | 293076.816 | 140529.8723 | 68242.93389 | 172634.0955 | 392133.2103 | 151636.0384 | 64266.43978 | 639959.8676 | 47953.15416 | 281659.4998 | 28820.63656 | 25369.13645 | ||
| O75074 | 4 | 2 | 78.43 | 0.828269261 | 1.068887447 | HN | XN | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP3 PE=2 SV=2 | 83875.72 | 141705.9 | 203955.2 | 112234.4 | 176406.2653 | 442910.5866 | 477863.6865 | 179774.2754 | 470452.371 | 88214.70342 | 365110.2265 | 115299.3145 | 458771.8943 | 265092.7392 | 153290.6805 | 631972.4619 | 99014.69134 | 129050.198 | 218407.7524 | 292512.8866 | 225847.1934 | 252756.0106 | 188239.564 | 305424.0672 | 243052.8957 | 213414.8952 | 217556.8114 | ||
| P78371 | 2 | 1 | 78.11 | 0.130219086 | 1.709133427 | XA | HN | T-complex protein 1 subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT2 PE=1 SV=4 | 386369.6 | 157727.9 | 289943.1 | 734586.4 | 97074.09985 | 363691.107 | 388205.6065 | 494426.8606 | 254705.0619 | 131856.8357 | 490660.3233 | 171307.6758 | 322092.9903 | 165988.2965 | 93824.97815 | 98357.3348 | 203774.4001 | 174964.8313 | 94669.23191 | 244130.385 | 338650.5835 | 148868.9105 | 402248.7496 | 334937.2596 | 225633.5529 | 212411.7417 | 208323.811 | ||
| P06703 | 3 | 1 | 77.72 | 0.130770292 | 1.942320084 | HN | XA | Protein S100-A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A6 PE=1 SV=1 | 1000078 | 578502.7 | 638216.9 | 738537 | 1084934.105 | 632597.235 | 1078507.469 | 1721657.394 | 983521.919 | 4582055.547 | 2590361.883 | 1628057.153 | 791898.701 | 2272202.099 | 1705416.262 | 1166285.448 | 852063.8106 | 836991.254 | 4280576.592 | 1583355.357 | 1849132.566 | 1111747.207 | 591724.2775 | 622967.0487 | 553877.3896 | 735695.2589 | 1378060.914 | ||
| Q96D42 | 4 | 2 | 77.6 | 0.821675118 | 2.057559874 | XA | XN | Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HAVCR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 517255.5 | 3007.181 | 71164.48 | 84812.05 | 21021.61759 | 394763.7621 | 167499.2507 | 570127.1592 | 189884.0696 | 103435.1867 | 79698.14392 | 62454.11588 | 282916.8036 | 526832.3786 | 32525.708 | 51546.58665 | 160398.2997 | 87992.05035 | 76160.97808 | 84521.97824 | 332682.1426 | 141268.0611 | 91948.99438 | 35178.7728 | 124683.3145 | 8526.958742 | 86548.26092 | ||
| P52943 | 1 | 1 | 77.37 | 0.691193884 | 1.431040735 | XA | XN | Cysteine-rich protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRIP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 11367.79 | 21378.19 | 385308.8 | 76879.3101 | 3101.41432 | 28157.69469 | 173981.2535 | 63017.21546 | 1406.079633 | 75053.15018 | 39555.16508 | 101578.689 | 11983.77352 | 34407.72512 | 248477.5689 | 91167.43445 | 11595.29529 | 6030.523478 | 36669.70879 | 166494.4242 | 28270.77533 | 42879.88844 | 392.4774793 | 142377.3923 | 27091.32983 | 83105.82611 | ||
| Q6E0U4 | 3 | 2 | 77.33 | 0.443246859 | 3.122722425 | XN | XA | Dermokine OS=Homo sapiens GN=DMKN PE=1 SV=3 | 264764.7 | 47592.69 | 114308 | 580143.8 | 116165.3387 | 18481.16705 | 18493.47792 | 193519.164 | 71565.08232 | 68711.85891 | 100976.7131 | 162364.8148 | 34454.11502 | 58622.75359 | 205946.3015 | 2121463.552 | 114969.3165 | 158043.8717 | 87400.30899 | 386130.7687 | 83073.77747 | 72823.68886 | 278675.1973 | 124557.8167 | 205555.0866 | 67418.28031 | 3144348.68 | ||
| Q8N1A0 | 3 | 1 | 77.08 | 0.97308109 | 1.165518081 | XN | HN | Keratin-like protein KRT222 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT222 PE=2 SV=1 | 193567.6 | 54463.14 | 172545.2 | 102387.5 | 135059.8311 | 273962.6708 | 393892.7614 | 288130.4918 | 255973.4747 | 276990.5411 | 263317.2833 | 374328.299 | 171321.8876 | 184637.7974 | 68194.26178 | 117170.0106 | 104523.0022 | 164794.1703 | 166254.3779 | 200883.8111 | 343694.2193 | 565042.8652 | 52788.40568 | 152886.2332 | 97646.79502 | 134862.577 | 296782.5495 | ||
| Q8WV92 | 2 | 1 | 76.91 | 0.134927112 | 2.200521308 | HN | XN | MIT domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MITD1 PE=1 SV=1 | 133880.4 | 46267.76 | 101152.5 | 74196.56 | 59207.85107 | 74390.9711 | 113334.721 | 55911.0919 | 23685.88141 | 38287.45329 | 237772.0849 | 56089.47883 | 47376.41399 | 153353.5875 | 56222.1485 | 29350.73651 | 43898.79448 | 143620.5703 | 60251.56089 | 73048.25087 | 52495.17113 | 8548.648865 | 13764.63219 | 0.095924353 | 16034.36908 | 59200.68752 | 82920.37079 | ||
| P21754;Q6PJE2 | 3 | 1 | 76.76 | 0.719387698 | 1.353286878 | XN | XA | Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZP3 PE=1 SV=2 | 241782.1 | 234002.1 | 32179.48 | 57563.44 | 138271.2524 | 51499.95532 | 384147.0316 | 51173.7858 | 103383.6415 | 36324.78374 | 13759.52773 | 194420.5776 | 129857.3521 | 185295.6387 | 224938.1473 | 29310.01419 | 305333.0047 | 486024.7057 | 224758.0506 | 174235.1963 | 60726.85109 | 80257.53118 | 215238.5963 | 93477.49552 | 88290.15191 | 139874.8677 | 674298.2236 | ||
| P51170 | 1 | 1 | 76.37 | 0.91328432 | 1.106400715 | HN | XN | Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel subunit gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCNN1G PE=1 SV=4 | 849801.6 | 363143.7 | 1443870 | 1219433 | 427011.0026 | 129101.3074 | 322313.9114 | 710673.7801 | 527681.5315 | 50514.77197 | 1238048.499 | 714401.3401 | 1535486.931 | 403888.2918 | 413632.9666 | 1663045.746 | 397488.8857 | 79732.83637 | 67685.56804 | 492842.3059 | 363467.2066 | 271382.3544 | 1417256.239 | 954610.1729 | 1240855.304 | 549558.25 | 513850.254 | ||
| P30048 | 2 | 2 | 76.3 | 0.040191379 | 7.701338461 | HN | XN | Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX3 PE=1 SV=3 | 76630.72 | 5806.409 | 19772.7 | 161047.2 | 43531.20574 | 22594.22009 | 13064.28519 | 58309.34837 | 104669.7079 | 140419.4013 | 112131.5403 | 1580029.652 | 263683.934 | 566425.3742 | 66576.94273 | 412799.2879 | 8262.481298 | 22011.78877 | 15792.73226 | 105.3827486 | 8789.453923 | 39295.39049 | 30527.51593 | 218891.5643 | 32430.54633 | 22649.11553 | 43438.95601 | ||
| P14151 | 3 | 2 | 76.29 | 0.496507201 | 1.840136612 | XN | XA | L-selectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SELL PE=1 SV=2 | 545696.7 | 940346.2 | 358999.7 | 420694 | 881408.9484 | 581006.8231 | 447041.2504 | 473369.8422 | 755741.5376 | 680657.9949 | 204236.2284 | 702478.1875 | 327737.7601 | 631525.8475 | 407011.1136 | 161959.9595 | 2021845.097 | 1657386.101 | 1288924.982 | 950964.5358 | 1416791.504 | 1609181.583 | 520855.4113 | 227230.7055 | 135354.7866 | 1628406.322 | 2166949.9 | ||
| Q13445 | 1 | 1 | 76.15 | 0.619266856 | 1.167050526 | XN | XA | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMED1 PE=1 SV=1 | 203290.8 | 204372.2 | 208251.1 | 164069.6 | 67569.49118 | 244281.1728 | 341138.0344 | 173778.7587 | 344105.2725 | 59816.82966 | 468155.8719 | 283639.9263 | 328881.5638 | 527019.1726 | 123431.5805 | 31588.11109 | 115017.0044 | 141515.1528 | 230861.3152 | 299347.2467 | 217611.0885 | 131829.9048 | 144282.5866 | 560234.3127 | 351996.6592 | 222416.3403 | 118168.4602 | ||
| Q9UGM5 | 4 | 3 | 76.09 | 0.105464168 | 2.376247074 | HN | XN | Fetuin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=FETUB PE=1 SV=2 | 406819.8 | 105686.9 | 142726.6 | 723871.8 | 626141.8182 | 151428.168 | 131340.3882 | 328332.6725 | 113087.1042 | 708920.114 | 398332.4386 | 887031.6153 | 188872.3121 | 224069.1864 | 240727.8264 | 1071600.012 | 310789.4261 | 117139.3524 | 170764.3909 | 203655.2399 | 239780.5228 | 99243.98644 | 290947.2594 | 106555.3972 | 286428.5348 | 211293.5216 | 136722.9998 | ||
| P46108 | 2 | 2 | 75.92 | 0.246931528 | 2.278384394 | HN | XN | Adapter molecule crk OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRK PE=1 SV=2 | 100286.6 | 43320.23 | 163802.6 | 237281.4 | 266983.2229 | 78616.14565 | 131604.2086 | 158350.4545 | 108872.7277 | 163528.2384 | 236692.6831 | 87459.12537 | 181386.3806 | 150125.6995 | 229673.1163 | 1272518.438 | 86277.73453 | 107765.7207 | 54439.66235 | 101678.1843 | 119327.5573 | 117901.7279 | 121755.1548 | 191479.9867 | 163991.443 | 94813.43107 | 138652.6904 | ||
| B3EWG3;B3EWG4;B3EWG5;B3EWG6 | 2 | 1 | 75.71 | 0.456612904 | 2.849878428 | XA | XN | Protein FAM25A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM25A PE=2 SV=1 | 140525.5 | 29887.62 | 83550.09 | 98871.69 | 23037.08127 | 187835.2075 | 3648007.584 | 1947905.239 | 554819.8751 | 463727.6163 | 633083.8203 | 1633450.129 | 327897.0112 | 45218.10959 | 54649.50577 | 131354.3343 | 37249.0437 | 12012.05806 | 76131.6935 | 1159352.384 | 778213.9359 | 137943.0495 | 791.972541 | 31049.99539 | 78437.89959 | 62477.335 | 31646.0697 | ||
| Q8TCZ2 | 2 | 1 | 75.68 | 0.487841997 | 1.687753052 | XN | HN | CD99 antigen-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD99L2 PE=2 SV=1 | 41090.06 | 103594.5 | 109275.4 | 70200.39 | 144665.9953 | 78989.66746 | 185788.8352 | 79071.06876 | 438969.8024 | 124443.9729 | 191857.5744 | 37940.85071 | 121570.6786 | 42205.36459 | 140772.1415 | 54089.84448 | 66806.41436 | 25105.83383 | 75926.91116 | 36791.93091 | 133264.7424 | 111188.386 | 28320.40793 | 602467.7499 | 125577.7014 | 165360.4718 | 79392.99234 | ||
| O14786 | 3 | 2 | 75.33 | 0.018939229 | 2.085082229 | XA | HN | Neuropilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NRP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 273480.8 | 79356.24 | 56629.09 | 120501 | 51490.95906 | 112555.6681 | 90985.42731 | 110270.3781 | 100838.2163 | 6225.931816 | 2882.531451 | 12345.51462 | 119285.4034 | 1545.552941 | 149894.4784 | 26804.48281 | 91703.4684 | 67043.34105 | 98810.31574 | 70873.79487 | 95310.69148 | 37070.16705 | 115572.7035 | 11903.48258 | 144512.0389 | 97290.1003 | 150117.6944 | ||
| P61088 | 3 | 1 | 75.29 | 0.509971371 | 1.579919042 | XA | XN | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBE2N PE=1 SV=1 | 259798.8 | 36149.16 | 43096.84 | 244894 | 36898.91232 | 144946.5197 | 188100.6203 | 294434.0354 | 143633.8802 | 227261.9123 | 102042.4865 | 212342.84 | 43717.22521 | 196729.7581 | 73405.7792 | 64358.34001 | 59332.72996 | 62216.93889 | 149033.4952 | 47445.29856 | 183357.0768 | 205447.6048 | 94242.82614 | 21204.40767 | 93617.33929 | 40679.07631 | 46000.76591 | ||
| Q9H9P2 | 2 | 1 | 75.27 | 0.249473241 | 2.826099355 | XA | HN | Chondrolectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHODL PE=2 SV=2 | 1722154 | 127374.2 | 47121.2 | 183926.5 | 76787.66835 | 242127.0725 | 388439.534 | 212211.4455 | 630345.5466 | 16319.92493 | 244939.5055 | 291016.9452 | 226189.6196 | 122538.0966 | 96486.2734 | 156079.5463 | 110580.0459 | 20478.1918 | 295904.6579 | 350188.2914 | 291446.1826 | 139224.5576 | 34032.8226 | 378081.7008 | 52109.05689 | 594669.9994 | 91721.14748 | ||
| O60784 | 3 | 1 | 75.23 | 0.310356146 | 1.749370514 | HN | XN | Target of Myb protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TOM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 28657.32 | 7704.459 | 11133.27 | 35013.42 | 8981.241412 | 9870.166369 | 19296.71645 | 41140.17085 | 26857.45665 | 35886.49447 | 29486.52115 | 41225.74436 | 22297.98731 | 40840.28193 | 9614.197039 | 17656.42759 | 2762.535353 | 17064.33002 | 11530.11911 | 4677.07481 | 14807.31652 | 5569.46668 | 16082.85575 | 5642.09208 | 27933.98848 | 12606.67568 | 25100.43603 | ||
| P52790 | 7 | 2 | 75.22 | 0.333423588 | 1.234115448 | HN | XN | Hexokinase-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HK3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1227557 | 1017984 | 1150427 | 757176.6 | 896904.8148 | 935932.5957 | 1226118.801 | 925497.5666 | 834293.117 | 1355776.43 | 1207773.436 | 1853767.704 | 734103.893 | 853372.6138 | 1147437.844 | 1069097.553 | 742362.3914 | 520237.1053 | 710282.9221 | 695397.1959 | 998990.1506 | 510920.6825 | 1092083.646 | 857058.5299 | 580537.2325 | 1320438.554 | 919089.9356 | ||
| Q15262 | 7 | 5 | 75.07 | 0.001682354 | 3.317965856 | HN | XA | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase kappa OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRK PE=1 SV=2 | 6346086 | 3623399 | 6146240 | 3822754 | 4105065.332 | 4421698.059 | 4561330.221 | 2756432.281 | 8225692.835 | 15010264.68 | 44589842.08 | 10564856.1 | 18192713.54 | 7819675.857 | 3636999.578 | 24973259.11 | 15313638.86 | 5918109.219 | 6795504.341 | 11844605.28 | 7478133.572 | 17759914.19 | 6440977.118 | 13981651.61 | 5512837.364 | 15331526.5 | 14162064.21 | ||
| Q14162 | 1 | 1 | 74.93 | 0.015588817 | 2.290644588 | XA | HN | Scavenger receptor class F member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCARF1 PE=1 SV=3 | 35417.93 | 73848.09 | 48813.02 | 18699.62 | 23886.9375 | 36566.27983 | 70061.77164 | 14349.04145 | 73935.47415 | 12497.44679 | 36213.33288 | 9810.159447 | 7691.13421 | 30985.15853 | 18210.22435 | 29904.02234 | 14348.90041 | 13032.56723 | 13047.92162 | 26888.43784 | 22951.20168 | 20399.37691 | 28428.33092 | 8629.830809 | 18326.60988 | 54960.57347 | 22070.48777 | ||
| P20742 | 3 | 1 | 74.7 | 0.177157667 | 20.36363394 | HN | XA | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 18001.3 | 3036.541 | 806.7294 | 0 | 11380.77428 | 1635.271611 | 286.1741248 | 1515.739852 | 7816.859037 | 32956.47938 | 721.1737588 | 895.050461 | 14113.33203 | 692262.4966 | 7017.725332 | 56021.49311 | 20647.20262 | 81127.00254 | 3661.648495 | 1056.596693 | 7325.325336 | 0 | 6736.726841 | 9480.649357 | 95352.13074 | 72748.86165 | 95687.73526 | ||
| P60033 | 3 | 3 | 74.62 | 0.162311766 | 1.512648179 | XA | HN | CD81 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD81 PE=1 SV=1 | 2168234 | 952090.9 | 535918.5 | 451165.1 | 1411265.009 | 835044.6653 | 1219893.598 | 1017086.532 | 575054.9972 | 760273.0907 | 970082.6695 | 479314.8987 | 866545.2476 | 992723.7662 | 710650.4828 | 389849.6471 | 480696.2806 | 409272.5357 | 858976.4735 | 604593.5537 | 624561.9248 | 386470.6504 | 841854.4378 | 437034.9188 | 690669.1985 | 704090.028 | 1212149.836 | ||
| Q9UI12 | 5 | 3 | 74.02 | 0.34853919 | 1.7763127 | XA | XN | V-type proton ATPase subunit H OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP6V1H PE=1 SV=1 | 298048.7 | 30419.81 | 162829.4 | 459358.5 | 54165.20759 | 209241.0265 | 176669.2864 | 275150.4522 | 74391.96368 | 375545.5282 | 86086.34246 | 225985.7775 | 140333.9967 | 65102.23086 | 76519.36909 | 197711.6955 | 51465.18705 | 47775.66863 | 60076.53237 | 69643.94048 | 169186.5174 | 107974.7649 | 225806.6452 | 3784.220072 | 171501.5851 | 126981.9324 | 44755.54212 | ||
| Q92765 | 2 | 2 | 73.78 | 0.564229978 | 1.943300155 | HN | XN | Secreted frizzled-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FRZB PE=1 SV=2 | 588390 | 1266503 | 1848417 | 922076.1 | 3090170.129 | 612262.9585 | 575133.9698 | 436934.4786 | 500120.0494 | 780242.533 | 784656.1328 | 680411.1878 | 494316.8211 | 494701.9047 | 1680578.528 | 7462178.303 | 1011822.709 | 773915.5835 | 460626.8073 | 1267185.496 | 288815.7143 | 260523.5006 | 1100655.251 | 844925.3766 | 699475.555 | 978889.5515 | 1386929.594 | ||
| P01702;P06316 | 3 | 2 | 73.64 | 0.595477549 | 1.419295366 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-I region NIG-64 OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1622500 | 2037448 | 1025842 | 872457.4 | 1878726.55 | 659470.6709 | 1362304.003 | 1173489.922 | 1050663.199 | 3660076.865 | 2585683.102 | 1172642.182 | 1642502.255 | 1031587.851 | 3180911.831 | 1689897.411 | 446354.7148 | 1171832.263 | 1505867.058 | 991828.2799 | 1198080.947 | 820109.6279 | 2618319.794 | 2252996.186 | 650087.5307 | 1095572.264 | 1804896.374 | ||
| O00144 | 2 | 2 | 73.63 | 0.632702145 | 1.284523812 | XN | HN | Frizzled-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD9 PE=2 SV=1 | 549139.2 | 447237.4 | 327843.7 | 2050882 | 234946.3652 | 567205.5196 | 453498.9269 | 546592.9949 | 598337.7958 | 392272.4771 | 967188.3055 | 426391.6117 | 490946.6187 | 749472.3599 | 312568.6422 | 403022.5009 | 445217.3226 | 491392.9233 | 1013864.982 | 982611.1237 | 867893.3148 | 455281.5555 | 231254.7918 | 776512.5796 | 400033.9539 | 649729.3847 | 632427.9808 | ||
| Q6KB66 | 5 | 1 | 73.53 | 0.650064676 | 1.571492079 | XN | XA | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 80 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT80 PE=1 SV=2 | 10325.27 | 13268.41 | 11412.73 | 4158.264 | 3061.933897 | 2822.514109 | 9210.916033 | 4447.554024 | 20809.17313 | 3064.321839 | 3655.852772 | 11669.61661 | 4705.044037 | 6908.895449 | 32821.87459 | 3535.957548 | 7952.771577 | 8759.34314 | 4950.62466 | 2998.935216 | 5885.317448 | 13198.9493 | 13432.09782 | 50208.41808 | 3324.976943 | 17404.62441 | 13556.01186 | ||
| P55327 | 4 | 3 | 73.44 | 0.72573037 | 1.474902869 | XN | XA | Tumor protein D52 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPD52 PE=1 SV=2 | 62338.28 | 107427.3 | 68048.88 | 352432.5 | 94572.88596 | 2671027.877 | 1625517.214 | 467789.9992 | 519032.7736 | 833835.4247 | 368025.2525 | 2943188.108 | 329006.0919 | 325656.2469 | 350509.1436 | 150408.256 | 437153.4607 | 389838.702 | 290421.3624 | 4148264.268 | 779008.2986 | 1989671.683 | 210302.0428 | 1083986.136 | 111846.8401 | 119070.5402 | 69926.00301 | ||
| Q99471 | 1 | 1 | 73.35 | 0.790947747 | 1.695579082 | XA | HN | Prefoldin subunit 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFDN5 PE=1 SV=2 | 13540.22 | 5692.037 | 5167.063 | 54357.25 | 0 | 37170.02905 | 46249.04079 | 48850.64141 | 37673.87368 | 40328.9105 | 4753.985606 | 27207.17644 | 23162.74384 | 10950.27921 | 11884.4104 | 10341.14228 | 14385.5297 | 3661.46576 | 38139.865 | 7786.892929 | 50333.97773 | 37016.09112 | 16481.99247 | 6215.463799 | 6068.534651 | 6294.632308 | 5251.671084 | ||
| P24752 | 3 | 2 | 73.3 | 0.296562891 | 2.539973317 | HN | XN | Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACAT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 595609 | 20698.49 | 53897.72 | 498489.6 | 53064.64294 | 128387.5888 | 92480.3475 | 284922.4154 | 63930.41601 | 519237.0898 | 230694.3265 | 838017.7978 | 55863.61595 | 698365.4406 | 275287.9485 | 325946.883 | 19523.31966 | 155908.0705 | 57343.4496 | 40657.99987 | 98036.89262 | 112317.2764 | 217848.4599 | 36613.48677 | 389354.099 | 191564.6025 | 84168.16498 | ||
| Q14031 | 4 | 2 | 72.77 | 0.646828537 | 1.161381851 | XA | XN | Collagen alpha-6(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A6 PE=2 SV=3 | 366801.1 | 370465.7 | 202838.3 | 223134.1 | 236488.9998 | 255017.2947 | 146398.913 | 171545.6986 | 151329.4423 | 219511.6256 | 88216.38379 | 115606.3938 | 299520.8076 | 205836.1934 | 201954.9149 | 312695.1616 | 234716.8814 | 196352.1844 | 251986.6255 | 176739.1988 | 220921.3242 | 171448.4072 | 251332.4812 | 98872.69162 | 171530.1337 | 207187.0183 | 278854.7863 | ||
| Q14108 | 2 | 2 | 72.64 | 0.019039668 | 2.078612625 | XA | HN | Lysosome membrane protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCARB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 48956.94 | 22889.27 | 38245.04 | 64257.15 | 83357.25695 | 80486.75371 | 50751.11573 | 80867.32293 | 42223.82237 | 35446.9576 | 28151.25544 | 26986.31513 | 28578.70773 | 75020.49035 | 5713.236762 | 9830.122921 | 19040.21519 | 17567.5226 | 29388.94372 | 16379.58952 | 37779.46208 | 78368.62417 | 12401.04981 | 51552.05637 | 38132.08128 | 14828.4861 | 52715.01114 | ||
| Q9UK41 | 2 | 2 | 72.56 | 0.25076095 | 5.278287157 | HN | XN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 28 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS28 PE=1 SV=1 | 327953.2 | 83042.09 | 80329.66 | 111629.1 | 91753.82733 | 90066.16701 | 213767.8406 | 267993.2034 | 221782.593 | 131728.3168 | 955685.7765 | 92855.92825 | 2800551.704 | 394320.8775 | 241159.5271 | 30237.78355 | 36257.10966 | 88269.30482 | 91673.57937 | 103659.4567 | 81990.66436 | 31729.41403 | 51113.48556 | 57781.80279 | 107109.3248 | 148832.4751 | 230014.0727 | ||
| Q15751 | 14 | 6 | 72.47 | 0.983190792 | 1.120638917 | HN | XA | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HERC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 29277323 | 29012821 | 14604233 | 25264802 | 24313593.93 | 12698869.69 | 7183295.929 | 12782738.5 | 11355264.68 | 43065105.38 | 7878727.805 | 11103300.89 | 6511068.789 | 18381525.54 | 20320565.04 | 37573217.94 | 22350652.26 | 19394307.15 | 14083543.03 | 15825780.91 | 13600975.61 | 26019808.03 | 42484238.58 | 6584554.55 | 15821370.77 | 14823866.39 | 28133256.22 | ||
| Q5T2W1 | 9 | 2 | 72.18 | 0.41688958 | 1.962774632 | XA | HN | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDZK1 PE=1 SV=2 | 125579.2 | 11142.94 | 58975.56 | 229861.5 | 27148.76519 | 88653.02869 | 80054.04373 | 77487.60713 | 54500.85768 | 37239.48959 | 34986.82151 | 97262.96192 | 18760.61973 | 41160.45296 | 11656.79673 | 36225.41655 | 48514.80161 | 58038.81364 | 30377.76508 | 15414.42637 | 157520.0428 | 96310.35275 | 111094.231 | 490.9452954 | 41965.77104 | 26854.64117 | 58758.41989 | ||
| P10092 | 2 | 1 | 72.18 | 0.678531461 | 1.928833852 | XA | HN | Calcitonin gene-related peptide 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALCB PE=1 SV=1 | 254486.1 | 3218.37 | 485890.6 | 1161852 | 9405.650004 | 4547.754709 | 177162.852 | 857574.8483 | 1546995.603 | 31097.02336 | 138662.7705 | 12008.38507 | 1351608.987 | 1230.165331 | 142094.3951 | 585332.3398 | 3842.184306 | 67727.49012 | 9926.115516 | 4414.997838 | 3587.949151 | 1884.630579 | 1251541.957 | 70691.60031 | 888917.0039 | 347709.9924 | 196266.7644 | ||
| Q9NWV4 | 2 | 2 | 72.06 | 0.383682344 | 3.915573591 | HN | XN | UPF0587 protein C1orf123 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1orf123 PE=1 SV=1 | 58649.64 | 38917.58 | 7317.015 | 29478.64 | 399906.8525 | 39708.73765 | 5388.349953 | 5486.458409 | 9967.738019 | 14001.25062 | 4170.242093 | 18132.25075 | 10805.49123 | 21721.34389 | 50197.24246 | 467394.3403 | 43386.16229 | 17519.00521 | 8572.184289 | 430.8928091 | 33024.94517 | 32442.64506 | 6414.738552 | 12208.70924 | 13416.77853 | 14619.89242 | 44190.41496 | ||
| P46531 | 4 | 1 | 71.93 | 0.420284992 | 1.35814487 | HN | XN | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOTCH1 PE=1 SV=4 | 441944.1 | 731585.6 | 741547.8 | 658366.1 | 418574.6236 | 599599.2763 | 197811.4471 | 589266.1278 | 500999.0904 | 357424.9053 | 273695.3131 | 108596.2756 | 997357.4484 | 409890.7705 | 1073279.757 | 215631.1611 | 861211.011 | 866166.2017 | 594548.7695 | 669837.1841 | 344677.0778 | 187576.7823 | 16098.07743 | 742187.5233 | 445687.7083 | 399997.9635 | 401084.1227 | ||
| Q8N335 | 6 | 3 | 71.64 | 0.285230104 | 2.353823408 | HN | XN | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPD1L PE=1 SV=1 | 85643.3 | 82493.78 | 45452.48 | 185550.8 | 39540.32217 | 22503.71753 | 19947.44614 | 62086.42283 | 22281.095 | 469703.4604 | 14586.50735 | 163504.0315 | 2771.07506 | 38034.80982 | 9486.162725 | 57314.31898 | 25550.36955 | 22785.12148 | 64986.89549 | 28321.39049 | 61609.33361 | 35952.19002 | 121187.1272 | 0 | 7256.772084 | 9276.7649 | 12869.23561 | ||
| P26572 | 5 | 2 | 71.59 | 0.215563571 | 1.609215086 | XN | XA | Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MGAT1 PE=2 SV=2 | 340958.3 | 242133.2 | 364491.4 | 464251.6 | 379081.2828 | 657383.8205 | 468450.6517 | 510608.255 | 658669.7323 | 4291.429828 | 245793.118 | 230210.5884 | 346056.0626 | 869390.3236 | 570732.7608 | 388855.4588 | 960884.217 | 798251.2521 | 692551.9282 | 585031.8809 | 740667.5359 | 779151.7529 | 1000275.982 | 209586.0315 | 988851.6412 | 707749.3531 | 871432.179 | ||
| P36405 | 1 | 1 | 71.48 | 0.992518841 | 1.212784855 | XA | XN | ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARL3 PE=1 SV=2 | 291887.9 | 18501.92 | 159802.7 | 732291.3 | 71729.17805 | 321024.6043 | 358747.7743 | 474724.4628 | 231825.8768 | 547423.227 | 211989.1569 | 394098.5176 | 363207.179 | 400985.745 | 64113.18925 | 285986.5592 | 30411.59381 | 98992.13594 | 201995.9593 | 243658.5597 | 649534.5547 | 209880.656 | 217722.4096 | 42281.19545 | 252167.9849 | 194073.6684 | 182425.9211 | ||
| Q9ULZ9 | 1 | 1 | 71.34 | 0.326308709 | 1.535644138 | XA | HN | Matrix metalloproteinase-17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP17 PE=1 SV=4 | 28246.34 | 4462.601 | 15469.46 | 48879.75 | 35308.78867 | 15694.23559 | 8096.083252 | 15075.17025 | 11492.07326 | 2699.587176 | 11490.63895 | 4218.596487 | 13367.76788 | 20364.87212 | 23684.04856 | 12087.50679 | 6103.252048 | 24972.5655 | 2488.210062 | 5507.90264 | 3162.524749 | 23605.25421 | 13423.26124 | 9196.873401 | 27119.51526 | 2903.29823 | 33488.59262 | ||
| Q96G03 | 9 | 2 | 71.32 | 0.773764057 | 1.292863645 | HN | XN | Phosphoglucomutase-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGM2 PE=1 SV=4 | 89222.02 | 173642.4 | 68496.59 | 34960.95 | 78688.04127 | 315869.7268 | 219506.7115 | 135656.7381 | 198621.4213 | 376441.4681 | 154425.2243 | 299691.4636 | 69061.08089 | 185048.603 | 121079.5451 | 34885.88358 | 125944.7081 | 253685.4142 | 237563.0889 | 281362.1752 | 192960.6132 | 123176.0025 | 52699.80549 | 52969.85979 | 123625.5835 | 124419.4905 | 64459.47946 | ||
| Q8TER0 | 3 | 2 | 70.89 | 0.197792999 | 1.502518081 | XA | HN | Sushi, nidogen and EGF-like domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SNED1 PE=1 SV=2 | 922348.5 | 1112969 | 522132.1 | 799905.8 | 417034.5765 | 273727.7527 | 397028.0903 | 544400.5065 | 659141.3966 | 476557.47 | 591142.3225 | 357800.2264 | 503769.0241 | 349993.6407 | 390695.6055 | 318153.2835 | 494601.889 | 276767.139 | 355965.7661 | 336945.8792 | 422801.0431 | 215423.6535 | 666589.3173 | 943500.9709 | 737400.9269 | 629552.6738 | 464902.2623 | ||
| Q9Y4D7 | 7 | 1 | 70.87 | 0.649314284 | 1.409561789 | XA | XN | Plexin-D1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLXND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 261474.1 | 901461.2 | 426202 | 252368.6 | 728334.7848 | 122065.8229 | 99442.38551 | 165076.2015 | 87955.87303 | 355419.718 | 236847.5216 | 173391.9264 | 118669.0738 | 283707.4014 | 702298.1089 | 326808.8033 | 250367.4649 | 447369.1311 | 108233.9985 | 293114.0051 | 108181.1161 | 181061.3238 | 287634.4022 | 421294.8815 | 193141.1747 | 170440.7874 | 396705.0318 | ||
| P59998 | 2 | 2 | 70.68 | 0.331507477 | 1.722824989 | XA | XN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARPC4 PE=1 SV=3 | 534380.3 | 184475.5 | 108660.7 | 783375.1 | 94778.76911 | 363835.6962 | 407849.9931 | 922542.9094 | 449681.6163 | 540303.7265 | 191520.8993 | 376222.3404 | 342984.1903 | 316104.9303 | 225338.5296 | 218012.3312 | 116114.8564 | 137283.1913 | 318056.1068 | 202023.3425 | 449545.6216 | 232734.6333 | 451223.7157 | 23177.86307 | 288858.3017 | 154961.3194 | 113877.3706 | ||
| Q9BWV1 | 5 | 2 | 70.45 | 0.197860926 | 1.604667967 | XA | XN | Brother of CDO OS=Homo sapiens GN=BOC PE=1 SV=1 | 417710.9 | 404905.5 | 478521.7 | 447490.7 | 203249.2719 | 856973.5217 | 1485440.816 | 407161.6409 | 1056977.526 | 359848.7122 | 853887.2512 | 155874.4623 | 448437.409 | 422005.193 | 428400.7901 | 450174.0724 | 203662.6923 | 370994.5066 | 284924.258 | 420866.9011 | 259772.4156 | 379622.3644 | 330765.2737 | 754763.1053 | 470328.6801 | 338004.1505 | 349503.1202 | ||
| P51580 | 3 | 3 | 70.3 | 0.019952302 | 8.624796187 | XA | HN | Thiopurine S-methyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPMT PE=1 SV=1 | 38870.17 | 8418.835 | 12801.36 | 243801.3 | 2878.978414 | 96114.56353 | 75845.91586 | 140362.3104 | 53398.2946 | 0 | 12516.44363 | 16271.7968 | 12814.17882 | 29183.71765 | 0 | 4244.935578 | 1330.506386 | 1610.320101 | 3003.472558 | 6382.652979 | 2669.284978 | 23177.97242 | 13815.59374 | 6639.982955 | 4942.130076 | 3018.353577 | 17965.99981 | ||
| P81605 | 2 | 2 | 70.3 | 0.114708382 | 8.749664845 | HN | XN | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 59284.89 | 2013.097 | 53449.06 | 65117.39 | 13477.42586 | 23182.74138 | 21876.07296 | 28116.38507 | 34548.7684 | 39101.51673 | 1377597.064 | 31738.11896 | 39711.1304 | 5146.696797 | 62052.45251 | 248182.5694 | 65936.92972 | 34076.30833 | 26814.3111 | 52092.07482 | 35202.98243 | 9013.063612 | 23995.63648 | 10576.39515 | 17342.09323 | 18537.56163 | 23981.96176 | ||
| Q9ULC0 | 1 | 1 | 69.89 | 0.916228891 | 7.361897905 | XA | HN | Endomucin OS=Homo sapiens GN=EMCN PE=1 SV=2 | 1754.19 | 13240.14 | 0 | 5737.252 | 18097.53546 | 4815.641992 | 153636.4885 | 17345.40355 | 249008.7564 | 5490.196902 | 11222.59511 | 21734.71829 | 7696.927497 | 695.7651138 | 1486.269498 | 7795.224047 | 3611.663257 | 3244.342322 | 13613.76587 | 10937.65308 | 22423.00899 | 1808.93383 | 6414.126521 | 25158.97908 | 4575.265359 | 9862.993247 | 1375.311384 | ||
| Q8IYT4 | 6 | 1 | 69.32 | 0.341506567 | 6.479279514 | XA | XN | Katanin p60 ATPase-containing subunit A-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KATNAL2 PE=2 SV=3 | 19149.83 | 796842.5 | 32491.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3864.767874 | 0 | 0 | 189354.1081 | 6048.509817 | 1037.03612 | 3677.522014 | 8205.368598 | 3209.230017 | 2478.452997 | 6324.559176 | 0 | 0 | 8262.606013 | 25.29949204 | 392.258436 | 2387.166107 | 11118.9465 | 0 | 3685.398747 | 105678.1748 | ||
| Q6MZW2 | 4 | 2 | 69.22 | 0.097357652 | 5.759148696 | XN | HN | Follistatin-related protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FSTL4 PE=2 SV=3 | 849827.2 | 181105.1 | 433561 | 562881.4 | 269850.7405 | 613572.9249 | 548988.9629 | 557539.9165 | 583409.4927 | 719692.2584 | 384652.3303 | 159006.7812 | 331752.3587 | 480803.6471 | 530947.1581 | 529340.0187 | 646668.9255 | 725304.4252 | 437406.9682 | 12109933.29 | 759521.9448 | 907635.253 | 696546.4622 | 179029.7964 | 573932.1182 | 696461.6954 | 9602741.776 | ||
| Q5VSG8 | 1 | 1 | 69.17 | 0.143108662 | 1.636516654 | XN | XA | Glycoprotein endo-alpha-1,2-mannosidase-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MANEAL PE=2 SV=1 | 21620.77 | 40225.46 | 43605.32 | 52393.78 | 33454.70467 | 13489.58215 | 19299.73673 | 9770.988825 | 28571.4429 | 41007.95679 | 107494.4747 | 15741.17489 | 23453.88427 | 43369.10014 | 52377.62809 | 39558.8304 | 41846.69733 | 49653.01871 | 10892.44854 | 28304.557 | 43038.7198 | 35883.60642 | 55444.45668 | 91633.76758 | 57215.06868 | 58295.33636 | 48766.01979 | ||
| P14778 | 4 | 1 | 69.02 | 0.595425707 | 1.61083039 | XN | HN | Interleukin-1 receptor type 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL1R1 PE=1 SV=1 | 187960 | 93886.48 | 106752.9 | 100493.6 | 12081.60919 | 141788.9276 | 59282.36417 | 122322.7648 | 69389.91499 | 47373.07692 | 7993.555325 | 68350.88084 | 295226.2286 | 0 | 57501.1083 | 64952.39111 | 77860.19759 | 74092.93202 | 245115.788 | 167393.3786 | 160777.2787 | 112614.7965 | 9486.272113 | 136901.0244 | 139528.0796 | 145053.2301 | 0 | ||
| P17927 | 4 | 2 | 68.84 | 0.162765963 | 1.85433111 | XN | HN | Complement receptor type 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 205229.2 | 84681.83 | 81270.42 | 112180.4 | 68645.8597 | 86175.66169 | 64897.31694 | 137488.7722 | 37843.1523 | 20555.46553 | 44655.62434 | 44076.73439 | 68730.80908 | 30123.3275 | 46455.05794 | 199971.9143 | 58500.30095 | 26010.01096 | 92697.15525 | 72013.66222 | 156274.8882 | 76461.1322 | 213721.4733 | 6835.069868 | 132420.9863 | 129638.7541 | 119568.2935 | ||
| P28676 | 3 | 2 | 68.75 | 0.379375463 | 3.783485346 | HN | XN | Grancalcin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GCA PE=1 SV=2 | 148681 | 112725.6 | 31372.95 | 17412.23 | 0 | 11348.84636 | 51427.33812 | 78454.04 | 205862.3339 | 623178.2218 | 118760.8055 | 150593.1848 | 85398.6618 | 46052.5826 | 93820.97409 | 35697.76417 | 22267.29416 | 9019.500065 | 112479.9765 | 10682.06879 | 24092.93938 | 6348.649011 | 1020.208787 | 9595.346294 | 105568.8449 | 35757.17507 | 7602.294367 | ||
| Q96HD1 | 2 | 1 | 68.69 | 0.184629798 | 1.508720024 | XN | XA | Cysteine-rich with EGF-like domain protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRELD1 PE=1 SV=3 | 256226.8 | 147402.4 | 151769.6 | 66456.86 | 68978.69225 | 138565.3099 | 169026.7392 | 98833.12057 | 110222.0745 | 183109.1676 | 361562.7757 | 41819.68619 | 217243.7099 | 369483.9832 | 153258.7473 | 80513.82362 | 139222.4381 | 268866.7571 | 129683.9631 | 216779.4644 | 178828.6952 | 127511.7774 | 249231.0022 | 261878.3767 | 216294.3481 | 145778.3691 | 295765.5504 | ||
| P41181 | 1 | 1 | 68.52 | 0.3662168 | 1.316726881 | XA | HN | Aquaporin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AQP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 276339.5 | 197850.4 | 627857.4 | 85246.96 | 217244.9594 | 129096.2424 | 200529.6868 | 259058.1304 | 49202.58913 | 92989.86202 | 249308.6381 | 193747.908 | 165068.4393 | 538089.1314 | 0 | 5551.147186 | 133708.2304 | 172675.1894 | 593561.5334 | 290233.7616 | 274106.1317 | 133601.4374 | 12780.09933 | 33709.8341 | 22680.29336 | 143741.8843 | 114431.0986 | ||
| P16083 | 6 | 3 | 68.52 | 0.80746431 | 1.217387835 | XN | HN | Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone] OS=Homo sapiens GN=NQO2 PE=1 SV=5 | 214349.5 | 51237.32 | 231098 | 210921.1 | 23389.13948 | 298045.8556 | 1874973.362 | 760231.3659 | 534311.1959 | 767452.2422 | 500574.5986 | 865889.2685 | 409175.1662 | 542706.3044 | 120983.0612 | 54546.00258 | 137796.2308 | 109044.3754 | 1128751.751 | 966153.3939 | 424332.3586 | 857678.6961 | 121119.054 | 286834.9893 | 191530.4997 | 173819.2184 | 120580.1729 | ||
| P28300 | 5 | 2 | 68.46 | 0.346812306 | 4.296441719 | HN | XA | Protein-lysine 6-oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LOX PE=1 SV=2 | 182454.1 | 300136.9 | 401264 | 1324584 | 668866.2268 | 5240.797815 | 105636.1863 | 139424.9001 | 118747.036 | 307471.2131 | 566068.7496 | 140943.5657 | 447824.5879 | 232899.985 | 752147.6008 | 11176509.39 | 195674.189 | 128234.5346 | 39904.556 | 100660.8518 | 62166.9224 | 74225.10881 | 482442.8536 | 1342062.605 | 1105996.399 | 141350.1328 | 197156.0073 | ||
| Q04721 | 8 | 3 | 68.14 | 0.544035824 | 1.241998275 | XN | XA | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOTCH2 PE=1 SV=3 | 372428.9 | 494839.8 | 535634.8 | 166114.1 | 178325.2618 | 420598.1916 | 201788.6737 | 95739.1085 | 304528.5347 | 201858.502 | 613711.7243 | 87702.273 | 186097.3996 | 565654.0874 | 225514.6893 | 136633.472 | 531228.5653 | 568364.2701 | 341700.7805 | 442753.9157 | 661434.1307 | 408431.2132 | 273329.9706 | 415384.48 | 157711.5197 | 453023.2223 | 286562.6343 | ||
| Q14410 | 4 | 1 | 67.78 | 0.263238535 | 7.018655252 | XA | HN | Glycerol kinase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GK2 PE=2 SV=2 | 3615.854 | 12730.98 | 9589.131 | 14175.01 | 13267.32414 | 481733.1267 | 41354.0012 | 4215.777719 | 43962.67375 | 27764.20234 | 6004.166777 | 6726.075929 | 4622.602911 | 10394.25967 | 2518.798177 | 4411.794741 | 15680.89503 | 10874.86201 | 18793.96793 | 104970.8384 | 52381.24166 | 2556.570248 | 3240.566291 | 15921.05884 | 8031.229024 | 21836.16615 | 21921.80141 | ||
| Q9NQX7 | 2 | 1 | 67.55 | 0.628410617 | 1.259486752 | XA | HN | Integral membrane protein 2C OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITM2C PE=1 SV=1 | 118768.7 | 94895.29 | 65771.9 | 143942.3 | 50359.9185 | 97347.73888 | 113507.2583 | 140467.9164 | 141183.1672 | 57879.99334 | 33526.52586 | 66236.0033 | 65940.5107 | 42911.2693 | 150187.5749 | 166109.3648 | 101127.9644 | 83253.78474 | 123104.6697 | 89777.303 | 133841.2516 | 35286.82839 | 137809.861 | 7720.935143 | 127289.0424 | 143413.052 | 158991.628 | ||
| Q15907;P62491 | 3 | 1 | 67.21 | 0.153987526 | 2.080721433 | HN | XN | Ras-related protein Rab-11B OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB11B PE=1 SV=4 | 166507.2 | 79240.74 | 155972.4 | 173706.8 | 98099.64376 | 98270.46244 | 150375.9924 | 161410.1117 | 74442.71887 | 332990.9395 | 387957.3798 | 210375.3934 | 67020.24634 | 289263.196 | 96755.16932 | 364754.323 | 64313.35063 | 57431.46108 | 47495.45062 | 133642.0411 | 147159.6694 | 108678.5734 | 71619.78171 | 95848.48409 | 88473.16803 | 117241.3921 | 88982.20385 | ||
| Q7Z4F1 | 5 | 3 | 67.15 | 0.616023362 | 1.125509204 | XA | HN | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP10 PE=1 SV=2 | 3269229 | 1936484 | 2967749 | 5209388 | 2795083.222 | 2441948.267 | 2907678.116 | 3461755.355 | 2092755.459 | 2307835.304 | 2678719.704 | 1310562.82 | 3740430.43 | 3816010.858 | 1115195.956 | 4403753.966 | 2286046.801 | 2403504.432 | 3293591.241 | 2895606.659 | 2759872.872 | 1804386.073 | 3629957.197 | 3139215.368 | 3164599.499 | 2013016.367 | 1637723.701 | ||
| P00439 | 3 | 2 | 67.1 | 0.05613621 | 3.850015721 | XA | HN | Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAH PE=1 SV=1 | 184636.4 | 255237.4 | 234523.1 | 1351541 | 15389.17144 | 61112.87635 | 164005.1809 | 199668.924 | 113917.2042 | 35831.98662 | 39460.25776 | 196952.5557 | 46389.4865 | 23661.48024 | 58050.89063 | 72498.97384 | 41675.31662 | 155614.2848 | 32954.71466 | 39788.10677 | 41871.99182 | 24630.26472 | 357538.7215 | 56020.25912 | 97797.00476 | 90881.60325 | 39189.17624 | ||
| Q6UWV6;Q9Y6X5 | 4 | 2 | 67.06 | 0.613294074 | 2.005129437 | HN | XN | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENPP7 PE=1 SV=3 | 48281.42 | 76548.38 | 100112.2 | 8553.807 | 22508.89294 | 32412.89509 | 42069.71273 | 32101.20273 | 70379.80906 | 14350.89321 | 51618.80519 | 48571.818 | 116415.6444 | 269509.9945 | 43748.93254 | 19806.62707 | 18420.28016 | 29211.17543 | 57316.46475 | 32444.8008 | 29578.80759 | 34164.45345 | 34772.58771 | 10536.2779 | 55944.76287 | 28223.42468 | 22063.1517 | ||
| P00492;Q9NRG1 | 2 | 2 | 66.75 | 0.982968387 | 1.190387129 | XN | XA | Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPRT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 47762.05 | 26506.33 | 18838.84 | 41444.79 | 20399.74715 | 28312.14413 | 57277.59337 | 33970.05128 | 64307.5354 | 66206.58128 | 70546.03228 | 63774.59698 | 55586.28088 | 27325.49716 | 57729.11149 | 7389.645753 | 18067.66019 | 26489.07069 | 181231.481 | 23237.60988 | 29510.31785 | 29653.20883 | 23027.77615 | 35367.07564 | 35281.98666 | 22521.65171 | 23494.76718 | ||
| Q14165 | 2 | 1 | 66.73 | 0.034350925 | 1.692183706 | XA | XN | Malectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MLEC PE=1 SV=1 | 140270.6 | 88555.29 | 122938.1 | 84681.96 | 116833.0089 | 67103.29448 | 75796.73217 | 113612.6226 | 98493.91027 | 75308.4691 | 97143.35127 | 38918.29025 | 100319.9357 | 185004.2407 | 100402.4281 | 82834.15006 | 55294.13391 | 83378.03079 | 56678.32985 | 61297.43865 | 74832.71788 | 43547.69239 | 7039.914433 | 53871.89283 | 87937.16665 | 63017.23941 | 88531.1314 | ||
| Q9BQI0 | 5 | 2 | 66.62 | 0.019761695 | 4.129389304 | XA | XN | Allograft inflammatory factor 1-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=AIF1L PE=1 SV=1 | 104682.3 | 28098.59 | 70738.99 | 546349.4 | 46332.71166 | 123901.8177 | 114226.09 | 219360.7172 | 92368.61764 | 92610.47084 | 77945.18848 | 208382.999 | 58676.2431 | 94782.00203 | 28797.63129 | 7585.18382 | 12699.99907 | 62177.10583 | 45581.38893 | 26758.87457 | 52224.68003 | 77132.1835 | 44760.30279 | 13775.0942 | 13200.51923 | 32204.47238 | 20333.01798 | ||
| Q9BZZ2 | 7 | 3 | 66.36 | 0.316493121 | 1.369708275 | XA | HN | Sialoadhesin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIGLEC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 296927.4 | 162951.9 | 177552.8 | 306410.8 | 192124.4993 | 364519.0193 | 598843.194 | 598491.405 | 338469.817 | 239764.0981 | 36577.48741 | 127914.0086 | 471367.8735 | 163151.2799 | 376029.764 | 146556.327 | 232504.9605 | 422876.8918 | 432917.8147 | 328670.3403 | 134520.9529 | 327581.8234 | 283772.5329 | 106906.4106 | 209196.0481 | 243867.1595 | 210767.9408 | ||
| Q9Y696 | 3 | 2 | 66.26 | 0.10500797 | 2.818771027 | XA | HN | Chloride intracellular channel protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLIC4 PE=1 SV=4 | 40272.2 | 4992.16 | 14257.3 | 77808.27 | 8784.507594 | 85337.98807 | 28486.30183 | 55185.15935 | 105937.515 | 22908.94062 | 10681.78744 | 10429.88346 | 32761.93667 | 14041.90979 | 13035.70098 | 28216.13878 | 5221.461323 | 12079.8948 | 26368.56007 | 14269.80046 | 16597.46484 | 58635.72098 | 16731.41061 | 2392.304288 | 10729.77961 | 14438.28505 | 9669.230142 | ||
| P58401 | 3 | 1 | 66.26 | 0.553026698 | 1.221036722 | HN | XA | Neurexin-2-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=NRXN2 PE=2 SV=1 | 113424.2 | 12979.2 | 45787.68 | 92668.22 | 138287.3812 | 153738.58 | 306032.0564 | 135408.1649 | 224732.163 | 157828.1303 | 445865.5999 | 262483.7005 | 359721.1663 | 62763.96531 | 117559.6019 | 0 | 30541.78732 | 56634.33537 | 32752.04555 | 473452.0959 | 111517.1687 | 57637.67403 | 70839.11846 | 153743.803 | 32395.41398 | 325937.4904 | 140814.6992 | ||
| P08118 | 3 | 3 | 66.14 | 0.56707476 | 1.945287173 | HN | XA | Beta-microseminoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSMB PE=1 SV=1 | 3724114 | 10591323 | 3133790 | 6960441 | 24803643.25 | 531892.3224 | 538604.1325 | 3588300.178 | 860617.2627 | 4929083.903 | 338217.5067 | 3586298.3 | 2179673.446 | 13628445 | 26147123.87 | 3804670.39 | 12536370.14 | 39320984.01 | 501638.27 | 489963.2125 | 356541.9811 | 410736.1659 | 5927206.34 | 46889713.83 | 6475990.159 | 19381569.36 | 11748858.47 | ||
| Q9Y2V2 | 2 | 1 | 66.02 | 0.794483639 | 1.429856875 | HN | XN | Calcium-regulated heat stable protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CARHSP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 99179.41 | 12896.18 | 9253.147 | 109203.6 | 9820.177389 | 47117.67644 | 124900.2114 | 183028.288 | 101853.5713 | 55710.10262 | 117743.8822 | 166382.9016 | 244929.9502 | 23623.2557 | 30174.41708 | 70310.13941 | 10425.28412 | 41556.96502 | 27092.85323 | 86201.42484 | 100863.8468 | 169369.007 | 43485.05673 | 6600.652008 | 46836.01572 | 39404.33999 | 12267.82311 | ||
| Q6H9L7 | 2 | 2 | 65.99 | 0.145759968 | 2.278211239 | XA | XN | Isthmin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ISM2 PE=2 SV=1 | 486656.5 | 46535.01 | 89610.43 | 476714.1 | 121276.8503 | 78695.28938 | 240502.2396 | 211457.3177 | 408629.6312 | 31526.6824 | 86135.701 | 407481.4604 | 200699.0221 | 112318.6121 | 60628.10971 | 45141.42224 | 66311.4627 | 182875.1126 | 106539.7814 | 140924.2982 | 116004.4993 | 86030.48314 | 132149.19 | 87857.93313 | 126253.1079 | 45372.54706 | 107014.3521 | ||
| P25685 | 5 | 1 | 65.94 | 0.067531895 | 2.297633471 | XA | HN | DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNAJB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 15763.82 | 1128.182 | 7237.892 | 29472 | 4728.299937 | 14010.18316 | 13635.97549 | 53332.37749 | 26240.85901 | 204.5265742 | 3775.762749 | 38626.84685 | 61.7892093 | 3004.565895 | 5452.41332 | 12566.78961 | 5058.710058 | 3300.817742 | 9390.640494 | 9969.856622 | 20828.06878 | 6050.73482 | 20553.60218 | 2762.918182 | 6575.043648 | 10143.20741 | 6496.368217 | ||
| Q13231 | 2 | 2 | 65.82 | 0.280075938 | 1.530243479 | HN | XA | Chitotriosidase-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHIT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 636986.7 | 466639.7 | 232915.7 | 21713.17 | 547089.0921 | 254112.3453 | 382613.5948 | 416096.5247 | 285140.7295 | 1162206.189 | 519936.6333 | 509474.2749 | 281757.7157 | 399060.6254 | 608174.5677 | 488535.3214 | 451706.931 | 542197.8749 | 116671.0386 | 265328.0607 | 153923.7436 | 347124.4142 | 793746.5031 | 785569.5033 | 27901.63046 | 475587.353 | 909970.7641 | ||
| P01769 | 4 | 3 | 65.79 | 0.106398842 | 1.476738993 | XN | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region GA OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 1411535 | 6468545 | 2144029 | 2871021 | 5668887.625 | 3546203.131 | 2219082.056 | 5357697.414 | 8757195.876 | 2599285.164 | 3226093.188 | 3558734.669 | 3874240.571 | 2187729.087 | 5374986.964 | 1713551.195 | 6186685.697 | 5788521.611 | 5275798.746 | 5227832.394 | 5203361.138 | 6154679.45 | 5234162.233 | 8971146.829 | 5023156.864 | 6817965.203 | 3053906.011 | ||
| Q01955 | 6 | 2 | 65.78 | 0.386115733 | 1.416099072 | XA | HN | Collagen alpha-3(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A3 PE=1 SV=3 | 13446.93 | 24679.83 | 63794.58 | 25072 | 34311.87997 | 14885.36902 | 11290.58787 | 38536.43009 | 3933.556839 | 6683.718436 | 9748.734693 | 9573.949555 | 134.2876881 | 1652.233998 | 44171.44971 | 50382.28554 | 22965.05867 | 17071.80564 | 5184.541418 | 1532.60248 | 2541.753428 | 49497.99138 | 34132.15362 | 21945.60548 | 12512.56561 | 38080.87257 | 43411.87815 | ||
| Q7L266 | 3 | 2 | 65.59 | 0.604854566 | 1.302878365 | XA | XN | L-asparaginase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASRGL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 42188.14 | 52812.05 | 141229.6 | 263615.2 | 1197.47611 | 147327.3056 | 170087.7182 | 89636.76161 | 143439.0874 | 52575.70993 | 96787.76015 | 244893.9235 | 117812.5859 | 196973.9265 | 44422.91526 | 0 | 86033.07782 | 116524.5116 | 104372.272 | 94245.92944 | 90475.25417 | 155778.4866 | 67280.30507 | 45156.49295 | 52647.57093 | 69550.64753 | 127577.8589 | ||
| O60812 | 3 | 1 | 65.45 | 0.565564319 | 8.512399369 | HN | XA | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C-like 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HNRNPCL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 10860.57 | 580.4449 | 9859.827 | 16320.34 | 12553.48256 | 502.8130887 | 2069.480972 | 1594.73245 | 2727.993464 | 0 | 70404.66783 | 105038.3919 | 0 | 104844.856 | 51743.62775 | 78918.5887 | 38199.67418 | 36650.1715 | 10275.51743 | 1665.282492 | 20560.2681 | 115682.644 | 10356.20328 | 11231.42559 | 93738.39509 | 7588.130652 | 18120.28748 | ||
| P04211 | 2 | 1 | 65.07 | 0.178461745 | 1.751690261 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V region 4A OS=Homo sapiens PE=4 SV=1 | 1762275 | 2856925 | 1538848 | 1531488 | 3462909.918 | 1116590.872 | 767409.2977 | 1231756.578 | 1053015.925 | 8941178.481 | 1422234.258 | 3048187.919 | 1489541.655 | 827175.6074 | 4033019.449 | 2295447.856 | 2311967.756 | 2469277.023 | 2216699.22 | 1721221.511 | 942419.1875 | 1565781.828 | 4114214.56 | 1237924.737 | 1489628.072 | 1209651.85 | 1343688.057 | ||
| Q8TE73 | 19 | 4 | 64.77 | 0.472344958 | 1.52715128 | XN | HN | Dynein heavy chain 5, axonemal OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNAH5 PE=1 SV=3 | 186941.6 | 449018.1 | 319379.6 | 273198 | 162012.8645 | 186794.4263 | 220970.9018 | 339328.4375 | 192033.7978 | 394742.7308 | 203027.5892 | 288900.3122 | 99065.68772 | 73600.48754 | 291813.3691 | 124484.8739 | 329815.9191 | 218484.4733 | 562305.8313 | 253657.3857 | 493391.8913 | 196908.0223 | 744456.5933 | 243724.5708 | 407738.4093 | 86418.62449 | 102254.2745 | ||
| Q13765;Q9BZK3 | 3 | 3 | 64.68 | 0.933997714 | 1.670989744 | XA | HN | Nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=NACA PE=1 SV=1 | 109614 | 2724.263 | 1575.66 | 111587 | 107795.5952 | 223663.0019 | 583832.166 | 1178639.462 | 544955.4196 | 366397.1585 | 190853.6458 | 594653.1969 | 222890.2876 | 34099.44979 | 27649.22612 | 63301.69586 | 74278.64348 | 140062.2718 | 1112861.912 | 138316.1927 | 227043.2348 | 220312.5888 | 25283.21586 | 126969.5689 | 30565.6739 | 94817.40391 | 36068.33553 | ||
