Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 29-37.doi: 10.24920/11802
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Astragaloside IV Protects Against Aβ1-42-induced Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Rats
Pan Yanfang1, Jia Xiaotao2, Song Erfei3, Peng Xiaozhong4, *( )
)
- 1Department of Pathology, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, Shaanxi 712046, China
2Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Xi'an Central Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University College of Medicine, Xi'an 710003, China;
3 Department of Biology, York University, Toronto, ON M3J 1P3, Canada
4State Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Biology, Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & School of Basic Medicine Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100005, China;
-
Received:2017-06-02Published:2018-02-13Online:2018-02-13 -
Contact:Peng Xiaozhong E-mail:pengxiaozhong@pumc.edu.cn -
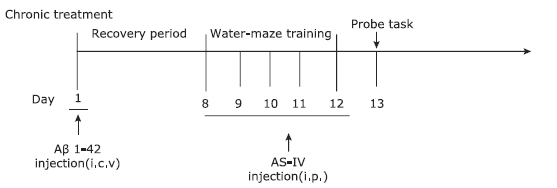
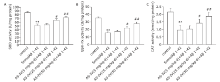
About author:This study investigated the neuroprotective action of astragaloside Ⅳon spatial learning and memory impairment induced by amyloid-beta 1-42 in rats and elucidated its underlying molecular mechanisms.
| This study investigated the neuroprotective action of astragaloside Ⅳon spatial learning and memory impairment induced by amyloid-beta 1-42 in rats and elucidated its underlying molecular mechanisms. |
Cite this article
Pan Yanfang, Jia Xiaotao, Song Erfei, Peng Xiaozhong. Astragaloside IV Protects Against Aβ1-42-induced Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Rats[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 29-37.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| 1. |
Goedert M, Spillantini MG.A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2006; 314(5800):777-81. doi: 10.1126/science.1132814.
doi: 10.1126/science.1132814 pmid: 17082447 |
| 2. |
Anand R, Gill KD, Mahdi AA. Therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease: past, present and future Neuropharmacology 2014; 76 PtA:27-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.004 pmid: 23891641 |
| 3. |
Esparza TJ, Zhao H, Cirrito JR, et al.Amyloid-beta oligomerization in Alzheimer dementia versus high-pathology controls. Ann Neurol 2013;73(1):104-19. doi: 10.1002/ana.23748.
doi: 10.1002/ana.23748 pmid: 3563737 |
| 4. |
Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Hanse E.Amyloid beta and APP as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol 2010; 45(1):23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2009.08.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2009.08.002 |
| 5. |
Yatin SM, Yatin M, Aulick T, et al.Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide associated free radicals increase rat embryonic neuronal polyamine uptake and ornithine decarboxylase activity: protective effect of vitamin E. NeurosciLett 1999; 263(1):17-20. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00101-96.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00101-96 pmid: 10218900 |
| 6. |
Zotova E, Nicoll JA, Kalaria R, et al.Inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: relevance to pathogenesis and therapy. Alzheimers Res Ther 2010; 2(1):1. doi: 10.1186/alzrt24.
doi: 10.1186/alzrt24 pmid: 2874260 |
| 7. |
Hickman SE, Allison EK, El KJ.Microglial dysfunction and defective beta-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neurosci 2008; 28(33):8354-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0616-08.2008.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0616-08.2008 pmid: 18701698 |
| 8. |
Johnston H, Boutin H, Allan SM.Assessing the contribution of inflammation in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 2011; 39(4):886-90. doi: 10.1042/BST0390886.
doi: 10.1042/BST0390886 pmid: 21787318 |
| 9. |
Godbout JP, Chen J, Abraham J, et al.Exaggerated neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in aged mice following activation of the peripheral innate immune system. FASEB J 2005; 19(10):1329-31. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3776fj.
doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3776fj pmid: 15919760 |
| 10. |
Ullah F, Ali T, Ullah N, et al.Caffeine prevents d-galactose-induced cognitive deficits, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the adult rat brain. Neurochem Int 2015; 90:114-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.07.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.07.001 pmid: 26209154 |
| 11. |
Tan CC, Yu JT, Wang HF, et al.Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 2014; 41(2):615-31. doi: 10.3233/JAD-132690.
