Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 239-247.doi: 10.24920/003662
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Novel Long Non-coding RNA Markers for Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Bladder Cancer
Li Wenxing1, 2, Zhang Yanli3, 4, *( )
)
- 1Department of Diagnosis, Heze Medical College, Heze, Shandong 274000, China
2Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of Heze Medical College, Heze, Shandong 274000, China
3School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4School of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2019-10-16Published:2020-09-30Online:2020-09-25 -
Contact:Zhang Yanli E-mail:yanlizhang12@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Cite this article
Li Wenxing, Zhang Yanli. Novel Long Non-coding RNA Markers for Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Bladder Cancer[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 239-247.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Overall information of seven novel prognosis related lncRNAs"
| Ensembl ID | Gene symbol | Hazard ratio | P value | - logL | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000248256.1 | OCIAD1-AS1 | 0.352498 | 0.000426 | 313.55 | 629.1 |
| ENSG00000260331.1 | RP11-111J6.2 | 0.124571 | 0.000367 | 309.8 | 623.61 |
| ENSG00000222035.3 | AC079354.3 | 132322.9 | 9.81E-06 | 304.4 | 614.79 |
| ENSG00000231652.2 | RP11-553A21.3 (AL590428.1) | 28.95384 | 4.98E-05 | 300.78 | 609.56 |
| ENSG00000256948.1 | RP11-598F7.3 | 0.324872 | 0.012715 | 293.77 | 597.55 |
| ENSG00000265787.1 | CYP4F35P | 0.473391 | 0.001861 | 291.21 | 594.41 |
| ENSG00000255503.1 | RP11-113K21.4 | 0.15136 | 0.000223 | 289.07 | 592.15 |
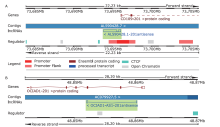
Figure 2.
Co-expressed protein coding genes (PCGs) for prognostic lncRNAs and their KEGG pathway enrichment network. Top 100 positively (A) or negatively correlated PCGs (B), and top ten KEGG pathways of positively (C) or negatively correlated PCGs (D) are presented. The significance of each term is represented by the length and color of the bar graph. Interaction networks of top ten KEGG pathways of positively (E) or negatively correlated PCGs (F) are shown."
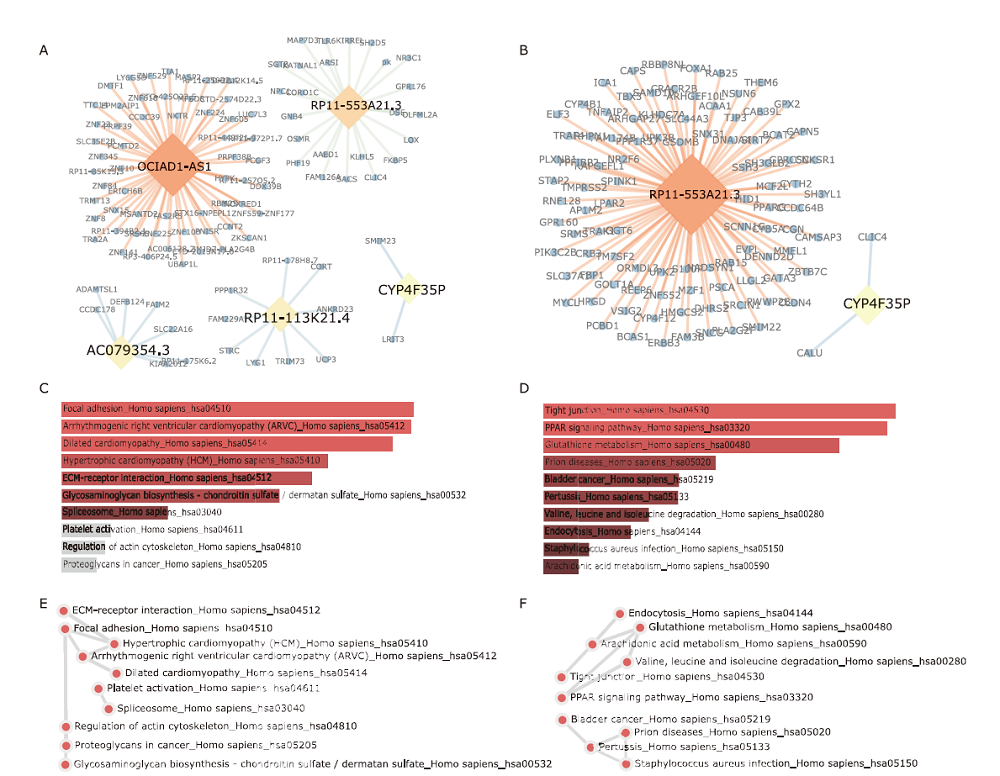
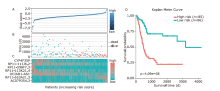
Figure 3.
