Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 265-274.doi: 10.24920/003994
Wnt5a在炎性疾病中具有双向调节性
- 1甘肃省人民医院病理科,兰州730000,中国
2甘肃省第三人民医院职业病科,兰州730000,中国
3甘肃省人民医院检验科,兰州730000,中国
-
收稿日期:2021-09-09接受日期:2022-03-06出版日期:2022-09-30发布日期:2022-05-11 -
通讯作者:赵凤辉 E-mail:zhaofh0931@163.com
Dual Role of Wnt5a in the Progression of Inflammatory Diseases
Xu Chen1,Hongling Liu2,Dehong Li3,Jinsui Wang1,Fenghui Zhao1,*( )
)
- 1Department of Pathology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lazhou 730000, China
2Department of Occupational Medicine, the Third Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, China
3Department of Clinical Laboratory, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2021-09-09Accepted:2022-03-06Published:2022-09-30Online:2022-05-11 -
Contact:Fenghui Zhao E-mail:zhaofh0931@163.com
摘要:
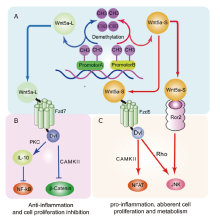
Wnt5a是一种分泌性的Wnt蛋白,在细胞通路及炎性疾病中扮演重要作用。WNT5A基因可编码形成Wnt5a长链蛋白和Wnt5a短链蛋白,这两种蛋白的形成取决于WNT5A基因启动子甲基化的部位,具有不同的功能。然而,WNT5A基因启动子甲基化的机制目前仍然不清楚。在炎性疾病中,因为WNT5A基因甲基化的部位不同,Wnt5a具有抑制炎症和促进炎症的双面功能,这或许涉及Wnt5a蛋白不同的亚型。因此,Wnt5a蛋白的不同亚型或许是潜在的炎性疾病诊断标记,WNT5A基因甲基化的具体机制也需要深入研究。
引用本文
Xu Chen, Hongling Liu, Dehong Li, Jinsui Wang, Fenghui Zhao. Dual Role of Wnt5a in the Progression of Inflammatory Diseases[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(3): 265-274.
| 1. |
Esse S, Mason KJ, Green AC, et al. Melanoma risk in patients treated with biologic therapy for common inflammatory diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol 2020; 156(7): 787-94. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1300.
doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1300 pmid: 32432649 |
| 2. |
Quandt J, Arnovitz S, Haghi L, et al. Wnt-β-catenin activation epigenetically reprograms Treg cells in inflammatory bowel disease and dysplastic progression. Nat Immunol 2021; 22(4): 471-84. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00889-2.
doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00889-2 |
| 3. |
Shoshkes-Carmel M, Wang YJ, Wangensteen KJ, et al. Subepithelial telocytes are an important source of Wnts that supports intestinal crypts. Nature 2018; 557(7704): 242-6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0084-4.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0084-4 |
| 4. |
Guo Z, Huang M, Yuan Y, et al. Nischarin downregulation attenuates cell injury induced by oxidative stress via Wnt signaling. Neuroreport 2020; 31(17): 1199-1207. doi: 10.1097/wnr.0000000000001536.
doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001536 pmid: 33075003 |
| 5. |
Yi M, Ha A, Lau WD, et al. Next-generation surrogate wnts support organoid growth and deconvolute frizzled pleiotropy in vivo. Cell Stem Cell 2020; 27(5): 840-51. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.07.020.
doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.07.020 |
| 6. |
Huang Y, Zhang Q, Song NN, et al. LRP5/6 are required for cerebellar development and for suppressing TH expression in Purkinje cells via β-catenin. Molecular Brain 2016; 9(1): 7. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0183-1.
doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0183-1 |
| 7. |
Ma SSQ, Srivastava S, Llamosas E, et al. ROR2 is epigenetically inactivated in the early stages of colorectal neoplasia and is associated with proliferation and migration. BMC Cancer 2016; 16(4): 508. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2576-7.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2576-7 |
| 8. |
Hollis ER, Ishiko N, Yu T, et al. Ryk controls remapping of motor cortex during functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci 2016; 19(5): 697-705. doi: 10.1038/nn.4282.
doi: 10.1038/nn.4282 pmid: 27065364 |
| 9. |
Hwang S-Y, Deng X, Byun S, et al. Direct targeting of β-Catenin by a small molecule stimulates proteasomal degradation and suppresses oncogenic Wnt/β-Catenin signaling. Cell Rep 2016; 16(1): 28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.071.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.071 |
| 10. |
Voloshanenko O, Schwartz U, Kranz D, et al. β-catenin-independent regulation of Wnt target genes by RoR2 and ATF2/ATF 4 in colon cancer cells. Sci Rep 2018(1); 8: 3178. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20641-5.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20641-5 |
| 11. |
Tompa M, Kajtar B, Galik B, et al. DNA methylation and protein expression of Wnt pathway markers in progressive glioblastoma. Pathol Res Pract 2021; 222(11): 153429. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153429.
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153429 |
| 12. |
Zou L, Chen L, Xia P F, et al. XIST knockdown suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-1264/WNT5A/β-catenin signaling in aneurysm. Biosci Rep 2021; 41(3): 221-30. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201810.
doi: 10.1042/BSR20201810 |
| 13. |
Zhao F, Xiao C, Evans KS, et al. Paracrine Wnt5a-β-catenin signaling triggers a metabolic program that drives dendritic cell tolerization. Immunity 2018; 48(1): 147-60.e147. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.12.004
doi: S1074-7613(17)30533-2 pmid: 29343435 |
| 14. |
Akiyama N, Yamamoto-Fukuda T, Yoshikawa M, et al. Regulation of DNA methylation levels in the process of oral mucosal regeneration in a rat oral ulcer model. Histol Histopathol 2020; 35(3): 247-256. doi: 10.14670/hh-18-147.
doi: 10.14670/HH-18-147 pmid: 31286466 |
| 15. |
Oz B, Yildirim A, Yolbas S, et al. Resveratrol inhibits Src tyrosine kinase, STAT3, and Wnt signaling pathway in collagen induced arthritis model. Biofactors 2019; 45(1): 69-74. doi: 10.1002/biof.1463.
doi: 10.1002/biof.1463 pmid: 30496633 |
| 16. |
Gerdes S, Laudes M, Neumann K, et al. Wnt5a: a potential factor linking psoriasis to metabolic complications. Exp Dermatol 2014; 23(6): 438-40. doi: 10.1111/exd.12413.
doi: 10.1111/exd.12413 pmid: 24750404 |
| 17. |
Ackers I, Szymanski C, Duckett KJ, et al. Blocking Wnt5a signaling decreases CD 36 expression and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol 2018; 34:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2018.01.008.
doi: S1054-8807(17)30311-3 pmid: 29474941 |
| 18. |
Schulte DM, Kragelund D, Müller N, et al. The wingless-related integration site-5a/secreted frizzled-related protein-5 system is dysregulated in human sepsis. Clin Exp Immunol 2015; 180(1): 90-7. doi: 10.1111/cei.12484.
doi: 10.1111/cei.12484 pmid: 25382802 |
| 19. |
Clark CC, Cohen I, Eichstetter I, et al. Molecular cloning of the human proto-oncogene Wnt-5A and mapping of the gene (WNT5A) to chromosome 3p14-p21. Genomics 1993; 18(2): 249-60. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1463.
doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1463 pmid: 8288227 |
| 20. |
Jin P, Song Y and Yu G. The Role of Abnormal Methylation of Wnt5a Gene Promoter Regions in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Clinical and Experimental Study. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2018; 2018(1): 6567081. doi: 10.1155/2018/6567081.
