Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 178-190.doi: 10.24920/004222
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Prognostic Prediction Value and Biological Functions of Non-Apoptotic Regulated Cell Death Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Hao-Ling Li1, 2, Jun-Xian Wang1, Heng-Wen Dai2, Jun-Jie Liu2, Zi-Yang Liu1, 2, Ming-Yuan Zou2, Lei Zhang1, 3, *( ), Wen-Rui Wang1, 4, *(
), Wen-Rui Wang1, 4, *( )
)
- 1Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Translational Cancer Research, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui 233030, China
2Department of Clinical Medicine, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui 233030, China
3Department of Life Sciences, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui 233030, China
4Department of Thoracic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui 233030, China
-
Received:2023-03-15Accepted:2023-07-10Published:2023-09-30Online:2023-08-25 -
Contact:* wenrui-wang, E-mail:wenrui-wang1983@163.com ; Lei Zhang, E-mail:727302227@qq.com
Cite this article
Hao-Ling Li, Jun-Xian Wang, Heng-Wen Dai, Jun-Jie Liu, Zi-Yang Liu, Ming-Yuan Zou, Lei Zhang, Wen-Rui Wang. Prognostic Prediction Value and Biological Functions of Non-Apoptotic Regulated Cell Death Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2023, 38(3): 178-190.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1.
The primers sequences used for real-time qPCR"
| Gene symbols | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-Forward | 5’GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT3’ |
| GAPDH-Reverse | 5’GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG3’ |
| RRM2-Forward | 5’-GCAGCAAGCGATGGCATAGT-3’ |
| RRM2-Reverse | 5’-GGGCTTCTGTAATCTGAACTTC-3’ |
| CDK5R1-Forward | 5’-TGAGCGGGTCTAGTGGAAAG-3’ |
| CDK5R1-Reverse | 5’-AGCAGCAGACAAGGGGGTAG-3’ |
| DDIT4-Forward | 5’-GGACCAAGTGTGTTTGTTGTTTG-3’ |
| DDIT4-Reverse | 5’-CACCCACCCCTTCCTACTCTT-3’ |
| AURKA-Forward | 5’-GGTCAGTACATGCTCCATCTTCCAG-3’ |
| AURKA-Reverse | 5’-AGAACTCCAAGGCTCCAGAGATCC-3’ |
| ATIC-Forward | 5’-CGGCCAGCTCGCCTTATTTA-3’ |
| ATIC-Reverse | 5’-ATTTGCTCCACAGCCTCCTC-3’ |
| ACTB-Forward | 5’-CCTGGCACCCAGCACAAT-3’ |
| ACTB-Reverse | 5’-GGGCCGGACTCGTCATAC-3’ |

Figure 1.
The differentially expressed NARCDs between LUAD tissues and normal tissues. (A) The volcano plot of differentially expressed ferroptosis genes. (B) The volcano plot of differentially expressed autophagy genes. (C) The volcano plot of differentially expressed pyroptosis genes. (D) The volcano plot of differentially expressed necroptosis genes. NARCDs: non-apoptotic regulated cell death genes; LUAD: lung adenocarcinoma; FDR: false discovery rate; FC: fold change."
