Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 281-288.doi: 10.24920/003495
• Technique Report • Previous Articles Next Articles
An Optimized Protocol of Azoxymethane-Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colorectal Tumor Model in Mice
Liang Xi, Hu Jingnan, He Jianming
- Department of Radiotherapy, Hebei Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
-
Received:2018-08-09Accepted:2018-10-10Published:2019-12-31Online:2019-12-04 -
Contact:Liang Xi,Hu Jingnan,He Jianming
Cite this article
Liang Xi, Hu Jingnan, He Jianming. An Optimized Protocol of Azoxymethane-Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colorectal Tumor Model in Mice[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 281-288.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

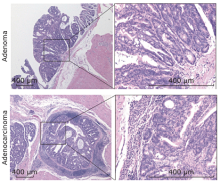
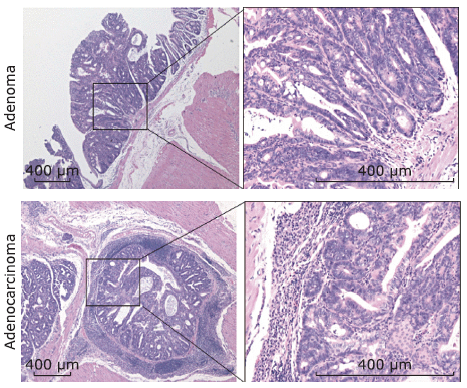
Figure 2.
Gross specimen photographs of colorectums in mice with colorectal tumors induced by AOM-DSS. A. Mouse sacrificed 10 weeks after AOM injection; B. mouse sacrificed 20 weeks after AOM injection. Colon was excised (up) and longitudinally opened (down), showing tumors were mainly distributed at the distal end of colorectum, increased in number and size along with time."
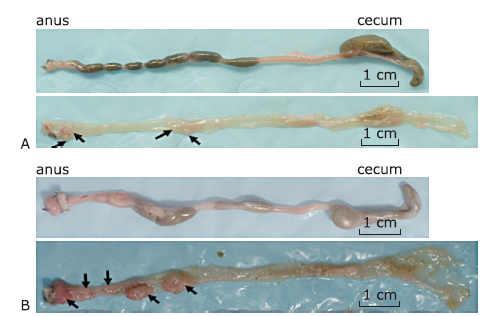
Table 2
TROUBLE SHOOTING"
| Problem | Possible reasons | Solutions | Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. High death rate of mice during AOM and DSS treatment | |||
| 1) Mouse strain highly susceptible to AOM | -Switch to a strain of lower susceptibility | 1 | |
| -Decrease AOM dose | 6 | ||
| 2) Injury of blood vessels and/or abdominal viscera | -Ensure precise injection technique | 7 | |
| 3) AOM injected into vein | -Ensure precise injection technique | 7 | |
| 2. High death rate of mice after DSS treatment | |||
| 1) Mouse strain highly susceptible to DSS | -Switch to a mouse strain of lower susceptibility | 1 | |
| -Decrease DSS concentration and/or reduce the time period of administration | 10-14 | ||
| 2) Too many and/or too large colorectal tumorous lesions | -Decrease AOM dose | 6 | |
| -Decrease DSS concentration and/or reduce the time period of administration | 10-14 | ||
| -Reduce the waiting time period | 15 | ||
| 3. Low tumor incidence and/or no or few tumors per mouse | |||
| 1) Mouse strain lowly susceptible to AOM/DSS | -Switch to a mouse strain of highly susceptibility | 1 | |
| -Increase AOM dose | 6 | ||
| -Increase DSS concentration and/or prolong the period of administration | 10-15 | ||
| 2) AOM dose too low | -Increase AOM dose | 10 | |
| 3) DSS concentration too low | -Increase DSS concentration | 10-14 | |
| 4) Waiting period too short | -Prolong waiting period | 15 | |
| 4.High variability within experimental groups | |||
| 1) Genetic backgrounds not pure | -Purify genetic background | 1 | |
| 2) Differences in origin | -Use mice from the same offspring | 1 | |
| 3) Differences in gender | -Do not use female mice | 1 | |
| 4) Affect by menstrual period | -Do not use female mice | 1 | |
| 5) Imprecise injection | -Ensure precise injection technique | 7 | |
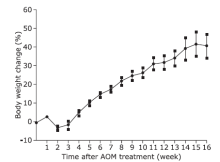
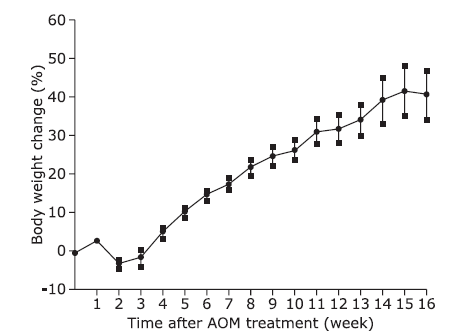
Figure 4.
