Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 52-59.doi: 10.24920/003953
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Crosstalk between CpG Methylation and Polymorphisms (CpG-SNPs) in the Promotor Region of DIO2 in Kashin-Beck Disease
Rongqiang Zhang1, 2, Dandan Zhang2, Di Zhang2, Xiaoli Yang2, Qiang Li2, Chen Wang2, Xuena Yang2, Yongmin Xiong2, *( )
)
- 1School of Public Health, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi, 712046, China
2Institute of Endemic Diseases and Key Laboratory of Trace Elements and Endemic Diseases, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, School of Public Health, Xi′an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi′an 710061, China
-
Received:2021-06-10Accepted:2021-12-17Published:2022-03-31Online:2022-03-01 -
Contact:Yongmin Xiong E-mail:xiongym@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
Cite this article
Rongqiang Zhang, Dandan Zhang, Di Zhang, Xiaoli Yang, Qiang Li, Chen Wang, Xuena Yang, Yongmin Xiong. Crosstalk between CpG Methylation and Polymorphisms (CpG-SNPs) in the Promotor Region of DIO2 in Kashin-Beck Disease[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 52-59.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
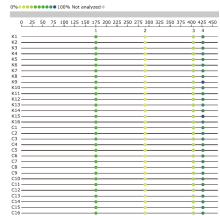
Figure 3.
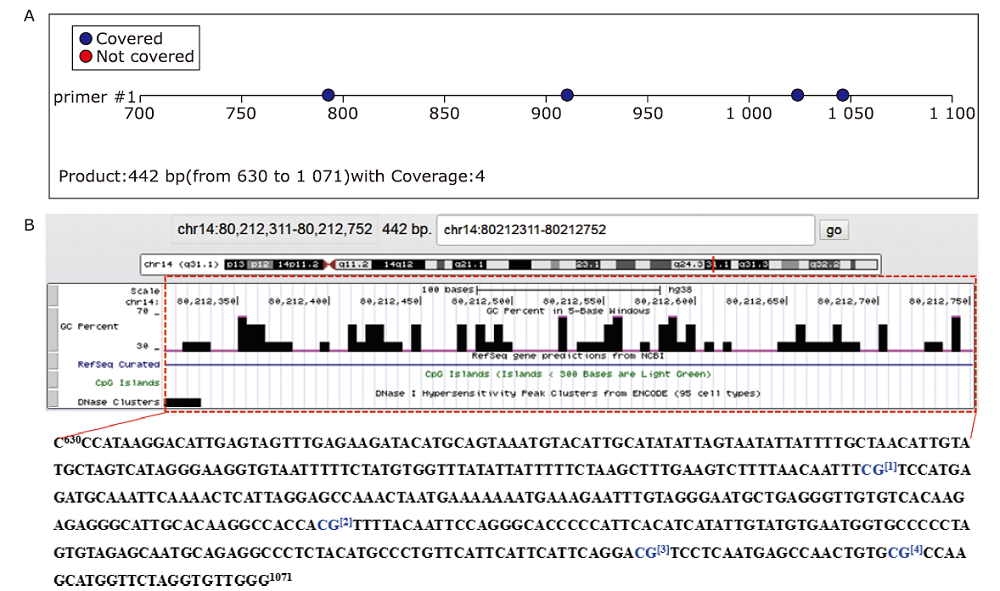
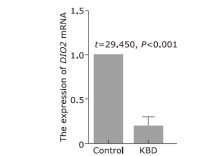
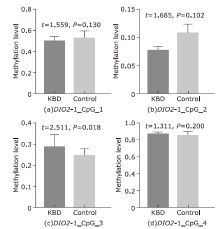
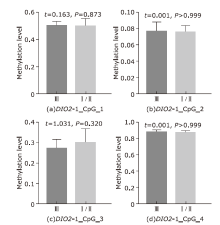
Methylation levels of CpGs in the promoter region of the DIO2 gene in KBD and controls (the color of the dots indicates the methylation level. The darker the color, the higher the methylation level. The numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the figure represent CpGs DIO2-1_CpG_1, DIO2-1_CpG_2, DIO2-1_CpG_3, DIO2-1_CpG_4; K: KBD patients, C: healthy controls)."