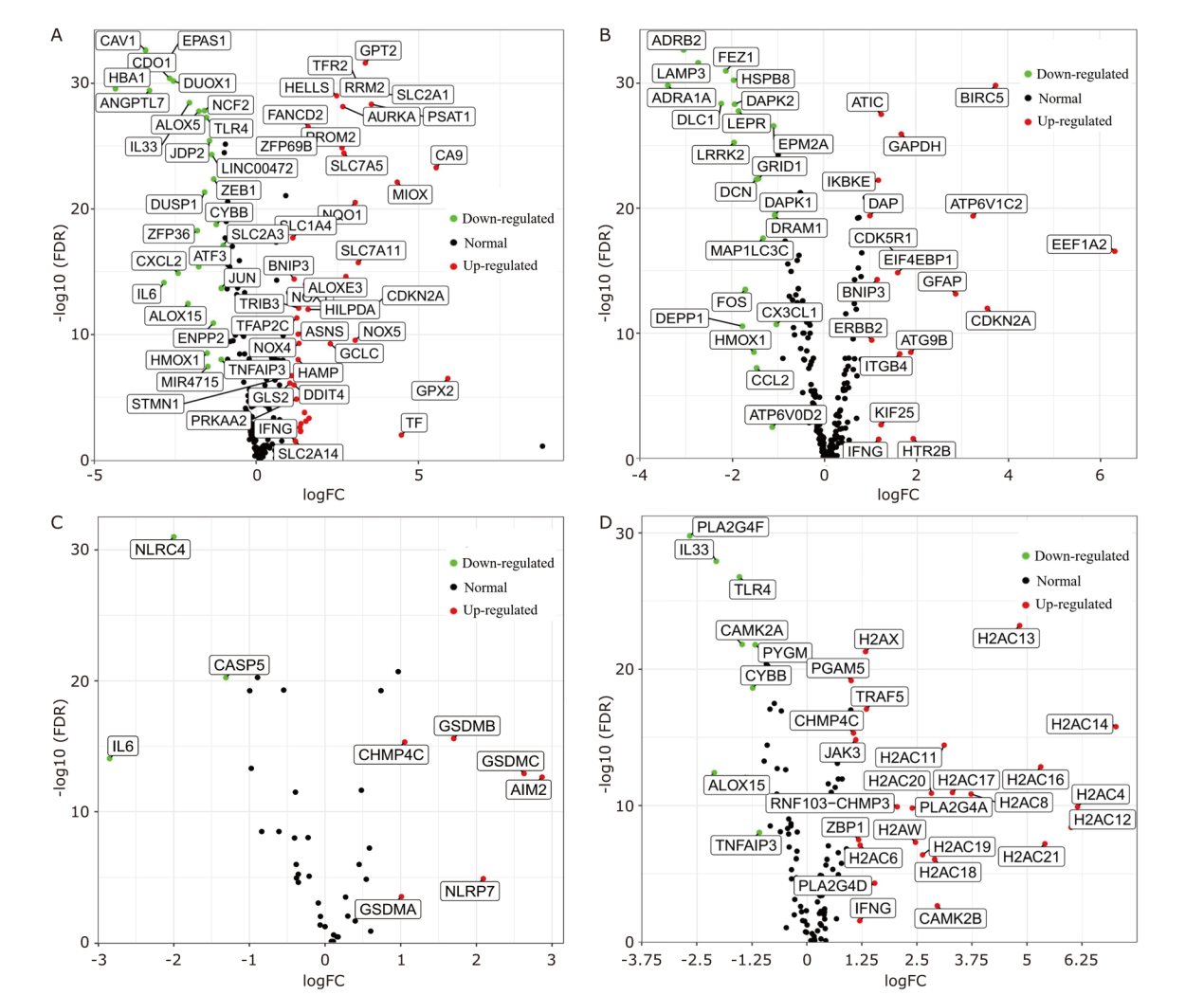
Figure 3.
Establishment of the NARCDs prognostic signature. (A, B) Screening of critical NARCDs by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator Cox regression. NARCDs score distribution of each LUAD patient in the training cohort (C) and in the validation cohorts (GSE31210, GSE30219) (D, E). Survival overview of each LUAD patient in the training cohort (F) and in the validation cohorts (G, H)."