| Q92890 | 4 | 1 | 64.66 | 0.628237861 | 1.384697322 | XA | HN | Ubiquitin fusion degradation protein 1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=UFD1L PE=1 SV=3 | 41451.11 | 46371.65 | 52.83819 | 78808.04 | 6561.784013 | 31923.75415 | 24397.10729 | 17039.83911 | 56023.13004 | 23414.03763 | 142.2524747 | 44182.5141 | 20899.13946 | 19709.92588 | 1084.078156 | 78479.96265 | 2626.175293 | 28014.55397 | 40251.10447 | 17039.61305 | 19584.55365 | 14229.84032 | 64850.36573 | 34400.40849 | 19842.53191 | 13266.05428 | 5433.831032 | ||
| P17643 | 2 | 1 | 64.66 | 0.862889205 | 1.404950907 | XA | XN | 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TYRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 290080.2 | 58668.88 | 168983.9 | 4689.846 | 124249.3835 | 209.092751 | 109.7921018 | 36115.46734 | 2629.175622 | 4815.066448 | 181.4253442 | 915.2446091 | 114.8353313 | 26758.26174 | 79431.44499 | 237874.7577 | 129358.0714 | 32222.3211 | 8035.341409 | 119291.5358 | 40500.91918 | 9899.799652 | 106.6173725 | 241474.9081 | 12394.42669 | 22753.70417 | 33627.99127 | ||
| Q6ZQQ6 | 23 | 6 | 64.57 | 0.849738905 | 1.150453033 | HN | XN | WD repeat-containing protein 87 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR87 PE=2 SV=3 | 1529861 | 1525905 | 1856452 | 2960727 | 5865441.056 | 2905778.454 | 3368522.48 | 2242351.85 | 3004601.137 | 1407318.984 | 2707596.402 | 2771282.21 | 2849700.204 | 1048147.94 | 6478931.751 | 3201111.813 | 2145393.507 | 3091029.065 | 5410482.111 | 2545884.108 | 1606091.793 | 2401471.996 | 2073885.263 | 2287045.307 | 1698507.034 | 1524118.774 | 2791984.357 | ||
| Q96DT5 | 32 | 11 | 64.5 | 0.988812267 | 1.028283232 | XA | HN | Dynein heavy chain 11, axonemal OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNAH11 PE=1 SV=3 | 1.03E+08 | 92016325 | 73175568 | 80964268 | 71822465.53 | 43524598.49 | 48251967.34 | 55903374.08 | 46529782.93 | 61928170.67 | 117015633.8 | 56752285.06 | 54711218.34 | 79087112.68 | 57678601.47 | 62670223.46 | 51493590.2 | 56892794.26 | 50060521.08 | 41238557.07 | 71872927.85 | 52975364.57 | 67784946.52 | 81959705.23 | 59261464.9 | 77143654.28 | 111162769.5 | ||
| P21802 | 5 | 2 | 64.22 | 0.155982238 | 1.70775734 | XA | HN | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGFR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 55684.22 | 460664.8 | 248648 | 92904.05 | 254145.3629 | 126297.1036 | 165708.7334 | 47807.52327 | 385623.7053 | 13804.62952 | 125904.2894 | 46322.91005 | 59457.80534 | 132555.8872 | 127984.3014 | 158784.4935 | 163538.4047 | 247610.148 | 103644.6806 | 117549.3745 | 105302.0161 | 232979.9021 | 200781.2752 | 339755.8318 | 178264.5712 | 255644.5597 | 198536.2082 | ||
| Q9HCM3 | 3 | 3 | 63.78 | 0.663589565 | 1.138851227 | XN | HN | UPF0606 protein KIAA1549 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA1549 PE=1 SV=4 | 510803.8 | 621943 | 531126.2 | 396355.7 | 365915.6216 | 495566.2214 | 494973.5095 | 483649.8151 | 539385.6883 | 211770.3026 | 463468.2706 | 651885.0791 | 629530.3802 | 481498.9349 | 380401.8435 | 86043.82767 | 762720.502 | 492967.1219 | 393566.3472 | 401912.0527 | 505669.1973 | 399536.7818 | 1099977.027 | 997644.3415 | 244941.2065 | 437686.1832 | 257013.9784 | ||
| Q9NZU0 | 6 | 3 | 63.56 | 0.618448373 | 1.205285072 | XN | HN | Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLRT3 PE=1 SV=1 | 215363.9 | 809682.3 | 624478.5 | 694035.7 | 492275.3725 | 577168.5075 | 236312.9433 | 688529.7323 | 649159.1913 | 444463.9068 | 478827.1078 | 643107.3167 | 411386.0853 | 392732.3122 | 670403.5797 | 253296.6796 | 632369.8723 | 575729.3957 | 1090083.448 | 609304.4738 | 355805.3071 | 413806.5718 | 546228.4357 | 746064.1997 | 465436.2472 | 658502.0015 | 541343.8856 | ||
| O15145 | 2 | 2 | 63.47 | 0.383725178 | 1.66846286 | XA | XN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARPC3 PE=1 SV=3 | 681781.8 | 59865.49 | 346007.5 | 591846.3 | 109781.0067 | 394971.8057 | 474729.6154 | 982351.308 | 289882.591 | 1073276.883 | 181065.5416 | 557858.8978 | 213661.5755 | 286495.139 | 174734.2168 | 126188.332 | 282114.5056 | 200023.935 | 182453.8803 | 255144.5765 | 486704.769 | 228017.7928 | 586404.4796 | 6961.323969 | 262304.9906 | 226009.5753 | 122189.7849 | ||
| Q9UJ72 | 1 | 1 | 63.26 | 0.359606989 | 1.867417082 | XN | XA | Annexin A10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA10 PE=1 SV=3 | 70893.14 | 111597.8 | 66764.64 | 14781.22 | 12513.87908 | 27935.70717 | 733.8097843 | 5915.079857 | 71550.87965 | 55563.26884 | 50513.19632 | 64997.8584 | 170522.2508 | 38971.96591 | 18937.80884 | 46723.93544 | 38685.85781 | 51188.08643 | 62860.35812 | 245104.7779 | 216701.8796 | 17961.11013 | 3321.599763 | 6144.596408 | 57063.12958 | 61963.75151 | 43513.39842 | ||
| P07197 | 8 | 2 | 63.03 | 0.275853123 | 1.768838427 | HN | XN | Neurofilament medium polypeptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEFM PE=1 SV=3 | 570952.5 | 723319.4 | 264322.6 | 518053.3 | 719798.5998 | 611340.387 | 547394.0943 | 459942.9793 | 304333.5567 | 1260679.661 | 1114837.121 | 2193804.398 | 323803.377 | 550827.4554 | 877760.0143 | 148414.9756 | 1018762.707 | 583979.3338 | 729643.1599 | 401542.5973 | 610494.674 | 479621.0586 | 403733.0949 | 227738.3756 | 317382.6817 | 525088.545 | 868693.8855 | ||
| P80303 | 2 | 2 | 63.01 | 0.462265871 | 1.720199861 | HN | XA | Nucleobindin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUCB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1234356 | 634660.4 | 570019.7 | 1647666 | 579466.451 | 474008.8588 | 788386.3322 | 1336007.078 | 643021.1926 | 683167.8987 | 4300872.801 | 614318.5973 | 1995255.216 | 3339743.05 | 687028.1285 | 922359.7079 | 578153.6279 | 481738.5826 | 821628.9383 | 1945920.416 | 1087219.919 | 483941.9292 | 1566545.848 | 1537983.194 | 828729.4904 | 1049809.506 | 1185761.896 | ||
| Q13201 | 7 | 2 | 62.97 | 0.575250678 | 1.358070717 | HN | XA | Multimerin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMRN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 611130 | 5745189 | 4484852 | 611012.4 | 1133440.413 | 2167117.42 | 5326068.473 | 702235.6125 | 4650243.992 | 586943.6473 | 17835024.42 | 403320.4812 | 5641125.79 | 3731120.971 | 2156542.304 | 1217759.642 | 1236948.138 | 1728704.137 | 1232710.672 | 4456862.371 | 4115622.437 | 3008042.995 | 1999836.222 | 7776685.568 | 2037623.511 | 6565053.868 | 1347097.554 | ||
| Q86Y38 | 5 | 3 | 62.86 | 0.760897555 | 1.688490352 | XA | HN | Xylosyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=XYLT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 335747.5 | 210724.8 | 124131.9 | 225039.5 | 48126.86013 | 24.80778118 | 144616.9993 | 1382.00786 | 241130.2842 | 216653.2888 | 165697.962 | 26987.89313 | 34898.19504 | 65363.7217 | 94817.82049 | 60794.23267 | 112132.6613 | 10887.72223 | 192581.7356 | 73980.02009 | 80720.58655 | 36328.0468 | 25062.12531 | 250031.648 | 58792.1533 | 144799.1675 | 18196.35553 | ||
| P26232 | 10 | 1 | 62.8 | 0.889629389 | 1.399092829 | XN | XA | Catenin alpha-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTNNA2 PE=1 SV=5 | 180792.6 | 165499.4 | 176329.8 | 53551.92 | 82940.8425 | 266110.283 | 238143.7548 | 330841.6995 | 92189.18341 | 162732.0271 | 256511.9411 | 422446.0393 | 215315.9331 | 241181.1466 | 308389.9164 | 17862.60573 | 384097.8074 | 163382.037 | 371753.1398 | 174876.9436 | 253802.9358 | 215665.3445 | 61931.76257 | 389658.3514 | 530447.8207 | 210837.5127 | 10546.23728 | ||
| Q13813 | 20 | 4 | 62.75 | 0.548487745 | 3.35669113 | XN | HN | Spectrin alpha chain, non-erythrocytic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPTAN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 374903.5 | 705257.7 | 308203.7 | 272401.6 | 241180.6356 | 540206.2494 | 1271189.75 | 379688.2607 | 1408816.453 | 534945.1453 | 1057990.584 | 196078.2996 | 592499.2027 | 739625.2879 | 604224.3235 | 456114.8247 | 244801.3631 | 624024.111 | 272184.1485 | 11744204.84 | 351899.6153 | 796168.6598 | 164940.0813 | 1643667.808 | 809567.5882 | 592576.349 | 577098.6735 | ||
| P01215 | 2 | 1 | 62.73 | 0.133590575 | 1.39906668 | HN | XA | Glycoprotein hormones alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CGA PE=1 SV=1 | 386774.1 | 340753.8 | 234638.3 | 521851.9 | 287696.3796 | 183922.3361 | 215942.8108 | 379020.5635 | 353073.2109 | 436797.2239 | 580200.6143 | 233885.1735 | 339254.8534 | 629263.1646 | 347133.2383 | 559168.9966 | 552504.0806 | 384225.4062 | 165113.7288 | 371824.269 | 374802.3359 | 93819.59743 | 559755.8707 | 435095.2864 | 327509.4507 | 285696.6851 | 385580.6854 | ||
| P37173 | 2 | 1 | 62.68 | 0.838470067 | 1.450979099 | XA | HN | TGF-beta receptor type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 34686.33 | 524216.8 | 193958.8 | 56896.81 | 204596.6255 | 24616.47012 | 18694.32004 | 42194.08765 | 171565.9655 | 126632.5941 | 121240.524 | 40296.21791 | 62588.5926 | 53638.58135 | 186410.7338 | 107647.3349 | 59010.48193 | 118788.8832 | 13620.93807 | 101738.1967 | 82535.01715 | 92974.35444 | 8921.406668 | 403289.1779 | 59689.1115 | 149104.4373 | 74945.29351 | ||
| P07357 | 1 | 1 | 62.43 | 0.041963495 | 2.678514617 | XA | HN | Complement component C8 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=C8A PE=1 SV=2 | 194292.4 | 38472.51 | 45634.81 | 71019.43 | 45387.68573 | 70118.2162 | 233264.8024 | 378073.6006 | 124992.1893 | 110003.3384 | 241.0619148 | 93172.3598 | 0 | 0 | 62292.28479 | 34525.58162 | 51506.013 | 96737.6382 | 167242.0007 | 290591.0514 | 115058.1656 | 129054.5427 | 106022.5783 | 1308.01708 | 210353.6038 | 63642.49378 | 86776.15342 | ||
| Q15084 | 3 | 2 | 62.03 | 0.24816253 | 1.481463775 | XA | XN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDIA6 PE=1 SV=1 | 231391.6 | 271557.2 | 347990.7 | 316052.8 | 123810.392 | 518981.8414 | 492276.673 | 684373.1028 | 702060.9374 | 283412.9929 | 304483.2447 | 466845.4944 | 229433.2691 | 110573.5396 | 230450.2789 | 311624.7204 | 334753.4533 | 293418.8836 | 262822.3466 | 343868.7853 | 234387.6178 | 281772.4479 | 567094.3136 | 256944.471 | 146144.0163 | 140026.285 | 256703.7161 | ||
| Q9ULK6 | 2 | 1 | 61.92 | 0.874686506 | 1.208268855 | HN | XN | RING finger protein 150 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNF150 PE=2 SV=2 | 656906.5 | 194916.7 | 189591.6 | 265829.9 | 99018.88926 | 156656.7577 | 284255.0867 | 275386.9277 | 208491.9604 | 296027.0456 | 429118.4369 | 115808.4959 | 489086.6665 | 368884.0029 | 120093.3803 | 155821.7447 | 163843.6148 | 222736.6588 | 188462.9359 | 182241.0119 | 243460.9346 | 98390.60892 | 204757.2973 | 175926.1416 | 287271.9185 | 257823.5626 | 316048.5369 | ||
| P54756 | 5 | 1 | 61.88 | 0.413817613 | 1.312261804 | XA | HN | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 3083196 | 1734222 | 3310621 | 1646698 | 3678750.64 | 2039976.702 | 1074978.401 | 2450893.67 | 753605.4569 | 1704223.572 | 1228558.977 | 3532401.95 | 780923.5546 | 1214965.012 | 2591003.511 | 1950292.45 | 1001493.944 | 1063969.43 | 1452908.098 | 746064.0452 | 618745.141 | 2046839.497 | 1674627.394 | 4820649.243 | 1853677.848 | 893003.5487 | 1248580.937 | ||
| Q13508 | 4 | 4 | 61.81 | 0.146922691 | 1.840910795 | HN | XN | Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ART3 PE=1 SV=2 | 561510 | 720583.7 | 1117536 | 1149273 | 1172583.942 | 836260.0066 | 983694.2408 | 821161.1734 | 1368512.858 | 806955.962 | 1325295.347 | 2930586.832 | 900492.1937 | 388306.9085 | 1241427.584 | 228573.835 | 1629986.023 | 1570245.068 | 959433.1134 | 943569.2827 | 552650.7171 | 288083.6692 | 1045262.291 | 842785.6948 | 449463.0905 | 586199.1487 | 319735.9574 | ||
| Q9UQN3 | 6 | 2 | 61.78 | 0.854486157 | 1.518940927 | HN | XA | Charged multivesicular body protein 2b OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP2B PE=1 SV=1 | 960113.2 | 367747 | 283658.3 | 343336 | 175639.4647 | 266978.394 | 405826.5972 | 464722.1089 | 500560.3367 | 433521.0141 | 1881835.019 | 315059.4087 | 765485.0713 | 1273436.916 | 159761.245 | 105426.6139 | 399998.8706 | 389728.2562 | 394200.1175 | 589732.7465 | 499268.3025 | 205515.1606 | 514871.8487 | 420754.3982 | 406774.708 | 781728.1613 | 279364.8049 | ||
| O75506 | 2 | 1 | 61.67 | 0.688367393 | 1.490070546 | XA | HN | Heat shock factor-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSBP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 11749.73 | 4433.942 | 5234.116 | 19757.44 | 10138.54712 | 29710.35108 | 40668.22297 | 86816.66662 | 77215.4408 | 2320.07094 | 32540.8873 | 35179.05092 | 63948.55966 | 12659.31347 | 9258.798015 | 17944.67189 | 6010.818695 | 11890.12717 | 92957.84102 | 17530.9704 | 31905.49013 | 102854.605 | 6149.055684 | 884.6880655 | 15669.55277 | 3002.951321 | 3127.635538 | ||
| Q9ULC6 | 3 | 3 | 61.45 | 0.216600074 | 5.053947071 | HN | XN | Protein-arginine deiminase type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PADI1 PE=1 SV=2 | 494406.5 | 426019.9 | 320405.5 | 2635799 | 7326120.262 | 636262.6654 | 384562.0245 | 1566492.692 | 516014.14 | 2065653.946 | 447609.249 | 9887317.986 | 317839.2431 | 1034059.93 | 479084.2068 | 467841.9728 | 28781150.18 | 14401658.26 | 6687743.524 | 457759.9836 | 648342.6898 | 211229.7009 | 368691.1811 | 372419.9267 | 1865942.913 | 184068.5576 | 656674.7237 | ||
| P36222 | 3 | 1 | 61.2 | 0.086002357 | 1.840132022 | XN | HN | Chitinase-3-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHI3L1 PE=1 SV=2 | 31804.23 | 38181.64 | 19037.73 | 8817.609 | 5533.511894 | 42827.13053 | 69663.85218 | 15606.7335 | 124013.1551 | 36296.48766 | 0 | 4522.600107 | 21700.43809 | 6576.665937 | 117626.0008 | 0 | 13234.70011 | 54633.01882 | 187755.8766 | 84406.94192 | 26888.46709 | 20070.32766 | 9508.90965 | 19810.34269 | 33374.40305 | 26686.90039 | 59976.87974 | ||
| Q9NTX5 | 2 | 2 | 61.07 | 0.245318914 | 1.795832972 | XA | HN | Ethylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECHDC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 336711.2 | 47883.08 | 218167.6 | 522721.8 | 112259.6132 | 497659.571 | 403554.9216 | 576285.071 | 351908.8108 | 253442.3931 | 134464.7827 | 301248.0615 | 162991.745 | 78530.2764 | 247349.8339 | 318254.219 | 99819.21935 | 111826.4798 | 182499.822 | 207548.1179 | 305418.9072 | 216025.1269 | 341161.1091 | 174786.7478 | 228020.5895 | 167358.7313 | 142203.4342 | ||
| P48163 | 4 | 2 | 60.96 | 0.388383175 | 1.32905857 | XA | XN | NADP-dependent malic enzyme OS=Homo sapiens GN=ME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 341076.2 | 411243.9 | 630403 | 306835.2 | 290053.3999 | 436138.5898 | 558042.6812 | 369104.5115 | 695934.5403 | 228903.022 | 449289.1025 | 1262174.563 | 313432.5242 | 414653.9856 | 400508.1681 | 142209.1639 | 339962.1385 | 323357.2901 | 413308.7112 | 418486.6797 | 329483.6987 | 233629.4268 | 475258.4921 | 372303.3403 | 316163.0966 | 209966.8752 | 270266.5487 | ||
| Q9P0K1 | 3 | 1 | 60.74 | 0.027619486 | 2.561793732 | XA | XN | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 22 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAM22 PE=1 SV=1 | 27599.45 | 39266.04 | 11318.63 | 17780.15 | 11126.38756 | 17181.87976 | 11965.5658 | 38038.4923 | 50615.33201 | 4566.897168 | 26885.9127 | 3521.760464 | 59615.35116 | 10204.0561 | 15641.21075 | 6716.476868 | 14486.49649 | 13409.4168 | 3440.867984 | 21314.98676 | 1907.502422 | 4300.711264 | 18932.81677 | 10128.34309 | 5870.58908 | 11313.87385 | 10577.20209 | ||
| P08237 | 6 | 4 | 60.46 | 0.253817318 | 1.987210387 | XA | XN | 6-phosphofructokinase, muscle type OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFKM PE=1 SV=2 | 229450.4 | 124122.5 | 282744 | 1550390 | 742046.9603 | 344488.8361 | 243647.9277 | 665728.3125 | 294465.4138 | 619430.1541 | 176884.3701 | 595133.3936 | 265914.4289 | 218108.4558 | 282122.1346 | 515435.1026 | 119569.9331 | 197034.3893 | 148576.3431 | 91113.06405 | 248339.4641 | 266034.273 | 350876.5186 | 383493.2801 | 336937.3751 | 216175.3138 | 211403.8139 | ||
| P01210 | 1 | 1 | 60.45 | 0.03868548 | 89.58910451 | HN | XA | Proenkephalin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=PENK PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 571.9956 | 0 | 5973.088276 | 5936.280276 | 1114.594486 | 0 | 0 | 68857.33607 | 19072.95051 | 3645.986367 | 3820.966839 | 35.70007568 | 14836.74489 | 1100350.671 | 0 | 7429.402638 | 2546.648927 | 12452.48145 | 11482.01395 | 5417.083897 | 0 | 27319.69343 | 4854.999702 | 35.1697489 | 339.6971968 | ||
| P43234 | 1 | 1 | 60.41 | 0.128353523 | 1.581304248 | XN | HN | Cathepsin O OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSO PE=2 SV=1 | 528672.2 | 413524.6 | 290027.1 | 675838.8 | 304028.9178 | 214095.4234 | 251407.715 | 227935.4761 | 265918.3859 | 187688.0528 | 208851.8115 | 119324.5558 | 524421.1442 | 107646.5037 | 103645.7342 | 340220.1824 | 401609.3864 | 209430.0905 | 307646.1005 | 276274.5166 | 809975.3726 | 272514.2782 | 362104.6318 | 119838.3966 | 396031.8496 | 229512.8701 | 709458.2197 | ||
| P20073 | 2 | 1 | 60.35 | 0.115951551 | 1.731842835 | XA | XN | Annexin A7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA7 PE=1 SV=3 | 577114.4 | 146353.5 | 231426.1 | 738179.2 | 808014.677 | 390761.9508 | 364483.4048 | 562603.0916 | 361207.2512 | 121340.1721 | 287739.5471 | 544978.0922 | 288895.0696 | 157983.9213 | 412840.6958 | 473839.7586 | 220792.7247 | 519084.0447 | 549062.0319 | 260415.6071 | 364635.6432 | 251661.6989 | 133540.2354 | 142525.4468 | 174079.5948 | 359787.1231 | 177989.4587 | ||
| Q9NPH3 | 6 | 4 | 59.89 | 0.283662185 | 1.303518054 | HN | XN | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL1RAP PE=1 SV=2 | 196415.6 | 505155.6 | 363438.9 | 347193.8 | 328607.048 | 575866.9312 | 629262.9437 | 222896.9858 | 441339.2344 | 529761.2554 | 443926.1092 | 545657.2518 | 159934.8722 | 490707.8517 | 522792.6804 | 518097.4649 | 510811.3174 | 339624.1422 | 617090.4774 | 178967.4465 | 225022.377 | 381897.7739 | 330668.4429 | 702479.6502 | 186716.7249 | 159736.5712 | 333075.844 | ||
| P30084 | 4 | 1 | 59.84 | 0.066451116 | 1.858735094 | HN | XA | Enoyl-CoA hydratase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECHS1 PE=1 SV=4 | 23713.31 | 7449.363 | 8265.555 | 36967.08 | 20908.73073 | 11972.13469 | 15537.95454 | 13711.78743 | 9905.478662 | 47735.21743 | 22441.93438 | 47835.35453 | 20024.21168 | 48803.27076 | 22939.14216 | 38733.21757 | 9597.654724 | 17784.6368 | 25434.14434 | 11586.83553 | 10851.7297 | 21912.8798 | 15795.17201 | 33069.53865 | 52554.95254 | 13925.61918 | 19488.18193 | ||
| P06576 | 2 | 2 | 59.82 | 0.502198972 | 2.199897942 | XN | XA | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP5B PE=1 SV=3 | 49908.8 | 535.2083 | 0 | 12104.2 | 0 | 61424.75642 | 128382.7019 | 11278.71952 | 17955.02978 | 2922.384359 | 39731.09832 | 103115.3339 | 3284.015489 | 24282.06519 | 2754.05766 | 1473.576632 | 97025.16283 | 21350.59719 | 56109.49219 | 311086.3541 | 18949.54502 | 14744.72638 | 1336.849054 | 0 | 6487.26124 | 126109.116 | 84644.62272 | ||
| Q96JG9 | 13 | 5 | 59.75 | 0.125077242 | 1.663378415 | XN | HN | Zinc finger protein 469 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF469 PE=1 SV=3 | 878632 | 413661 | 1094776 | 1305780 | 458579.5124 | 1339010.188 | 1954603.833 | 1698751.55 | 3262728.652 | 792690.2604 | 1736001.942 | 1989478.246 | 1057491.993 | 917720.9095 | 946062.6067 | 666687.5007 | 1527340.195 | 630359.7487 | 934263.1066 | 2301369.215 | 2941745.315 | 1598673.192 | 1923291.053 | 1182426.526 | 995590.7301 | 3493991.926 | 1701287.876 | ||
| P32241 | 1 | 1 | 59.74 | 0.137090235 | 1.650740265 | XN | HN | Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VIPR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 324427.7 | 130916.1 | 228065.8 | 312990.1 | 127422.4457 | 119068.7739 | 138406.2299 | 114288.0902 | 175142.17 | 152428.5543 | 126121.1546 | 31658.84459 | 171735.0965 | 207208.0602 | 47149.63449 | 195734.9051 | 112107.8824 | 107301.8912 | 53072.10093 | 145515.3492 | 265854.2925 | 91507.1734 | 320293.8152 | 334439.7523 | 236427.1792 | 218838.321 | 234790.3301 | ||
| P22732 | 2 | 1 | 59.29 | 0.229989331 | 13.14825477 | XN | HN | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC2A5 PE=1 SV=1 | 272670.2 | 119538.3 | 431072.6 | 123053.3 | 47881.57124 | 140092.8593 | 405017.4905 | 427398.7106 | 387404.7421 | 69359.18882 | 226060.2639 | 207938.578 | 324206.5706 | 192109.136 | 137588.6327 | 37451.52999 | 98925.70581 | 100325.4434 | 112535.7724 | 16735980.07 | 147052.6433 | 156712.3477 | 200305.822 | 273424.5776 | 286600.9593 | 190360.5307 | 225234.8889 | ||
| P35268 | 4 | 1 | 58.95 | 0.534017871 | 1.305665149 | XN | HN | 60S ribosomal protein L22 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPL22 PE=1 SV=2 | 1348741 | 563668 | 177320.7 | 240435.8 | 564497.8184 | 312824.9617 | 256556.1051 | 336565.2193 | 295878.3366 | 627557.441 | 81102.75268 | 542962.1778 | 162039.8096 | 611207.0673 | 391718.7798 | 500447.7174 | 301520.7032 | 471752.2516 | 639932.717 | 615058.2477 | 580850.9556 | 253920.0009 | 403338.5177 | 912324.3655 | 199859.5467 | 347630.2454 | 865392.8617 | ||
| Q02539 | 3 | 1 | 58.89 | 0.453796366 | 5.052053309 | XN | HN | Histone H1.1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H1A PE=1 SV=3 | 58820.96 | 0 | 0 | 16863.31 | 2065.99087 | 2082.526769 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67.68366456 | 0 | 0 | 1659.793992 | 0 | 46667.27771 | 4425.73 | 0 | 14369.20821 | 3433.913349 | 3804.164873 | 0 | 0 | 212825.1116 | 31638.9241 | 0 | 780.5857316 | ||
| Q9ULZ3 | 1 | 1 | 58.87 | 0.126264443 | 4.211532809 | HN | XA | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD OS=Homo sapiens GN=PYCARD PE=1 SV=2 | 1654.358 | 5304.596 | 12281.68 | 0 | 170.9531978 | 16106.20564 | 3216.137704 | 8214.8866 | 17137.29384 | 52875.48801 | 2018.647997 | 20508.64943 | 1747.720418 | 12417.14809 | 24719.74661 | 131350.0248 | 22244.6779 | 2018.657987 | 25156.92562 | 6783.626481 | 0 | 0 | 7574.530445 | 12099.92333 | 5185.549252 | 8733.989365 | 0 | ||
| Q16378 | 2 | 1 | 58.7 | 0.535057076 | 3.634633257 | XN | HN | Proline-rich protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRR4 PE=1 SV=3 | 2795731 | 4486600 | 102362.4 | 3846854 | 3803449.522 | 6257.57252 | 43943.88624 | 2133525.89 | 69351.71504 | 141651.6386 | 32773.05246 | 1441225.147 | 3960562.51 | 56099.36643 | 3536441.278 | 231707.6955 | 90715.7523 | 18841.79243 | 161672.3608 | 31816.72691 | 5765967.433 | 75604.92061 | 39818.3848 | 8303887.63 | 11184021.48 | 3469068.097 | 5533571.507 | ||
| P80723 | 4 | 3 | 58.23 | 0.235244827 | 1.873630004 | HN | XA | Brain acid soluble protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BASP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 128143.4 | 44767.29 | 31353.82 | 59182.2 | 239088.3272 | 6190.493177 | 75639.86104 | 30948.35847 | 71552.894 | 80501.21647 | 456871.3682 | 142864.5739 | 38481.95889 | 76830.52174 | 184273.2476 | 48253.66214 | 46379.13484 | 212478.1827 | 17072.85397 | 78324.11357 | 133650.4271 | 38033.09446 | 37881.48464 | 138460.5111 | 57187.24062 | 98699.44302 | 88144.89322 | ||
| P12318;P31995 | 3 | 2 | 58.13 | 0.446872769 | 1.15597129 | HN | XN | Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor II-a OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCGR2A PE=1 SV=4 | 332709.5 | 762065.3 | 661583 | 370244.3 | 550513.9029 | 322446.5406 | 295389.1861 | 252817.7716 | 232998.9061 | 287276.1268 | 410988.9122 | 549273.3143 | 704830.1168 | 506608.7368 | 501590.2292 | 417017.7941 | 498351.707 | 357011.679 | 265834.3411 | 205301.6325 | 363405.8945 | 735272.1136 | 295389.37 | 917721.9264 | 228887.7899 | 327146.5505 | 322851.5823 | ||
| P01266 | 12 | 2 | 58.11 | 0.292979729 | 2.189458362 | XN | HN | Thyroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TG PE=1 SV=5 | 225595.8 | 209231.5 | 280823.2 | 449704.3 | 234181.8567 | 185746.8531 | 437584.3962 | 215239.153 | 327892.833 | 32704.8069 | 182557.6656 | 260424.5502 | 249151.3478 | 159538.8895 | 84011.12359 | 464994.1608 | 225436.941 | 191485.6972 | 122136.5124 | 314002.5924 | 248739.2692 | 2111454.763 | 445654.9485 | 89075.88066 | 331692.0736 | 101879.521 | 286530.5941 | ||
| P50453 | 5 | 1 | 57.96 | 0.516216935 | 1.457252383 | XN | HN | Serpin B9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB9 PE=1 SV=1 | 45314.12 | 32479.48 | 37150.87 | 62120.4 | 58030.1653 | 29870.61904 | 6069.603858 | 43644.89393 | 30094.49399 | 2683.096756 | 43061.85231 | 18685.22551 | 10404.30474 | 48515.00094 | 36347.10951 | 19647.35501 | 108823.1195 | 44414.89474 | 48172.79129 | 22576.70599 | 44809.87433 | 46721.38888 | 127937.8746 | 7248.325216 | 28749.45106 | 42810.00015 | 115629.4406 | ||
| Q96D15 | 2 | 2 | 57.76 | 0.451801231 | 2.565269491 | HN | XN | Reticulocalbin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RCN3 PE=1 SV=1 | 87943.44 | 163618.7 | 88397.36 | 109308.4 | 59227.14232 | 17631.92226 | 36182.72791 | 65692.7312 | 52395.60452 | 800327.284 | 40405.99402 | 33942.07913 | 28609.9836 | 17024.41366 | 19728.69226 | 119058.3807 | 5820.396773 | 52791.24367 | 4014.766528 | 103389.1609 | 20482.46848 | 19459.69346 | 35019.04148 | 63639.44761 | 35334.46774 | 108849.1774 | 45519.7874 | ||
| O94903 | 3 | 1 | 57.69 | 0.742488311 | 5.819902477 | XA | HN | Proline synthase co-transcribed bacterial homolog protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROSC PE=1 SV=1 | 63702.87 | 24.43542 | 106991.5 | 317785.4 | 5655.904342 | 43396.75616 | 42931.84365 | 220637.694 | 81297.89459 | 11037.25769 | 7923.736764 | 21541.54724 | 20885.32986 | 14321.66776 | 12693.59461 | 35772.10176 | 4507.115447 | 22939.47475 | 3547.048689 | 7086.77937 | 48798.21633 | 9912.368931 | 112710.1282 | 5243.361611 | 54237.70579 | 27803.71984 | 18263.5541 | ||
| Q86YD5 | 1 | 1 | 57.65 | 0.076382165 | 1.459417698 | XN | XA | Low-density lipoprotein receptor class A domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDLRAD3 PE=2 SV=3 | 309761.3 | 564211.8 | 389055 | 1178511 | 1104457.889 | 421834.1847 | 252657.6176 | 439855.7015 | 431840.0351 | 1123602.361 | 459008.7557 | 234279.0108 | 427678.1578 | 404074.2417 | 655519.1003 | 1018232.697 | 727112.8932 | 724133.6701 | 537715.6768 | 672484.1163 | 698947.0168 | 995559.4585 | 915785.416 | 883846.48 | 648218.6942 | 995586.7882 | 1083480.641 | ||
| Q9NRW1;P20340 | 2 | 1 | 57.49 | 0.501741997 | 56.04849621 | XN | XA | Ras-related protein Rab-6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB6B PE=1 SV=1 | 361609.9 | 805398 | 169557.3 | 141549.5 | 21558.11376 | 193245.1441 | 244984.5421 | 234029.7002 | 168138.7478 | 317012.8255 | 352097.3238 | 861862.3058 | 159321.9698 | 250649.4039 | 77327.93745 | 369221.5289 | 95108.60826 | 94261.41694 | 475074.1127 | 128875283.6 | 402100.538 | 148056.464 | 673822.9854 | 107676.4981 | 69009.3038 | 346752.8477 | 59681.08931 | ||
| Q13361 | 1 | 1 | 57.45 | 0.350906743 | 4.668539667 | HN | XA | Microfibrillar-associated protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFAP5 PE=1 SV=1 | 45673.36 | 52080.88 | 96085.21 | 81004.23 | 322556.3055 | 22413.42983 | 51323.88258 | 25876.72907 | 29959.06248 | 107998.9305 | 54378.73656 | 68125.67089 | 28581.07105 | 75066.26975 | 183322.4623 | 2730480.394 | 90105.50954 | 55843.64633 | 23530.77003 | 84074.5927 | 56026.37314 | 38349.88489 | 133371.0622 | 154027.0272 | 140055.0404 | 69136.50116 | 69386.68301 | ||
| Q5T011 | 7 | 2 | 57.35 | 0.048631276 | 1.816076336 | HN | XA | Protein SZT2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SZT2 PE=2 SV=3 | 1.83E+08 | 2.13E+08 | 2.22E+08 | 1.32E+08 | 175856452 | 71990271.08 | 86160032.79 | 122492190.7 | 116027376 | 342925568.8 | 487818427.6 | 126215815.1 | 399893489.5 | 219877522.1 | 131676652 | 168974151.8 | 291741183.8 | 234960328.8 | 98889342.03 | 473888281.3 | 228881550.8 | 127623868 | 166209886.1 | 284485988.6 | 139776490.1 | 330992562.2 | 160739076.3 | ||
| P55011 | 3 | 2 | 57.31 | 0.19241518 | 1.377360363 | HN | XA | Solute carrier family 12 member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC12A2 PE=1 SV=1 | 411797.6 | 266468.2 | 303734.4 | 951003.5 | 276039.6148 | 499823.4558 | 810436.2032 | 646547.8378 | 441967.5824 | 958758.6119 | 647538.1507 | 1041109.662 | 767750.5116 | 350784.2467 | 567326.7153 | 675380.8133 | 439838.2086 | 898139.5964 | 426743.9673 | 288905.0447 | 754726.6004 | 662909.4798 | 705016.5731 | 647190.6094 | 928892.5773 | 489685.9138 | 325701.6802 | ||
| Q9NR16 | 3 | 2 | 57 | 0.79770975 | 1.538911005 | HN | XA | Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich type 1 protein M160 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD163L1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1919596 | 1551231 | 2402951 | 308946.3 | 2943792.932 | 924547.7891 | 1075163.859 | 1722351.272 | 748885.4779 | 2870090.29 | 1361520.882 | 2157336.95 | 119941.6229 | 862499.4443 | 1354395.844 | 6450514.127 | 3165250.316 | 2583740.563 | 2559859.659 | 866780.0822 | 2528256.027 | 1012452.452 | 2509448.661 | 272710.0701 | 591068.2071 | 2054812.21 | 1261702.828 | ||
| P98153 | 3 | 2 | 56.97 | 0.222251472 | 1.328135824 | XN | XA | Integral membrane protein DGCR2/IDD OS=Homo sapiens GN=DGCR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 406545.5 | 262678.8 | 370580.1 | 688085 | 224274.9995 | 299326.7109 | 241452.6774 | 190495.4296 | 196440.808 | 376211.2418 | 541822.5872 | 106860.3352 | 473706.2955 | 355254.8807 | 441087.5682 | 441452.7117 | 288187.9651 | 306920.6209 | 414738.8265 | 407660.085 | 371922.7364 | 360378.2232 | 578132.5414 | 688241.4457 | 293897.5072 | 354602.2326 | 355298.3179 | ||
| Q13404;Q15819 | 2 | 2 | 56.84 | 0.087847664 | 1.423434216 | XA | XN | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 variant 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBE2V1 PE=1 SV=2 | 687699.6 | 1579045 | 761049.9 | 598368.1 | 1659127.963 | 715927.6787 | 1134791.016 | 937387.7057 | 1058504.258 | 639404.3396 | 1371598.63 | 708177.7315 | 645270.9889 | 498424.5765 | 976178.8202 | 622367.7686 | 445552.3405 | 672303.1641 | 1873355.18 | 589562.3269 | 496249.9714 | 803048.1085 | 458526.6338 | 589246.7031 | 539375.922 | 347252.7331 | 718783.4202 | ||
| P35580 | 12 | 1 | 56.81 | 0.227798754 | 1.839858644 | XA | HN | Myosin-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH10 PE=1 SV=3 | 165452.7 | 40828.66 | 101850.7 | 73488.76 | 378546.8508 | 134375.5026 | 420197.7261 | 143646.6918 | 294139.9062 | 140668.24 | 205302.26 | 163359.7262 | 162843.9343 | 50860.79141 | 83139.65248 | 60944.24654 | 51290.06963 | 34124.8537 | 589021.403 | 57194.80294 | 80719.03889 | 101682.4441 | 26659.99878 | 81751.45276 | 137540.3904 | 60661.54797 | 60859.57508 | ||
| O43504 | 1 | 1 | 56.72 | 0.245636555 | 1.935136001 | HN | XN | Hepatitis B virus X-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBXIP PE=1 SV=1 | 248477.6 | 22866.88 | 43125.53 | 263362.7 | 31180.30313 | 68727.75994 | 87596.65297 | 177328.7295 | 58795.41826 | 318525.0545 | 206755.8829 | 213545.4342 | 159735.7473 | 20084.33527 | 22256.22689 | 249991.5131 | 50960.83052 | 71757.71857 | 103909.5355 | 33413.23709 | 275181.361 | 127406.8334 | 0 | 23608.23355 | 31456.15183 | 50475.35446 | 33371.21692 | ||
| P22234 | 5 | 2 | 56.65 | 0.896580419 | 1.171627215 | XN | HN | Multifunctional protein ADE2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAICS PE=1 SV=3 | 1072423 | 3607431 | 1564072 | 1330661 | 1939621.28 | 644979.2098 | 720484.4883 | 658600.9113 | 804114.6224 | 1059802.286 | 911114.5513 | 778035.7689 | 489366.922 | 1283333.839 | 1939031.573 | 1922961.713 | 1677814.522 | 569656.4709 | 1021152.764 | 378092.0282 | 1028116.52 | 1596024.442 | 1692151.098 | 3256337.198 | 957601.5878 | 890029.8189 | 1636201.304 | ||
| Q9Y4L1 | 4 | 1 | 56.62 | 0.126006244 | 1.249394023 | XA | HN | Hypoxia up-regulated protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HYOU1 PE=1 SV=1 | 45269.9 | 50698.65 | 39343.75 | 53196.26 | 64129.06515 | 45293.88573 | 32603.40125 | 42627.0541 | 66948.37515 | 43616.75092 | 31026.00697 | 26654.85751 | 50165.70206 | 54999.43701 | 45232.63877 | 23159.09104 | 30386.3615 | 47018.20144 | 30942.91854 | 51336.74277 | 29411.5052 | 38216.30453 | 39454.64435 | 30897.60138 | 54416.2339 | 33804.3013 | 49190.89449 | ||
| Q9H254 | 13 | 1 | 56.58 | 0.723185708 | 2.287188852 | XN | HN | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPTBN4 PE=1 SV=2 | 397874.2 | 117649.6 | 134279.5 | 475460.2 | 116498.1235 | 474635.1206 | 3559360.009 | 2009780.919 | 783647.2657 | 89090.99678 | 808580.458 | 1424623.737 | 778176.3121 | 219528.8707 | 342939.6242 | 98697.56894 | 151487.8982 | 200422.221 | 262781.3164 | 4474397.333 | 535778.2046 | 3071022.321 | 204849.0472 | 58791.33759 | 287852.7337 | 173675.1215 | 339312.9968 | ||
| Q14667 | 12 | 2 | 56.57 | 0.625170077 | 2.46884466 | HN | XA | UPF0378 protein KIAA0100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA0100 PE=1 SV=3 | 22288.64 | 55215.64 | 16906.25 | 51511.48 | 72640.42074 | 448921.0564 | 7448.619196 | 33544.8341 | 6165.816674 | 6276.66905 | 310923.0391 | 84303.8375 | 21578.39337 | 905345.9995 | 18189.84167 | 144270.2256 | 250209.893 | 23244.04414 | 28170.43112 | 4322.280222 | 3346.554502 | 23395.22384 | 531910.2217 | 95435.20997 | 7322.385296 | 591289.6078 | 246209.3892 | ||
| Q9UHF0 | 1 | 1 | 56.55 | 0.663276672 | 1.787090506 | XN | HN | Tachykinin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAC3 PE=1 SV=1 | 119139.7 | 57042.49 | 35396.66 | 232162.6 | 10260.80387 | 88897.86903 | 244923.1121 | 296018.7299 | 55011.29541 | 73490.44225 | 31257.4681 | 36938.03937 | 131478.078 | 327669.4512 | 24487.22366 | 101955.9975 | 32494.35403 | 38288.28581 | 94460.95451 | 170465.5527 | 177153.1582 | 123448.5661 | 77599.48064 | 3635.744113 | 197818.8313 | 80858.09366 | 500763.8883 | ||
| Q86YW5 | 1 | 1 | 56.11 | 0.800603609 | 4.091499154 | HN | XN | Trem-like transcript 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TREML1 PE=1 SV=2 | 27137.83 | 13103.25 | 19999.26 | 60909.73 | 135825.4826 | 3308.972423 | 27705.90732 | 14198.43033 | 18256.18174 | 375427.4316 | 9347.215502 | 65518.33387 | 10091.12735 | 0 | 14093.06567 | 465850.8418 | 16000.1659 | 11292.52238 | 113478.8118 | 8210.981714 | 4877.130712 | 6917.380859 | 20277.0476 | 56945.38019 | 16811.17778 | 5834.035645 | 3143.44756 | ||
| P29317 | 5 | 2 | 56.08 | 0.582433623 | 1.247113877 | XN | XA | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1314035 | 4132294 | 1187934 | 2730412 | 3892261.614 | 5795776.365 | 2728748.831 | 1921746.227 | 2244081.88 | 4008640.545 | 2876661.23 | 5128115.533 | 3222538.984 | 2184504.838 | 3636779.529 | 1632868.207 | 2888483.403 | 2511086.042 | 3288338.52 | 1708041.598 | 3077812.742 | 2884532.086 | 8264091.188 | 4403931.859 | 4469480.038 | 2568746.256 | 1694250.573 | ||
| P61160 | 3 | 2 | 56.04 | 0.244197816 | 1.407559775 | HN | XN | Actin-related protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTR2 PE=1 SV=1 | 261570.1 | 67070.26 | 295919.4 | 245926 | 127227.9231 | 220546.639 | 199624.4136 | 485876.6547 | 293952.1417 | 395234.6821 | 467472.1827 | 295741.3043 | 249441.3742 | 357784.5928 | 223251.6865 | 238519.6713 | 217131.1864 | 158954.7252 | 263091.6014 | 148946.9184 | 208624.2436 | 251439.9196 | 224213.6462 | 173317.2768 | 211491.539 | 160180.3395 | 208371.8454 | ||
| Q14525 | 4 | 1 | 55.68 | 0.89520422 | 2.365522761 | XN | HN | Keratin, type I cuticular Ha3-II OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT33B PE=2 SV=3 | 77217.26 | 190415.2 | 101277.8 | 80683.97 | 216172.7809 | 1277942.995 | 2351740.709 | 1100801.951 | 1962256.598 | 52195.23927 | 283531.1872 | 783978.8299 | 1301918.393 | 90786.70714 | 660261.7148 | 547288.439 | 368994.6711 | 481781.1186 | 7843392.122 | 334889.088 | 222144.1514 | 425732.6781 | 242758.5452 | 976515.131 | 273136.4599 | 191385.8559 | 302226.7204 | ||
| Q86YT9 | 3 | 2 | 55.51 | 0.177992928 | 1.474532713 | XA | XN | Junctional adhesion molecule-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMICA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 71236.53 | 69551.86 | 84051.87 | 59805.59 | 174935.3629 | 94488.94363 | 60109.50673 | 103610.8065 | 89577.98209 | 46413.99583 | 92320.3219 | 23820.54415 | 84218.86632 | 111498.9714 | 68993.75949 | 128945.5177 | 73088.21357 | 38712.57031 | 74818.20703 | 42050.7259 | 12408.15135 | 59689.60726 | 119039.7976 | 54714.43125 | 57873.23996 | 63041.20494 | 63906.54349 | ||
| O43399 | 2 | 1 | 55.51 | 0.333529053 | 2.647171731 | HN | XN | Tumor protein D54 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPD52L2 PE=1 SV=2 | 26180.62 | 2955.03 | 6399.722 | 62242.11 | 14854.89385 | 14756.75647 | 104710.0544 | 129842.1615 | 88099.79672 | 80368.53893 | 40078.02272 | 140906.1734 | 26901.93852 | 28339.30937 | 18609.56771 | 270169.2687 | 2882.031105 | 12746.50997 | 57165.24964 | 50681.13911 | 71537.66373 | 28466.87219 | 4070.772615 | 8030.06194 | 3485.088376 | 7264.777342 | 3888.882768 | ||
| Q9UJW2 | 1 | 1 | 55.46 | 0.350281092 | 1.502290637 | HN | XA | Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=TINAG PE=2 SV=3 | 10369.83 | 224041.8 | 65106.5 | 41457.73 | 27634.71221 | 35878.06905 | 112801.3945 | 8415.958335 | 163869.7559 | 7064.837663 | 156949.2384 | 2195.446832 | 242269.1582 | 175991.6661 | 55794.19075 | 268301.1585 | 31576.33969 | 95801.14126 | 17.58893018 | 662.8278088 | 2898.549268 | 44214.22631 | 109537.2462 | 511355.8621 | 228822.876 | 20723.9623 | 36022.2097 | ||
| P09455 | 1 | 1 | 55.35 | 0.147663801 | 2.011838434 | XN | HN | Retinol-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 67061.62 | 9176.747 | 9104.994 | 29903.32 | 227922.7909 | 27660.0425 | 14425.48044 | 23532.37579 | 93814.41665 | 8330.020827 | 0 | 24720.7729 | 127.343273 | 12219.41972 | 47686.93748 | 191273.967 | 14209.8641 | 11519.63614 | 163087.0946 | 4017.891314 | 290809.429 | 58437.85649 | 16833.18428 | 17055.85586 | 9179.406028 | 51564.74242 | 12861.41882 | ||
| Q12866 | 3 | 1 | 55.31 | 0.740177479 | 1.269450651 | HN | XA | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer OS=Homo sapiens GN=MERTK PE=1 SV=2 | 365153.7 | 124248.8 | 57187.78 | 572063.1 | 312472.9971 | 390337.6569 | 203012.5473 | 292255.1519 | 181592.0039 | 580485.6007 | 470070.9682 | 89687.38422 | 766816.3256 | 461707.8155 | 92733.06119 | 262431.5666 | 136986.0463 | 310579.9499 | 379925.5108 | 248170.3745 | 384500.6878 | 356222.5402 | 222246.7698 | 358117.8132 | 292580.6506 | 241702.5885 | 196292.3351 | ||
| Q9NSB2 | 5 | 1 | 55.14 | 0.040752004 | 2.19944855 | XN | HN | Keratin, type II cuticular Hb4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT84 PE=1 SV=2 | 878566.7 | 3040276 | 1899305 | 984961 | 1802779.879 | 4359863.514 | 570585.0363 | 1294757.521 | 1638558.939 | 329909.9835 | 306551.0659 | 826850.027 | 782246.1476 | 1201132.045 | 1478403.987 | 1036010.328 | 1004743.826 | 871126.0838 | 1974067.33 | 1034200.179 | 1419999.37 | 1804884.627 | 698842.6358 | 5019711.49 | 3530937.272 | 926595.4103 | 827781.6716 | ||
| Q86YS6;A6NDJ8 | 4 | 1 | 55.12 | 0.749276542 | 1.364497623 | HN | XN | Ras-related protein Rab-43 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB43 PE=1 SV=1 | 1617766 | 13819047 | 14113535 | 1548757 | 14500923.42 | 3070154.866 | 1336803.15 | 1912108.864 | 1761174.981 | 4148984.487 | 4130028.505 | 1898990.08 | 1250526.508 | 4898209.817 | 12221951.15 | 13539959.27 | 4798251.894 | 7595972.394 | 1244821.874 | 2808973.148 | 2397507.264 | 2444371.057 | 9175847.483 | 4078951.83 | 3716401.21 | 8701108.972 | 5360906.129 | ||
| P02655 | 1 | 1 | 55.04 | 0.079296153 | 2.940141947 | HN | XA | Apolipoprotein C-II OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOC2 PE=1 SV=1 | 329727.4 | 447017.3 | 690928.5 | 1417529 | 156579.2666 | 453283.669 | 453559.5827 | 378138.3217 | 398293.7235 | 228823.401 | 3131492.836 | 829046.1485 | 1441598.365 | 1988533.044 | 487111.2626 | 3961138.659 | 351983.1384 | 1472609.253 | 137538.3969 | 860106.1025 | 673785.1556 | 1535177.87 | 693002.8875 | 919822.1906 | 905683.1264 | 479985.7666 | 1189020.339 | ||
| Q9NS68 | 2 | 1 | 55 | 0.182745231 | 1.715999712 | XA | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF19 PE=1 SV=1 | 4845.466 | 226895.1 | 35964.32 | 0 | 56508.53488 | 49682.02624 | 89107.74362 | 75865.34931 | 42130.40133 | 0 | 17340.04497 | 0 | 8141.030294 | 130260.3786 | 72411.05709 | 0 | 34722.59064 | 75702.41433 | 7834.729465 | 43133.64326 | 75956.02047 | 23516.16685 | 6788.91201 | 17362.21076 | 40071.83399 | 59348.30566 | 89579.80279 | ||
| O95747 | 3 | 1 | 54.58 | 0.394922486 | 4.058919328 | XA | XN | Serine/threonine-protein kinase OSR1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=OXSR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 78602.1 | 0 | 7426.608 | 50791.42 | 0 | 37673.48637 | 40993.22948 | 42543.42175 | 45656.56051 | 0 | 0 | 10812.91696 | 12069.62265 | 41553.39696 | 3788.511666 | 3202.840543 | 2081.444285 | 5462.893483 | 0 | 0 | 2205.827698 | 17737.51135 | 33622.10861 | 7368.454263 | 13885.72305 | 0 | 0 | ||
| O95433 | 2 | 1 | 54.54 | 0.959734327 | 1.651979077 | XN | HN | Activator of 90 kDa heat shock protein ATPase homolog 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 414623.9 | 31401.77 | 37830.01 | 581503.8 | 86350.13315 | 288603.8817 | 239449.9681 | 346545.2647 | 308324.4956 | 318694.4293 | 111916.4699 | 281929.4835 | 541455.4599 | 40498.76831 | 131566.8266 | 235387.1457 | 85781.20223 | 87872.97725 | 1551610.181 | 90608.7945 | 490644.8491 | 309841.7688 | 187881.7127 | 19832.34805 | 206868.6271 | 106932.1367 | 67330.95049 | ||
| P35442 | 3 | 1 | 54.47 | 0.00102753 | 2.60884748 | XN | XA | Thrombospondin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS2 PE=1 SV=2 | 6281690 | 12976159 | 9618252 | 15753974 | 15050800.6 | 16601309.97 | 9157109.352 | 9005144.073 | 9185812.909 | 14721902.21 | 28159192.04 | 11176157.57 | 50006792.46 | 26001802.3 | 20154762.73 | 60037516.26 | 22271813.88 | 20300708.97 | 18751858.49 | 19073917.75 | 16081253.46 | 37457151.93 | 21042257.49 | 73653735.3 | 46058409.64 | 21658449.43 | 16578488.82 | ||
| P34932 | 4 | 2 | 54.44 | 0.845724802 | 1.92465868 | XA | HN | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA4 PE=1 SV=4 | 42888.09 | 21643.18 | 34290.29 | 87418.61 | 35867.76877 | 122343.8212 | 333539.9638 | 496138.2754 | 330372.9453 | 114611.1453 | 136786.6242 | 144311.097 | 141834.7627 | 61161.87525 | 67431.57923 | 50723.88283 | 42517.51277 | 22320.09546 | 143013.9989 | 311076.1669 | 174518.3825 | 280571.2069 | 47866.5942 | 33081.12112 | 67548.20702 | 19748.65687 | 33320.21581 | ||
| Q07812 | 3 | 1 | 54.14 | 0.878386864 | 21.34747841 | HN | XA | Apoptosis regulator BAX OS=Homo sapiens GN=BAX PE=1 SV=1 | 10594.38 | 0 | 0 | 12375.13 | 4787.311426 | 0 | 4955.030885 | 0 | 0 | 9720.381488 | 3523.095514 | 0 | 0 | 0.172737589 | 16524.61751 | 668547.0944 | 0 | 0 | 71459.82279 | 0 | 13376.69222 | 9693.606991 | 6397.633596 | 0 | 0 | 3258.221069 | 0 | ||
| P30101 | 3 | 2 | 54.11 | 0.103494216 | 2.466065393 | HN | XN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDIA3 PE=1 SV=4 | 77250.43 | 48054.32 | 13788.54 | 21319.74 | 19026.85913 | 41621.34545 | 83318.00891 | 134211.932 | 262833.758 | 147941.1742 | 56959.85853 | 40063.36998 | 59439.82411 | 60399.40886 | 59254.50963 | 255004.8121 | 33214.66996 | 32977.99644 | 30283.66889 | 36847.47144 | 35165.90231 | 23675.41951 | 39690.08855 | 9439.317748 | 53469.70582 | 17579.80331 | 56052.94591 | ||
| Q16581 | 1 | 1 | 53.9 | 0.222253272 | 1.221576985 | XA | HN | C3a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3AR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 279951.2 | 362777.3 | 370455.7 | 354545.7 | 323692.7132 | 519660.0524 | 454871.0618 | 336512.7129 | 520224.581 | 79561.61267 | 748943.2308 | 163848.6474 | 379834.5774 | 213376.953 | 94804.20366 | 244598.1128 | 242143.8304 | 716612.9511 | 174906.3121 | 648139.3622 | 445834.1117 | 218485.9061 | 214381.619 | 593415.7848 | 243978.6411 | 605587.0423 | 339761.2627 | ||
| P08709 | 2 | 2 | 53.8 | 0.87752403 | 1.703421048 | XA | XN | Coagulation factor VII OS=Homo sapiens GN=F7 PE=1 SV=1 | 993744.3 | 8867434 | 7538803 | 1405904 | 8152313.296 | 1114884.128 | 458598.312 | 685486.2225 | 904222.0338 | 716387.8828 | 1410125.538 | 238962.8369 | 546759.8601 | 1842530.08 | 5229472.448 | 4808538.387 | 2028481.278 | 4831322.933 | 353430.8749 | 1040840.721 | 606449.1271 | 640628.0523 | 4862125.256 | 2201118.328 | 1670809.984 | 3553045.424 | 2754431.791 | ||
| P35613 | 3 | 2 | 53.72 | 0.352811853 | 1.545587192 | XA | HN | Basigin OS=Homo sapiens GN=BSG PE=1 SV=2 | 48130.33 | 89093.91 | 114660.6 | 69389.86 | 106976.2583 | 19409.219 | 18211.10028 | 29290.20506 | 76970.81675 | 15080.66463 | 54406.81937 | 11306.39585 | 25555.63932 | 78882.24513 | 47511.6482 | 15422.82355 | 54066.75862 | 67938.51201 | 23283.65571 | 49312.09685 | 36372.78969 | 34552.29132 | 42143.66355 | 134959.3375 | 38620.54662 | 39569.86251 | 43924.33706 | ||
| Q15771 | 2 | 1 | 53.64 | 0.29635891 | 2.850343555 | XA | HN | Ras-related protein Rab-30 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB30 PE=1 SV=2 | 1318961 | 9853.136 | 957092.6 | 2251577 | 38934.41946 | 128448.1328 | 365009.7809 | 930607.3159 | 1398204.711 | 245480.4882 | 365420.904 | 105855.0093 | 61920.39854 | 41806.3871 | 686165.1379 | 1046293.457 | 24844.3524 | 17931.63896 | 42473.18093 | 35702.84461 | 5813.765803 | 17795.08681 | 1475941.71 | 169801.7237 | 195100.8492 | 592753.2583 | 297673.7846 | ||
| Q9Y274 | 2 | 2 | 53.58 | 0.422319262 | 1.44599518 | XA | HN | Type 2 lactosamine alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ST3GAL6 PE=1 SV=1 | 466359.5 | 159653.5 | 212806.7 | 235960.9 | 92288.35636 | 181388.2855 | 195535.7213 | 500106.5615 | 216931.8209 | 196017.6638 | 117369.7176 | 99659.98946 | 224296.6102 | 145235.8762 | 163136.4538 | 284180.664 | 192860.4243 | 140893.3124 | 155876.7689 | 251646.9366 | 256274.5126 | 297351.1643 | 300429.8558 | 52701.72236 | 372583.1312 | 310114.4273 | 149494.331 | ||
| Q9UHA7 | 1 | 1 | 53.38 | 0.112011769 | 1.261310672 | XN | XA | Interleukin-36 alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL36A PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 76917.89602 | 0 | 2816.508385 | 60041.94479 | 3930.229184 | 0 | 0 | 1260.793255 | 19901.21337 | 0 | 97017.36311 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P32929 | 2 | 1 | 53.31 | 0.034164116 | 3.584123062 | XA | HN | Cystathionine gamma-lyase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTH PE=1 SV=3 | 15103.31 | 5461.639 | 25477.61 | 61084.43 | 5049.495777 | 122471.5624 | 171173.5718 | 87969.3605 | 40708.63568 | 0 | 114.3623032 | 41199.96843 | 87920.44779 | 3411.99472 | 0 | 0 | 12616.05946 | 3866.982704 | 59728.71952 | 18850.35439 | 56309.71759 | 184051.9906 | 6124.864362 | 11281.69371 | 13283.89575 | 8439.847934 | 0 | ||
| P22748 | 2 | 2 | 53.18 | 0.075093426 | 2.809922966 | HN | XN | Carbonic anhydrase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CA4 PE=1 SV=2 | 55899.1 | 37378.95 | 66133.99 | 111336.3 | 71273.17545 | 77313.17335 | 97045.2761 | 97089.3408 | 95829.6219 | 66793.10396 | 420345.8062 | 268053.606 | 48603.4383 | 115705.4795 | 31180.98168 | 16054.38087 | 220124.7278 | 40857.06822 | 127257.196 | 13328.99854 | 85240.09658 | 43385.13721 | 33108.06857 | 8990.647141 | 47535.30261 | 67501.98989 | 10575.07245 | ||