LncRNA risk score analysis in the training data. A. Distribution of risk scores; B. Distribution of survival time; C. Relative expression levels of the seven lncRNAs related to prognosis; D. The Kaplan-Meier curve used the median risk score as a cut-off point to divide patients into the high-risk group and low-risk group."
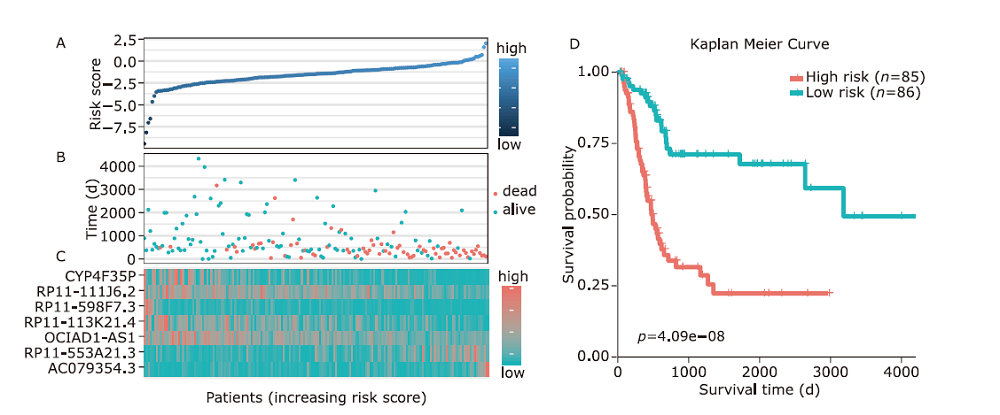
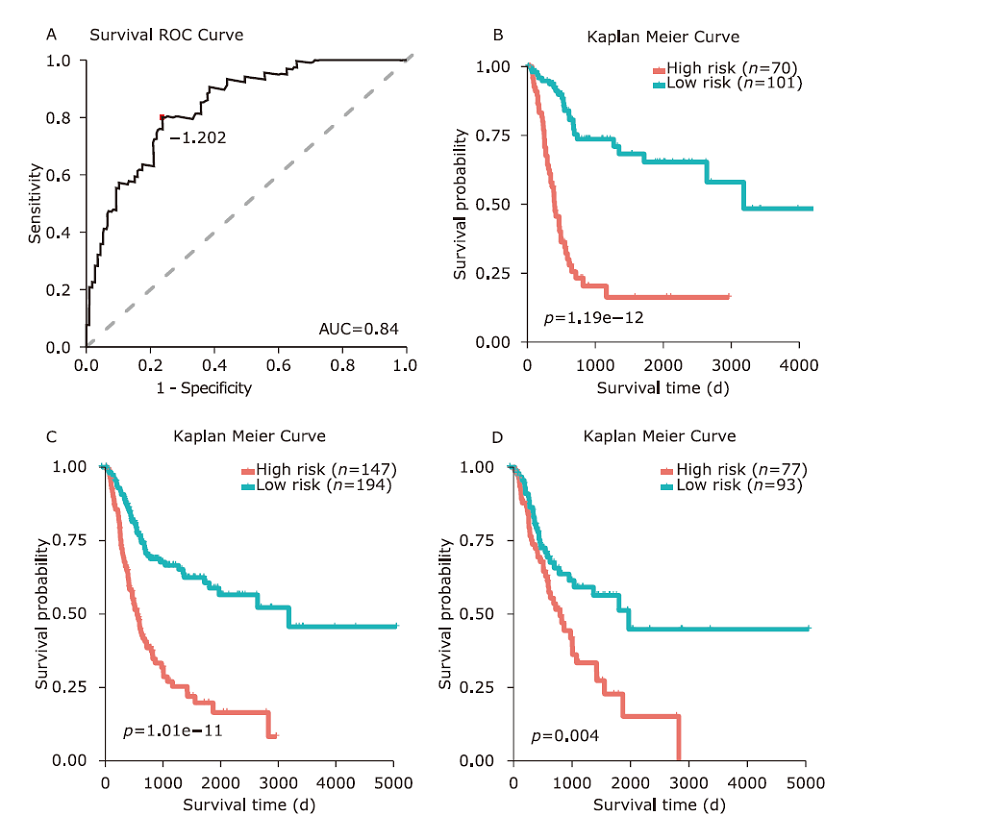
Figure 4.
