Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 19-28.doi: 10.24920/004338
基于数据非依赖性采集定量蛋白质组学分析的原发性干燥综合征潜在唾液生物标志物研究
田艺超1,郭春岚1,李珍1,尤欣2,刘晓燕3,苏金梅2,赵斯佳1,穆月1,孙伟3,*( ),李倩1,*(
),李倩1,*( )
)
- 1中国医学科学院北京协和医院口腔科,北京 100730,中国
2中国医学科学院北京协和医院风湿病与临床免疫学系,北京 100730,中国
3北京协和医学院基础医学院中国医学科学院基础医学研究所仪器核心设施蛋白质组学中心,北京 100730,中国
-
收稿日期:2024-01-15接受日期:2024-03-08出版日期:2024-03-31 -
通讯作者:孙伟,李倩
Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Potential Salivary Biomarkers of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome
Yi-Chao Tian1,Chun-Lan Guo1,Zhen Li1,Xin You2,Xiao-Yan Liu3,Jin-Mei Su2,Si-Jia Zhao1,Yue Mu1,Wei Sun3,*( ),Qian Li1,*(
),Qian Li1,*( )
)
- 1Department of Stomatology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3Proteomics Center, Core Facility of Instrument, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & School of Basic Medicine Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2024-01-15Accepted:2024-03-08Published:2024-03-31 -