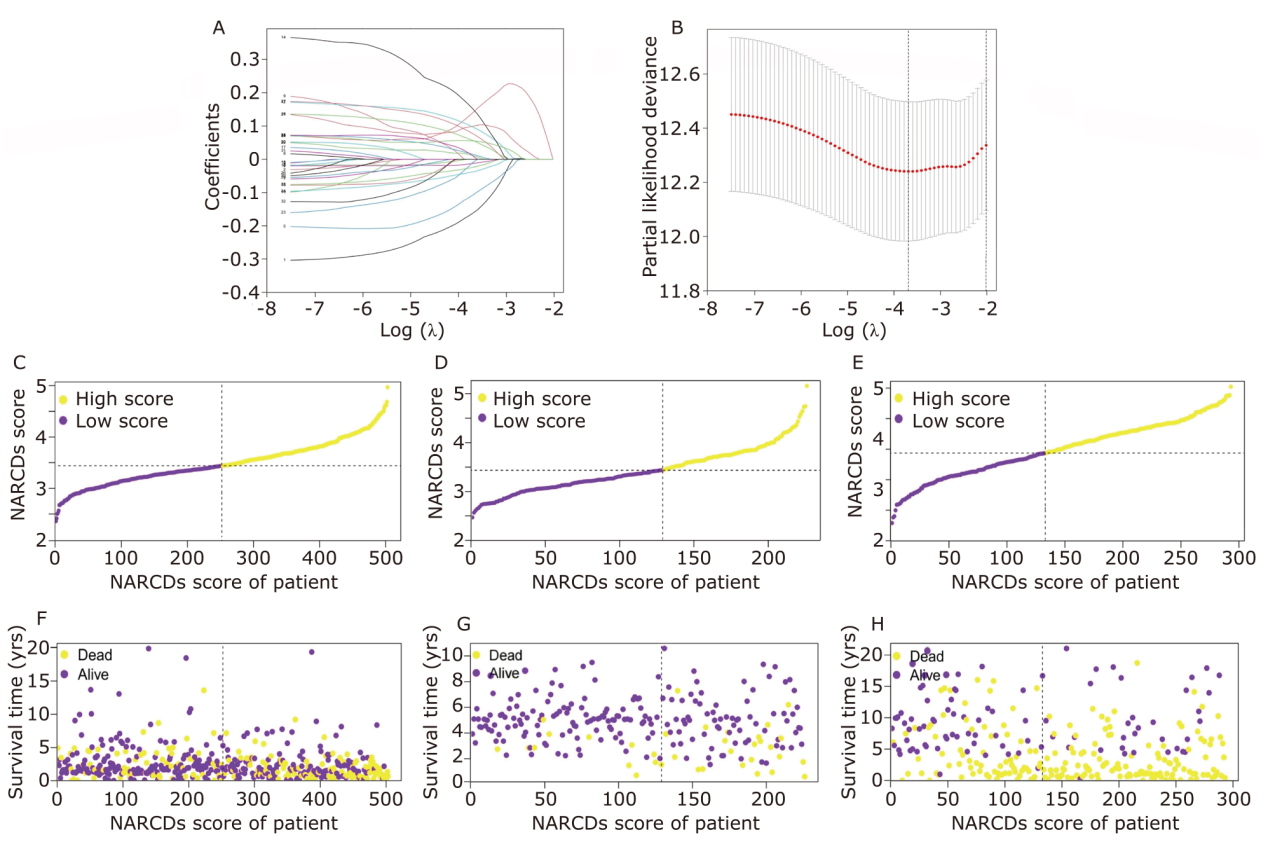

Figure 4.
Prognostic value of the NARCDs signature in the training and validation datasets. Survival analysis of the signature in the training cohort (A) and in the validation cohorts including GSE31210 (B) and GSE30219 (C). ROC curves of the signature in the training cohort (D) and in the validation cohorts (GSE31210, GSE30219) (E, F). 3D scatter plots of the signature in the training cohort (G) and in the validation cohorts (GSE31210, GSE30219) (H, I). ROC: receiver operating characteristic; AUC: area under curve; PCA: principal component analysis."