| Q02083 | 6 | 4 | 52.9 | 0.000427695 | 2.28989021 | XN | XA | N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAAA PE=1 SV=3 | 984560.9 | 328637.7 | 896324 | 789979.7 | 410105.4005 | 684705.7589 | 749127.7037 | 733830.7832 | 677016.7672 | 1106342.599 | 1328095.908 | 630695.9482 | 2130551.874 | 2066029.589 | 622627.9841 | 1464743.976 | 931220.2757 | 959093.4946 | 1386998.143 | 901062.7736 | 1785730.419 | 1356936.282 | 1634019.327 | 2232090.621 | 2593309.691 | 1100160.851 | 1331326.436 | ||
| O00194 | 2 | 1 | 52.84 | 0.953577828 | 3.688390053 | XA | XN | Ras-related protein Rab-27B OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB27B PE=1 SV=4 | 6416.889 | 3663.309 | 0 | 9034.365 | 114178.9008 | 0 | 1625.499395 | 7097.676106 | 1398.627085 | 7949.881169 | 1870.823181 | 121.1967023 | 0 | 11544.13984 | 51643.16848 | 3696.813442 | 168.7173429 | 26104.65588 | 1346.773718 | 542.1933164 | 216.3680512 | 0 | 544.0221767 | 3667.080203 | 14318.84392 | 11418.32827 | 6829.280961 | ||
| Q9HC38 | 1 | 1 | 52.78 | 0.166913835 | 1.834248133 | XA | XN | Glyoxalase domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLOD4 PE=1 SV=1 | 206651.6 | 322897.7 | 370055.4 | 219961.7 | 72781.74078 | 436023.5085 | 620655.5552 | 593138.0619 | 473007.6136 | 142313.0704 | 384880.1925 | 599440.3529 | 413261.2279 | 311404.1462 | 108227.282 | 66446.93476 | 130868.1721 | 51683.31893 | 373551.8517 | 167479.4404 | 310275.8797 | 164797.9338 | 218028.8353 | 147855.8511 | 125984.3341 | 160603.3561 | 138796.8648 | ||
| P24394 | 2 | 1 | 52.76 | 0.124483409 | 2.001986244 | XN | HN | Interleukin-4 receptor subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL4R PE=1 SV=1 | 104393 | 192793.3 | 528672 | 99092.77 | 118522.2367 | 103203.0563 | 200423.5938 | 168863.5232 | 247761.0899 | 17043.97404 | 138632.7119 | 275147.2835 | 32690.75565 | 20911.92469 | 380494.0218 | 69081.96715 | 229086.5496 | 111292.7869 | 53188.06819 | 182547.688 | 88352.84659 | 335655.3792 | 244661.3038 | 1063383.018 | 210590.9693 | 189694.4975 | 183221.4136 | ||
| Q6P5W5 | 3 | 3 | 52.13 | 0.154732496 | 2.213238754 | XA | XN | Zinc transporter ZIP4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC39A4 PE=1 SV=3 | 713736.1 | 130026.7 | 347922 | 531372.8 | 55519.14257 | 158867.1135 | 796594.4915 | 390591.939 | 944792.8114 | 50663.97427 | 203434.8659 | 238783.3403 | 97312.54581 | 203441.3435 | 189726.4593 | 392646.5356 | 84867.44704 | 470753.655 | 124505.2217 | 202018.9744 | 93540.75815 | 109966.6313 | 300485.8248 | 120478.3332 | 453204.4184 | 213004.3599 | 221468.8405 | ||
| P41250 | 2 | 2 | 52.13 | 0.363335167 | 1.514559918 | XA | HN | Glycine--tRNA ligase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GARS PE=1 SV=3 | 600551.4 | 1533171 | 1965269 | 382092.2 | 570699.0954 | 1126783.319 | 1448619.227 | 561801.2854 | 1652394.975 | 324346.0802 | 915402.8196 | 744082.1687 | 633795.0235 | 743793.4434 | 909041.2114 | 168103.8142 | 861094.049 | 1198190.267 | 527949.0426 | 908329.9212 | 684390.3139 | 265486.3494 | 1788681.625 | 1464880.777 | 756779.2324 | 556361.8841 | 542809.7614 | ||
| Q16775 | 4 | 2 | 51.96 | 0.02799074 | 1.993261488 | XA | HN | Hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=HAGH PE=1 SV=2 | 186085.5 | 77346.04 | 199742.4 | 265861.5 | 49145.77799 | 188765.1301 | 244851.2992 | 212366.5092 | 233106.2704 | 83316.01313 | 75272.65031 | 153256.0064 | 154329.0579 | 54737.0723 | 53464.52918 | 73848.55013 | 79063.41041 | 104149.2472 | 93470.56543 | 98603.96406 | 232921.6979 | 182489.8245 | 183610.1761 | 144675.5865 | 93060.04774 | 61003.66785 | 97407.38294 | ||
| Q8IUE6 | 3 | 1 | 51.43 | 0.432486475 | 4.120564725 | XA | HN | Histone H2A type 2-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H2AB PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 120367.1894 | 150242.6544 | 42521.02985 | 199275.1304 | 31669.24559 | 5373.346127 | 22757.78971 | 0 | 0 | 62024.51628 | 0 | 0 | 2528.446622 | 136652.7058 | 0 | 0 | 13204.43432 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q9BRF8 | 2 | 1 | 51.24 | 0.600489911 | 1.140987454 | XN | HN | Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPPED1 PE=1 SV=3 | 29117.2 | 2311.366 | 1571.829 | 0 | 1992.068036 | 0 | 0 | 6112.53403 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3164.005068 | 0 | 6317.260356 | 3338.734615 | 19683.24195 | 3830.833965 | 2635.047276 | 7392.326137 | 4026.335744 | 7779.305613 | 0 | 6131.257091 | 1701.838744 | 0 | 14170.79507 | 3261.422327 | ||
| P46439 | 3 | 1 | 51.19 | 0.361431665 | 1.933612234 | XN | XA | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTM5 PE=1 SV=3 | 207146.1 | 1198596 | 453305.4 | 318912.7 | 282125.0213 | 179494.6616 | 300304.338 | 179984.039 | 282225.7861 | 210483.6426 | 162847.7141 | 948621.7465 | 301097.2255 | 605827.8984 | 1782001.59 | 351299.2459 | 96779.65753 | 365039.7946 | 267691.8352 | 248872.2438 | 274496.7995 | 605904.9528 | 581041.7805 | 3010194.767 | 604375.7161 | 413944.3535 | 571808.9371 | ||
| Q5JXA9 | 3 | 1 | 51.04 | 0.562004279 | 2.280058494 | HN | XN | Signal-regulatory protein beta-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIRPB2 PE=2 SV=1 | 34016.26 | 45028.33 | 23776.76 | 56829.65 | 42058.28776 | 137577.7648 | 47606.45515 | 96696.68484 | 209654.1245 | 344716.1569 | 25167.42564 | 337014.6569 | 83602.82124 | 12240.5401 | 23019.58325 | 25624.63275 | 106959.5623 | 58201.74161 | 125480.4632 | 77968.34901 | 24020.64732 | 40486.09733 | 22949.36708 | 67348.43218 | 21309.76396 | 35693.98883 | 30585.4531 | ||
| Q86UN2 | 6 | 3 | 50.94 | 0.367937274 | 1.561020701 | HN | XA | Reticulon-4 receptor-like 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RTN4RL1 PE=2 SV=1 | 1361595 | 1582927 | 2079803 | 871465.3 | 4706673.389 | 733785.1267 | 471777.6996 | 924532.4774 | 664304.7276 | 1985603.901 | 1426123.78 | 840911.466 | 1004257.006 | 2229974.479 | 7418805.273 | 3476827.6 | 1148895.489 | 1381382.225 | 1461423.701 | 491518.9871 | 492853.8264 | 2165819.305 | 2230949.002 | 3075704.726 | 1418499.287 | 1324051.399 | 1395025.085 | ||
| P04233 | 1 | 1 | 50.5 | 0.155123535 | 1.547666329 | HN | XN | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD74 PE=1 SV=3 | 1788397 | 3489716 | 1779383 | 1504434 | 1771878.851 | 1306453.925 | 2780863.73 | 832175.0452 | 1593920.48 | 3652805.749 | 4107367.279 | 1098520.834 | 2821444.985 | 1443842.448 | 3669654.71 | 4487459.889 | 1135127.673 | 3035909.965 | 1052929.013 | 2073211.066 | 1591954.066 | 1336394.788 | 1768313.656 | 4061970.266 | 1143224.212 | 1832629.038 | 1584865.437 | ||
| O95428 | 6 | 3 | 50.48 | 0.531544656 | 1.554013847 | HN | XA | Papilin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAPLN PE=2 SV=4 | 350649.5 | 441690 | 618899.9 | 571147.3 | 361672.291 | 365566.9443 | 583047.9792 | 509842.3362 | 253482.5378 | 371516.6621 | 1913975.22 | 577690.1636 | 1501783.99 | 472755.6031 | 380109.2831 | 473676.9872 | 409416.043 | 202154.2043 | 315636.4437 | 649185.3942 | 585322.7799 | 518018.2184 | 833956.3847 | 697153.8065 | 407768.2949 | 557458.0986 | 437822.9457 | ||
| O75369 | 14 | 2 | 50.36 | 0.582088834 | 1.983914716 | XA | XN | Filamin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLNB PE=1 SV=2 | 176848.3 | 769038.3 | 1468061 | 418359.9 | 2303923.448 | 187532.8951 | 127284.2748 | 178452.002 | 159716.486 | 162235.4576 | 18492.08159 | 214714.6471 | 103922.7709 | 262253.3202 | 584773.089 | 910472.0093 | 522685.5265 | 321231.4124 | 199429.0393 | 47880.18737 | 217876.409 | 422963.9927 | 462724.2821 | 626660.9585 | 176264.7075 | 460307.7269 | 303970.2033 | ||
| P55899 | 2 | 1 | 49.93 | 0.115450246 | 9.312745816 | XA | HN | IgG receptor FcRn large subunit p51 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCGRT PE=1 SV=1 | 47087.81 | 0 | 76785.45 | 8946.998 | 15038.05161 | 19381.97825 | 13560.10995 | 100797.9861 | 13049.85135 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4304.127117 | 17639.07367 | 1523.798082 | 5091.629414 | 0 | 3080.615433 | 3349.07319 | 30287.66992 | 4851.674387 | 0 | 1123.750991 | 0 | 35167.04465 | 0 | 23021.70847 | ||
| Q9NYL9 | 2 | 1 | 49.93 | 0.468460532 | 1.642244218 | XA | HN | Tropomodulin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMOD3 PE=1 SV=1 | 553952.9 | 1177337 | 1895672 | 292047.1 | 1980593.741 | 601737.3249 | 337925.1362 | 366089.3532 | 369606.7914 | 267219.0986 | 461259.8782 | 380608.1794 | 270619.759 | 540152.6534 | 433791.741 | 780773.624 | 540464.9142 | 937676.6359 | 171258.3023 | 477115.8937 | 254425.7626 | 465785.8354 | 559102.5519 | 517814.9429 | 622007.1938 | 1117456.814 | 741287.7739 | ||
| Q13449 | 3 | 2 | 49.64 | 0.60709276 | 1.201863894 | HN | XN | Limbic system-associated membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LSAMP PE=1 SV=2 | 186414.5 | 822715.1 | 302907.2 | 135701.1 | 402004.8646 | 171487.5295 | 293629.4139 | 119317.822 | 288701.5887 | 251882.9717 | 338245.5153 | 328107.3582 | 238294.4666 | 282107.0771 | 669601.7303 | 183791.0458 | 288206.0273 | 398641.3616 | 230308.9428 | 110421.4287 | 154377.6808 | 225429.1759 | 325379.8864 | 395999.9592 | 365663.0897 | 354002.3483 | 316965.6567 | ||
| Q96JP9 | 2 | 1 | 49.59 | 0.844352978 | 1.057158738 | HN | XN | Cadherin-related family member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDHR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 152629.6 | 64535.87 | 119216.1 | 91561 | 168861.3625 | 43017.5186 | 23274.0633 | 120188.1125 | 49764.2499 | 28857.6761 | 34629.61111 | 10112.44783 | 55418.18993 | 100539.3623 | 151044.3961 | 122916.5528 | 202388.7111 | 140533.4579 | 20830.4281 | 11332.65833 | 47638.12238 | 36055.81445 | 206111.633 | 162398.1777 | 117716.1066 | 50691.46515 | 147900.4361 | ||
| P30626 | 3 | 2 | 49.14 | 0.791041528 | 1.344992703 | HN | XN | Sorcin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SRI PE=1 SV=1 | 644265.5 | 172485.3 | 685109.1 | 74253.1 | 289752.5933 | 648730.6197 | 673121.0377 | 952208.1794 | 256620.744 | 668231.2455 | 820463.1751 | 740930.4632 | 134277.392 | 663641.8776 | 372403.3077 | 674329.6178 | 141013.1861 | 260535.2551 | 338380.7054 | 143916.5868 | 428522.6215 | 396896.0424 | 219869.6869 | 360802.9145 | 167144.6388 | 580888.0431 | 691348.1305 | ||
| Q8NCM8 | 19 | 3 | 49.04 | 0.693894686 | 1.362394104 | HN | XN | Cytoplasmic dynein 2 heavy chain 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DYNC2H1 PE=1 SV=4 | 7425228 | 12446268 | 17749886 | 12245372 | 24381113.72 | 5627083.379 | 4659287.516 | 5781456.681 | 4865616.012 | 10092653 | 4523820.8 | 6844438.005 | 4776595.137 | 10560147.08 | 11808857.95 | 31558398.52 | 8530195.741 | 10531761.75 | 6263387.828 | 7206271.524 | 4455065.106 | 5912824.055 | 11262960.82 | 12772133.96 | 8386249.871 | 5179378.433 | 11394448.18 | ||
| P10809 | 5 | 2 | 49.03 | 0.084130863 | 2.136395696 | HN | XN | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 106235.7 | 38728.29 | 10645.19 | 699.4694 | 12281.33068 | 22697.67782 | 11415.01652 | 14337.31264 | 24000.26351 | 59310.78853 | 1213.85232 | 176949.6555 | 2872.477734 | 11917.1048 | 6459.735882 | 4062.677922 | 1824.76287 | 9862.627171 | 28436.80833 | 5737.549585 | 0 | 13203.18577 | 56020.52585 | 0 | 0 | 12957.11296 | 12119.93252 | ||
| Q7Z3F1 | 3 | 1 | 48.9 | 0.101938327 | 21.48278494 | XA | HN | Integral membrane protein GPR155 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPR155 PE=1 SV=2 | 3860.441 | 0 | 0 | 1424.031 | 0 | 2886.678938 | 27101.36886 | 24857.1682 | 10539.6466 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1129.577847 | 0 | 0 | 2160.001884 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14795.73534 | 0 | 1279.145982 | 0 | 13872.21435 | ||
| Q14314 | 8 | 4 | 48.61 | 0.102679304 | 1.713511498 | XA | HN | Fibroleukin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 658783.2 | 676912.5 | 465878.8 | 383903.4 | 396516.4474 | 285222.7873 | 196529.1496 | 846592.7217 | 352882.9819 | 101748.9069 | 133310.2976 | 161963.1241 | 144981.1709 | 185310.1223 | 391410.1838 | 939804.8936 | 241495.6037 | 187978.8643 | 183085.984 | 254509.1359 | 103684.2389 | 131697.7337 | 584202.2644 | 69051.94524 | 535258.8852 | 484961.4324 | 785734.6491 | ||
| O15273 | 1 | 1 | 48.35 | 0.783058408 | 101.2641593 | XA | HN | Telethonin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCAP PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 14565.84 | 210417.7 | 773933.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 396.7083564 | 3468.401042 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5999.358639 | 0 | 12758.99413 | 0 | 0 | 3507.124511 | 24253.01534 | 9448.577967 | 0 | 0 | ||
| O60218 | 2 | 2 | 48.25 | 0.263611098 | 38.1195159 | XA | XN | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1B10 PE=1 SV=2 | 514.4898 | 4618.244 | 0 | 1181.819 | 1822.412828 | 14919.67302 | 54617.44325 | 127598.5558 | 279995.6624 | 0 | 1173.45803 | 31972.74015 | 0 | 0 | 11131.30904 | 5226.432829 | 6578.313898 | 351.23833 | 105.0032943 | 2414.829109 | 0 | 575.5782456 | 266.6432642 | 21.26512018 | 1749.853318 | 2611.435547 | 4985.572124 | ||
| P45381 | 1 | 1 | 48.18 | 0.93038257 | 2.681980872 | XA | XN | Aspartoacylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASPA PE=1 SV=1 | 14755.16 | 5096.901 | 0 | 31082.91 | 0 | 86676.49965 | 96604.5251 | 55761.71503 | 34883.27969 | 50930.2812 | 0 | 16217.53297 | 4328.041127 | 32066.93381 | 4746.291513 | 0 | 8795.782423 | 8315.478767 | 25960.82859 | 8871.177643 | 16904.33535 | 25797.41542 | 33104.53131 | 0 | 7269.224447 | 0 | 3219.743495 | ||
| P01607 | 2 | 1 | 48.08 | 0.905624869 | 44.9478545 | XN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region Rei OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 41.55012 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3722.818369 | 0 | 5.0724155 | 39.3316071 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34.63227163 | 71.9984726 | 1848.925942 | 0 | 1.734165181 | 2727.662217 | 0.128255213 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.057998298 | 166696.3902 | 0 | 4492.576314 | 0 | ||
| Q7Z3E2 | 15 | 4 | 48.04 | 0.240872075 | 1.644032841 | HN | XA | Uncharacterized protein C10orf118 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C10orf118 PE=2 SV=2 | 41580140 | 42008905 | 21781689 | 15720988 | 45191567.46 | 15886435.45 | 10836272.03 | 13578436.7 | 15231057.45 | 68936720.83 | 12989491.36 | 16932397.66 | 18036848.43 | 26226828.17 | 64260616.73 | 96491268.67 | 31890207.83 | 28907570.3 | 22197610.94 | 21423652.64 | 23758297.95 | 25527766.4 | 47819962.81 | 25803809.22 | 34520933.48 | 36739940.29 | 48577278.86 | ||
| Q70SY1 | 2 | 2 | 48.01 | 0.160993915 | 1.439789949 | XN | XA | Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CREB3L2 PE=1 SV=3 | 11060569 | 5927651 | 6413998 | 6610996 | 2673441.727 | 3337882.809 | 3562631.345 | 3651571.367 | 3758336.906 | 5422281.212 | 5917383.651 | 2644498.219 | 5986751.132 | 4630003.201 | 4754444.516 | 14479358.92 | 9665828.486 | 8224833.5 | 7507882.812 | 4913228.403 | 9218752.305 | 5759464.903 | 7866158.658 | 3468450.02 | 11131548.49 | 7869509.901 | 9930926.865 | ||
| Q15435 | 3 | 1 | 47.58 | 0.323491834 | 1.330368416 | XA | XN | Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPP1R7 PE=1 SV=1 | 43714.16 | 19903.13 | 66301.61 | 69588.83 | 108736.3553 | 88117.57149 | 51219.8159 | 70464.96092 | 66629.0165 | 53239.80774 | 52941.21259 | 30082.37273 | 48707.35457 | 41735.56183 | 51815.46206 | 84691.12152 | 54645.04461 | 28486.77148 | 24484.11042 | 33157.02353 | 53852.69549 | 60181.98444 | 60729.08712 | 44156.86385 | 108728.8737 | 24932.70399 | 29260.52212 | ||
| Q8NFY4 | 3 | 2 | 47.58 | 0.541255876 | 1.397022457 | XA | HN | Semaphorin-6D OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMA6D PE=1 SV=1 | 103600.3 | 158544.8 | 86802.48 | 611889.8 | 223140.2515 | 278552.5029 | 380123.0645 | 456021.5848 | 311836.6176 | 130669.8073 | 44868.60414 | 388779.7973 | 183762.2599 | 294904.6956 | 245545.6304 | 246750.8534 | 238931.425 | 94412.17544 | 166775.1701 | 119240.5018 | 135541.9837 | 163592.5265 | 170495.4606 | 400310.5739 | 456313.4127 | 138352.4804 | 236437.7684 | ||
| Q6ZWJ8 | 4 | 2 | 47.43 | 0.106275308 | 2.897254508 | XA | HN | Kielin/chordin-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=KCP PE=2 SV=2 | 171787.2 | 17166.6 | 19036.95 | 73914.34 | 45579.72699 | 87333.96755 | 100733.0423 | 134902.3504 | 50445.08739 | 41994.36805 | 12561.49204 | 18666.15959 | 15878.09504 | 34263.50815 | 25985.17692 | 37330.87982 | 28032.62055 | 27206.12974 | 20218.57862 | 28351.65229 | 193486.3571 | 80520.7077 | 49383.82574 | 3625.552798 | 66071.00456 | 64451.17884 | 13967.20615 | ||
| Q9H1U4 | 2 | 1 | 47.39 | 0.156597918 | 2.578054479 | XA | HN | Multiple epidermal growth factor-like domains protein 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MEGF9 PE=2 SV=3 | 0 | 40151.73 | 42219.46 | 1443.482 | 0 | 16359.58897 | 65084.06738 | 0 | 47712.33499 | 0 | 15731.26922 | 0 | 0 | 40470.4069 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26407.38446 | 0 | 8271.599944 | 34275.94516 | 21700.92883 | 18324.37032 | 67006.33959 | 0 | 45602.27979 | 13173.09903 | ||
| Q7Z406 | 13 | 4 | 47.37 | 0.243124218 | 1.315700978 | HN | XA | Myosin-14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH14 PE=1 SV=2 | 952337.2 | 1440394 | 905293.5 | 1431827 | 985072.7728 | 1185240.771 | 611063.6292 | 561695.6483 | 522430.7318 | 998204.3195 | 1171933.803 | 1417785.67 | 915824.7581 | 1600918.169 | 1509259.169 | 1968817.053 | 909177.1298 | 816998.1855 | 1082352.169 | 2448528.689 | 777351.1386 | 574128.7162 | 944132.2963 | 1261461.247 | 1010262.002 | 1013542.193 | 934246.2243 | ||
| P14784 | 1 | 1 | 47.35 | 0.002612178 | 2.476712118 | XA | HN | Interleukin-2 receptor subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL2RB PE=1 SV=1 | 253817.1 | 270436.7 | 162926.5 | 189287.9 | 129438.1148 | 202207.7024 | 240405.6432 | 241678.7987 | 129173.8808 | 19598.77757 | 263675.9578 | 70202.32883 | 111196.3822 | 52743.13767 | 97306.87393 | 6603.104667 | 53314.65496 | 59950.53356 | 97137.02088 | 47888.06958 | 91451.9017 | 98711.85325 | 29087.99795 | 136637.2696 | 96536.16168 | 166774.5336 | 80412.90216 | ||
| Q9Y5Y2 | 1 | 1 | 47.35 | 0.788467467 | 1.362182631 | XA | XN | Cytosolic Fe-S cluster assembly factor NUBP2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 82300.35 | 13937.45 | 23302.75 | 214529.7 | 19560.6425 | 53602.31528 | 62576.77354 | 107587.2731 | 35219.86574 | 47497.70197 | 10609.68515 | 57012.3444 | 13883.21583 | 31853.79589 | 171281.1366 | 79986.46844 | 24275.45097 | 33394.68988 | 33079.47995 | 23889.6543 | 142323.5492 | 42028.96762 | 63800.75582 | 37588.99462 | 58240.61501 | 27342.55125 | 21437.45819 | ||
| P30711 | 4 | 3 | 47.03 | 0.758073064 | 1.414320084 | XA | XN | Glutathione S-transferase theta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTT1 PE=1 SV=4 | 5175384 | 18184524 | 26160321 | 8550056 | 30663277.48 | 9133231.905 | 4626616.151 | 7068135.538 | 6282514.457 | 5488108.58 | 6154481.538 | 3044777.553 | 6127426.516 | 11135675.82 | 11762292.75 | 23067920.5 | 10498181.68 | 13081287.99 | 4249059.659 | 5990517.524 | 5936090.449 | 10715985.09 | 9577762.996 | 15511673.41 | 8503206.057 | 9610472.142 | 11813183.99 | ||
| Q5SGD2 | 1 | 1 | 46.83 | 0.581864684 | 1.15623445 | XN | HN | Protein phosphatase 1L OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPM1L PE=1 SV=1 | 82851.96 | 41995.72 | 21293.66 | 104475.4 | 7259.015553 | 6198.332616 | 40151.99508 | 87806.61042 | 9524.246016 | 3963.629813 | 0 | 52737.94645 | 15432.79795 | 60687.78896 | 51705.43865 | 90578.90281 | 6848.587487 | 119153.8286 | 259.7988118 | 52007.83828 | 54242.51398 | 34667.36466 | 69966.36993 | 9397.915193 | 132865.089 | 22587.456 | 87781.60627 | ||
| Q14974 | 1 | 1 | 46.55 | 0.171513026 | 3.637100887 | XA | XN | Importin subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KPNB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 31909.47 | 2704.697 | 10421.3 | 55129.91 | 6213.647842 | 8458.491616 | 10207.00085 | 47031.73298 | 41079.86567 | 18369.90887 | 4382.233329 | 11104.33904 | 2314.015152 | 10253.35282 | 9375.257857 | 6590.656141 | 526.2492506 | 0 | 3415.338339 | 0 | 12978.5992 | 1422.308054 | 18848.00852 | 1355.917772 | 13815.75894 | 2112.302671 | 4657.815985 | ||
| P26641 | 4 | 3 | 46.47 | 0.81382008 | 1.121236731 | XA | HN | Elongation factor 1-gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1G PE=1 SV=3 | 192566.3 | 408008.1 | 415761.7 | 588406.6 | 211058.698 | 205203.8933 | 218701.3264 | 191211.466 | 235739.7124 | 188369.4932 | 188625.1914 | 205439.9774 | 557131.1298 | 221027.8738 | 400519.3572 | 144054.1021 | 174367.3094 | 298783.9407 | 178269.4509 | 298587.2798 | 617674.2377 | 121412.2977 | 121788.2157 | 288203.8394 | 321311.4744 | 303442.9667 | 206902.217 | ||
| Q9NRV9 | 3 | 2 | 46.25 | 0.662306443 | 1.196754738 | XN | HN | Heme-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEBP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1349136 | 799351.6 | 503255 | 1266427 | 406118.817 | 184894.0485 | 191384.9821 | 275228.4174 | 438707.2909 | 957934.7613 | 305413.1085 | 289841.9477 | 301786.3668 | 486773.0848 | 514910.9605 | 1167777.594 | 418939.8868 | 468050.6285 | 322162.0796 | 241504.3562 | 779024.0724 | 912919.6584 | 877640.0162 | 899016.0168 | 569490.4212 | 471934.1795 | 804084.3374 | ||
| Q96F10 | 3 | 1 | 46.23 | 0.180963153 | 1.901060623 | XN | XA | Diamine acetyltransferase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SAT2 PE=1 SV=1 | 2604422 | 1675987 | 3688227 | 1070041 | 1110640.18 | 2707133.495 | 1430422.889 | 745435.003 | 1562263.045 | 539563.3706 | 3828323.868 | 573807.7359 | 5040180.92 | 1905811.256 | 1362321.684 | 4844471.943 | 678124.4579 | 2855411.321 | 1436103.484 | 6084791.093 | 3527994.695 | 2905611.608 | 1619494.591 | 3114312.143 | 6833295.682 | 4951222.23 | 1074462.312 | ||
| Q9GZM5 | 2 | 2 | 46.1 | 0.014188773 | 3.049538343 | XA | HN | Protein YIPF3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=YIPF3 PE=1 SV=1 | 5015660 | 25107869 | 21639484 | 7019464 | 5033916.481 | 5630708.29 | 17570670.97 | 5494778.286 | 32175722.02 | 2055384.336 | 5772845.427 | 2270618.392 | 4150022.007 | 3019234.009 | 4582086.327 | 3557126.467 | 5729570.497 | 9750702.626 | 2475048.855 | 7744260.536 | 5812246.197 | 3242563.022 | 3932415.725 | 11580010.73 | 3235452.805 | 16516410.49 | 6496403.389 | ||
| Q16352 | 3 | 1 | 46.08 | 0.286236146 | 3.12779172 | HN | XA | Alpha-internexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=INA PE=1 SV=2 | 86461.34 | 151410.2 | 212524.6 | 97324.84 | 4756.166859 | 91256.28123 | 153771.2533 | 51762.60214 | 222076.3589 | 14459.49124 | 703487.1864 | 1484696.136 | 92861.20685 | 231191.2044 | 222920.8462 | 27176.9021 | 340765.9532 | 233380.8892 | 80476.85411 | 246509.3443 | 222895.1814 | 135581.9505 | 203776.0337 | 511962.4828 | 112240.606 | 237881.0835 | 120180.6882 | ||
| Q9Y6N8 | 4 | 1 | 45.99 | 0.146535089 | 1.406114913 | HN | XA | Cadherin-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH10 PE=1 SV=2 | 102070.3 | 354914.6 | 411275.2 | 110688.6 | 421430.0598 | 149868.2676 | 115364.5472 | 110122.7983 | 65429.80747 | 234993.3008 | 346700.489 | 184953.5096 | 135733.9797 | 360111.9725 | 309100.5415 | 556576.0997 | 265978.4852 | 194739.9922 | 133813.3771 | 172348.8193 | 155306.8165 | 287807.7912 | 315146.2511 | 301169.0303 | 207729.9734 | 206399.4125 | 201661.6833 | ||
| Q92542 | 6 | 2 | 45.76 | 0.483406339 | 1.771635536 | XN | XA | Nicastrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCSTN PE=1 SV=2 | 33369.37 | 17050.54 | 22257.06 | 7997.993 | 16867.68303 | 48519.07817 | 45671.3596 | 54972.90932 | 51025.69523 | 35261.84172 | 1829.199189 | 5364.814188 | 8692.034306 | 26644.81947 | 24387.07612 | 8173.614976 | 213135.0835 | 58237.73582 | 68244.57727 | 118803.7357 | 137744.3217 | 26212.54538 | 31560.8681 | 4564.894246 | 56789.33287 | 4155.288132 | 79396.47617 | ||
| P28331 | 6 | 2 | 45.68 | 0.156268228 | 1.479518895 | XA | XN | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=NDUFS1 PE=1 SV=3 | 298112.4 | 544851.4 | 1014082 | 448448.6 | 400469.8015 | 450767.8698 | 577913.7296 | 430983.9461 | 878395.2174 | 197320.4807 | 436875.6807 | 1271667.57 | 349509.1512 | 519489.7508 | 398293.3914 | 336817.6115 | 547259.3438 | 710323.4495 | 173926.3907 | 478435.7196 | 430202.53 | 210442.0391 | 811624.8614 | 329574.965 | 363469.2788 | 351269.3335 | 260287.8827 | ||
| Q9BRV8 | 2 | 1 | 45.66 | 0.900907618 | 1.152815268 | XA | XN | Suppressor of IKBKE 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIKE1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3676406 | 2057256 | 1539893 | 2353135 | 1027948.599 | 992891.0544 | 807630.0178 | 561600.1871 | 1206555.381 | 2823952.287 | 702819.5317 | 1472658.646 | 654251.8866 | 889352.7187 | 1341949.763 | 2709484.089 | 864024.4817 | 1042788.245 | 558122.7428 | 829940.2465 | 2055892.74 | 1625608.823 | 2159415.222 | 951127.3296 | 1087020.345 | 1268923.653 | 1801846.065 | ||
| Q9UFH2 | 17 | 2 | 45.57 | 0.149021221 | 1.679458183 | XA | HN | Dynein heavy chain 17, axonemal OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNAH17 PE=2 SV=2 | 92274.72 | 335728.8 | 484714.7 | 96181.66 | 226965.5586 | 151924.6423 | 148878.0942 | 88960.53414 | 105444.5955 | 78913.31579 | 203506.8001 | 70154.04985 | 150362.5516 | 99181.34167 | 128404.3118 | 108906.9994 | 73545.05005 | 117758.7451 | 107273.5281 | 116344.6856 | 115054.484 | 158403.6073 | 150246.9699 | 109981.7944 | 41088.51015 | 108026.0614 | 135005.3107 | ||
| Q9Y5I2;Q9Y5I1 | 6 | 2 | 45.52 | 0.955370578 | 1.168391982 | HN | XA | Protocadherin alpha-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHA10 PE=2 SV=1 | 243133.4 | 61445.72 | 99189.49 | 151125.5 | 24264.68018 | 75713.67205 | 122154.0083 | 198652.5237 | 93436.5763 | 62794.38491 | 307490.2824 | 67971.81081 | 268105.8621 | 188104.1021 | 100101.1837 | 49207.97808 | 159829.9261 | 45540.53754 | 78522.18855 | 64006.50897 | 111845.2639 | 23344.92827 | 247849.6436 | 78164.51829 | 239567.4733 | 100905.3943 | 279793.4564 | ||
| Q8WXE0 | 7 | 3 | 45.19 | 0.072319014 | 2.177914359 | HN | XA | Caskin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CASKIN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 837857.1 | 637174.8 | 857732.8 | 590437.5 | 353479.4452 | 542254.1407 | 750172.0257 | 232534.2261 | 489127.0772 | 1476960.064 | 2531580.269 | 455923.4936 | 1924342.129 | 927582.4876 | 775964.8254 | 245440.5937 | 1516159.571 | 1668888.641 | 476911.267 | 386746.9694 | 782916.6885 | 1159037.728 | 403262.0225 | 583537.9719 | 509336.0615 | 1024183.948 | 1524213.674 | ||
| Q14353 | 1 | 1 | 44.91 | 0.022502319 | 8.298285238 | XA | HN | Guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAMT PE=1 SV=1 | 44866.77 | 3785.166 | 20886.44 | 440770.7 | 24786.21047 | 97610.78352 | 116984.4521 | 196571.5829 | 85079.03201 | 1058.116631 | 15446.85885 | 8544.481213 | 26236.02653 | 3658.022149 | 4782.120046 | 29764.33144 | 18530.04038 | 16263.64507 | 1366.406322 | 26614.08858 | 55743.13098 | 13590.66259 | 119837.2548 | 11989.86588 | 111696.5119 | 25466.25166 | 19819.39117 | ||
| Q16663 | 1 | 1 | 44.91 | 0.197687536 | 1.534723781 | HN | XN | C-C motif chemokine 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCL15 PE=1 SV=2 | 219438.4 | 125837 | 58383.48 | 256332.2 | 150874.2703 | 21521.15219 | 120789.872 | 43826.77272 | 69974.41075 | 124353.1489 | 183577.1732 | 97779.96332 | 117663.9545 | 127037.0144 | 134371.806 | 109805.3784 | 57370.93771 | 219830.1509 | 40667.86595 | 15674.88046 | 111551.3603 | 94299.82664 | 36528.79511 | 120944.2634 | 152097.5211 | 38663.36193 | 153090.3177 | ||
| Q9Y5F2;Q96TA0 | 6 | 1 | 44.88 | 0.423132809 | 1.992348047 | XN | XA | Protocadherin beta-11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB11 PE=2 SV=1 | 221337.7 | 180952 | 45561.89 | 0 | 218995.129 | 34148.24261 | 61518.0489 | 129025.4689 | 45441.09189 | 161620.729 | 62585.48742 | 9263.925534 | 61657.89147 | 0 | 111513.8031 | 334608.8431 | 228625.0774 | 47428.58962 | 343805.4503 | 135851.2924 | 156945.5989 | 81129.76963 | 423083.8005 | 21339.28575 | 261034.5793 | 59140.10713 | 384459.4646 | ||
| P50452 | 2 | 1 | 44.83 | 0.792841314 | 4.680125947 | HN | XA | Serpin B8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB8 PE=1 SV=2 | 22961.8 | 0 | 4628.49 | 51237.8 | 0 | 13157.90025 | 15347.88673 | 39552.54418 | 17939.19747 | 22012.40762 | 26027.28746 | 682641.7494 | 11617.91484 | 1720.754086 | 0 | 2457.369301 | 2343.234792 | 22583.93188 | 11966.67599 | 25937.5273 | 63026.26168 | 50551.94793 | 32185.80751 | 0 | 3742.885039 | 10134.95869 | 37506.4737 | ||
| O43291 | 4 | 2 | 44.71 | 0.662326586 | 1.242451496 | HN | XA | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1506047 | 4513743 | 3325700 | 2611558 | 3437569.487 | 3709873.71 | 4902242.63 | 1821509.933 | 3163130.921 | 1868397.878 | 6600649.811 | 1637672.356 | 4238132.089 | 3649059.878 | 5453602.286 | 5837994.518 | 2563535.384 | 4171334.01 | 2220076.045 | 5021184.469 | 2296351.759 | 2477922.718 | 2491508.121 | 5660857.015 | 2828387.21 | 3972122.058 | 3848604.513 | ||
| O14745 | 3 | 1 | 44.69 | 0.43608291 | 1.57682845 | HN | XN | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC9A3R1 PE=1 SV=4 | 1066389 | 452961.1 | 576062.9 | 479185.8 | 341894.5684 | 336548.8004 | 485298.5987 | 592988.2419 | 667508.286 | 640072.2905 | 1006681.223 | 948616.2095 | 700426.721 | 1983428.511 | 192856.5242 | 550333.3017 | 277802.4739 | 500710.963 | 343583.5001 | 235886.1011 | 432874.8446 | 451505.9902 | 585021.225 | 356223.7737 | 452322.9324 | 711875.9408 | 743748.2552 | ||
| Q9UQE7 | 12 | 5 | 44.19 | 0.140415747 | 1.48028988 | HN | XA | Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMC3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1.07E+08 | 50550048 | 41326855 | 28905964 | 50821330.29 | 51167369.25 | 34094463.23 | 22501251.82 | 8438499.745 | 116356814.1 | 65654435.05 | 55905293.96 | 80267854.43 | 51770972.17 | 73939710.86 | 73079864.08 | 33472040.11 | 34371495.61 | 24342414.63 | 58755061.4 | 82818732.67 | 44292595.82 | 85348273.28 | 84394905.9 | 61722007.51 | 27326611.46 | 43616998.86 | ||
| Q9UIQ6 | 4 | 1 | 44.18 | 0.68710503 | 2.105186646 | HN | XN | Leucyl-cystinyl aminopeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LNPEP PE=1 SV=3 | 14276.86 | 17477.68 | 6498.98 | 5380.169 | 2778.000728 | 13658.12022 | 25715.56952 | 8594.599824 | 26002.3499 | 13975.85349 | 38715.68196 | 10550.31055 | 43683.20375 | 50261.77576 | 20827.12216 | 1081.213248 | 6225.810464 | 6762.689989 | 8582.427781 | 12398.6635 | 16310.20826 | 5974.643694 | 4038.198566 | 9888.699317 | 13098.00462 | 15271.55314 | 5680.656325 | ||
| Q14966 | 14 | 2 | 44.03 | 0.144265648 | 10.93219015 | HN | XN | Zinc finger protein 638 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF638 PE=1 SV=2 | 12481.52 | 0 | 22.05728 | 18409.66 | 258897.2128 | 10337.75177 | 36170.57451 | 32666.75919 | 24863.18346 | 2871.803035 | 6458.463758 | 0 | 0 | 2713.387199 | 3835.980761 | 16505.39088 | 0 | 383444.8046 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2070.992409 | 0 | 9927.42563 | 17880.0142 | 8158.761072 | ||
| P52798 | 2 | 1 | 43.93 | 0.947850445 | 1.091057651 | HN | XA | Ephrin-A4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFNA4 PE=1 SV=1 | 670758.7 | 277370.8 | 214423.9 | 667359.9 | 686155.7453 | 500251.0429 | 478822.1773 | 589737.5089 | 462188.2376 | 360522.369 | 687136.334 | 149783.9399 | 862431.1636 | 914205.8733 | 229289.9578 | 666976.7942 | 772469.2899 | 318297.5247 | 416773.0688 | 430090.4687 | 447704.0827 | 344206.9471 | 527229.4479 | 695427.4918 | 528594.6983 | 497173.1289 | 750331.3696 | ||
| A6NES4 | 6 | 1 | 43.9 | 0.469673382 | 58.6193746 | HN | XN | HEAT repeat-containing protein 7B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEATR7B1 PE=4 SV=3 | 0 | 25085.69 | 0 | 12582.28 | 270979.6878 | 26133.67524 | 228.211804 | 80318.15794 | 35340.91894 | 8458.394611 | 151.8640683 | 212428.3867 | 0 | 8581.442534 | 1367.033815 | 66446.34526 | 2334228.588 | 79667.2365 | 0 | 17606.50444 | 2290.857481 | 14819.11271 | 0 | 1321.653184 | 7407.402246 | 151.69324 | 2655.902222 | ||
| Q8N1I0 | 4 | 1 | 43.89 | 0.127587391 | 1.897770545 | XA | XN | Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DOCK4 PE=1 SV=3 | 842620.3 | 133783.6 | 166672.9 | 316327.3 | 119073.6837 | 153997.7955 | 161431.2787 | 129684.4224 | 123167.9563 | 270694.0127 | 101322.5114 | 63896.89165 | 105392.7032 | 111653.3447 | 45766.51607 | 101082.9584 | 151840.3822 | 227942.4719 | 37369.39221 | 141763.264 | 158871.0977 | 102918.978 | 224848.2135 | 76230.37924 | 123292.1932 | 61948.26492 | 203958.8645 | ||
| Q02224 | 23 | 5 | 43.77 | 0.374435417 | 1.258806791 | HN | XA | Centromere-associated protein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=CENPE PE=1 SV=2 | 12392490 | 9905388 | 11938549 | 8601622 | 10144914.36 | 16192434.18 | 13096710.63 | 6154725.852 | 9430141.426 | 9328060.61 | 26090460.82 | 10586340.58 | 15042833.1 | 15575256.9 | 16100738.67 | 13775135 | 9092766.313 | 7591433.538 | 11096703.47 | 8496441.024 | 11057554.27 | 17438188.11 | 12878239.14 | 16536686.56 | 15023430 | 9178260.887 | 12000388.79 | ||
| P22894 | 3 | 2 | 43.77 | 0.731435598 | 1.702816733 | XA | HN | Neutrophil collagenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP8 PE=1 SV=1 | 26264.63 | 37239.45 | 7964.183 | 1984.288 | 0 | 291132.2141 | 332844.2057 | 40387.43643 | 369324.18 | 336830.0602 | 27612.63067 | 151862.0947 | 12564.34034 | 2849.565847 | 112704.1216 | 0.178825556 | 5758.891067 | 0 | 643537.1383 | 4246.594536 | 0 | 49511.55414 | 0 | 20308.91801 | 105284.0485 | 12933.01722 | 8196.750547 | ||
| P49327 | 8 | 4 | 43.38 | 0.622573645 | 1.616319482 | XN | HN | Fatty acid synthase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FASN PE=1 SV=3 | 132487.7 | 158359.8 | 29855.88 | 161821.1 | 226638.2258 | 292056.1763 | 213143.4803 | 562888.791 | 427585.5094 | 351616.4446 | 95248.39262 | 273325.5684 | 72074.73142 | 49222.33527 | 203805.9497 | 129728.5499 | 270281.3449 | 274749.6634 | 922489.4207 | 741535.9522 | 112259.2616 | 210865.9224 | 166134.9993 | 167123.5489 | 147055.6918 | 183206.8258 | 129483.5189 | ||
| Q969T9 | 4 | 1 | 43.29 | 0.077658658 | 16.65056887 | XN | XA | WW domain-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 3295.62 | 0 | 34.79465 | 0 | 184.6227024 | 0 | 0 | 3042.461555 | 0 | 116.5893948 | 18569.17581 | 5808.882777 | 7120.039002 | 3810.419323 | 4653.106958 | 637.3374008 | 0 | 4460.251071 | 70816.44154 | 24825.92615 | 0 | 3164.769095 | 7.918463505 | 4362.260148 | 0 | 6008.779114 | 0 | ||
| P63096;P04899;P08754;P19087 | 4 | 2 | 43.14 | 0.928244208 | 1.3036594 | HN | XA | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNAI1 PE=1 SV=2 | 343673 | 412242.1 | 219844.8 | 168880 | 201189.1927 | 152682.7844 | 95186.23652 | 64449.00659 | 72972.4469 | 216715.9674 | 151929.4274 | 191139.1069 | 103809.0391 | 49556.95208 | 730496.5764 | 551155.729 | 137199.1711 | 124788.3989 | 157401.2374 | 363348.2228 | 64912.37493 | 129782.4774 | 127522.5584 | 132833.2749 | 194907.6879 | 445016.2219 | 202499.3175 | ||
| P58546 | 1 | 1 | 43.06 | 0.229040986 | 1.565583674 | XA | XN | Myotrophin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MTPN PE=1 SV=2 | 203957.7 | 109007.3 | 127643 | 462100.7 | 116084.9021 | 370242.0744 | 428517.2676 | 528873.6878 | 374518.0925 | 183964.5175 | 157448.1215 | 421528.8829 | 372080.0088 | 263502.9274 | 109093.4655 | 100447.3 | 69787.69009 | 78845.18576 | 138291.7494 | 129470.4838 | 263120.5236 | 331857.8308 | 81642.67109 | 223779.1871 | 195965.5482 | 180538.0607 | 193308.5259 | ||
| P62333 | 4 | 2 | 42.83 | 0.890305455 | 1.189296309 | XA | XN | 26S protease regulatory subunit 10B OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMC6 PE=1 SV=1 | 421539.3 | 155856.8 | 157308.9 | 572985.5 | 136546.5469 | 490262.0959 | 585495.2595 | 587943.243 | 464608.8669 | 688292.7186 | 390283.6036 | 472317.613 | 605451.523 | 157305.5601 | 230706.6698 | 213508.5309 | 202506.1938 | 219984.193 | 504776.586 | 149068.3299 | 558741.8901 | 152035.7804 | 412070.2467 | 334585.77 | 355123.024 | 315224.7958 | 222289.852 | ||
| Q96A23 | 2 | 1 | 42.7 | 0.996778216 | 1.144393951 | HN | XA | Copine-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPNE4 PE=2 SV=1 | 611332.1 | 474670.3 | 533561 | 765858.4 | 1472404.94 | 820232.2244 | 675896.9393 | 575140.6928 | 645352.5295 | 1343503.77 | 1380373.038 | 1709361.546 | 835109.9302 | 362119.0801 | 324058.2629 | 652715.3891 | 382326.4467 | 534192.3615 | 1223385.603 | 1080792.538 | 1079944.045 | 350718.6667 | 533519.7894 | 839051.3767 | 344253.7364 | 903700.6984 | 509799.1787 | ||
| O95711 | 3 | 2 | 42.63 | 0.56276865 | 2.274825079 | XA | XN | Lymphocyte antigen 86 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LY86 PE=1 SV=1 | 2837.311 | 353839.9 | 116433.3 | 29055.1 | 318978.1807 | 20852.50934 | 6545.695922 | 9803.119817 | 19404.10914 | 16500.25564 | 0 | 22295.92136 | 3142.73625 | 31511.07826 | 150982.9956 | 150098.5537 | 32462.15125 | 48595.23511 | 13963.48726 | 7565.145624 | 2874.825187 | 43929.56425 | 44178.61057 | 55462.1472 | 28678.92893 | 79544.5701 | 109656.2226 | ||
| P62906 | 3 | 2 | 42.62 | 0.546876287 | 3.412910312 | XN | HN | 60S ribosomal protein L10a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPL10A PE=1 SV=2 | 1322.898 | 0 | 2488.986 | 14434.04 | 0 | 7182.891042 | 10901.41937 | 43081.56195 | 7716.399348 | 0 | 0 | 2268.696082 | 3721.863703 | 0 | 1059.581746 | 5288.490902 | 24120.77973 | 0 | 2761.884525 | 82958.97384 | 1259.039452 | 8474.161243 | 0 | 0 | 22376.54572 | 0 | 6602.098941 | ||
| A1L4H1 | 3 | 2 | 42.57 | 0.74389348 | 1.143660345 | HN | XA | Soluble scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain-containing protein SSC5D OS=Homo sapiens GN=SSC5D PE=2 SV=3 | 829849.5 | 2293143 | 3559692 | 683133.7 | 2528127.884 | 1157317.357 | 561554.5765 | 937207.4904 | 789768.4889 | 663418.5858 | 927807.798 | 639450.4385 | 967951.6479 | 2670656.167 | 2398042.176 | 2801188.748 | 2071379.589 | 2116298.124 | 1021200.782 | 1353630.075 | 781605.245 | 1221644.027 | 1696445.894 | 2882834.803 | 2628482.182 | 1135026.819 | 1412878.038 | ||
| O00233 | 2 | 1 | 42.53 | 0.062559536 | 8.123088745 | XA | HN | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMD9 PE=1 SV=3 | 2744.876 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13103.13877 | 128328.9275 | 28922.41742 | 33928.89526 | 0 | 0 | 25486.39578 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41881.60591 | 19282.37616 | 24428.4675 | 0 | 3612.821294 | 356.8984653 | 0 | 0 | 2885.650041 | ||
| Q7Z304 | 3 | 1 | 42.52 | 0.272207401 | 1.425317335 | XN | HN | MAM domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAMDC2 PE=2 SV=3 | 543164 | 374923.4 | 273627.8 | 166934.4 | 1374687.967 | 185000.028 | 475614.3994 | 337076.3646 | 325523.1788 | 200212.9739 | 481355.9202 | 76161.31609 | 216884.5354 | 962213.1792 | 310144.0313 | 332325.9281 | 260848.0645 | 371122.2378 | 613729.8254 | 552998.1521 | 622016.4983 | 261739.7027 | 420337.9597 | 218339.7667 | 633546.6274 | 890460.539 | 363907.1434 | ||
| P05060 | 2 | 1 | 42.4 | 0.45531788 | 1.353611826 | XN | XA | Secretogranin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHGB PE=1 SV=2 | 310921.1 | 414244.2 | 361099.1 | 463825.3 | 354963.8956 | 147782.0798 | 73033.20017 | 129514.9929 | 105601.1665 | 444454.9984 | 146202.3984 | 219391.5884 | 199067.9543 | 445223.0281 | 241433.2952 | 352965.5302 | 404083.1808 | 238039.1721 | 230320.9401 | 186780.5324 | 250934.0397 | 468921.2977 | 1051010.068 | 200256.2251 | 331510.2763 | 217109.0523 | 259014.7717 | ||
| P07359 | 3 | 1 | 42.34 | 0.612256984 | 3.323002422 | HN | XN | Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=GP1BA PE=1 SV=1 | 7812.924 | 407396.4 | 176950.1 | 0 | 206892.9375 | 5726.877256 | 12006.27402 | 10171.27937 | 23974.81755 | 9148.825917 | 26593.58937 | 668400.1829 | 6173.600616 | 18452.66249 | 76101.57098 | 3416.930439 | 151824.6131 | 94797.4542 | 4902.290941 | 12068.28239 | 19487.05283 | 6598.895898 | 109613.3002 | 116326.1618 | 17703.3351 | 28035.84514 | 2721.549819 | ||
| Q14623 | 3 | 1 | 42.33 | 0.42502094 | 2.995822317 | XA | HN | Indian hedgehog protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IHH PE=1 SV=4 | 194469.3 | 0 | 0 | 307719 | 33230.84803 | 92892.38205 | 115228.19 | 237095.5611 | 121104.0672 | 33731.01244 | 388.4003977 | 21658.91353 | 13229.99061 | 38916.32894 | 4751.062448 | 211247.5638 | 9720.212376 | 34115.07889 | 13742.4879 | 19112.84266 | 94290.09862 | 76208.21619 | 203233.0746 | 84558.276 | 133681.3915 | 45096.3165 | 102425.2663 | ||
| P01116;P01111;P01112 | 3 | 1 | 42.31 | 0.689600032 | 1.729187711 | XA | XN | GTPase KRas OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRAS PE=1 SV=1 | 71481.66 | 15479.57 | 15858.42 | 0 | 12482.80993 | 22924.7447 | 46672.24279 | 66208.13427 | 27910.9059 | 107816.2576 | 0 | 45707.93076 | 0 | 9495.355656 | 22762.15436 | 2355.703544 | 9633.624611 | 17592.88646 | 29578.11129 | 15741.49151 | 27500.67456 | 18555.97064 | 45042.09355 | 3221.574549 | 0 | 11383.7196 | 10334.49104 | ||
| Q5SYB0 | 10 | 2 | 42.3 | 0.336263413 | 1.2126003 | XA | HN | FERM and PDZ domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FRMPD1 PE=1 SV=1 | 752475.5 | 567463.1 | 616616.5 | 721223.3 | 608663.1812 | 444647.4095 | 1042383.418 | 782965.4172 | 354303.8134 | 747000.9868 | 289885.5275 | 465780.3719 | 381454.6589 | 204619.4916 | 502245.5777 | 1591354.482 | 476453.7014 | 199146.9942 | 930899.5203 | 502049.7199 | 595423.1917 | 221301.8213 | 831143.1624 | 253302.6412 | 865821.2732 | 687888.7428 | 818963.8049 | ||
| Q9H3K6 | 3 | 2 | 42.25 | 0.596437847 | 4.440376414 | HN | XN | BolA-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BOLA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 70626.59 | 49731.74 | 173152 | 71615.22 | 225243.4805 | 43537.43604 | 61965.52913 | 67872.17136 | 24655.82155 | 88009.52191 | 112707.3969 | 72100.1636 | 35089.89737 | 53621.56286 | 76930.85846 | 1918919.854 | 59702.72603 | 24053.31809 | 37371.58285 | 79207.80712 | 62356.21988 | 32037.17976 | 98085.82462 | 49660.63289 | 80271.15454 | 55574.07856 | 55194.15998 | ||
| Q7LBR1 | 4 | 2 | 41.99 | 0.621995759 | 1.689461877 | HN | XA | Charged multivesicular body protein 1b OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP1B PE=1 SV=1 | 796876.3 | 477296.1 | 535219.7 | 1742044 | 298849.9514 | 607324.4391 | 838803.7591 | 766193.1897 | 811169.8722 | 1208293.437 | 4539105.582 | 2047642.027 | 861424.196 | 1066866.522 | 470566.3816 | 250209.3309 | 628585.379 | 540291.2706 | 783836.1487 | 1051277.196 | 743587.3193 | 893133.2447 | 510968.567 | 518498.722 | 2694386.705 | 876349.1966 | 718176.7263 | ||
| Q9UJU6 | 6 | 5 | 41.83 | 0.796659507 | 1.089444891 | HN | XA | Drebrin-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DBNL PE=1 SV=1 | 15934554 | 20454904 | 44195307 | 10990158 | 16032045.04 | 4358164.505 | 8167062.055 | 8163938.926 | 11793736.12 | 9018168.087 | 25198735.58 | 5520696.565 | 14693896.18 | 22591939.06 | 14500377.94 | 29552241.47 | 24540381.32 | 7003755.871 | 5455068.047 | 8581576.201 | 4428280.709 | 10371992.05 | 20885834.85 | 56352768.19 | 26393414.65 | 9171776.465 | 6774527.192 | ||
| Q86VZ4 | 2 | 2 | 41.82 | 0.487059377 | 2.56678748 | XN | XA | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP11 PE=2 SV=2 | 143208.6 | 9949.016 | 21470.33 | 39541.71 | 15077.20091 | 21146.18422 | 8172.941071 | 10768.02811 | 5155.157495 | 112350.9465 | 57091.0982 | 95863.32567 | 54670.73732 | 37707.50008 | 22602.01455 | 90168.89866 | 55814.1619 | 50017.68972 | 126075.8236 | 33819.25885 | 180558.3013 | 95055.45608 | 129895.7038 | 0 | 30291.08104 | 100154.9263 | 8704.796129 | ||
| Q99996 | 24 | 10 | 41.77 | 0.135612803 | 1.911585276 | HN | XN | A-kinase anchor protein 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKAP9 PE=1 SV=3 | 990266.8 | 1476185 | 2019938 | 2040477 | 2963262.593 | 1477401.904 | 1792267.483 | 1898360.632 | 1810828.924 | 1752684.748 | 2020236.944 | 4569629.85 | 1231130.06 | 1172995.216 | 1950728.201 | 9545450.941 | 2186657.118 | 1806956.744 | 1168520.972 | 1958725.3 | 1275347.091 | 1850913.842 | 1910899.476 | 1966360.765 | 1578834.013 | 1052102.769 | 963275.8474 | ||
| Q86YB8 | 3 | 2 | 41.7 | 0.424343114 | 5.438722573 | XA | HN | ERO1-like protein beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERO1LB PE=1 SV=2 | 146005.5 | 56000.72 | 21921.3 | 78497.12 | 4280.344211 | 3305311.207 | 1014805.617 | 201734.273 | 1993565.275 | 325276.7987 | 52655.26457 | 128338.7683 | 147730.4155 | 26472.34037 | 221687.1975 | 28069.49357 | 142523.7433 | 181606.9526 | 3556533.576 | 248688.3813 | 107019.3568 | 370630.2499 | 109218.6122 | 486346.9372 | 144719.8157 | 99168.71542 | 256585.4259 | ||
| Q9NRC6 | 20 | 3 | 41.62 | 0.022897813 | 1.519691629 | XA | XN | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPTBN5 PE=1 SV=1 | 24768004 | 11796141 | 11724561 | 22985768 | 10980764.35 | 14381098.61 | 13424781 | 12602338.92 | 12460055.78 | 12424267.02 | 8334325.504 | 14269283.89 | 13522774.68 | 7885786.64 | 5107293.46 | 8639104.849 | 10657118.7 | 16495456.88 | 13557919.12 | 13226635.97 | 11397876.56 | 9986585.737 | 7887508.898 | 6309058.92 | 9038274.592 | 8252898.951 | 9258327.75 | ||
| P00167 | 1 | 1 | 41.51 | 0.239335425 | 9.834463294 | XA | XN | Cytochrome b5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CYB5A PE=1 SV=2 | 14227.08 | 5200.341 | 11034.21 | 117894.3 | 0 | 4149.909175 | 6.904967563 | 7112.089824 | 12511.48131 | 510.6395774 | 0 | 0 | 8932.735273 | 238.4568281 | 0 | 94650.25963 | 1101.512271 | 7036.646933 | 0 | 5548.19803 | 1952.638893 | 0 | 0 | 6835.40723 | 3076.497882 | 90.63065272 | 0 | ||
| Q9NYC9 | 12 | 3 | 41.22 | 0.803045435 | 1.130167286 | HN | XN | Dynein heavy chain 9, axonemal OS=Homo sapiens GN=DNAH9 PE=1 SV=3 | 748922.3 | 993516.9 | 833363.6 | 310073.1 | 1329392.74 | 324479.5038 | 166180.1676 | 635543.9421 | 275864.6239 | 978418.9006 | 718941.7456 | 451908.8993 | 312148.8083 | 503293.2657 | 470464.9453 | 749647.202 | 1136777.659 | 496666.3217 | 280867.2234 | 373809.5433 | 492492.531 | 425817.2385 | 1021142.516 | 693915.2838 | 616471.4053 | 442795.8123 | 800835.8226 | ||
| Q9UGM3 | 2 | 1 | 41.15 | 0.532362141 | 1.587784671 | XA | XN | Deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DMBT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 29043.94 | 1305.785 | 58734.26 | 10863.98 | 22244.79164 | 11520.29949 | 790445.439 | 8617.209607 | 19085.7092 | 160061.9799 | 8227.94635 | 307839.4698 | 1602.605656 | 80651.55095 | 6623.727605 | 83409.19769 | 45937.00329 | 0 | 260694.4679 | 48771.57724 | 5300.551183 | 9657.084391 | 31183.30065 | 52440.72257 | 38474.76438 | 100784.9508 | 52182.82178 | ||
