Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 239-247.doi: 10.24920/003662
用于膀胱癌预后预测的lncRNA分子标记物开发
- 1菏泽医学专科学校诊断教研室,山东菏泽,274000
2菏泽医学专科学校附属医院泌尿外科,山东菏泽,274000
3清华大学生命科学学院,北京,100084
4华中农业大学动物科学动物医学学院,武汉,430072
-
收稿日期:2019-10-16出版日期:2020-09-30发布日期:2020-09-25 -
通讯作者:张彦丽 E-mail:yanlizhang12@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Novel Long Non-coding RNA Markers for Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Bladder Cancer
Li Wenxing1,2,Zhang Yanli3,4,*( )
)
- 1Department of Diagnosis, Heze Medical College, Heze, Shandong 274000, China
2Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of Heze Medical College, Heze, Shandong 274000, China
3School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4School of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2019-10-16Published:2020-09-30Online:2020-09-25 -
Contact:Zhang Yanli E-mail:yanlizhang12@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨与膀胱癌预后相关的长链非编码RNA (lncRNA)分子标志物,建立膀胱癌患者的预后预测模型。
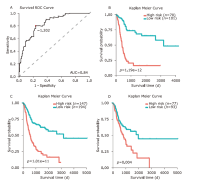
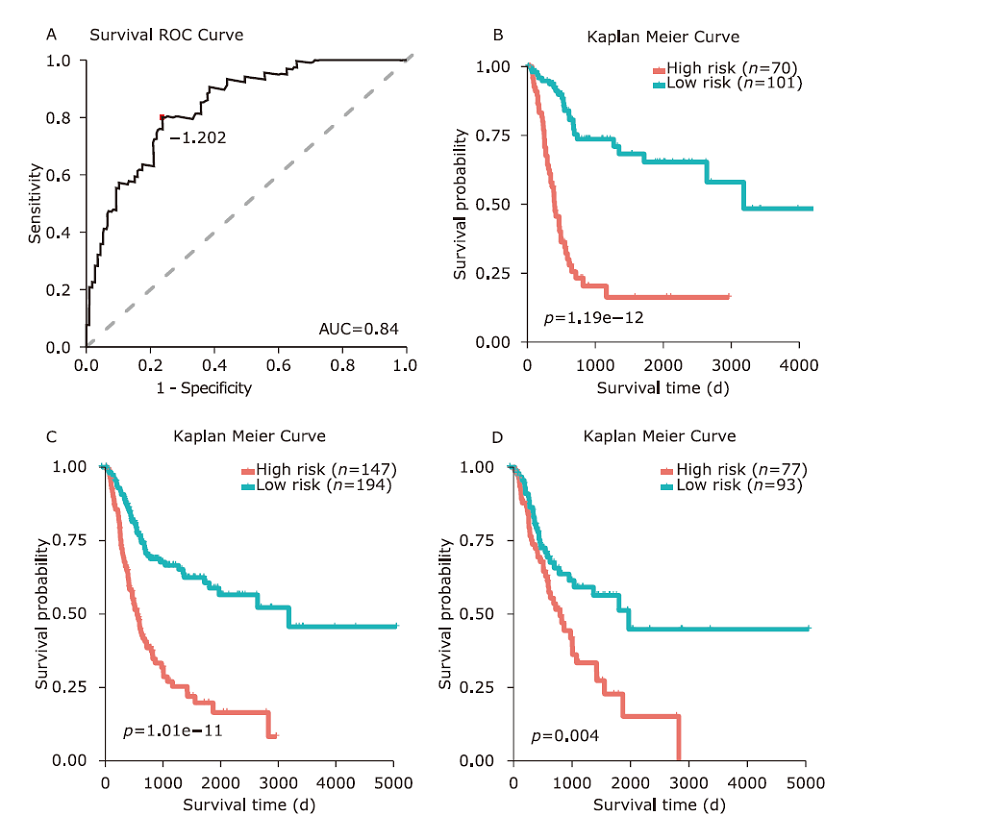
方法 从TCGA数据库中下载膀胱癌患者lncRNA的表达数据。使用单变量Cox回归和基于似然的生存分析发现预后相关的lncRNA分子标记。通过共表达分析和代谢通路富集分析对预后相关的lncRNA进行功能研究。采用多变量Cox回归分析建立风险评分模型,ROC分析确定模型的最佳分界点。通过Kaplan-Meier估计法和log-rank检验对风险评分模型进行验证。
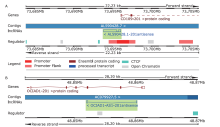
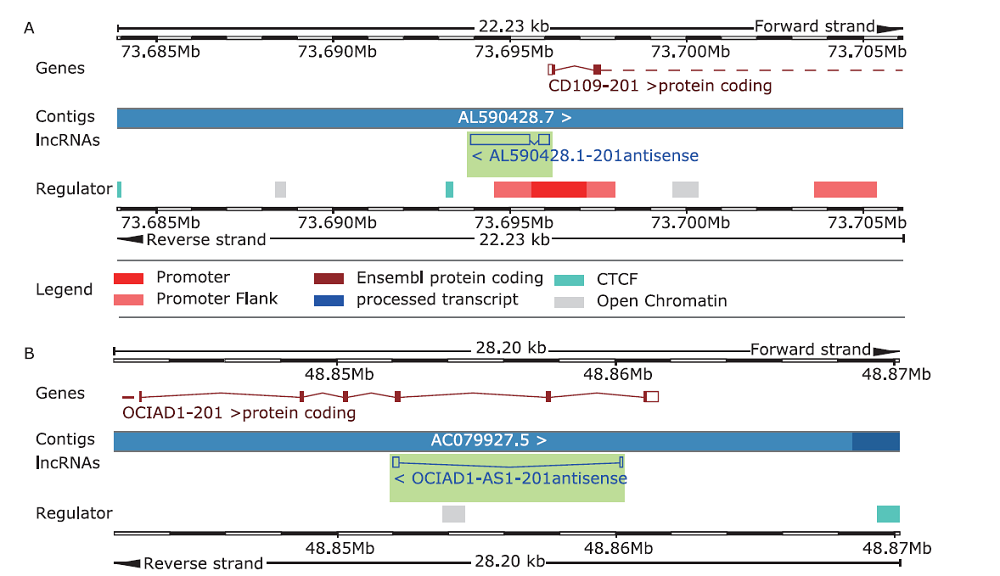
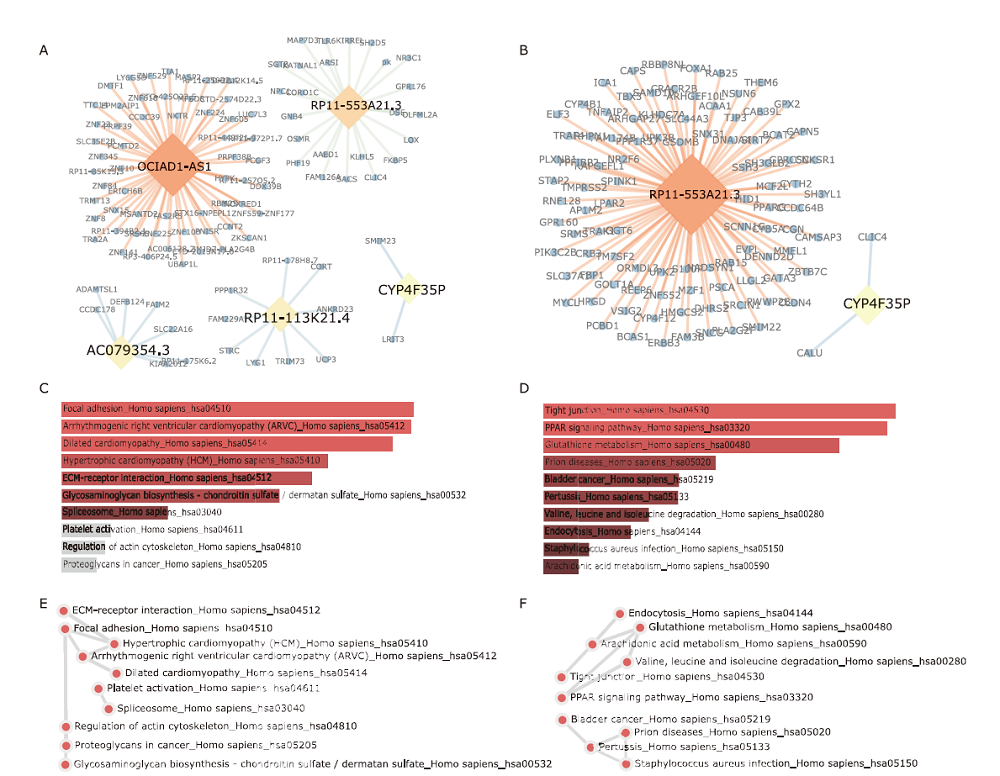