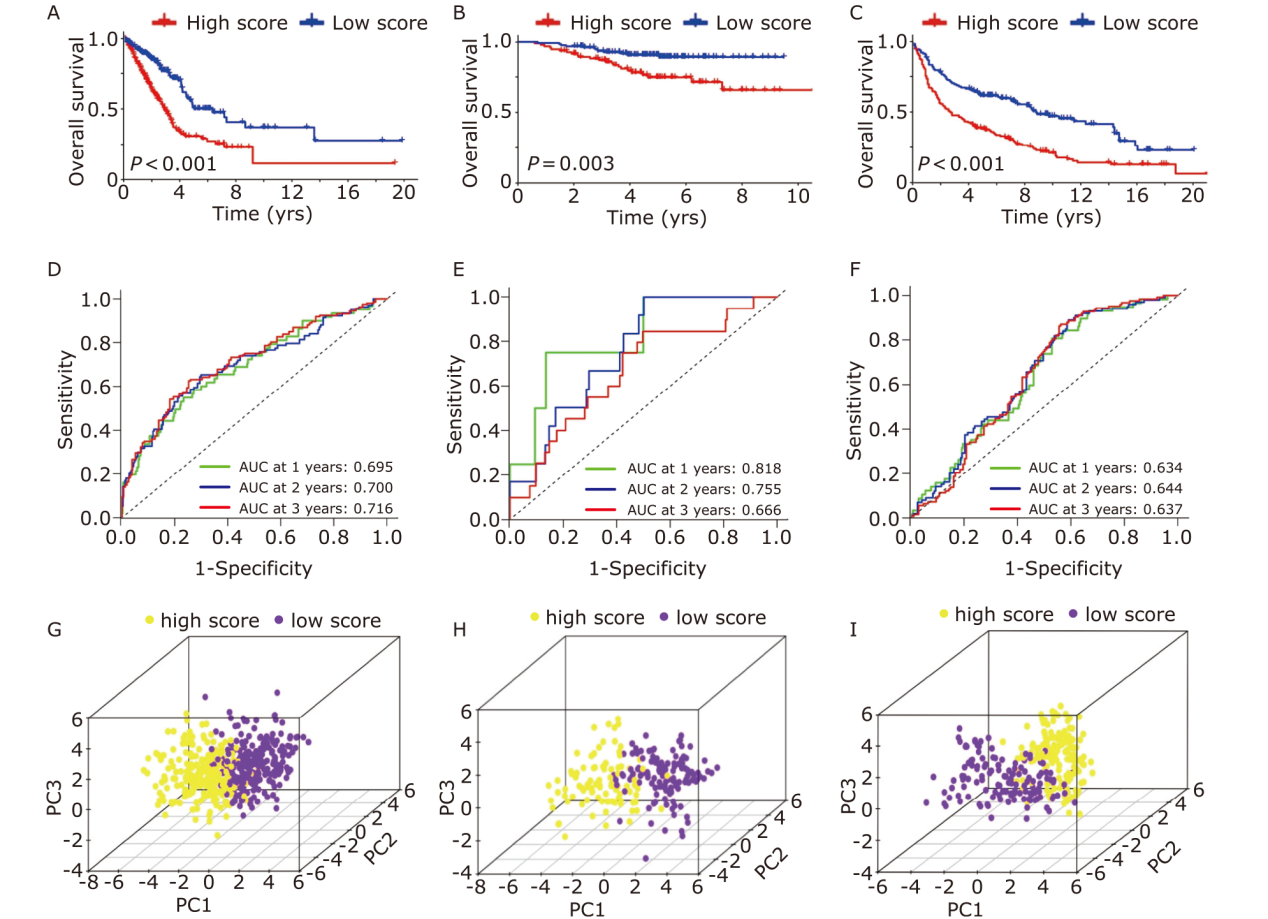
Figure 5.
Assessing the independence of the prognostic signature in the TCGA training cohort and GEO validation cohorts. Univariate Cox regression of NARCDs score and clinical characteristics in the TCGA-LUAD (A), GSE31210 (B), and GSE30219 (C). Multivariate Cox regression of NARCDs score and clinical characteristics in the TCGA-LUAD (D), GSE31210 (E), and GSE30219 (F). TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; GEO: Gene Expression Omnibus database; T: tumor; N: node; M: metastasis."