Contact:* Qian Li E-mail:liqian4230@pumch.cn ;Wei Sun, E-mail:sunwei@ibms.pumc.edu.cn .
摘要:
目的 唾液腺是原发性干燥综合征(pSS)的主要靶器官,因此唾液被认为是腺体病理生理学和疾病状态的镜子。本研究旨在说明pSS患者的唾液蛋白质组学特征,并鉴定可能辅助诊断的潜在生物标志物。
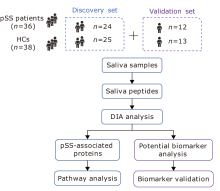
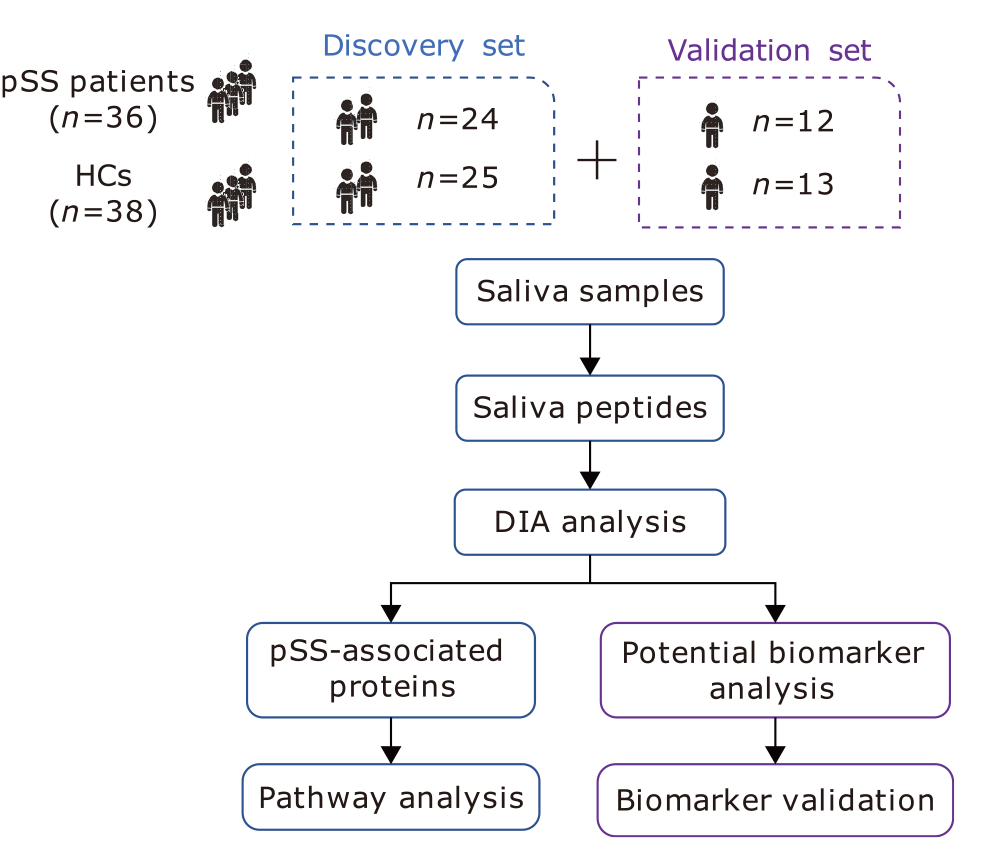
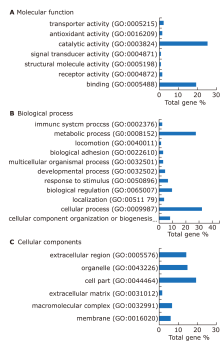
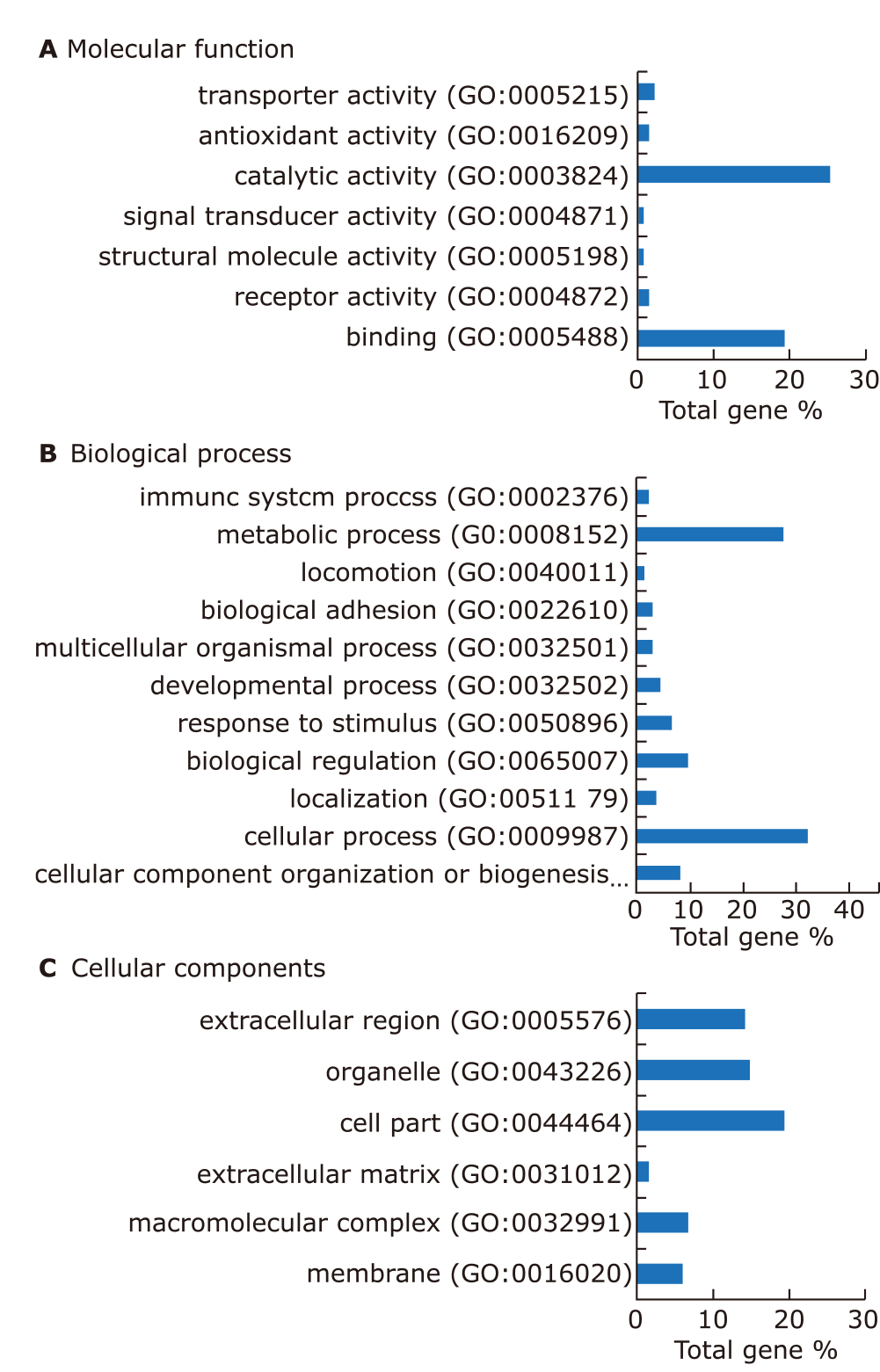