Determination of the optimal threshold and validation of the model. A. The sensitivity and specificity of survival time were analyzed by Receiver Operating Characteristic. The red dot represents the risk score at the optimal cut-off point. B. In the Kaplan-Meier curve, the optimal cut-off point is used to estimate the patient’s survival time in the training data. C. Kaplan-Meier curve is used to estimate the survival time of all patients. D. Kaplan-Meier curve is used to estimate patient’s survival time in the test data."
| 1. |
Witjes JA, Compérat Eva, Cowan NC, et al. EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2013 Guidelines. Eur Urol 2014; 65(4):778-92. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.046.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.046 |
| 2. |
Ghafouri-Fard S, Nekoohesh L, Motevaseli E. Bladder cancer biomarkers: review and update. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15(6):2395-403. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.6.2395.
pmid: 24761840 |
| 3. |
Dunham I, Kundaje A, Aldred SF, et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012; 489(7414):57-74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247.
doi: 10.1038/nature11247 pmid: 22955616 |
| 4. |
Brosnan CA, Voinnet O. The long and the short of noncoding RNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21(3):416-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.04.001 |
| 5. |
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10(3):155-9. doi: 10.1038/nrg2521.
pmid: 19188922 |
| 6. | Wu Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR involvement in cancer. Tumor Biol 2014; 35(10):9531-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2523-7. |
| 7. |
Zhu X, Tian X, Yu C, et al. A long non-coding RNA signature to improve prognosis prediction of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 2016; 15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0544-0.
pmid: 27647437 |
| 8. | Meng J, Li P, Zhang Q, et al. A four-long non-coding RNA signature in predicting breast cancer survival. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2014; 33(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0084-7. |
| 9. |
Sun J, Cheng L, Shi H, et al. A potential panel of six-long non-coding RNA signature to improve survival prediction of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep 2016; 6(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/srep27842.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 pmid: 28442746 |
| 10. |
Cao W, Liu J, Liu Z, et al. A three-lncRNA signature derived from the Atlas of ncRNA in cancer (TANRIC) database predicts the survival of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2017; 65:94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.12.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.12.017 pmid: 28109476 |
| 11. |
Song J, Zhang W, Wang S, et al. A panel of 7 prognosis-related long non-coding RNAs to improve platinum-based chemoresistance prediction in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol 2018; 53(2):866-76. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4403.
doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4403 pmid: 29749482 |
| 12. |
Mao X, Qin X, Li L, et al. A 15-long non-coding RNA signature to improve prognosis prediction of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 2018; 149(1):181-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.011 pmid: 29525275 |
| 13. |
Zhang Q, Su M, Lu G, et al. The complexity of bladder cancer: long noncoding RNAs are on the stage. Mol Cancer 2013; 12(1):101. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-101.
doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-101 pmid: 24006935 |
| 14. | Robertson AG, Kim J, Al-Ahmadie H, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of muscle-invasive bladder cancer cell 2017; 171(3):540-56. e25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.007. |
| 15. |
Xue Y, Ma G, Zhang Z, et al. A novel antisense long noncoding RNA regulates the expression of MDC1 in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2015; 6(1):484-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2861.
pmid: 25514464 |
| 16. |
Dudek AM, Boer SJ, Boon N, et al. Identification of long non-coding RNAs that stimulate cell survival in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017; 8(21):34442-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16284.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16284 pmid: 28415801 |
| 17. |
Duan W, Du L, Jiang X, et al. Identification of a serum circulating lncRNA panel for the diagnosis and recurrence prediction of bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016; 7(48):78850-8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12880.