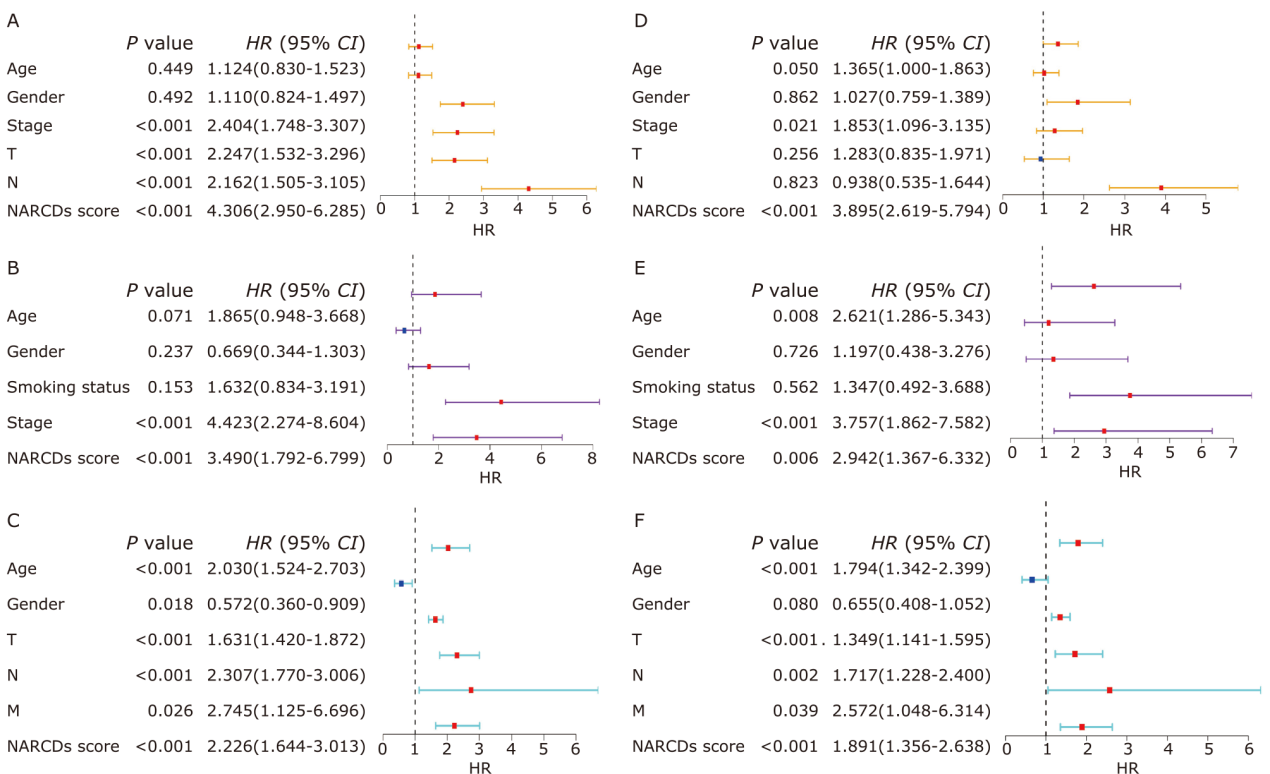
Figure 6.
Correlation between expression levels of six signature genes and risk score. (A-F) Correlation between top six NARCDs of prognostic signature and risk score. (G-L) RT-qPCR was used to detect the mRNA expression levels of six prognostic marker genes including GAPDH, RRM2, AURKA, CDK5R1, DDIT4, and ATIC in BEAS-2B, A549, and H1299 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared between two different cell lines."

| 1 | Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018; 553(7689):446-54. doi: 10.1038/nature25183. |
| 2 | Miller K D, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019; 69(5):363-85. doi: 10.3322/caac.21565. |
| 3 | Gao W, Wang X, Zhou Y, et al. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022; 7(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01046-3. |
| 4 | Liu J, Sun M, Sun Y, et al. TMEM189 promotes breast cancer through inhibition of autophagy-regulated ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2022; 622:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.06.024. |
| 5 |
Xie Y, Zhao Y, Shi L, et al. Gut epithelial TSC1/mTOR controls RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in intestinal inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 2020; 130(4):2111-28. doi: 10.1172/jci133264.
pmid: 31961824 |
| 6 |
Carleton G, Lum JJ. Autophagy metabolically suppresses CD8(+) T cell antitumor immunity. Autophagy 2019; 15(9):1648-9. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1628545.