doi: 10.1155/2018/6567081 |
| 21. |
Chiba N, Furukawa KI, Takayama S, et al. Decreased DNA methylation in the promoter region of the WNT5A and GDNF genes may promote the osteogenicity of mesenchymal stem cells from patients with ossified spinal ligaments. J Pharmacol Sci 2015; 127(4): 467-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2015.03.008.
doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2015.03.008 pmid: 25913759 |
| 22. |
Bauer M, Bénard J, Gaasterland T, et al. WNT5A encodes two isoforms with distinct functions in cancers. PloS one 2013; 8(11): e80526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080526.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080526 |
| 23. |
Santos JMA, Mendes-Silva L, Afonso V, et al. Exogenous WNT5A and WNT 11 proteins rescue CITED2 dysfunction in mouse embryonic stem cells and zebrafish morphants. Cell Death Dis 2019; 10(8): 582. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1816-6.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1816-6 pmid: 31378782 |
| 24. |
Huang TC, Lee PT, Wu MH, et al. Distinct roles and differential expression levels of Wnt5a mRNA isoforms in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One 2017; 12(8): e0181034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181034.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181034 |
| 25. |
van Amerongen R, Fuerer C, Mizutani M, et al. Wnt5a can both activate and repress Wnt/β-catenin signaling during mouse embryonic development. Dev Biol 2012; 369(1): 101-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.020.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.020 pmid: 22771246 |
| 26. |
Liu H, Zhang C-X, Ma Y, et al. SphK1 inhibitor SKI II inhibits the proliferation of human hepatoma HepG2 cells via the Wnt5A/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci 2016; 151:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.098.
doi: S0024-3205(16)30148-5 pmid: 26944438 |
| 27. |
Fu HD, Wang BK, Wan ZQ, et al. Wnt5a mediated canonical Wnt signaling pathway activation in orthodontic tooth movement: possible role in the tension force-induced bone formation. J Mol Histol 2016; 47(5): 455-66. doi: 10.1007/s10735-016-9687-y.
doi: 10.1007/s10735-016-9687-y |
| 28. |
Xing F, Yi WJ, Miao F, et al. Baicalin increases hair follicle development by increasing canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling and activating dermal papillar cells in mice. Int J Mol Med 2018; 41(4): 2079-85. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3391.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3391 pmid: 29336472 |
| 29. |
Cao M, Chan RWS, Cheng FHC, et al. Myometrial cells stimulate self-renewal of endometrial mesenchymal stem-like cells through WNT5A/β-Catenin signaling. Stem Cell 2019; 37(11): 1455-66. doi: 10.1002/stem.3070.
doi: 10.1002/stem.3070 |
| 30. |
Ren D, Dai Y, Yang Q, et al. Wnt5a induces and maintains prostate cancer cells dormancy in bone. J Exp Med 2019; 216(2): 428-49. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180661.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20180661 |
| 31. |
Flores-Hernández E, Velázquez DM, Castañeda-Patlán MC, et al. Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling are simultaneously activated by Wnts in colon cancer cells. Cell Signal 2020; 72:109636. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109636.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109636 |
| 32. |
Yin N, Liu Y, Khoor A, et al. Protein Kinase Cι and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: Alternative Pathways to Kras/Trp53-Driven Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2019; 36(2): 156-167.e157. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.07.002.
doi: S1535-6108(19)30329-0 pmid: 31378680 |
| 33. |
Kondo A and Kaestner KH. FoxL1+ mesenchymal cells are a critical source of Wnt5a for midgut elongation during mouse embryonic intestinal development. Cells Dev 2021; 165:203662. doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203662.