| 1. |
Song QQ, Sun LY, Li CH, et al. The urinary levels of CTX-II, C2C, PYD, and Helix-II increased among adults with KBD: a cross-sectional study. J Orthop Surg Res 2019; 14(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1392-6.
doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1392-6 |
| 2. |
Han LX, Yang XL, Sun WY, et al. The study of GPX3 methylation in patients with Kashin-Beck Disease and its mechanism in chondrocyte apoptosis. Bone 2018; 117:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.08.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.08.017 |
| 3. | NHFPC. China Health and Family Planning Statistical Yearbook. 2021, Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press. |
| 4. |
Avery JC, Hoffmann PR. Hoffmann. Selenium, selenoproteins, and immunity. Nutrients 2018; 10(9):1203. doi: 10.3390/nu10091203.
doi: 10.3390/nu10091203 |
| 5. |
Majumdar B, Saini N, Agrawal S, et al. Familiar manifestations of unfamiliar selenium toxicity. Indian J Dermatol 2018; 63(5):430-1. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_455_17.
doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_455_17 |
| 6. |
Sahebari M, Rezaieyazdi Z, Khodashahi M. Selenium and autoimmune diseases: a review article. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2019; 15(2):123-34. doi: 10.2174/1573397114666181016112342.
doi: 10.2174/1573397114666181016112342 pmid: 30324883 |
| 7. |
Wang W, Wei S, Luo M, et al. Oxidative stress and status of antioxidant enzymes in children with Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21(11):1781-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.08.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.08.002 |
| 8. |
Dai XX, Li YY, Zhang RQ, et al. Effects of sodium selenite on c-Jun N-terminal kinase signalling pathway induced by oxidative stress in human chondrocytes and c-Jun N-terminal kinase expression in patients with Kashin-Beck disease, an endemic osteoarthritis. Br J Nutr 2016; 115(9):1547-55. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516000362.
doi: 10.1017/S0007114516000362 |
| 9. |
Zhang RQ, Guo H, Yang XL, et al. Pathway-based network analyses and candidate genes associated with Kashin-Beck disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019; 98(18):e15498. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015498.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015498 |
| 10. |
Wen Y, Zhang F, Li CY, et al. Gene expression analysis suggests bone development-related genes GDF5 and DIO2 are involved in the development of Kashin-Beck disease in children rather than adults. PLoS One 2014; 9(7):e103618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103618.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103618 |
| 11. |
den Hollander W and Meulenbelt I. Meulenbelt. DNA Methylation in Osteoarthritis. Curr Genomics 2015; 16(6):419-26. doi: 10.2174/1389202916666150817212711.
doi: 10.2174/1389202916666150817212711 pmid: 27019616 |
| 12. |
Shi ZM, Pan PJ, Feng YW, et al. Environmental water chemistry and possible correlation with Kaschin-Beck Disease (KBD) in northwestern Sichuan, China. Environ Int 2017; 99:282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.006 |
| 13. |
Guo YN, Li HR, Yang LS, et al. Trace element levels in scalp hair of school children in Shigatse, Tibet, an endemic area for Kaschin-Beck disease (KBD). Biol Trace Elem Res 2017; 180(1):15-22. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-0988-0.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-0988-0 |
| 14. |
Fu Q, Cao JL, Renner JB, et al. Radiographic features of hand osteoarthritis in adult Kashin-Beck Disease (KBD): the Yongshou KBD study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015; 23(6):868-73. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.009 |
| 15. |
Luo R, Liu G, Liu W, et al. Efficacy of celecoxib, meloxicam and paracetamol in elderly Kashin-Beck disease (KBD) patients. Int Orthop 2011; 35(9):1409-14. doi: 10.1007/s00264-010-1062-0.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-010-1062-0 |
| 16. |
Jin TB, Wang L, He X, et al. Association between DIO2 polymorphism and the risk of Kashin-Beck disease in the Tibetan population. J Gene Med 2019; 21(10):e3123. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3123.