pmid: 27793008 |
| 18. |
Wang M, Niu Z, Zhou L, et al. Prognostic impact of cell division cycle zssociated 2 expression on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinom. Chin Med Sci J 2016; 31(3):149-54. doi: 10.1016/S1001-9294(16)30043-8.
doi: 10.1016/s1001-9294(16)30043-8 pmid: 27733221 |
| 19. |
Renaud G, Stenzel U, Maricic T, et al. DeML: robust demultiplexing of Illumina sequences using a likelihood-based approach. Bioinformatics 2015; 31(5):770-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu719 pmid: 25359895 |
| 20. |
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, et al. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics 2013; 14(1):128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128 |
| 21. |
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2016; 44(W1):W90-W7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377.
pmid: 27141961 |
| 22. |
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T, Pepe MS. Time-dependent ROC curves for censored survival data and a diagnostic marker. Biometrics 2000; 56(2):337-44. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00337.x.
pmid: 10877287 |
| 23. |
Yokoyama M, Ichinoe M, Okina S, et al. CD109, a negative regulator of TGF-β signaling, is a putative risk marker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol 2017; 105(5):614-22. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2173-1.
doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2173-1 pmid: 28032275 |
| 24. |
Jia W, Ren C, Wang L, et al. CD109 is identified as a potential nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarker using aptamer selected by cell-SELEX. Oncotarget 2016; 7(34):55328-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10530.
pmid: 27419372 |
| 25. |
Pelechano V, Steinmetz LM. Gene regulation by antisense transcription. Nat Rev Genetics 2013; 14(12):880-93. doi: 10.1038/nrg3594.
doi: 10.1038/nrg3594 pmid: 24217315 |
| 26. |
Sengupta S, Michener CM, Escobar P, et al. Ovarian cancer immuno-reactive antigen domain containing 1 (OCIAD1), a key player in ovarian cancer cell adhesion. Gynecol Oncol 2008; 109(2):226-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.024 pmid: 18328549 |
| 27. |
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, et al. Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol 2013; 11(1):59. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-59.
doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-59 |
| 28. |
Liao Q, Liu C, Yuan X, et al. Large-scale prediction of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39(9):3864-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1348.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1348 pmid: 21247874 |
| 29. |
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, et al. The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5(7):505-15. doi: 10.1038/nrc1647.
doi: 10.1038/nrc1647 pmid: 16069815 |
| 30. |
Badylak SF. Xenogeneic extracellular matrix as a scaffold for tissue reconstruction. Transpl Immunol 2004; 12(3-4):367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2003.12.016.
doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2003.12.016 pmid: 15157928 |
| 31. |
Krupp M, Maass T, Marquardt JU, et al. The functional cancer map: a systems-level synopsis of genetic deregulation in cancer. BMC Med Genomics 2011; 4(1):53. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-53.
doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-53 |
| 32. |
Sasisekharan R, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, et al. Roles of heparan-sulphate glycosaminoglycans in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2(7):521-8. doi: 10.1038/nrc842.
doi: 10.1038/nrc842 pmid: 12094238 |
| 33. |
Rangel MP, de Sá VK, Prieto T, et al. Biomolecular analysis of matrix proteoglycans as biomarkers in non small cell lung cancer. Glycoconj J 2018; 35(2):233-42. doi: 10.1007/s10719-018-9815-x.
doi: 10.1007/s10719-018-9815-x pmid: 29502190 |
| 34. |
Gao F, Alwhaibi A, Artham S, et al. Endothelial Akt1 loss promotes prostate cancer metastasis via β-catenin-regulated tight-junction protein turnover. Br J Cancer 2018; 118(11):1464-75. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0110-1.
pmid: 29755115 |
| 35. |
Runkle EA, Mu D. Tight junction proteins: from barrier to tumorigenesis. Cancer Let 2013; 337(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.038.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.038 |
| 36. |
Soini Y. Tight junctions in lung cancer and lung metastasis: a review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2012; 5(2):126-36.
pmid: 22400072 |
| 37. |
Chen YZ, Xue JY, Chen CM, et al. PPAR signaling pathway may be an important predictor of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2012; 70(5):637-44. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-1949-0.
pmid: 22903535 |
| 38. |
Pazienza V, Vinciguerra M, Mazzoccoli G. PPARs signaling and cancer in the gastrointestinal system. PPAR Res 2012; 2012:560846. doi: 10.1155/2012/560846.