doi: 10.1016/j.cdev.2021.203662 |
| 34. |
Kim S, Nie H, Nesin V, et al. The polycystin complex mediates Wnt/Ca2+ signalling. Nat Cell Biol 2016; 18(7): 752-64. doi: 10.1038/ncb3363
doi: 10.1038/ncb3363 |
| 35. |
Chattopadhyay S, Chatterjee R and Law S. Noncanonical Wnt5a-Ca(2+) -NFAT signaling axis in pesticide induced bone marrow aplasia mouse model: A study to explore the novel mechanism of pesticide toxicity. Environ Toxicol 2016; 31(10): 1163-75. doi: 10.1002/tox.22123.
doi: 10.1002/tox.22123 pmid: 25846497 |
| 36. |
Ulmer B, Tingler M, Kurz S, et al. A novel role of the organizer gene Goosecoid as an inhibitor of Wnt/PCP-mediated convergent extension in Xenopus and mouse. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 43010. doi: 10.1038/srep43010.
doi: 10.1038/srep43010 pmid: 28220837 |
| 37. |
Hasegawa D, Wada N, Yoshida S, et al. Wnt5a suppresses osteoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cell-like cells via Ror2/JNK signaling. J Cell Physiol 2018; 233(2): 1752-62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26086.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.26086 pmid: 28681925 |
| 38. |
Sessa R, Yuen D, Wan S, et al. Monocyte-derived Wnt5a regulates inflammatory lymphangiogenesis. Cell Res 2016; 26(2): 262-5. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.105.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.105 pmid: 26337801 |
| 39. |
Wu T, Zhang J, Geng M, et al. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) induce pro-inflammatory cytokines in the CNS via Wnt5a signaling. Sci Rep 2017; 7(1): 4117. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03446-w.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03446-w |
| 40. |
Li Z, Zhang K, Li X, et al. Wnt5a suppresses inflammation-driven intervertebral disc degeneration via a TNF-α/NF-κB-Wnt5a negative-feedback loop. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 2018; 26(7): 966-977. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.04.002.
doi: S1063-4584(18)31143-9 pmid: 29656141 |
| 41. |
González P, González‐Fernández C, Javier Rodriguez F. Effects of Wnt5a overexpression in spinal cord injury. J Cell Mol Med 2021; 25(11): 5150-63. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16507.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16507 pmid: 33939286 |
| 42. |
Cui J, Li M, Liu W, et al. Liver kinase B 1 overexpression controls mycobacterial infection in macrophages via FOXO1/Wnt5a signaling. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120(1): 224-31. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27322.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.27322 |
| 43. |
Rauner M, Stein N, Winzer M, et al. WNT5A is a novel regulator of cytokine and chemokine expression in bone marrow stromal cells. Bone 2011; 48(Supplement 2): S100. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.03.149.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.03.149 |
| 44. |
Zhao Y, Wang CL, Li RM, et al. Wnt5a promotes inflammatory responses via nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways in human dental pulp cells. J Biol Chem 2017; 292(10): 4358. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A113.546523.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.A113.546523 pmid: 28283587 |
| 45. |
Kim J, Kim J, Kim DW, et al. Wnt5a induces endothelial inflammation via beta-catenin-independent signaling. J Immunol 2010; 185(2): 1274-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000181.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000181 pmid: 20554957 |
| 46. |
Zhao C, Bu X, Wang W, et al. GEC-derived SFRP5 inhibits Wnt5a-induced macrophage chemotaxis and activation. PLoS One 2014; 9(1): e85058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085058.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085058 |
| 47. |
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, et al. Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater 2021; 122:306-24. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046 pmid: 33359765 |
| 48. |
Benam KH, Villenave R, Lucchesi C, et al. Small airway-on-a-chip enables analysis of human lung inflammation and drug responses in vitro. Nat Methods 2016; 13(2): 151-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3697.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3697 pmid: 26689262 |
| 49. |
Feng Y, Liang Y, Zhu X, et al. The signaling protein Wnt5a promotes TGFβ1-mediated macrophage polarization and kidney fibrosis by inducing the transcriptional regulators Yap/Taz. J Biol Chem 2018; 293(50): 19290-302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005457.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005457 pmid: 30333225 |
| 50. |
Qin L, Hu R, Zhu N, et al. The novel role and underlying mechanism of Wnt5a in regulating cellular cholesterol accumulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2014; 41(9): 671-8. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12258.
doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12258 |
| 51. |
Arderiu G, Espinosa S, Peña E, et al. Monocyte-secreted Wnt5a interacts with FZD 5 in microvascular endothelial cells and induces angiogenesis through tissue factor signaling. J Mol Cell Biol 2014; 6(5): 380-93. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju036.
doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju036 pmid: 25240054 |
| 52. |
Skaria T, Schoedon G. Inflammatory Wnt5A signalling pathways affecting barrier function of human vascular endothelial cells. J Inflamm (Lond) 2017; 14: 15. doi: 10.1186/s12950-017-0163-6.
doi: 10.1186/s12950-017-0163-6 |
| 53. |
Ochiai M, Tanaka E, Sato E, et al. Successful discontinuation of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in real-world settings. Mod Rheumatol 2021; 31(4): 790-5. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1883252.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1883252 |
| 54. |
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang J, et al. The triptolide-induced apoptosis of osteoclast precursor by degradation of cIAP2 and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of TNF-transgenic mice. Phytother Res 2019; 33(2): 342-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6224
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6224 pmid: 30417444 |
| 55. |
MacLauchlan S, Zuriaga MA, Fuster JJ, et al. Genetic deficiency of Wnt5a diminishes disease severity in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2017; 19(1): 166. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1375-0.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1375-0 pmid: 28724439 |
| 56. |
Rodriguez-Trillo A, Mosquera N, Pena C, et al. Non-canonical WNT5A signaling through RYK contributes to aggressive phenotype of the rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front Immunol 2020; 11: 555245. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.555245.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.555245 |
| 57. |
Martineau X, Abed É, Martel-Pelletier J, et al. Alteration of Wnt5a expression and of the non-canonical Wnt/PCP and Wnt/PKC-Ca2+ pathways in human osteoarthritis osteoblasts. PLoS One 2017; 12(8): e0180711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180711.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180711 |
| 58. |
Cao W, Niu M, Tong Y, et al. Depleting the carboxy-terminus of human Wnt5a attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commu 2018; 504(4): 679-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.030.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.030 |
| 59. |
Sharma S, Mahajan A, Mittal A, et al. Epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of osteoclastogenesis in the pathogenesis of skeletal diseases: A systematic review. Bone 2020; 138: 115507. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115507.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115507 |
| 60. |
Satoh Y, Nakano K, Yoshinari H, et al. A case of refractory lupus nephritis complicated by psoriasis vulgaris that was controlled with secukinumab. Lupus 2018; 27(7): 1202-6. doi: 10.1177/0961203318762598.
doi: 10.1177/0961203318762598 pmid: 29523055 |
| 61. |
Mohamed EA, Atef LM, Ibrahim GH, et al. Expression pattern of WNT5A among Egyptian patients with psoriasis treated with platelet-rich plasma versus conventional therapy: Toward a better understanding of the disease. Gene Reports 2021; 23: 101114. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101114.
doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101114 |
| 62. |
Zhang Y, Tu C, Zhang D, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin and Wnt5a/Ca pathways regulate proliferation and apoptosis of keratinocytes in psoriasis lesions. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 36(5): 1890-902. doi: 10.1159/000430158.
doi: 10.1159/000430158 pmid: 26202350 |
| 63. |
Vahav I, van den Broek LJ, Thon M, et al. Reconstructed human skin shows epidermal invagination towards integrated neopapillae indicating early hair follicle formation in vitro. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2020; 14(6): 761-73. doi: 10.1002/term.3039.