doi: 10.1002/jgm.3123 |
| 17. |
Wang S, Duan C, Zhang F, et al. The roles of the interaction of bcl2-antagonist/killer 1, apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 and selenium in the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 2016; 170(1):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0424-2.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0424-2 pmid: 26179084 |
| 18. |
Du XA, Wang HM, Dai XX, et al. Role of selenoprotein S (SEPS1) -105G>A polymorphisms and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2015; 23(2):210-6. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.11.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.11.017 |
| 19. |
Schneider MJ, Fiering SN, Pallud SE, et al. Targeted disruption of the type 2 selenodeiodinase gene (DIO2) results in a phenotype of pituitary resistance to T4. Mol Endocrinol 2001; 15(12):2137-48. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.12.0740.
doi: 10.1210/mend.15.12.0740 pmid: 11731615 |
| 20. |
Bianco AC, Larsen PR. Cellular and structural biology of the deiodinases. Thyroid 2005; 15(8):777-86. doi: 10.1089/thy.2005.15.777.
doi: 10.1089/thy.2005.15.777 |
| 21. |
Wang L, Shao YY, Ballock RT. Thyroid hormone-mediated growth and differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes involves IGF-1 modulation of beta-catenin signaling. J Bone Miner Res 2010; 25(5):1138-46. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5.
doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5 pmid: 20200966 |
| 22. |
Moreno-Reyes R, Suetens C, Mathieu F, et al. Kashin-Beck disease and iodine deficiency in Tibet. Int Orthop 2001; 25(3):164-6. doi: 10.1007/s002640000216.
doi: 10.1007/s002640000216 pmid: 11482533 |
| 23. |
Bomer N, den Hollander W, Ramos YF, et al. Underlying molecular mechanisms of DIO2 susceptibility in symptomatic osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74(8):1571-9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204739.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204739 pmid: 24695009 |
| 24. |
Hubertsson J, Turkiewicz A, Petersson IF, et al. Understanding occupation, sick leave, and disability pension due to knee and hip osteoarthritis from a sex perspective. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017; 69(2):226-33. doi: 10.1002/acr.22909.
doi: 10.1002/acr.22909 pmid: 27110664 |
| 25. |
Lei J, Amhare AF, Wang LY, et al. Proteomic analysis of knee cartilage reveals potential signaling pathways in pathological mechanism of Kashin-Beck disease compared with osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 2020; 10(1):6824. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63932-6.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63932-6 |
| 26. |
Liu HM, Wang YF, Wu JM, et al. A comparative study of clinical effect of total knee arthroplasty in the treatment of primary osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis of Kashin-Beck disease. Int Orthop 2020. doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04542-9.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04542-9 |
| 27. |
Shoemaker R, Deng J, Wang W, et al. Allele-specific methylation is prevalent and is contributed by CpG-SNPs in the human genome. Genome Res 2010; 20(7):883-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.104695.109.
doi: 10.1101/gr.104695.109 pmid: 20418490 |
| 28. |
Chen JP, Jiang Y, Zhou J, et al. Evaluation of CpG-SNPs in miRNA promoters and risk of breast cancer. Gene 2018; 651:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.070.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.070 |
| 29. |
Chen XM, Chen XY, Xu Y, et al. Association of six CpG-SNPs in the inflammation-related genes with coronary heart disease. Hum Genomics 2016; 10(Suppl 2):21. doi: 10.1186/s40246-016-0067-1.
doi: 10.1186/s40246-016-0067-1 |
| [1] | He Ying,Zhang Ying,Wang Mengying,Zhang Meng,Zhang Dan,Zhang Ying,Jiang Zhuocheng,Wu Feng,Chen Jinghong. Gene Expression Profile of Hypertrophic Chondrocytes Treated with H2O2: A Preliminary Investigation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 45-52. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|