方法 发现集包含49个样本[24个来自pSS,25个来自年龄和性别匹配的健康对照(HCs)],验证集包括25个样本(12个来自pSS,13个来自HCs)。36 例 pSS 患者和 38 例健康对照者以 2:1 的比例集中随机分配至 Discovery 组或验证组。在2D LC-HRMS/MS平台上使用数据非依赖性采集(DIA)策略分析来自pSS患者和健康对照组的未刺激性全唾液样本,以揭示差异蛋白。根据基因本体(GO)分析和国际药学文摘(IPA)分析的蛋白质注释,使用DIA分析验证了关键蛋白质。随机森林用于建立SS的预测模型。
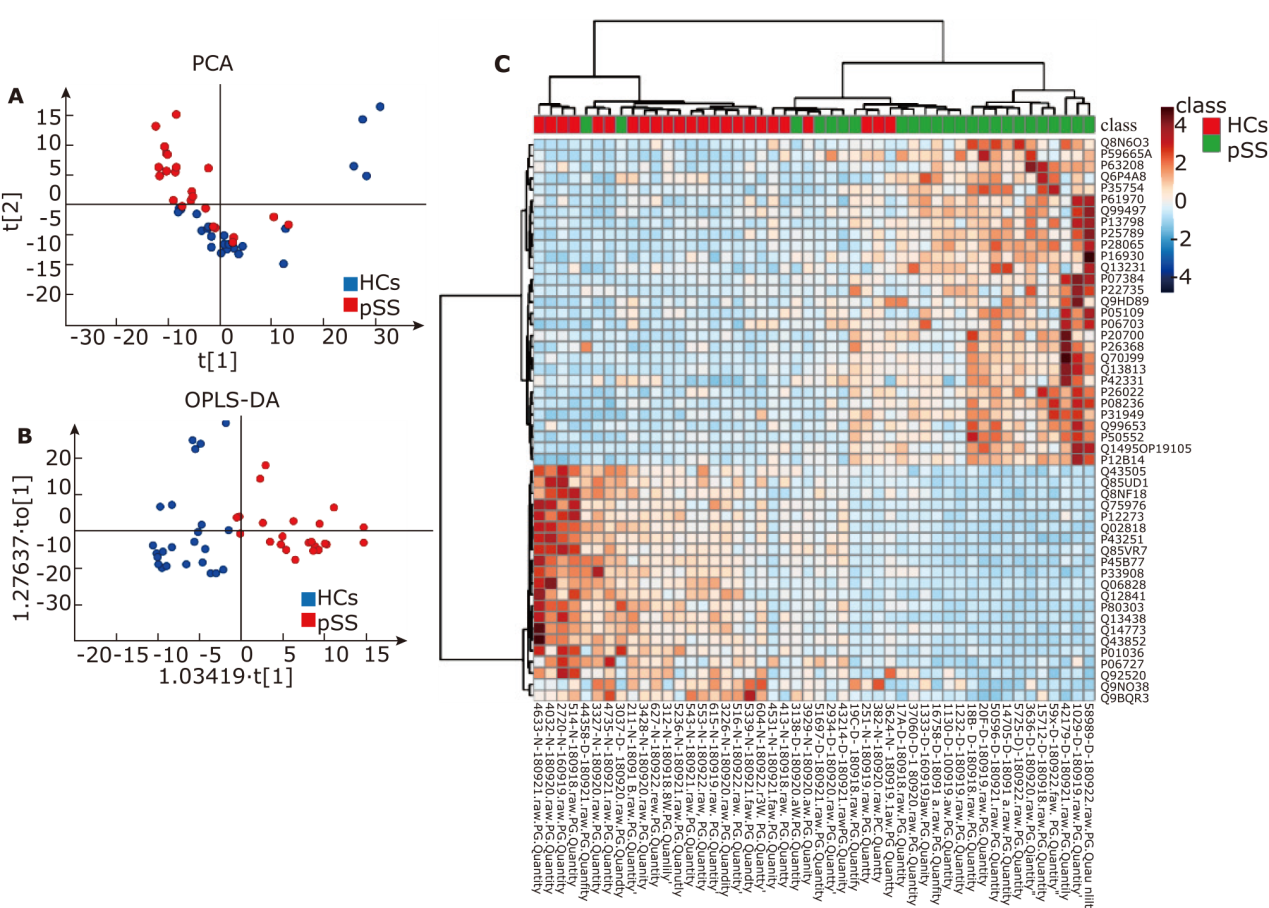
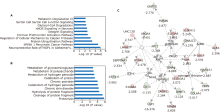
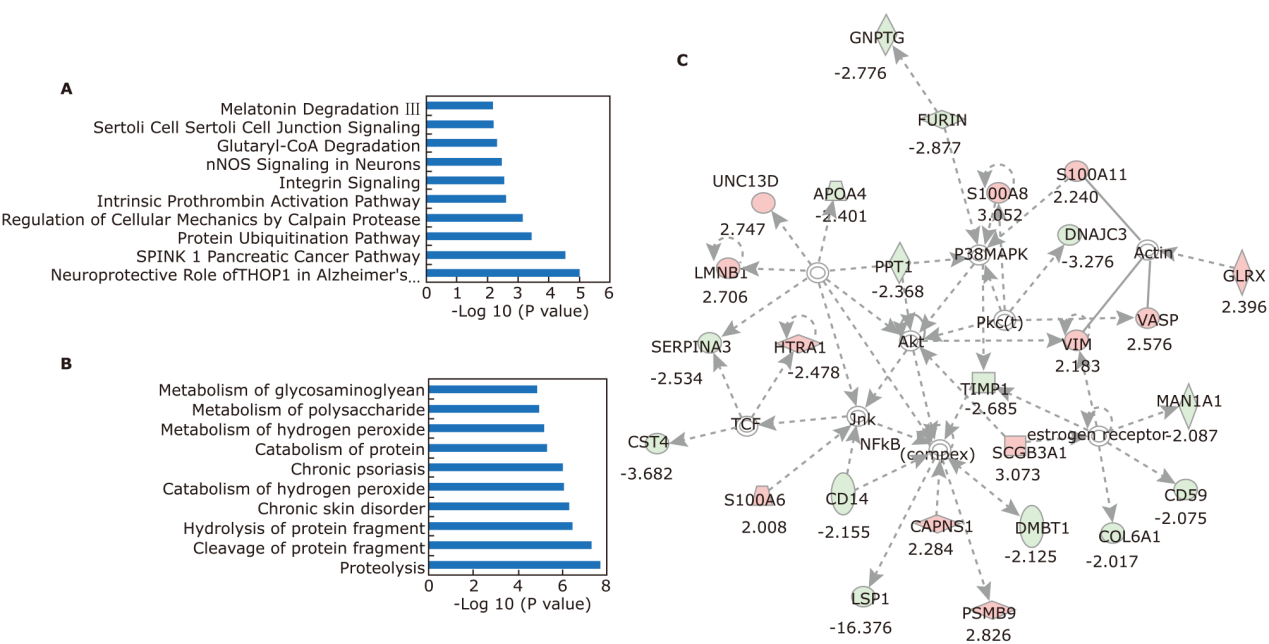
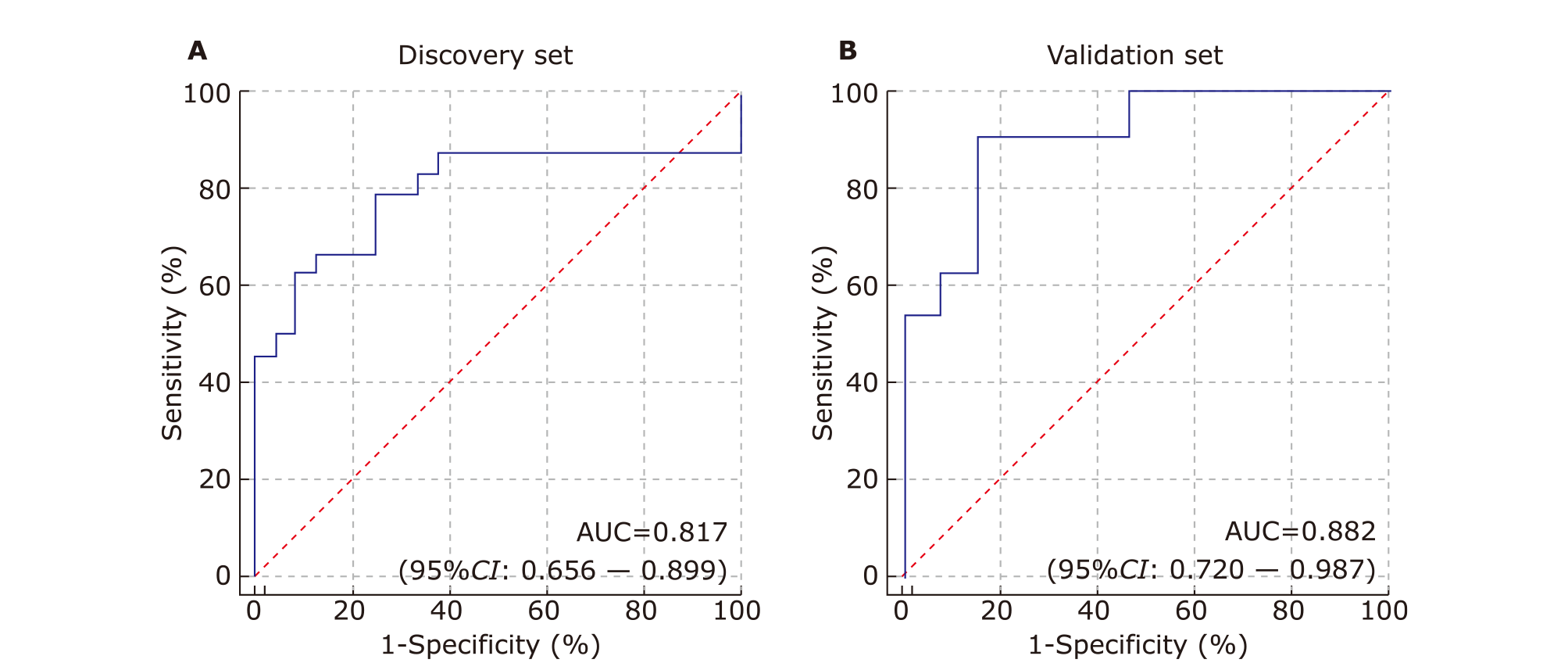
结果 共发现1,963个蛋白,其中136个蛋白在pSS患者中表现出差异性。生物信息学研究表明这些蛋白质主要与免疫功能、新陈代谢和炎症有关。一组19个蛋白质生物标志物通过基于P 值和随机森林的排序顺序进行鉴定,并验证为具有特殊曲线下面积 (AUC) 值(发现集:0.817;验证集:0.882)的潜在生物标志物,可用于鉴别pSS 患者和健康对照人群。
结论 新发现的候选蛋白组合可能有助于pSS的诊断。唾液蛋白质组学分析是一种很有前途的无创方法,可用于对pSS患者进行预后评估以及早期和精确治疗。DIA具备最佳的时间效率和数据可靠性,可望成为未来唾液蛋白质组研究的合适选择。
引用本文
Yi-Chao Tian, Chun-Lan Guo, Zhen Li, Xin You, Xiao-Yan Liu, Jin-Mei Su, Si-Jia Zhao, Yue Mu, Wei Sun, Qian Li. Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Potential Salivary Biomarkers of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2024, 39(1): 19-28.
