Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 152-160.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.036
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Time Series Models for Short Term Prediction of the Incidence of Japanese Encephalitis in Xianyang City, P R China△
Zhang Rong-qiang1, 2, Li Feng-ying3, Liu Jun-li3, Liu Mei-ning3, Luo Wen-rui3, Ma Ting3, Ma Bo3, Zhang Zhi-gang1, *
- 1School of Public Health, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
2Institute of Endemic Diseases, School of Public Health, Health Science Center, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Key Laboratory of Trace Elements and Endemic Diseases of National Health and Family Planning Commission, Xi’an 710061, China;
3Department of Immunology, Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Xianyang City, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
-
Received:2016-12-21Published:2017-09-27Online:2017-09-27 -
Contact:Zhang Zhi-gang
Cite this article
Zhang Rong-qiang, Li Feng-ying, Liu Jun-li, Liu Mei-ning, Luo Wen-rui, Ma Ting, Ma Bo, Zhang Zhi-gang. Time Series Models for Short Term Prediction of the Incidence of Japanese Encephalitis in Xianyang City, P R China△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(3): 152-160.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Key measures to judge the powers of the models"
| Models | R2 | Adjusted R2 | BIC | AIC | MAE | MAPE | White noise |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(0, 1, 0)12 | 0.3593 | 0.3523 | -1.5550 | -1.6091 | 0.0448 | 42.4177 | No |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(0, 1, 1)12 | 0.5253 | 0.5149 | -1.8066 | -1.8878 | 0.0349 | 20.2465 | Yes |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(0, 1, 2)12 | 0.7281 | 0.7281 | -2.4714 | -2.4983 | 0.0298 | 25.5302 | No |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(1, 1, 0)12 | 0.3921 | 0.3767 | -1.7403 | -1.8284 | 0.0388 | 48.3811 | Yes |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(1, 1, 1)12 | 0.5767 | 0.5604 | -2.0486 | -2.1660 | 0.0355 | 43.4823 | Yes |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(1, 1, 2)12 | 0.5229 | 0.5110 | -3.1737 | -2.0836 | 0.0336 | 34.8344 | No |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(2, 1, 0)12 | 0.6557 | 0.6507 | -3.0530 | -3.1167 | 0.0205 | 18.4136 | Yes |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(2, 1, 1)12 | 0.7675 | 0.7569 | -3.3085 | -3.4370 | 0.0181 | 21.1313 | Yes |
| SARIMA(1, 1, 1)(2, 1, 2)12 | 0.7142 | 0.7012 | -3.1024 | -3.2309 | 0.0186 | 17.0829 | Yes |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(0, 1, 0)12 | 0.2399 | 0.2315 | -1.3727 | -1.4271 | 0.0670 | 45.8096 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(0, 1, 1)12 | 0.4602 | 0.4482 | -1.6661 | -1.7478 | 0.0490 | 31.168 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(0, 1, 2)12 | 0.8080 | 0.8038 | -2.7001 | 2.7818 | 0.0327 | 24.6900 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(1, 1, 0)12 | 0.3187 | 0.3012 | -1.6125 | -1.7012 | 0.0543 | 48.0692 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(1, 1, 1)12 | 0.5012 | 0.4817 | -1.8700 | -1.9982 | 0.0505 | 34.5438 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(1, 1, 2)12 | 0.8623 | 0.8569 | -3.1569 | -3.2752 | 0.0258 | 22.5722 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(2, 1, 0)12 | 0.6558 | 0.6454 | -2.9607 | -3.0578 | 0.0211 | 48.9294 | Yes |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(2, 1, 1)12 | 0.7342 | 0.7220 | -3.1580 | -3.2874 | 0.0248 | 21.8292 | No |
| SARIMA(2, 1, 1)(2, 1, 2)12 | 0.6763 | 0.6668 | -3.3054 | -3.1503 | 0.0278 | 16.7768 | Yes |
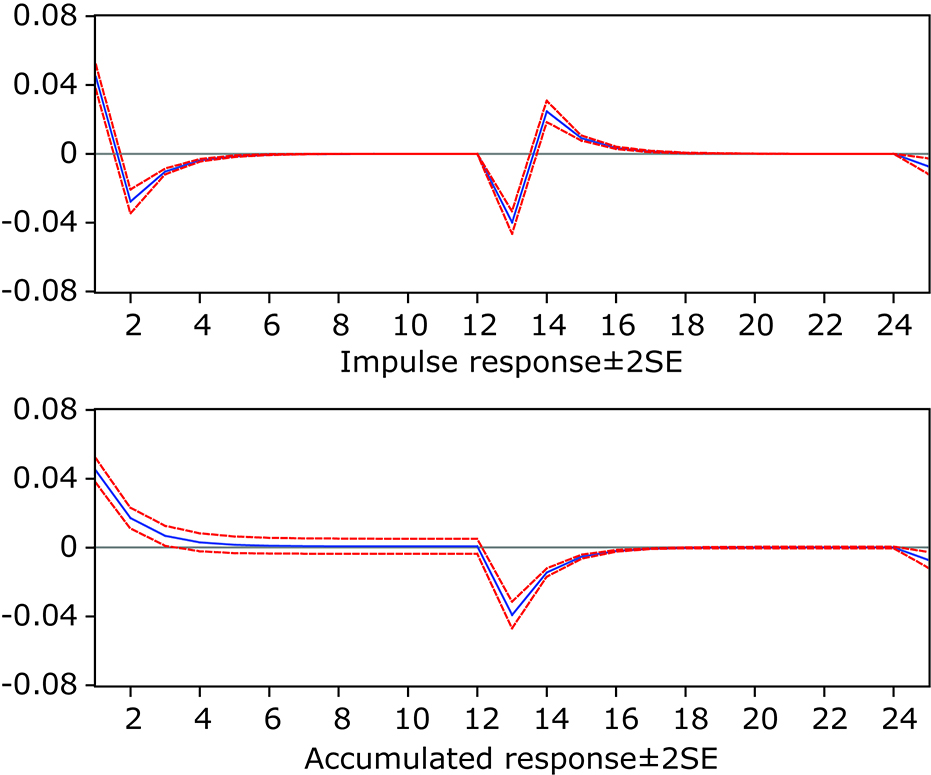
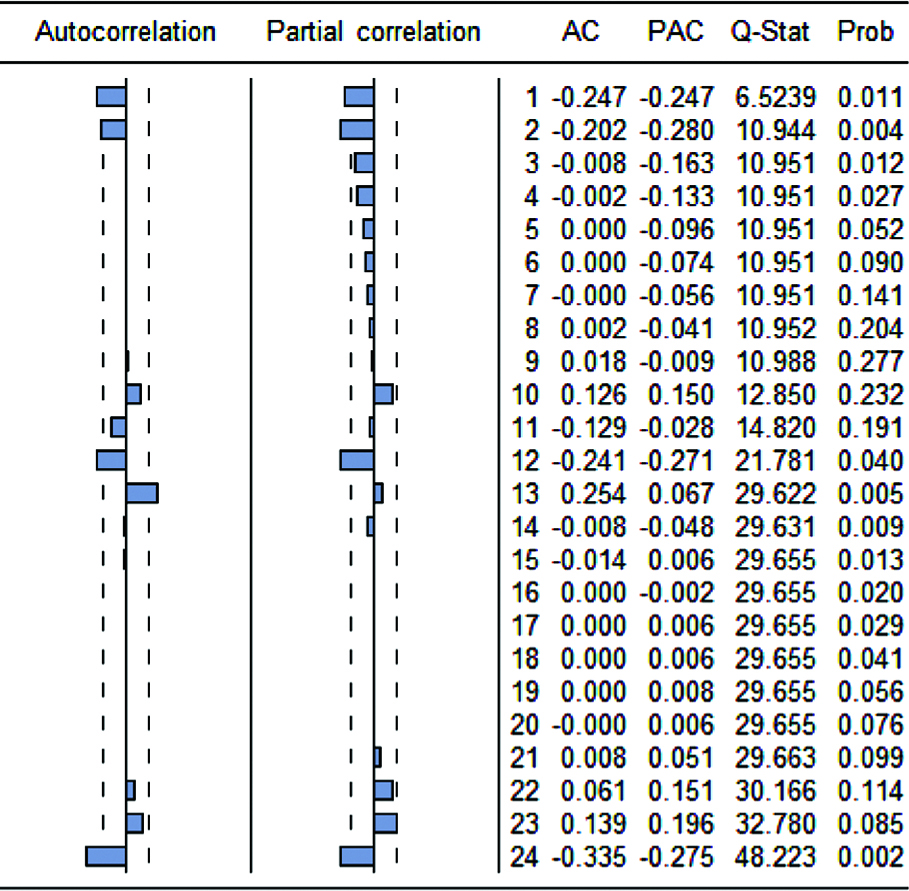
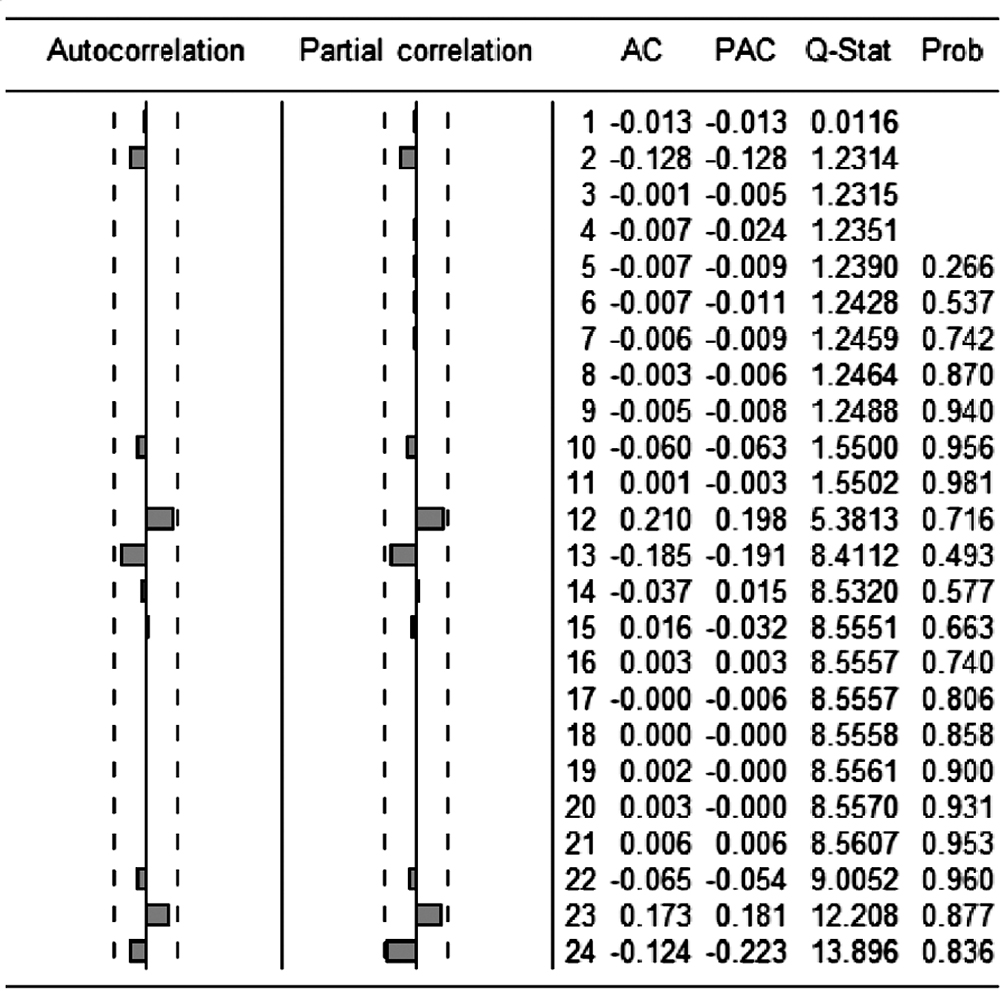
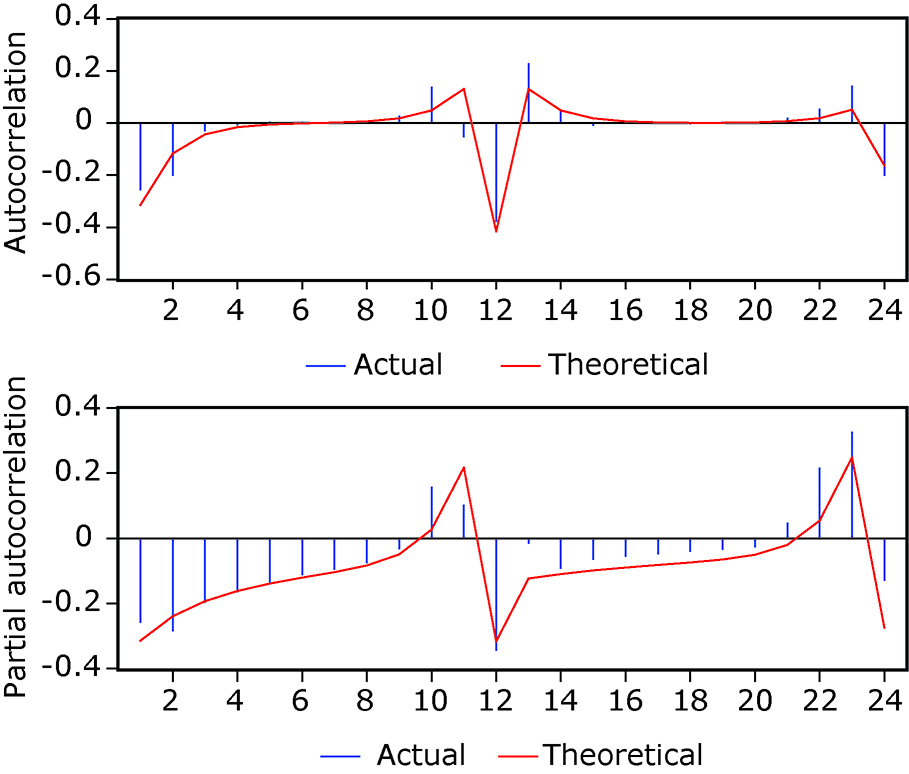
Figure 4.