Body weight changes of the mice treated with AOM-DSS along with time (n=10). The body weight of mice decreased at the beginning of and early after DSS treatment (the second week), regained to the level before DSS treatment in two weeks after the termination of DSS treatment. The data shown are the mean ± standard error."
| 1. | Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL , et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65(2):87-108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. |
| 2. | He J, Shin H, Wei X , et al. NPC1L1 knockout protects against colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. BMC Cancer 2015; 15:189. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1230-0. |
| 3. | Jain R, Austin Pickens C, Fenton JI . The role of the lipidome in obesity-mediated colon cancer risk. J Nutr Biochem 2018; 59:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.02.015. |
| 4. | Dudley-Brown S, Freivogel M . Hereditary colorectal cancer in the gastroenterology clinic: how common are at-risk patients and how do we find them? Gastroenterol Nurs 2009; 32(1):8-16. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0b013e3181965d04. |
| 5. | Zelga P, Przybylowska-Sygut K, Zelga M , et al. Polymorphism of Gly39Glu (c.116G>A) hMSH6 is associated with sporadic colorectal cancer development in the Polish population: Preliminary results. Adv Clin Exp Med 2017; 26(9):1425-29. doi: 10.17219/acem/64877. |
| 6. | He J, Liang X, Luo F , et al. P53 is involved in a three-dimensional architecture-mediated decrease in chemosensitivity in colon cancer. J Cancer 2016; 7(8):900-9. doi: 10.7150/jca.14506. |
| 7. | Neufert C, Becker C, Neurath MF . An inducible mouse model of colon carcinogenesis for the analysis of sporadic and inflammation-driven tumor progression. Nat Protoc 2007; 2(8):1998-2004. doi: nprot.2007.279. |
| 8. | Taketo MM, Edelmann W . Mouse models of colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2009; 136(3):780-98. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.049. |
| 9. | Tong Y, Yang W, Koeffler HP . Mouse models of colorectal cancer. Chin J Cancer 2011; 30(7):450-62. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10041. |
| 10. | He JM, Wang FC, Qi HB , et al. Down-regulation of alphav integrin by retroviral delivery of small interfering RNA reduces multicellular resistance of HT29. Cancer Lett 2009; 284(2):182-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.023. |
| 11 | 11. Mikalsen SG, Mikalsen LTG, Sandvik JA , et al. Low dose-rate irradiation with [(3)H]-labelled valine to selectively target hypoxic cells in a human colorectal cancer xenograft model. Acta Oncol 2018; 57(9):1216-24. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1457223. |
| 12. | O’Rourke KP, Loizou E, Livshits G , et al. Transplantation of engineered organoids enables rapid generation of metastatic mouse models of colorectal cancer. Nat Biotechnol 2017; 35(6):577-82. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3837. |
| 13. | Fleet JC . Animal models of gastrointestinal and liver diseases. New mouse models for studying dietary prevention of colorectal cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2014; 307(3):G249-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00019.2014. |
| 14. | Tanaka T, Kohno H, Suzuki R , et al. A novel inflammation-related mouse colon carcinogenesis model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci 2003; 94(11):965-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01386.x. |
| 15. | Kim IJ, Kang HC, Park JH , et al. Development and applications of a beta-catenin oligonucleotide microarray: beta-catenin mutations are dominantly found in the proximal colon cancers with microsatellite instability. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9(8):2920-5. |
| 16. | Turpin B, Miller W, Rosenfeldt L , et al. Thrombin drives tumorigenesis in colitis-associated colon cancer. Cancer Res 2014; 74(11):3020-30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3276. |
| 17. | Bugni JM, Meira LB, Samson LD . Alkylation-induced colon tumorigenesis in mice deficient in the Mgmt and Msh6 proteins. Oncogene 2009; 28(5):734-41. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.426. |
| 18. | Chen Y, Zhang P, Xu SC , et al. Enhanced colonic tumori-genesis in alkaline sphingomyelinase (NPP7) knockout mice. Mol Cancer Ther 2015; 14(1):259-67. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0468-T. |