"
| Characteristics | pSS group | HCs group | t/X2 | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery (n=24) | Validation (n=12) | Discovery (n=25) | Validation (n=13) | ||||
| Age, yrs, mean±SD | 41.1±10.9 | 40.6±12.8 | 41.4±12.2 | 44.1±12.7 | 0.049 | 0.88 | |
| Sex, females [n(%)] | 21(87.5) | 10(83.3) | 23 (92) | 12 (92.3) | 0.075 | 0.60 | |
| Anti-SSA/Ro antibody + [n(%)] | 16(66.7) | 9(75.0) | / | / | 0.574 | 0.682 | |
| Anti-SSB/La antibody + [n(%)] | 3(12.5) | 1(8.3) | / | / | 0.112 | 1 | |
| Immunoglobulin G + [n(%)] | 12(50.0) | 6(50.0) | / | / | 0 | 1 | |
| Labial gland biopsy + [n(%)] | 13(54.2) | 9(75.0) | / | / | 2.595 | 0.205 | |
"
| No. | Protein name | AUC | P value | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q13217 | 0.86285 | 0.002438 | 2.0129 |
| 2 | P01034 | 0.85764 | 0.006314 | 2.6949 |
| 3 | P07711 | 0.85243 | 0.001923 | 1.831 |
| 4 | P09958 | 0.85069 | 0.001031 | 1.8654 |
| 5 | P28065 | 0.85069 | 7.72E-06 | -1.2467 |
| 6 | O43852 | 0.84201 | 6.80E-04 | 1.4389 |
| 7 | O43505 | 0.83854 | 2.39E-04 | 1.4676 |
| 8 | P25789 | 0.82812 | 9.41E-05 | -1.276 |
| 9 | Q9UBX7 | 0.81771 | 0.00464 | 1.3578 |
| 10 | Q9NRJ3 | 0.81597 | 0.024021 | 1.4358 |
| 11 | P35030 | 0.81424 | 0.001265 | 1.3919 |
| 12 | P12109 | 0.8125 | 0.008958 | 1.3342 |
| 13 | O75976 | 0.80903 | 6.50E-04 | 1.3292 |
| 14 | Q92743 | 0.80035 | 0.46752 | 1.0645 |
| 15 | P16870 | 0.7934 | 0.001147 | 1.3544 |
| 16 | P13798 | 0.78646 | 5.01E-04 | -1.0262 |
| 17 | P01011 | 0.75347 | 0.018898 | 2.5295 |
| 18 | P32320 | 0.74306 | 0.001919 | -0.88055 |
| 19 | P08670 | 0.73785 | 0.006534 | -1.581 |
| 1. | González S, Sung H, Sepúlveda D, et al. Oral manifestations and their treatment in Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Dis 2014; 20: 153-61. doi: 10.1111/odi.12105. |
| 2. | Brito-Zerón P, Baldini C, Bootsma H, et al. Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016; 2: 16047. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2022.10.007. |
| 3. | Soret P le Dantec C, Desvaux E, et al. A new molecular classification to drive precision treatment strategies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Nat Commun 2021; 12: 3523. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23472-7. |
| 4. |
Vitorino R, Lobo MJC, Ferrer-Correira AJ, et al. Identification of human whole saliva protein components using proteomics. Proteomics 2004; 4: 1109-15. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300638.
pmid: 15048992 |
| 5. |
Malamud D. Saliva as a diagnostic fluid. BMJ 1992; 305: 207-8. doi:10.1016/j.cden.2010.08.004.
pmid: 1290500 |
| 6. |
Loo J A, Yan W, Ramachandran P, et al. Comparative human salivary and plasma proteomes. J Dent Res 2010; 89: 1016-23. doi:10.1177/0022034510380414.
pmid: 20739693 |
| 7. | Hu S, Vissink A, Arellano M, et al. Identification of autoantibody biomarkers for primary Sjögren’s syndrome using protein microarrays. Proteomics 2011; 11: 1499-507. doi:10.1002/pmic.201000206. |
| 8. |
Deutsch O, Krief G, Konttinen YT, et al. Identification of Sjögren’s syndrome oral fluid biomarker candidates following high-abundance protein depletion. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2015; 54: 884-90. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu405.