Graphs for impulse response and accumulated response. The abscissa represents the number of lags, and the ordinate represents the impulse response and accumulated response. The blue line means the average response, the red line above means the average response+2SE, the red line below means the average response-2 SE."

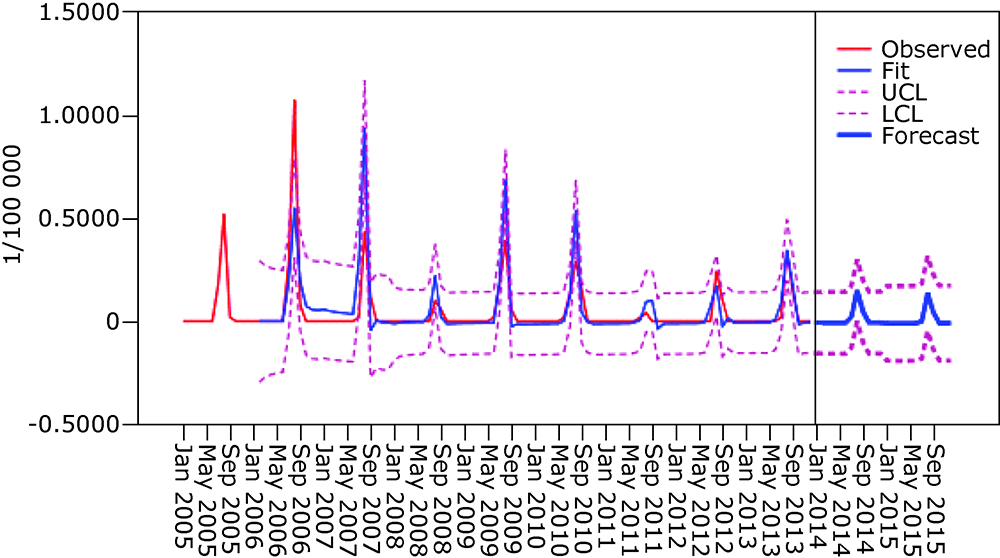
Table 3
Comparison of observed incidences and forecasting incidences from SARIMA (1, 1, 1) (2, 1, 1)12"
| Months | Observed incidence (1/105) | Forecast incidence (1/105) | Upper limit of 95%CI | Low limit of 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0062 | 0.1413 | -0.1538 |
| Feb-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0072 | 0.1430 | -0.1575 |
| Mar-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0073 | 0.1431 | -0.1577 |
| Apr-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0072 | 0.1432 | -0.1576 |
| May-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0071 | 0.1434 | -0.1575 |
| Jun-14 | 0.0000 | -0.0069 | 0.1435 | -0.1574 |
| Jul-14 | 0.0000 | 0.0220 | 0.1725 | -0.1284 |
| Aug-14 | 0.0203 | 0.1505 | 0.3010 | 0.0001 |
| Sep-14 | 0.0203 | 0.0451 | 0.1955 | -0.1054 |
| Oct-14 | - | -0.0064 | 0.1440 | -0.1568 |
| Nov-14 | - | -0.0063 | 0.1442 | -0.1567 |
| Dec-14 | - | -0.0061 | 0.1443 | -0.1566 |
| Jan-15 | - | -0.0101 | 0.1705 | -0.1907 |
| Feb-15 | - | -0.0106 | 0.1711 | -0.1924 |
| Mar-15 | - | -0.0106 | 0.1713 | -0.1924 |
| Apr-15 | - | -0.0103 | 0.1715 | -0.1922 |
| May-15 | - | -0.0101 | 0.1717 | -0.192 |
| Jun-15 | - | -0.0099 | 0.1719 | -0.1917 |
| Jul-15 | - | 0.0010 | 0.1828 | -0.1809 |
| Aug-15 | - | 0.1358 | 0.3176 | -0.046 |
| Sep-15 | - | 0.0427 | 0.2245 | -0.1391 |
| Oct-15 | - | -0.0090 | 0.1728 | -0.1908 |
| Nov-15 | - | -0.0088 | 0.1731 | -0.1906 |
| Dec-15 | - | -0.0085 | 0.1733 | -0.1903 |
| 1. | Diagana M, Preux PM, Dumas M.Japanese encephalitis revisited. J Neurol Sci 2007; 262(1-2):165-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.06.041. |