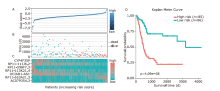
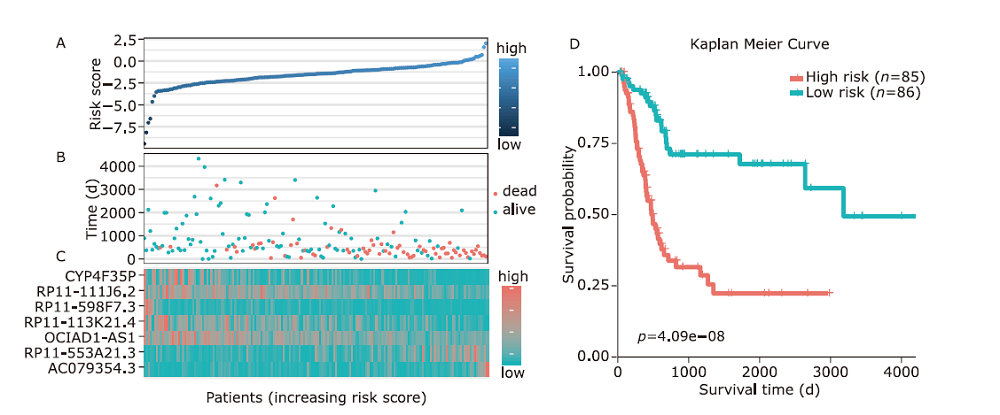
结果 我们发现7个预后相关的lncRNA标记(OCIAD1-AS1, RP11-111J6.2, AC079354.3, RP11-553A21.3, RP11-598F7.3, CYP4F35P, RP11-113K21.4)可以预测膀胱癌患者的生存期。通过对这些lncRNA的特点、其靶基因的共表达和代谢通路分析进一步揭示了lncRNA在膀胱癌的发生和发展中发挥重要作用。此外,我们建立并验证了基于7个lncRNA分子标记的的膀胱癌患者预后预测风险评分模型。值得注意的是,我们首次发现了两种与肿瘤相关的反义lncRNA (OCIAD1-AS1和RP11-553A21.3)在膀胱癌预后中的潜在意义。
结论 这些lncRNA分子标记可作为治疗膀胱癌的潜在靶点,值得进一步进行功能验证研究。
引用本文
Li Wenxing, Zhang Yanli. Novel Long Non-coding RNA Markers for Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Bladder Cancer[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 239-247.
"
| Ensembl ID | Gene symbol | Hazard ratio | P value | - logL | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000248256.1 | OCIAD1-AS1 | 0.352498 | 0.000426 | 313.55 | 629.1 |
| ENSG00000260331.1 | RP11-111J6.2 | 0.124571 | 0.000367 | 309.8 | 623.61 |
| ENSG00000222035.3 | AC079354.3 | 132322.9 | 9.81E-06 | 304.4 | 614.79 |
| ENSG00000231652.2 | RP11-553A21.3 (AL590428.1) | 28.95384 | 4.98E-05 | 300.78 | 609.56 |
| ENSG00000256948.1 | RP11-598F7.3 | 0.324872 | 0.012715 | 293.77 | 597.55 |
| ENSG00000265787.1 | CYP4F35P | 0.473391 | 0.001861 | 291.21 | 594.41 |
| ENSG00000255503.1 | RP11-113K21.4 | 0.15136 | 0.000223 | 289.07 | 592.15 |
| 1. |
Witjes JA, Compérat Eva, Cowan NC, et al. EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2013 Guidelines. Eur Urol 2014; 65(4):778-92. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.046.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.046 |
| 2. |
Ghafouri-Fard S, Nekoohesh L, Motevaseli E. Bladder cancer biomarkers: review and update. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15(6):2395-403. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.6.2395.
pmid: 24761840 |
| 3. |
Dunham I, Kundaje A, Aldred SF, et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489(7414):57-74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247.
doi: 10.1038/nature11247 pmid: 22955616 |
| 4. |
Brosnan CA, Voinnet O. The long and the short of noncoding RNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21(3):416-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.001 |
| 5. |
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10(3):155-9. doi: 10.1038/nrg2521.
pmid: 19188922 |
| 6. | Wu Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR involvement in cancer. Tumor Biol 2014; 35(10):9531-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2523-7. |
| 7. |
Zhu X, Tian X, Yu C, et al. A long non-coding RNA signature to improve prognosis prediction of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 2016; 15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0544-0.