pmid: 31170865 |
| 7 | Snyder AG, Hubbard NW, Messmer MN, et al. Intratumoral activation of the necroptotic pathway components RIPK1 and RIPK 3 potentiates antitumor immunity. Sci Immunol 2019; 2019; 4(36):eaaw2004. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw2004. |
| 8 | Wang Q, Wang Y, Ding J, et al. A bioorthogonal system reveals antitumour immune function of pyroptosis. Nature 2020; 579(7799):421-6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2079-1. |
| 9 | Xu C, Sun S, Johnson T, et al. The glutathione peroxidase Gpx 4 prevents lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis to sustain Treg cell activation and suppression of antitumor immunity. Cell Rep 2021; 35(11):109235. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109235. |
| 10 | Fang Q, Chen H. Development of a novel autophagy-related prognostic signature and nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 2020; 10:591356. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.591356. |
| 11 | Xu D, Ji Z, Qiang L. Molecular characteristics, clinical implication, and cancer immunity interactions of pyroptosis-related genes in breast cancer. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021; 8:702638. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.702638. |
| 12 | Zhang X, Yang Q. A pyroptosis-related gene panel in prognosis prediction and immune microenvironment of human endometrial cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021; 9:705828. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.705828. |
| 13 |
Xing M, Li J. Diagnostic and prognostic values of pyroptosis-related genes for the hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Bioinformatics 2022; 23(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04726-7.
pmid: 35562678 |
| 14 | Zhang Z, Hu X, Qiu D, et al. Development and validation of a necroptosis-related prognostic model in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Oncol 2022; 2022:8402568. doi: 10.1155/2022/8402568. |
| 15 |
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics 2013; 14:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-7.
pmid: 23323831 |
| 16 |
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun 2013; 4:2612. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3612.
pmid: 24113773 |
| 17 |
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, et al. Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 2018; 24(10):1550-8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1.
pmid: 30127393 |
| 18 | Yang W, Soares J, Greninger P, et al. Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC): a resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41:D955-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1111. |
| 19 |
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, et al. STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31(1):258-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg034.
pmid: 12519996 |
| 20 | Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 2014; 8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S11. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-s4-s11. |
| 21 | Han H, Yang C, Ma J, et al.N(7)-methylguanosine tRNA modification promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via the RPTOR/ULK1/autophagy axis. Nat Commun 2022; 13(1):1478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29125-7. |
| 22 | Lan H, Liu Y, Liu J, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote oxaliplatin resistance via METTL3-mediated m(6)A of TRAF5 and necroptosis in colorectal cancer. Mol Pharm 2021; 18(3):1026-37. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00961. |
| 23 | Xu Y, Lv D, Yan C, et al. METTL3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma tumor growth and inhibits ferroptosis by stabilizing SLC7A11 m(6)A modification. Cancer Cell Int 2022; 22(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02433-6. |
| 24 | Li N, Wang J, Zhan X. Identification of immune-related gene signatures in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Front Immunol 2021; 12:752643. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.752643. |
| 25 |
Wu X, Zhu J, Liu W, et al. A novel prognostic and predictive signature for lung adenocarcinoma derived from combined hypoxia and infiltrating immune cell-related genes in TCGA patients. Int J Gen Med 2021; 14:10467-81. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.S342107.
pmid: 35002303 |
| 26 |
Niu N, Zeng J, Ke X, et al. ATIC facilitates cell growth and migration by upregulating Myc expression in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett 2022; 23(4):131. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13251.
pmid: 35251351 |
| 27 |
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, et al. Tanshinone IIA suppresses the progression of lung adenocarcinoma through regulating CCNA2-CDK2 complex and AURKA/PLK1 pathway. Sci Rep 2021; 11(1):23681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03166-2.
pmid: 34880385 |
| 28 | Zhang X, Liu X, Cui W, et al. Sohlh2 alleviates malignancy of EOC cells under hypoxia via inhibiting the HIF1α/CA9 signaling pathway. Biol Chem 2020; 401(2):263-71. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2019-0119. |
| 29 |
Gan L, Meng J, Xu M, et al. Extracellular matrix protein 1 promotes cell metastasis and glucose metabolism by inducing integrin β4/FAK/SOX2/HIF-1α signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2018; 37(6):744-55. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.363.