| 2. | Ghimire S, Dhakal S.Japanese encephalitis: challenges and intervention opportunities in Nepal. Vet World 2015, 8(1):61-5. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.61-65. |
| 3. | Misra UK, Kalita J.Overview: Japanese encephalitis. Prog Neurobiol 2010; 91(2):108-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.01.008. |
| 4. | Jasik KP, Okła H, Słodki J, Rozwadowska B, Słodki A, Rupik W.Congenital tick borne diseases: is this an alternative route of transmission of tick-borne pathogens in mammals? Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2015; 15(11):637-44. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2015.1815. |
| 5. | Ai J, Xie Z, Liu G, Chen Z, Yang Y, Li Y, et al.Etiology and prognosis of acute viral encephalitis and meningitis in Chinese children: a multicentre prospective study. BMC Infect Dis 2017; 17(1):494. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2572-9. |
| 6. | Feng H, Duan G, Zhang R, Zhang W.Time series analysis of hand-foot-mouth disease hospitalization in Zhengzhou: establishment of forecasting models using climate variables as predictors. PLoS One 2014; 9(1):e87916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087916.eCollection2014. |
| 7. | Cappelle J, Duong V, Pring L, Kong L, Yakovleff M, Prasetyo DB, et al.Intensive circulation of Japanese Encephalitis virus in peri-urban Sentinel Pigs near Phnom Penh, Cambodia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016; 10(12):e0005149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005149. |
| 8. | Luo L, Luo L, Zhang X, He X.Hospital daily outpatient visits forecasting using a combinatorial model based on ARIMA and SES models. BMC Health Serv Res 2017; 17(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2407-9. |
| 9. | Bozkurt ÖÖ, Biricik G, Tayşi ZC.Artificial neural network and SARIMA based models for power load forecasting in Turkish electricity market. PLoS One 2017; 12(4): e0175915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175915. |