| 19. | Lavi I, Nimri L, Levinson D , et al. Glucans from the edible mushroom Pleurotus pulmonarius inhibit colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis in mice. J Gastroenterol 2012; 47(5):504-18. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0514-7. |
| 20. | Suzuki R, Kohno H, Sugie S , et al. Sequential observations on the occurrence of preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in mouse colon treated with azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci 2004; 95(9):721-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03252.x. |
| 21. | Shirakami Y, Kochi T, Kubota M , et al. Inhibitory effects of pentoxifylline on inflammation-related tumorigenesis in rat colon. Oncotarget 2018; 9(74):33972-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26119. |
| 22. | Chen L, Jiang B, Zhong C , et al. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer by black raspberry anthocyanins involved the modulation of gut microbiota and SFRP2 demethylation. Carcinogenesis 2018; 39(3):471-81. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy009. |
| 23. | Yao J, Zhao L, Zhao Q , et al. NF-kappaB and Nrf2 signaling pathways contribute to wogonin-mediated inhibition of inflammation-associated colorectal carcinogenesis. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5:e1283. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.221. |
| 24. | Clapper ML, Cooper HS, Chang WC . Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis-associated neoplasia: a promising model for the development of chemopreventive interventions. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28(9):1450-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00695.x. |
| 25. | Femia AP, Dolara P, Luceri C , et al. Mucin-depleted foci show strong activation of inflammatory markers in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced carcinogenesis and are promoted by the inflammatory agent sodium dextran sulfate. Int J Cancer 2009; 125(3):541-7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24417. |
| 26. | Boddicker RL, Whitley EM, Davis JE , et al. Low-dose dietary resveratrol has differential effects on colorectal tumorigenesis in adiponectin knockout and wild-type mice. Nutr Cancer 2011; 63(8):1328-38. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2011.607538. |
| 27. | Osburn WO, Karim B, Dolan PM , et al. Increased colonic inflammatory injury and formation of aberrant crypt foci in Nrf2-deficient mice upon dextran sulfate treatment. Int J Cancer 2007; 121(9):1883-91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22943. |
| [1] | Jianbo Xiu, Lanlan Li, Qi Xu. Minocycline Activates the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract-Associated Network to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 1-14. |
| [2] | Jie Zhao, Yimeng Yang, Shuhong Ming. Pregnancy-Induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: A Case Report and Literature Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 371-376. |
| [3] | Hao Qiufa, Wang Baobao, Zhang Wei, Qiu Wei, Liu Qianling, Li Xuemei. NF-κB Inhibitor Parthenolide Promotes Renal Tubules Albumin Uptake in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 31-42. |
| [4] | Wang Guorong, Wang Zhiwei, Jin Zhengyu. Application and Progress of Texture Analysis in the Therapeutic Effect Prediction and Prognosis of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [5] | Pan Yanfang, Jia Xiaotao, Song Erfei, Peng Xiaozhong. Astragaloside IV Protects Against Aβ1-42-induced Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Rats [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 29-37. |
| [6] | Yi-jun Zhou*, Ai Li, Yu-ling Song, Yan Li, Hui Zhou. Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain-1 Ligand Induces Inflammation and Attenuates Glucose Uptake in Human Adipocytes△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2012, 27(3): 147-152. |
| [7] | Peng Jin, Jian-qiu Sheng*, Ying-hui Zhang, Ai-qin Li, Zi-tao Wu and Shi-rong Li. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and its relationship with mismatch repair and microsatellite instability in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(4): 206-210. |
| [8] | Peng Jin, Xiao-ming Meng, Jian-qiu Sheng*, Zi-tao Wu, Lei Fu, He-juan An, Ying Han and Shi-rong Li. Clinicopathological features of non-familial colorectal cancer with high-frequency microsatellite instability [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(4): 228-232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|