Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 103-109.doi: 10.24920/003792
亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因C677T多态性与中国2型糖尿病患者冠心病风险增加相关
吴坤荣1,张恕芳2,关紫菀1,李晓黎2,李蕊1,尹影2,李妍1,*( )
)
- 1山东第一医科大学第一附属医院临床药学科,济南 250014
2山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)药学院,山东,泰安 271000
-
收稿日期:2020-08-18出版日期:2021-06-30 -
通讯作者:李妍 E-mail:prof_liyan@126.com
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism C677T is Associated with Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Kunrong Wu1,Shufang Zhang2,Ziwan Guan1,Xiaoli Li2,Rui Li1,Ying Yin2,Yan Li1,*( )
)
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250014, China
2School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shandong First Medical University (Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences) Tai’an 271000, Shandong, China
-
Received:2020-08-18Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:Yan Li E-mail:prof_liyan@126.com
摘要:
目的 长期血糖控制不佳引起的慢性心血管疾病是2型糖尿病患者主要的死亡原因。研究表明:亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因(methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene,MTHFR)多态性可能会影响2型糖尿病患者冠心病的发生。本研究旨在评估MTHFR C677T和A1298C基因突变是否与2型糖尿病患者冠心病的发生风险相关。
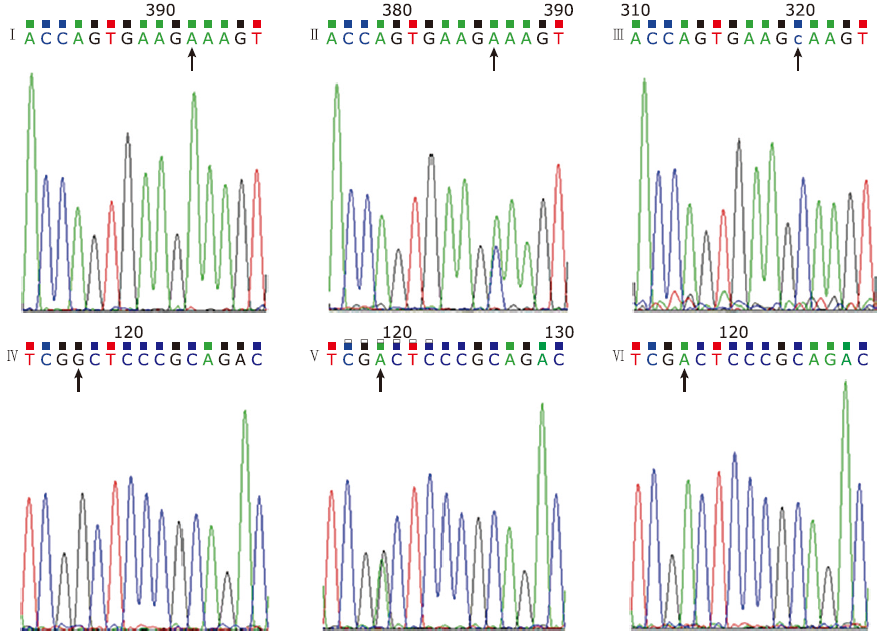
方法 本研究一共纳入197例2型糖尿病受试者,其中95例受试者合并冠心病。采用双脱氧链终止法对MTHFR C677T和A1298C进行基因分型,并分析比较合并冠心病与不合并冠心病受试者等位基因频率的差异。
结果 合并冠心病2型糖尿病受试者的677T等位基因频率明显高于不合并冠心病的受试者(P=0.011)。单倍型频率在合并冠心病与不合并冠心病的2型糖尿病受试者之间无显著的差异。在同型半胱氨酸水平较低的糖尿病受试者中(≤15μmol/L),携带677T等位基因的受试者发生冠心病风险更高(P=0.006),而在同型半胱氨酸水平较高的糖尿病受试者中(>15μmol/L),MTHFR基因多态性对冠心病的发生风险无影响(P=0.491)。
结论 MTHFRC677T基因多态性与糖尿病患者发生冠心病的风险相关,对于具有正常同型半胱氨酸水平的中国糖尿病人群,其可作为预测冠心病风险的有效标志物。
引用本文
Kunrong Wu, Shufang Zhang, Ziwan Guan, Xiaoli Li, Rui Li, Ying Yin, Yan Li. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism C677T is Associated with Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Patients[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 103-109.
