Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 1-9.doi: 10.24920/003531
• 论著 • 下一篇
体素内不相干运动成像参数的纹理分析在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺癌鉴别诊断中的价值
王英伟1,2,张兴华2,王波涛1,王叶2,刘梦琦1,2,王海屹1,叶慧义2,*( )
)
- 1 解放军总医院海南医院放射诊断科,海南,三亚 572013
2 放军总医院放射诊断科,北京 100853
-
收稿日期:2018-10-18修回日期:2019-02-22出版日期:2019-03-30发布日期:2019-04-08 -
通讯作者:叶慧义 E-mail:13701100368@163.com;yyqf@hotmail.com
Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Wang Yingwei1,2,Zhang Xinghua2,Wang Botao1,Wang Ye2,Liu Mengqi1,2,Wang Haiyi1,Ye Huiyi2,*( ),Chen Zhiye1,2,*(
),Chen Zhiye1,2,*( )
)
- 1 Department of Radiology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
2 Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2018-10-18Revised:2019-02-22Published:2019-03-30Online:2019-04-08 -
Contact:Ye Huiyi,Chen Zhiye E-mail:13701100368@163.com;yyqf@hotmail.com
摘要:
目的 评价体素内不相干运动成像(intravoxel incoherent motion,IVIM)参数的纹理特征在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺癌鉴别诊断上的价值。
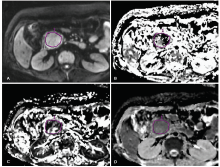
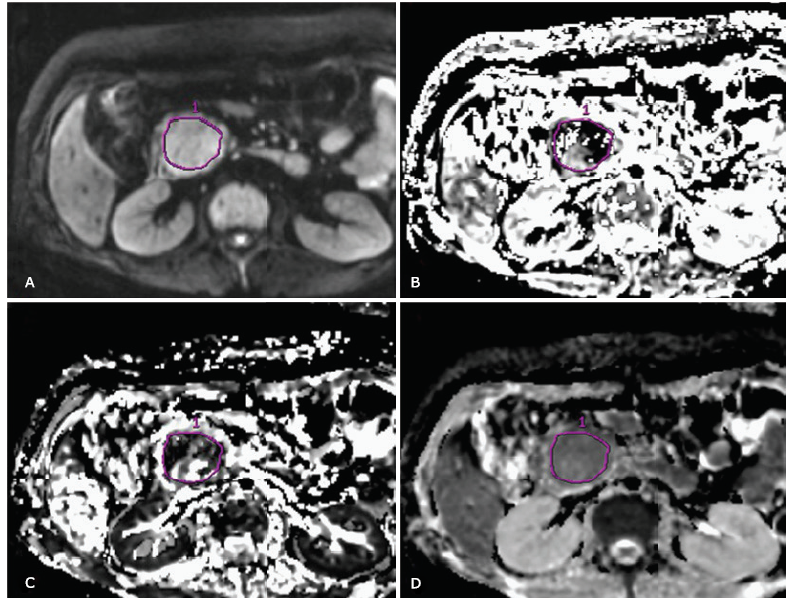
方法 18例胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤患者和32例胰腺癌患者纳入此项回归性研究。所有患者术前均接受了10个b值(0-800 s/mm2)的扩散加权成像(diffusion-weighted imaging,DWI)检查,所获得图像数据应用IVIM模型进行分析,获得灰度编码的灌注分数(perfusion fraction,f)、快池扩散(fast component of diffusion,Dfast)和慢池扩散(slow component of diffusion,Dslow)参数图。在各组参数图上测量肿瘤最大截面的参数均值和纹理特征(包括角二阶矩,逆差距、自相关、对比度和熵)。采用独立样本t检验及Mann-Whitney U检验比较两组肿瘤间IVIM参数均值和纹理特征的差异,同时进行二元Logistic回归分析法建立回归模型,并进行受试者工作特征曲线分析评价诊断效能。
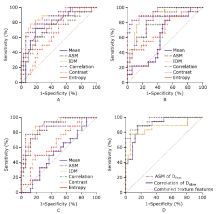
结果 胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤组的参数f值显著高于胰腺癌组(27.0% 比19.0%, P = 0.001),而参数Dfast值和Dslow值在两组肿瘤间的差异不具有统计学意义。各IVIM参数的所有纹理特征在两组肿瘤间的差异具有统计学意义(P = 0.000~0.043)。二元Logisic回归分析提示参数Dfast的纹理特征角二阶矩和参数Dslow的纹理特征自相关可以作为鉴别两者肿瘤的独立变量。受试者工作特征曲线分析显示IVIM参数的多个纹理特征鉴别胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺癌的诊断效能要优于参数的均值(曲线下面积0.849~0.899比0.526~0.776)。进入Logistic回归模型的纹理特征组合(参数Dfast的角二阶矩和参数Dslow的自相关)鉴别胰腺神经内分泌中和胰腺癌的诊断效能最高(曲线下面积0.934,切值0.378,敏感性0.889,特异性0.854)。
结论 IVIM参数的纹理特征分析可以作为一种有效的胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤与胰腺癌的鉴别诊断工具。
引用本文
Wang Yingwei, Zhang Xinghua, Wang Botao, Wang Ye, Liu Mengqi, Wang Haiyi, Ye Huiyi, Chen Zhiye. Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9.
"
| Parameters | PAC (n=32) | pNET (n=18) | U/t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | ||||