| 10. | Sharafi M, Ghaem H, Tabatabaee HR, Faramarzi H.Forecasting the number of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis cases in south of Fars province, Iran using seasonal ARIMA time series method. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2017; 10(1):79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.12.007. |
| 11. | Yousefzadeh-Chabok S, Ranjbar-Taklimie F, Malekpouri R, Razzaghi A.A time series model for assessing the trend and forecasting the road traffic accident mortality. Arch Trauma Res 2016; 5(3):e36570. doi: 10.5812/atr.36570. |
| 12. | Azeez A, Obaromi D, Odeyemi A, Ndege J, Muntabayi R. Seasonality and trend forecasting of tuberculosis prevalence data in Eastern Cape, South Africa, using a hybrid model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016; 13(8). pii: E757. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13080757. |
| 13. | Zhang G, Huang S, Duan Q, Shu W, Hou Y, Zhu S, et al.Application of a hybrid model for predicting the incidence of tuberculosis in Hubei, China. PLoS One 2013; 8(11): e80969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080969. |
| 14. | Kam HJ, Sung JO, Park RW.Prediction of daily patient numbers for a regional emergency medical center using time series analysis. Healthc Inform Res 2010; 16(3): 158-65. doi: 10.4258/hir.2010.16.3.158. |
| 15. | Guo Chen, Amy K. Glasmeier, Min Zhang, et al.Urbanization and income inequality in post-reform China: a causal analysis based on time series data. PLoS One 2016; 11(7):e0158826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158826. |
| 16. | Box GE, Jenkins GM.Time series analysis: forecasting and control. editors. Oakland: Holden-Day; 1976. p. 300-33. |