pmid: 27647437 |
| 8. | Meng J, Li P, Zhang Q, et al. A four-long non-coding RNA signature in predicting breast cancer survival. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2014; 33(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0084-7. |
| 9. |
Sun J, Cheng L, Shi H, et al. A potential panel of six-long non-coding RNA signature to improve survival prediction of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep 2016; 6(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/srep27842.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 pmid: 28442746 |
| 10. |
Cao W, Liu J, Liu Z, et al. A three-lncRNA signature derived from the Atlas of ncRNA in cancer (TANRIC) database predicts the survival of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2017; 65:94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.12.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.12.017 pmid: 28109476 |
| 11. |
Song J, Zhang W, Wang S, et al. A panel of 7 prognosis-related long non-coding RNAs to improve platinum-based chemoresistance prediction in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol 2018; 53(2):866-76. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4403.
doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4403 pmid: 29749482 |
| 12. |
Mao X, Qin X, Li L, et al. A 15-long non-coding RNA signature to improve prognosis prediction of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 2018; 149(1):181-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.011 pmid: 29525275 |
| 13. |
Zhang Q, Su M, Lu G, et al. The complexity of bladder cancer: long noncoding RNAs are on the stage. Mol Cancer 2013; 12(1):101. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-101.
doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-101 pmid: 24006935 |
| 14. | Robertson AG, Kim J, Al-Ahmadie H, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of muscle-invasive bladder cancer cell 2017; 171(3):540-56. e25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.007. |
| 15. |
Xue Y, Ma G, Zhang Z, et al. A novel antisense long noncoding RNA regulates the expression of MDC1 in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2015; 6(1):484-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2861.
pmid: 25514464 |
| 16. |
Dudek AM, Boer SJ, Boon N, et al. Identification of long non-coding RNAs that stimulate cell survival in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017; 8(21):34442-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16284.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16284 pmid: 28415801 |
| 17. |
Duan W, Du L, Jiang X, et al. Identification of a serum circulating lncRNA panel for the diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016; 7(48):78850-8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12880.
pmid: 27793008 |
| 18. |
Wang M, Niu Z, Zhou L, et al. Prognostic impact of cell division cycle zssociated 2 expression on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinom. Chin Med Sci J 2016; 31(3):149-54. doi: 10.1016/S1001-9294(16)30043-8.
doi: 10.1016/s1001-9294(16)30043-8 pmid: 27733221 |
| 19. |
Renaud G, Stenzel U, Maricic T, et al. DeML: robust demultiplexing of Illumina sequences using a likelihood-based approach. Bioinformatics 2015; 31(5):770-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719 pmid: 25359895 |
| 20. |
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, et al. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics 2013; 14(1):128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128 |
| 21. |
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2016; 44(W1):W90-W7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377.
pmid: 27141961 |
| 22. |
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T, Pepe MS. Time-dependent ROC curves for censored survival data and a diagnostic marker. Biometrics 2000; 56(2):337-44. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00337.x.
pmid: 10877287 |
| 23. |
Yokoyama M, Ichinoe M, Okina S, et al. CD109, a negative regulator of TGF-β signaling, is a putative risk marker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol 2017; 105(5):614-22. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2173-1.
doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2173-1 pmid: 28032275 |
| 24. |
Jia W, Ren C, Wang L, et al. CD109 is identified as a potential nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarker using aptamer selected by cell-SELEX. Oncotarget 2016; 7(34):55328-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10530.
pmid: 27419372 |
| 25. |
Pelechano V, Steinmetz LM. Gene regulation by antisense transcription. Nat Rev Genetics 2013; 14(12):880-93. doi: 10.1038/nrg3594.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3594 pmid: 24217315 |
| 26. |
Sengupta S, Michener CM, Escobar P, et al. Ovarian cancer immuno-reactive antigen domain containing 1 (OCIAD1), a key player in ovarian cancer cell adhesion. Gynecol Oncol 2008; 109(2):226-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.024 pmid: 18328549 |
| 27. |
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, et al. Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol 2013; 11(1):59. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-59.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-59 |
| 28. |
Liao Q, Liu C, Yuan X, et al. Large-scale prediction of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39(9):3864-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1348.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1348 pmid: 21247874 |
| 29. |
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, et al. The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5(7):505-15. doi: 10.1038/nrc1647.