| ASM | 0.398 (0.047) | 0.468 (0.079) | -4.224 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.779±0.032 | 0.806±0.033 | -2.810 | 0.007 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.065±0.007 | 0.076±0.009 | -4.954 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 4367.155 (1740.747) | 3785.633 (1.70.172) | -2.021 | 0.043 |
| Entropy | 2.294±0.173 | 2.080±0.234 | 3.687 | 0.001 |
| Dfast | ||||
| ASM | 0.350±0.049 | 0.450±0.623 | -6.283 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.701 (0.069) | 0.740 (0.045) | -3.456 | 0.001 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.083±0.007 | 0.102±0.016 | -5.905 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 2961.827±514.595 | 2469.961±618.127 | 3.016 | 0.004 |
| Entropy | 3.398 (0.587) | 2.947 (0.534) | -4.143 | 0.000 |
| Dslow | ||||
| ASM | 0.315±0.049 | 0.407±0.053 | -6.169 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.589±0.048 | 0.659±0.044 | -5.129 | 0.000 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.198±0.034 | 0.269±0.057 | -5.562 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 483.639±97.783 | 422.838±97.344 | 2.114 | 0.040 |
| Entropy | 4.570±0.441 | 3.833±0.421 | 5.768 | 0.000 |
"
| Parameters | AUC | 95%CI | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | |||||
| Mean value | 0.776 | 0.636-0.882 | 25.700a | 0.772 | 0.812 |
| ASM | 0.863 | 0.736-0.944 | 0.439a | 0.778 | 0.875 |
| IDM | 0.715 | 0.570-0.834 | 0.802a | 0.611 | 0.781 |
| Correlation | 0.849 | 0.719-0.934 | 0.069a | 0.778 | 0.812 |
| Contrast | 0.674 | 0.526-0.799 | 4675.279b | 1.000 | 0.406 |
| Entropy | 0.762 | 0.621-0.871 | 2.313b | 0.833 | 0.594 |
| Dfast | |||||
| Mean value | 0.611 | 0.463-0.746 | 28.000a | 0.833 | 0.500 |
| ASM | 0.899 | 0.781-0.966 | 0.389a | 0.889 | 0.844 |
| IDM | 0.797 | 0.659-0.897 | 0.727a | 0.778 | 0.750 |
| Correlation | 0.887 | 0.766-0.959 | 0.094a | 0.833 | 0.937 |
| Contrast | 0.724 | 0.579-0.841 | 2224.521b | 0.444 | 0.937 |
| Entropy | 0.856 | 0.718-0.939 | 3.231b | 0.944 | 0.656 |
| Dslow | |||||
| Mean value | 0.526 | 0.380-0.669 | 0.900 | 1.000 | 0.125 |
| ASM | 0.898 | 0.779-0.965 | 0.348a | 0.889 | 0.812 |
| IDM | 0.858 | 0.730-0.940 | 0.636a | 0.722 | 0.875 |
| Correlation | 0.856 | 0.728-0.939 | 0.245a | 0.778 | 0.937 |
| Contrast | 0.667 | 0.519-0.794 | 401.811b | 0.500 | 0.812 |
| Entropy | 0.880 | 0.757-0.955 | 4.218b | 0.889 | 0.750 |
| Combined texture features | 0.934 | 0.826-0.985 | 0.378a | 0.889 | 0.854 |
| 1. |
Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D , et al. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol 2017; 3(10):1335-42. doi: 10.1001/ jamaoncol.2017.0589.
doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0589 pmid: 28448665 |
| 2. |
Saif MW . Pancreatic neoplasm in 2011: an update. Jop 2011; 12(4):316-21.
doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/721 pmid: 21737886 |
| 3. |
Wong KP, Tsang JS, Lang BH . Role of surgery in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Gland Surg 2018; 7(1):36-41. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.12.05
doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.12.05 pmid: 29629318 |
| 4. |
Clancy TE . Surgical management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2016; 30(1):103-18. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2015.09.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2015.12.002 pmid: 27013372 |
| 5. |
Doi R . Determinants of surgical resection for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015; 22(8):610-7. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.224.
doi: 10.1002/jhbp.224 pmid: 25773163 |
| 6. |
Chua TC, Yang TX, Gill AJ , et al. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of enucleation versus standardized resection for small pancreatic lesions. Ann Surg Oncol 2016; 23(2):592-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4826-3.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4826-3 pmid: 26307231 |
| 7. |
Bednar F, Simeone DM . Recent advances in pancreatic surgery. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2014; 30(5):518-23. doi: 10.1097/mog.0000000000000096.
doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000096 pmid: 25010685 |
| 8. |
Lewis RB, Lattin GE , Jr., Paal E. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: radiologic-clinicopathologic correlation. Radiographics 2010; 30(6):1445-64. doi: 10.1148/rg.306105523.
doi: 10.1148/rg.306105523 pmid: 21071369 |
| 9. |
Manfredi R, Bonatti M, Mantovani W , et al. Non-hyperfunctioning neuroendocrine tumours of the pancreas: MR imaging appearance and correlation with their biological behaviour. Eur Radiol 2013; 23(11):3029-39. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2929-4.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2929-4 pmid: 23793519 |
| 10. |
Iima M, Le Bihan D . Clinical intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion MR imaging: past, present, and future. Radiology 2016; 278(1):13-32. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150244.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150244 pmid: 26690990 |
| 11. |
Lee HJ, Rha SY, Chung YE , et al. Tumor perfusion-related parameter of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with histological microvessel density. Magn Reson Med 2014; 71(4):1554-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24810.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24810 pmid: 23798038 |
| 12. |
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D , et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988; 168(2):497-505. doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671 pmid: 3393671 |
| 13. |
Ma W, Zhang G, Ren J , et al. Quantitative parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI): potential application in predicting pathological grades of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2018; 8(3):301-10. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.04.08.
doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.04.08 pmid: 29774183 |
| 14. |
Ma C, Li Y, Wang L , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion DWI of the pancreatic adenocarcinomas: monoexponential and biexponential apparent diffusion parameters and histopathological correlations. Cancer Imaging 2017; 17(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40644-017-0114-8.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-017-0114-8 pmid: 5410078 |
| 15. |
Hwang EJ, Lee JM, Yoon JH , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: prediction of the histologic grade using pure diffusion coefficient and tumor size. Invest Radiol 2014; 49(6):396-402. doi: 10.1097/rli.0000000000000028.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000028 |
| 16. |
Concia M, Sprinkart AM, Penner AH , et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas: diagnostic benefit from an intravoxel incoherent motion model-based 3 b-value analysis. Invest Radiol 2014; 49(2):93-100. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182a71cc3.