pmid: 25339641 |
| 9. | Katsiougiannis S, Wong DTW. The proteomics of saliva in Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2016; 42: 449-56. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2016.03.004. |
| 10. | Jonsson R, Brokstad KA, Jonsson MV, et al. Current concepts on Sjögren’s syndrome - classification criteria and biomarkers. Eur J Oral Sci 2018; 126 Suppl 1: 37-48. doi: 10.1111/eos.12536. |
| 11. |
Ferraccioli G, de Santis M, Peluso G, et al. Proteomic approaches to Sjögren’s syndrome: a clue to interpret the pathophysiology and organ involvement of the disease. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: 622-6. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.010.
pmid: 20462525 |
| 12. |
Baldini C, Giusti L, Bazzichi L, et al. Proteomic analysis of the saliva: a clue for understanding primary from secondary Sjögren’s syndrome? Autoimmun Rev 2008; 7: 185-91. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.002.
pmid: 18190876 |
| 13. | Chen WQn, Cao H, Lin J, et al. Biomarkers for primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2015; 13: 219-23. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0297. |
| 14. |
Vogel C, Marcotte EM. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet 2012; 13: 227-32. doi: 10.1038/nrg3185.
pmid: 22411467 |
| 15. |
Callister SJ, Barry RC, Adkins JN, et al. Normalization approaches for removing systematic biases associated with mass spectrometry and label-free proteomics. J Proteome Res 2006; 5: 277-86. doi: 10.1021/pr050300l.
pmid: 16457593 |
| 16. | Maddali BS, Campana G, D’Agata A, et al. The diagnosis value of beta 2-microglobulin and immunoglobulins in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 1995; 14: 151-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02214934. |
| 17. |
Baldini C, Gallo A, Perez P, et al. Saliva as an ideal milieu for emerging diagnostic approaches in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2012; 30: 785-90.
pmid: 23009763 |
| 18. | Jin YB, Dai YJ, Chen JL, et al. Anti-carbonic anhydrase II antibody reflects urinary acidification defect especially in proximal renal tubules in patients with primary Sjögren syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023; 102: e32673. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032673. |
| 19. | Qin BD, Wang JQ, Yang ZX, et al. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74: 1983-9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205375. |
| 20. | Goules AV, Tzioufas AG. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: clinical phenotypes, outcome and the development of biomarkers. Immunol Res 2017; 65: 331-344. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8844-4. |
| 21. | Chaudhury NMA, Proctor GB, Karlsson NG, et al. Reduced mucin-7 (Muc7) sialylation and altered saliva rheology in sjögren’s syndrome associated oral dryness. Mol Cell Proteomics 2016; 15: 1048-59. doi:10.1074/mcp.M115.052993. |
| 22. | Horvatovich P, Végvári Á, Saul J, et al. In vitro transcription/translation system: a versatile tool in the search for missing proteins. J Proteome Res 2015; 14: 3441-51. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00486. |
| 23. | Meyer JG, D’Souza AK, Sorensen DJ, et al. Quantification of lysine acetylation and succinylation stoichiometry in proteins using mass spectrometric data-independent acquisitions (SWATH). J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2016; 27: 1758-1771. doi:10.1007/s13361-016-1476-z. |
| 24. | Gao TG, Lou CX, Wang Y, et al. Anti-carbonic anhydrase goldbodies by conformational reconstruction of the complementary-determining regions of phage-displayed antibodies. ChemMedChem 2023; 18: e202300185. doi:10.1002/cmdc.202300185. |
| 25. | Guo ZG, Liu XJ, Li ML, et al. Differential urinary glycoproteome analysis of type 2 diabetic nephropathy using 2D-LC-MS/MS and iTRAQ quantification. J Transl Med 2015; 13: 371. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0712-9. |