| Q86VB7 | 6 | 1 | 40.99 | 0.482619835 | 1.623730609 | HN | XN | Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich type 1 protein M130 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD163 PE=1 SV=2 | 372734.7 | 564760.3 | 1001389 | 682510.5 | 808753.0644 | 293025.8928 | 148748.2981 | 405832.5484 | 165774.0748 | 88441.66788 | 400926.7262 | 245524.3826 | 765307.426 | 189448.3639 | 220822.923 | 1667971.495 | 370188.0249 | 509008.8782 | 117909.6253 | 449689.6575 | 206441.8493 | 248659.2642 | 197264.7641 | 269822.1462 | 429569.7141 | 326707.7749 | 499242.747 | ||
| Q8TCA0 | 3 | 2 | 40.84 | 0.889180744 | 6.632788257 | XN | HN | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRRC20 PE=2 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 127233.4513 | 47543.85288 | 21102.25131 | 13624.09623 | 17645.71279 | 2575.498053 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 202496.9799 | 21991.77536 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P20700 | 5 | 1 | 40.62 | 6.15E-05 | 51.61394327 | HN | XA | Lamin-B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LMNB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 30.33749 | 0 | 1818.007 | 41.91607 | 23.88760594 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.74827722 | 1011.294378 | 4924.752426 | 4826.660657 | 253.0775105 | 6328.958715 | 78414.94931 | 2927.109835 | 85.1688155 | 146.3484285 | 3166.195417 | 374.9911616 | 1496.89506 | 2419.991023 | 2427.575743 | 84.67999233 | 2473.417218 | 166.3307078 | ||
| P28827 | 5 | 2 | 40.56 | 0.572614383 | 1.321914406 | HN | XN | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase mu OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRM PE=1 SV=2 | 90690.68 | 248152.6 | 180188.4 | 102728.7 | 88551.40724 | 59246.82737 | 108713.5961 | 49940.65758 | 92291.16183 | 57161.59886 | 171460.768 | 93922.09832 | 171316.3039 | 253526.4432 | 87131.5625 | 73428.90332 | 90292.49396 | 76326.12508 | 60514.83157 | 119107.3987 | 91497.17149 | 85821.91391 | 82558.49988 | 148996.2025 | 103843.5426 | 73771.93322 | 46774.94712 | ||
| Q7Z333 | 10 | 3 | 40.43 | 0.221104397 | 1.498146766 | HN | XN | Probable helicase senataxin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SETX PE=1 SV=4 | 71527063 | 1.2E+08 | 75651225 | 57824656 | 129636846.1 | 50733436.48 | 40882598.07 | 44846849.9 | 43191148.84 | 179135401.2 | 78682468.56 | 103798092.6 | 44839155.73 | 50862905.24 | 161727502.4 | 125405599.7 | 66910004.7 | 54536811.98 | 65503550.62 | 59068217.96 | 32563974.6 | 44770148.09 | 96632212.66 | 121622298.5 | 53205730.02 | 45110887.34 | 59502362.33 | ||
| Q92485 | 2 | 2 | 40.2 | 0.672856281 | 1.7183935 | HN | XA | Acid sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMPDL3B PE=2 SV=2 | 105290.2 | 22757.5 | 24689.19 | 63982.94 | 20528.86667 | 62629.32697 | 39111.12846 | 67771.04177 | 43709.4658 | 8934.50642 | 209932.0698 | 219449.4646 | 107878.2883 | 124991.4449 | 44287.95327 | 6359.259016 | 9529.458481 | 42721.62789 | 131392.0761 | 108179.3893 | 71368.8422 | 45879.36023 | 35207.24642 | 44976.65922 | 34017.00755 | 113847.6782 | 43742.01297 | ||
| P02794 | 3 | 2 | 40.18 | 0.583115058 | 1.466170869 | XN | HN | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 291142.4 | 362399.2 | 551828.7 | 507304.3 | 207252.1268 | 176467.2922 | 476566.0461 | 228829.369 | 46522.53829 | 82261.56037 | 69737.52132 | 240718.2138 | 600687.5983 | 217723.2174 | 669486.2018 | 226116.4282 | 79273.6954 | 65896.79785 | 526493.9392 | 27048.69174 | 21025.49279 | 61666.39932 | 257629.3479 | 1525057.581 | 625181.4487 | 201245.1769 | 56323.91196 | ||
| O76013 | 4 | 1 | 40.15 | 0.672981585 | 1.139419732 | XN | XA | Keratin, type I cuticular Ha6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT36 PE=1 SV=1 | 1378704 | 2465718 | 1778435 | 1836131 | 2653105.07 | 1290953 | 871113.9659 | 1005697.23 | 1247978.831 | 1426489.448 | 1692243.82 | 987846.6023 | 926360.6873 | 1833794.971 | 2313786.873 | 2082151.881 | 2898150.224 | 2114068.396 | 1557734.373 | 1292675.676 | 1360564.984 | 2190584.044 | 1625197.587 | 2801409.696 | 1330736.256 | 1413540.492 | 2980859.269 | ||
| P01597;P01600;P01606;P01608;P80362 | 5 | 2 | 40.15 | 0.78497974 | 1.165272005 | XN | HN | Ig kappa chain V-I region DEE OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 372776.1 | 391843.1 | 388614.1 | 245740 | 608936.5691 | 192034.7543 | 247332.4098 | 320770.0968 | 105969.5827 | 353808.4894 | 121304.9945 | 265668.5573 | 125703.6129 | 166202.168 | 591652.5395 | 470093.8326 | 287650.1468 | 205737.3183 | 332982.3888 | 163874.4317 | 168647.8759 | 270208.051 | 453989.3919 | 812693.267 | 322986.8639 | 179483.0854 | 310650.7773 | ||
| A2VDF0 | 2 | 1 | 40.11 | 0.487800542 | 1.230118336 | HN | XA | Fucose mutarotase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FUOM PE=1 SV=2 | 17856.26 | 923.4429 | 4142.163 | 17511.24 | 0 | 27544.57236 | 25765.54324 | 14912.33194 | 22299.82983 | 19178.79413 | 29971.92499 | 14320.68092 | 50890.29406 | 19535.98095 | 6695.208544 | 9676.719303 | 1693.912805 | 9127.099013 | 19091.31303 | 22190.21144 | 31687.75224 | 52749.68653 | 7916.539882 | 3169.205557 | 3631.526142 | 3946.049906 | 2122.339008 | ||
| P21796 | 1 | 1 | 40.09 | 0.026836757 | 3.020285572 | XA | XN | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VDAC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 173641.6 | 80446.29 | 342121.7 | 32883.34 | 19613.10206 | 85410.75619 | 149700.6261 | 209828.1849 | 33265.51748 | 72851.54026 | 38682.25729 | 35633.65373 | 40068.59332 | 13970.14915 | 11232.27649 | 66906.12551 | 152400.691 | 34700.30446 | 55469.6414 | 4597.848176 | 135057.392 | 10562.51562 | 3200.649785 | 5462.958812 | 100936.773 | 41135.09094 | 16691.202 | ||
| Q9UJ68 | 1 | 1 | 40.08 | 0.047884747 | 3.599326733 | XA | XN | Mitochondrial peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSRA PE=1 SV=1 | 141515.8 | 12728.07 | 90089.55 | 365131.1 | 15648.69235 | 134417.913 | 196024.1437 | 200285.9163 | 179067.4913 | 20993.19197 | 104394.3161 | 79182.49918 | 123087.1822 | 161582.3228 | 25324.16206 | 41339.09289 | 26262.05674 | 74411.7069 | 16908.73372 | 32586.27003 | 28434.98992 | 69630.85398 | 2475.050244 | 41043.87466 | 88006.01316 | 81108.42269 | 10683.12706 | ||
| Q8TCT8 | 3 | 2 | 40.07 | 0.144851801 | 1.938346172 | HN | XA | Signal peptide peptidase-like 2A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPPL2A PE=1 SV=2 | 686251.2 | 858099.7 | 710061 | 389006 | 647351.3389 | 435729.0516 | 697490.3163 | 488193.5816 | 690877.0238 | 2476394.298 | 2121783.424 | 481966.0002 | 2058126.047 | 1118485.214 | 542970.8246 | 373926.6618 | 753195.6603 | 933820.2323 | 496808.6574 | 1198455.461 | 666311.744 | 396335.5454 | 626442.7233 | 1335153.353 | 432156.7017 | 929327.2036 | 1110050.648 | ||
| Q1L6U9 | 1 | 1 | 40.06 | 0.684886537 | 2.105419184 | HN | XA | Prostate-associated microseminoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSMP PE=1 SV=1 | 147352.6 | 126737.5 | 48376.22 | 244653.1 | 92958.50268 | 8783.504509 | 57403.24008 | 5419.842207 | 2917.095727 | 87471.15976 | 20344.91249 | 247348.6992 | 3889.736959 | 42679.12989 | 31712.39136 | 837937.5734 | 65623.65696 | 209637.2017 | 5217.771999 | 67861.74338 | 52900.75192 | 25069.37346 | 188368.5828 | 29608.92726 | 121849.0043 | 174385.4107 | 209743.974 | ||
| Q9Y5E5 | 6 | 1 | 39.99 | 0.586473088 | 1.817292057 | HN | XA | Protocadherin beta-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB4 PE=2 SV=1 | 83264.7 | 294704.6 | 451716.5 | 136601.4 | 824689.6682 | 99188.00615 | 48128.4778 | 117976.6397 | 93488.07562 | 323801.3869 | 38737.05715 | 450118.1652 | 37540.51866 | 184513.2391 | 527751.1213 | 230857.7468 | 929226.2368 | 1184192.953 | 123965.1483 | 442608.0314 | 204501.4781 | 188322.0277 | 245841.4699 | 77583.50825 | 122756.6716 | 188363.7128 | 1197590.11 | ||
| P18859 | 1 | 1 | 39.67 | 0.697269483 | 131.0290853 | HN | XA | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP5J PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 292.1106 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2009.571683 | 4.15771027 | 231.3519194 | 31488.92988 | 15056.59987 | 285900.4011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13401.14254 | 0 | 2222.642661 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q7Z2Y8 | 11 | 2 | 39.44 | 0.191951485 | 2.382534213 | XA | XN | Interferon-induced very large GTPase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GVINP1 PE=2 SV=2 | 352859.2 | 1777527 | 1933312 | 545747.5 | 2443744.889 | 2421982.716 | 325809.5589 | 598841.4884 | 423788.2405 | 162912.6251 | 1720048.152 | 82902.68073 | 1640144.325 | 819532.684 | 964282.5318 | 878482.7185 | 857876.8564 | 1079129.3 | 186754.6649 | 574872.4449 | 398533.7881 | 218225.1551 | 214141.6066 | 1354821.832 | 701175.9449 | 576255.0776 | 318118.4516 | ||
| P36639 | 1 | 1 | 39.41 | 0.87497859 | 1.317989511 | XA | XN | 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine triphosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUDT1 PE=1 SV=3 | 139342.6 | 937242.3 | 797051.1 | 324764.8 | 54112.1708 | 242554.7428 | 98272.4896 | 115034.9217 | 602626.6388 | 157545.147 | 226744.8352 | 501462.4157 | 275694.5823 | 480375.9979 | 272490.2279 | 94676.85447 | 457558.5357 | 373571.326 | 71640.44577 | 356975.0332 | 144557.1306 | 315337.3186 | 233865.8699 | 524524.076 | 423897.2894 | 342646.6953 | 98717.10785 | ||
| Q5VU43 | 9 | 3 | 39.13 | 0.17457873 | 1.788713886 | XN | XA | Myomegalin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDE4DIP PE=2 SV=1 | 797130.7 | 69030 | 167932.1 | 102811.1 | 116947.445 | 110082.1717 | 12019.57802 | 16005.33518 | 10460.56181 | 317557.0609 | 153433.7259 | 106141.5778 | 489816.7391 | 20679.77497 | 112497.0097 | 198780.3075 | 95260.43965 | 135740.4583 | 354373.3821 | 739492.072 | 390486.7478 | 60996.63586 | 274823.0678 | 23732.24636 | 82942.59166 | 213859.3434 | 367820.1928 | ||
| O43776 | 4 | 1 | 38.89 | 0.327900358 | 9.558656976 | XA | HN | Asparagine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic OS=Homo sapiens GN=NARS PE=1 SV=1 | 23058.34 | 0 | 0 | 99139.61 | 3723.649462 | 15301.14408 | 23788.57823 | 58368.74464 | 12025.61036 | 0 | 0 | 4468.214338 | 3968.465463 | 0 | 2804.52492 | 12179.73627 | 0 | 1206.54329 | 2839.954659 | 1902.209393 | 18768.92752 | 0 | 13314.53483 | 0 | 4840.663775 | 1407.983032 | 0 | ||
| P07305 | 5 | 1 | 38.86 | 0.250732764 | 2.418567325 | HN | XA | Histone H1.0 OS=Homo sapiens GN=H1F0 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 2429.4 | 1580.018 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 58460.36701 | 8864.023295 | 0 | 83153.13243 | 0 | 89263.9974 | 22.88825749 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 85.59822092 | 323.6428294 | 10379.71334 | 6936.412401 | 58317.2839 | 7074.662075 | 11663.70849 | 0 | 0 | 3058.651538 | ||
| Q14103 | 1 | 1 | 38.72 | 0.530937964 | 1.786805375 | XA | XN | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HNRNPD PE=1 SV=1 | 11763.37 | 7287.894 | 6108.968 | 9905.906 | 7373.588692 | 888.4405139 | 25348.95462 | 3524.702032 | 24524.21981 | 1153.959867 | 6808.455066 | 35622.58591 | 11487.85929 | 916.7811997 | 17962.85271 | 14358.62758 | 0 | 1417.355182 | 4698.038745 | 4966.752649 | 11651.82294 | 0 | 4545.332034 | 6727.998623 | 3389.872555 | 9953.131275 | 8200.560647 | ||
| P42702 | 7 | 2 | 38.7 | 0.347571771 | 1.301949104 | XN | HN | Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=LIFR PE=1 SV=1 | 728983.2 | 1009748 | 656110.4 | 1151489 | 596932.2649 | 894259.7072 | 490687.8112 | 986934.8952 | 649930.4892 | 460078.9176 | 832554.8739 | 862570.8194 | 686186.7038 | 762928.7513 | 398626.1123 | 469986.3219 | 912106.3467 | 829176.7816 | 602151.3846 | 677639.7235 | 741963.7673 | 1085033.564 | 830706.8982 | 1951894.007 | 906307.7738 | 782370.435 | 512524.916 | ||
| P12110 | 10 | 1 | 38.61 | 0.493315953 | 1.142732805 | HN | XN | Collagen alpha-2(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 1005901 | 870648.2 | 967423.5 | 680966.6 | 872963.6572 | 934050.3138 | 1284176.157 | 854827.9301 | 1057739.151 | 1224368.852 | 1002453.373 | 1690479.765 | 671952.5452 | 830729.7982 | 971140.4103 | 933247.4051 | 758307.0306 | 685457.7234 | 985122.2348 | 728169.1785 | 946827.2966 | 568443.7967 | 910238.3988 | 772013.5032 | 511369.8746 | 1190580.852 | 1060189.438 | ||
| Q92496 | 1 | 1 | 38.58 | 0.770734246 | 11.2005846 | HN | XN | Complement factor H-related protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFHR4 PE=1 SV=2 | 5102.199 | 1086.257 | 2045.697 | 58314.27 | 432275.7464 | 1403.233154 | 2588.765896 | 5648.71168 | 1748.438603 | 1121.535822 | 1347.482656 | 2070.073019 | 8119.409017 | 9729.831793 | 28238.44545 | 1117594.163 | 36290.20837 | 1058.690129 | 17849.73643 | 2924.896024 | 758.85248 | 1784.669835 | 641.858722 | 63283.28932 | 4200.356805 | 9498.776933 | 6692.109539 | ||
| Q9NUW8 | 5 | 3 | 38.37 | 0.914774975 | 1.033717372 | XA | XN | Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TDP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1686387 | 1393114 | 1567926 | 1349501 | 1228982.713 | 742471.7284 | 707967.2509 | 920137.4185 | 548530.492 | 1523166.417 | 698547.3276 | 789660.2898 | 699828.2393 | 537450.0743 | 1424686.993 | 2683905.859 | 945837.0492 | 633363.2336 | 794598.0191 | 594234.8413 | 1334262.122 | 850365.488 | 2139372.071 | 660438.5716 | 1650279.961 | 809732.6819 | 980827.205 | ||
| P01701 | 3 | 2 | 38.25 | 0.500280292 | 1.253952303 | XN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-I region NEW OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 5128693 | 8305942 | 4027992 | 2416146 | 3684681.454 | 2124633.535 | 2868385.945 | 3103049.754 | 2819491.078 | 7263237.681 | 5017139.448 | 6875507.701 | 2879494.8 | 2207642.727 | 6689427.33 | 5116324.41 | 1517551.42 | 2681606.446 | 5596623.974 | 7448556.433 | 4186910.614 | 2071637.972 | 4415046.063 | 5481652.43 | 3430397.785 | 5924160.76 | 4680054.63 | ||
| Q8NBK3 | 1 | 1 | 38.09 | 0.131977856 | 1.367072912 | XN | XA | Sulfatase-modifying factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SUMF1 PE=1 SV=3 | 193930.6 | 84600.23 | 76985.11 | 154760.9 | 181708.4587 | 321150.5518 | 287802.7509 | 133610.8568 | 179424.027 | 57776.89461 | 9731.73192 | 45841.74052 | 35243.63598 | 10066.70938 | 283611.1142 | 1441620.94 | 91723.96896 | 222943.2324 | 230973.497 | 473577.0361 | 195663.1123 | 105247.2674 | 79445.19473 | 474831.0471 | 376401.6375 | 102331.6993 | 167948.9317 | ||
| Q6UXB3 | 1 | 1 | 37.95 | 0.015674738 | 3.536564002 | XN | HN | Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPD2 PE=2 SV=1 | 77419.81 | 517524 | 678128.3 | 141197 | 94458.45958 | 195246.5351 | 722072.0866 | 130460.8206 | 1408297.702 | 116429.9313 | 48266.77865 | 126746.4765 | 238358.3149 | 87197.61386 | 267093.9007 | 65638.50682 | 29854.46591 | 175156.4247 | 129562.5375 | 1046117.153 | 376684.0684 | 291959.295 | 128810.375 | 745643.4771 | 159626.7286 | 784610.1336 | 420806.6826 | ||
| P01762 | 2 | 2 | 37.95 | 0.069296383 | 1.665559449 | XN | HN | Ig heavy chain V-III region TRO OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 242805.8 | 447541.7 | 316459.3 | 289201.6 | 606619.994 | 467553.6745 | 318333.6589 | 213073.6668 | 440276.9978 | 43572.14103 | 203730.2768 | 317505.6687 | 252892.6337 | 354680.6326 | 221719.9134 | 187760.8232 | 232013.8111 | 227865.5363 | 370319.2348 | 272500.8381 | 298155.4141 | 241956.4275 | 302098.3054 | 402237.4395 | 152446.5387 | 222234.3175 | 1138693.226 | ||
| Q969E4 | 2 | 1 | 37.94 | 0.140873624 | 2.059416527 | XA | XN | Transcription elongation factor A protein-like 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCEAL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 26342.77 | 4400.535 | 6576.914 | 67107.47 | 15997.64549 | 6200.111548 | 10286.94797 | 14664.84599 | 14318.3652 | 17272.22103 | 23562.73403 | 26571.90336 | 6440.318809 | 5529.637866 | 21858.52072 | 19634.00153 | 7407.652927 | 15569.2174 | 6016.187169 | 6726.819258 | 17225.02193 | 3831.462997 | 17513.24163 | 2884.551472 | 6303.024583 | 6504.243111 | 13550.11037 | ||
| P55289 | 6 | 1 | 37.86 | 0.923966173 | 1.190708618 | HN | XA | Cadherin-12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH12 PE=1 SV=2 | 1933660 | 2702628 | 1673868 | 853624.6 | 1334313.471 | 1070203.265 | 1403998.182 | 1013160.275 | 1142704.13 | 2205460.987 | 848293.9315 | 1089273.662 | 2498701.2 | 4018299.372 | 2294666.428 | 947071.1566 | 906498.3641 | 823548.5484 | 1719638.93 | 2068085.488 | 1057863.275 | 1013281.422 | 2021617.89 | 1263176.548 | 1249172.98 | 2201116.987 | 1213647.592 | ||
| Q58FF6 | 6 | 1 | 37.82 | 0.572176384 | 1.480624946 | XA | XN | Putative heat shock protein HSP 90-beta 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB4P PE=5 SV=1 | 117983.2 | 193538.3 | 261764.8 | 66181.68 | 545652.8711 | 98289.34778 | 25975.18855 | 86014.6738 | 29724.86886 | 90050.83926 | 105000.7969 | 80611.76954 | 82721.1381 | 167397.8075 | 108464.7341 | 355993.7537 | 165734.9555 | 122487.41 | 22003.86793 | 119062.449 | 68303.86994 | 141680.1218 | 131587.9266 | 219904.4742 | 161229.7172 | 67770.84191 | 30972.58467 | ||
| Q9UIF8 | 12 | 2 | 37.64 | 0.603577082 | 1.164517035 | XA | HN | Bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain protein 2B OS=Homo sapiens GN=BAZ2B PE=1 SV=3 | 435671.6 | 500252.3 | 343142.3 | 313416.1 | 358001.5682 | 275702.9638 | 281473.2876 | 248714.451 | 136862.2122 | 317723.8067 | 454273.2347 | 342267.6375 | 219381.5939 | 268207.2139 | 274578.3595 | 180006.7958 | 171514.7837 | 256541.6109 | 514651.4653 | 225502.3019 | 151046.3576 | 251661.5314 | 283687.1099 | 248584.5356 | 242798.0252 | 277495.6078 | 303398.5648 | ||
| Q9BUD6 | 2 | 1 | 37.53 | 0.340720654 | 3.189501154 | HN | XA | Spondin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPON2 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 8613.022 | 0 | 3285.057 | 14623.38111 | 0 | 0 | 6698.858978 | 7856.45532 | 0 | 2965.065292 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 128049.3548 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9343.425424 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5272.786361 | 28797.29155 | 34891.88217 | 3037.443997 | ||
| Q7Z7G8 | 7 | 2 | 37.46 | 0.291416559 | 1.4230154 | XN | HN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 13B OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS13B PE=1 SV=2 | 649207.9 | 207580.7 | 561095.3 | 855204.8 | 1081905.47 | 502333.3097 | 247331.7892 | 301336.8778 | 290077.3744 | 646450.7951 | 834026.2614 | 146199.4609 | 767692.4221 | 430560.1627 | 197521.1434 | 557142.3307 | 225855.5622 | 617856.452 | 577040.1807 | 908370.9264 | 829509.2062 | 191442.2781 | 488119.2319 | 916816.1605 | 539171.742 | 1050834.77 | 793126.0566 | ||
| P17181 | 3 | 3 | 37.45 | 0.363024296 | 1.275494091 | XN | HN | Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IFNAR1 PE=1 SV=3 | 385999.5 | 485110.8 | 472195.6 | 213991.6 | 200025.6313 | 412257.8016 | 489325.2637 | 186054.8848 | 362086.2981 | 148583.7815 | 549367.4836 | 201373.5635 | 255692.8617 | 365695.9509 | 377913.6062 | 287972.5053 | 213062.0072 | 280574.7163 | 302693.1715 | 537022.7438 | 301485.0064 | 178775.3547 | 496799.1114 | 279007.8247 | 476451.5483 | 349037.7881 | 497353.2379 | ||
| O00526 | 3 | 2 | 37.31 | 0.450095497 | 4.738376729 | HN | XN | Uroplakin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UPK2 PE=2 SV=2 | 451199.1 | 383816.3 | 207464.6 | 212190.2 | 169877.283 | 127482.6686 | 438636.653 | 175991.0995 | 151699.9688 | 785199.0899 | 1003329.026 | 531701.6348 | 110092.1244 | 634613.7679 | 154427.6306 | 7365359.956 | 63116.17383 | 82063.00055 | 279257.7903 | 193592.8962 | 172656.0812 | 283573.735 | 99909.14689 | 254959.2447 | 190740.6962 | 276541.9354 | 513236.459 | ||
| O43280 | 2 | 1 | 37.28 | 0.441839398 | 1.428755724 | XN | HN | Trehalase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TREH PE=1 SV=2 | 60661.35 | 7766.284 | 12192.48 | 35331.44 | 21792.21816 | 20275.4624 | 39396.28815 | 11065.74117 | 58207.92054 | 46160.49633 | 54814.64917 | 30032.78527 | 8962.236606 | 13835.20375 | 0 | 16154.4663 | 19362.16908 | 58257.06165 | 12602.4352 | 95691.33909 | 41904.59608 | 32090.94378 | 41644.76555 | 1969.01448 | 18014.60957 | 50272.72115 | 59539.58597 | ||
| O94929 | 4 | 1 | 37.08 | 0.629717273 | 1.487473968 | HN | XN | Actin-binding LIM protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABLIM3 PE=1 SV=3 | 176386.1 | 408825.7 | 330339.6 | 343800.3 | 486064.5984 | 383518.1633 | 252285.1709 | 275216.489 | 151385.7402 | 1224642.836 | 227761.9336 | 422076.3305 | 284621.6439 | 215939.0888 | 1023769.822 | 225332.5407 | 422510.0258 | 100600.5426 | 300511.634 | 99213.96556 | 135521.8507 | 389213.069 | 697328.6375 | 119949.4808 | 357481.803 | 259928.4351 | 428970.3475 | ||
| Q10570 | 7 | 4 | 37.07 | 0.674492081 | 1.151053099 | XN | HN | Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPSF1 PE=1 SV=2 | 4744694 | 762143.4 | 737813.4 | 1144838 | 720345.4657 | 608579.3574 | 823048.3553 | 433234.4122 | 854685.6132 | 1450850.248 | 1739622.856 | 2582065.046 | 56488.63005 | 753442.4009 | 799165.3354 | 159953.3134 | 712919.6357 | 1519186.544 | 885340.844 | 1835259.548 | 481323.316 | 471705.9209 | 924346.3397 | 2013578.283 | 2999784.998 | 443404.5338 | 1195296.999 | ||
| P23327 | 2 | 2 | 37.01 | 0.112621172 | 1.604864291 | HN | XN | Sarcoplasmic reticulum histidine-rich calcium-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRC PE=2 SV=1 | 1735947 | 7577688 | 2690956 | 2810360 | 3075359.602 | 3947533.122 | 1838636.598 | 1071866.499 | 1776456.542 | 5865495.63 | 4420849.375 | 7040557.698 | 3357928.997 | 2359894.173 | 5736900.903 | 3779182.595 | 2555631.103 | 1824343.521 | 1969286.085 | 2129483.668 | 1331591.916 | 2459697.947 | 3081456.312 | 4613164.648 | 3123443.035 | 2362717.259 | 1947170.19 | ||
| Q13464 | 11 | 2 | 36.91 | 0.586083314 | 1.67471172 | XN | XA | Rho-associated protein kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ROCK1 PE=1 SV=1 | 30961.31 | 1204713 | 205452.8 | 77156.88 | 152176.5883 | 132610.7637 | 211804.732 | 123408.9656 | 321028.8571 | 229884.7967 | 755578.2817 | 135006.3814 | 70220.94173 | 728881.9682 | 236732.3062 | 64953.7434 | 543169.4108 | 195383.3386 | 1748503.808 | 329076.3919 | 303524.7323 | 666957.3155 | 32720.80168 | 404610.8491 | 79185.65574 | 340749.6598 | 213313.1057 | ||
| Q8IYD8 | 7 | 1 | 36.78 | 0.425288175 | 2.588919458 | XA | HN | Fanconi anemia group M protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=FANCM PE=1 SV=2 | 1726.097 | 137282 | 1073.296 | 11295.61 | 81365.80231 | 59488.03161 | 219469.7681 | 131604.9259 | 43313.27213 | 8630.985997 | 16240.65076 | 4471.221797 | 5153.756952 | 19010.0133 | 5605.46031 | 78.36089661 | 198531.2248 | 7492.754693 | 117680.3132 | 0 | 11251.98285 | 2890.716288 | 5715.653108 | 60203.53205 | 18770.90906 | 47358.78101 | 40336.49916 | ||
| P61960 | 1 | 1 | 36.76 | 0.993854124 | 1.449489535 | XA | XN | Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UFM1 PE=1 SV=1 | 338014.4 | 48691.26 | 54926.45 | 546142 | 25364.22825 | 326694.585 | 679056.7282 | 723064.8963 | 392571.6461 | 247269.6423 | 430669.1237 | 277904.029 | 338499.0066 | 197912.995 | 69160.44642 | 679726.5941 | 75062.30783 | 89161.56723 | 233409.8383 | 276982.7336 | 547511.8875 | 225966.4923 | 305618.9621 | 116212.0896 | 179864.1891 | 157749.7222 | 119187.5443 | ||
| Q9NRJ7;Q9UN67;Q9Y5E1;Q9Y5E6 | 6 | 1 | 36.67 | 0.141546708 | 10.47872953 | XN | XA | Protocadherin beta-16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB16 PE=1 SV=3 | 80939.72 | 44933.59 | 129437.7 | 51874.71 | 32067.24815 | 123537.2504 | 172192.9131 | 76148.64944 | 159583.0424 | 178727.72 | 137973.0126 | 121332.2717 | 383722.8565 | 134643.7868 | 72571.38703 | 62012.81711 | 113177.742 | 160977.9801 | 101747.1829 | 1081335.723 | 152986.72 | 118347.557 | 87459.94548 | 96364.43092 | 67405.84033 | 153519.8357 | 7264817.913 | ||
| Q9NZ08 | 3 | 2 | 36.52 | 0.452650846 | 2.042610801 | HN | XN | Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERAP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 41929.07 | 864236.2 | 1318799 | 451373 | 4687462.661 | 1402089.602 | 178210.5363 | 239764.3704 | 559637.8744 | 108318.6367 | 1008110.982 | 159959.2792 | 425758.3575 | 418819.6174 | 3338040.25 | 2351891.181 | 1133676.23 | 1994600.084 | 116307.0821 | 211982.696 | 94846.78048 | 87660.15915 | 738302.2393 | 370925.0238 | 1101704.001 | 2117187.646 | 516570.8956 | ||
| Q13938 | 2 | 2 | 36.41 | 0.112924681 | 2.875627213 | HN | XN | Calcyphosin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPS PE=1 SV=1 | 517467 | 1152308 | 269772.1 | 358495.2 | 743801.6512 | 253140.5987 | 254767.9978 | 370888.0293 | 718641.4642 | 723355.8564 | 250847.1251 | 4185528.123 | 135269.05 | 1019454.585 | 808247.9679 | 335081.233 | 1035154.29 | 667568.568 | 301676.0953 | 196663.4481 | 490826.6824 | 217265.5696 | 867330.9391 | 300327.3864 | 438976.1459 | 213526.61 | 158975.3904 | ||
| Q9NUM4 | 1 | 1 | 36.29 | 0.369600015 | 1.667386674 | HN | XN | Transmembrane protein 106B OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMEM106B PE=1 SV=2 | 175911.7 | 251234.4 | 1106005 | 19105.55 | 1042764.884 | 208320.9639 | 109066.3092 | 329163.3163 | 70764.02947 | 533407.8356 | 213193.7942 | 233677.5832 | 129043.0545 | 315232.4155 | 577183.5923 | 1141176.649 | 699519.8898 | 257529.0078 | 225823.0239 | 90405.18391 | 238275.712 | 417116.7339 | 498095.5871 | 272215.2363 | 14068.19743 | 292503.8161 | 410412.5403 | ||
| Q9H4A4 | 2 | 2 | 36.21 | 0.110529927 | 1.829336147 | XA | XN | Aminopeptidase B OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNPEP PE=1 SV=2 | 228459.1 | 93490.19 | 114324.9 | 460605.3 | 106688.1514 | 211144.1737 | 324456.5196 | 512056.3231 | 315565.6284 | 148864.0274 | 107861.0153 | 137023.7073 | 189522.7051 | 222023.2595 | 119803.0354 | 433467.9332 | 138796.2872 | 164789.5092 | 186021.7014 | 161537.7112 | 116469.0963 | 246077.9644 | 245428.3118 | 57430.71686 | 127105.7613 | 87642.79163 | 66083.32584 | ||
| P20061 | 3 | 1 | 35.88 | 0.379406349 | 3.047887404 | XA | XN | Transcobalamin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0 | 4655.343 | 18281.02 | 4503.123 | 0 | 47989.85502 | 279669.8573 | 0 | 309872.1756 | 36066.3493 | 3537.053949 | 0 | 0 | 181709.7977 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 165085.1083 | 0 | 0 | 4318.679782 | 0 | 19802.23619 | 0 | 15591.67346 | 13376.82203 | ||
| O14556 | 5 | 1 | 35.75 | 0.350564714 | 1.539565819 | XN | HN | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, testis-specific OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDHS PE=1 SV=2 | 42830.84 | 14283.39 | 34016.77 | 50791.24 | 9167.79988 | 33608.81885 | 40578.22973 | 58980.90612 | 39791.80585 | 18521.74054 | 31105.38403 | 26462.82076 | 59970.3794 | 29728.64863 | 36921.66103 | 78942.76574 | 17011.70356 | 23126.13065 | 20205.36671 | 28633.24138 | 69078.72432 | 49781.60572 | 132664.7017 | 21591.28129 | 97841.79196 | 34442.62155 | 41179.45058 | ||
| O14818 | 2 | 1 | 35.72 | 0.137553932 | 1.518230795 | XA | HN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA7 PE=1 SV=1 | 11508.32 | 14716.93 | 15674.26 | 0 | 47970.83654 | 63051.18692 | 276818.7565 | 209011.1632 | 145059.2386 | 53166.75322 | 88410.67638 | 40954.80678 | 193455.6424 | 32105.7565 | 42599.53866 | 12945.55882 | 10948.56221 | 41678.53717 | 523690.3857 | 23810.82553 | 19865.56707 | 112254.8502 | 11640.74222 | 6470.35506 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| A6NGN9 | 2 | 1 | 35.7 | 0.430067191 | 1.497614392 | XA | XN | IgLON family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLON5 PE=2 SV=4 | 134645.8 | 352376.6 | 104531.2 | 83439.81 | 215568.3819 | 345845.4518 | 163634.779 | 75898.32112 | 415399.3667 | 266901.2398 | 20031.85676 | 265360.6655 | 106455.6755 | 136299.5494 | 258449.034 | 158333.9256 | 91688.4211 | 60867.70426 | 83855.49814 | 114755.9138 | 100524.4993 | 90115.47527 | 211001.6911 | 256092.4507 | 73006.69259 | 183388.9234 | 150160.4939 | ||
| Q9Y592 | 13 | 4 | 35.66 | 0.596044253 | 1.360959664 | XN | HN | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 41 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCDC41 PE=1 SV=2 | 460191.7 | 158394.6 | 576346 | 532911.3 | 2171452.539 | 1101129.613 | 1298441.272 | 1014372.733 | 1750162.567 | 1429324.739 | 491133.0485 | 609222.0321 | 607035.9845 | 991212.2051 | 497331.4172 | 534015.1889 | 1896453.205 | 992241.2937 | 1340525.069 | 1328780.444 | 817834.7021 | 2932020.248 | 597261.7202 | 464528.6782 | 652663.1838 | 1793697.687 | 1025649.61 | ||
| Q6UXS9 | 1 | 1 | 35.6 | 0.252624886 | 1.189975675 | XA | HN | Inactive caspase-12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CASP12 PE=2 SV=2 | 64992617 | 72700006 | 72770917 | 50882857 | 54317249.85 | 45439921.67 | 40037945.32 | 54817794.26 | 53046131.12 | 45065960.31 | 53316320.15 | 51825375.66 | 53761471.69 | 51429276.42 | 25280450.14 | 51986788.68 | 38964479.08 | 56114285.58 | 54173066.54 | 61349253.89 | 45425423.5 | 41002980.23 | 36092093.78 | 48975421.82 | 31206207.12 | 71928320.87 | 53070235.3 | ||
| O60476 | 2 | 1 | 35.53 | 0.089248041 | 1.797504304 | XA | XN | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase IB OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN1A2 PE=2 SV=1 | 203560.3 | 74267.41 | 181156.2 | 353168.4 | 77978.34192 | 268544.8014 | 227378.8481 | 228917.2807 | 131821.5197 | 284421.514 | 58397.64519 | 220911.9592 | 64972.52128 | 162478.7438 | 117647.7925 | 24819.87355 | 85577.78421 | 62912.87627 | 124810.0876 | 68690.23172 | 194648.3384 | 113223.0185 | 214142.1861 | 23244.62134 | 101765.7332 | 67082.16167 | 64181.58956 | ||
| P46821 | 7 | 1 | 35.41 | 0.787114251 | 2.505837135 | XA | XN | Microtubule-associated protein 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP1B PE=1 SV=2 | 19524.1 | 533919.6 | 480853.2 | 134869.8 | 880079.5606 | 172202.0939 | 15479.43344 | 96740.00511 | 79665.39159 | 82145.53801 | 13910.95915 | 5288.245956 | 52851.52209 | 79238.93111 | 633927.6036 | 590219.2637 | 343853.5205 | 142911.3209 | 49616.43212 | 120689.9592 | 40886.02032 | 282725.0926 | 89232.22206 | 88876.46842 | 111982.7537 | 63054.97145 | 116020.6918 | ||
| Q96QR1 | 1 | 1 | 35.27 | 0.110860012 | 12.87005326 | XN | XA | Secretoglobin family 3A member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCGB3A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 14286.07 | 4696.477 | 26310.74 | 225726.3 | 13306.84696 | 0 | 0 | 25310.53832 | 0 | 3886.563301 | 0 | 31040.67395 | 36504.61535 | 144430.5276 | 11132.31496 | 2556530.053 | 6927.033689 | 0 | 3460.977339 | 2800.396885 | 5586.613721 | 8600.502044 | 610592.2667 | 338827.4852 | 347890.3302 | 1325522.048 | 1341763.543 | ||
| Q7Z7M8 | 2 | 1 | 35.18 | 0.48278348 | 7.101857014 | XA | HN | UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=B3GNT8 PE=1 SV=1 | 30088.74 | 0 | 18533.24 | 27675.14 | 4332.93375 | 0 | 0 | 7628.362373 | 3300.748903 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1734.637553 | 2331.025726 | 0 | 6339.850482 | 0 | 2486.772289 | 4486.770757 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3602.816493 | 0 | 22303.76929 | 4855.79613 | 6362.819739 | ||
| Q9Y5F0;Q9UN66 | 5 | 1 | 35.1 | 0.980393044 | 1.032184709 | XN | HN | Protocadherin beta-13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB13 PE=2 SV=1 | 674615.9 | 1084899 | 844189.3 | 555561.1 | 655211.52 | 483899.7876 | 443134.271 | 418638.7288 | 462991.749 | 417817.4679 | 797639.2145 | 362125.9574 | 646409.371 | 563626.7848 | 831724.0741 | 510953.7447 | 625286.0796 | 840990.2387 | 303272.6466 | 503381.2116 | 554165.1245 | 588856.4299 | 613217.7393 | 664006.7331 | 743899.5729 | 778323.7948 | 1027573.751 | ||
| O60896 | 1 | 1 | 34.94 | 0.215591131 | 1.301139003 | XA | HN | Receptor activity-modifying protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAMP3 PE=2 SV=1 | 2742233 | 704782.8 | 784186.1 | 1187558 | 897982.2393 | 847416.3269 | 1253168.02 | 1101954.779 | 984452.3169 | 262088.0724 | 1367436.2 | 540359.3667 | 899811.9419 | 1788329.979 | 555259.7062 | 183705.5517 | 968538.4362 | 1507193.123 | 973221.6112 | 1611821.405 | 1350035.724 | 716218.6429 | 1387844.702 | 774406.2664 | 553501.4154 | 1387254.907 | 1504583.33 | ||
| Q9Y5E4 | 5 | 1 | 34.91 | 0.694237663 | 1.275163314 | XA | XN | Protocadherin beta-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB5 PE=1 SV=1 | 1101158 | 5203253 | 4487098 | 0 | 1233356.017 | 3067770.482 | 1837484.01 | 1586432.032 | 4017310.054 | 105252.2054 | 492458.6236 | 3648225.873 | 626768.061 | 1930117.037 | 3294141.473 | 420193.8713 | 3746308.657 | 3480234.627 | 3091856.391 | 2910232.489 | 3519356.08 | 403299.0364 | 4391044.385 | 503620.5239 | 971235.4401 | 1180486.289 | 700222.0426 | ||
| Q9Y5E9 | 5 | 1 | 34.72 | 0.553768749 | 4.457982719 | XA | HN | Protocadherin beta-14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB14 PE=2 SV=1 | 242837.4 | 59830.92 | 0 | 0 | 20461.5666 | 1926651.78 | 311914.5156 | 94178.53138 | 438045.5692 | 117676.6106 | 57190.97592 | 133338.76 | 169677.8838 | 96996.13337 | 81451.77566 | 22332.80093 | 10282.81604 | 5070.248493 | 37998.13845 | 307167.1606 | 7718.176177 | 138956.1097 | 24956.9985 | 39299.7265 | 49324.18869 | 88327.09624 | 69757.25858 | ||
| Q5VYK3 | 9 | 2 | 34.67 | 0.52660235 | 1.733868308 | HN | XN | Proteasome-associated protein ECM29 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECM29 PE=1 SV=2 | 9551987 | 2790938 | 1814781 | 3491470 | 7279759.319 | 980478.9142 | 245928.8039 | 1035082.108 | 629113.2853 | 4094533.598 | 490202.7812 | 1734355.706 | 862539.7602 | 6780873.1 | 3390537.93 | 16675097.45 | 5842082.906 | 2733283.796 | 2228560.361 | 2142622.746 | 3864896.709 | 1610998.635 | 3644017.627 | 4728638.479 | 2076535.775 | 1324466.666 | 2950625.678 | ||
| O14686 | 10 | 3 | 34.65 | 0.034160151 | 3.184465521 | XA | HN | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MLL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1325088 | 17379212 | 13279997 | 4672656 | 27599170.84 | 9762860.583 | 1947566.645 | 6486103.62 | 2972822.92 | 2885595.075 | 3033749.825 | 1299777.153 | 1289450.077 | 2235662.123 | 6640845.429 | 4783608.888 | 2020098.035 | 2636900.947 | 3472694.815 | 3944913.547 | 1591652.607 | 978430.2498 | 5139520.171 | 9586061.637 | 1667877.997 | 1317319.713 | 930250.8558 | ||
| Q9BZ95 | 10 | 4 | 34.51 | 0.897533144 | 3.437636604 | XA | XN | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase NSD3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WHSC1L1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1236388 | 1007943 | 335430.8 | 341218.3 | 927206.962 | 967089.0692 | 942755.0916 | 697258.2076 | 23798903.56 | 1802514.517 | 1122211.187 | 389348.6126 | 1173425.977 | 2057153.527 | 528003.6019 | 468571.7858 | 2349882.799 | 652617.7716 | 2123140.192 | 788160.7551 | 1394525.339 | 642409.0399 | 751830.9549 | 679932.7881 | 565409.9436 | 915088.6568 | 940372.3147 | ||
| Q8N201 | 10 | 4 | 34.47 | 2.55E-05 | 2.335369535 | XN | XA | Integrator complex subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=INTS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 15560339 | 10773723 | 5075841 | 14127882 | 7348245.912 | 11570925.53 | 6758024.203 | 9172429.633 | 9058864.49 | 14156756.43 | 29313464.92 | 9883872.375 | 14614225.29 | 17267856.08 | 14630370.49 | 14476786.05 | 30021949.99 | 31692594.17 | 21033456.45 | 24474996.35 | 26065165.11 | 20729986.21 | 20066439.52 | 17533860.26 | 29470475.24 | 30023039.95 | 19492684.85 | ||
| Q8N612 | 4 | 1 | 34.3 | 0.415507585 | 1.401240035 | XN | HN | FTS and Hook-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM160A2 PE=1 SV=3 | 3495473 | 1626044 | 1301715 | 954508.3 | 1157138.363 | 2932958.607 | 1829204.113 | 1705158.906 | 2079790.268 | 1379993.067 | 1032912.102 | 1582626.323 | 2001588.448 | 682282.5934 | 1905216.501 | 1804751.614 | 1400176.335 | 1525323.095 | 3313941.575 | 2462316.679 | 2083959.087 | 1519593.739 | 1671924.522 | 466184.398 | 2113859.002 | 2719551.913 | 2305998.105 | ||
| Q9Y5E8 | 5 | 1 | 34.06 | 0.132812928 | 13.16147092 | XN | HN | Protocadherin beta-15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB15 PE=1 SV=1 | 45823.43 | 0 | 17131.78 | 1680.373 | 547252.8939 | 46656.13169 | 12393.3112 | 0 | 4650.897564 | 10446.39452 | 0 | 3243.46224 | 2551.555291 | 0 | 26052.8766 | 14936.13705 | 6391.795646 | 0 | 251476.4287 | 8088.78583 | 43085.60388 | 1421.767659 | 37240.53603 | 476606.6526 | 5724.040452 | 11228.49554 | 2489.705469 | ||
| P82094 | 10 | 2 | 33.99 | 0.690470097 | 1.291300494 | XN | XA | TATA element modulatory factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMF1 PE=1 SV=2 | 40831.87 | 109788.7 | 202118.5 | 195053.9 | 308522.6247 | 113307.7937 | 104691.5343 | 115578.5374 | 80726.30983 | 336383.1873 | 72126.29076 | 147630.0906 | 55435.40405 | 116151.1618 | 449359.461 | 129947.1526 | 145969.3888 | 147748.3205 | 111938.457 | 484751.1082 | 83456.24203 | 124219.6493 | 94868.1219 | 138563.842 | 189184.6041 | 129637.2148 | 284132.6206 | ||
| O75752 | 3 | 1 | 33.77 | 0.161092448 | 1.6194214 | XN | XA | UDP-GalNAc:beta-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=B3GALNT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 54340.76 | 17392.4 | 15156.99 | 34455.62 | 32145.96887 | 62232.28614 | 24569.25477 | 55840.70012 | 44516.32798 | 18104.04311 | 51021.88639 | 12902.24251 | 88989.28263 | 89860.73303 | 33547.75477 | 44887.93585 | 45004.17377 | 36782.33666 | 62440.97173 | 64269.24269 | 30035.55484 | 43371.68967 | 55089.76571 | 123931.8246 | 77987.98279 | 29166.22595 | 65363.13985 | ||
| O75871 | 3 | 1 | 33.75 | 0.557997301 | 1.226160458 | XN | HN | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEACAM4 PE=1 SV=2 | 273856 | 147078 | 88965.56 | 401411.5 | 69507.1126 | 171302.6873 | 260829.8662 | 229924.8764 | 201161.342 | 268104.3424 | 184079.3642 | 122925.164 | 174764.144 | 148365.4702 | 69120.3613 | 279893.8382 | 65122.28936 | 270622.341 | 197742.9638 | 150574.652 | 106957.9548 | 265409.9962 | 191913.8827 | 330591.3928 | 334179.8668 | 137750.423 | 225887.5808 | ||
| P49721 | 3 | 1 | 33.74 | 0.239022069 | 2.245208824 | XA | HN | Proteasome subunit beta type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB2 PE=1 SV=1 | 42031.78 | 30809.81 | 51732.18 | 97325.69 | 11434.42717 | 143887.6997 | 239363.0507 | 177441.3917 | 238016.8995 | 31769.15186 | 61033.36704 | 88350.35368 | 132274.4509 | 22402.49658 | 97150.43457 | 288.6048931 | 12180.01815 | 14215.68487 | 562077.7366 | 16489.64882 | 101370.0405 | 141271.6752 | 55731.98876 | 10248.94536 | 30048.57259 | 39035.54445 | 10613.58966 | ||
| Q9Y5E2 | 4 | 1 | 33.73 | 0.566561869 | 1.319896033 | XA | HN | Protocadherin beta-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB7 PE=2 SV=1 | 579996.9 | 572410 | 423592.8 | 684760 | 216794.312 | 166694.1067 | 106922.4927 | 152501.2369 | 223882.4812 | 425396.4296 | 53873.06051 | 191013.5176 | 43559.73407 | 149557.1331 | 396123.9966 | 490421.0427 | 400696.9653 | 218904.1189 | 104581.1179 | 268548.1061 | 310629.252 | 202132.0117 | 744313.3253 | 191457.18 | 233124.92 | 178774.3024 | 391906.1991 | ||
| Q9Y4K0 | 2 | 1 | 33.54 | 0.035173583 | 3.279242879 | XA | XN | Lysyl oxidase homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LOXL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 270028.8 | 1438110 | 495239.1 | 1707482 | 1782203.486 | 538461.5954 | 78397.20478 | 996262.3951 | 550393.6237 | 596941.7974 | 729613.4187 | 120143.3764 | 428656.2191 | 298527.8125 | 375854.5166 | 680133.3981 | 504406.8212 | 157675.5772 | 336005.7813 | 649404.8004 | 163437.2968 | 182642.088 | 365994.8724 | 278309.8187 | 170212.3334 | 145754.072 | 104090.4611 | ||
| P01708 | 2 | 1 | 33.5 | 0.696214949 | 1.776638798 | HN | XN | Ig lambda chain V-II region BUR OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 67406.95 | 243639.6 | 147924.6 | 21312.09 | 242623.6878 | 112337.2065 | 218101.0919 | 239061.6694 | 63390.337 | 272917.8126 | 48898.03156 | 776112.3133 | 133613.507 | 15328.01435 | 412177.7412 | 273356.5094 | 251034.6388 | 183258.8924 | 118274.1524 | 155030.7279 | 105883.6687 | 134328.6865 | 180952.3036 | 175800.3258 | 196221.146 | 214607.0911 | 51022.67788 | ||
| P62136;P36873;P62140 | 4 | 2 | 33.44 | 0.373223746 | 1.374926944 | XA | XN | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPP1CA PE=1 SV=1 | 555721.8 | 153039.8 | 130916.9 | 254513.9 | 112785.7652 | 142306.4565 | 214960.5651 | 223959.1909 | 210978.3954 | 210588.0268 | 96857.31825 | 192490.3923 | 189167.6074 | 139131.5704 | 172453.8142 | 201475.5792 | 142237.9675 | 235504.3878 | 161171.3715 | 241781.2512 | 128760.5287 | 119939.9305 | 205820.8314 | 109575.5471 | 136099.9662 | 136672.0906 | 214206.7736 | ||
| Q53SF7 | 7 | 3 | 33.43 | 0.24350256 | 1.647235353 | HN | XA | Cordon-bleu protein-like 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=COBLL1 PE=1 SV=2 | 7492.658 | 9286.9 | 5060.947 | 58003.86 | 251865.8225 | 218953.2875 | 552592.8796 | 244515.5954 | 540110.4384 | 96083.55305 | 143517.3264 | 292779.969 | 95565.54704 | 213683.8827 | 232965.3522 | 142935.7778 | 1487016.356 | 405238.8408 | 1062842.026 | 148240.1131 | 103907.2003 | 339243.8744 | 25302.32259 | 58233.10332 | 81866.87856 | 87219.81092 | 116998.3299 | ||
| P22061 | 2 | 1 | 33.36 | 0.10850382 | 2.346759952 | XA | XN | Protein-L-isoaspartate(D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCMT1 PE=1 SV=4 | 69395.08 | 44552.01 | 113331.5 | 580004.4 | 124033.1925 | 57328.49139 | 215066.4696 | 464544.5994 | 229898.0745 | 144396.0502 | 79685.852 | 119358.6895 | 73135.43816 | 111259.3255 | 137766.9924 | 241089.8715 | 119385.1777 | 87377.18546 | 19243.42155 | 96889.21529 | 100661.2434 | 29151.34247 | 208037.1669 | 37355.68128 | 149209.9625 | 70757.18444 | 97535.00737 | ||
| O75373 | 4 | 2 | 33.03 | 0.420825019 | 4.019463766 | HN | XA | Zinc finger protein 737 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF737 PE=2 SV=3 | 26655.46 | 130391 | 17590.88 | 16301.24 | 22279.46092 | 77672.9159 | 6469.176394 | 13769.9313 | 35105.41789 | 896910.7165 | 142477.8793 | 91879.18846 | 12180.26366 | 27829.20109 | 19413.12803 | 35824.6735 | 50588.53797 | 114577.3384 | 59318.29717 | 794806.7804 | 365055.2641 | 22308.14854 | 1932.715619 | 9266.481024 | 14793.63881 | 26012.94262 | 95591.42555 | ||
| O00622 | 1 | 1 | 32.97 | 0.855617624 | 1.144921998 | XA | HN | Protein CYR61 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CYR61 PE=1 SV=1 | 571633.4 | 1019520 | 336155 | 418572.5 | 394795.5558 | 338964.8741 | 254636.9117 | 396523.8564 | 308494.4888 | 290471.215 | 290820.7556 | 424226.5135 | 305147.2534 | 226075.5954 | 484077.2655 | 553064.2149 | 348222.5169 | 605904.6466 | 322501.6189 | 879743.6698 | 492065.5264 | 193093.8324 | 413139.2289 | 292464.7485 | 502156.6722 | 371114.7061 | 439183.0518 | ||
| Q9Y2E4 | 4 | 1 | 32.61 | 0.702410459 | 2.470082192 | HN | XA | Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog C OS=Homo sapiens GN=DIP2C PE=2 SV=2 | 48390.64 | 21732.99 | 351582.7 | 189152.4 | 73448.70725 | 31336.16637 | 36086.3014 | 43419.47648 | 14927.24822 | 20683.95933 | 55278.43448 | 14163.92187 | 750701.0569 | 349454.3149 | 19995.42473 | 32902.87393 | 380672.0816 | 377103.7483 | 4571.497641 | 81158.42297 | 48421.76762 | 197404.471 | 38411.98243 | 73953.16539 | 17986.95392 | 54233.45157 | 974687.6296 | ||
| P01772 | 1 | 1 | 32.52 | 0.473584968 | 1.753772228 | HN | XA | Ig heavy chain V-III region KOL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 2014946 | 2560296 | 2282879 | 2334695 | 1250418.339 | 2411713.495 | 2084795.945 | 1052568.785 | 1599085.45 | 3902712.866 | 1935074.597 | 11504861.53 | 4471734.91 | 986246.3601 | 860673.9079 | 1484654.589 | 2399186.261 | 3306159.84 | 3320713.114 | 3616338.282 | 4207551.915 | 2542578.448 | 6036964.931 | 1801006.964 | 830052.3112 | 4319877.537 | 1246435.336 | ||
| P98082 | 4 | 2 | 32.33 | 0.005859836 | 4.902493793 | XN | HN | Disabled homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DAB2 PE=1 SV=3 | 71390.34 | 29642.34 | 41217.95 | 16957.8 | 20940.79066 | 29948.94936 | 69508.6759 | 81339.46891 | 32060.50763 | 35435.30486 | 37863.67298 | 39947.93331 | 30042.51167 | 25698.73747 | 29092.09502 | 24741.03326 | 19508.35306 | 93440.17936 | 49727.58785 | 233404.8373 | 89794.07088 | 248676.1764 | 357354.234 | 17085.94163 | 23034.40719 | 347213.5344 | 279818.6735 | ||
| Q92614 | 11 | 1 | 32.08 | 0.77718485 | 5.52863468 | HN | XA | Unconventional myosin-XVIIIa OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYO18A PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 10516.1 | 9741.118 | 13040.39 | 0 | 9908.391364 | 7695.465963 | 10126.98417 | 25889.72898 | 442098.4499 | 13581.32221 | 0 | 16267.91003 | 3647.764183 | 2432.263927 | 0 | 2511.180054 | 0 | 46692.73942 | 34354.31834 | 3419.174931 | 9619.618854 | 0 | 7410.138839 | 701.0709623 | 534.2646415 | 1247.503708 | ||
| Q7L9L4;Q9H8S9 | 3 | 1 | 31.96 | 0.903792373 | 2.832771379 | XA | HN | MOB kinase activator 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=MOB1B PE=1 SV=3 | 182525.1 | 24937.72 | 115057.1 | 292788.3 | 0 | 196374.8307 | 364069.5591 | 387008.7508 | 111205.2983 | 126687.1085 | 51183.07925 | 173870.271 | 45593.54765 | 68561.06813 | 31406.36825 | 74011.09847 | 10275.64846 | 9340.773832 | 5867.007877 | 90755.83534 | 168267.4593 | 144491.8864 | 226743.2386 | 26997.02243 | 99452.53723 | 82769.39185 | 45877.63355 | ||
| Q9UBQ6 | 4 | 2 | 31.8 | 0.223858688 | 1.509879694 | XN | HN | Exostosin-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EXTL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 3516654 | 2290673 | 1121126 | 758911.2 | 1370022.943 | 1711600.211 | 3561697.875 | 2058494.895 | 1451374.609 | 687924.1257 | 2445108.722 | 2595979.121 | 1025280.036 | 1767959.216 | 1357549.088 | 757759.9323 | 1211455.065 | 2516007.497 | 1309103.45 | 4021001.339 | 2782401.548 | 2438386.551 | 803122.2092 | 2595951.363 | 2146238.253 | 3582995.973 | 2010255.545 | ||
| Q76NI1 | 6 | 1 | 31.76 | 0.209239071 | 1.533567337 | XA | HN | Protein very KIND OS=Homo sapiens GN=KNDC1 PE=2 SV=2 | 167169.9 | 125954.4 | 400351.1 | 197840.9 | 128516.1799 | 105319.3588 | 154439.8419 | 116192.0812 | 46202.3973 | 19544.83861 | 15376.55306 | 174969.7747 | 91019.89769 | 101399.1875 | 136921.9553 | 279264.7235 | 42788.69527 | 78996.59701 | 106013.4359 | 70120.42265 | 79550.49817 | 152749.8964 | 260127.8566 | 373663.0282 | 180175.3468 | 40785.61114 | 75594.9171 | ||
| O43708 | 2 | 1 | 31.67 | 0.11409862 | 3.18970219 | XA | XN | Maleylacetoacetate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTZ1 PE=1 SV=3 | 25529.25 | 7619.768 | 19800.76 | 196253.7 | 25003.2065 | 111816.1835 | 48967.76125 | 126024.5212 | 48473.3904 | 0 | 31219.2154 | 0 | 10556.58823 | 23288.37368 | 44945.66373 | 13052.68614 | 15396.85482 | 102184.4835 | 23559.72447 | 1512.576092 | 16854.21362 | 32370.20902 | 39008.92442 | 5059.60922 | 21246.60038 | 24163.96119 | 27304.26403 | ||