doi: 10.1097/RMR.0b013e3181b48667 pmid: 19687725 |
| 17. |
Klauss M, Lemke A, Grunberg K , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the differentiation between mass forming chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Invest Radiol 2011; 46(1):57-63. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181fb3bf2.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181fb3bf2 pmid: 21139505 |
| 18. |
Kang KM, Lee JM, Yoon JH , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging for characterization of focal pancreatic lesions. Radiology 2014; 270(2):444-53. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122712.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122712 pmid: 24126370 |
| 19. |
Kim B, Lee SS, Sung YS , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas: characterization of benign and malignant pancreatic pathologies. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 45(1):260-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25334.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25334 pmid: 27273754 |
| 20. |
Klau M, Mayer P, Bergmann F , et al. Correlation of histological vessel characteristics and diffusion-weighted imaging intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Invest Radiol 2015; 50(11):792-7. doi: 10.1097/rli.0000000000000187.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000187 pmid: 26186280 |
| 21. |
Li J, Liang L, Yu H , et al. Whole-tumor histogram analysis of non-Gaussian distribution DWI parameters to differentiation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Magn Reson Imaging 2019; 55:52-9. doi: 10.1016/ j.mri.2018.09.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.09.017 |
| 22. | Wang BT, He L, Liu G , et al. Value of magnetic resonance imaging texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis between pancreatic serous cystadenoma and mucinous cystadenoma. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2018; 40(2):187-93. doi: 10.3881/ j.issn.1000-503X.2018.02.008. |
| 23. |
Shindo T, Fukukura Y, Umanodan T , et al. Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient in differentiating pancreatic adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumor. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(4):e2574. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000002574.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002574 pmid: 5291570 |
| 24. |
Chen Z, Feng F, Yang Y , et al. MR imaging findings of the corpus callosum region in the differentiation between multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Radiol 2012; 81(11):3491-5. doi: 10.1016/ j.ejrad.2012.02.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.02.010 pmid: 22445592 |
| 25. |
Xia J, Broadhurst DI, Wilson M , et al. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: an introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 2013; 9(2):280-99. doi: 10.1007/s11306-012-0482-9.
doi: 10.1007/s11306-012-0482-9 |
| 26. |
Wu H, Liang Y, Jiang X , et al. Meta-analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating focal lesions of the liver. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018; 97(34):e12071. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000012071.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012071 |
| 27. | Mohanaiah P, Sathyanarayana P, Gurukumar L . Image texture feature extraction using GLCM approach. Inter J Sci Res Publications 2014; 3(5):1-5. |
| 28. |
Wang B, Liu G, Fan W , et al. Value of texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis of hepatic cyst and hemangioma in magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2017; 39(2):169-76. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002.
doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002 pmid: 28483013 |
| 29. |
Chen Z, Chen X, Liu M , et al. Magnetic resonance image texture analysis of the periaqueductal gray matter in episodic migraine patients without T2-visible lesions. Korean J Radiol 2018; 19(1):85. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.85.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.85 |
| 30. |
Chen Z, Chen X, Chen Z , et al. Alteration of gray matter texture features over the whole brain in medication-overuse headache using a 3-dimentional texture analysis. J Headache Pain 2017; 18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0820-4.
doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0820-4 pmid: 29285575 |
| [1] | 王亮, 李刚, 邴运韬, 田茂霖, 王行雁, 原春辉, 修典荣. 既往癌症对局限性胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤患者的 生存结果有影响吗?[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 284-294. |
| [2] | 李刚, 邴运韬, 田茂霖, 原春辉, 修典荣. 使用列线图预测老年胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤患者手术前远处转移的风险[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 218-224. |
| [3] | 曹剑, 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. CT纹理分析:结直肠癌KRAS基因突变状态评估的潜在生物标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [4] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [5] | 刘洪娟, 周欢粉, 宗林雄, 刘梦琦, 魏世辉, 陈志晔. 视神经炎患者视神经磁共振成像直方图分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 18-23. |
| [6] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 游燕, 王勤, 王士阗, 薛华丹. 钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [7] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [8] | 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. 纹理分析在结直肠癌新辅助放化疗疗效预测及预后分析中的应用及研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|