pmid: 29059156 |
| 30 | Fan CC, Cheng WC, Huang YC, et al. EFHD2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and correlates with postsurgical recurrence of stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 2017; 7(1):14617. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15186-y. |
| 31 | Jiang X, Li Y, Zhang N, et al. RRM2 silencing suppresses malignant phenotype and enhances radiosensitivity via activating cGAS/STING signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Biosci 2021; 11(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00586-5. |
| 32 | Peng J, Li W, Tan N, et al. USP47 stabilizes BACH1 to promote the Warburg effect and non-small cell lung cancer development via stimulating Hk2 and Gapdh transcription. Am J Cancer Res 2022; 12(1):91-107. |
| 33 | Lv X, Yu H, Zhang Q, et al. SRXN1 stimulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis through modulating ROS/p65/BTG2 signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2020; 24(18):10714-29. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15693. |
| 34 | Yu X, Liu W, Chen S, et al. Immunologically programming the tumor microenvironment induces the pattern recognition receptor NLRC4-dependent antitumor immunity. J Immunother Cancer 2021; 9(1):e001595. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001595. |
| 35 | Suzuki S, Venkatesh D, Kanda H, et al. GLS2 is a tumor suppressor and a regulator of ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2022; 82(18):3209-22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-21-3914. |
| 36 |
Lu T, Zheng C, Fan Z. Cardamonin suppressed the migration, invasion, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and lung metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating ADRB2 expression. Pharm Biol 2022; 60(1):1011-21. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2069823.
pmid: 35645356 |
| 37 | Tang W, Jia P, Zuo L, et al. Suppression of CX3CL 1 by miR-497-5p inhibits cell growth and invasion through inactivating the ERK/AKT pathway in NSCLC cells. Cell Cycle 2022; 21(16):1697-709. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2067438. |
| 38 | Duan L, Pang HL, Chen WJ, et al. The role of GDF 15 in bone metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 2019; 41(4):2379-88. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7024. |
| 39 | Zhao H, Xu Y, Xie Y, et al. m6A regulators are differently expressed and correlated with immune response of esophageal cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021; 9:650023. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.650023. |
| 40 |
Demelash A, Rudrabhatla P, Pant HC, et al. Achaete-scute homologue-1 (ASH1) stimulates migration of lung cancer cells through Cdk5/p35 pathway. Mol Biol Cell 2012; 23(15):2856-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-1010.
pmid: 22696682 |
| 41 | Du F, Sun L, Chu Y, et al. DDIT4 promotes gastric cancer proliferation and tumorigenesis through the p53 and MAPK pathways. Cancer Commun (Lond) 2018; 38(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0315-y. |
| 42 |
Nakae S, Suto H, Iikura M, et al. Mast cells enhance T cell activation: importance of mast cell costimulatory molecules and secreted TNF. J Immunol 2006; 176(4):2238-48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.4.2238.
pmid: 16455980 |
| 43 |
Lorente E, García R, López D. Allele-dependent processing pathways generate the endogenous human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I peptide repertoire in transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP)-deficient cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286(44):38054-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.281808.
pmid: 21914809 |
| 44 | Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The roles of IFN gamma in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2002; 13(2):95-109. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00038-7. |
| 45 |
Vatner RE, Janssen EM. STING, DCs and the link between innate and adaptive tumor immunity. Mol Immunol 2019; 110:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.001.
pmid: 29273394 |
| 46 | Kirtonia A, Sethi G, Garg M. The multifaceted role of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2020; 77(22):4459-83. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03536-5. |
| 47 | Stenzinger A, Allen JD, Maas J, et al. Tumor mutational burden standardization initiatives: recommendations for consistent tumor mutational burden assessment in clinical samples to guide immunotherapy treatment decisions. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019; 58(8):578-88. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22733. |
| 48 |
Xu J, Zhang Y, Jia R, et al. Anti-PD-1 antibody SHR-1210 combined with apatinib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric, or esophagogastric junction cancer: an open-label, dose escalation and expansion study. Clin Cancer Res 2019; 25(2):515-23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-2484.