| P0C7P4;P47985 | 2 | 1 | 31.55 | 0.191793628 | 7.242672512 | HN | XA | Putative cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UQCRFS1P1 PE=5 SV=1 | 0 | 19403.83 | 39475.96 | 12702.06 | 32107.39359 | 2505.851768 | 25332.8304 | 8349.592898 | 1474.697518 | 521141.9491 | 52595.72126 | 286570.1323 | 17437.02641 | 8286.9957 | 558.9559155 | 15335.35955 | 88252.50156 | 33589.15807 | 50997.75567 | 28813.28495 | 3704.206331 | 10626.66361 | 22509.84041 | 14459.00187 | 3111.420619 | 4421.528803 | 6590.979409 | ||
| Q9ULL1 | 12 | 4 | 31.46 | 0.050994822 | 1.65106918 | XA | HN | Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family G member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLEKHG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 337353.3 | 453613.7 | 521469.9 | 419935.2 | 357913.5137 | 289273.881 | 202322.873 | 186398.376 | 288141.2261 | 299421.0192 | 92916.7018 | 143547.0425 | 207584.2166 | 121602.793 | 183965.1704 | 271441.8465 | 228225.2191 | 302473.3761 | 280456.9203 | 585315.7344 | 134424.9459 | 281546.3913 | 323046.2569 | 358402.2185 | 151052.609 | 270960.8616 | 133699.686 | ||
| P22455 | 6 | 3 | 31.46 | 0.092288078 | 1.569836514 | HN | XN | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGFR4 PE=1 SV=2 | 959375.1 | 1970506 | 1999310 | 1486830 | 2642455.742 | 1744664.733 | 2257997.884 | 1666672.042 | 3169965.095 | 1546950.628 | 1477358.714 | 4146952.485 | 2736250.871 | 1964199.558 | 3311571.085 | 1399819.918 | 3539717.829 | 4653923.679 | 2799100.66 | 1360942.303 | 1407815.607 | 1109255.146 | 2767221.748 | 1883919.69 | 1677427.538 | 1367728.912 | 1409597.996 | ||
| P14207 | 1 | 1 | 31.37 | 0.093699 | 4.888320194 | XA | XN | Folate receptor beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=FOLR2 PE=1 SV=4 | 2179.063 | 125734.4 | 100509 | 14375.92 | 378158.6442 | 8689.723187 | 3910.248981 | 13102.32342 | 13039.06586 | 11097.71691 | 4064.714719 | 20180.42027 | 2265.068771 | 17146.76748 | 96373.84023 | 78025.58464 | 58469.0962 | 34145.79808 | 3913.406055 | 0 | 0 | 17905.67109 | 24996.80336 | 52227.83057 | 3484.991199 | 8083.4615 | 24341.84198 | ||
| P62879;Q9HAV0 | 3 | 1 | 31.37 | 0.970934307 | 1.596477379 | HN | XN | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNB2 PE=1 SV=3 | 1364004 | 1176859 | 2818897 | 895916.5 | 1029752.134 | 301245.2246 | 547669.7324 | 878858.4672 | 386729.5765 | 1979494.636 | 362706.7256 | 646776.5906 | 317918.2982 | 686904.564 | 578973.7348 | 6745519.494 | 193859.2642 | 1400968.652 | 927415.3805 | 1008947.891 | 874700.9056 | 298762.9787 | 1085442.271 | 778720.0996 | 1023285.146 | 609029.6203 | 1482204.901 | ||
| P06889;P01715 | 1 | 1 | 31.3 | 0.878732457 | 1.317753305 | HN | XA | Ig lambda chain V-IV region MOL OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 4477206 | 5056337 | 5068403 | 3589148 | 5616013.736 | 3783634.914 | 2767921.597 | 2924704.903 | 3509576.579 | 12927434.6 | 3708293.361 | 5341657.2 | 827108.4973 | 3305275.036 | 8610773.177 | 7370978.609 | 4055562.753 | 2336943.057 | 2254856.319 | 3546800.6 | 1857317.848 | 4159958.53 | 5009149.614 | 10707237.01 | 2589698.33 | 4072307.463 | 3522301.886 | ||
| P63130 | 7 | 3 | 31.28 | 0.214108623 | 1.509460701 | XN | XA | HERV-K_1q22 provirus ancestral Gag polyprotein OS=Homo sapiens PE=3 SV=2 | 149198.8 | 653575.3 | 1828654 | 728272 | 487028.6209 | 734327.4362 | 1280017.523 | 784651.7303 | 719213.4114 | 501913.5271 | 1541789.308 | 298217.1941 | 1740704.247 | 1245529.622 | 1167790.738 | 1241724.673 | 751652.0073 | 872232.393 | 609769.6525 | 2120761.869 | 991437.2269 | 686337.2663 | 818278.9836 | 1127133.695 | 1521778.778 | 1053163.153 | 2188424.573 | ||
| Q9HC57 | 2 | 1 | 31.25 | 0.980907047 | 1.668546185 | XN | XA | WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WFDC1 PE=2 SV=2 | 71820.42 | 1198.052 | 3554.239 | 1959.724 | 15374.79057 | 6270.037551 | 4213.745573 | 3292.416561 | 6406.891086 | 6228.570266 | 7255.991764 | 12960.86434 | 1552.682779 | 11.62095199 | 22223.02921 | 11127.21031 | 24921.56558 | 34580.8323 | 8024.100974 | 30086.2447 | 16017.61932 | 16530.7915 | 26187.16253 | 0 | 16530.58464 | 29557.31658 | 47431.13759 | ||
| Q9UPZ6 | 2 | 1 | 31.23 | 0.293798887 | 1.598229543 | XA | HN | Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing protein 7A OS=Homo sapiens GN=THSD7A PE=1 SV=4 | 230733.8 | 121364.4 | 76388.55 | 85889.6 | 170520.7364 | 101050.6203 | 55428.8862 | 196234.8238 | 51729.23066 | 24955.49005 | 37588.29219 | 50199.47794 | 131144.0511 | 0 | 79432.95142 | 195017.004 | 52801.17758 | 110453.6624 | 93145.37025 | 128498.4257 | 214555.1409 | 25034.38539 | 52209.11337 | 263881.0004 | 73908.50652 | 97688.71352 | 8140.365441 | ||
| Q8TEU7 | 7 | 2 | 31.18 | 0.011290008 | 2.807031612 | HN | XA | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAPGEF6 PE=1 SV=2 | 1714005 | 1664499 | 2602122 | 306959.7 | 598723.2462 | 1317085.312 | 1888888.142 | 850870.6009 | 1785273.969 | 5703245.527 | 8713048.861 | 4950599.323 | 4185179.085 | 2795380.646 | 1510974.205 | 479925.6726 | 3844069.553 | 3546673.454 | 3237689.433 | 2113245.022 | 2914533.043 | 2572687.49 | 1462470.24 | 2247275.913 | 2638426.09 | 2783506.065 | 3037389.976 | ||
| Q9BQS8 | 7 | 3 | 31.16 | 0.808811268 | 1.224139926 | XN | XA | FYVE and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FYCO1 PE=1 SV=3 | 397434.4 | 769048.8 | 1315785 | 346449.1 | 850883.3077 | 610792.9297 | 805237.4083 | 366211.6927 | 533938.3574 | 217125.781 | 515314.3051 | 1720511.247 | 329095.2638 | 570177.1801 | 385731.8626 | 330976.5513 | 2021118.778 | 207726.4587 | 219856.7648 | 356016.6891 | 359245.8766 | 346984.6466 | 439747.7459 | 3022687.684 | 2080989.876 | 336530.4075 | 177615.8094 | ||
| Q68CJ9 | 3 | 2 | 31.15 | 0.739120149 | 2.153194302 | HN | XN | Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CREB3L3 PE=1 SV=2 | 401311.7 | 160983.4 | 414368.7 | 592274.6 | 359085.4296 | 347677.0445 | 518936.0038 | 176030.0192 | 515396.6865 | 686052.5865 | 399825.3869 | 3886053.062 | 99802.38594 | 344939.7848 | 511494.9466 | 194227.3009 | 409147.2085 | 291218.9686 | 207989.1067 | 290670.8023 | 337204.1226 | 317826.3258 | 475105.2406 | 304620.5547 | 291179.0713 | 279762.6827 | 664311.8347 | ||
| Q9NZR2 | 9 | 3 | 31.14 | 0.890587221 | 1.225234752 | XA | XN | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1B PE=1 SV=2 | 28558874 | 28788817 | 27982475 | 37727313 | 94948137.06 | 9836499.734 | 14007449.13 | 19407247.64 | 10142290.97 | 25389150.19 | 11703237.93 | 31984495.88 | 17214056.66 | 26507123.25 | 39522757.33 | 32251407.78 | 18800065.76 | 35758916.68 | 18253422.86 | 11875115.08 | 11874522.3 | 19637690.81 | 23451093.61 | 54233326.53 | 35639039.24 | 19606175.26 | 26937453.75 | ||
| Q86XI8 | 5 | 1 | 31.04 | 0.395410135 | 1.475545105 | HN | XA | Uncharacterized protein C19orf68 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C19orf68 PE=1 SV=2 | 472668.2 | 495755.4 | 791223.9 | 641537.4 | 696345.5246 | 637157.2553 | 441598.3812 | 231527.4344 | 220569.3296 | 1204682.798 | 279843.0137 | 1325069.621 | 338799.5053 | 382908.2719 | 1324320.483 | 878881.4314 | 637172.179 | 457710.312 | 613970.7791 | 287882.2545 | 647217.9779 | 440752.232 | 683307.1582 | 749294.951 | 369366.4195 | 680038.0401 | 515260.2747 | ||
| P52746 | 6 | 1 | 31 | 0.454388893 | 1.778224585 | HN | XA | Zinc finger protein 142 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF142 PE=1 SV=4 | 27093.3 | 186346 | 345703.3 | 74411.21 | 95988.03994 | 857268.7693 | 834919.4288 | 205073.6301 | 685977.5825 | 377304.9625 | 920311.654 | 1122499.611 | 1012712.587 | 793397.3513 | 66609.77852 | 26702.37604 | 1192310.992 | 379019.8229 | 477001.8731 | 531876.9551 | 352341.9373 | 320972.6397 | 123094.7275 | 2022523.858 | 1067878.14 | 372003.1885 | 124922.021 | ||
| Q9Y5E7 | 5 | 1 | 30.88 | 0.079904222 | 5.240922001 | XA | XN | Protocadherin beta-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB2 PE=1 SV=1 | 324778.5 | 435502 | 1362307 | 47669.17 | 22961.75424 | 103661.2725 | 165358.8788 | 17520.95814 | 74888.88496 | 208501.1352 | 479315.8851 | 27698.89722 | 28940.46346 | 394126.4867 | 60328.38763 | 262782.958 | 78357.52537 | 90341.70232 | 2957.429204 | 65267.14474 | 17423.60919 | 26056.09729 | 109732.9954 | 106980.5185 | 66253.11795 | 75413.10925 | 17358.62111 | ||
| P10720;P02776 | 5 | 3 | 30.86 | 0.979045523 | 1.396438337 | HN | XN | Platelet factor 4 variant OS=Homo sapiens GN=PF4V1 PE=1 SV=1 | 266695.8 | 334716.3 | 148120 | 199886.8 | 288414.848 | 84201.20959 | 62311.528 | 64862.71743 | 95537.44572 | 223625.2084 | 59094.51475 | 110749.9425 | 67377.98724 | 83507.68524 | 198058.4255 | 887671.192 | 226735.0748 | 126051.6236 | 135140.9848 | 165244.5469 | 167125.5627 | 101891.723 | 275589.6514 | 145151.0654 | 87572.2305 | 169761.9299 | 172471.616 | ||
| Q2TAC2 | 9 | 3 | 30.73 | 0.337280195 | 1.429194464 | XN | HN | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 57 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCDC57 PE=2 SV=2 | 441078.5 | 4180979 | 4482891 | 1879303 | 10472971.7 | 4807744.713 | 22255820.81 | 661595.7884 | 7499977.989 | 200924.8059 | 479970.7013 | 20120688.47 | 9778493.409 | 7559724.312 | 263973.7025 | 161064.2999 | 3341306.045 | 789990.258 | 908601.6034 | 11047760.18 | 7537053.241 | 3718990.441 | 6644022.344 | 544376.9834 | 639670.7317 | 26880817.53 | 3099788.143 | ||
| Q96RD9 | 3 | 2 | 30.58 | 0.854482799 | 1.186613203 | HN | XN | Fc receptor-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCRL5 PE=1 SV=3 | 659440.6 | 1002319 | 1118849 | 830589.5 | 851640.8246 | 2222050.569 | 2053726.403 | 1055335.502 | 3449862.51 | 796796.4672 | 1256871.999 | 3200735.026 | 1567322.705 | 1312034.506 | 1615680.206 | 519454.5793 | 1752562.077 | 2050142.047 | 1558398.52 | 1448882.538 | 970964.6172 | 1204865.614 | 503777.9253 | 2312468.595 | 1665046.909 | 1074792.892 | 1119426.228 | ||
| P09429;B2RPK0 | 3 | 3 | 30.55 | 0.805122251 | 1.452608218 | HN | XN | High mobility group protein B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HMGB1 PE=1 SV=3 | 320819.6 | 455204.9 | 186443.1 | 221424 | 202697.7863 | 416984.9998 | 343062.9003 | 158365.6068 | 184383.2793 | 711847.0207 | 268356.2645 | 477897.1995 | 72094.4743 | 71571.10557 | 504889.2261 | 321119.8849 | 855946.4177 | 192026.6634 | 249362.6282 | 446605.0754 | 51068.35234 | 164272.6624 | 375053.4183 | 377797.7667 | 279934.9411 | 202742.118 | 245926.7664 | ||
| Q8N3A8 | 6 | 2 | 30.37 | 0.451448646 | 1.471598233 | XN | XA | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PARP8 PE=1 SV=1 | 4977136 | 3110010 | 1297951 | 1809788 | 1697067.434 | 3410925.865 | 3873152.035 | 2039735.775 | 1959419.879 | 2596680.804 | 3998526.964 | 8482343.312 | 1762578.92 | 1297560.613 | 2383774.321 | 1380968.567 | 1905130.596 | 3657311.892 | 4657109.526 | 10126798.25 | 3506823.098 | 2123138.286 | 1373838.971 | 2721822.391 | 4477239.167 | 4726860.375 | 1862530.101 | ||
| P49908 | 2 | 1 | 30.25 | 0.379964304 | 1.648811804 | XA | XN | Selenoprotein P OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEPP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 604774.3 | 1293720 | 1258812 | 550008.8 | 587870.522 | 873627.2169 | 3401682.443 | 250459.9336 | 1503791.122 | 562240.0229 | 1225035.001 | 161586.4785 | 839731.8182 | 787393.5186 | 713364.1034 | 728458.1281 | 477434.3611 | 885711.3122 | 290724.2344 | 462776.1807 | 302815.8267 | 239196.3169 | 849913.4218 | 1247651.669 | 900317.8929 | 1108158.303 | 860377.2438 | ||
| P22004 | 3 | 1 | 29.95 | 0.109887875 | 1.987573251 | XN | HN | Bone morphogenetic protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BMP6 PE=1 SV=1 | 109368.1 | 28449.02 | 14915.29 | 43310.82 | 13158.18854 | 65689.03032 | 48360.81316 | 58395.73884 | 33634.41386 | 15195.30909 | 14745.6051 | 25754.29982 | 32056.01517 | 6748.339399 | 32156.78062 | 33531.46965 | 38495.85542 | 79864.77792 | 47826.66077 | 54263.31039 | 63896.37919 | 46788.93891 | 86357.78613 | 8431.567089 | 96142.58677 | 77749.01886 | 72179.20465 | ||
| Q9H4L5 | 6 | 2 | 29.89 | 0.055347814 | 1.439350539 | HN | XA | Oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=OSBPL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 1070376 | 837191 | 571754.3 | 635628.4 | 374662.1892 | 470089.3371 | 442096.5328 | 585945.5822 | 755181.4984 | 1091184.75 | 941058.7746 | 524913.3486 | 1350965.119 | 839499.7637 | 497951.679 | 708401.3278 | 990884.7024 | 1321222.518 | 643246.665 | 1114200.92 | 854847.106 | 607607.3176 | 904234.5727 | 732691.2982 | 1194406.131 | 592853.5995 | 1305279.048 | ||
| P13928;Q5T2P8;Q5VT79 | 3 | 1 | 29.81 | 0.965998755 | 1.122454362 | XN | XA | Annexin A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 49319.72 | 90385.93 | 104950.4 | 263658.3 | 61939.19036 | 22656.86461 | 102151.7637 | 54335.8109 | 34010.50783 | 155186.9081 | 21736.52302 | 140626.3777 | 174149.0266 | 156763.4359 | 47640.31185 | 28728.98809 | 43532.70108 | 91652.86 | 19967.57382 | 15451.37858 | 155990.3729 | 94354.21662 | 62521.32429 | 297821.4 | 67565.28294 | 120961.4613 | 44707.31287 | ||
| P05386 | 1 | 1 | 29.59 | 0.767821816 | 2.787244114 | XA | XN | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPLP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 475143.9 | 21292.1 | 190965 | 932701.8 | 69911.73086 | 44456.52557 | 239176.1066 | 1415819.293 | 964937.6693 | 493794.6311 | 323790.936 | 1221051.385 | 369993.3909 | 172291.8025 | 368975.727 | 356769.7053 | 2081.339592 | 260136.5378 | 150432.8945 | 90166.79591 | 262893.7341 | 79475.6586 | 445481.0577 | 91258.27754 | 217226.7305 | 116501.3834 | 108824.9484 | ||
| Q92887 | 5 | 1 | 29.54 | 0.053457323 | 10.06802925 | HN | XN | Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABCC2 PE=1 SV=3 | 19526.68 | 432528 | 199974.5 | 80416.72 | 108672.0849 | 39604.13285 | 8165.104539 | 10004.03254 | 14943.65479 | 420511.3678 | 386099.0001 | 1181313.352 | 17205.49071 | 329481.7008 | 2121274.686 | 321550.6105 | 42899.05143 | 1218895.421 | 89157.59319 | 93468.07799 | 7038.236776 | 0 | 137028.0874 | 136626.5293 | 43225.20862 | 12767.21153 | 80531.4405 | ||
| P16562 | 2 | 2 | 29.53 | 0.391134702 | 1.736946773 | HN | XN | Cysteine-rich secretory protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRISP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 30053.43 | 53762.12 | 47534.73 | 45262.14 | 32115.24241 | 34466.28425 | 31881.09582 | 24049.58783 | 39331.94746 | 20901.80133 | 298819.0681 | 22270.27207 | 21283.9202 | 40174.27168 | 47686.58127 | 34274.96278 | 23156.58012 | 14343.88949 | 5889.519367 | 23615.51257 | 18654.19476 | 10561.26725 | 77506.54784 | 98154.13882 | 20214.07564 | 32048.86257 | 14407.9083 | ||
| Q14449 | 2 | 1 | 29.46 | 0.858734577 | 1.434447298 | XA | XN | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRB14 PE=1 SV=2 | 1534865 | 1944363 | 778742 | 2094421 | 1340133.03 | 405072.9388 | 76124.52104 | 457278.1622 | 377380.0652 | 937845.1008 | 199702.65 | 691680.602 | 225930.1011 | 376611.1826 | 431137.1392 | 2475889.676 | 826173.2126 | 1129169.535 | 409781.6599 | 487469.5083 | 509777.9691 | 646673.4367 | 2205443.727 | 164922.6743 | 980158.252 | 442930.3249 | 432877.4485 | ||
| Q86T26 | 2 | 1 | 29.4 | 0.465834574 | 1096.379611 | XA | HN | Transmembrane protease serine 11B OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMPRSS11B PE=2 SV=3 | 14.3566 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4141.964566 | 137099.6217 | 8525.326535 | 0 | 53.40474416 | 2.489889219 | 49.44635429 | 0 | 0 | 31.27343666 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 374.7993839 | 0 | 191.3397975 | 2.291852912 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2885.642654 | 1259.551922 | ||
| Q93091 | 1 | 1 | 29.4 | 0.765905071 | 1.857593089 | HN | XN | Ribonuclease K6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNASE6 PE=1 SV=2 | 52420.3 | 11593.62 | 134999.1 | 81450.76 | 177469.1422 | 130025.7727 | 136661.9424 | 56306.71062 | 53094.96893 | 130911.7268 | 56289.86478 | 229330.2744 | 145833.2364 | 15224.98285 | 74734.5039 | 535074.2798 | 32589.99309 | 51106.73096 | 26684.8196 | 141911.0145 | 43489.3643 | 43981.39682 | 122669.5099 | 70940.12221 | 145432.1012 | 32125.53775 | 57036.33302 | ||
| P52788 | 3 | 3 | 29.23 | 0.007960679 | 23.65483649 | XA | XN | Spermine synthase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMS PE=1 SV=2 | 27970.24 | 3027.055 | 2021.229 | 383987.1 | 23927.46772 | 12887.00901 | 16125.17373 | 18514.37207 | 13768.22293 | 0 | 38402.7067 | 81552.4803 | 4872.657996 | 0 | 882.7301366 | 1399.119827 | 0 | 9756.091398 | 88.97690527 | 0 | 421.053926 | 1788.675587 | 18404.22758 | 0 | 528.5727973 | 0 | 0 | ||
| P28070 | 2 | 1 | 29.11 | 0.285984751 | 1.669732209 | XA | HN | Proteasome subunit beta type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB4 PE=1 SV=4 | 40456.33 | 79936.44 | 84859.2 | 59306.09 | 92888.05906 | 116796.8049 | 199822.5466 | 121268.6393 | 102917.92 | 56080.42441 | 88235.75418 | 139087.8614 | 38231.2607 | 21419.93366 | 110900.712 | 26167.04513 | 32061.20148 | 25777.54223 | 356586.0612 | 80814.98078 | 107173.4552 | 178040.2589 | 42846.18673 | 34442.60802 | 3546.97741 | 19320.91938 | 54870.1393 | ||
| P62195 | 1 | 1 | 29.04 | 0.381020043 | 14.01175916 | XA | HN | 26S protease regulatory subunit 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMC5 PE=1 SV=1 | 17402.74 | 0 | 5100.191 | 51180.38 | 9690.706969 | 4728.113452 | 26233.92206 | 43290.68317 | 25883.31288 | 273.6851949 | 754.2765204 | 1379.527017 | 1285.451156 | 222.565496 | 1272.101082 | 3545.029002 | 2756.007185 | 1608.216887 | 1405.12051 | 11518.26785 | 4118.131687 | 104.5909691 | 17114.17821 | 69.99628693 | 8487.164292 | 2398.170513 | 3417.869135 | ||
| Q04725 | 5 | 1 | 28.98 | 0.000152568 | 3.697329915 | HN | XA | Transducin-like enhancer protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLE2 PE=1 SV=2 | 353985 | 145193.2 | 246609.3 | 209109.1 | 129381.0622 | 215948.3763 | 134005.635 | 97377.80545 | 133283.4321 | 924714.9707 | 930525.1274 | 730553.7504 | 595175.8319 | 1096230.189 | 651141.1671 | 570312.9243 | 282219.3416 | 374785.327 | 585486.9409 | 365604.9086 | 595539.2372 | 501706.2234 | 329343.3722 | 63099.12385 | 778458.4838 | 300029.2821 | 333478.308 | ||
| Q9Y5X3 | 3 | 1 | 28.67 | 0.152939026 | 2.142792527 | XA | HN | Sorting nexin-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SNX5 PE=1 SV=1 | 63385.72 | 33403.94 | 70529.07 | 336839.3 | 75987.47932 | 293260.5593 | 459509.8463 | 314111.7273 | 632140.5332 | 25583.08695 | 88.44720452 | 50843.37459 | 293893.6371 | 184214.8098 | 104821.5314 | 98710.56761 | 141739.617 | 163748.802 | 74071.2725 | 264944.9258 | 255813.3309 | 159184.8091 | 265758.3762 | 317829.1087 | 344961.4579 | 59669.35175 | 264393.6868 | ||
| Q92626 | 8 | 1 | 28.67 | 0.924062521 | 1.0447269 | XN | HN | Peroxidasin homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=PXDN PE=1 SV=2 | 75299.73 | 15887.67 | 43394.86 | 117435.7 | 54429.84651 | 99658.88074 | 43735.71708 | 74165.39389 | 32848.28409 | 40403.09195 | 25940.4027 | 39803.92624 | 49452.68126 | 62420.42811 | 92455.67918 | 151447.7755 | 44214.25666 | 42029.81424 | 16118.91954 | 34386.74564 | 74381.31212 | 8364.48828 | 102887.7605 | 90373.81924 | 56134.21963 | 47880.82453 | 142157.8239 | ||
| Q7L775;Q53TN4 | 5 | 2 | 28.54 | 0.268347548 | 2.151948916 | HN | XN | EPM2A-interacting protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPM2AIP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1240248 | 1008921 | 2443145 | 225999.3 | 2366826.801 | 486550.347 | 518139.25 | 738585.7889 | 167514.6346 | 813089.9038 | 114579.0598 | 1609757.648 | 410232.5495 | 2757317.926 | 1504137.333 | 3388296.455 | 1058244.381 | 640614.8496 | 144397.2195 | 211204.7 | 317809.7492 | 456038.2031 | 1670001.481 | 278265.2788 | 1663672.97 | 536045.9701 | 436580.2263 | ||
| O14950;P19105 | 3 | 2 | 28.49 | 0.365321294 | 1.374550462 | HN | XA | Myosin regulatory light chain 12B OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYL12B PE=1 SV=2 | 366348.8 | 530490.9 | 565453 | 324834 | 337034.0296 | 213584.815 | 333248.7744 | 264145.5553 | 397334.3497 | 279196.3757 | 545940.5099 | 848591.0135 | 263891.684 | 439545.993 | 947817.321 | 327409.4593 | 458860.2934 | 469401.2415 | 165673.9577 | 284718.5675 | 263101.6234 | 283336.4756 | 407262.9473 | 1179695.261 | 357537.5851 | 278435.9934 | 555729.565 | ||
| Q9BXU1 | 4 | 1 | 28.49 | 0.528291745 | 1.045780257 | XN | HN | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 31 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STK31 PE=2 SV=2 | 15521.71 | 26658.96 | 38504.57 | 15961.46 | 50971.8897 | 27968.962 | 16354.8996 | 23188.57919 | 29722.70706 | 2308.851229 | 15526.96767 | 3198.378844 | 17148.16681 | 43466.83128 | 39243.78073 | 59345.8202 | 26115.83129 | 30527.94512 | 26066.68165 | 35032.70923 | 20859.87897 | 35606.04304 | 41193.54814 | 6903.815456 | 23055.80569 | 27163.18135 | 31845.45464 | ||
| Q8N3D4 | 8 | 3 | 28.46 | 0.834986881 | 1.973514848 | XN | HN | EH domain-binding protein 1-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EHBP1L1 PE=1 SV=2 | 471031.4 | 562386.4 | 1070832 | 1039357 | 1611801.808 | 3243947.135 | 2702533.167 | 6488991.995 | 979917.635 | 3404936.66 | 1255275.474 | 4197039.932 | 2239937.449 | 466529.202 | 1004176.681 | 1521095.4 | 726939.8778 | 832643.789 | 1658259.191 | 9153773.984 | 2991500.057 | 12622734.1 | 975407.332 | 1841182.267 | 548021.3186 | 562984.9943 | 528830.811 | ||
| Q9BV20 | 6 | 3 | 28.33 | 0.490142057 | 1.157887001 | HN | XN | Methylthioribose-1-phosphate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRI1 PE=1 SV=1 | 760326.6 | 1851744 | 1454074 | 1842714 | 1072570.585 | 679130.11 | 979049.9964 | 1006205.415 | 535153.9178 | 1293210.576 | 543827.4618 | 659544.1509 | 684833.265 | 777973.0229 | 1319254.731 | 1677612.646 | 1309683.138 | 2113993.415 | 474570.961 | 628760.1694 | 606778.1087 | 972479.3408 | 957007.9841 | 3274028.127 | 775168.4617 | 437348.3216 | 838405.4943 | ||
| P20142 | 2 | 1 | 28.29 | 0.918491874 | 2.510214013 | HN | XN | Gastricsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGC PE=1 SV=1 | 1457.16 | 35155.21 | 9740.039 | 3310.393 | 303071.152 | 827.7388704 | 0 | 139429.8473 | 0 | 230590.1731 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26014.3285 | 418529.1809 | 60621.35858 | 52770.13075 | 95493.06981 | 0 | 0 | 2745.685835 | 0 | 4456.359744 | 227006.6489 | 55832.20525 | 52310.14417 | 9817.431319 | ||
| Q14676 | 6 | 3 | 28.25 | 0.005362667 | 2.000379563 | XN | XA | Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MDC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 6342539 | 3131139 | 3616511 | 3195375 | 4160981.03 | 4901189.408 | 7957252.498 | 3539343.897 | 4580114.8 | 5799079.341 | 12864707.14 | 12697448.01 | 8101237.508 | 5085520.755 | 5526568.859 | 7097808.416 | 2486795.573 | 6010736.829 | 6181013.673 | 11909625.8 | 10414867.84 | 6598071.27 | 5634680.15 | 11598861.56 | 14107358.71 | 10869367.61 | 5550769.722 | ||
| P31146 | 2 | 1 | 28.25 | 0.982237902 | 5.063867603 | XA | XN | Coronin-1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CORO1A PE=1 SV=4 | 0 | 38664.49 | 6354.928 | 0 | 38106.54431 | 268556.3935 | 307618.4154 | 67527.94221 | 355488.8604 | 51295.06239 | 11872.94007 | 102623.8847 | 6278.61778 | 13561.91396 | 207662.6456 | 48800.85039 | 4897.395088 | 0 | 54786.84579 | 12649.80986 | 4070.216537 | 51100.38942 | 9327.715461 | 13939.72949 | 44169.98977 | 23688.69006 | 0 | ||
| P05161 | 1 | 1 | 28.23 | 0.661385222 | 176.11973 | HN | XA | Ubiquitin-like protein ISG15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ISG15 PE=1 SV=5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 920.1847 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55.32149909 | 0 | 10.03234293 | 161997.3239 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1851.836075 | 0 | 45.620227 | 0 | ||
| Q9NW13 | 6 | 2 | 28.1 | 0.706695182 | 1.124125568 | HN | XN | RNA-binding protein 28 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBM28 PE=1 SV=3 | 64058.56 | 326454.2 | 299234.9 | 137430.8 | 452471.2138 | 758329.9158 | 426229.1342 | 866789.811 | 575248.2465 | 273292.0523 | 255635.5485 | 1029115.043 | 568548.6284 | 197444.9893 | 597148.4423 | 603826.9617 | 450546.9449 | 359338.565 | 433028.339 | 994848.5523 | 339553.5563 | 1057564.024 | 337773.7363 | 207486.9717 | 159155.0684 | 182367.1903 | 144461.846 | ||
| Q9NPG1 | 5 | 2 | 28.09 | 0.258628567 | 1.478394652 | XN | XA | Frizzled-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FZD3 PE=1 SV=1 | 1785795 | 1174226 | 940060.8 | 117815.7 | 860732.9621 | 1194132.438 | 1119167.093 | 1573077.274 | 1272640.444 | 1650851.639 | 1204615.189 | 1962756.081 | 476847.0527 | 1244183.927 | 2016351.573 | 652717.9932 | 2022052.276 | 1278585.721 | 1415286.603 | 1825306.604 | 1765134.332 | 1316699.305 | 1395105.884 | 1642721.523 | 505046.7093 | 2440588.852 | 2533715.473 | ||
| O75326 | 3 | 2 | 28.02 | 0.610636167 | 1.25544506 | XN | XA | Semaphorin-7A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEMA7A PE=1 SV=1 | 278868.9 | 117996.1 | 77986.78 | 240114.1 | 101205.1577 | 191567.7194 | 121722.3101 | 103180.6677 | 122454.7224 | 117341.2166 | 153932.0225 | 126911.6431 | 223749.4009 | 35510.70032 | 206485.1465 | 209469.1651 | 158664.6271 | 135261.9839 | 207643.5033 | 221882.8685 | 244685.575 | 137613.8932 | 94313.25909 | 61514.22028 | 354824.5182 | 196659.5855 | 182111.8133 | ||
| P04431 | 2 | 1 | 27.89 | 0.087099136 | 1.313255327 | HN | XA | Ig kappa chain V-I region Walker OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 361969.8 | 892522.2 | 326732 | 572167.2 | 406875.8165 | 135870.6538 | 202092.7274 | 140759.2989 | 105247.3104 | 488647.304 | 414760.5782 | 639107.1758 | 331684.8237 | 366675.2808 | 534539.1012 | 524263.7716 | 441133.9409 | 388374.0752 | 488059.2758 | 329700.4598 | 372930.3007 | 413079.1279 | 453375.1861 | 350188.0682 | 314393.6206 | 306657.3034 | 384495.1922 | ||
| Q7Z3K3 | 4 | 1 | 27.83 | 0.27402512 | 1.903727346 | XA | HN | Pogo transposable element with ZNF domain OS=Homo sapiens GN=POGZ PE=1 SV=2 | 85171.89 | 20058.6 | 5955.242 | 514220 | 539353.306 | 219835.366 | 58025.0168 | 258423.2499 | 239429.7589 | 48231.53891 | 6893.907216 | 0 | 25955.22841 | 78288.75522 | 90423.54572 | 133221.3706 | 339579.4064 | 296707.9045 | 102073.1342 | 24166.16594 | 236026.7405 | 319211.4314 | 87434.20203 | 139785.5941 | 291239.028 | 44057.49676 | 128471.593 | ||
| Q15642 | 6 | 4 | 27.74 | 0.22522737 | 10.14797744 | HN | XN | Cdc42-interacting protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRIP10 PE=1 SV=3 | 2165678 | 1099409 | 1898449 | 1373001 | 3322154.855 | 3284395.159 | 1930867.939 | 6570508.452 | 25334319.97 | 2101074.441 | 4037341.767 | 195121141.8 | 2970771.651 | 1768782.211 | 2428217.15 | 3311603.221 | 4759902.345 | 8352306.478 | 2474164.265 | 1624021.698 | 1484239.36 | 1331954.818 | 1635381.986 | 3116841.832 | 1515621.609 | 3783637.885 | 5191373.535 | ||
| Q96SN8 | 8 | 2 | 27.71 | 0.969569782 | 1.033508844 | XA | XN | CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK5RAP2 PE=1 SV=5 | 15217225 | 15935439 | 16859629 | 20039608 | 40393259.56 | 10844619.32 | 8522452.583 | 14015138.41 | 10740812.01 | 17814385.02 | 8664863.306 | 15111599.27 | 11922649.1 | 15594604.45 | 23034308.17 | 26627701.72 | 17037386.15 | 14771925.57 | 16463582.54 | 11810246.32 | 12809618.75 | 14168969.4 | 15033769.26 | 31104258.96 | 16007197.03 | 13145033.38 | 17078879.27 | ||
| Q86VD9 | 2 | 2 | 27.5 | 0.443529419 | 1.678673123 | XA | HN | GPI mannosyltransferase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PIGZ PE=2 SV=4 | 41914.48 | 212669.2 | 1264056 | 3039405 | 3455767.654 | 3254587.007 | 852908.4848 | 1834381.816 | 2168479.67 | 81501.02258 | 121712.444 | 1453372.957 | 1863750.004 | 386066.1186 | 145392.8938 | 1125945.095 | 4383458.923 | 44106.6416 | 5454491.855 | 186015.0079 | 1336726.665 | 3366931.68 | 1043486.825 | 186332.278 | 30073.58307 | 610092.6494 | 84494.15602 | ||
| O75264 | 1 | 1 | 27.41 | 0.445312134 | 2.078428117 | HN | XN | Transmembrane protein C19orf77 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C19orf77 PE=2 SV=2 | 34199.33 | 11917.62 | 0 | 139975.5 | 9958.369596 | 42886.98578 | 123415.9931 | 79708.31195 | 5009.345099 | 242180.8798 | 149254.8704 | 126820.5201 | 10701.39031 | 59753.79204 | 7433.698744 | 2166.25322 | 23181.63231 | 20084.0796 | 33363.06025 | 26771.99945 | 93969.0249 | 40908.27182 | 17576.6472 | 0 | 0 | 22928.71729 | 73166.09228 | ||
| Q6PGN9 | 5 | 2 | 27.4 | 0.180497884 | 1.459893714 | XN | HN | Proline/serine-rich coiled-coil protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSRC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 323452.1 | 366985.3 | 272163 | 177100.7 | 123541.8783 | 275526.2755 | 322835.6678 | 472520.2679 | 347292.5671 | 182905.9202 | 139293.3376 | 394949.0127 | 451176.2768 | 411041.1142 | 131317.4014 | 47426.82625 | 166032.8093 | 202634.5352 | 311509.9142 | 641215.171 | 495163.8352 | 263338.9635 | 144959.166 | 157064.2242 | 335733.682 | 387951.3953 | 367932.3635 | ||
| P01599 | 3 | 1 | 27.19 | 0.317491184 | 4.410256485 | XA | XN | Ig kappa chain V-I region Gal OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 11970.54 | 543221.5 | 14050.66 | 7487.76 | 23110.5053 | 1112.564606 | 3158.396324 | 3416.575433 | 4746.498931 | 17275.50408 | 15675.64016 | 216336.0916 | 7479.986508 | 8287.577039 | 14915.61344 | 33894.24867 | 2171.726471 | 17224.54581 | 16651.33088 | 3557.829357 | 1579.998504 | 8846.068661 | 0 | 67593.7271 | 7671.527143 | 3075.366618 | 29853.94647 | ||
| Q96PQ7 | 6 | 2 | 27.13 | 0.068188392 | 4.921078345 | XA | HN | Kelch-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLHL5 PE=2 SV=3 | 156124.5 | 2174782 | 43255.02 | 69379.65 | 71791.91141 | 196259.4872 | 160509.9888 | 255542.445 | 1124276.899 | 101479.2945 | 73617.95439 | 44785.77537 | 51415.53696 | 51254.9961 | 145638.077 | 23052.57241 | 86090.66031 | 286687.4466 | 186612.2041 | 75527.36555 | 97760.29475 | 100413.2906 | 153464.924 | 167674.5168 | 131108.4757 | 225722.0456 | 205735.4426 | ||
| O75962 | 12 | 3 | 27.11 | 0.55822382 | 1.542016588 | HN | XN | Triple functional domain protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRIO PE=1 SV=2 | 6549469 | 10238046 | 11418902 | 10494259 | 10004793.09 | 2889565.44 | 4815045.626 | 6524834.241 | 3816916.669 | 10638655.93 | 9843060.222 | 13953958.36 | 2723589.862 | 4816989.721 | 4420631.119 | 30062039.59 | 17716365.31 | 3649838.265 | 2188192.5 | 8257175.53 | 3855522.238 | 6005672.846 | 17822585.66 | 9643140.963 | 8626980.329 | 3669775.296 | 3370692.683 | ||
| P31942 | 3 | 1 | 27.1 | 0.009564128 | 2.298405702 | HN | XA | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HNRNPH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1561765 | 518733.4 | 660284.2 | 34749.64 | 363045.2579 | 550198.5688 | 798725.4349 | 819315.9985 | 686825.1166 | 1618321.69 | 1570239.011 | 1711354.767 | 1099797.091 | 3302269.854 | 988024.9576 | 1327626.94 | 1485394.999 | 672792.4299 | 1380138.967 | 886972.026 | 1559605.759 | 1098179.335 | 1557275.973 | 528054.6472 | 1678361.073 | 852326.1781 | 2006298.44 | ||
| O00186 | 4 | 1 | 27 | 0.379911174 | 1.135155628 | XA | HN | Syntaxin-binding protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STXBP3 PE=1 SV=2 | 86883.38 | 310762.9 | 100067 | 159564.1 | 117329.5406 | 33263.32918 | 76705.90449 | 244743.7654 | 60641.98057 | 93485.26679 | 67836.55913 | 168424.9552 | 12470.83284 | 311573.4066 | 66194.05916 | 304470.8034 | 18853.45383 | 4971.476657 | 38149.31377 | 114985.458 | 48792.2333 | 103470.3899 | 166047.796 | 88668.08321 | 157640.2017 | 66147.47069 | 270737.1048 | ||
| Q8WXD0 | 4 | 1 | 26.98 | 0.802062563 | 2.609667913 | XA | HN | Relaxin receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RXFP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 27533.17 | 21445.07 | 40242.14 | 46432.38 | 11757.64622 | 913240.3623 | 548398.7639 | 50262.89848 | 204188.3683 | 265573.6202 | 38212.40528 | 94743.60455 | 43360.25033 | 103009.0371 | 34852.27163 | 57842.80217 | 38892.99734 | 37588.84673 | 609309.5135 | 35359.75265 | 804089.7534 | 195350.7836 | 54070.86266 | 37985.66773 | 20332.6178 | 46321.2753 | 60299.38036 | ||
| P16989 | 3 | 2 | 26.97 | 0.243243694 | 5.686641005 | XA | HN | DNA-binding protein A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSDA PE=1 SV=4 | 16035.93 | 96.78145 | 3755.609 | 12727.42 | 9244.362243 | 88819.42182 | 375858.6211 | 263249.8238 | 151270.27 | 19.75341452 | 13296.71148 | 73162.91244 | 37662.63224 | 1708.714881 | 23679.71338 | 499.2311749 | 11360.29281 | 578.8066897 | 12877.97903 | 221518.8458 | 76230.60551 | 108117.2041 | 684.6231654 | 7379.45648 | 36783.50339 | 2871.257601 | 10872.10341 | ||
| O95450 | 4 | 2 | 26.92 | 0.880988365 | 2.809338816 | XA | XN | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTS2 PE=2 SV=2 | 13270.06 | 0 | 0 | 12716.1 | 6145.934192 | 710216.2073 | 49848.80928 | 10251.93694 | 182353.549 | 10206.26155 | 46138.87641 | 147371.1025 | 19743.28369 | 11098.38648 | 12577.15303 | 224075.7286 | 0 | 5171.626059 | 78367.38335 | 20641.56196 | 84525.57948 | 136784.2 | 5124.975372 | 15818.22584 | 3822.069414 | 0 | 5462.044872 | ||
| P60981 | 3 | 1 | 26.82 | 0.316241953 | 1.90269252 | XA | HN | Destrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSTN PE=1 SV=3 | 57682.69 | 17279.57 | 40890.72 | 144107.3 | 40365.31973 | 80341.99028 | 63023.73805 | 132082.2812 | 40019.33593 | 53966.40987 | 30769.33341 | 62987.11395 | 2354.522913 | 67599.90369 | 27436.16908 | 51773.61248 | 21229.81387 | 5526.028921 | 26369.49033 | 41823.68588 | 43548.0678 | 40277.2862 | 133916.0604 | 0 | 44269.79382 | 35398.23155 | 6647.276865 | ||
| B1ANS9 | 5 | 1 | 26.78 | 0.582902955 | 1.287513892 | HN | XA | WD repeat-containing protein 64 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR64 PE=2 SV=1 | 524210 | 89974.66 | 100169.6 | 340191.3 | 235682.7086 | 195714.3339 | 177110.7169 | 301742.7033 | 262375.2156 | 405723.2313 | 106709.3219 | 232618.4605 | 294257.7791 | 592067.4817 | 170057.4015 | 600001.223 | 270401.5133 | 195677.4945 | 196353.2772 | 380725.2532 | 454187.9199 | 158304.8414 | 80724.99449 | 66690.04018 | 349493.65 | 273540.4062 | 290875.5816 | ||
| Q9NQW7 | 7 | 3 | 26.64 | 0.692133011 | 1.478801071 | HN | XA | Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=XPNPEP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 527187 | 773053.5 | 1841843 | 927321.3 | 280780.8024 | 1715567.996 | 1508129.301 | 881318.0548 | 1053223.397 | 989518.7839 | 2372844.186 | 4263433.448 | 1247626.773 | 1405598.48 | 857171.552 | 220015.9416 | 2075482.826 | 629375.9042 | 879853.1229 | 939679.6274 | 896818.7496 | 928927.1625 | 648235.2091 | 4848251.267 | 2173458.551 | 940456.9341 | 991060.3082 | ||
| P22897 | 3 | 1 | 26.44 | 0.654114688 | 1.172801099 | XA | HN | Macrophage mannose receptor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 99483.95 | 73622.98 | 129389.5 | 162900.6 | 6315.636101 | 219823.0262 | 215122.7976 | 192419.7739 | 234994.9617 | 41510.9127 | 398508.9921 | 43994.93719 | 143141.3055 | 174729.7437 | 62654.12421 | 20824.82684 | 105182.3512 | 146963.0262 | 219842.807 | 98002.91098 | 167685.9347 | 164893.7892 | 58147.32847 | 231153.651 | 88171.92581 | 111331.6505 | 148998.5025 | ||
| Q8IY17 | 5 | 1 | 26.2 | 0.00028396 | 3.087733661 | XN | XA | Neuropathy target esterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PNPLA6 PE=1 SV=2 | 426251.1 | 64778.52 | 110615.1 | 195061.5 | 135645.6408 | 318723.0334 | 169692.3245 | 180498.9768 | 151644.1092 | 407407.6629 | 954416.0906 | 188597.4124 | 374498.2335 | 1160356.681 | 326009.2436 | 325761.8369 | 756826.0374 | 338554.175 | 431098.7775 | 249492.4953 | 808219.7639 | 251081.6415 | 748812.6749 | 538976.7519 | 719647.2226 | 674032.3451 | 991158.7311 | ||
| Q6VUC0 | 3 | 1 | 26.17 | 0.829472121 | 5.633055953 | XA | HN | Transcription factor AP-2-epsilon OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFAP2E PE=2 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2538.052 | 0 | 305168.9036 | 398885.2497 | 67605.84197 | 313763.6706 | 5289.453591 | 80304.8957 | 10399.23519 | 0 | 26054.92215 | 64242.19661 | 6848.105773 | 0 | 0 | 230420.1694 | 825.4152286 | 0 | 25168.10147 | 3290.930314 | 0 | 4224.116324 | 0 | 0 | ||
| O95502 | 1 | 1 | 26.06 | 0.53026494 | 2.882303762 | HN | XA | Neuronal pentraxin receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPTXR PE=2 SV=2 | 29373.44 | 38473.41 | 24719.39 | 973.5978 | 79303.37785 | 22194.07861 | 9094.248245 | 12241.59207 | 39968.04049 | 58310.07468 | 42061.11485 | 0 | 14872.28113 | 75375.64823 | 75425.56643 | 415198.5916 | 11792.30591 | 45817.56751 | 5635.272015 | 107537.3214 | 37149.28608 | 48244.54855 | 99711.4361 | 61019.50154 | 52604.74157 | 40886.77605 | 131192.3724 | ||
| P09327 | 3 | 1 | 25.96 | 0.0154717 | 7.727785649 | XA | HN | Villin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VIL1 PE=1 SV=4 | 67596.61 | 24844.18 | 41004.51 | 134772 | 34006.74919 | 112985.4463 | 83199.59886 | 200621.4257 | 50551.24112 | 0 | 0 | 34294.59536 | 36386.86767 | 5484.915891 | 2351.97524 | 18479.91082 | 0 | 0 | 13156.08721 | 3780.389749 | 78580.37177 | 23850.03226 | 55827.37286 | 0 | 7734.384502 | 31755.2743 | 0 | ||
| P49641 | 5 | 1 | 25.89 | 0.811027404 | 1.428800565 | HN | XN | Alpha-mannosidase 2x OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2A2 PE=2 SV=3 | 192131.5 | 286127 | 101760 | 212197.9 | 405893.9867 | 160367.9319 | 131646.4314 | 229734.7022 | 74078.6132 | 332530.6774 | 178510.9655 | 879387.6261 | 68200.37606 | 163006.4284 | 328024.877 | 189696.5642 | 150298.5056 | 88294.21097 | 97196.01502 | 135838.7608 | 162881.3866 | 96149.40841 | 383585.1037 | 317904.0997 | 138169.9355 | 132208.012 | 200365.4938 | ||
| P10696;P05187 | 2 | 1 | 25.88 | 0.338231847 | 1.74080034 | XA | HN | Alkaline phosphatase, placental-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALPPL2 PE=1 SV=4 | 338969.7 | 98325.3 | 179725.9 | 463092.6 | 116973.8933 | 397565.8941 | 90085.41298 | 456671.4588 | 110621.4414 | 206964.469 | 206959.0307 | 285609.2725 | 129516.5616 | 32023.78694 | 49121.94963 | 177197.1186 | 55222.97729 | 151060.8845 | 493255.5654 | 273064.4457 | 404318.2963 | 250972.4436 | 354609.9781 | 53243.83694 | 119157.3925 | 108866.7573 | 33562.86643 | ||
| O14519 | 1 | 1 | 25.87 | 0.150390072 | 1.413629985 | HN | XA | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2-associated protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK2AP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2232530 | 9488788 | 4644396 | 11783905 | 7097099.249 | 5672196.349 | 4265846.187 | 10828804.75 | 6458525.41 | 5787773.857 | 9251278.23 | 7062146.41 | 7350300.522 | 16039901.4 | 3507067.015 | 11158389.71 | 11524233.97 | 16631328.9 | 5976284.368 | 8158874.04 | 9766090.839 | 9927058.634 | 7100152.299 | 16391317.49 | 11968626.96 | 8672650.802 | 8225718.547 | ||
| P41217 | 2 | 1 | 25.82 | 0.15405186 | 1.62298551 | XA | HN | OX-2 membrane glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD200 PE=1 SV=4 | 1194248 | 3218844 | 685189.2 | 1103665 | 1008402.42 | 1296265.2 | 2398557.654 | 1148612.627 | 3130653.487 | 830369.0688 | 1749349.613 | 622045.4913 | 1536157.779 | 1320716.056 | 543636.6405 | 464734.9215 | 1596423.734 | 692434.7312 | 1092555.63 | 1073197.262 | 880221.9952 | 819261.2484 | 1039968.698 | 2803745.887 | 930584.1505 | 1960733.916 | 1393011.416 | ||
| Q9C075 | 5 | 2 | 25.62 | 0.012604505 | 3.184101142 | HN | XA | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 23 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT23 PE=1 SV=2 | 243850.7 | 1379995 | 650604.7 | 528960.9 | 621484.238 | 377201.3158 | 87585.37926 | 86677.17815 | 217294.7236 | 2223667.314 | 473524.1229 | 4914867.001 | 1452160.237 | 1110556.168 | 1434185.551 | 937035.659 | 230420.4838 | 576601.1825 | 723814.7806 | 1159523.643 | 979170.8703 | 778903.3957 | 912299.6515 | 1496828.475 | 1071835.878 | 395872.3324 | 394224.3871 | ||
| Q86SJ2 | 2 | 1 | 25.57 | 0.353380541 | 1.331748621 | XN | XA | Amphoterin-induced protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMIGO2 PE=1 SV=1 | 144957.6 | 71928.76 | 82886.06 | 77877.71 | 55374.37505 | 64270.87345 | 63008.07596 | 95047.9718 | 136621.2893 | 56018.12444 | 82079.6028 | 47838.17638 | 102283.2883 | 99396.93782 | 140063.4842 | 87295.00364 | 144675.583 | 102045.9624 | 50135.11298 | 80769.18971 | 74633.3166 | 88536.67589 | 122153.2261 | 185697.6495 | 153353.4298 | 172352.9544 | 127077.035 | ||
| Q8NAC3 | 2 | 1 | 25.48 | 0.646767093 | 1.454289742 | XA | XN | Interleukin-17 receptor C OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL17RC PE=1 SV=2 | 121142 | 339335.8 | 200743.2 | 231156.5 | 753935.2187 | 122139.2639 | 193365.1077 | 130524.3629 | 67326.66204 | 194464.9677 | 162944.5805 | 337942.3895 | 42614.53265 | 86899.61491 | 223469.877 | 462176.213 | 146012.2166 | 109410.8414 | 177142.1807 | 218925.3427 | 49951.52038 | 81777.82278 | 274252.7537 | 348275.1339 | 145281.5144 | 104670.6976 | 84755.94386 | ||
| Q9HD42 | 3 | 1 | 25.35 | 0.939783702 | 1.500585056 | HN | XN | Charged multivesicular body protein 1a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP1A PE=1 SV=1 | 219750.8 | 88026.09 | 163898.4 | 76590.72 | 80408.84915 | 101632.3383 | 174721.5799 | 201510.0364 | 130445.7137 | 261992.6785 | 569522.5147 | 179059.6443 | 7514.759571 | 253261.4265 | 99960.12812 | 70764.56661 | 73514.16092 | 114325.1383 | 138238.8646 | 161842.7867 | 133242.0202 | 98225.50252 | 104298.3773 | 74230.79972 | 153832.5109 | 88942.47525 | 133333.0215 | ||
| P30050 | 3 | 1 | 25.34 | 0.878231466 | 1.087356048 | XA | HN | 60S ribosomal protein L12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPL12 PE=1 SV=1 | 66051.66 | 75428.97 | 73714.72 | 120715.4 | 30218.23659 | 134359.6769 | 228850.5945 | 279887.1069 | 205848.44 | 219143.2346 | 282194.4571 | 143153.4743 | 152965.0988 | 110138.7777 | 93628.29483 | 40356.22001 | 27306.81746 | 48571.7239 | 200301.2447 | 188712.4802 | 155809.7541 | 121324.35 | 121404.2785 | 141293.0219 | 94997.07726 | 40508.77881 | 63489.00603 | ||
| P98175 | 7 | 3 | 25.33 | 0.218198737 | 1.434143388 | XN | XA | RNA-binding protein 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBM10 PE=1 SV=3 | 1600440 | 843050.7 | 1854543 | 2100159 | 677370.2294 | 984145.6762 | 1351794.057 | 862454.9267 | 778789.0221 | 1735477.578 | 1258978.185 | 1108952.789 | 1002388.329 | 2316694.454 | 1083925.799 | 1419853.994 | 2250911.085 | 1611388.909 | 1346578.891 | 1003010.84 | 2765385.2 | 2938798.362 | 1902927.934 | 615297.4822 | 1720762.361 | 1372176.51 | 2186286.051 | ||
| Q6UXY8 | 4 | 2 | 25.19 | 0.645263008 | 1.27018284 | XN | HN | Transmembrane channel-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMC5 PE=2 SV=3 | 3440247 | 1344064 | 1153704 | 2360891 | 991647.136 | 1643703.887 | 2155848.372 | 2457040.201 | 2032724.471 | 1177166.441 | 682705.0854 | 3170561.336 | 1111064.377 | 606193.4144 | 1074464.096 | 2020925.185 | 3099432.37 | 921838.2476 | 2678094.199 | 1448320.86 | 3147920.994 | 1414309.008 | 81408.83096 | 1190659.375 | 3267971.663 | 2507017.911 | 1874557.326 | ||
| P35556 | 4 | 1 | 25.19 | 0.728198902 | 1.656060478 | HN | XN | Fibrillin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 42934.2 | 63695.74 | 39474.29 | 146391.9 | 54717.4702 | 58406.49312 | 31556.33341 | 107122.1957 | 39926.80767 | 154695.6671 | 3893.415246 | 19975.39188 | 53877.53059 | 57372.58852 | 40751.57055 | 135076.2511 | 112162.8669 | 146737.0403 | 84708.91688 | 21840.54174 | 73321.4259 | 33292.33474 | 27792.02795 | 38196.43425 | 21136.0629 | 61629.30181 | 75592.53258 | ||
| P26640 | 5 | 2 | 25.15 | 0.088452407 | 1.769651129 | XN | HN | Valine--tRNA ligase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VARS PE=1 SV=4 | 4085565 | 22215761 | 20264834 | 5340518 | 5616702.73 | 11902250.85 | 26819477.49 | 6578639.269 | 32545174.14 | 2830961.243 | 30740758.63 | 4689828.576 | 11746108.99 | 9284954.922 | 4891035.428 | 1714035.48 | 8101763.423 | 16216884.62 | 8119704.072 | 23296765.63 | 17034603.35 | 17133884.77 | 8932419.382 | 32343468.05 | 17607040.66 | 25245610.76 | 9937935.886 | ||
| O75023 | 2 | 1 | 25.13 | 0.554113419 | 1.700380323 | XA | XN | Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LILRB5 PE=1 SV=1 | 7044756 | 1205177 | 6153560 | 5245865 | 413171.2449 | 1884459.409 | 2672424.569 | 4252937.021 | 2983.971601 | 2408506.252 | 6329844.884 | 2728013.541 | 3055677.477 | 3212.091401 | 1978823.384 | 2685359.044 | 2283959.41 | 27970.8297 | 5176.893159 | 3352669.1 | 0 | 1539015.112 | 1956677.099 | 1616661.224 | 4116107.622 | 907559.0092 | 3487825.432 | ||
| O60271 | 7 | 1 | 25.1 | 0.090737372 | 1.688432076 | XN | XA | C-Jun-amino-terminal kinase-interacting protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPAG9 PE=1 SV=4 | 28594.25 | 4195.175 | 1912.696 | 2933.385 | 32533.2315 | 197.5601218 | 0 | 2100.681259 | 395.0110023 | 325.2543116 | 12222.28072 | 11664.83805 | 593.8188187 | 24755.07855 | 16922.79289 | 9658.8757 | 36584.86266 | 8601.02346 | 10910.61853 | 6676.241164 | 50787.45682 | 11731.66084 | 15311.37685 | 2707.290819 | 12660.43652 | 5175.654759 | 7061.788988 | ||
| Q08945 | 6 | 3 | 25.1 | 0.858205536 | 1.225928703 | XN | XA | FACT complex subunit SSRP1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SSRP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1599242 | 1052267 | 964820.1 | 1705920 | 2034851.184 | 847882.9876 | 1326840.388 | 1409770.676 | 1013383.379 | 1798909.444 | 1540733.997 | 1978905.724 | 1486713.368 | 1198632.044 | 1641816.79 | 1476276.537 | 1009295.849 | 623387.0432 | 1594562.112 | 965799.0939 | 1572024.744 | 1315883.96 | 2332421.779 | 4033954.728 | 1186688.451 | 981770.9231 | 672844.6346 | ||
| O43921 | 1 | 1 | 24.98 | 0.411732685 | 3.703037584 | XN | XA | Ephrin-A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFNA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 3398.687 | 0 | 7263.715 | 17723.98 | 663.7178261 | 41520.56536 | 12407.87178 | 1588.886122 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50711.30621 | 0 | 7397.666257 | 9321.212468 | 113633.586 | 0 | 0 | 1240.674079 | 9244.494737 | 4529.637599 | 24989.24264 | 0 | 0 | 258709.1602 | 4714.367188 | 9728.782728 | ||
| B7ZC32 | 6 | 3 | 24.93 | 0.001552226 | 1.925097182 | XN | XA | Kinesin-like protein KLP6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLP6 PE=3 SV=2 | 672883.1 | 843286.9 | 364077.4 | 327910.8 | 199102.9483 | 404049.5669 | 319510.5608 | 542826.8717 | 444704.7635 | 642612.5244 | 1126509.751 | 476319.8104 | 1009285.88 | 836725.232 | 570758.2569 | 729100.183 | 339445.0273 | 485978.5575 | 552558.9017 | 1056939.225 | 841388.803 | 700720.5675 | 1101739.14 | 1201564.077 | 671268.2845 | 953491.9214 | 848558.5168 | ||