"
| Items | T2DM patients without CHD | T2DM patients with CHD | Pvalue |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 102 | 95 | |
| Male [n (%)] | 67 (65.69) | 62 (65.26) | 0.950 |
| Age (yrs) | 63.14±6.78 | 64.34±8.11 | 0.263 |
| Current smoker [n (%)] | 26 (25.49) | 27 (28.42) | 0.547 |
| Age at T2DM diagnosis (yrs) | 50.23±7.93 | 51.67±9.80 | 0.257 |
| Diabetes duration (yrs) | 12.91±5.97 | 12.66±6.66 | 0.642 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.07±2.99 | 25.18±2.79 | 0.787 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 7.95±2.08 | 8.10±2.33 | 0.733 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.57±1.67 | 8.33±2.17 | 0.115 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.59±1.02 | 4.44±1.05 | 0.337 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.60±0.96 | 1.42±0.67 | 0.553 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.21±0.28 | 1.20±0.39 | 0.523 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.64±0.83 | 2.52±0.75 | 0.436 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 133.26±12.42 | 131.01±13.62 | 0.228 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 75.85±7.34 | 74.89±9.17 | 0.420 |
| Scr (μmol/L) | 66.21±18.40 | 70.25±22.48 | 0.128 |
"
| Hcy levels (μmol/L) | MTHFR genotypes | Patients without CHD (n) | Patients with CHD (n) | OR(95%CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-15.0 | 677CC | 21 | 4 | ||
| 677CT+TT | 67 | 56 | 4.39 (1.42-13.54) | 0.006 | |
| 1298AA | 55 | 31 | |||
| 1298AC+CC | 31 | 10 | 0.57 (0.25-1.32) | 0.189 | |
| >15.0 | 677CC | 1 | 5 | ||
| 677CT+TT | 13 | 30 | 0.46 (0.05-4.35) | 0.491 | |
| 1298AA | 9 | 17 | |||
| 1298AC+CC | 5 | 9 | 0.95 (0.25-3.71) | 0.945 |
| [1.] |
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus-present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2011; 8(4):228-36. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.183.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.183 pmid: 22064493 |
| [2.] |
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Group. Update of mortality attributable to diabetes for the IDF Diabetes Atlas: estimates for the year 2013. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015; 109(3):461-5. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.05.037.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.05.037 |
| [3.] |
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2004; 27 Suppl 1:S5-S10. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.2007.s5.
doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.2007.s5 |
| [4.] |
Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001; 414(6865):813-20. doi: 10.1038/414813a.
doi: 10.1038/414813a pmid: 11742414 |
| [5.] |
Rizvi S, Raza ST, Mahdi F. Association of genetic variants with diabetic nephropathy. World J Diabetes 2014; 5(6):809-16. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i6.809.
doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i6.809 |
| [6.] |
Sun J, Xu Y, Zhu Y, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism, homocysteine and risk of macroangiopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol Invest 2006; 29(9):814-20. doi: 10.1007/BF03347376.
doi: 10.1007/BF03347376 |
| [7.] |
Fekih-Mrissa N, Mrad M, Ibrahim H, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) (C677T and A1298C) polymorphisms and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes . Can J Diabetes 2017; 41(4):366-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2016.11.007.
doi: S1499-2671(16)30784-5 pmid: 28341195 |
| [8.] |
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet 1995; 10(1):111-3. doi: 10.1038/ng0595-111.