doi: 10.1002/term.3039 pmid: 32293116 |
| 64. |
Nagira T, Nagahata-Ishiguro M, Tsuchiya T. Effects of sulfated hyaluronan on keratinocyte differentiation and Wnt and Notch gene expression. Biomaterials 2007; 28(5): 844-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.09.041.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.09.041 pmid: 17084447 |
| 65. |
Verma D, Ekman AK, Bivik Eding C, et al. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Differential Methylation in Uninvolved Psoriatic Epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 2018; 138(5): 1088-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.11.036.
doi: S0022-202X(17)33280-3 pmid: 29247660 |
| 66. |
Parvin A, Yaghmaei P, Noureddini M, et al. Comparative effects of quercetin and hydroalcoholic extract of Otostegia persica boiss with atorvastatin on atherosclerosis complication in male wistar rats. Food Sci Nut 2019; 7(9): 2875-87. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1136.
doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1136 |
| 67. |
Malgor R, Bhatt PM, Connolly BA, et al. Wnt5a, TLR2 and TLR4 are elevated in advanced human atherosclerotic lesions. Inflamm Res 2014; 63(4): 277-85. doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0697-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0697-x pmid: 24346141 |
| 68. |
Zhang C-J, Zhu N, Liu Z, et al. Wnt5a/Ror 2 pathway contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and inflammatory response in atherosclerosis. Biochem et Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2020; 1865(2): 158547. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158547.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158547 |
| 69. |
Fuster JJ, Zuriaga MA, Ngo DT, et al. Noncanonical Wnt signaling promotes obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction independent of adipose tissue expansion. Diabetes 2015; 64(4): 1235-48. doi: 10.2337/db14-1164.
doi: 10.2337/db14-1164 pmid: 25352637 |
| 70. |
Tong S, Du Y, Ji Q, et al. Expression of Sfrp5/Wnt5a in human epicardial adipose tissue and their relationship with coronary artery disease. Life Sci 2020; 245:117338. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117338.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117338 |
| 71. |
Yang L, Chu Y, Wang Y, et al. siRNA-mediated silencing of Wnt5a regulates inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Int J Mol Med 2014; 34(4): 1147-52. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1860.
doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1860 pmid: 25050997 |
| 72. |
He XW, Zhao Y, Shi YH, et al. DNA methylation analysis identifies differentially methylated sites associated with early-onset intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 2020; 27(1): 71-99. doi: 10.5551/jat.47704.
doi: 10.5551/jat.47704 |
| 73. |
Pesaro AE, Bittencourt MS, Franken M, et al. The Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC), incident diabetes and low-grade inflammation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2021; 171: 108558. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108558.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108558 |
| 74. |
Mir E, Moazzami M, Bijeh N, et al. Changes in SFRP5, WNT5A, HbA1c, BMI, PBF, and insulin resistance in men with type 2 diabetes after 12 weeks of combined exercise (HIIT and resistance). Int J Diabetes Dev C 2020; 40:248-54. doi: 10.1007/s13410-019-00790-7.
doi: 10.1007/s13410-019-00790-7 |
| 75. |
Carstensen-Kirberg M, Niersmann C, Roehrig K, et al. The molecular role of WNT5A and its antagonist SFRP 5 in gluconeogenesis and inflammation in human hepatocytes. Diabetes 2018; 67(Suppl 1): 1845-56. doi: 10.2337/db18-1845-P.
doi: 10.2337/db18-1845-P |
| 76. |
Xu W, Jones PM, Geng H, et al. Islet stellate cells regulate insulin secretion via Wnt5a in Min6Cells. Int J Endocrinol 2020; 2020:4708132. doi: 10.1155/2020/4708132.
doi: 10.1155/2020/4708132 |
| 77. |
Lin CL, Cheng H, Tung CW, et al. Simvastatin reverses high glucose-induced apoptosis of mesangial cells via modulation of Wnt signaling pathway. Am J Nephrol 2008; 28(2): 290-7. doi: 10.1159/000111142.