| P48723 | 4 | 2 | 24.91 | 0.820520422 | 1.115214732 | XA | XN | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA13 PE=1 SV=1 | 315899.5 | 87513.83 | 101929.1 | 195372.1 | 27510.61344 | 53436.95239 | 68563.9699 | 133618.6074 | 96058.08976 | 49747.92379 | 165057.4651 | 63220.08386 | 134385.031 | 272419.7254 | 66780.03967 | 47551.49131 | 80867.0555 | 136527.7848 | 23365.73807 | 55939.26649 | 72264.06796 | 23051.04714 | 166652.0204 | 53506.29737 | 175164.6042 | 141959.7717 | 256433.2966 | ||
| Q86XT2 | 3 | 1 | 24.9 | 0.27915921 | 1.823236603 | XA | XN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 37D OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS37D PE=1 SV=2 | 182346 | 60304.4 | 48526.21 | 21003.61 | 18254.08464 | 60709.39953 | 82338.71933 | 221099.0307 | 25114.66579 | 58140.73611 | 410622.2752 | 84243.5071 | 29733.51538 | 73924.32021 | 5698.599992 | 4676.110526 | 26073.73587 | 11032.23247 | 53130.91432 | 19218.30817 | 55973.77161 | 4116.669953 | 19159.07677 | 0 | 13988.72102 | 112768.6304 | 116379.3518 | ||
| Q53GD3 | 4 | 2 | 24.61 | 0.067883944 | 2.129742084 | XA | XN | Choline transporter-like protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC44A4 PE=2 SV=2 | 49343.33 | 20291.02 | 80986.87 | 28620.04 | 66380.90128 | 71380.12714 | 198742.4345 | 139574.7453 | 53405.4186 | 31238.07556 | 28278.12443 | 34610.79561 | 27450.79605 | 64505.89638 | 12055.36364 | 82063.43502 | 19251.80498 | 46355.59023 | 22104.41968 | 27408.82175 | 75187.28425 | 12670.20164 | 39997.73289 | 3517.953753 | 19142.20874 | 71534.07484 | 61212.28451 | ||
| Q9P2N4 | 4 | 1 | 24.59 | 0.079181757 | 2.172003263 | XA | HN | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTS9 PE=2 SV=4 | 17422.71 | 2346.412 | 2695.066 | 16452.94 | 0 | 55999.92902 | 14883.46372 | 31659.52125 | 23763.91233 | 48813.87993 | 0 | 3699.7118 | 6928.386633 | 5937.234718 | 4368.986995 | 0 | 6321.646218 | 0 | 38210.83999 | 11940.25769 | 17706.3466 | 28660.76556 | 7130.561591 | 7824.730838 | 12386.22107 | 9365.821755 | 16099.86684 | ||
| O76081 | 1 | 1 | 24.56 | 0.682333497 | 1.143035863 | HN | XA | Regulator of G-protein signaling 20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RGS20 PE=1 SV=4 | 11295515 | 2515199 | 1993949 | 4551142 | 2780331.757 | 2805504.116 | 3177233.879 | 5803949.371 | 2738504.668 | 9519956.614 | 2814211.768 | 5218659.239 | 5752285.391 | 2765418.606 | 4428658.204 | 4673597.931 | 3085101.927 | 4790359.626 | 4352890.514 | 4450034.378 | 6017054.639 | 3234632.19 | 6288611.421 | 978404.8224 | 5246650.761 | 3121658.737 | 6020237.445 | ||
| Q96DR8 | 1 | 1 | 24.55 | 0.412659103 | 2.852849846 | XA | HN | Mucin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUCL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 112191.7 | 1071660 | 346085.2 | 20678.32 | 112373.5904 | 40319.42547 | 196500.4347 | 24850.21832 | 465037.1144 | 19151.39573 | 74815.35478 | 38455.96552 | 134617.5645 | 175726.1031 | 211563.9691 | 16558.91516 | 145575.8813 | 21187.0933 | 59329.75985 | 54682.14995 | 56678.68357 | 22115.82077 | 57731.57682 | 656480.6122 | 102620.8945 | 207549.218 | 32859.23571 | ||
| Q96C12 | 7 | 4 | 24.51 | 0.007964381 | 3.883702203 | HN | XA | Armadillo repeat-containing protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARMC5 PE=2 SV=2 | 382377.4 | 103279.9 | 115018.9 | 320014 | 111426.1871 | 119033.5885 | 147571.6526 | 332389.5473 | 281577.9418 | 478423.4802 | 426370.3653 | 4298030.737 | 425180.7911 | 414670.8894 | 121748.1998 | 324806.3401 | 629244.7389 | 309839.2628 | 303486.6518 | 393881.0417 | 554127.0981 | 364842.6025 | 501545.0128 | 378644.4792 | 947257.4733 | 408522.6227 | 1387644.08 | ||
| P60985 | 1 | 1 | 24.5 | 0.390995483 | 11.89937331 | XA | HN | Keratinocyte differentiation-associated protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRTDAP PE=1 SV=1 | 275.7853 | 152.0119 | 39.29586 | 68.92036 | 636.4848965 | 1432.095066 | 29662.8621 | 98816.55815 | 76239.62719 | 10589.61514 | 1.939522513 | 1087.392679 | 1067.744159 | 31.63260322 | 87.47303839 | 3771.248982 | 676.6138834 | 109.4122327 | 16389.50731 | 3148.771419 | 3212.080732 | 325.0559059 | 859.8794461 | 7096.928314 | 933.8621082 | 87.36411481 | 107.0649097 | ||
| P25786 | 5 | 1 | 24.49 | 0.296044144 | 2.489838262 | XN | HN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 6201.955 | 6616.424 | 13145 | 13605.92 | 1857.593506 | 27614.36219 | 75343.31573 | 55233.76892 | 73015.39592 | 22233.47394 | 19497.25351 | 14439.78237 | 31585.52978 | 1658.953392 | 17988.16831 | 0 | 0 | 5897.991133 | 185435.473 | 5279.083116 | 14205.59647 | 32849.68959 | 23099.94169 | 0 | 9700.786606 | 4193.854309 | 7337.119664 | ||
| Q9P2R6 | 11 | 3 | 24.26 | 0.063975819 | 5.162877016 | XA | HN | Arginine-glutamic acid dipeptide repeats protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=RERE PE=1 SV=2 | 148816.4 | 155576.5 | 174800.9 | 552738.1 | 1925862.769 | 2980238.976 | 1464990.328 | 3992644.742 | 1947822.8 | 73465.76555 | 79284.86012 | 178144.6289 | 181497.5863 | 294313.7501 | 409044.2529 | 286086.1481 | 349727.5145 | 732942.4421 | 177180.4816 | 359257.1154 | 513048.9327 | 827212.3019 | 397487.1203 | 2954629.652 | 4045564.914 | 128760.8961 | 330790.1258 | ||
| Q9BSH5 | 3 | 2 | 24.24 | 0.004436886 | 4.781266542 | XA | XN | Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HDHD3 PE=1 SV=1 | 68333.98 | 686903.2 | 378484 | 65988.5 | 533830.5836 | 386250.1472 | 249657.996 | 478903.9454 | 353477.8355 | 121378.4221 | 27749.09968 | 51941.04688 | 9967.904028 | 120355.3648 | 279428.4578 | 133451.4066 | 62772.88346 | 60191.78348 | 68757.30909 | 75779.29437 | 10068.36477 | 2299.979977 | 134425.6677 | 178493.8705 | 78351.50264 | 64431.91246 | 57053.61115 | ||
| P21291 | 1 | 1 | 24.18 | 0.222684417 | 1.581678013 | XA | XN | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSRP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 91799.14 | 10328.49 | 21678.54 | 96914.33 | 22944.56624 | 16023.41833 | 39414.65479 | 29076.48264 | 47006.83091 | 49.15166143 | 28034.12116 | 69282.2453 | 181.039163 | 24546.54682 | 40703.69061 | 63164.17238 | 8362.882456 | 9508.424316 | 9066.643583 | 13160.52178 | 16871.66577 | 32905.85978 | 29647.8137 | 993.5768995 | 42661.29268 | 55150.59313 | 36749.89655 | ||
| Q9HC29 | 3 | 2 | 24.16 | 0.136038858 | 2.133554013 | HN | XA | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOD2 PE=1 SV=1 | 960540.1 | 1775788 | 1045587 | 265349.1 | 3422802.237 | 969971.9459 | 548252.4354 | 707703.5483 | 143585.0543 | 2334996.889 | 549048.2041 | 1904079.146 | 1074639.508 | 2014424.629 | 4180688.249 | 7049169.061 | 791812.6295 | 1094415.266 | 858242.4286 | 1633232.284 | 1343190.585 | 769718.2366 | 2459796.704 | 2976728.599 | 280185.3718 | 679183.1487 | 1285620.047 | ||
| Q5SRE7 | 1 | 1 | 24.14 | 0.000871841 | 8.384449089 | XN | XA | Phytanoyl-CoA dioxygenase domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHYHD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5110.489 | 5363.234 | 2097.989 | 4176.817 | 3056.223847 | 735.4780357 | 5539.417922 | 1159.796792 | 3534.65978 | 777.974635 | 22156.55285 | 28415.20996 | 8240.811764 | 40619.31175 | 9097.582853 | 4539.046217 | 7482.171897 | 5250.270341 | 10300.66441 | 11254.75376 | 25619.57387 | 108481.7512 | 12149.97698 | 43451.16194 | 25540.32089 | 14335.30906 | 6890.407915 | ||
| Q9UQ49 | 1 | 1 | 24.08 | 0.697859021 | 1.110700658 | XN | HN | Sialidase-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEU3 PE=1 SV=1 | 7193809 | 7537030 | 5135595 | 6104511 | 5907840.783 | 4059811.26 | 5787559.065 | 4458462.691 | 6517149.805 | 3143739.892 | 5863842.204 | 2283604.121 | 6507532.148 | 5042004.712 | 7165674.831 | 5136098.54 | 5607199.179 | 7788745.964 | 2904389.769 | 6014229.05 | 6171114.125 | 3779473.044 | 8726304.035 | 6743339.869 | 5503832.485 | 4762284.993 | 9306711.637 | ||
| P50135 | 3 | 1 | 23.88 | 0.78626989 | 5.382691061 | XA | XN | Histamine N-methyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=HNMT PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29653.99982 | 48926.07994 | 35407.74945 | 1075.851778 | 16647.9542 | 0 | 3534.09358 | 7377.787069 | 24077.88411 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9851.972702 | 0 | 10603.12561 | 0 | 921.5104637 | ||
| Q9NXJ5 | 1 | 1 | 23.77 | 0.428072949 | 3.410015358 | XA | XN | Pyroglutamyl-peptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGPEP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 13749.92 | 17523.11 | 12656.44 | 100991 | 0 | 45812.11253 | 20634.34957 | 47366.28188 | 25151.89421 | 1476.192236 | 1046.95313 | 51861.88237 | 0 | 41493.00489 | 4744.433808 | 0 | 3296.533699 | 7263.104747 | 3411.33643 | 5439.789257 | 4336.075975 | 0 | 34230.70676 | 0 | 15361.09929 | 7193.230604 | 13278.16516 | ||
| P08183 | 5 | 2 | 23.73 | 0.401100342 | 1.349362211 | XA | XN | Multidrug resistance protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABCB1 PE=1 SV=3 | 283849.5 | 90527.93 | 120124.4 | 125906 | 71305.15062 | 80166.95659 | 109829.2722 | 134868.7357 | 122229.1664 | 60642.05766 | 70415.09515 | 412957.9673 | 40761.01401 | 44602.87631 | 51635.94703 | 113205.9684 | 231656.8926 | 34928.0213 | 67022.5945 | 75797.57337 | 128638.4582 | 67314.32158 | 105568.7275 | 25432.31799 | 141275.8462 | 61570.22134 | 171339.4057 | ||
| O75626 | 3 | 1 | 23.63 | 0.810036876 | 1.100887302 | XN | HN | PR domain zinc finger protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 381698.5 | 542433.9 | 246962.8 | 10234.92 | 314403.9595 | 559470.2426 | 474336.8265 | 486401.7434 | 745192.3585 | 399023.1557 | 447061.5525 | 617743.9716 | 229554.5133 | 333170.714 | 284213.879 | 495126.8011 | 424806.7159 | 512748.2929 | 418079.1758 | 830486.764 | 577365.1254 | 317059.6354 | 638470.3929 | 366184.4229 | 19040.09433 | 630026.0279 | 324404.4879 | ||
| Q9P2J9 | 2 | 2 | 23.61 | 0.569917393 | 9.39992306 | XN | HN | [Pyruvate dehydrogenase [acetyl-transferring]]-phosphatase 2, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDP2 PE=2 SV=2 | 58483.16 | 170371 | 173902.9 | 143600.9 | 196075.3949 | 697047.3397 | 775087.5481 | 265144.596 | 505382.413 | 84229.8808 | 204987.989 | 126345.6276 | 182847.9116 | 161001.3353 | 84902.03365 | 206797.6617 | 103160.9609 | 214286.0517 | 11610030.65 | 77680.53233 | 86784.07156 | 292317.7552 | 120710.1654 | 63821.99933 | 308568.0276 | 42532.13017 | 261908.2172 | ||
| Q9BYC5 | 4 | 1 | 23.29 | 0.009216996 | 1.769370653 | XN | HN | Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FUT8 PE=1 SV=2 | 1338788 | 1221263 | 470661.6 | 1833465 | 1068626.996 | 1199403.089 | 1594967.341 | 2445613.058 | 1061899.783 | 600147.9992 | 471099.0539 | 411943.1638 | 1726437.525 | 1385956.19 | 559443.0519 | 1160610.958 | 1350528.519 | 361695.8243 | 1812508.652 | 1174317.306 | 1518141.779 | 1618612.841 | 1862300.1 | 1227707.551 | 2164694.8 | 1147471.267 | 1678509.634 | ||
| Q496H8 | 1 | 1 | 23.08 | 0.124636549 | 2.947051381 | XA | HN | Neuritin-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=NRN1L PE=2 SV=2 | 22103.59 | 192477 | 30020.75 | 52889.58 | 15037.98773 | 8077.818214 | 19338.32222 | 16880.26134 | 34413.26653 | 0 | 1683.168027 | 6.043109609 | 21112.86959 | 5058.295838 | 60586.7663 | 6379.103897 | 256.9683251 | 37672.72456 | 1775.641966 | 2606.748271 | 0 | 29215.58211 | 50319.35714 | 58856.01731 | 43809.74229 | 24169.86939 | 30510.72323 | ||
| Q8TAA3 | 2 | 1 | 23.01 | 0.616346591 | 1.505743575 | XN | XA | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 59141.65 | 87318.48 | 193721.9 | 35521.96 | 5781.645108 | 30718.43198 | 90770.31201 | 47826.69802 | 8315.621347 | 70270.91607 | 131850.339 | 228972.8583 | 35842.25759 | 86679.12284 | 28364.8458 | 24268.30236 | 205403.5779 | 23726.57561 | 5548.612214 | 56431.80231 | 63953.78015 | 81028.52193 | 53599.31618 | 319047.8085 | 200726.3932 | 14552.01282 | 46998.17543 | ||
| P46459 | 3 | 1 | 22.97 | 0.114882888 | 10.43648076 | XA | HN | Vesicle-fusing ATPase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NSF PE=1 SV=3 | 658863.3 | 19136.41 | 25.27505 | 314368.9 | 270296.547 | 0 | 31644.6188 | 11744.0067 | 477.7170604 | 4785.132504 | 0 | 83101.45436 | 4.493608962 | 0 | 37297.11932 | 0 | 0 | 3.114402362 | 79101.37019 | 41176.28567 | 0 | 0 | 15.528792 | 0 | 21021.39163 | 0 | 41508.17418 | ||
| Q01196 | 7 | 3 | 22.6 | 0.442471078 | 1.453802816 | HN | XN | Runt-related transcription factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RUNX1 PE=1 SV=3 | 240468.2 | 653479.4 | 916091.6 | 562499.5 | 1260454.797 | 375470.2441 | 227884.4633 | 185269.9897 | 558390.3273 | 269335.9286 | 361243.8119 | 1493110.533 | 394696.7706 | 1044012.379 | 757400.3877 | 802937.4793 | 685195.149 | 437264.1292 | 783616.2302 | 374871.0521 | 331914.6747 | 453832.6707 | 561859.2129 | 689761.2563 | 451066.6483 | 329862.9764 | 318981.1822 | ||
| Q4G0N4 | 3 | 1 | 22.52 | 0.934414326 | 1.112950697 | XN | HN | NAD kinase domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NADKD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1374160 | 1037048 | 722706 | 501635.4 | 807308.1512 | 1047703.609 | 860356.816 | 1308536.76 | 1114622.582 | 474548.4165 | 1323653.652 | 531156.0647 | 742546.7317 | 478564.9701 | 1289885.993 | 1128198.842 | 1159523.592 | 1459410.549 | 1021511.778 | 1568810.584 | 1937480.567 | 1049015.98 | 312788.5409 | 761451.3248 | 1442490.447 | 951273.8049 | 512628.6294 | ||
| P56545 | 4 | 2 | 22.48 | 0.674730341 | 1.341721649 | XA | XN | C-terminal-binding protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTBP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 783429.9 | 5767407 | 4119598 | 1363162 | 3091729.99 | 2472027.876 | 267386.9732 | 5589472.696 | 224512.2038 | 6393510.217 | 3473450.135 | 1177158.361 | 1867530.38 | 1507572.413 | 830401.5769 | 4064641.011 | 2247062.497 | 1816495.341 | 801016.6472 | 3691921.369 | 3172668.522 | 653617.5781 | 715312.4809 | 2666394.206 | 378996.1192 | 2896446.474 | 2671643.576 | ||
| Q9H0B8 | 3 | 1 | 22.39 | 0.776109578 | 3.616408731 | XA | XN | Cysteine-rich secretory protein LCCL domain-containing 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRISPLD2 PE=1 SV=1 | 2387.355 | 0 | 3716.598 | 0 | 301680.7498 | 0 | 1598.543198 | 3966.208578 | 0 | 0 | 7039.162141 | 0 | 0 | 28336.09447 | 111917.3104 | 7803.920705 | 6647.059826 | 37573.47526 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 649.6258436 | 8077.715959 | 24372.80693 | 5526.988785 | 35933.61792 | 12085.82622 | ||
| Q96GX8 | 1 | 1 | 22.15 | 0.011440243 | 2.915695498 | XN | XA | Uncharacterized protein C16orf74 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C16orf74 PE=1 SV=2 | 89159.82 | 128281 | 119915 | 63690.5 | 132533.8802 | 92009.82711 | 172303.8969 | 89248.28972 | 43666.64874 | 346282.5294 | 54487.76256 | 19244.98377 | 390104.1926 | 143245.7896 | 184837.7742 | 407194.8496 | 176274.0468 | 268154.982 | 342911.604 | 225341.6984 | 260862.0096 | 600446.1253 | 167366.3207 | 180288.1309 | 278569.2046 | 202980.4719 | 455189.5634 | ||
| Q86SJ6 | 2 | 2 | 22.11 | 0.35067621 | 3.782679359 | XN | XA | Desmoglein-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSG4 PE=1 SV=1 | 137898.7 | 254396.9 | 179489.9 | 95276.76 | 213887.606 | 71411.42473 | 97310.7698 | 111983.1274 | 70830.23657 | 93243.25838 | 169121.8376 | 77362.00574 | 137037.4947 | 275315.1226 | 175086.2913 | 312167.6249 | 153671.4259 | 95563.03088 | 84181.49419 | 1512978.624 | 93911.25119 | 67047.93729 | 181661.4365 | 161748.3902 | 171855.1728 | 122788.196 | 2265924.677 | ||
| P78330 | 1 | 1 | 22.07 | 0.321836985 | 3.990800976 | XA | HN | Phosphoserine phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSPH PE=1 SV=2 | 2561.605 | 0 | 22207.94 | 13792.5 | 0 | 14302.47749 | 51076.38315 | 34881.14094 | 11595.17802 | 14711.13922 | 8669.186354 | 39.30669838 | 0 | 6396.999899 | 0 | 5179.888749 | 0 | 2694.465673 | 70533.53649 | 2948.180847 | 6090.767815 | 22315.83806 | 17704.39587 | 6705.70888 | 4517.784836 | 2627.830688 | 0 | ||
| Q9UHX3 | 2 | 1 | 22.03 | 0.572678929 | 1.32620429 | HN | XA | EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EMR2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1100192 | 699444.5 | 471588.7 | 617595 | 555026.8404 | 555641.3315 | 471348.0258 | 616851.2564 | 559694.5254 | 964013.4051 | 695433.1633 | 1257758.942 | 788344.6661 | 1017824.192 | 594958.4099 | 187090.7764 | 955554.2925 | 1028605.275 | 1062687.778 | 747079.3507 | 772176.3962 | 413752.7089 | 1057837.808 | 313454.0644 | 822930.6055 | 678481.4547 | 1013076.208 | ||
| P48039 | 2 | 1 | 22.02 | 0.698895953 | 1.239562633 | XA | HN | Melatonin receptor type 1A OS=Homo sapiens GN=MTNR1A PE=2 SV=1 | 2020.823 | 34235.57 | 84995.16 | 39726.19 | 55518.4303 | 17792.42202 | 12170.83183 | 10866.54895 | 24696.33792 | 6847.837756 | 25436.4077 | 2.844559256 | 29046.57352 | 17753.24749 | 25167.49225 | 96634.4828 | 15194.44414 | 11434.26866 | 0 | 7642.71612 | 15595.51685 | 55582.35846 | 39568.02034 | 70475.15232 | 24439.57495 | 18674.67543 | 23774.27459 | ||
| Q9NZV5 | 2 | 1 | 21.99 | 0.573399032 | 1.10510077 | XN | HN | Selenoprotein N OS=Homo sapiens GN=SEPN1 PE=1 SV=5 | 411101.6 | 708391.6 | 257692 | 364634 | 296763.2023 | 368588.8915 | 134186.3373 | 741583.9802 | 360710.0256 | 361861.4331 | 348660.3374 | 829867.7416 | 60945.09464 | 114930.361 | 391262.0835 | 43024.81389 | 568516.8041 | 604014.5995 | 435373.0901 | 308238.9113 | 461463.3587 | 239328.2233 | 613008.9214 | 228622.9748 | 85781.85102 | 588017.9749 | 712506.5734 | ||
| Q93009 | 6 | 2 | 21.95 | 0.744530722 | 1.451249452 | HN | XN | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=USP7 PE=1 SV=2 | 978556.8 | 961248.9 | 475637.3 | 2429087 | 2545678.117 | 2802249.149 | 556415.7815 | 899864.4211 | 935653.2566 | 1427977.585 | 1066021.012 | 2795014.718 | 389150.64 | 1017959.77 | 2136698.363 | 3694612.395 | 310444.7294 | 1228356.197 | 842824.4738 | 813950.4035 | 561996.8831 | 1417560.536 | 1368021.452 | 2561990.869 | 866055.7898 | 543636.0643 | 716463.5961 | ||
| O95755 | 1 | 1 | 21.89 | 0.054691744 | 10.88383067 | HN | XA | Ras-related protein Rab-36 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAB36 PE=1 SV=2 | 97676.11 | 23344.32 | 39852.41 | 143908.4 | 62323.55819 | 0 | 73231.09865 | 18659.94241 | 0 | 280794.2455 | 14464.22591 | 206599.3949 | 31146.16533 | 61311.24564 | 403539.8418 | 3807785.952 | 164981.5882 | 25010.59117 | 41564.33336 | 148801.9456 | 114074.0193 | 96534.75764 | 210820.8959 | 46014.88106 | 41849.9301 | 71430.01543 | 176242.6306 | ||
| P25189 | 5 | 2 | 21.65 | 0.683711354 | 1.060157688 | XN | HN | Myelin protein P0 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MPZ PE=1 SV=1 | 1071467 | 907248.4 | 1135344 | 884564.4 | 761109.3077 | 1307943.885 | 1443515.02 | 1057027.238 | 857064.1032 | 1389448.997 | 667119.6417 | 508053.9087 | 584046.7976 | 1797399.85 | 637545.8679 | 797749.9733 | 1291421.899 | 1246805.363 | 959067.8857 | 814772.8172 | 1230963.237 | 1141218.471 | 1519171.56 | 608408.8626 | 905370.148 | 834425.5061 | 1442775.864 | ||
| P55283 | 5 | 2 | 21.61 | 0.315279868 | 1.090735522 | HN | XA | Cadherin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH4 PE=2 SV=2 | 1221649 | 3668089 | 300282.2 | 127458.6 | 2159842.561 | 54353.20688 | 205738.754 | 113904.9277 | 166961.8054 | 2343754.519 | 415132.0951 | 513797.1842 | 259645.1517 | 734553.935 | 1006284.803 | 401778.4782 | 1612061.515 | 1458815.41 | 2622193.437 | 2234811.456 | 478943.2268 | 656223.7919 | 350863.0845 | 509993.7783 | 95436.27274 | 602016.5933 | 659110.5645 | ||
| O96033 | 3 | 1 | 21.58 | 0.954563477 | 1.04791353 | XA | XN | Molybdopterin synthase sulfur carrier subunit OS=Homo sapiens GN=MOCS2 PE=1 SV=1 | 82503.8 | 106387.2 | 154942.1 | 77814.39 | 46941.3426 | 80866.43324 | 181014.8454 | 86453.81699 | 129722.4095 | 93084.50453 | 211864.421 | 71914.47341 | 91162.23766 | 104238.0192 | 125992.9956 | 71345.98699 | 60284.91605 | 77279.15763 | 90947.10457 | 196846.9134 | 112777.0897 | 126241.7554 | 94021.30271 | 55279.8981 | 99371.82249 | 44349.68678 | 83527.48171 | ||
| Q92636 | 3 | 1 | 21.46 | 0.47636732 | 1.488404604 | HN | XN | Protein FAN OS=Homo sapiens GN=NSMAF PE=1 SV=2 | 936789.5 | 3463677 | 2536454 | 1252609 | 3932695.988 | 1909160.156 | 3259444.944 | 1502379.619 | 767495.4699 | 1757194.399 | 1877323.357 | 2014621.115 | 1101290.704 | 2287750.481 | 9126880.322 | 2961431.477 | 4114992.901 | 984069.7022 | 1249103.182 | 839762.0421 | 500506.6839 | 617305.807 | 3290292.991 | 3505735.224 | 3857619.974 | 1959213.648 | 1800369.978 | ||
| Q13444 | 2 | 1 | 21.45 | 0.31763311 | 1.814467283 | XN | XA | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAM15 PE=1 SV=4 | 203025.4 | 587698.2 | 279058.3 | 161602.3 | 1344164.928 | 112551.3983 | 96268.58793 | 620758.4112 | 95659.75526 | 521789.5931 | 114002.4022 | 494741.6479 | 181669.1656 | 314089.1495 | 1688016.206 | 818242.2449 | 177480.5975 | 274642.2953 | 166854.9117 | 102768.2816 | 562403.3829 | 222443.1181 | 1518405.711 | 1362718.81 | 532902.3141 | 701537.5199 | 1182029.937 | ||
| Q96HC4 | 1 | 1 | 21.45 | 0.822010777 | 3.902732327 | HN | XN | PDZ and LIM domain protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDLIM5 PE=1 SV=5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21636.34101 | 5867.973518 | 0 | 0 | 94662.41714 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4997.765489 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25536.00254 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q9ULU8 | 8 | 3 | 21.05 | 0.642223597 | 1.883586937 | HN | XN | Calcium-dependent secretion activator 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CADPS PE=1 SV=3 | 1336411 | 5333262 | 3341885 | 2236342 | 7358398.606 | 947551.6883 | 868142.5222 | 1746234.719 | 1493565.357 | 3733480.109 | 968592.2126 | 5386682.344 | 572598.6123 | 1105209.906 | 3764420.164 | 2112161.773 | 11137332.18 | 5391175.137 | 2028894.277 | 1138454.612 | 2051626.225 | 2419939.692 | 3354595.85 | 938783.7352 | 1879230.409 | 1964467.822 | 2365804.688 | ||
| O95630 | 2 | 1 | 20.92 | 0.433686364 | 1.435058679 | XN | HN | STAM-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=STAMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 697892.9 | 129430.4 | 144436.7 | 343661.4 | 744786.8998 | 706217.5257 | 1304983.324 | 935031.6659 | 682906.4246 | 533367.4153 | 1022510.9 | 1528089.333 | 667441.8447 | 280347.6023 | 412904.9027 | 219530.5793 | 199959.885 | 317577.8126 | 537326.6536 | 862346.0114 | 686347.8682 | 746809.2719 | 531464.6316 | 851258.9617 | 983282.6716 | 2051182.175 | 186068.7578 | ||
| Q9NZU1 | 2 | 1 | 20.92 | 0.809960417 | 29.23290073 | XA | XN | Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane protein FLRT1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLRT1 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25699.83307 | 504813.992 | 186617.5199 | 326333.255 | 0 | 0 | 226255.052 | 37802.34914 | 3462.284254 | 0 | 21483.4555 | 0 | 6255.88125 | 2335.929881 | 17148.29689 | 0 | 0 | 11476.70488 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4733.938652 | ||
| P17844 | 4 | 2 | 20.86 | 0.126221233 | 1.445559872 | XN | XA | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDX5 PE=1 SV=1 | 9099964 | 5862969 | 3990075 | 941550.6 | 2299993.328 | 3844070.853 | 5134571.431 | 5705067.552 | 3163199.674 | 2838681.58 | 5427597.65 | 3049588.371 | 4427085.3 | 6568993.985 | 4436830.327 | 3700955.984 | 6082123.731 | 4765494.784 | 5898766.374 | 5216552.735 | 7517341.879 | 4014492.404 | 10121465.1 | 3634456.662 | 9707945.824 | 4151746.507 | 7619562.642 | ||
| P11717 | 8 | 3 | 20.86 | 0.886913654 | 1.227610491 | HN | XN | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 1881001 | 2205288 | 6199967 | 3342713 | 3947046.206 | 2871993.148 | 3509157.752 | 3439565.539 | 2028902.613 | 4223916.911 | 2091466.301 | 10015678.09 | 2953661.409 | 2627027.306 | 1738207.027 | 5256631.112 | 1602887.429 | 1776321.606 | 3025108.237 | 2597087.747 | 3085389.498 | 2823435.012 | 4237373.188 | 4505147.072 | 2627057.671 | 2151235.204 | 1247874.166 | ||
| Q9UPQ7 | 7 | 3 | 20.85 | 0.712576524 | 1.248305807 | XA | HN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase PDZRN3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDZRN3 PE=1 SV=2 | 865136.9 | 1045581 | 1190340 | 5395157 | 3198366.188 | 1124847.215 | 1750893.502 | 1081082.484 | 923007.7165 | 689603.2323 | 451042.6888 | 781560.3173 | 1733071.517 | 2536326.354 | 1950675.883 | 3477834.328 | 1128130.379 | 529280.9905 | 1430102.2 | 659969.561 | 1274668.705 | 1298410.857 | 1837594.1 | 4354808.29 | 1780861.404 | 848548.5508 | 1158928.819 | ||
| O43681 | 1 | 1 | 20.85 | 0.751982957 | 4.54980351 | XA | HN | ATPase ASNA1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASNA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 92519.81 | 1817.631 | 8118.092 | 197336.6 | 0 | 33898.14006 | 71851.55567 | 126771.8052 | 40784.30347 | 29691.73646 | 12980.65274 | 10320.09347 | 16435.05158 | 2588.541692 | 0 | 36409.05419 | 4130.998933 | 13404.89693 | 16577.94189 | 0 | 11503.48737 | 29634.74089 | 195418.1749 | 0 | 20802.33574 | 36501.54806 | 17381.52882 | ||
| O00570 | 1 | 1 | 20.63 | 0.34378593 | 1.210579491 | XA | XN | Transcription factor SOX-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOX1 PE=1 SV=2 | 577760.4 | 1200210 | 699741.6 | 948235.9 | 814622.5675 | 330227.85 | 44089.25955 | 226814.8568 | 362780.4764 | 172631.3441 | 117557.9627 | 264882.1174 | 21836.01851 | 45623.22187 | 201340.1043 | 1947254.392 | 565314.9308 | 1050731.332 | 763726.6105 | 449320.1312 | 259304.7172 | 595859.9792 | 759253.5625 | 166799.0898 | 623843.1317 | 478002.016 | 203057.5735 | ||
| Q8N6Y2 | 3 | 2 | 20.61 | 0.866157204 | 2.953282877 | HN | XN | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRRC17 PE=2 SV=1 | 194886.2 | 322898.1 | 324041.4 | 182376.9 | 1682141.35 | 357622.8538 | 109881.4038 | 193627.6608 | 613434.7525 | 50274.71602 | 85178.78737 | 2573.138618 | 104270.1719 | 7569333.906 | 425270.3999 | 1286424.568 | 668696.1162 | 939378.0038 | 217016.1794 | 623761.9976 | 438173.7032 | 662252.9907 | 165289.4219 | 126518.7606 | 686998.9069 | 218005.9382 | 631143.4964 | ||
| Q08830 | 2 | 1 | 20.23 | 0.157973615 | 1.534525638 | XA | XN | Fibrinogen-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGL1 PE=1 SV=3 | 84822.6 | 73540.18 | 209260.5 | 89233.05 | 80588.05585 | 101100.4255 | 180019.8674 | 141829.48 | 216081.6079 | 19793.25253 | 81526.85441 | 310011.598 | 97415.89885 | 133732.6993 | 63513.64308 | 61963.11868 | 39005.80155 | 60156.00218 | 95387.45163 | 195132.9657 | 90532.17764 | 32054.83467 | 47660.48209 | 90656.53616 | 91712.21348 | 51815.38897 | 71718.6183 | ||
| Q13277 | 4 | 1 | 20.22 | 0.260147188 | 2.720561239 | XA | HN | Syntaxin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STX3 PE=1 SV=3 | 0 | 0 | 8333.872 | 73856.56 | 0 | 40505.19311 | 70810.74993 | 42541.29288 | 25078.7106 | 3877.214739 | 17455.14499 | 12903.7319 | 14060.26792 | 34697.03257 | 4207.072753 | 2921.249426 | 0 | 5860.826798 | 0 | 0 | 18801.17468 | 19482.83596 | 49148.75626 | 0 | 16631.9524 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q6ZMP0 | 6 | 4 | 19.9 | 0.073516163 | 1.921510106 | XA | HN | Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THSD4 PE=2 SV=2 | 8079739 | 1790320 | 2507795 | 6175027 | 2460221.613 | 7211410.762 | 7500367.86 | 2918522.912 | 5087969.064 | 2872179.368 | 2016707.803 | 2099988.188 | 2029852.848 | 1906610.504 | 2128398.056 | 3070462.929 | 2873967.936 | 3760689.021 | 4452051.643 | 3668332.491 | 3342413.858 | 3051830.959 | 2081916.105 | 676383.4002 | 3074478.489 | 3092635.245 | 5080205.866 | ||
| Q6XPR3 | 3 | 2 | 19.89 | 0.919547488 | 1.610206197 | HN | XA | Repetin OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPTN PE=1 SV=1 | 248800.7 | 614137 | 191051.7 | 248228.7 | 326243.5363 | 272231.0379 | 369873.0232 | 319328.9587 | 154208.3048 | 1690963.667 | 421108.0519 | 569072.2103 | 86402.93035 | 126615.4689 | 516700.3758 | 147557.2962 | 704250.6786 | 155901.0161 | 492987.9487 | 278802.8815 | 321408.0247 | 234802.5764 | 788300.2817 | 240497.8309 | 215046.2162 | 302892.8029 | 128538.0032 | ||
| Q9NXD2 | 1 | 1 | 19.88 | 0.595019987 | 1.559602182 | XN | HN | Myotubularin-related protein 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MTMR10 PE=1 SV=3 | 3653711 | 5013201 | 2554092 | 11869011 | 4002067.954 | 2705468.633 | 1920028.754 | 8650379.316 | 4771312.734 | 2584573.852 | 1685355.476 | 4416724.452 | 5043191.856 | 4518479.858 | 4803681.255 | 13099486.13 | 2364986.118 | 1760568.06 | 5156851.788 | 3616070.528 | 1591978.991 | 1645234.732 | 11110846.04 | 12105191.19 | 17576330.79 | 3194253.809 | 6819412.582 | ||
| A6NHY2 | 4 | 1 | 19.83 | 0.999269992 | 1.197144238 | HN | XA | Ankyrin repeat and death domain-containing protein 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANKDD1B PE=4 SV=2 | 2314313 | 1326549 | 825923.8 | 1783709 | 2386204.639 | 354128.3113 | 148826.3903 | 741288.7917 | 121213.3903 | 1959323.146 | 126967.4982 | 476432.2723 | 59855.58132 | 1067536.326 | 930202.4658 | 1052805.532 | 4708902.021 | 1591997.858 | 1811963.71 | 775564.1034 | 1408179.646 | 1046895.199 | 5121877.057 | 81455.61642 | 175250.5913 | 690727.601 | 434462.7411 | ||
| P42126 | 1 | 1 | 19.71 | 0.343816015 | 1.453883657 | HN | XA | Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECI1 PE=1 SV=1 | 45014.14 | 5743.867 | 631.7491 | 0.324583 | 591.3214487 | 46445.3653 | 13216.65138 | 22031.09061 | 10421.64866 | 66201.55791 | 0 | 30160.9159 | 16583.9657 | 0 | 4689.993497 | 3187.5122 | 9006.022724 | 79669.08481 | 148333.1941 | 0 | 2220.050479 | 24302.66332 | 8269.987846 | 0 | 0 | 2950.43741 | 0 | ||
| Q96A44 | 3 | 1 | 19.55 | 0.630528293 | 1.509859379 | XN | XA | SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPSB4 PE=1 SV=1 | 29326.86 | 165353.3 | 55186.6 | 19461.65 | 206385.8365 | 24755.61325 | 15303.50387 | 9658.132152 | 24657.09025 | 22010.76067 | 34954.62863 | 37240.62515 | 92998.10238 | 74158.60148 | 99620.83868 | 25026.97878 | 159707.378 | 67306.95738 | 70155.17572 | 14137.57589 | 15562.57712 | 10316.04809 | 98384.61512 | 31322.06019 | 53330.70716 | 333577.3256 | 203770.2966 | ||
| Q5KU26 | 5 | 2 | 19.48 | 0.47446615 | 1.593896733 | XN | XA | Collectin-12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=COLEC12 PE=1 SV=3 | 638222.1 | 633887.1 | 1300553 | 140347.8 | 249765.5499 | 859465.7207 | 1026958.811 | 684863.0518 | 1000939.53 | 538729.38 | 1291244.933 | 3043564.913 | 581098.7779 | 1083767.251 | 451861.5888 | 342987.3914 | 1603348.675 | 699504.56 | 490335.8356 | 1067949.181 | 765129.872 | 752710.2788 | 530921.853 | 4133135.986 | 1561478.811 | 527442.2736 | 587015.6304 | ||
| Q13233 | 6 | 1 | 19.28 | 0.086944102 | 1.593776667 | XA | HN | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP3K1 PE=1 SV=4 | 472470.4 | 357716.2 | 980360.8 | 936880.7 | 848184.5009 | 579545.7207 | 411917.9354 | 473592.4803 | 314616.2284 | 289017.6524 | 134062.377 | 760807.0455 | 253123.2255 | 105590.5565 | 565867.1288 | 480303.1895 | 373234.5369 | 410665.7253 | 622833.5495 | 280127.9537 | 328474.7417 | 507039.3925 | 207303.4935 | 1178451.207 | 841131.4796 | 712170.3303 | 670217.5275 | ||
| Q99832 | 3 | 1 | 19.25 | 0.956401095 | 1.881367352 | XA | HN | T-complex protein 1 subunit eta OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCT7 PE=1 SV=2 | 47966.24 | 0 | 8728.484 | 13693.05 | 0 | 26387.85629 | 32079.85173 | 53284.27469 | 10493.2219 | 46325.35365 | 7048.702437 | 15631.00277 | 17687.39833 | 0 | 5596.016526 | 7311.477988 | 2789.933126 | 0 | 41151.27169 | 0 | 17433.59717 | 7747.929881 | 32706.60711 | 0 | 4480.607872 | 7553.344849 | 6731.335669 | ||
| Q15631 | 2 | 1 | 19.05 | 0.013555567 | 2.983739176 | XA | HN | Translin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSN PE=1 SV=1 | 47175.49 | 11228.44 | 17730.49 | 149866.5 | 22138.86146 | 133798.6639 | 113037.317 | 131040.5337 | 91458.6661 | 465.1993661 | 1911.079411 | 76945.53882 | 67009.92153 | 1891.168031 | 71954.68147 | 2730.624287 | 5370.337129 | 12183.15364 | 151212.2867 | 30956.29647 | 54802.50343 | 67574.42874 | 27010.16798 | 10030.36338 | 34482.28759 | 11295.64484 | 13575.94263 | ||
| O75077 | 2 | 1 | 19.02 | 0.4721969 | 1.337096838 | XA | XN | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 23 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAM23 PE=1 SV=1 | 197136.4 | 60766.64 | 103874.3 | 178794.5 | 250375.369 | 168640.459 | 50423.56657 | 67714.38088 | 28444.62015 | 109648.7291 | 27402.50749 | 148232.8804 | 9166.464755 | 78963.66566 | 107873.9779 | 360317.3494 | 89665.02349 | 80053.44396 | 95958.29513 | 151835.8763 | 46164.86615 | 94486.16166 | 99567.05276 | 0 | 108411.1295 | 89513.93752 | 141355.2741 | ||
| P08887 | 2 | 1 | 18.68 | 0.053220027 | 3.310794528 | XN | HN | Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL6R PE=1 SV=1 | 73690.88 | 4174.406 | 14049.18 | 26125.38 | 57221.9563 | 40360.8611 | 15272.10436 | 89800.98532 | 34717.26061 | 5614.152036 | 2513.588655 | 4544.684222 | 17233.54505 | 0 | 22695.04803 | 43300.91152 | 23784.5839 | 32031.21619 | 47079.59925 | 76664.22937 | 94092.07303 | 18436.30755 | 23960.3184 | 79172.75788 | 52064.06349 | 56032.54285 | 54804.33712 | ||
| Q8N1Y9 | 2 | 1 | 18.65 | 0.975559846 | 1.39200216 | HN | XA | Putative uncharacterized protein FLJ37218 OS=Homo sapiens PE=5 SV=2 | 732927.2 | 203044.4 | 470644.1 | 736071.5 | 549005.9586 | 244886.8529 | 568847.6245 | 525577.2837 | 1958101.92 | 166660.1235 | 679586.7751 | 147416.9165 | 3400659.621 | 267798.2018 | 454604.0008 | 2475970.759 | 428307.5199 | 315845.9354 | 326737.8494 | 308514.8653 | 258575.8446 | 85773.06379 | 2706456.261 | 508153.5608 | 2201930.199 | 1053620.79 | 807789.4033 | ||
| Q9NTG1 | 5 | 1 | 18.41 | 0.286854992 | 1.908643238 | XA | XN | Polycystic kidney disease and receptor for egg jelly-related protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKDREJ PE=2 SV=2 | 35297.21 | 85246.74 | 68987.33 | 36040.07 | 57731.31135 | 22724.44755 | 7429.514708 | 42041.69882 | 16666.69398 | 19754.7216 | 4801.060989 | 25163.3691 | 6232.035987 | 13998.60672 | 43770.24144 | 52949.04085 | 40891.03763 | 16926.39992 | 23347.08789 | 11061.74538 | 21551.87164 | 40523.23868 | 44617.77127 | 12098.0855 | 18599.9972 | 23187.08105 | 2.428578107 | ||
| P10070 | 5 | 1 | 18.26 | 0.682664576 | 1.299228403 | HN | XN | Zinc finger protein GLI2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLI2 PE=1 SV=4 | 318815.2 | 165987.1 | 152898.5 | 423514.6 | 297242.8257 | 331898.7095 | 269814.9567 | 255023.62 | 142100.4657 | 170555.762 | 186434.3239 | 113825.1354 | 563763.6212 | 602144.7949 | 235116.4583 | 145377.6462 | 191260.7465 | 321146.6246 | 266725.875 | 227364.2582 | 337690.3871 | 152458.009 | 176059.3627 | 194811.0819 | 281041.1789 | 139823.8455 | 171047.1006 | ||
| Q6PIY7 | 2 | 1 | 18.25 | 0.349013639 | 2.554803649 | HN | XN | Poly(A) RNA polymerase GLD2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAPD4 PE=1 SV=1 | 201680.6 | 439628.3 | 92252.77 | 175660.9 | 1463986.22 | 203089.094 | 279623.7804 | 154287.0812 | 168519.2961 | 273541.0466 | 262650.3199 | 140499.2161 | 184850.4879 | 987085.5472 | 220341.2995 | 139439.8541 | 2633769.838 | 311915.7087 | 601441.1389 | 156738.5008 | 234734.9075 | 298833.3602 | 161788.293 | 53863.02807 | 143087.4148 | 169436.4418 | 197489.611 | ||
| P51570 | 3 | 1 | 18.19 | 0.391612065 | 1.488974706 | HN | XN | Galactokinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALK1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1395814 | 961255.9 | 706932 | 3114383 | 12953229.18 | 96347.91713 | 105463.3714 | 176109.4099 | 160057.549 | 2022341.312 | 123806.558 | 782761.1872 | 207212.3269 | 5996188.135 | 5292716.38 | 4235759.38 | 2690117.437 | 6682406.935 | 65894.88889 | 58971.17776 | 113631.7204 | 53820.99736 | 1831281.692 | 4502616.181 | 5358041.865 | 4446250.122 | 2396748.484 | ||
| Q9NQU5 | 1 | 1 | 18.19 | 0.938498331 | 1.598721054 | HN | XN | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAK6 PE=1 SV=1 | 1007139 | 834443.6 | 355035.9 | 2474572 | 1381270.165 | 186231.9517 | 392809.6044 | 470159.0136 | 152902.7851 | 919078.2856 | 156139.687 | 1066261.952 | 174987.9711 | 1422771.776 | 1891232.086 | 3744404.83 | 470234.4566 | 142254.5943 | 426006.3895 | 187366.5547 | 323540.0282 | 419812.0525 | 1219541.04 | 1764223.972 | 967751.9305 | 423173.8727 | 515681.2438 | ||
| Q9UBQ0 | 1 | 1 | 18.13 | 0.056858905 | 1.927223966 | XN | HN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 29 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS29 PE=1 SV=1 | 5567067 | 15006369 | 14497729 | 9236566 | 6768123.353 | 14965979.6 | 31183206.5 | 10236883.65 | 37780324.06 | 3292116.592 | 25846901.12 | 5253041.68 | 16538186.95 | 6927377.096 | 7440765.483 | 2290795.703 | 6252842.262 | 16922747.29 | 16641253.72 | 33279218.23 | 24083998.37 | 10302468.3 | 7383588.468 | 34535962.73 | 13873820.91 | 25824305.89 | 8999431.466 | ||
| P50750 | 3 | 1 | 18.04 | 0.548117323 | 1.344248445 | HN | XA | Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK9 PE=1 SV=3 | 565126.6 | 536008.2 | 560780.2 | 432738.1 | 313713.0238 | 485908.3777 | 643027.1832 | 462447.1787 | 734324.7921 | 431125.5852 | 949998.3801 | 492843.8418 | 1127388.696 | 1411704.907 | 632446.4561 | 606453.4664 | 358494.746 | 353315.0282 | 466680.9196 | 731490.2463 | 333469.2021 | 188314.089 | 486772.8833 | 789643.1356 | 885822.9664 | 829924.1789 | 476951.2289 | ||
| Q86SX6 | 1 | 1 | 17.99 | 0.467606481 | 9.159412437 | HN | XN | Glutaredoxin-related protein 5, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLRX5 PE=1 SV=2 | 5182.703 | 1271.922 | 9410.057 | 3746.046 | 1971.302125 | 9485.327373 | 13762.36085 | 3375.521362 | 0 | 9262.168145 | 30123.38044 | 0 | 6163.114081 | 22213.31135 | 16455.03115 | 256546.6769 | 5508.761778 | 11875.25541 | 6073.758053 | 3338.432868 | 0 | 9264.339592 | 3106.102765 | 9380.736974 | 4967.334728 | 2970.896973 | 0 | ||
| Q8N653 | 3 | 1 | 17.93 | 0.272289757 | 1.327501042 | XN | HN | Leucine-zipper-like transcriptional regulator 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LZTR1 PE=2 SV=2 | 4310952 | 6245067 | 5068560 | 3822519 | 1837446.889 | 2838771.502 | 5917324.022 | 3682739.284 | 5719420.419 | 2447900.694 | 8985969.163 | 1556074.572 | 7991022.746 | 4613558.18 | 5043382.757 | 1153389.296 | 2439170.172 | 3150378.877 | 3003585.861 | 6023577.543 | 4630221.433 | 4911915.191 | 5118777.681 | 12618775.84 | 4016290.601 | 5658454.534 | 3641513.96 | ||
| Q96IY4 | 3 | 1 | 17.91 | 0.06829835 | 2.457971826 | XA | HN | Carboxypeptidase B2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 16768.49 | 3802.558 | 3110.884 | 36023.88 | 18712.28638 | 27271.7803 | 15846.67427 | 14314.92924 | 12498.73631 | 0 | 7761.392069 | 56.72623772 | 9186.657823 | 0 | 7950.576889 | 9871.150805 | 25446.78879 | 81.43678573 | 0 | 1538.942973 | 191.2202815 | 6414.259698 | 28.7412179 | 0 | 59939.88618 | 3914.194805 | 19575.51323 | ||
| Q8IWY4 | 1 | 1 | 17.77 | 0.661516052 | 1.258417967 | HN | XN | Signal peptide, CUB and EGF-like domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCUBE1 PE=1 SV=3 | 300141.5 | 519836.3 | 2187096 | 691214.6 | 1168534.416 | 187932.201 | 98078.35136 | 175173.1007 | 77108.62881 | 560729.3231 | 135580.8667 | 1177163.085 | 160775.4897 | 350946.4448 | 1498636.927 | 1718569.916 | 377922.5043 | 401851.7941 | 273234.8942 | 327960.5477 | 195104.0918 | 293870.3697 | 682890.6103 | 1438206.409 | 833489.297 | 390866.4124 | 635964.4859 | ||
| O14960 | 1 | 1 | 17.47 | 0.811506297 | 1.426147413 | HN | XN | Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LECT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 141388.7 | 22300.85 | 44884.5 | 146354.2 | 96492.39862 | 46545.56676 | 119689.8388 | 87804.30683 | 18156.22279 | 101605.5243 | 2150.267298 | 10015.45366 | 27374.31355 | 78452.92856 | 39351.43852 | 214691.7654 | 161032.7781 | 195976.107 | 79930.02629 | 37908.36123 | 134754.3091 | 39982.1999 | 51790.9172 | 2062.550971 | 88265.26464 | 53470.89008 | 94279.18081 | ||
| O95149 | 2 | 1 | 17.43 | 0.798371053 | 13.23928114 | XN | XA | Snurportin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SNUPN PE=1 SV=1 | 3068.897 | 460.2203 | 6547.822 | 5716.345 | 2872.662514 | 15232.13952 | 5289.346049 | 2275.945092 | 2906.015567 | 91025.97936 | 19433.01041 | 15802.65634 | 16214.5342 | 1103.211864 | 0 | 26248.37702 | 0 | 2612.188573 | 491144.653 | 47443.33873 | 7485.76267 | 198.4250855 | 3997.429576 | 0 | 2415.056999 | 26352.85586 | 8381.355125 | ||
| Q5VVH5 | 1 | 1 | 17.32 | 0.316347032 | 1.992357394 | XA | HN | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IRAK1BP1 PE=2 SV=1 | 2558.282 | 22381.01 | 2510.333 | 8578.084 | 19630.67496 | 401872.7275 | 480841.8927 | 353907.0228 | 180217.7792 | 84267.99292 | 186349.0917 | 335188.74 | 116368.3046 | 710.3018751 | 15911.06171 | 0 | 0 | 277.634338 | 446196.111 | 268520.6325 | 53761.59378 | 310614.4224 | 0 | 630.4793513 | 8806.393051 | 31740.89346 | 7603.024279 | ||
| Q9UKM7 | 4 | 2 | 17.29 | 0.553488005 | 2.990859934 | XA | HN | Endoplasmic reticulum mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN1B1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0 | 10055.19 | 6159.821 | 76538.25 | 26103.15545 | 33731.64873 | 104439.0881 | 76021.41805 | 99076.37918 | 17.02768286 | 11221.88247 | 13430.81274 | 28797.30455 | 0 | 27620.8177 | 50486.04867 | 3861.208851 | 9046.737673 | 0 | 0 | 7830.938357 | 32552.24247 | 71526.15861 | 11673.0135 | 88608.73095 | 152.6070711 | 10617.49396 | ||
| Q8TDB6 | 4 | 3 | 17.16 | 0.216154534 | 5.376214424 | HN | XN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase DTX3L OS=Homo sapiens GN=DTX3L PE=1 SV=1 | 563232.7 | 2020877 | 1557333 | 2752135 | 3588062.769 | 751268.1295 | 414748.8664 | 882746.2587 | 2556165.705 | 883288.3793 | 620024.861 | 24673329.82 | 392940.7183 | 1191953.345 | 1062166.759 | 3609662.128 | 26688417.7 | 3327497.452 | 5051534.171 | 1041571.053 | 661920.1173 | 326337.0412 | 931108.6271 | 1136312.013 | 1104521.495 | 613048.4936 | 749493.4259 | ||
| O43837 | 1 | 1 | 16.84 | 0.241716307 | 1.623128324 | HN | XA | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit beta, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=IDH3B PE=1 SV=2 | 3548638 | 8893642 | 8954761 | 21404405 | 5710839 | 1091967.09 | 3603017.583 | 1333241.751 | 3458414.256 | 9636128.243 | 5231776.106 | 13064223.8 | 4024279.086 | 3401322.556 | 8510236.102 | 29255811.24 | 8934980.154 | 12080942.76 | 12669872.44 | 3694353.264 | 5943545.415 | 4617476.204 | 11746646.49 | 21790082.25 | 1649526.273 | 5996740.937 | 2913101.31 | ||
| P06748 | 4 | 2 | 16.65 | 0.345411221 | 2.171402892 | XA | XN | Nucleophosmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 66076.68 | 22131.75 | 11949.87 | 36786.53 | 29968.04427 | 121276.7806 | 107806.1547 | 95522.20447 | 214904.7678 | 8554.391139 | 45988.65474 | 178963.3679 | 29257.82034 | 80019.83498 | 27716.39234 | 26171.18578 | 49158.14394 | 182504.2944 | 13072.96348 | 61787.53743 | 22998.30329 | 37039.6893 | 79607.95833 | 16865.8552 | 26149.33386 | 31817.8154 | 35990.67019 | ||
| Q8NCW5 | 3 | 2 | 16.29 | 0.446315224 | 1.324738732 | XN | XA | NAD(P)H-hydrate epimerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1BP PE=1 SV=2 | 942385 | 590277.6 | 387780.8 | 759217.4 | 247097.8348 | 1648744.415 | 2618571.638 | 1232123.76 | 2590576.619 | 1323157.013 | 3415013.108 | 1619358.547 | 2226784.485 | 2419703.09 | 614996.7204 | 379496.4901 | 706762.3513 | 1465561.213 | 1617648.414 | 2527035.091 | 2375434.923 | 3338514.06 | 784021.7713 | 1292681.669 | 869808.5414 | 1055724.98 | 733479.1344 | ||
| O15162 | 1 | 1 | 16.28 | 0.414842994 | 1.393675738 | XA | HN | Phospholipid scramblase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLSCR1 PE=1 SV=1 | 76899.46 | 23565.04 | 10275.32 | 1021.527 | 35648.22538 | 32595.31121 | 34969.97831 | 32619.36808 | 9192.278227 | 0 | 53105.99913 | 21451.93125 | 6979.777773 | 51213.98733 | 17822.00539 | 8307.32611 | 8106.430349 | 17263.79665 | 36175.76899 | 35633.6227 | 29541.67419 | 1820.734173 | 13659.30454 | 0 | 0 | 37121.16145 | 45574.06398 | ||
| Q9NQA5;Q9H1D0 | 1 | 1 | 16.25 | 0.705297256 | 2.739791802 | HN | XN | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRPV5 PE=1 SV=2 | 61568.74 | 53888.25 | 16470.2 | 8847.075 | 135882.5311 | 5162.769602 | 8561.132442 | 3612.78247 | 42987.7221 | 5248.437328 | 0 | 490857.9578 | 24092.63314 | 27388.82322 | 50424.43337 | 27548.70373 | 7591.865385 | 88262.93471 | 6296.089646 | 31393.12731 | 64549.97241 | 29581.67038 | 13998.14444 | 38808.90936 | 24529.23131 | 15579.59956 | 38573.69693 | ||
| P25942 | 2 | 1 | 16.04 | 0.018480412 | 11.30183385 | XA | HN | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD40 PE=1 SV=1 | 3149.7 | 24596.56 | 149958.3 | 0 | 106.0967704 | 5990.590617 | 67418.48504 | 5994.078643 | 26430.50643 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 196.4474683 | 0 | 181.8374905 | 0 | 0 | 24718.90933 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20531.55523 | 12485.87481 | 1309.109931 | 2630.064089 | 104065.157 | 11373.42284 | ||
| Q8NDA8 | 4 | 2 | 16.01 | 0.155935315 | 1.721484355 | XA | HN | HEAT repeat-containing protein 7A OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEATR7A PE=1 SV=3 | 199045.2 | 429885.3 | 265141.6 | 84501.62 | 248611.4295 | 144080.2733 | 219096.7686 | 130588.065 | 286284.7558 | 218628.3584 | 4057.309517 | 251871.7169 | 95731.73977 | 34542.41275 | 218830.6309 | 241038.0325 | 41985.48847 | 59305.17415 | 963702.5656 | 54680.20046 | 109853.0702 | 91888.58723 | 279579.8307 | 110862.3954 | 18975.64033 | 43549.99981 | 72594.33381 | ||
| Q9H0K4 | 2 | 1 | 16 | 0.600748311 | 5.250947325 | HN | XN | Radial spoke head protein 6 homolog A OS=Homo sapiens GN=RSPH6A PE=2 SV=1 | 4907.264 | 46483.96 | 361475.4 | 70474.97 | 833735.7009 | 283666.1985 | 25819.94452 | 686090.9797 | 33210.23439 | 2189541.423 | 22554.26733 | 532111.8888 | 47001.87766 | 182981.0074 | 123051.0209 | 15769.52318 | 17464.78328 | 2523.288679 | 166382.7895 | 48301.52981 | 11162.59896 | 55913.80366 | 30048.15009 | 56327.78378 | 28122.92193 | 14774.24183 | 185620.248 | ||
| P20853 | 4 | 1 | 15.93 | 0.476699989 | 1.546627973 | XN | HN | Cytochrome P450 2A7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CYP2A7 PE=1 SV=2 | 2.22E+08 | 94069989 | 1.29E+08 | 2.9E+08 | 85409225.86 | 212649829.9 | 356539812.3 | 336589868.7 | 239273263.8 | 287475975.3 | 81437366.62 | 102910506.9 | 119128814.3 | 246868216.4 | 68141597.89 | 150698907.7 | 304877591.7 | 436050212.3 | 318988301.2 | 176229842.6 | 355951566.2 | 812367668.3 | 340454781.5 | 49615783.46 | 131639947.3 | 246739155.8 | 348214678.1 | ||
