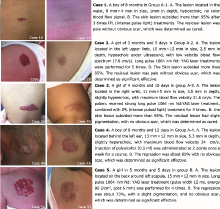
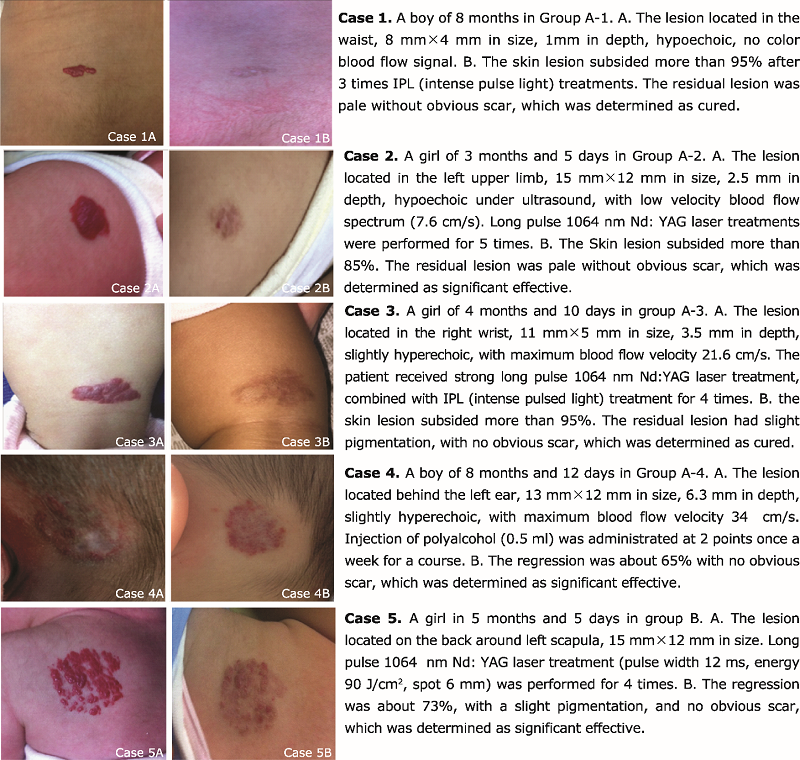
| 1. |
Kilcline C and Frieden IJ. Infantile hemangiomas: how common are they? A systematic review of the medical literature. Pediatr Dermatol 2008; 25: 168-73. doi:10.1111/j. 1525-1470.2008.00626.x.
|
| 2. |
Alcántara-González J, Boixeda P, Truchuelo-Díez MT, et al.Infantile hemangiomas treated by sequential application of pulsed dye laser and Nd:YAG laser radiation: a retrospective study. Actas Dermosifiliogr 2013;104: 504-11. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2012.12.010.
|
| 3. |
Bauland CG, Lüning TH, Smit JM, et al.Untreated hemangiomas: growth pattern and residual lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011;127: 1643-8. doi:10.1097/PRS. 0b0- 13e318208d2ac.
|
| 4. |
Luu, M. and I.J. Frieden. Haemangioma: clinical course, complications and management. Br J Dermatol 2013; 169: 20-30. doi:10.1111/bjd.12436.
|
| 5. |
Harikrishna B, Ganesh A, Al-Zuahibi S, et al.Oral propranolol for the treatment of periorbital infantile hemangioma: a preliminary report from oman. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 2011;18: 298-303. doi:10.4103/0974-9233.90131.
|
| 6. |
Wilder D.Pulsed 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser therapy for noninvasive treatment of a massive hemangioma: case report. J Clin Laser Med Surg 1999; 17: 245-7. doi:10.1089/ clm.1999.17.245.
|
| 7. |
Astner S, Anderson RR.Treating vascular lesions. Dermatol Ther 2005; 18: 267-81. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019. 2005.05025.x.
|
| 8. |
Kaune KM1, Lauerer P, Kietz S, et al. Combination therapy of infantile hemangiomas with pulsed dye laser and Nd: YAG laser is effective and safe. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2014;12: 473-8. doi:10.1111/ddg.12354.
|
| 9. |
Landthaler M,Hohenleutner U.Laser therapy of vascular lesions.Photedennatol Photoirnmunol Photomed 2006; 22: 324-32. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0781.2006.00254.x.
|
| 10. |
Ouvry P, Allaert FA, Desnos P, et al.Efficacy of polidocanol foam versus liquid in sclerotherapy of the great saphenous vein: a multicentre randomised controlled trial with a 2-year follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2008; 36: 366-70. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2008.04.010.
|
| 11. |
Miyatake K, Okamoto M, Kinoshita N, et al.Clinical applications of a new type of real-time two-dimensional Doppler flow imaging system. Am J Cardiol 1984; 54: 857-68.
|
| 12. |
Wortsman X.Common applications of dermatologic sonography. J Ultrasound Med 2012; 31: 97-111.
|
| 13. |
Dubois J, Patriquin HB, Garel L, et al.Soft-tissue hemangiomas in infants and children: diagnosis using Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998; 171: 247-52. doi:10.2214/ajr.171.1.9648798.
|
| 14. |
Zvulunov A, McCuaig C, Frieden IJ, et al. Oral propranolol therapy for infantile hemangiomas beyond the proliferation phase: a multicenter retrospective study. Pediatr Dermatol 2011; 28: 94-8. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470. 2010.01379.x.
|
| 15. |
Wortsman X, Wortsman J, Arellano J, et al.Pilomatrixomas presenting as vascular tumors on color Doppler ultrasound. J Pediatr Surg 2010; 45: 2094-8. doi:10.1016/ j.jpedsurg.2010.07.009.
|
| 16. |
Lee GK, Suh KJ, Lee JH, et al.Lobular capillary hemangioma in the soft tissue of the finger: sonographic findings. Skeletal Radiol 2010; 39: 1097-102. doi:10.1007/s00256- 010-0934-0.
|
| 17. |
Shi H, Song H, Wang J, et al.Ultrasound in assessing the efficacy of propranolol therapy for infantile hemangiomas. Ultrasound Med Biol 2014; 40: 2622-9. doi:10.1016/j. ultrasmedbio.2014.06.021.
|
| 18. |
Kutz AM, Aranibar L, Lobos N, et al.Color doppler ultrasound follow-up of infantile hemangiomas and peripheral vascularity in patients treated with propranolol. Pediatr Dermatol 2015; 32: 468-75. doi:10.1111/pde. 12596.
|
| 19. |
Dubois J, Patriquin HB, Garel L, et al.Soft-tissue hemangiomas in infants and children: diagnosis using Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998; 171: 247-52. doi:10.2214/ajr.171.1.9648798.
|
| 20. |
Kaune KM, Lauerer P, Kietz S, et al.Combination therapy of infantile hemangiomas with pulsed dye laser and Nd: YAG laser is effective and safe. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2014; 12: 473-8. doi:10.1111/ddg. 12354.
|
 ), Zhou Bingrong2, *(
), Zhou Bingrong2, *( )
)