doi: 10.1159/000111142 |
| 78. |
Hsu YC, Lee PH, Lei CC, et al. Nitric oxide donors rescue diabetic nephropathy through oxidative-stress-and nitrosative-stress-mediated Wnt signaling pathways. J Diabetes Investig 2015; 6(1): 24-34. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12244.
doi: 10.1111/jdi.12244 |
| 79. |
Relling I, Akcay G, Fangmann D, et al. Role of Wnt5a in metabolic inflammation in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018; 103(11): 4253-64. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01007.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01007 pmid: 30137542 |
| 80. |
Li X, Wen J, Dong Y, et al. Wnt5a promotes renal tubular inflammation in diabetic nephropathy by binding to CD 146 through non-canonical Wnt signaling. Cell Death Dis 2021; 12(1): 92. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03377-x.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03377-x |
| 81. |
Burcher GC, Caspani G, Cooper M, et al. Post-traumatic stress symptoms following childhood sepsis: The impact of inflammation and corticosteroids. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2019; 29(Suppl 1): 463-4. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.11.693.
doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.11.693 |
| 82. |
Schulte DM, Kragelund D, Müller N, et al. The wingless-related integration site-5a/secreted frizzled-related protein-5 system is dysregulated in human sepsis. Clin Exp Immunol 2015; 180(1): 90-7. doi: 10.1111/cei.12484.
doi: 10.1111/cei.12484 pmid: 25382802 |
| 83. |
Villar J, Cabrera-Benítez NE, Ramos-Nuez A, et al. Early activation of pro-fibrotic WNT5A in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care 2014; 18(5): 568. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0568-z.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0568-z |
| 84. |
Chen M, Zhong W, Hu Y, et al. Wnt5a/FZD5/CaMKII signaling pathway mediates the effect of BML-111 on inflammatory reactions in sepsis. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8(10): 17824-9.
pmid: 26770375 |
| 85. |
Jati S, Kundu S, Chakraborty A, et al. Wnt5A signaling promotes defense against bacterial pathogens by activating a host autophagy circuit. Frontiers in Immunology 2018; 9: 679-89. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00679.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00679 pmid: 29686674 |
| 86. |
Cao L, Zhu T, Lang X, et al. Inhibiting DNA methylation improves survival in severe sepsis by regulating NF-κB pathway. Front in Immunol 2020; 11: 1360. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01360.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01360 |
| 87. |
Lorente-Pozo S, Navarrete P, Garzón MJ, et al. DNA methylation analysis to unravel altered genetic pathways underlying early onset and late onset neonatal sepsis. A Pilot Study. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 622599. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622599.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622599 |
| 88. |
Petit A, Knabe L, Khelloufi K, et al. Bronchial epithelial calcium metabolism impairment in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. decreased ORAI 3 signaling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2019; 61(4): 501-511. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0228OC.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0228OC |
| 89. |
Feller D, Kun J, Ruzsics I, et al. Cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation becomes systemic by circulating extracellular vesicles containing Wnt5a and inflammatory cytokines. Front immunol 2018; 9: 1724-35. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01724.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01724 pmid: 30090106 |
| 90. |
Zhu Z, Yin S, Wu K, et al. Downregulation of Sfrp5 in insulin resistant rats promotes macrophage-mediated pulmonary inflammation through activation of Wnt5a/JNK1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018; 505(2): 498-504. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.070.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.070 |
| 91. |
Chen YC, Tsai YH, Wang CC, et al. Epigenome-wide association study on asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap reveals aberrant DNA methylations related to clinical phenotypes. Sci Rep 2021; 11(1): 5022-31. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83185-1.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83185-1 |
| 92. |
Moll M, Jackson VE, Yu B, et al. A systematic analysis of protein-altering exonic variants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2021; 321(1): 1130-43. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00009.2021.
doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00009.2021 |
| [1] | 陈旭, 刘红玲, 赵凤辉, 焦宗宪, 王金穗, 党雅梅. Wnt5a在肿瘤进展中的作用具有争议性[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 357-365. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|