| Q92786 | 4 | 2 | 15.89 | 0.140182968 | 1.808555339 | HN | XA | Prospero homeobox protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROX1 PE=1 SV=2 | 125417.9 | 126979.9 | 118330 | 7393.21 | 118858.6639 | 77035.79375 | 112297.7433 | 135960.2354 | 90551.32703 | 324369.3571 | 369997.4077 | 232231.5053 | 147696.9979 | 167269.0873 | 86354.62802 | 90276.55409 | 125901.8251 | 106796.7093 | 334099.4036 | 119897.726 | 129500.926 | 148997.6796 | 143370.9297 | 47624.02664 | 97945.11537 | 134802.5194 | 74149.48513 | ||
| Q11128;P21217;P51993 | 1 | 1 | 15.86 | 0.794840544 | 2.263981086 | HN | XN | Alpha-(1,3)-fucosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FUT5 PE=2 SV=1 | 80752.5 | 178031.5 | 183054.3 | 208382.2 | 289616.5374 | 75237.02311 | 41866.80118 | 45951.11272 | 73543.61026 | 29229.90337 | 201772.4971 | 45809.54785 | 62362.84501 | 128958.2803 | 238400.3539 | 1283367.323 | 129454.9713 | 78139.16371 | 75870.83952 | 102799.8763 | 56160.01261 | 41191.23612 | 177206.7667 | 208690.3719 | 122734.0558 | 63295.08166 | 122684.8178 | ||
| Q9BT22 | 3 | 1 | 15.82 | 0.989546563 | 1.238663807 | HN | XA | Chitobiosyldiphosphodolichol beta-mannosyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 843546.8 | 185862.7 | 26022.07 | 115316.4 | 264605.3233 | 816006.6314 | 699478.9583 | 425988.2837 | 204283.1298 | 202388.2026 | 733575.1957 | 1995062.408 | 604799.1892 | 71997.76213 | 423273.7919 | 91344.51951 | 149341.7934 | 164008.9261 | 654084.0638 | 1099433.324 | 299207.3476 | 346842.1529 | 88754.7656 | 21186.414 | 522063.1989 | 1053679.221 | 137440.0056 | ||
| Q16891 | 3 | 1 | 15.81 | 0.251439879 | 1.760074603 | HN | XN | Mitochondrial inner membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IMMT PE=1 SV=1 | 482326.3 | 1068494 | 1352376 | 318711.1 | 1245577.741 | 596147.4889 | 825128.554 | 628594.2653 | 563711.3959 | 666637.5916 | 750573.5516 | 2842529.616 | 555248.1164 | 809742.5691 | 1654429.844 | 3619780.987 | 707028.3856 | 539990.7165 | 614929.4583 | 579562.0839 | 403923.3333 | 425309.2393 | 853978.2764 | 1580461.857 | 548962.3123 | 757128.5775 | 1136566.768 | ||
| Q9BWC9 | 4 | 2 | 15.7 | 0.936996845 | 165.7182897 | XA | XN | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 106 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCDC106 PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 4781.001 | 0 | 635458.029 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 182729.5585 | 0 | 0 | 737.0242934 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2859.26483 | 0 | 0 | 1004.153209 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q96PD2 | 2 | 1 | 15.66 | 0.763138739 | 1.638181392 | XN | XA | Discoidin, CUB and LCCL domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCBLD2 PE=1 SV=1 | 76178.22 | 73478.47 | 38883.99 | 22738.54 | 9075.097132 | 48609.0055 | 56945.73565 | 28962.09569 | 54622.16776 | 24217.96457 | 220855.0312 | 15278.65767 | 138135.6322 | 91220.68185 | 20364.21609 | 4947.934504 | 48489.92343 | 19992.89514 | 51250.79748 | 8392.995675 | 35993.71 | 26774.459 | 253117.8772 | 53580.12726 | 143665.5642 | 38763.83635 | 59284.99433 | ||
| Q99102 | 3 | 1 | 15.59 | 0.444095404 | 65.55824756 | XA | XN | Mucin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MUC4 PE=1 SV=4 | 1592.521 | 1069.569 | 793.3453 | 644108.7 | 255.0613832 | 1089.599352 | 897.3244615 | 1225.648163 | 1135.687178 | 1043.932427 | 2280.762015 | 657.91683 | 889.8636525 | 468.5371093 | 1373.967708 | 10421.47937 | 1647.258217 | 409.5466839 | 374.2247381 | 838.9834537 | 328.7289439 | 861.366779 | 4710.118499 | 794.4335612 | 473.1674224 | 505.8226155 | 1061.063239 | ||
| P23497 | 5 | 4 | 15.51 | 0.321920663 | 1.968114478 | XA | HN | Nuclear autoantigen Sp-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SP100 PE=1 SV=3 | 206927.9 | 2406488 | 1837711 | 441456.6 | 991337.347 | 774383.6171 | 581107.7411 | 250694.9494 | 851093.3114 | 308898.1054 | 370685.1577 | 672831.8349 | 312709.908 | 232984.3009 | 654548.3295 | 544091.4814 | 502417.2905 | 639002.295 | 357874.207 | 634362.6717 | 198410.3348 | 1013959.552 | 565512.7469 | 1477674.254 | 385222.2183 | 649850.4661 | 471358.9737 | ||
| O15169 | 3 | 2 | 15.51 | 0.511789701 | 1.324821269 | HN | XA | Axin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AXIN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3673083 | 5407721 | 3915038 | 764143.4 | 4215959.379 | 2192900.376 | 1513454.489 | 1764256.551 | 1723644.133 | 6086094.651 | 1394068.013 | 3459405.603 | 879623.4929 | 3941516.973 | 3826064.966 | 5262825.17 | 4839801.657 | 3656615.891 | 2415049.288 | 2156270.542 | 4473593.935 | 4134920.753 | 6409614.233 | 1475021.412 | 3162849.312 | 3556095.982 | 2388497.82 | ||
| Q08708 | 1 | 1 | 15.45 | 0.095975046 | 1.534271668 | XN | HN | CMRF35-like molecule 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD300C PE=2 SV=1 | 376747.5 | 164215.6 | 167332.6 | 68545.24 | 90103.129 | 115674.3321 | 456542.5772 | 69126.32102 | 199681.2492 | 5405.035938 | 439935.0835 | 26308.65991 | 402828.0659 | 78292.66213 | 48226.1797 | 10964.89103 | 45820.68513 | 263602.4034 | 180347.799 | 284086.3697 | 463080.0996 | 50422.28504 | 99694.17258 | 431201.9435 | 92130.12021 | 295560.5357 | 130838.1967 | ||
| Q9NX08 | 3 | 2 | 15.44 | 0.991488051 | 1.476082574 | HN | XN | COMM domain-containing protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMMD8 PE=1 SV=1 | 503396.4 | 837558.6 | 937986.7 | 321516.5 | 794038.5744 | 1186124.17 | 1082331.462 | 986658.0295 | 1333765.018 | 539451.7485 | 856702.9653 | 5587230.41 | 541000.5444 | 681280.8599 | 644735.818 | 210209.5813 | 925346.9922 | 1641529.6 | 815367.5234 | 1781878.87 | 854842.1031 | 411205.4537 | 756727.2817 | 1306934.079 | 621133.3002 | 689343.7836 | 639829.1656 | ||
| Q13724 | 2 | 1 | 15.41 | 0.099188701 | 1.986690746 | HN | XA | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MOGS PE=1 SV=5 | 225643.3 | 124676.6 | 57230.74 | 269443.6 | 350896.9334 | 0 | 0 | 63342.05924 | 4012.489546 | 356452.6782 | 181527.0275 | 187240.1192 | 36908.3578 | 57078.61 | 171572.6966 | 716764.0672 | 377840.6005 | 90530.38758 | 546923.3628 | 249251.4458 | 81978.24527 | 136563.8574 | 9892.025088 | 74892.2889 | 13759.22204 | 93518.96628 | 97979.84651 | ||
| Q6ZMH5 | 1 | 1 | 15.21 | 0.848311759 | 4.842626868 | HN | XA | Zinc transporter ZIP5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC39A5 PE=2 SV=3 | 106731 | 25689.81 | 15972.15 | 89862.89 | 118282.6804 | 30656.70915 | 14124.72061 | 35372.41852 | 17504.76935 | 233396.224 | 72774.19662 | 49116.76697 | 71.3477706 | 1289691.271 | 47988.72509 | 348300.0149 | 68371.2936 | 89797.61595 | 34867.8542 | 37936.11643 | 56225.23 | 9220.45833 | 95747.82176 | 36855.31776 | 72227.22335 | 59866.67547 | 74698.83947 | ||
| Q495M3 | 1 | 1 | 15.06 | 0.64073756 | 1.973569484 | HN | XA | Proton-coupled amino acid transporter 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC36A2 PE=1 SV=1 | 124434.8 | 8042.688 | 65312.12 | 13997.64 | 5067.927868 | 32025.26886 | 50826.46237 | 13693.43835 | 6653.979797 | 71143.8492 | 131152.3659 | 33586.16031 | 5455.663823 | 376005.7156 | 50.29194179 | 0 | 8819.41583 | 5435.903698 | 81221.60808 | 31474.08193 | 101681.4383 | 3599.54633 | 38411.04457 | 0 | 12788.73665 | 67704.1906 | 79884.27925 | ||
| Q92585 | 1 | 1 | 15.05 | 0.97934946 | 7.832298235 | XA | HN | Mastermind-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAML1 PE=1 SV=3 | 829.5903 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 159127.5126 | 16128.10782 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 372.4704529 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7525.912488 | 0 | 0 | 14583.5509 | 0 | 1028.378333 | 0 | 0 | 13290.04748 | 96511.08211 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q9NP84 | 1 | 1 | 14.98 | 0.30686187 | 4.719351111 | HN | XA | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 12A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF12A PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 4044.969 | 4389.905 | 0 | 5525.447891 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2991.689501 | 0 | 35443.57904 | 4243.423274 | 11057.89785 | 4320.045863 | 14673.28393 | 10264.26212 | 0 | 0 | 2293.357895 | 2.40124E-05 | 4018.459866 | 3900.412397 | 10803.75511 | 11804.48523 | 4006.057601 | 12455.91373 | 0 | ||
| O43310 | 3 | 2 | 14.82 | 0.001127955 | 2.305678902 | HN | XA | CBP80/20-dependent translation initiation factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTIF PE=1 SV=1 | 42764880 | 17958217 | 11120601 | 10744981 | 8942917.75 | 14210405.2 | 19598449.72 | 14344287.87 | 18125478.56 | 59148354.73 | 47572710.18 | 22324770.05 | 46557246.98 | 68930348.43 | 21573870.26 | 53549949.64 | 17268989.84 | 26933451.39 | 27028188.82 | 19847651.6 | 30137804.76 | 26102155.91 | 37785700.81 | 21476774.34 | 44094986.6 | 24072727.98 | 40794361.33 | ||
| Q8NFH3 | 2 | 2 | 14.63 | 0.675305302 | 1.131490781 | HN | XA | Nucleoporin Nup43 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NUP43 PE=1 SV=1 | 558866.1 | 195707.5 | 273666.9 | 403507 | 743966.0195 | 654050.6033 | 507738.9084 | 722994.0252 | 755757.6407 | 585488.0992 | 1373959.703 | 359689.6153 | 829702.1073 | 161557.2666 | 586466.2088 | 448419.2524 | 407693.9423 | 696571.6484 | 290957.1807 | 346921.5148 | 197263.5692 | 303930.7722 | 1930272.24 | 504616.6713 | 181645.594 | 335781.9769 | 848415.3007 | ||
| B0YJ81 | 3 | 2 | 14.59 | 0.442590255 | 1.230239583 | HN | XN | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPLA PE=1 SV=1 | 296178.2 | 324091.1 | 300277 | 527608.5 | 555205.1993 | 563380.6309 | 468087.3347 | 268584.4874 | 244900.6634 | 198058.911 | 394891.5764 | 467985.8468 | 411368.9008 | 889117.9091 | 315629.9164 | 230286.5372 | 337798.3446 | 307468.0219 | 427518.2815 | 197693.8405 | 285680.5823 | 276259.683 | 361516.4572 | 106482.9889 | 516539.3542 | 366593.045 | 349450.8188 | ||
| Q6ZMZ3 | 7 | 1 | 14.56 | 0.528201377 | 1.550245602 | XN | XA | Nesprin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SYNE3 PE=1 SV=2 | 194232.7 | 62276.55 | 148340.9 | 253653.9 | 171106.7216 | 272234.6156 | 133469.068 | 145694.0809 | 204451.8859 | 129175.8811 | 382235.4807 | 195533.7979 | 308354.7109 | 27780.36764 | 173968.5664 | 346308.5847 | 121993.9269 | 151089.9158 | 220307.5319 | 347772.0436 | 121088.4456 | 88273.90031 | 86348.06973 | 586636.1917 | 265751.1776 | 271762.9725 | 469912.8259 | ||
| Q9H1B5 | 4 | 1 | 14.46 | 0.00644731 | 2.323095484 | XN | XA | Xylosyltransferase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=XYLT2 PE=2 SV=2 | 123439.4 | 164986.1 | 139443.8 | 87275.41 | 75525.52398 | 52851.27719 | 123430.798 | 65810.66559 | 277772.5403 | 232306.5708 | 815781.8553 | 103589.2521 | 263247.6145 | 270395.7731 | 183201.2734 | 128504.4888 | 202781.7946 | 259190.9465 | 98123.36825 | 204129.3831 | 216597.5562 | 150002.5079 | 280450.8991 | 592884.6969 | 412251.1748 | 385802.7358 | 239637.7981 | ||
| Q9P2D8 | 7 | 1 | 14.4 | 0.506598067 | 2.003880616 | XN | HN | Protein unc-79 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=UNC79 PE=2 SV=3 | 725287.4 | 208805.9 | 126723.5 | 97224.12 | 156458.6745 | 3350461.867 | 276899.5332 | 177575.1923 | 324967.0327 | 180852.2241 | 63203.515 | 112896.6792 | 126587.2501 | 202353.3422 | 149205.066 | 55732.44627 | 199729.9905 | 2359411.925 | 597067.1644 | 1422127.33 | 1130160.943 | 158331.5899 | 563589.3144 | 4250.769938 | 167283.3171 | 1386346.966 | 1484175.501 | ||
| P15529 | 2 | 2 | 14.18 | 0.767239274 | 1.139981825 | XA | HN | Membrane cofactor protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD46 PE=1 SV=3 | 523573.8 | 969311.7 | 990233.2 | 91438.74 | 251568.2633 | 468333.039 | 483394.0014 | 460313.3614 | 274209.4562 | 193309.2087 | 810628.4463 | 740492.5108 | 571752.4702 | 360323.3802 | 507725.0933 | 109369.3637 | 303798.6497 | 360888.0835 | 280450.3769 | 457255.2881 | 637155.5382 | 643435.6778 | 875122.5684 | 421814.1596 | 521406.6009 | 406151.6729 | 235428.2861 | ||
| Q6PIJ6 | 2 | 2 | 14.15 | 0.301163938 | 1.338618907 | XN | XA | F-box only protein 38 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXO38 PE=1 SV=3 | 177768.5 | 155019.8 | 258048.2 | 62418.86 | 29393.20337 | 222210.7922 | 270372.2317 | 104210.2828 | 509861.7213 | 288874.2887 | 387872.3046 | 119241.0983 | 210890.3857 | 206687.7611 | 172288.3333 | 112133.9772 | 156240.2424 | 312297.0311 | 124229.7879 | 202624.0788 | 266984.3557 | 189058.1234 | 134230.8456 | 495364.9896 | 226561.2912 | 462753.7911 | 293388.315 | ||
| P26718 | 1 | 1 | 14.12 | 0.269118308 | 1.612818937 | XN | XA | NKG2-D type II integral membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLRK1 PE=1 SV=1 | 11433.57 | 78650.33 | 35722.46 | 5891.969 | 36675.57176 | 21175.68073 | 13399.64078 | 6776.940873 | 8147.67227 | 85996.78533 | 0 | 11323.4337 | 13007.02124 | 31729.70043 | 12714.18686 | 0 | 137644.6785 | 48325.75156 | 118789.1721 | 25795.0908 | 38830.34004 | 46139.3319 | 1228.639606 | 56400.34135 | 15503.97062 | 25497.97961 | 23206.17939 | ||
| P0CG01 | 1 | 1 | 13.99 | 0.300585274 | 12.80531116 | XA | HN | Gastrokine-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GKN3P PE=3 SV=1 | 0 | 1575.596 | 800.9175 | 0 | 534877.2886 | 1578.117018 | 5711.344896 | 3993.501688 | 16628.07115 | 0 | 0 | 3649.452275 | 0 | 26035.70444 | 0 | 5342.90562 | 54.62937943 | 9052.497955 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7844.427925 | 0 | 238012.0846 | 0 | 0 | 13324.70302 | ||
| P22307 | 2 | 2 | 13.66 | 0.551867616 | 1.176334834 | HN | XN | Non-specific lipid-transfer protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 286446.1 | 219383.4 | 263578.1 | 175765.6 | 206198.0471 | 264919.6269 | 318338.2475 | 264786.9548 | 202606.0899 | 356305.5776 | 239473.8413 | 412677.3562 | 160420.7227 | 161425.0039 | 231408.1514 | 397407.1625 | 156521.3453 | 110688.2307 | 192279.7109 | 155728.8217 | 241648.3764 | 232322.0215 | 238533.3606 | 152147.2021 | 119816.4268 | 337421.2381 | 222699.5137 | ||
| A4D1E1 | 1 | 1 | 13.55 | 0.062837764 | 1.661237181 | HN | XA | Zinc finger protein 804B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF804B PE=1 SV=2 | 3574923 | 7871400 | 11908883 | 6146549 | 14211337.11 | 7375127.484 | 4761526.837 | 5186458.127 | 4188871.293 | 7569745.059 | 11828070.11 | 7835009.379 | 15256469.26 | 9800232.765 | 8065652.097 | 31524868.13 | 8819181.869 | 7655090.183 | 9028956.74 | 6230663.905 | 6509216.733 | 16876708.52 | 10550581.61 | 13517627.58 | 8300050.828 | 13887622.49 | 6736483.159 | ||
| P36969 | 1 | 1 | 13.48 | 0.506038172 | 2.040053136 | XA | HN | Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPX4 PE=1 SV=3 | 315662.3 | 14747.31 | 80899.75 | 196351.2 | 51660.94511 | 75411.7865 | 145942.7442 | 266540.2378 | 83985.98844 | 109487.0635 | 52623.00233 | 127410.0328 | 21907.00677 | 75572.55421 | 61394.91175 | 94395.8808 | 18318.81043 | 42405.52264 | 30350.54423 | 62580.97448 | 339029.7323 | 8108.889142 | 184259.8958 | 2272.232471 | 150343.6745 | 194282.6816 | 98340.86068 | ||
| P61968 | 1 | 1 | 13.33 | 0.250744471 | 1.814143213 | XN | XA | LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LMO4 PE=1 SV=1 | 682269.6 | 108251.5 | 290106.2 | 429137.9 | 111006.2987 | 283055.6817 | 714924.5973 | 485672.2313 | 363856.943 | 1423677.211 | 209028.2501 | 171672.8432 | 253526.3112 | 1266779.876 | 348681.2048 | 531547.9814 | 1062460.332 | 541418.485 | 1013474.671 | 162299.6585 | 967458.5959 | 1279123.47 | 831990.4096 | 172699.1575 | 763387.399 | 519721.1116 | 581803.7072 | ||
| Q96GG9 | 3 | 3 | 13.1 | 0.24381214 | 2.133256379 | HN | XA | DCN1-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCUN1D1 PE=1 SV=1 | 2908942 | 3735353 | 5599814 | 3583058 | 4826753.387 | 947424.1332 | 375365.2586 | 1109174.947 | 853693.0933 | 3407959.555 | 1224447.924 | 3480943.101 | 1633853.703 | 4397369.839 | 5769070.321 | 24942769.79 | 4094228.952 | 2118612.374 | 1144204.549 | 2164462.511 | 1461752.687 | 2643652.869 | 6497556.578 | 5610040.271 | 4441897.597 | 2913306.377 | 3442255.342 | ||
| Q9NS15 | 2 | 2 | 10.24 | 0.191502122 | 1.677357577 | XA | HN | Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTBP3 PE=1 SV=4 | 1078141 | 2116958 | 906639.9 | 1746547 | 2741708.695 | 694660.455 | 421074.9912 | 1824138.894 | 1186068.03 | 748946.9637 | 668306.486 | 1264814.495 | 569703.0025 | 1300714.08 | 696128.3946 | 1174966.238 | 721476.571 | 435877.7691 | 1300041.85 | 1302320.635 | 351457.244 | 2171745.574 | 579128.7718 | 1726588.648 | 419595.3169 | 574157.7558 | 380044.9311 | ||
| P18850 | 4 | 2 | 9.92 | 0.046005826 | 5.906627299 | XA | XN | Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-6 alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATF6 PE=1 SV=3 | 8339.503 | 16446.93 | 3885.505 | 7150.069 | 27486.38616 | 399433.1151 | 552457.3939 | 37867.79775 | 56321.11881 | 328.4526145 | 15128.68721 | 202262.7943 | 2767.610015 | 16637.48966 | 3717.238941 | 304907.41 | 78513.50853 | 1259.930378 | 158974.1162 | 13378.23695 | 6567.834706 | 2799.848878 | 3601.381545 | 269.1603619 | 1688.984448 | 117.1458043 | 424.1515561 | ||
| Q12802 | 7 | 2 | 8.54 | 0.620857974 | 2.373416839 | XN | XA | A-kinase anchor protein 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKAP13 PE=1 SV=2 | 45898.23 | 135854.4 | 88863.54 | 55650.63 | 191475.2591 | 174987.3017 | 125512.2105 | 109942.9135 | 101032.3718 | 64136.04813 | 119676.4848 | 324034.6183 | 104249.7917 | 68754.60658 | 953629.3035 | 129254.6001 | 144578.3556 | 156195.0547 | 1441395.289 | 69081.71164 | 84954.47354 | 102650.6284 | 109454.9458 | 352906.8274 | 24660.51198 | 136482.393 | 121173.7115 | ||
| P98174 | 3 | 1 | 7.2 | 0.566619775 | 1.366413411 | XA | HN | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 5810.282 | 43270.74 | 188385.2 | 9529.431 | 59802.32834 | 27746.95381 | 0 | 6891.51647 | 2455.201359 | 7304.893549 | 0 | 10134.0746 | 53731.38235 | 25348.97578 | 49472.78326 | 25641.77118 | 67987.66368 | 12053.14314 | 4806.65368 | 15093.70273 | 27318.87557 | 49723.14869 | 14021.60498 | 81635.72185 | 96032.10722 | 8729.985629 | 34734.58649 | ||
| Q9H741 | 1 | 1 | 6.97 | 0.063463957 | 1.883715912 | HN | XA | UPF0454 protein C12orf49 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C12orf49 PE=2 SV=1 | 242957.6 | 69419.33 | 39815.69 | 76241.56 | 72625.43146 | 73307.19554 | 77965.5493 | 109520.1758 | 85920.62389 | 513203.5726 | 260394.371 | 122315.0083 | 105329.7875 | 166011.6436 | 78379.59476 | 112924.6557 | 99294.40626 | 139110.7655 | 116359.2024 | 118042.6713 | 133324.5169 | 65923.22322 | 152875.6859 | 58129.19797 | 94126.90412 | 103181.9487 | 203742.4641 | ||
| Q9H223 | 3 | 1 | 5.42 | 0.172919932 | 1.361348659 | HN | XA | EH domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EHD4 PE=1 SV=1 | 0 | 0 | 2309.004 | 54566.81 | 19507.0059 | 30864.82763 | 27906.4406 | 36981.74763 | 39948.05799 | 6285.367926 | 9520.999159 | 48178.99492 | 40995.45616 | 66590.38434 | 8051.077472 | 12484.72373 | 21896.96086 | 74716.16067 | 2701.872648 | 20245.40495 | 41180.96337 | 11695.79535 | 32834.80154 | 5783.134755 | 45955.07617 | 57140.52419 | 32964.81916 | ||
| Q92547 | 4 | 2 | 4.77 | 0.272826457 | 1.985795506 | HN | XN | DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TOPBP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 151319.3 | 566118.4 | 165090.3 | 112263.4 | 835801.6656 | 57883.86356 | 30917.27058 | 17669.49981 | 955.7047715 | 529969.7862 | 244757.5264 | 23954.56342 | 89255.91335 | 49239.76305 | 812852.1182 | 1621766.193 | 242365.2068 | 206517.6396 | 196662.7712 | 34574.87699 | 208210.402 | 232286.5013 | 268189.7832 | 38527.1077 | 365198.2535 | 224258.7227 | 356095.6886 | ||
| Q6ZP01 | 5 | 2 | 4.7 | 0.367124523 | 1.621446662 | XN | XA | RNA-binding protein 44 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBM44 PE=2 SV=2 | 845237 | 1131709 | 260228 | 468405.2 | 1605951.154 | 1504325.466 | 1021754.032 | 525250.7782 | 738982.7722 | 1463524.08 | 615248.7194 | 978733.754 | 220272.2829 | 1690779.365 | 1426920.337 | 537008.8412 | 1628420.351 | 2800855.665 | 1402390.979 | 1503216.498 | 2237149.456 | 1540727.728 | 1871675.662 | 331550.3851 | 528709.2788 | 1202558.918 | 2518728.159 | ||
| P49862 | 2 | 1 | 4.58 | 0.544310812 | 2.182989943 | XA | XN | Kallikrein-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK7 PE=1 SV=1 | 9307.9 | 69641.83 | 96.21897 | 51956.4 | 34030.18815 | 86201.98032 | 322694.5886 | 185560.3395 | 176175.4787 | 238952.8955 | 123944.5827 | 12184.40471 | 56445.99775 | 75641.46231 | 18437.71101 | 4186.810778 | 353.6381095 | 13638.6265 | 223576.8601 | 0.346479047 | 1744.726356 | 67431.14131 | 16814.77645 | 32159.80267 | 50328.81685 | 17739.69977 | 18820.05935 | ||
| O95372 | 3 | 1 | 4.41 | 0.182873621 | 22.6678827 | XN | HN | Acyl-protein thioesterase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPLA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 384665.8 | 177618.2 | 213719.5 | 266236.3 | 504302.0119 | 452261.3146 | 1245895.483 | 586594.6051 | 527929.2253 | 236512.1147 | 250290.6518 | 104224.0956 | 235545.9523 | 195883.1671 | 344311.4358 | 666561.6208 | 232061.7645 | 155609.2124 | 177320.0437 | 10362448.02 | 130159.0599 | 42269760.61 | 201572.9702 | 438705.421 | 331031.8824 | 264564.0687 | 703382.2919 | ||
| P16109 | 5 | 3 | 4.33 | 0.639826306 | 1.749614882 | XN | XA | P-selectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SELP PE=1 SV=3 | 1135226 | 596769.6 | 644421.8 | 193211.2 | 916925.5785 | 907973.0788 | 1362657.973 | 781512.3409 | 1011816.173 | 1629931.711 | 1428511.978 | 398275.4073 | 2123384.34 | 1286067.35 | 1006401.534 | 1025164.378 | 625455.2127 | 613224.9952 | 437363.3682 | 6811897.141 | 410621.7546 | 471886.6395 | 1101601.702 | 706732.0675 | 1180343.375 | 896071.9924 | 1193973.638 | ||
| Q9NZM3 | 8 | 2 | 4.22 | 0.320953742 | 89.82190377 | XN | HN | Intersectin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITSN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 5122.133 | 0 | 7357.743 | 1326.748 | 182.8293297 | 33889.31661 | 27523.11929 | 2807.502628 | 12902.98801 | 1660.637427 | 19180.66933 | 720.3972862 | 8924.240001 | 4341.458347 | 8013.872046 | 0 | 9699.151989 | 11610.33033 | 5817.3478 | 4466778.363 | 2318.331931 | 5615.856283 | 1851.396863 | 4531.764375 | 1302.885164 | 4904.090027 | 1269023.064 | ||
| P61567 | 2 | 1 | 3.08 | 0.765570727 | 2.938936059 | XA | XN | HERV-K_1q22 provirus ancestral Env polyprotein OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 1993.938 | 34338.91 | 20612.58 | 0 | 21760.15386 | 190750.1545 | 332939.8126 | 11508.28909 | 26326.45883 | 13509.25883 | 0 | 33958.90251 | 8081.736966 | 19211.71276 | 10628.64242 | 328277.0834 | 0 | 18841.16632 | 12359.82285 | 30276.20762 | 51903.74727 | 24198.35814 | 8037.480356 | 68662.42536 | 22406.1998 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q86TI2 | 3 | 1 | 2.89 | 0.028484438 | 725.1040396 | XN | HN | Dipeptidyl peptidase 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPP9 PE=1 SV=3 | 9981.507 | 10.49779 | 0 | 0 | 0.160321307 | 113.4010504 | 45.46552052 | 68.60484597 | 394.4292172 | 24.5256379 | 0 | 3.397977933 | 0 | 3.165043343 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.660589209 | 94.34036039 | 38.58135752 | 1533.748525 | 21597.57394 | 0 | 165.8833551 | 0 | 9.185878125 | 307.2988846 | ||
| Q96GP6 | 2 | 1 | 2.88 | 0.659258137 | 61.82682062 | HN | XA | Scavenger receptor class F member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCARF2 PE=1 SV=4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3063.597 | 0 | 631.0267863 | 9105.203143 | 380.3279026 | 280.4779496 | 161.3841806 | 0 | 661234.2907 | 133688.9581 | 74.50302781 | 0 | 36672.1694 | 0 | 396.804191 | 0 | 1084.758244 | 2781.555925 | 37718.21324 | 58.90819317 | 1745.807839 | 1247.896025 | 0 | 45.77506514 | ||
| O60749 | 5 | 3 | 2.52 | 0.158240903 | 2.821852733 | HN | XA | Sorting nexin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SNX2 PE=1 SV=2 | 19815.83 | 15115.33 | 130240.3 | 49173.48 | 46634.08354 | 36745.31513 | 64881.28141 | 27666.10025 | 36512.51701 | 5027.170393 | 64225.1722 | 196202.8778 | 39712.24218 | 195113.622 | 139982.1497 | 28869.94782 | 427602.2164 | 107586.7478 | 130599.0651 | 71884.74739 | 51136.0071 | 160384.1686 | 15809.49801 | 315834.5476 | 110486.3636 | 75874.44704 | 209333.5147 | ||
| A4D161 | 3 | 1 | 2.42 | 0.144564185 | 1.574867486 | XN | HN | Protein FAM221A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM221A PE=2 SV=1 | 2880544 | 2189995 | 302000.3 | 106076.3 | 450494.0045 | 5497203.667 | 228917.6134 | 442520.6446 | 1019968.447 | 959351.7366 | 279732.185 | 1924152.805 | 583417.9476 | 2229121.225 | 1882088.738 | 678956.6544 | 1126732.284 | 3026119.803 | 2307911.451 | 3235036.209 | 5239658.269 | 1804792.276 | 1017472.485 | 1227144.648 | 462107.968 | 2201006.614 | 2489424.096 | ||
| P08842 | 3 | 1 | 2.41 | 0.295370988 | 1.875925066 | XA | XN | Steryl-sulfatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=STS PE=1 SV=2 | 62508.05 | 149833.5 | 27296.5 | 55429.74 | 357238.1102 | 124228.0174 | 70672.36235 | 212243.0362 | 1632780.721 | 420295.0811 | 417390.8876 | 801969.2855 | 262966.9267 | 111641.6472 | 198625.5075 | 91838.5087 | 199135.443 | 95387.68446 | 637918.5372 | 99102.09532 | 71656.67876 | 86471.81135 | 82218.49371 | 113300.6381 | 65888.64871 | 65892.92124 | 212698.1213 | ||
| O15394 | 4 | 3 | 1.92 | 0.782087551 | 1.534212028 | HN | XN | Neural cell adhesion molecule 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCAM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2092437 | 689353 | 277798.9 | 1424727 | 1071862.958 | 1559783.701 | 745053.0822 | 633447.575 | 1435424.45 | 5614028.44 | 464884.5984 | 536475.7889 | 1183870.064 | 1342115.643 | 604947.6721 | 1553216.263 | 563357.5099 | 986772.6382 | 1510295.513 | 1180574.113 | 585500.1987 | 1195209.994 | 1572038.005 | 276638.0794 | 567350.8906 | 709936.0187 | 777876.2223 | ||
| Q96PZ7 | 2 | 1 | 1.71 | 0.761666634 | 1.227216062 | HN | XN | CUB and sushi domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSMD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 126410.8 | 242261.4 | 1273956 | 459638.9 | 494999.8577 | 82075.32373 | 181936.5903 | 256036.4807 | 108455.2273 | 272325.7529 | 104913.7639 | 129997.9234 | 122301.095 | 658463.0727 | 517859.8044 | 499859.5837 | 758226.6582 | 264582.7536 | 225466.5395 | 43398.09938 | 105701.523 | 411801.4001 | 558057.7855 | 587647.3799 | 531271.6551 | 164331.3248 | 84585.41053 | ||
| Q9P2F8 | 3 | 1 | 1.52 | 0.938789707 | 1.118444652 | XN | XA | Signal-induced proliferation-associated 1-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SIPA1L2 PE=1 SV=2 | 447246.8 | 575955.7 | 646644.7 | 1410387 | 753276.2843 | 648047.5034 | 237493.1432 | 429720.343 | 363403.5745 | 812504.4488 | 219634.028 | 1504526.951 | 1198814.745 | 247788.8523 | 298805.7019 | 823848.4431 | 349020.1976 | 283741.3215 | 281727.2133 | 445490.646 | 272098.3165 | 1854345.981 | 424226.9337 | 1274792.992 | 760076.9289 | 455037.0496 | 397267.193 | ||
| Q6NXP0 | 3 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.553504862 | 1.529606732 | XA | XN | EF-hand calcium-binding domain-containing protein 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFCAB12 PE=2 SV=1 | 4381798 | 5101301 | 15708873 | 1278338 | 6914726.945 | 4179411.391 | 3855496.107 | 5102175.302 | 1748798.13 | 4155378.75 | 1381293.098 | 4828405.528 | 1543914.952 | 5845487.098 | 5038030.794 | 11101119.92 | 6697877.39 | 6519383.686 | 3077106.112 | 2112211.736 | 4004340.756 | 3944156.874 | 5063468.177 | 1258597.211 | 3310841.948 | 4921074.53 | 3865933.37 | ||
| P17693 | 2 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.451575058 | 2.535704897 | XN | XA | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-G PE=1 SV=1 | 159143.7 | 350468.6 | 1161661 | 195746.2 | 75571.41614 | 495661.3937 | 565653.3458 | 233974.2011 | 363625.675 | 316748.1037 | 835079.3268 | 2083286.279 | 512815.7855 | 798989.9642 | 123329.7903 | 24098.11993 | 1868497.952 | 394115.6147 | 238088.5914 | 764261.8354 | 445863.6408 | 438803.4506 | 397170.6806 | 4149812.764 | 2168827.954 | 306137.4453 | 223389.1037 | ||
| P17040 | 3 | 2 | 0.41 | 0.609736532 | 1.241671939 | HN | XA | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZSCAN20 PE=2 SV=3 | 94386.39 | 131458.5 | 124938.4 | 20414.45 | 141665.6473 | 244841.3925 | 154646.4064 | 63160.85163 | 126251.8606 | 54653.9704 | 157256.0976 | 174846.2894 | 187374.6761 | 254027.7641 | 89172.69921 | 167794.178 | 166714.4759 | 116189.2041 | 225881.811 | 81236.7284 | 175621.403 | 61590.05804 | 195581.0264 | 30751.97418 | 341983.7835 | 106570.3178 | 74091.01434 | ||
| Q9GZN4 | 2 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.401851374 | 8.832998869 | XN | XA | Brain-specific serine protease 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRSS22 PE=1 SV=1 | 43560.98 | 227370.5 | 151419.9 | 104508.2 | 166517.8367 | 439031.4323 | 191545.1141 | 81202.12501 | 62771.77964 | 111808.3969 | 160697.7812 | 82907.02028 | 81838.0182 | 163594.6026 | 277698.7973 | 393849.6834 | 159528.4406 | 898050.0025 | 60083.24811 | 3701077.606 | 46326.59147 | 89057.28543 | 1758796.452 | 138537.9316 | 68393.49633 | 174750.3009 | 6929182.861 | ||
| P01778 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.359332125 | 1.79556191 | XN | XA | Ig heavy chain V-III region ZAP OS=Homo sapiens PE=1 SV=1 | 59558.99 | 409117.6 | 331851.3 | 337648 | 95050.24305 | 170834.1985 | 98512.04432 | 170206.4219 | 65116.02677 | 520550.0999 | 128413.2994 | 667144.8059 | 192160.2448 | 62626.15995 | 507066.1717 | 222454.4662 | 124429.2736 | 405374.394 | 338525.0442 | 433462.8901 | 232361.929 | 113035.5899 | 288236.7325 | 237709.8489 | 1198983.539 | 222594.6508 | 55587.47803 | ||
| Q8NCL4 | 1 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.567977836 | 98.80865717 | XA | HN | Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GALNT6 PE=2 SV=2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2740578.587 | 5734674.28 | 971317.3786 | 90856.47385 | 0 | 90716.45368 | 3628.501842 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2179.245821 | 579879.2598 | 20292.80037 | 915.0467494 | 45973.30703 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Q9NQX5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.539754953 | 1.176165326 | XA | XN | Neural proliferation differentiation and control protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NPDC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 2574602 | 3280697 | 1898819 | 1632020 | 2625448.509 | 2257607.191 | 3458208.919 | 3166581.696 | 4912304.416 | 2835935.568 | 1564129.125 | 4991183.086 | 2255302.934 | 1133003.126 | 2368617.506 | 891762.7124 | 2556822.887 | 3966039.564 | 4004901.96 | 3479450.432 | 1646358.678 | 916912.6299 | 4249659.271 | 2363305.924 | 1401846.724 | 1989163.352 | 1889439.732 | ||
"
| Accession | Regional difference | Ratio | P | Description | XA1 | XA2 | XA3 | XA4 | XA5 | XA6 | XA7 | XA8 | XA9 | HN1 | HN2 | HN3 | HN4 | HN5 | HN6 | HN7 | HN8 | HN9 | XN1 | XN2 | XN3 | XN4 | XN5 | XN6 | XN7 | XN8 | XN9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P20618 | XA/HN | 32.64 | 0.005 | Proteasome subunit beta type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 89715.08495 | 21992.45053 | 56788.27015 | 49725.56938 | 40553.20898 | 2513739.568 | 5091629.182 | 596067.9257 | 195164.2194 | 13145.26363 | 14785.33875 | 22732.44404 | 30563.64293 | 7809.652894 | 39946.5564 | 46629.72034 | 35342.25915 | 54208.58322 | 985719.5348 | 27940.35752 | 50636.71072 | 118757.3999 | 37293.84215 | 2991.247241 | 26734.826 | 45125.5574 | 22227.98159 |
| P52788 | XA/XN | 23.65 | 0.002 | Spermine synthase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMS PE=1 SV=2 | 27970.24031 | 3027.054552 | 2021.22945 | 383987.0519 | 23927.46772 | 12887.00901 | 16125.17373 | 18514.37207 | 13768.22293 | 0 | 38402.7067 | 81552.4803 | 4872.657996 | 0 | 882.7301366 | 1399.119827 | 0 | 9756.091398 | 88.97690527 | 0 | 421.053926 | 1788.675587 | 18404.22758 | 0 | 528.5727973 | 0 | 0 |
| P51580 | XA/HN; XA/XN | 8.62;8.24 | 0.012;0.019 | Thiopurine S-methyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPMT PE=1 SV=1 | 38870.16959 | 8418.834725 | 12801.35891 | 243801.3108 | 2878.978414 | 96114.56353 | 75845.91586 | 140362.3104 | 53398.2946 | 0 | 12516.44363 | 16271.7968 | 12814.17882 | 29183.71765 | 0 | 4244.935578 | 1330.506386 | 1610.320101 | 3003.472558 | 6382.652979 | 2669.284978 | 23177.97242 | 13815.59374 | 6639.982955 | 4942.130076 | 3018.353577 | 17965.99981 |
| P30048 | HN/XN | 7.70 | 0.038 | Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX3 PE=1 SV=3 | 76630.71754 | 5806.409197 | 19772.70404 | 161047.199 | 43531.20574 | 22594.22009 | 13064.28519 | 58309.34837 | 104669.7079 | 140419.4013 | 112131.5403 | 1580029.652 | 263683.934 | 566425.3742 | 66576.94273 | 412799.2879 | 8262.481298 | 22011.78877 | 15792.73226 | 105.3827486 | 8789.453923 | 39295.39049 | 30527.51593 | 218891.5643 | 32430.54633 | 22649.11553 | 43438.95601 |
| P31944 | XA/HN | 5.98 | 0.031 | Caspase-14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CASP14 PE=1 SV=2 | 275501.4015 | 245947.4103 | 185259.286 | 592993.5652 | 251081.6342 | 471825.7083 | 6020743.646 | 1456198.894 | 2841876.606 | 355501.1323 | 357167.931 | 332546.2192 | 183482.057 | 211286.9141 | 166192.8098 | 260199.413 | 86653.74674 | 109326.4294 | 465092.9219 | 198224.3002 | 258574.5687 | 1435763.989 | 177710.1961 | 123991.8754 | 212971.2054 | 357647.3468 | 151096.5821 |
| Q9UBN7 | XA/XN | 3.68 | 0.002 | Histone deacetylase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HDAC6 PE=1 SV=2 | 404278.4975 | 254830.3826 | 384491.8254 | 837592.0647 | 761393.9862 | 159645.4764 | 233981.5356 | 292711.7296 | 109756.3323 | 71280.05268 | 38245.03085 | 92804.78816 | 82700.24509 | 157666.2001 | 219329.5576 | 3888888.886 | 487087.4326 | 184511.1148 | 96149.24347 | 45559.68296 | 68164.02815 | 97944.23204 | 360274.5693 | 30960.84649 | 63311.5586 | 52772.3868 | 118278.4236 |
| P04040 | HN/XN | 4.14 | 0.015 | Catalase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAT PE=1 SV=3 | 408763.368 | 215118.8757 | 151433.796 | 1306015.184 | 254561.6348 | 1895998.411 | 4249031.309 | 1152616.173 | 3968680.742 | 382417.4525 | 409094.6291 | 5953423.974 | 885424.4965 | 477566.8948 | 1417199.301 | 237087.2872 | 1047851.832 | 513673.1593 | 547525.1114 | 202179.7728 | 261727.875 | 566662.9452 | 351343.1819 | 148988.0134 | 294418.2825 | 221184.4295 | 143518.0926 |
| P98082 | XA/XN;HN/XN | 0.24;0.20 | 0.006 | Disabled homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DAB2 PE=1 SV=3 | 71390.33737 | 29642.33941 | 41217.9543 | 16957.7984 | 20940.79066 | 29948.94936 | 69508.6759 | 81339.46891 | 32060.50763 | 35435.30486 | 37863.67298 | 39947.93331 | 30042.51167 | 25698.73747 | 29092.09502 | 24741.03326 | 19508.35306 | 93440.17936 | 49727.58785 | 233404.8373 | 89794.07088 | 248676.1764 | 357354.234 | 17085.94163 | 23034.40719 | 347213.5344 | 279818.6735 |
| Q92597 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 4.00;4.36 | 0.009;0.019 | Protein NDRG1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NDRG1 PE=1 SV=1 | 281783.3343 | 18814.32207 | 140403.0534 | 1201875.262 | 158967.1912 | 211717.8501 | 239589.241 | 448209.853 | 171558.2412 | 77016.25836 | 22562.04508 | 269307.3898 | 47046.05004 | 20571.67599 | 94900.32698 | 92753.31214 | 32013.34492 | 62574.67001 | 45514.76753 | 41136.06493 | 93489.03475 | 82380.36227 | 210054.2635 | 6793.210883 | 65972.56345 | 49349.57407 | 64569.96985 |
| P30153 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 4.18;3.65 | 0.029;0.041 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 65 kDa regulatory subunit A alpha isoform OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPP2R1A PE=1 SV=4 | 135050.1521 | 12658.85901 | 84426.00623 | 441817.1282 | 38416.06112 | 65602.10013 | 79424.21505 | 266339.8456 | 161756.8967 | 54783.35394 | 24474.52676 | 49491.5888 | 50790.9206 | 12194.18759 | 31451.22615 | 61502.48121 | 5207.49712 | 17357.09487 | 18769.96713 | 14160.12111 | 43360.51075 | 10112.73526 | 120742.4932 | 1654.131134 | 71709.86225 | 41603.28605 | 29644.87182 |
| Q9BQI0 | XA/XN | 4.13 | 0.049 | Allograft inflammatory factor 1-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=AIF1L PE=1 SV=1 | 104682.2807 | 28098.58714 | 70738.9935 | 546349.4192 | 46332.71166 | 123901.8177 | 114226.09 | 219360.7172 | 92368.61764 | 92610.47084 | 77945.18848 | 208382.999 | 58676.2431 | 94782.00203 | 28797.63129 | 7585.18382 | 12699.99907 | 62177.10583 | 45581.38893 | 26758.87457 | 52224.68003 | 77132.1835 | 44760.30279 | 13775.0942 | 13200.51923 | 32204.47238 | 20333.01798 |
| P34913 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 4.03;3.17 | <0.01 | Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPHX2 PE=1 SV=2 | 2370420.886 | 732419.3273 | 887685.6426 | 3922648.991 | 1731683.279 | 3522389.842 | 2787456.826 | 4377232.422 | 2387898.605 | 1211482.691 | 330969.49 | 1498429.635 | 263536.0256 | 798896.6756 | 592043.4506 | 431837.8194 | 343355.1144 | 161137.8774 | 88397.34595 | 231914.8745 | 1777195.743 | 1367177.577 | 889956.0805 | 344056.6605 | 1242301.394 | 955729.163 | 267073.0607 |
| P68036 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 0.34;0.27 | 0.014;0.007 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 L3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBE2L3 PE=1 SV=1 | 21569329.67 | 16571967.36 | 23268704.28 | 8478521.091 | 3517328.94 | 28901574.54 | 36031145.82 | 14415715.72 | 26197194.86 | 46521982.21 | 97784472.07 | 136794383.7 | 48980520.33 | 82112810.32 | 15375705.08 | 22298144.13 | 59915170.02 | 17134862.64 | 24584057.19 | 46332779.39 | 45848887.23 | 28856095.24 | 43831535.94 | 324278749 | 105486568.8 | 25354616.43 | 28670203.26 |
| P24298 | XA/HN | 3.73 | 0.023 | Alanine aminotransferase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPT PE=1 SV=3 | 605666.56 | 347620.8917 | 372170.6159 | 675084.6207 | 157411.8133 | 3213261.3 | 2070506.946 | 2450101.928 | 1384443.736 | 596611.5642 | 253991.1848 | 288186.6199 | 494914.321 | 261388.7609 | 321347.8589 | 139355.3786 | 319219.1264 | 344385.9355 | 905164.4554 | 719095.8522 | 1556885.841 | 1674315.361 | 647656.4401 | 376313.8242 | 547292.382 | 271584.8993 | 235622.694 |
| P04424 | XA/HN | 3.69 | 0.021 | Argininosuccinate lyase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASL PE=1 SV=4 | 379303.6392 | 273951.8214 | 506174.1958 | 1999722.112 | 363372.4133 | 3064994.106 | 2207794.602 | 3586480.792 | 1376397.755 | 845984.2561 | 120497.1004 | 1111466.578 | 245597.067 | 277517.2108 | 472869.9004 | 155290.2007 | 251201.6035 | 246398.8645 | 823804.9001 | 851829.7676 | 1985831.898 | 2271971.33 | 849079.2221 | 408364.2945 | 501417.0033 | 391965.9957 | 179928.9822 |
| Q15262 | XA/HN | 0.30 | 0.016 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase kappa OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPRK PE=1 SV=2 | 6346086.454 | 3623399.375 | 6146240.047 | 3822753.913 | 4105065.332 | 4421698.059 | 4561330.221 | 2756432.281 | 8225692.835 | 15010264.68 | 44589842.08 | 10564856.1 | 18192713.54 | 7819675.857 | 3636999.578 | 24973259.11 | 15313638.86 | 5918109.219 | 6795504.341 | 11844605.28 | 7478133.572 | 17759914.19 | 6440977.118 | 13981651.61 | 5512837.364 | 15331526.5 | 14162064.21 |
| O14686 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 3.18;2.98 | 0.042;0.038 | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MLL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1325088.158 | 17379211.73 | 13279996.89 | 4672655.705 | 27599170.84 | 9762860.583 | 1947566.645 | 6486103.62 | 2972822.92 | 2885595.075 | 3033749.825 | 1299777.153 | 1289450.077 | 2235662.123 | 6640845.429 | 4783608.888 | 2020098.035 | 2636900.947 | 3472694.815 | 3944913.547 | 1591652.607 | 978430.2498 | 5139520.171 | 9586061.637 | 1667877.997 | 1317319.713 | 930250.8558 |
| P02675 | XA/XN | 3.69 | <0.001 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 3819433.329 | 5094343.442 | 3560043.203 | 5353567.378 | 5093210.826 | 3134837.287 | 2447187.523 | 5828585.98 | 2530145.559 | 3502048.996 | 438905.6488 | 7539414.887 | 479699.26 | 999402.4022 | 4732626.529 | 2292389.048 | 1524806.089 | 877184.3189 | 2920013.711 | 920491.073 | 683870.1071 | 319623.7625 | 1759430.832 | 1412270.953 | 2518903.86 | 889986.4019 | 512942.6662 |
| Q9GZM5 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 3.05 | 0.019 | Protein YIPF3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=YIPF3 PE=1 SV=1 | 5015659.829 | 25107869.45 | 21639484.24 | 7019464.156 | 5033916.481 | 5630708.29 | 17570670.97 | 5494778.286 | 32175722.02 | 2055384.336 | 5772845.427 | 2270618.392 | 4150022.007 | 3019234.009 | 4582086.327 | 3557126.467 | 5729570.497 | 9750702.626 | 2475048.855 | 7744260.536 | 5812246.197 | 3242563.022 | 3932415.725 | 11580010.73 | 3235452.805 | 16516410.49 | 6496403.389 |
| P19652 | XA/HN;HN/XN | 0.37;3.02 | 0.019;0.009 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ORM2 PE=1 SV=2 | 990356.77 | 2782663.771 | 2572427.157 | 1745311.472 | 10796733.74 | 1153241.288 | 792278.9953 | 1329177.3 | 1003987.481 | 2475384.044 | 2472545.889 | 3398376.24 | 4120916.318 | 2244251.657 | 4287676.918 | 33607425.63 | 3781676.454 | 7021715.097 | 1344987.894 | 2453717.794 | 1559672.933 | 5487802.551 | 1884474.247 | 2027533.641 | 3108485.294 | 1571384.863 | 1580449.135 |
| Q06278 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.59;2.97 | 0.031;0.009 | Aldehyde oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AOX1 PE=2 SV=2 | 1010327.918 | 166998.0771 | 1036184.399 | 2118114.709 | 802074.1135 | 1113724.88 | 368869.9114 | 1212327.229 | 344214.9321 | 65396.77193 | 105913.7541 | 491432.5029 | 1319056.475 | 123668.7715 | 354619.8504 | 334171.6811 | 283107.7535 | 79777.38723 | 255636.1739 | 174964.1629 | 231958.7594 | 618650.5769 | 267687.1228 | 170518.5761 | 472294.3882 | 367133.1929 | 193185.7706 |
| P42330;P52895;Q04828 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.96;2.22 | 0.002;0.012 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1C3 PE=1 SV=4 | 3664160.006 | 745151.7835 | 1896833.111 | 5839211.788 | 1314640.701 | 3190250.993 | 2870115.357 | 5655678.654 | 4162343.987 | 1086543.996 | 752531.2524 | 1176037.672 | 1969948.231 | 534984.0673 | 812228.8931 | 1798134.645 | 1021380.912 | 746313.0081 | 1242439.166 | 940902.1888 | 2247210.451 | 1327761.342 | 3156573.551 | 357960.6072 | 1879770.757 | 891871.2208 | 1141750.364 |
| O75891 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.94;2.45 | 0.015;0.023 | Cytosolic 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDH1L1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3060594.657 | 534134.8056 | 1576229.849 | 5847916.75 | 892781.7586 | 2247025.23 | 1739226.811 | 3755615.633 | 1691563.588 | 759727.3108 | 596247.0394 | 1259715.312 | 2040917.538 | 486227.4181 | 562255.4273 | 788898.4532 | 476526.6328 | 279151.439 | 938553.6926 | 554598.0705 | 1243585.656 | 654006.3473 | 1749202.423 | 774363.562 | 1154291.464 | 829408.3251 | 829939.1873 |
| Q99536 | XA/HN | 2.86 | 0.015 | Synaptic vesicle membrane protein VAT-1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VAT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 499893.8297 | 219485.2291 | 364427.3487 | 1433108.425 | 130982.1327 | 795035.7675 | 866996.1082 | 1506445.9 | 626384.7549 | 592108.9947 | 157113.0549 | 309394.6711 | 237259.9609 | 215532.6053 | 208763.1701 | 143897.6791 | 269966.4223 | 119345.5161 | 609448.3432 | 706749.199 | 560838.6537 | 652787.4238 | 303333.9687 | 151625.4695 | 187991.2634 | 167564.822 | 351000.3572 |
| Q14697 | XA/HN | 2.85 | 0.012 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Homo sapiens GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=3 | 213343.4499 | 82828.01905 | 149525.1828 | 319536.7134 | 115137.7716 | 261360.8119 | 958538.1638 | 367937.8265 | 188225.3823 | 18243.88971 | 17729.40222 | 11478.68104 | 114820.8034 | 46494.98208 | 164764.5862 | 304704.3907 | 111628.0121 | 142854.8491 | 111324.4793 | 88047.16942 | 143748.7591 | 13429.2049 | 192280.3132 | 49691.54791 | 437192.9417 | 141473.9578 | 160064.2302 |
| P17858 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.81;2.29 | 0.010;0.020 | 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFKL PE=1 SV=6 | 978256.8034 | 180608.1189 | 641485.5993 | 2627866.017 | 702317.8278 | 676226.1244 | 433026.2416 | 1241435.712 | 621465.4725 | 260698.905 | 261098.0355 | 410480.9219 | 488060.992 | 173167.3 | 454945.0166 | 491878.7649 | 125429.4207 | 214659.3657 | 294555.5343 | 161584.2884 | 637749.6845 | 168805.505 | 683272.4589 | 138574.8817 | 526994.1296 | 314143.5615 | 608782.8429 |
| Q8TEU7 | XA/HN | 0.36 | 0.008 | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAPGEF6 PE=1 SV=2 | 1714004.793 | 1664498.768 | 2602122.261 | 306959.6838 | 598723.2462 | 1317085.312 | 1888888.142 | 850870.6009 | 1785273.969 | 5703245.527 | 8713048.861 | 4950599.323 | 4185179.085 | 2795380.646 | 1510974.205 | 479925.6726 | 3844069.553 | 3546673.454 | 3237689.433 | 2113245.022 | 2914533.043 | 2572687.49 | 1462470.24 | 2247275.913 | 2638426.09 | 2783506.065 | 3037389.976 |
| Q14117 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.76;2.07 | 0.009;0.033 | Dihydropyrimidinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPYS PE=1 SV=1 | 545694.4239 | 271002.1176 | 518662.4525 | 1668182.82 | 121766.6432 | 775574.4176 | 755972.4939 | 1171135.678 | 1076347.73 | 205295.4612 | 176479.9858 | 361132.9277 | 546338.3639 | 358211.7875 | 311390.5391 | 203431.6024 | 214733.0344 | 127220.499 | 329995.0914 | 170628.2898 | 434953.1516 | 655952.2872 | 519191.2313 | 323888.6752 | 493660.71 | 222123.1722 | 183672.3749 |
| P06744 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.44;2.65 | 0.009;0.007 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPI PE=1 SV=4 | 4517588.2 | 1111114.401 | 3293215.909 | 7513023.098 | 1983713.279 | 2169453.247 | 3013875.77 | 4962468.848 | 2730260.695 | 1834567.624 | 1227374.144 | 1967291.149 | 1153837.804 | 517428.8221 | 2939179.66 | 1674408.284 | 892171.9208 | 594606.2284 | 819103.4401 | 635035.8874 | 1398729.897 | 717658.2064 | 3024686.425 | 934480.3814 | 2553081.433 | 781090.3682 | 939277.7686 |
| P19801 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.56;2.20 | 0.006;0.018 | Amiloride-sensitive amine oxidase [copper-containing] OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 10550360.57 | 4375727.789 | 5464946.013 | 2719353.852 | 11358794.77 | 5436726.969 | 3900475.31 | 4107271.231 | 2685322.026 | 1615072.61 | 1156147.701 | 2665100.575 | 2054915.817 | 1452244.231 | 3013209.942 | 1622386.826 | 2689185.053 | 3460725.391 | 1838520.266 | 2596711.307 | 1968224.111 | 1427660.08 | 5007835.321 | 1973166.04 | 4941559.284 | 2066703.031 | 1203050.075 |
| P30039 | XA/HN | 2.56 | 0.008 | Phenazine biosynthesis-like domain-containing protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PBLD PE=1 SV=2 | 6015110.906 | 6583559.488 | 6047653.379 | 11223560.3 | 2766846.514 | 20204173.18 | 16223029.39 | 16223449.5 | 7630370.893 | 8417452.543 | 2864836.081 | 5934047.799 | 3364634.579 | 4948391.626 | 2714213.009 | 1666140.246 | 3901227.258 | 2456066.878 | 7492068.343 | 5923429.397 | 12637019.46 | 22773300.88 | 6692501.065 | 1805295.037 | 3214549.952 | 6368721.12 | 2668850.563 |