| 17. | Ren X, Fu S, Dai P, Wang H, Li Y, Li X, et al.Pigsties near dwellings as a potential risk factor for the prevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus in adult in Shanxi, China. Infect Dis Poverty 2017; 6(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0312-4. |
| 18. | Yu L, Zhou L, Tan L, Jiang H, Wang Y, Wei S, et al.Application of a new hybrid model with seasonal auto-regressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) and nonlinear auto-regressive neural network (NARNN) in forecasting incidence cases of HFMD in Shenzhen, China. PLoS One 2014; 9(6):e98241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098241. |
| 19 | IHS EViews EViews 7. [cited 2016 Nov 1]. Available from: . |
| 20. | Wang X, Li SH, Zhu L, Nian QG, Yuan S, Gao Q, et al.Near-atomic structure of Japanese encephalitis virus reveals critical determinants of virulence and stability. Nat Commun 2017; 8(1):14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00024-6. |
| 21. | Parmar KS, Bhardwaj R.Statistical, time series, and fractal analysis of full stretch of river Yamuna (India) for water quality management. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2015; 22(1):397-414. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3346-1. |
| 22. | Heffelfinger JD, Li X, Batmunkh N, Grabovac V, Diorditsa S, Liyanage JB, et al.Japanese Encephalitis Surveillance and Immunization-Asia and Western Pacific Regions, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2017; 66(22):579-83. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6622a3. |
| [1] | Li Wenxing, Zhang Yanli. Novel Long Non-coding RNA Markers for Prognostic Prediction of Patients with Bladder Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 239-247. |
| [2] | Bai Bing, Tian Yuan, Zhang Yuelun, Ma Manjiao, Yu Xuerong, Huang Yuguang. Prediction of Hidden Blood Loss During Posterior Spinal Surgery [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 38-44. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|