doi: 10.1038/nrc1647 pmid: 16069815 |
| 30. |
Badylak SF. Xenogeneic extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Transpl Immunol 2004; 12(3-4):367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2003.12.016.
doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2003.12.016 pmid: 15157928 |
| 31. |
Krupp M, Maass T, Marquardt JU, et al. The functional cancer map: a systems-level synopsis of genetic deregulation in cancer. BMC Med Genomics 2011; 4(1):53. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-53.
doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-53 |
| 32. |
Sasisekharan R, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, et al. Roles of heparan-sulphate glycosaminoglycans in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2(7):521-8. doi: 10.1038/nrc842.
doi: 10.1038/nrc842 pmid: 12094238 |
| 33. |
Rangel MP, de Sá VK, Prieto T, et al. Biomolecular analysis of matrix proteoglycans as biomarkers in non small cell lung cancer. Glycoconj J 2018; 35(2):233-42. doi: 10.1007/s10719-018-9815-x.
doi: 10.1007/s10719-018-9815-x pmid: 29502190 |
| 34. |
Gao F, Alwhaibi A, Artham S, et al. Endothelial Akt1 loss promotes prostate cancer metastasis via β-catenin-regulated tight-junction protein turnover. Br J Cancer 2018; 118(11):1464-75. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0110-1.
pmid: 29755115 |
| 35. |
Runkle EA, Mu D. Tight junction proteins: from barrier to tumorigenesis. Cancer Let 2013; 337(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.038.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.038 |
| 36. |
Soini Y. Tight junctions in lung cancer and lung metastasis: a review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2012; 5(2):126-36.
pmid: 22400072 |
| 37. |
Chen YZ, Xue JY, Chen CM, et al. PPAR signaling pathway may be an important predictor of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2012; 70(5):637-44. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-1949-0.
pmid: 22903535 |
| 38. |
Pazienza V, Vinciguerra M, Mazzoccoli G. PPARs signaling and cancer in the gastrointestinal system. PPAR Res 2012; 2012:560846. doi: 10.1155/2012/560846.
doi: 10.1155/2012/560846 pmid: 23028383 |
| 39. |
Fanale D, Amodeo V, Caruso S. The interplay between metabolism, PPAR signaling pathway, and cancer. PPAR Res 2017; 2017:1830626. doi: 10.1155/2017/1830626.
doi: 10.1155/2017/1830626 pmid: 28529521 |
| [1] | 徐文琴, 叶静静, 陈天兵. 鉴定并验证与肺腺癌预后相关的新的miRNA-mRNA调节网络[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 31-43. |
| [2] | 刘婕妤, 王嘉祥, 许力, 邓飞艳. 骨质疏松性骨折风险评估的潜在生物分子:一项综述回顾[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 135-149. |
| [3] | 王站, 王旭, 王文达, 郑国洋, 郭浩, 张玉石. 术前中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值预测可切除泌尿系肿瘤预后的价值:系统综述和荟萃分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 262-271. |
| [4] | 朱卫华,谢文勇,张哲栋,李澍,张大方,刘以俊,朱继业,冷希圣. 59例肝门部胆管癌切除术后并发症和生存率分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 157-169. |
| [5] | 李旭, 吴蔽野, 张明珠, 申乐. 全身麻醉下剖宫产术的单中心回顾性队列研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 256-262. |
| [6] | 陈强, 张丽伟, 黄党生, 张春红, 王秋霜, 沈东, 熊敏俊, 杨菲菲. 冠状动脉疾病合并糖尿病患者经StentBoost技术指导的经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后5年的随访分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 177-183. |
| [7] | 白冰, 田园, 张越伦, 马满娇, 虞雪融, 黄宇光. 后路脊柱手术隐性失血的预测[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 38-44. |
| [8] | 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. 纹理分析在结直肠癌新辅助放化疗疗效预测及预后分析中的应用及研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [9] | 刘永胜, 赵宇. 术中神经电生理监测在胸椎管狭窄症外科治疗中的应用进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 260-264. |
| [10] | 陈振杰, 李航, 蔡建芳, 张鑫, 李超, 邹佩美, 李明喜, 陈丽萌, 李雪梅, 李学旺, 文煜冰. 肾小球皮质密度对随访5年的IgA肾病不良预后的预测△[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 145-151. |
| [11] | 张荣强, 李凤英, 刘军礼, 刘美宁, 罗文瑞, 马婷, 马波, 张志刚. 构建预测陕西省咸阳市日本脑炎疫情的季节性时间序列模型[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 152-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|