doi: 10.3233/JAD-132690 pmid: 24662102 |
| 12. |
Saini SS, Gesselllee DL, Peterson JW.The cox-2-specific inhibitor celecoxib inhibits adenylyl cyclase.Inflammation 2003; 27(2):79-88. doi: 10.1023/A:1023226616526.
doi: 10.1023/A:1023226616526 pmid: 12797547 |
| 13. |
Fu J, Wang Z, Huang L, et al.Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother Res 2014; 28(9):1275-83. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5188.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.5188 pmid: 25087616 |
| 14. |
Zhang ZG, Wu L, Wang JL, et al.AstragalosideIV prevents MPP(+)-induced SH-SY5Y cell death via the inhibition of Bax-mediated pathways and ROS production. Mol Cell Biochem 2012; 364(1-2):209-16. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1219-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1219-1 |
| 15. |
Li X, Wang X, Han C, et al.Astragaloside IV suppresses collagen production of activated hepatic stellate cells via oxidative stress-mediated p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2013; 60:168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed pmid: 23459070 |
| 16. |
Hu JY, Han J, Chu ZG, et al.AstragalosideIVattenuates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte damage in rats by upregulating superoxide dismutase-1 levels. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2009; 36(4):351-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05059.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05059.x pmid: 18986331 |
| 17. |
Li M, Qu YZ, Zhao ZW, et al.AstragalosideIVprotects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem Int 2012; 60(5):458-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.01.026.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.01.026 pmid: 22342823 |
| 18. |
Liu G, Song J, Guo Y, et al.Astragalus injection protects cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and the expression of JNK3 after cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Behav Brain Funct 2013; 9:36. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-9-36.
doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-9-36 pmid: 24083559 |
| 19. |
Kim S, Kang IH, Nam JB, et al.Ameliorating the effect of astragalosideIVon learning and memory deficit after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Molecules 2015; 20(2):1904-21. doi: 10.3390/molecules20021904.
doi: 10.3390/molecules20021904 pmid: 25625683 |
| 20. |
Paranjape GS, Terrill SE, Gouwens LK, et al.Amyloid-β(1-42) protofibrils formed in modified artificial cerebrospinal fluid bind and activate microglia. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2013; 8(1):312-22. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9424-6.
doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9424-6 pmid: 23242692 |
| 21. |
Nakamura S, Murayama N, Noshita T, et al.Progressive brain dysfunction following intracerebroventricular infusion of beta (1-42)-amyloid peptide. Brain Res 2001; 912(2):128-36. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02704-4.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02704-4 pmid: 11532428 |
| 22. |
Pan YF, Chen XR, Wu MN, et al.Arginine vasopressin prevents against Aβ25-35-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. Horm Behav 2010; 57(4-5):448-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.01.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.01.015 pmid: 20138885 |
| 23. |
Butterfield DA, Boyd-Kimball D. Amyloid β-peptide(1-42) contributes to the oxidative stress and neurodegeneration found in Alzheimer disease brain. Brain Pathol 2004; 14(4):426-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00087.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00087.x pmid: 15605990 |
| 24. |
Praticò D.Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: a reappraisal. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2008; 29(12):609-15. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.09.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.09.001 pmid: 18838179 |
| 25. |
Kamer A, Craig RG, Dasanayake AP, et al.Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease: possible role of periodontal diseases. Alzheimers Dement 2008; 4(4):242-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2007.08.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2007.08.004 pmid: 18631974 |
| 26. |
Cai HY, Holscher C, Yue XH, et al.Lixisenatide rescues spatial memory and synaptic plasticity from amyloid β protein-induced impairments in rats. Neuroscience 2014; 277:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.022.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.022 pmid: 24583037 |
| 27. |
Klein WL, Jr SW, Teplow DB.Small assemblies of unmodified amyloid beta-protein are the proximate neurotoxin in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2004; 25(5):569-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.02.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.02.010 pmid: 15172732 |
| 28. |
Nillert N, Pannangrong W, Welbat JU, et al. Neuroprotective effects of aged garlic extract on cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation induced by β-amyloid in rats. Nutrients2017; 9(1). pii: E24. doi: 10.3390/nu9010024.