doi: 10.1155/2012/560846 pmid: 23028383 |
| 39. |
Fanale D, Amodeo V, Caruso S. The interplay between metabolism, PPAR signaling pathway, and cancer. PPAR Res 2017; 2017:1830626. doi: 10.1155/2017/1830626.
doi: 10.1155/2017/1830626 pmid: 28529521 |
| [1] | Wenqin Xu, Jingjing Ye, Tianbing Chen. Identifying and Validating a Novel miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Associated with Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 31-43. |
| [2] | Zhu Weihua,Xie Wenyong,Zhang Zhedong,Li Shu,Zhang Dafang,Liu Yijun,Zhu Jiye,Leng Xisheng. Postoperative Complications and Survival Analysis of Surgical Resection for Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma: A Retrospective Study of Fifty-Nine Consecutive Patients [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 157-169. |
| [3] | Chen Qiang, Zhang Liwei, Huang Dangsheng, Zhang Chunhong, Wang Qiushuang, Shen Dong, Xiong Minjun, Yang Feifei. Five-year Clinical Outcomes of CAD Patients Complicated with Diabetes after StentBoost-optimized Percutaneous Coronary Intervention [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 177-183. |
| [4] | Bai Bing, Tian Yuan, Zhang Yuelun, Ma Manjiao, Yu Xuerong, Huang Yuguang. Prediction of Hidden Blood Loss During Posterior Spinal Surgery [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 38-44. |
| [5] | Wang Guorong, Wang Zhiwei, Jin Zhengyu. Application and Progress of Texture Analysis in the Therapeutic Effect Prediction and Prognosis of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [6] | Liu Yongsheng, Zhao Yu. Progress in Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring for the Surgical Treatment of Thoracic Spinal Stenosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 260-264. |
| [7] | Zhang Rong-qiang, Li Feng-ying, Liu Jun-li, Liu Mei-ning, Luo Wen-rui, Ma Ting, Ma Bo, Zhang Zhi-gang. Time Series Models for Short Term Prediction of the Incidence of Japanese Encephalitis in Xianyang City, P R China△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 152-160. |
| [8] | Meng-yi Wang, Zhe-yu Niu, Xiang-Gao, Li Zhou, Quan Liao, Yu-pei Zhao. Prognostic Impact of Cell Division Cycle Associated 2 Expression on Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(3): 149-154. |
| [9] | Min Xu, Zheng-song Gu, Cun-zu Wang, Xiao-feng Lu, Ding-chao Xiang, Zhi-cheng Yuan, Qiao-yu Li, Min Wu. Impact of Intraoperative Blood Pressure Control and Temporary Parent Artery Blocking on Prognosis in Cerebral Aneurysms Surgery [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(2): 89-94. |
| [10] | Shu-bo Tian, Jian-chun Yu*, Wei-ming Kang, Zhi-qiang Ma, Xin Ye, Chao Yan, Ya-kai Huang. Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Treatment on Prognosis of Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer: a Retrospective Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(2): 84-89. |
| [11] | Jin Wen, Han-zhong Li, Zhi-gang Ji, Jing Jin. Effects of Sunitinib Malate on Growth of Human Bladder Transitional Cell Line T24 In Vitro [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(1): 51-55. |
| [12] | Li Wang, Jin-hua He, Ze-ping Han. Characteristics of PVT1 and Its Roles in Diseases [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(4): 236-238. |
| [13] | You-xin Ji,Zhong-fa Zhang,Ke-tao Lan,Ke-ke Nie,Chuan-xin Geng,Shi-chao Liu,Ling Zhang,Xing-jun Zhuang,Xiao Zou,Lei Sun,Zong-chun Zhang. Sorafenib in Liver Function Impaired Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2014, 29(1): 7-14. |
| [14] | Jin-hua He, Yu-guang Li. Characteristics of Antisense Non-coding RNA in the INK4 Locus and Its Roles in Disease [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2013, 28(2): 122-123. |
| [15] | Xie-qun Xu, Wei Liu, Bing-lu Li, Tao Hong, Chao-ji Zheng, Chu Wang, and Yu-pei Zhao. Unsuspected Gallbladder Cancer During or After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2013, 28(2): 102-106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|