| 26. | Xiao XP, Liu YR, Guo ZG, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the influence of gender and acid stimulation on normal human saliva using LC/MS/MS. Proteomics Clin Appl 2017; 11: undefined. doi: 10.1002/prca.201600142. |
| Garza-García F, Delgado-García G, Garza-Elizondo M, et al. Salivary β2-microglobulin positively correlates with ESSPRI in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed 2017; 57: 182-4. doi: 10.1016/j.rbre.2016.11.001. | |
| 27. | Thatayatikom A, Jun I, Bhattacharyya I, et al. The diagnostic performance of early Sjögren’s syndrome autoantibodies in juvenile Sjögren’s syndrome: The University of Florida Pediatric Cohort study. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 704193. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.704193. |
| 28. | Margaretten M. Neurologic manifestations of primary Sjögren syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2017; 43: 519-29. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2017.06.002. |
| 29. | Silva LM, Clements JA. Mass spectrometry based proteomics analyses in kallikrein-related peptidase research: implications for cancer research and therapy. Expert Rev Proteomics 2017; 14: 1119-30. doi:10.1080/14789450.2017.1389637. |
| 30. | Botrè F, Botrè C, Podestà E, et al. Effect of anti-carbonic anhydrase antibodies on carbonic anhydrases I and II. Clin Chem 2003; 49: 1221-3. doi: 10.1373/49.7.1221. |
| 31. |
Makino K, Jinnin M, Makino T, et al. Serum levels of soluble carbonic anhydrase IX are decreased in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis compared to those with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Biosci Trends 2014; 8: 144-8. doi: 10.5582/bst.2014.01020.
pmid: 25030848 |
| 32. |
Aparisi L, Farre A, Gomez-Cambronero L, et al. Antibodies to carbonic anhydrase and IgG4 levels in idiopathic chronic pancreatitis: relevance for diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2005; 54: 703-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.047142.
pmid: 15831920 |
| 33. |
Invernizzi P, Selmi C, Zuin M, et al. Lack of serum antibodies to membrane bound carbonic anhydrase IV in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Gut 2005; 54: 1665. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.072389.
pmid: 16227372 |
| 34. | Gillet LC, Navarro P, Tate S, et al. Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent acquisition: a new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics 2012; 11: O111.016717. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.016717. |
| [1] | 刘长宜, 刘晓清, 侍效春. 自发缓解的经典型不明原因发热的临床特征[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(2): 134-141. |
| [2] | 欧阳思文, 康维明. 角蛋白在胃肠道肿瘤中的作用和研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 73-78. |
| [3] | 徐潋滟, 闫轲, 吕乐, 张伟宏, 陈旭, 霍晓菲, 陆菁菁. CT图像中多器官占位性病变的计算机辅助检测模型的外部和内部验证[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 210-217. |
| [4] | 刘婕妤, 王嘉祥, 许力, 邓飞艳. 骨质疏松性骨折风险评估的潜在生物分子:一项综述回顾[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 135-149. |
| [5] | 刘炬,徐志坚,毕晓峰,孙萍,黄佳琴. 135个父母双亲和子女均患癌症的中国家庭发病特征回顾性分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 27-34. |
| [6] | 李大胜,王大为,王娜娜,徐海旺,黄河,董建平,夏晨. 北京首例由输入病例导致社区感染的新型冠状病毒肺炎患者:深度学习CT辅助诊断的作用[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 66-71. |
| [7] | 王小磊, 孟珊珊, 段科行, 胡耀炜, 魏锋. 诊治1例腹膜后海绵状淋巴管瘤[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 283-285. |
| [8] | 刘昕超, 叶素素, 王文泽, 张月秋, 张丽帆, 潘晓承, 周子月, 张妙颜, 刘江浩, 梁智勇, 刘晓清. γ干扰素释放试验对结核性淋巴结炎的诊断价值研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 233-240. |
| [9] | 武子荃, 曾德禄, 姚江凌, 卞阳阳, 顾运涛, 孟珠龙, 彭磊, 傅鉴. 慢性骨髓炎的诊断与治疗研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 211-220. |
| [10] | 王英伟, 张兴华, 王波涛, 王叶, 刘梦琦, 王海屹, 叶慧义. 体素内不相干运动成像参数的纹理分析在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺癌鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [12] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [13] | 柏明见, 冯璟, 梁国威. 尿液髓过氧化物酶肌酐比值作为诊断泌尿系感染的新标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 152-159. |
| [14] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|