pmid: 30348638 |
| 49 | Ning XH, Li NY, Qi YY, et al. Identification of a hypoxia-related gene model for predicting the prognosis and formulating the treatment strategies in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front Oncol 2021; 11:806264. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.806264. |
| 50 |
Zhou G, Liu Z, Myers JN. TP53 mutations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and their impact on disease progression and treatment response. J Cell Biochem 2016; 117(12):2682-92. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25592.
pmid: 27166782 |
| 51 | Canale M, Andrikou K, Priano I, et al. The role of TP 53 mutations in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical significance and implications for therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2022; 14(5):1143. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051143. |
| [1] | Wenqin Xu, Jingjing Ye, Tianbing Chen. Identifying and Validating a Novel miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Associated with Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 31-43. |
| [2] | Huang Chao, Xiang Keming, Liang Bingjun, Huang Weixuan, Zhang Fanjun, Shao Yuwan, Wang Xiulian, Liu Haosheng, Shen Weizeng. Combination of Evodiamine with Berberine Reveals a Regulatory Effect on the Phenotypic Transition of Colon Epithelial Cells Induced by CCD-18Co [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 195-206. |
| [3] | Ou Jinhuan, Li Yiran, Wang Zhipeng, Jin Cheng, Li Kai, Lu Yan, Zou Dingfeng, Li Pengyu, Li Mengzhen, Miao Shiying, Wang Linfang, Song Wei. Lrrc34 Is Highly Expressed in SSCs and Is Necessary for SSC Expansion In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 20-30. |
| [4] | Ni Jieming, Ni Anping. Landscape of PD-1/PD-L1 Regulation and Targeted Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 174-182. |
| [5] | Zhao Zhimei, Liu Shichao, Xu Xiajuan, Zhang Zhongfa, Nie Keke, Ji Youxin. Treatment of Skin Reaction Induced by Nivolumab Combined with Radiotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 183-187. |
| [6] | Zhu Yimin, Xu Fuying. Up-regulation of Let-7a Expression Induces Gastric Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(1): 44-47. |
| [7] | Yun-jie Chen, Hai-tao Jiang, Jing-yu Cao. Influence of Photodynamic Therapy on Apoptosis and Invasion of Human Cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 Cell Line [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(4): 252-259. |
| [8] | Jin-hui Shao, Gui-hua Feng. Inhibition Mechanism of Novel Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrazin-4(5H)-one Derivatives Against Proliferation of A549 and H322 Cancer Cells [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(4): 260-265. |
| [9] | Ying-qiu Pan, Wei-wu Shi, Dan-ping Xu, Hui-hui Xu, Mei-ying Zhou, Wei-hua Yan*. Associations Between Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutation and Serum Tumor Markers in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Retrospective Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(3): 156-161. |
| [10] | Ling Li, Hong-jie Li, Jian-sheng zhi, Hong Chen, Wen-li Xie. ZM-66, a New Podophyllotoxin Derivative Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in K562/ADM Cells [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(3): 174-179. |
| [11] | Zong-ming Wan, Lu Liu, Jian-yu Li, Rui-xin Li, Yong Guo, Hao Li, Jian-ming Zhang, Xi-zheng Zhang. Mechanical Stimulus Inhibits the Growth of a Bone Tissue Model Cultured In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2013, 28(4): 218-224. |
| [12] | Hong-bo Yang, Wen-jie Zheng, Xuan Zhang, Fu-lin Tang. Induction of Endothelial Cell Apoptosis by Anti-alpha-enolase Antibody [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2011, 26(3): 152-157. |
| [13] | Jian-ling Tao, Xiong-zhong Ruan, Hang Li, Xue-mei Li and Xue-wang Li. Lipids-induced Apoptosis Is Aggravated by Acyl-coenzyme A: Cholesterol Acyltransferase Inhibitor [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(2): 76-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|