doi: 10.1038/ng0595-111 pmid: 7647779 |
| [9.] |
Harmon DL, Woodside JV, Yarnell JW, et al. The common ‘thermolabile’ variant of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase is a major determinant of mild hyperhomocysteinaemia. QJM 1996; 89(8):571-7. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/89.8.571.
doi: 10.1093/qjmed/89.8.571 |
| [10.] |
van der Put NM, Gabreëls F, Stevens EM, et al. A second common mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene: an additional risk factor for neural-tube defects? Am J Hum Genet 1998; 62(5):1044-51. doi: 10.1086/301825.
doi: 10.1086/301825 pmid: 9545395 |
| [11.] |
van der Put NM, Blom HJ. Neural tube defects and a disturbed folate dependent homocysteine metabolism. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2000; 92(1):57-61. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(00)00426-7.
doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(00)00426-7 pmid: 10986435 |
| [12.] |
Hankey GJ, Eikelboom JW. Homocysteine and vascular disease. Lancet 1999; 354(9176):407-13. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)11058-9.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)11058-9 pmid: 10437885 |
| [13.] |
Stehouwer CD, Weijenberg MP, van den Berg M, et al Serum homocysteine and risk of coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular disease in elderly men: a 10-year follow-up. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18(12):1895-901. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.12.1895.
doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.12.1895 |
| [14.] |
Aso Y, Yoshida N, Okumura K, et al. Coagulation and inflammation in overt diabetic nephropathy: association with hyperhomocysteinemia. Clin Chim Acta 2004; 348(1-2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.05.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.05.006 |
| [15.] |
Doupis J, Eleftheriadou I, Kokkinos A, et al. Acute hyperhomocysteinemia impairs endothelium function in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2010; 118(7):453-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1248290.
doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1248290 |
| [16.] |
Mtiraoui N, Ezzidi I, Chaieb M, et al. MTHFR C677T and A1298C gene polymorphisms and hyperhomocysteinemia as risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients . Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007; 75(1):99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.05.018.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.05.018 |
| [17.] | Sun J, Xu Y, Zhu Y, et al. The relationship between MTHFR gene polymorphisms, plasma homocysteine levels and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus . Chin Med J (Engl) 2003; 116(1):145-7. |
| [18.] | Cao H, Huang DF, Mao L, et al. Association of homocysteine, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus with cerebral infarction. Chin J Dis Control Prev 2010; 14(3):196-8. (In Chinese) |
| [19.] | Luo D, Yan SK, Cheng XQ, et al. Levels of homocysteine and polymorphisms of homocysteine metabolism related enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. J Hygiene Res 2009; 38(1):39-42. (In Chinese) |
| [20.] |
Sun J, Xu Y, Xue J, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism associated with susceptibility to coronary heart disease in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2005; 229(1-2):95-101. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2004.09.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2004.09.003 |
| [21.] |
Wu XF, Cheng LX, He MA. Association between polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and coronary heart disease. Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong 2009; 38(3):296-300. doi: 10.3870/ j.issn.1672-0741.2009.03.004. (In Chinese)
doi: 10.3870/ j.issn.1672-0741.2009.03.004. (In Chinese |
| [22.] |
Zhao XD, Wang L. The relationship of plasma homocysteine and the polymorphism of MTHFR gene with brain infaction in type 2 diabetes mellitus . Chin J Diabetes 2015; 23(2):107-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2015.02.003. (In Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2015.02.003. (In Chinese |
| [23.] |
Wang GB, Shen QD, ping LD. Correlation between homocysteine levels and MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism of cerebral infarction . J Med Res 2017; 46(5):154-8. doi: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.05.038. (In Chinese)
doi: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.05.038. (In Chinese |
| [24.] |
Mata-Cases M, Artola S, Escalada J, et al. Consensus on the detection and management of prediabetes. Consensus and Clinical Guidelines Working Group of the Spanish Diabetes Society. Rev Clin Esp 2015; 215(2):117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.rce.2014.10.012.