| Q8WUM4 | XA/XN | 2.50 | 0.015 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6IP PE=1 SV=1 | 1823165.278 | 581025.626 | 1205299.374 | 1402252.331 | 1068639.93 | 8917852.809 | 1593022.16 | 2220441.486 | 986796.0007 | 785213.0105 | 1293505.042 | 1674656.199 | 755700.7223 | 1798392.43 | 461386.2199 | 950787.6538 | 413794.9222 | 588091.3216 | 959218.5372 | 842475.2175 | 766616.2556 | 474228.3791 | 562417.0834 | 460070.7908 | 1054797.921 | 1047239.032 | 1738275.075 |
| Q9Y3B3 | XA/HN | 2.48 | 0.036 | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TMED7 PE=1 SV=2 | 52908.93385 | 558530.0409 | 366415.4046 | 126082.6193 | 133469.2746 | 182286.4518 | 134492.4178 | 107827.4102 | 217606.5764 | 25544.54766 | 52708.64321 | 52119.85574 | 65528.32486 | 138399.0342 | 128456.4591 | 55130.90877 | 105865.1027 | 132683.3302 | 88738.29124 | 68323.03256 | 61086.61454 | 126016.3045 | 95337.95498 | 580945.0263 | 228504.1838 | 99309.29663 | 84999.30419 |
| P98172 | XA/HN | 2.45 | 0.024 | Ephrin-B1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFNB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 392467.8077 | 4183207.734 | 3005808.728 | 1184638.654 | 1175091.962 | 1658777.064 | 2284362.408 | 955071.3253 | 3470976.684 | 294442.8404 | 981099.026 | 492779.8416 | 935314.5518 | 642466.2786 | 1280985.418 | 722181.6995 | 782158.4916 | 1338235.067 | 505351.755 | 1006351.905 | 597208.2582 | 1114779.554 | 1032832.921 | 2096258.509 | 707293.2417 | 1198846.508 | 913309.9311 |
| P01031 | XA/XN | 2.41 | 0.031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 1142725.24 | 1942156.536 | 1273295.285 | 521507.7598 | 4183787.589 | 553197.3255 | 546796.3828 | 808991.3928 | 507771.3831 | 811566.7376 | 726068.8782 | 481248.6001 | 593277.9622 | 1854198.274 | 784900.5353 | 618578.5213 | 1202672.392 | 1140578.197 | 624002.4354 | 425471.9354 | 492051.1756 | 291216.5173 | 745731.442 | 489352.5019 | 401584.5997 | 593176.8717 | 699403.687 |
| P61604 | HN/XN | 2.38 | 0.032 | 10 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPE1 PE=1 SV=2 | 579152.783 | 97235.89797 | 1440142.169 | 1060359.767 | 649459.3057 | 616205.0882 | 441942.752 | 290723.7101 | 296615.4514 | 2102926.154 | 817872.5391 | 2632010.421 | 458823.4085 | 414908.3888 | 1273845.859 | 617161.2918 | 656515.5944 | 767297.1577 | 701964.6421 | 476678.5394 | 261990.3189 | 357132.1431 | 638862.1934 | 673631.1053 | 391376.4746 | 292705.7372 | 301523.9855 |
| P28332 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.32;2.34 | 0.022;0.019 | Alcohol dehydrogenase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADH6 PE=2 SV=2 | 1561678.238 | 423501.3464 | 466684.8341 | 2865503.425 | 319483.9235 | 1454630.107 | 1708853.007 | 2186025.294 | 2384555.35 | 985004.2836 | 175954.5865 | 1439234.381 | 948996.2987 | 351652.6272 | 353167.559 | 361438.0764 | 584096.2778 | 567486.0804 | 894876.6943 | 536295.6062 | 1271354.015 | 795524.0079 | 872551.1085 | 160359.6241 | 545594.3693 | 276551.0873 | 350419.4795 |
| Q8N201 | XA/XN | 0.43 | <0.001 | Integrator complex subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=INTS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 15560338.69 | 10773723.46 | 5075840.672 | 14127881.66 | 7348245.912 | 11570925.53 | 6758024.203 | 9172429.633 | 9058864.49 | 14156756.43 | 29313464.92 | 9883872.375 | 14614225.29 | 17267856.08 | 14630370.49 | 14476786.05 | 30021949.99 | 31692594.17 | 21033456.45 | 24474996.35 | 26065165.11 | 20729986.21 | 20066439.52 | 17533860.26 | 29470475.24 | 30023039.95 | 19492684.85 |
| O43895 | XA/XN | 0.43 | <0.001 | Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=XPNPEP2 PE=1 SV=3 | 35541949.81 | 21678616.85 | 11524698.38 | 38917743.66 | 14596074.6 | 28561539.38 | 18877627.93 | 23773591.28 | 21004531.31 | 39189431.63 | 79869221.82 | 23487010.07 | 31104135.58 | 40366580.01 | 28041129.38 | 21838727.09 | 68126683.07 | 74055422.25 | 51599138.15 | 60764397.71 | 62570030.77 | 53615713.1 | 49870883.36 | 42835091.27 | 63341833.84 | 67801563.85 | 45034841.91 |
| Q10567 | XA/HN;HN/XN | 2.25;0.43 | 0.039;0.003 | AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AP1B1 PE=1 SV=2 | 123650.9139 | 65394.85388 | 64511.22335 | 238153.7573 | 568680.1783 | 520650.1346 | 219342.7442 | 613625.513 | 339108.263 | 249635.9957 | 19329.1406 | 228742.3666 | 117800.5295 | 116750.2584 | 96503.00885 | 92371.62014 | 124294.3433 | 175478.7094 | 491495.4121 | 369590.8953 | 310769.264 | 178115.3994 | 215852.5517 | 240390.0681 | 146362.3759 | 358447.9976 | 515279.4241 |
| Q02083 | XA/XN | 0.44 | <0.001 | N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAAA PE=1 SV=3 | 984560.9003 | 328637.7415 | 896324.0032 | 789979.6752 | 410105.4005 | 684705.7589 | 749127.7037 | 733830.7832 | 677016.7672 | 1106342.599 | 1328095.908 | 630695.9482 | 2130551.874 | 2066029.589 | 622627.9841 | 1464743.976 | 931220.2757 | 959093.4946 | 1386998.143 | 901062.7736 | 1785730.419 | 1356936.282 | 1634019.327 | 2232090.621 | 2593309.691 | 1100160.851 | 1331326.436 |
| P60709;P63261 | XA/XN | 2.29 | 0.011 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 107623747.2 | 26671995.4 | 38269533.72 | 112023489.9 | 23789580.84 | 57245129.22 | 62781048.49 | 129535352.8 | 62590410.88 | 76494806.33 | 35888231.49 | 82061322.74 | 46191281.45 | 43592499.82 | 42586841.36 | 18842880.74 | 22451345.2 | 24712472.25 | 22449946.17 | 29822570.39 | 49189819.94 | 37489970.27 | 46190304.86 | 11094443.12 | 23555881.64 | 28309974.46 | 23038829.01 |
| P32189;Q14409 | XA/HN;XA/XN | 2.29;2.04 | 0.009;0.022 | Glycerol kinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GK PE=1 SV=3 | 264241.1079 | 96897.31459 | 134819.4095 | 323587.6285 | 84045.12157 | 514651.5677 | 503697.5493 | 312332.4692 | 419990.2997 | 165339.4462 | 163313.9572 | 132084.9476 | 115131.529 | 78379.12131 | 125098.867 | 123133.2299 | 156501.8115 | 101099.002 | 229753.4445 | 86393.33108 | 148995.4997 | 135851.9338 | 264047.8509 | 160544.388 | 115970.4225 | 69918.58886 | 91495.00929 |
| P10768 | XA/XN | 2.26 | <0.001 | S-formylglutathione hydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ESD PE=1 SV=2 | 2156454.809 | 1393787.339 | 924387.273 | 2895141.773 | 1235525.993 | 1569747.838 | 1842903.551 | 1238741.167 | 1218002.792 | 1081141.005 | 909548.0098 | 1415209.376 | 523587.5379 | 905298.6373 | 1340419.926 | 753884.5183 | 635118.0363 | 633973.1071 | 900804.1614 | 684289.7139 | 737453.8156 | 718662.5352 | 796203.2167 | 414917.9076 | 987337.5155 | 720334.8984 | 440655.8761 |
| Q96DG6 | XA/HN | 2.25 | 0.009 | Carboxymethylenebutenolidase homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=CMBL PE=1 SV=1 | 2010623.853 | 489666.6766 | 1173503.82 | 2130991.374 | 618296.364 | 2605559.176 | 2583643.31 | 3714776.595 | 1863137.56 | 777801.6195 | 1026233.069 | 1332170.092 | 1103920.231 | 843541.7609 | 293469.4271 | 951662.869 | 794804.4862 | 529159.8761 | 770637.3545 | 2924121.707 | 1185692.443 | 1544837.381 | 1924014.355 | 953644.4928 | 1530114.003 | 858821.2364 | 1497208.765 |
| Q9UBQ7 | XA/HN | 2.20 | 0.019 | Glyoxylate reductase/hydroxypyruvate reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRHPR PE=1 SV=1 | 3604271.569 | 1071460.239 | 1979141.497 | 6966828.849 | 1056775.618 | 2892369.196 | 3885221.429 | 5231889.68 | 2639809.294 | 2451787.506 | 1528168.675 | 2586165.558 | 1304417.883 | 870252.5148 | 1199421.786 | 1785516.177 | 736785.1814 | 848142.3477 | 1509619.167 | 801071.8872 | 3008611.876 | 2018843.99 | 3147055.686 | 683874.6471 | 1615364.778 | 1441912.52 | 942081.6222 |
| Q9HBT6 | XA/HN | 0.45 | 0.020 | Cadherin-20 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDH20 PE=2 SV=2 | 3345014.738 | 1935191.239 | 1272064.291 | 2821874.557 | 1094177.399 | 2573066.72 | 4056570.535 | 791748.2898 | 3370994.257 | 8674344.44 | 10490967.16 | 5282544.479 | 4626058.076 | 7661011.636 | 2851714.971 | 1302496.52 | 2648202.726 | 3296322.962 | 6990570.764 | 3014579.281 | 4692648.637 | 2992453.941 | 1676556.753 | 2512711.823 | 4204920.084 | 4464610.305 | 4744152.465 |
| Q96KN2 | XA/HN | 0.46 | 0.032 | Beta-Ala-His dipeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNDP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 164875.8543 | 447157.8489 | 469388.8333 | 190644.755 | 800786.4362 | 364178.579 | 224879.7383 | 156686.9574 | 358277.1629 | 551749.8785 | 495589.3894 | 1260012.34 | 270622.8603 | 634967.9145 | 615834.6613 | 442229.6346 | 1866144.24 | 812473.8855 | 633918.5893 | 631672.8818 | 1287658.39 | 414565.2397 | 681181.7633 | 1133157.54 | 422655.8097 | 567831.675 | 543322.5697 |
| Q8N114 | XA/HN | 2.17 | 0.042 | Protein shisa-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHISA5 PE=2 SV=1 | 10296453.77 | 86828325.41 | 71717611.02 | 30707654.79 | 20640146.58 | 32158420.36 | 71218359.02 | 16689136.45 | 89539636.13 | 7142471.93 | 21756699.44 | 5143695.433 | 27546534.91 | 25770658.11 | 25456643.21 | 10247150.74 | 19624407.66 | 54972909.51 | 18756877.02 | 51752817.07 | 34947618.71 | 33372457.04 | 39603822.48 | 58491329.35 | 36746484.52 | 66570502.68 | 28908150.9 |
| Q8TCD5 | XA/HN | 2.13 | 0.030 | 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase, cytosolic type OS=Homo sapiens GN=NT5C PE=1 SV=2 | 987458.0759 | 710968.9946 | 1213041.665 | 3343622.38 | 931998.2931 | 728535.1367 | 1490346.161 | 1449488.338 | 974635.7952 | 244625.8671 | 352131.2966 | 451272.0953 | 369559.0198 | 813250.1445 | 1012313.083 | 1229928.528 | 646534.5955 | 441613.5828 | 604268.4336 | 1343706.849 | 1552075.587 | 367969.8303 | 274905.36 | 275966.9264 | 860403.0507 | 569240.5212 | 825434.2652 |
| Q9H6S3 | XA/HN | 2.12 | 0.021 | Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EPS8L2 PE=1 SV=2 | 974870.7413 | 352406.6407 | 612598.1821 | 1911969.78 | 309753.8354 | 641153.8807 | 1016309.207 | 1757094.028 | 952882.5148 | 234486.8505 | 604400.6073 | 335566.5826 | 424591.1866 | 623311.1268 | 626317.0712 | 597922.9298 | 334990.5734 | 236546.0353 | 369661.076 | 229797.6355 | 413473.6205 | 535116.9203 | 334640.7807 | 862170.8695 | 1038957.552 | 376842.5722 | 1108031.965 |
| O00560 | XA/XN | 0.47 | 0.002 | Syntenin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDCBP PE=1 SV=1 | 152732259.7 | 84877566.78 | 149931101.8 | 125658261.1 | 58421807.48 | 82056405.2 | 104168417.6 | 112865293.7 | 105696325.4 | 208291918.1 | 137055892.8 | 79499912.79 | 137046727.6 | 330019775.9 | 54314211.39 | 173070288 | 182279362.3 | 241839206.6 | 261674214.3 | 182170268.7 | 363954634.3 | 278979489.9 | 137865837 | 78616625.24 | 185280125.9 | 220232752.6 | 348449038.2 |
| P20933 | XA/HN | 2.11 | 0.017 | N(4)-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AGA PE=1 SV=2 | 386162.4872 | 641101.9238 | 580937.0611 | 418145.1579 | 306462.3876 | 788189.0176 | 980746.1925 | 256033.0872 | 1247523.817 | 119381.8433 | 415149.2554 | 270870.5584 | 515786.4056 | 397460.559 | 180351.2974 | 58538.6298 | 269516.1457 | 434489.8638 | 1450663.561 | 395752.41 | 271442.9161 | 264805.1876 | 132604.0439 | 421921.2705 | 368769.5592 | 487597.0481 | 290888.2419 |
| P08174 | XA/HN | 2.09 | 0.041 | Complement decay-accelerating factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD55 PE=1 SV=4 | 10984079.21 | 82981843.13 | 80979722.86 | 24610648.87 | 25075928.77 | 31717274.2 | 19477839.73 | 29705011.44 | 35088786.68 | 9588867.378 | 16401190.18 | 22914677 | 15424070.72 | 13483591.56 | 25826594.08 | 13178661.24 | 21574372.31 | 24784714.05 | 18742614.91 | 24835942.97 | 20312313.66 | 34027257.23 | 23509749.34 | 67900927.6 | 20277985.8 | 27370778.13 | 23327626.26 |
| O14786 | XA/HN | 2.09 | 0.040 | Neuropilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NRP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 273480.8262 | 79356.23519 | 56629.09439 | 120500.9981 | 51490.95906 | 112555.6681 | 90985.42731 | 110270.3781 | 100838.2163 | 6225.931816 | 2882.531451 | 12345.51462 | 119285.4034 | 1545.552941 | 149894.4784 | 26804.48281 | 91703.4684 | 67043.34105 | 98810.31574 | 70873.79487 | 95310.69148 | 37070.16705 | 115572.7035 | 11903.48258 | 144512.0389 | 97290.1003 | 150117.6944 |
| Q14108 | XA/HN | 2.08 | 0.009 | Lysosome membrane protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCARB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 48956.94488 | 22889.27019 | 38245.03869 | 64257.14916 | 83357.25695 | 80486.75371 | 50751.11573 | 80867.32293 | 42223.82237 | 35446.9576 | 28151.25544 | 26986.31513 | 28578.70773 | 75020.49035 | 5713.236762 | 9830.122921 | 19040.21519 | 17567.5226 | 29388.94372 | 16379.58952 | 37779.46208 | 78368.62417 | 12401.04981 | 51552.05637 | 38132.08128 | 14828.4861 | 52715.01114 |
"
| Male samples | Female samples | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Description | Ratio | p | XA1 | XA2 | XA3 | XA4 | XA5 | HN5 | HN6 | HN7 | HN8 | HN9 | XN5 | XN6 | XN7 | XN8 | XN9 | XA6 | XA7 | XA8 | XA9 | HN1 | HN2 | HN3 | HN4 | XN1 | XN2 | XN3 | XN4 | |
| P07288 | Prostate-specific antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK3 PE=1 SV=2 | 13.50263 | 0.020747 | 1.8E+08 | 1.34E+08 | 90163193 | 5.19E+08 | 2.42E+09 | 2.82E+08 | 3.64E+08 | 2.18E+08 | 2.39E+08 | 7.85E+08 | 1.55E+08 | 2.34E+08 | 2.35E+08 | 4.86E+08 | 3.36E+08 | 14424923 | 15200688 | 67284507 | 12594483 | 1.81E+08 | 11243152 | 16766540 | 15228453 | 16570992 | 12954545 | 18352369 | 13287581 | |
| P11684 | Uteroglobin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCGB1A1 PE=1 SV=1 | 11.92568 | 9.9E-05 | 4551073 | 14026178 | 7434851 | 15721978 | 26156237 | 16847906 | 57703164 | 49845069 | 14948556 | 9754939 | 16035087 | 16811755 | 27280884 | 22867019 | 25535569 | 906314.3 | 495968.8 | 934383.7 | 342108.1 | 7615044 | 809862.4 | 6499422 | 956895.8 | 491189.8 | 730343.1 | 831158.7 | 1223908 | |
| P08118 | Beta-microseminoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSMB PE=1 SV=1 | 10.26998 | 0.00125 | 3724114 | 10591323 | 3133790 | 6960441 | 24803643 | 13628445 | 26147124 | 3804670 | 12536370 | 39320984 | 5927206 | 46889714 | 6475990 | 19381569 | 11748858 | 531892.3 | 538604.1 | 3588300 | 860617.3 | 4929084 | 338217.5 | 3586298 | 2179673 | 501638.3 | 489963.2 | 356542 | 410736.2 | |
| P20151 | Kallikrein-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK2 PE=2 SV=1 | 10.25825 | 0.00158 | 554706.2 | 1073715 | 519183.5 | 1873425 | 7176985 | 1387565 | 1675060 | 2867412 | 810091.2 | 4810830 | 981917 | 968084.3 | 2794359 | 2482836 | 1177482 | 118655.3 | 66836.59 | 58241.61 | 77283.27 | 871304.5 | 140427.8 | 95693.27 | 90930.68 | 188927.8 | 338499.1 | 195463.7 | 187286.5 | |
| P08709 | Coagulation factor VII OS=Homo sapiens GN=F7 PE=1 SV=1 | 5.574545 | 0.000156 | 993744.3 | 8867434 | 7538803 | 1405904 | 8152313 | 1842530 | 5229472 | 4808538 | 2028481 | 4831323 | 4862125 | 2201118 | 1670810 | 3553045 | 2754432 | 1114884 | 458598.3 | 685486.2 | 904222 | 716387.9 | 1410126 | 238962.8 | 546759.9 | 353430.9 | 1040841 | 606449.1 | 640628.1 | |
| P01033 | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TIMP1 PE=1 SV=1 | 3.345794 | 0.008724 | 2654833 | 2296294 | 2736019 | 4826204 | 19520879 | 5516484 | 5407978 | 5779500 | 4105778 | 5631713 | 1752572 | 3224136 | 4472448 | 4485808 | 3631993 | 708345.8 | 871142.3 | 2651267 | 1160075 | 4396061 | 1114479 | 1740254 | 1149035 | 1983607 | 930121.4 | 584101.5 | 893771.5 | |
| P07942 | Laminin subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.481737 | 3.6E-05 | 523452.3 | 1135687 | 592651.7 | 666350.4 | 710354.5 | 365323.1 | 776001.7 | 354540.6 | 452045.6 | 489490.5 | 584488.6 | 762448.5 | 460020.7 | 738007.9 | 754379.8 | 2068339 | 1183368 | 800350.3 | 1426419 | 857052.3 | 1091924 | 1614146 | 832067.5 | 1154160 | 2131407 | 1558237 | 834976.6 | |
| P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.402299 | 1.58E-06 | 5363817 | 1738099 | 3362638 | 6724783 | 2123814 | 4374267 | 3042570 | 1851618 | 1803463 | 2210824 | 3531471 | 1707746 | 2197865 | 2386784 | 2550466 | 6851699 | 8607937 | 11624085 | 9298773 | 7625438 | 7991177 | 9638167 | 6994128 | 6929632 | 3440388 | 5593901 | 4831117 | |
| O95171 | Sciellin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCEL PE=1 SV=2 | 0.302925 | 5.97E-05 | 782014.8 | 617018.6 | 574561.4 | 655415 | 260402 | 1414707 | 1005027 | 531080.1 | 494321.5 | 989950.8 | 788545.4 | 2571354 | 564077.1 | 1551299 | 898569.6 | 1417592 | 6825005 | 3284557 | 2608383 | 2907671 | 1930664 | 1751539 | 2173948 | 5206830 | 3505346 | 1967618 | 2597041 | |
| Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ECM1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.259532 | 0.000598 | 2487016 | 3831640 | 2924237 | 2543544 | 2209129 | 2388427 | 1474538 | 1429936 | 1689856 | 2181254 | 2167698 | 5038453 | 2532918 | 4665619 | 2499065 | 5411840 | 15799834 | 11819629 | 8171594 | 4326086 | 9343024 | 7310365 | 5895089 | 31750755 | 10187185 | 7239144 | 6239640 | |
| Q9NQ79 | Cartilage acidic protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRTAC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.256252 | 0.008925 | 3756476 | 1262346 | 1434804 | 1337628 | 697046.3 | 1534023 | 1514142 | 607839.8 | 926921.6 | 1458716 | 1528398 | 616879 | 1319164 | 1583922 | 998495.3 | 2748720 | 7158444 | 6501593 | 3965548 | 1789154 | 3180854 | 3039474 | 4300551 | 21785911 | 2829735 | 3256808 | 3682532 | |
| P20810 | Calpastatin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAST PE=1 SV=4 | 0.244432 | 6.38E-05 | 62112.14 | 42315.38 | 45077.66 | 176714.5 | 60472.05 | 35869.44 | 44485.84 | 48051.61 | 55535.42 | 48852.03 | 106846.4 | 85152.93 | 51984.01 | 32868.36 | 34039.4 | 92500.57 | 240875.5 | 575276.9 | 246544 | 175562.6 | 471908.1 | 226193 | 371179.4 | 144666.3 | 105058.9 | 265033.9 | 130225.5 | |
| P10599 | Thioredoxin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TXN PE=1 SV=3 | 0.205731 | 1E-07 | 9419799 | 5345811 | 8149808 | 9110886 | 2755230 | 8602446 | 3826277 | 2096808 | 4542386 | 5521727 | 6502223 | 11439138 | 5677165 | 8274976 | 4839006 | 34499029 | 60080082 | 28457388 | 39516723 | 13260581 | 36815642 | 30576337 | 30677916 | 13734183 | 38656540 | 20090345 | 27342153 | |
| P04632 | Calpain small subunit 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPNS1 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.204208 | 0.024304 | 1022065 | 563831.7 | 422624.5 | 973819.1 | 603574.3 | 404007.2 | 550280.9 | 639590.1 | 352684.5 | 480517.4 | 341634.4 | 323917.2 | 469746.6 | 346490.8 | 435275.2 | 1285105 | 1605311 | 4121776 | 1884162 | 3366183 | 662378.1 | 1475032 | 1275297 | 12645855 | 725172.2 | 870294.5 | 1150093 | |
| Q96P63 | Serpin B12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB12 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.199988 | 7.83E-05 | 815613.7 | 1027203 | 448611.8 | 2093159 | 487955.5 | 653287.3 | 477705.7 | 1909395 | 335805.5 | 663313.6 | 612657.6 | 1218403 | 1096403 | 838622 | 768000.3 | 3428379 | 8066450 | 6443330 | 10670577 | 1695098 | 2696571 | 2977012 | 3151183 | 7335210 | 2475175 | 1704535 | 3144265 | |
| P34932 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA4 PE=1 SV=4 | 0.195764 | 4.7E-06 | 42888.09 | 21643.18 | 34290.29 | 87418.61 | 35867.77 | 61161.88 | 67431.58 | 50723.88 | 42517.51 | 22320.1 | 47866.59 | 33081.12 | 67548.21 | 19748.66 | 33320.22 | 122343.8 | 333540 | 496138.3 | 330372.9 | 114611.1 | 136786.6 | 144311.1 | 141834.8 | 143014 | 311076.2 | 174518.4 | 280571.2 | |
| P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOA PE=1 SV=2 | 0.191907 | 0.001709 | 3481574 | 2103855 | 2105703 | 4981014 | 2107937 | 2397645 | 4117391 | 1417954 | 1439181 | 1996842 | 1462054 | 817641.8 | 2647794 | 1804361 | 1709100 | 6387516 | 11336145 | 16597374 | 10966411 | 29118122 | 5714216 | 7897419 | 3388115 | 37255384 | 6002392 | 4729891 | 4801718 | |
| P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.186587 | 2.31E-05 | 24661997 | 7595601 | 10853687 | 54685316 | 8509778 | 10811826 | 8164346 | 21899251 | 13181876 | 11604914 | 21827780 | 7407107 | 17958132 | 16417880 | 13770935 | 56848091 | 96193779 | 2.35E+08 | 95048369 | 53447136 | 35065916 | 1.08E+08 | 1.21E+08 | 83319925 | 50490227 | 57283573 | 77697246 | |
| Q01469;A8MUU1 | Fatty acid-binding protein, epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=FABP5 PE=1 SV=3 | 0.160214 | 8.54E-05 | 12389195 | 4031133 | 2838949 | 6503818 | 2181357 | 9223699 | 4291812 | 7051096 | 5716543 | 8760068 | 6728745 | 4007160 | 7464158 | 8065491 | 11332945 | 29381400 | 1.11E+08 | 30876805 | 69196174 | 11122145 | 69647016 | 44659099 | 37876633 | 10229560 | 31572436 | 15858055 | 41194195 | |
| O95274 | Ly6/PLAUR domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYPD3 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.159815 | 1.42E-06 | 588946.4 | 1272356 | 809747.7 | 372895.3 | 590190.1 | 620876.9 | 548424.1 | 361966.4 | 549538 | 989712.1 | 681199 | 1794597 | 528735.5 | 910318.5 | 746446.8 | 3960756 | 7361348 | 2922387 | 9765820 | 3966898 | 4068476 | 2322696 | 5101154 | 7144407 | 6058375 | 1534438 | 2688650 | |
| P31949 | Protein S100-A11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A11 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.147725 | 0.008298 | 1391437 | 1104851 | 1307414 | 2672485 | 2111482 | 1339570 | 2571647 | 2390872 | 1406143 | 1825479 | 1394948 | 1660838 | 2328811 | 899560.1 | 1218319 | 4006971 | 7450679 | 13319204 | 11674749 | 18514513 | 8439737 | 4662090 | 5731621 | 51528182 | 4432965 | 3868162 | 5135985 | |
| Q9UIV8 | Serpin B13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB13 PE=2 SV=2 | 0.146765 | 0.000322 | 1227899 | 1432957 | 1050177 | 1186825 | 729066.8 | 1581541 | 998199.2 | 1106457 | 1158837 | 1098515 | 857092.7 | 2337755 | 877681 | 1174972 | 1673741 | 4736423 | 13109370 | 14168344 | 9659715 | 4921770 | 5234183 | 6262184 | 3742249 | 26209356 | 4863228 | 2824884 | 5064309 | |
| Q13765;Q9BZK3 | Nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=NACA PE=1 SV=1 | 0.140802 | 0.000203 | 109614 | 2724.263 | 1575.66 | 111587 | 107795.6 | 34099.45 | 27649.23 | 63301.7 | 74278.64 | 140062.3 | 25283.22 | 126969.6 | 30565.67 | 94817.4 | 36068.34 | 223663 | 583832.2 | 1178639 | 544955.4 | 366397.2 | 190853.6 | 594653.2 | 222890.3 | 1112862 | 138316.2 | 227043.2 | 220312.6 | |
| P07355;A6NMY6 | Annexin A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.124772 | 2.6E-05 | 5773205 | 6270428 | 4735017 | 5730988 | 6427542 | 6801270 | 5744900 | 5569869 | 5803992 | 7621912 | 3686686 | 5684860 | 6170726 | 8845123 | 8953885 | 38660729 | 98014039 | 55074193 | 45734609 | 23016160 | 29545655 | 34861928 | 33295045 | 1.3E+08 | 25071312 | 22455701 | 66148091 | |
| Q9BQR3 | Serine protease 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRSS27 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.12222 | 0.000633 | 72730.16 | 56431.78 | 55381.44 | 75823.56 | 48577.68 | 40803.44 | 97564.07 | 21512.46 | 158080.2 | 92338.68 | 30733.47 | 113531 | 140918.1 | 61749.66 | 118619.1 | 175531.5 | 764717.5 | 650847.1 | 766990 | 691601.4 | 742033.9 | 350854.4 | 288890.4 | 2273109 | 619435.9 | 220299 | 210828.5 | |
| Q9NZT1 | Calmodulin-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CALML5 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.116636 | 0.000887 | 256794.5 | 75655.71 | 136636.5 | 466850.7 | 426018.3 | 94987.07 | 122721 | 177075.8 | 73730.86 | 91866.6 | 118025.5 | 118098.3 | 277362.6 | 310998.4 | 67410.09 | 733400.7 | 4804387 | 1272816 | 4143601 | 718415.4 | 722403.2 | 802657.5 | 573610.3 | 2589418 | 1117386 | 452564.3 | 1372078 | |
| P04083 | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.11596 | 0.004502 | 42396713 | 16911596 | 24709171 | 13224040 | 14155231 | 32745166 | 22992424 | 19259624 | 18468099 | 42229109 | 28197669 | 8645132 | 17091617 | 40143407 | 40065884 | 97748665 | 2.18E+08 | 4.3E+08 | 2.07E+08 | 1.07E+08 | 98354208 | 1.14E+08 | 89662669 | 9.22E+08 | 1.39E+08 | 98309145 | 1.1E+08 | |
| P31947 | 14-3-3 protein sigma OS=Homo sapiens GN=SFN PE=1 SV=1 | 0.113507 | 0.000807 | 336405.1 | 154644.3 | 120523.6 | 330291 | 101578.2 | 177717.4 | 259869.5 | 1057901 | 144765.6 | 332566.9 | 175373.7 | 204403.5 | 192126.6 | 160628.6 | 359294.7 | 1050662 | 1729053 | 5988804 | 7096306 | 1702048 | 749718 | 4288151 | 1882962 | 1908490 | 1123508 | 765453.2 | 668678.5 | |
| P31151;Q86SG5 | Protein S100-A7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A7 PE=1 SV=4 | 0.10747 | 0.001778 | 683147.1 | 723397.4 | 712061.7 | 774531.9 | 1050052 | 667582.7 | 464727.8 | 1176893 | 1142197 | 652274.3 | 475881.3 | 820820.1 | 537707.6 | 598614.5 | 543822.4 | 2398630 | 2755312 | 2720712 | 22458260 | 5893270 | 2232399 | 5203610 | 2873951 | 14326649 | 1784032 | 3747340 | 15665703 | |
| Q14002 | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CEACAM7 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.103467 | 0.003482 | 69858.93 | 176544.9 | 34329.45 | 31537.13 | 93949.92 | 28508.78 | 40059.82 | 55712.3 | 58296.4 | 93802.18 | 32544.46 | 54913.6 | 19810.82 | 8505.776 | 53713.88 | 155157.9 | 511028.8 | 387436.1 | 716844.6 | 1000989 | 60937.65 | 931063.8 | 235292.6 | 2122858 | 233275.1 | 57600.75 | 175811.5 | |
| P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.102763 | 3.47E-05 | 1139513 | 1267418 | 1004752 | 1460295 | 1089541 | 975466.2 | 2553764 | 1318892 | 928645.3 | 719259.3 | 1274834 | 915388.8 | 2256637 | 1332261 | 848520.1 | 9410516 | 23999168 | 11671637 | 25040228 | 8947478 | 8277907 | 9076889 | 3853537 | 28577741 | 10327300 | 2634448 | 6759742 | |
| P22735 | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase K OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGM1 PE=1 SV=4 | 0.097767 | 0.012117 | 1229642 | 395248.2 | 86571.04 | 181423.6 | 2088576 | 141693.2 | 123898.4 | 841341.2 | 58445.06 | 25095.02 | 113530.4 | 249571.4 | 65755.36 | 133152.4 | 612005.7 | 4369091 | 2426978 | 4268256 | 2948083 | 2908496 | 449666.4 | 4192211 | 1429688 | 21542196 | 2551558 | 866298.1 | 3974429 | |
| P04080 | Cystatin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=CSTB PE=1 SV=2 | 0.093107 | 2.65E-06 | 2357539 | 1402689 | 1245295 | 2454616 | 1440702 | 1704404 | 1723581 | 3899094 | 941317.7 | 1215838 | 1724743 | 1927354 | 2327094 | 1661777 | 1246524 | 6217925 | 15603585 | 38781770 | 35259420 | 25873212 | 22857723 | 27529319 | 18128542 | 22098457 | 12619600 | 6240285 | 3122122 | |
| Q92876 | Kallikrein-6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KLK6 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.088769 | 0.000291 | 277343.1 | 146945.5 | 49084.84 | 194518.1 | 201129.7 | 90429.55 | 263102.6 | 108308.3 | 101605.2 | 120581.5 | 634107.7 | 209827.1 | 113023.9 | 257694.7 | 168057.3 | 2216449 | 3403269 | 2369402 | 4285543 | 1037632 | 821003.7 | 1311751 | 551529.8 | 6686608 | 773066.1 | 495621.7 | 2505588 | |
| P15104 | Glutamine synthetase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLUL PE=1 SV=4 | 0.08712 | 0.001011 | 58352.8 | 187903.8 | 63135.66 | 238294.7 | 210238.1 | 106186.1 | 222683.1 | 323185.9 | 70030 | 97272.09 | 399471.8 | 91781.66 | 184078.4 | 34396.2 | 28765.27 | 1335792 | 3441430 | 1868345 | 3449745 | 327843.7 | 586153.2 | 1761355 | 676394.6 | 5868916 | 605870.3 | 302549.9 | 1040869 | |
| P07476 | Involucrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=IVL PE=1 SV=2 | 0.085642 | 0.000923 | 2201221 | 1851860 | 1525343 | 3232737 | 1800618 | 1590696 | 1686040 | 3131711 | 1852253 | 1014208 | 1719958 | 1687870 | 2141910 | 1378314 | 1567156 | 11439523 | 39537552 | 31834090 | 7171526 | 4940697 | 26757855 | 21014933 | 32060789 | 4094174 | 74978962 | 4995342 | 6297325 | |
| P29508 | Serpin B3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.082007 | 6.27E-07 | 4189307 | 3257082 | 3429980 | 3684479 | 5736199 | 4785617 | 4784205 | 3513540 | 4237420 | 4672310 | 3020985 | 7018359 | 4261032 | 3646389 | 4803712 | 61491225 | 1.24E+08 | 54124685 | 56149668 | 22206400 | 55485060 | 35187019 | 32587403 | 51133979 | 43501057 | 17335550 | 81469113 | |
| P48594 | Serpin B4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINB4 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.076532 | 0.001017 | 232100.8 | 50894.17 | 237949.7 | 352998.8 | 173655.9 | 112264.5 | 172049.6 | 454153.4 | 207591.7 | 198141.9 | 342773 | 172270.1 | 158451.9 | 295503.2 | 63483.26 | 1519298 | 3439497 | 5103804 | 7170420 | 2628877 | 609676 | 1185540 | 503587.8 | 8448477 | 674250.6 | 835198.8 | 1585067 | |
| P60903 | Protein S100-A10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A10 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.070871 | 0.005052 | 178401.4 | 30166.69 | 59846.15 | 330392.4 | 177101.6 | 151506.4 | 195230.9 | 126247.6 | 60620.82 | 146587.8 | 68048.23 | 483124.5 | 42942.22 | 93373.4 | 67055.18 | 518005.4 | 3254509 | 8920272 | 1651970 | 989707.9 | 555443.7 | 2585263 | 566108.9 | 3824059 | 682874.6 | 675554.8 | 730167.7 | |
| Q96L46 | Calpain small subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAPNS2 PE=2 SV=2 | 0.070205 | 0.02656 | 408059.4 | 187714.5 | 200282.1 | 365110.8 | 78354.49 | 335989.9 | 225336.1 | 211003.9 | 214545.8 | 250649.5 | 224316 | 467092.1 | 243538.8 | 164351 | 249479.5 | 1050297 | 3442841 | 7202179 | 2828132 | 1025236 | 1330982 | 1679958 | 485339 | 20388767 | 1792506 | 1438981 | 930805.3 | |
| P18510 | Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL1RN PE=1 SV=1 | 0.067585 | 0.000293 | 290090.3 | 224404.9 | 352090.1 | 791414.1 | 387076 | 291570 | 143573.1 | 225522.1 | 325272.1 | 405902.3 | 241210.3 | 147243.9 | 239941.6 | 292237.1 | 337404.8 | 1907598 | 5188256 | 4621365 | 6564722 | 3635960 | 4844049 | 3614419 | 2360633 | 16241716 | 3888107 | 1265542 | 1441849 | |
| A8K2U0 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2ML1 PE=1 SV=3 | 0.061595 | 0.000381 | 4198410 | 3105566 | 3133319 | 3556536 | 3365601 | 4082644 | 1946060 | 6515051 | 2876084 | 3017079 | 4111453 | 2749324 | 3409874 | 3314471 | 3441589 | 54896503 | 1.19E+08 | 64536007 | 63611640 | 20209589 | 19126578 | 26355866 | 23571129 | 1.88E+08 | 59699291 | 11976740 | 35082310 | |
| P05109 | Protein S100-A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A8 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.060423 | 0.02909 | 2966862 | 3682990 | 2420657 | 2726474 | 2421608 | 4219510 | 19596397 | 3111181 | 2926716 | 4038091 | 1666093 | 2705134 | 13189156 | 2712544 | 3056689 | 43627041 | 1.25E+08 | 54993734 | 88157240 | 12229665 | 24008654 | 36886217 | 43964628 | 4.6E+08 | 24000292 | 14325587 | 19352281 | |
| P99999 | Cytochrome c OS=Homo sapiens GN=CYCS PE=1 SV=2 | 0.059011 | 2.34E-06 | 406931.1 | 190976.9 | 302737 | 313907.7 | 137249 | 129156.9 | 235536.6 | 82664.03 | 119388.1 | 51184.12 | 113881.2 | 116154.1 | 66009.98 | 916672.4 | 33054.63 | 686133.8 | 3553782 | 3886286 | 2402593 | 3076325 | 6860047 | 6931426 | 1972528 | 2501730 | 7087993 | 1754747 | 2878358 | |
| P13646;Q2M2I5 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 0.056396 | 0.001106 | 1957361 | 2271798 | 2199953 | 1428073 | 3807747 | 1195383 | 3515759 | 1950736 | 1502178 | 2103060 | 1544776 | 1919564 | 1560618 | 2073342 | 2688803 | 1.24E+08 | 34121111 | 19627251 | 90924812 | 4200502 | 3457635 | 45832774 | 24344551 | 23984000 | 16620857 | 3896851 | 59173327 | |
| P58062 | Serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPINK7 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.050394 | 2.76E-05 | 233215.3 | 316502.2 | 213644.3 | 161741.9 | 332948.9 | 184599.3 | 388039 | 411240.1 | 386347.8 | 188088.8 | 236361 | 272284.3 | 193595.2 | 156979.7 | 231879.8 | 3574379 | 3893902 | 6882312 | 3147244 | 481727.1 | 6892558 | 2940850 | 5799596 | 14404474 | 7782634 | 738769.6 | 5492618 | |
| Q9UBG3 | Cornulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CRNN PE=1 SV=1 | 0.041373 | 1.03E-05 | 5326365 | 6417852 | 5816530 | 3113366 | 3877855 | 4282440 | 6801430 | 5187514 | 4030860 | 4628915 | 4581098 | 6007118 | 5496568 | 8576129 | 4952719 | 61634390 | 2.84E+08 | 2.48E+08 | 1.24E+08 | 85905059 | 74050386 | 1.1E+08 | 66039836 | 2.63E+08 | 1.08E+08 | 48039783 | 56633535 | |
| P35321 | Cornifin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR1A PE=1 SV=2 | 0.040463 | 3.49E-06 | 535814 | 294105.9 | 236872.8 | 306964.2 | 239748.1 | 453434.9 | 359077.3 | 768761.2 | 186696.1 | 251343.9 | 518645 | 792358.3 | 818209.9 | 312725.8 | 347380.6 | 4969762 | 10496119 | 8430496 | 8906265 | 1567150 | 18846096 | 14051173 | 7225182 | 6428813 | 24016000 | 4736492 | 17300642 | |
| P67936 | Tropomyosin alpha-4 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPM4 PE=1 SV=3 | 0.0371 | 4.63E-07 | 14350.16 | 10562.46 | 37536.33 | 54365.86 | 6892.477 | 8716.38 | 17987.3 | 1026.097 | 1725.139 | 73989.21 | 13622.4 | 16213.19 | 20521.71 | 6561.185 | 34979.09 | 978765.9 | 700465.1 | 589183.8 | 388457.9 | 242954.5 | 486529.4 | 651232.1 | 260680.2 | 1155490 | 364500.6 | 148971.1 | 912471 | |
| P06702 | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 0.032172 | 0.009503 | 14066405 | 10298293 | 8909613 | 12711352 | 7122079 | 17822017 | 62625882 | 6827921 | 12512144 | 9027568 | 7615657 | 11175473 | 39454730 | 13791380 | 9686591 | 2.61E+08 | 7.22E+08 | 3.62E+08 | 7.48E+08 | 79985214 | 1.35E+08 | 4.1E+08 | 2.71E+08 | 2.54E+09 | 2.31E+08 | 1.09E+08 | 1.9E+08 | |
| P22528 | Cornifin-B OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR1B PE=1 SV=2 | 0.021967 | 9.71E-08 | 429043.6 | 782849.1 | 488584.5 | 3455423 | 3959262 | 288615.2 | 2176153 | 882957.4 | 1554036 | 449578.6 | 1195553 | 1876405 | 890847.4 | 607040 | 2628346 | 30166618 | 74327338 | 82733052 | 88624345 | 9767031 | 81802649 | 82764272 | 43737331 | 25500589 | 1.11E+08 | 45692480 | 1.13E+08 | |
| P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 0.012855 | 0.011739 | 28590.46 | 20467.83 | 9752.882 | 148095 | 258617.5 | 4429.076 | 16790.85 | 35252.44 | 9299.648 | 45006.48 | 28497.42 | 69525.27 | 38634.49 | 40874.37 | 44144.92 | 19309851 | 3032225 | 490892.6 | 11452531 | 457342.8 | 122211.6 | 2807272 | 1780323 | 2278430 | 540365.7 | 212713.1 | 7176238 | |
| Q9UBC9 | Small proline-rich protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPRR3 PE=1 SV=2 | 0.010998 | 2.74E-08 | 9752629 | 6669882 | 6531074 | 5089837 | 7782861 | 4724891 | 13286908 | 10077256 | 6436782 | 7305115 | 5906856 | 20253465 | 13388819 | 11506061 | 8481985 | 2.77E+08 | 1.03E+09 | 1.26E+09 | 5.84E+08 | 1.92E+08 | 1.22E+09 | 1.19E+09 | 7.52E+08 | 5.34E+08 | 1.18E+09 | 5E+08 | 1.26E+09 | |
"
| Accession | Entry | Regional difference 1 | Ratio 1 | p 1 | Regional difference 2 | Ratio 2 | p 2 | Description | XA1 | XA2 | XA3 | XA4 | XA5 | HN5 | HN6 | HN7 | HN8 | HN9 | XN5 | XN6 | XN7 | XN8 | XN9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO3_HUMAN | P01024 | XA/HN | 2.45 | 0.006 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 5E+06 | 2E+06 | 3E+06 | 5E+06 | 5E+06 | 910256 | 2E+06 | 1E+06 | 3E+06 | 1E+06 | 3E+06 | 490210 | 3E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | |||
| VMO1_HUMAN | Q7Z5L0 | HN/XN | 0.42 | 0.006 | Vitelline membrane outer layer protein 1 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VMO1 PE=1 SV=1 | 9E+07 | 6E+07 | 3E+07 | 5E+07 | 6E+07 | 3E+07 | 3E+07 | 2E+07 | 4E+07 | 4E+07 | 8E+07 | 9E+07 | 6E+07 | 6E+07 | 1E+08 | |||
| ITLN1_HUMAN;ITLN2_HUMAN | Q8WWA0; Q8WWU7 | XA/HN | 10.19 | 0.016 | XA/XN | 8.92 | 0.032 | Intelectin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITLN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 1E+06 | 474885 | 1E+06 | 1E+07 | 608473 | 299576 | 305642 | 506872 | 229945 | 332138 | 234297 | 496362 | 316499 | 489819 | 375452 |
| PBLD_HUMAN | P30039 | XA/HN | 2.57 | 0.010 | Phenazine biosynthesis-like domain-containing protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PBLD PE=1 SV=2 | 1E+06 | 1E+06 | 1E+06 | 2E+06 | 630823 | 843652 | 268520 | 171274 | 656432 | 391267 | 1E+06 | 301343 | 655063 | 780907 | 561179 | |||
| CAH1_HUMAN | P00915 | HN/XN | 3.40 | 0.008 | XA/XN | 2.33 | 0.016 | Carbonic anhydrase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 617254 | 557629 | 1E+06 | 601241 | 2E+06 | 751478 | 1E+06 | 705126 | 4E+06 | 1E+06 | 485178 | 253531 | 461446 | 573798 | 499914 |
| PAG15_HUMAN | Q8NCC3 | XA/XN | 2.17 | 0.032 | Group XV phospholipase A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLA2G15 PE=1 SV=2 | 704132 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 1E+06 | 1E+06 | 753795 | 797996 | 914852 | 437667 | 683347 | 982429 | 502329 | |||
| MATN4_HUMAN | O95460 | HN/XA | 4.06 | 0.016 | Matrilin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MATN4 PE=1 SV=3 | 2E+06 | 3E+06 | 3E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+07 | 8E+06 | 5E+06 | 3E+06 | 9E+06 | 3E+06 | 4E+06 | 4E+06 | 3E+06 | 7E+06 | |||
| CO1A1_HUMAN | P02452 | HN/XA | 3.27 | 0.032 | XA/XN | 0.48 | 0.032 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 1E+06 | 598038 | 722323 | 304890 | 694498 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 7E+06 | 1E+06 | 817802 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 2E+06 | 1E+06 | 1E+06 |
| DDC_HUMAN | P20711 | XA/HN | 3.90 | 0.008 | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDC PE=1 SV=2 | 2E+06 | 393124 | 1E+06 | 2E+06 | 337877 | 286344 | 331940 | 196735 | 328530 | 310291 | 2E+06 | 391793 | 937166 | 490000 | 478018 | |||
| GLYC_HUMAN;GLYM_HUMAN | P34896; P34897 | HN/XN | 0.40 | 0.013 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, cytosolic OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHMT1 PE=1 SV=1 | 845418 | 276701 | 802407 | 889186 | 158015 | 225674 | 301874 | 73200 | 360490 | 195825 | 783051 | 702034 | 486645 | 450901 | 451929 | |||
| IBP5_HUMAN | P24593 | XN/XA | 2.83 | 0.024 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP5 PE=1 SV=1 | 1E+06 | 236894 | 230590 | 400424 | 293825 | 302532 | 1E+06 | 2E+06 | 727422 | 830264 | 1E+06 | 878440 | 2E+06 | 1E+06 | 2E+06 | |||
| TCO2_HUMAN | P20062 | XN/HN | 2.40 | 0.034 | Transcobalamin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCN2 PE=1 SV=3 | 411451 | 544601 | 395982 | 337187 | 178200 | 347745 | 101309 | 125848 | 149593 | 151110 | 301043 | 591831 | 285975 | 576175 | 345321 | |||
| UGDH_HUMAN | O60701 | XA/HN | 8.85 | 0.032 | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=UGDH PE=1 SV=1 | 306404 | 70748 | 175532 | 2E+06 | 89412 | 56334 | 40530 | 59884 | 48237 | 102986 | 156501 | 38362 | 94333 | 49279 | 36254 | |||
| CATA_HUMAN | P04040 | HN/XN | 6.49 | 0.032 | Catalase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAT PE=1 SV=3 | 24839 | 19721 | 6516.8 | 48306 | 16920 | 49908 | 223680 | 11590 | 177233 | 85880 | 10166 | 8482.2 | 36235 | 22325 | 7261.3 | |||
| CD226_HUMAN | Q15762 | XA/HN | 2.51 | 0.016 | CD226 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD226 PE=1 SV=2 | 240235 | 229885 | 139619 | 187972 | 86000 | 111618 | 38805 | 23084 | 61467 | 117044 | 117370 | 157266 | 53699 | 96719 | 110218 | |||
| SG3A1_HUMAN | Q96QR1 | XN/XA | 15.54 | 0.008 | Secretoglobin family 3A member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCGB3A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 38063 | 2507.9 | 12395 | 81185 | 6864.9 | 80671 | 5606.2 | 1E+06 | 3536.4 | 5441.2 | 317005 | 168681 | 192142 | 840699 | 673211 |
| 1. | Gao Y . Urine—an untapped goldmine for biomarker discovery? Sci China Life Sci 2013; 56(12):1145-6. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4574-1. |
| 2. | Wu J, Gao Y . Physiological conditions can be reflected in human urine proteome and metabolome. Expert Rev Proteomics 2015; 12(6):623-36. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2015.1094380. |
| 3. | Shao C, Li M, Li X , et al. A tool for biomarker discovery in the urinary proteome: a manually curated human and animal urine protein biomarker database. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011; 10(11): M111.010975. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.010975. |
| 4. | Zhao M, Wu J, Li X , et al. Urinary candidate biomarkers in an experimental autoimmune myocarditis rat model. J Proteomics 2018; 179:71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.02.032. |
| 5. | Yin W, Qin W, Gao Y . Urine glucose levels are disordered before blood glucose level increase was observed in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Sci China Life Sci 2017; 61(7):844-8. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9134-6. |
| 6. | Wu J, Guo Z, Gao Y . Dynamic changes of urine proteome in a Walker 256 tumor-bearing rat model. Cancer Med 2017; 6(11):2713-22. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1225. |
| 7. | Wu J, Li X, Zhao M , et al. Early detection of urinary proteome biomarkers for effective early treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in a rat model. Proteomics Clin Appl 2017; 11(11-12). doi: 10.1002/prca.201700103. |
| 8. | Bakun M, Senatorski G, Rubel T , et al. Urine proteomes of healthy aging humans reveal extracellular matrix (ECM) alterations and immune system dysfunction. Age (Dordr) 2014; 36(1):299-311. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9562-7. |
| 9. | Castagna A, Olivieri O, Milli A , et al. Female urinary proteomics: new insight into exogenous and physiological hormone-dependent changes. Proteomics Clin Appl 2011; 5(5-6):343-53. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000105. |
| 10. | Kohler M, Walpurgis K, Thomas A , et al. Effects of endurance exercise on the urinary proteome analyzed by 2-D PAGE and Orbitrap MS. Proteomics Clin Appl 2010; 4(5):568-76. doi: 10.1002/prca.200900209. |
| 11. | Zhao M, Wu J, Gao Y . The specific alpha1-adrenergic receptor antagonist prazosin influences the urine proteome. PLoS One 2016; 11(10):e0164796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164796. |
| 12. | Jia L, Liu X, Liu L , et al. Urimem, a membrane that can store urinary proteins simply and economically, makes the large-scale storage of clinical samples possible. Sci China Life Sci 2014; 57(3):336-9. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4582-1. |
| 13. | Wang X, Li X, Jia L , et al. Comparison of two urinary protein preparation methods: nitrocellulose membrane preservation and acetone precipitation. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2014; 30(6):982-9. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.130652. |
| 14. | Qin W, Gao Y . Elution of urinary proteins preserved on nitrocellulose membrane with heating. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2015; 31(9):1387-92. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.150039. |
| 15. | Hauck SM, Dietter J, Kramer RL , et al. Deciphering membrane-associated molecular processes in target tissue of autoimmune uveitis by label-free quantitative mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 2010; 9(10):2292-305. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.001073. |
| 16. | Huang da W, Sherman B, Lempicki R . Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 2009; 4(1):44-57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. |
| 17. | Kanehisa M, Goto S . KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28(1):27-30. |
| 18. | Li X, Zhao M, Li M , et al. Effects of three commonly-used diuretics on the urinary proteome. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2014; 12(3):120-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2013.12.002. |
| 19. | Yin B, Wang X, Zhao L , et al. The investigation of reference values of serum proteins within healthy crowd in Xi’an area. Hainan Med J (Chinese) 2008; 19(6):11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2008.06.006. |
| 20. | Zi J, Zi Y, Li Q , et al. Analysis on biochemical indexes of healthy population in different altitude areas in western Yunnan. J High Altitude Med (Chinese) 2014; 24(4):35-8. |
| 21. | Gu S . The change of lymphocyte subsets, platelet and coagulation function in healthy person at different altitudes. Chin J Blood Transfusion (Chinese) 2016; 29(7):700-3. doi: 10.13303/j.cjbt.issn.1004-549x.2016.07.013. |
| 22. | Guo Z, Zhang Y, Zou L , et al. A proteomic analysis of individual and gender variations in normal human urine and cerebrospinal fluid using iTRAQ quantification. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0133270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133270. |
| 23. | Kurutas EB, Gumusalan Y, Cetinkaya A , et al. Evaluation of method performance for oxidative stress biomarkers in urine and biological variations in urine of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Biol Proced Online 2015; 17(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12575-015-0015-9. |
| 24. | Smalley DM, Sheman NE, Nelson K , et al. Isolation and identification of potential urinary microparticle biomarkers of bladder cancer. J Proteome Res 2008; 7(5):2088-96. doi: 10.1021/pr700775x. |
| 25. | Wang M, Liu X, Jia L , et al. Comparison of cost-effectiveness between Urimem and direct freezing for urinary protein preservation. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 2014; 30(7):1128-33. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.140099. |
| 26. | Chutipongtanate S, Changtong C, Weeraphan C , et al. Syringe-push membrane absorption as a simple rapid method of urine preparation for clinical proteomics. Clin Proteomics 2015; 12(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12014-015-9087-4. |
| 27. | Zhang F, Cheng X, Yuan Y , et al. Urinary microRNA can be concentrated, dried on membranes and stored at room temperature in vacuum bags. PeerJ 2015; 3:e1082. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1082. |
| 28. | Gao Y . Using fibers for rapid extraction of proteins from urine. Proteomics Clin Appl 2015; 9(5-6):445-6. doi: 10.1002/prca.201500034. |
| [1] | 杨威, 张梅. 抗癌治疗中对心脏毒性效应具有潜在预测价值的生物标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 333-341. |
| [2] | 杨万水, 蒋涵羽, 刘超, 魏靖伟, 周宇, 宫鹏云, 宋彬, 田捷. 多组学技术及其在肝细胞癌中的临床应用:当前进展与未来机遇[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 173-186. |
| [3] | 曹剑, 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. CT纹理分析:结直肠癌KRAS基因突变状态评估的潜在生物标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [4] | 王站, 王旭, 王文达, 郑国洋, 郭浩, 张玉石. 术前中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值预测可切除泌尿系肿瘤预后的价值:系统综述和荟萃分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 262-271. |
| [5] | 柏明见, 冯璟, 梁国威. 尿液髓过氧化物酶肌酐比值作为诊断泌尿系感染的新标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 152-159. |
| [6] | 董德鑫, 纪志刚, 李汉忠, 严维刚, 张玉石. 磁珠联合基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱技术检测肾透明细胞癌尿液差异蛋白的初步应用[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 248-252. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|