doi: 10.3390/nu9010024 |
| 29. |
Wang J, Ho L, Zhao W, et al.Grape-derived polyphenolics prevent Aβ oligomerization and attenuate cognitive deterioration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2008; 28(25):6388-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0364-08.2008.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0364-08.2008 pmid: 18562609 |
| 30. |
Dong Z, Bai Y, Wu X, et al.Hippocampal long-term depression mediates spatial reversal learning in the Morris water maze. Neuropharmacology 2013; 64:65-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.027.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.06.027 |
| 31. |
Jia XT, Ye-Tian, Yuan-Li, et al.Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, protects against amyloid-β peptide-induced impairment of spatial learning and memory in rats. Physiol Behav 2016; 159:72-9.doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh. 2016.03.016.
doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh. 2016.03.016 pmid: 26992957 |
| 32. |
Wan L, Nie G, Zhang J, et al.β-Amyloid peptide increases levels of iron content and oxidative stress in human cell and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med 2011; 50(1):122-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.10.707.
doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.10.707 pmid: 21034809 |
| 33. |
Abdul HM, Sultana R, St Clair DK, et al.Oxidative damage in brain from human mutant APP/PS-1 double knock-in mice as a function of age. Free Radic Biol Med 2008; 45(10):1420-5. doi: 10.1016/j.freerad biomed.2008.08.012.
doi: 10.1016/j.freerad biomed.2008.08.012 pmid: 2597707 |
| 34. |
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, et al.Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011; 14(8):1505-17. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3576.
doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3576 pmid: 20812869 |
| 35. |
Pong K, Rong Y, Doctrow SR, et al.Attenuation of zinc-induced intracellular dysfunction and neurotoxicity by a synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic, in cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res 2002; 950(1-2):218-30. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03040-8.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03040-8 pmid: 12231247 |
| 36. |
Hofmann U, Heuer S, Meder K, et al.The proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta impair economy of contraction in human myocardium. Cytokine 2007; 39(3):157-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.07.185.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.07.185 pmid: 17825578 |
| 37. |
Detloff MR, Fisher LC, Mcgaughy V, et al.Remote activation of microglia and pro-inflammatory cytokines predict the onset and severity of below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 2008; 212(2):337-47. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.04.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.04.009 pmid: 18511041 |
| 38. |
Rogers JT, Leiter LM, Mcphee J, et al.Translation of the alzheimer amyloid precursor protein mRNA is up-regulated by interleukin-1 through 5’-untranslated region sequences. J Biol Chem 1999; 274(10):6421-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.10.6421.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.10.6421 |
| [1] | Jianbo Xiu, Lanlan Li, Qi Xu. Minocycline Activates the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract-Associated Network to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 1-14. |
| [2] | Ping Fen, Cao Qin, Lin Hua, Han Shuzhi. Antagonistic Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway Activation, Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in Rats with PM2.5 Induced Lung Injuries [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(4): 270-276. |
| [3] | He Ying,Zhang Ying,Wang Mengying,Zhang Meng,Zhang Dan,Zhang Ying,Jiang Zhuocheng,Wu Feng,Chen Jinghong. Gene Expression Profile of Hypertrophic Chondrocytes Treated with H2O2: A Preliminary Investigation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 45-52. |
| [4] | Kong Xiangyi, Guan Jian, Gong Shun, Wang Renzhi. Neuroprotective Effects of Grape Seed Procyanidin Extract on Ischemia-Reperfusion Brain Injury△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 92-99. |
| [5] | Fen Ping, Zhen-sheng Li, Feng-rui Zhang, De-xin Li, Shu-zhi Han. Effects of Lianhua Qingwen on Pulmonary Oxidative Lesions Induced by Fine Particulates (PM2.5) in Rats [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(4): 233-238. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|