doi: 10.1016/j.rce.2014.10.012 pmid: 25553948 |
| [25.] | Cardiovascular Specialty Group in the First National Internal Medicine Conference. Recommendations on the naming and diagnostic criteria of coronary heart disease. Chin J Int Med 1981; 20(4):253-5. (In Chinese) |
| [26.] | Dzida G, Biłan A, Golon-Siekierska P, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Pol Arch Med Wewn 2001; 106(1):543-9. |
| [27.] |
Beneš P, Kaňková K, Mužı́k J, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism, typeⅡ diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and essential hypertension in the Czech population. Mol Genet Metab 2001; 73(2):188-95. doi: 10.1006/mgme.2001.3188.
doi: 10.1006/mgme.2001.3188 |
| [28.] |
Settin A, El-Baz R, Ismaeel A, et al. Association of ACE and MTHFR genetic polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus: susceptibility and complications . J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 2015; 16(4):838-43. doi: 10.1177/1470320313516172.
doi: 10.1177/1470320313516172 pmid: 24452036 |
| [29.] |
Böger CA, Stubanus M, Haak T, et al. Effect of MTHFR C677T genotype on survival in type 2 diabetes patients with end-stage diabetic nephropathy . Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007; 22(1):154-62. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl512.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl512 |
| [30.] |
Brulhart MC, Dussoix P, Ruiz J, et al. The (Ala-Val) mutation of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase as a genetic risk factor for vascular disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 60(1):228-9.
pmid: 8981966 |
| [31.] |
Wirta V, Huang XH, Wirta O, et al. Mutation C677T of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is not associated with coronary artery disease, but possibly with albuminuria, in type 2 diabetic patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 1998; 36(8):625-8. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.1998.109.
doi: 10.1515/CCLM.1998.109 pmid: 9806473 |
| [32.] |
Audelin MC, Genest JJ. Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2001; 159(2):497-511. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(01)00531-7.
doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(01)00531-7 pmid: 11730832 |
| [33.] |
Hoogeveen EK, Kostense PJ, Beks PJ, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, especially in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a population-based study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18(1):133-8. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.1.133.
doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.1.133 |
| [34.] | Yeromenko Y, Lavie L, Levy Y. Homocysteine and cardiovascular risk in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2001; 11(2):108-16. |
| [1] | 陈紫晗,赵洲,邓垂文,李乃适. 发展中国家空气污染与2型糖尿病的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(3): 218-227. |
| [2] | 祖红林,侯骊坤,刘洪伟,詹渊博,何菊. 应用BITOLA系统筛选腹主动脉瘤与2型糖尿病相互作用的候选基因[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 50-56. |
| [3] | 林烨, 王祯莲, 严敏, 朱飞雨, 端烨, 孙志琴. 曲美他嗪对糖尿病合并冠心病患者的疗效:一项随机对照试验的荟萃分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 226-238. |
| [4] | 沈畅, 赵萌, 李芸云, 刘宁朴. 荟萃分析:亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因C677T(MTHFR-C677T)多态性与糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)的关系[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 71-84. |
| [5] | 尹影, 李蕊, 李晓黎, 吴坤荣, 李玲, 徐曰东, 廖琳, 杨蕊, 李妍. 伴血脂异常2型糖尿病患者亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶基因多态性与血浆同型半胱氨酸水平的相关性[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 85-91. |
| [6] | 周梦馨, 孙蕊, 陈跃鑫. 合并冠心病的静脉血栓栓塞症患者的抗栓治疗[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 120-126. |
| [7] | 黎简平, 傅永平, 常文秀, 易昌容, 刘丽华, 邢海燕. 过氧化物酶体增值物激活受体-γ2基因启动子区C-689T多态性与汉族人群冠心病的相关性[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 177-184. |
| [8] | 陈志晔, 臧秀娟, 刘梦琦, 刘梦雨, 李金锋, 谷昭艳, 马林. 16例新发2型糖尿病患者脑部皮层厚度异常变化的MRI初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|